
NEURAL NETWORK MODEL BASED ON FUZZY ARTMAP FOR
FORECASTING OF HIGHWAY TRAFFIC DATA
D. Boto-Giralda, M. Antón-Rodríguez, F. J. Díaz -Pernas, J. F. Díez Higuera
Departamento de Teoría de la Señal, Comunicaciones e Ingeniería Telemática
ETSIT Universidad de Valladolid, Campus Miguel Delibes s/n, 47011 Valladolid, España
Keywords: Fuzzy ARTMAP, travel cost estimates, ATIS.
Abstract: In this article, a neural network model is presented for forecasting the average speed values at highway
traffic detectors locations using the Fuzzy ARTMAP theory. The performance of the model is measured by
the deviation between the speed values provided by the loop detectors and the predicted speed values.
Different Fuzzy ARTMAP configuration cases are analysed in their training and testing phases. Some ad-
hoc mechanisms added to the basic Fuzzy ARTMAP structure are also described to improve the entire
model performance. The achieved results make this model suitable for being implemented on advanced
traffic management systems (ATMS) and advanced traveller information system (ATIS).
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional models of traffic congestion and
management lack the adaptability and sophistication
needed to effectively and reliably deal with
increasing traffic volume on certain road stretches.
A realistic estimate of planned routes travel cost
with reasonable accuracy is essential for successful
implementation on an advanced traveller
information system (ATIS) for use in an intelligent
transportation system (ITS). An ATIS consists of a
route guiding system (RGS) that recommend the
most suitable route based on the traveller’s
requirements, using the information gathered from
various sources as loop detectors and probe vehicles.
The success of an RGS will depend on its ability to
predict the anticipatory travel cost in addition to the
historical and real-time travel cost. (Dharia, A. and
Adeli, H., 2003)
Several aspects should be taken into account to
evaluate the travel cost such as distance, time,
economy, danger or personal preferences. From the
distance point of view, the travel cost quantification
will be strictly static, only dependent on the sum of
the stretches length. A time based estimate will be
dynamic and dependent on multiple factors. It could
be directly measured or by the distance-speed
relationship. For a economic estimate, toll fares,
vehicle consumption and wear will be considered.
Road accident risks as well as driving easiness at
some particular stretches might be a decisive factor
to rule out a route. Finally the traveller’s preferences
for route services or particular scenarios such as
mountain or landscape roads could affect the
decision eventually. This article will focus on speed
estimate in road stretches with traffic detectors using
a Fuzzy ARTMAP neural network structure. As said
before, speed may be used to calculated the travel
time cost as long as distance is known.
Neural network computing applied to travel cost
forecast appeared to overcome the shortcomings of
preceding methods whose forecasts deteriorate over
multiple time steps (Park, D. and Rilett, L.R., 1999).
A neural network provides a mapping between a set
of inputs and corresponding outputs (Adeli, H. and
Hung, S.L., 1995). The network is trained to learn
this mapping using a number of training examples.
Backpropagation (BP) is the most widely used
neural network model in civil engineering
applications, primarily due to its simplicity.
However, backpropagation has shortcomings,
including a very slow rate of convergence and
arbitrary and problem-dependent selection of the
learning and momentum ratios (Adeli, H. and Hung,
S.L., 1994).
A neural model for forecasting the freeway link
travel time using counter propagation neural (CPN)
network is presented in (Dharia, A. and Adeli, H.,
2003). There, it was showed that CPN model was
nearly two orders of magnitudes faster than BP
training algorithm for the same level of accuracy. In
19
Boto-Giralda D., Antón-Rodríguez M., J. Díaz -Pernas F. and F. Díez Higuera J. (2006).
NEURAL NETWORK MODEL BASED ON FUZZY ARTMAP FOR FORECASTING OF HIGHWAY TRAFFIC DATA.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 19-25
DOI: 10.5220/0001213000190025
Copyright
c
SciTePress

this article, a neural network model based on Fuzzy
ARTMAP is presented for forecasting the average
speed values at highway traffic detectors locations.
Faster as the aforesaid CPN model, the presented
model gives lightly better average errors in
forecasting values in more realistic both training and
testing scenarios.
2 FUZZY ARTMAP BASIS
The Fuzzy ARTMAP, introduced by (Carpenter et
al., 1992) is a supervised network composed of two
Fuzzy ARTs (ART
a
and ART
b
) interconnected by a
series of connections between their output layers.
Each connection has an associated weight value (w
ij
)
between 0 and 1, and may be considered as the
membership function value in the fuzzy sets theory
of the corresponding network category.
a
1
a
2
a
1
a
2
a
1
c
a
2
c
b
1
b
2
b
1
b
2
A
x
a
y
a
B
x
b
y
b
a
b
ART
a
ART
b
F
ab
x
ab
Figure 1: Sample Fuzzy ARTMAP network.
These connections form what is called the map
field F
ab
. The weights of the map field are all
initialised to 1. The map field has two parameters:
the learning rate β
ab
, and vigilance criterion ρ
ab
, and
an output vector x
ab
. Figure 1 shows a graphic
sample representation of a Fuzzy ARTMAP
network.
The input data of both ART
a
and ART
b
are
normalized values, between 0 and 1 (minimum and
maximum expected input values respectively), and
form the network input vectors a and b. This
normalization ensures a proportional response of the
network from the input data. Input vector of ART
a
is
put in complement coding form, resulting in vector
A. Complement coding is not necessary in ART
b
so
the input vector B directly presented to the network.
2.1 Training
Fuzzy ARTMAP networks usage requires a training
process before being able to classify input data. In
this process, a vector representing a data pattern is
presented to ARTa, and a vector which is the desired
output corresponding to this pattern is presented to
ART
b
. The relationship between these two vectors is
learned through the weight values of the map field.
The vigilance criterion of ART
a
, ρ
a
, varies during
learning from a initial value called the baseline
vigilance
a
ρ
. The vigilance parameter of ART
b
, ρ
b
,
is set to 1 to perfectly distinguish the desired output
vectors.
When vectors A and B are presented to ART
a
and
ART
b
, both networks soon enter resonance. The map
field vigilance criterion is then evaluated to verify if
the winning neuron of ART
a
corresponds to the
desired output vector presented to ART
b
. This
criterion is:
ab
b
ab
J
b
y
wy
ρ
≥
∧
(1)
where y
b
is the output vector of ART
b
, J is the index
of the winning neuron on the output layer of ART
a
,
w
ab
J
corresponds to the weights of the connections to
the Jth neuron of the output layer of ART
a
and
ρ
ab
∈[0,1] is the vigilance criterion of the map field.
If the criterion is not respected, the vigilance of
ART
a
is increased just enough to select another
winning neuron (ρ
a
>|A∧w
J
|/|A| ) and the vector A is
repropagated in ART
a
.
When the vigilance criterion is respected, the
vigilance value of ART
a
is set to its initial baseline
value
a
ρ
and the map field learns the association
between vectors A and B by modifying its weights
as follows:
(
)
ab
Jab
ab
ab
ab
J
wxw
ββ
−+= 1
(2)
The weights in ART
a
are also modified as:
(
)( )
JaJaJ
wwAw
β
β
−
+
∧
=
1
(3)
In practice, the ART
a
learning rate, β
a
, is set equal
to β
ab
, or simply β, defining the learning network
capability.
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
20

2.2 Classifying
During the training process the weight values of the
Fuzzy ARTMAP were updating, as new patterns
were presented to the network, till they reached a
final value. At this point the network can be used as
a classifier of the vector data presented to ART
a
.
ART
b
is not used during this classifying process and
learning network capability is deactivated (β=0).
ART
a
will establish a winning node on its
output layer from each input vector A presented to
the network. The output vector of the map field is
then set to:
ab
J
ab
wx =
(4)
where J is the index of the winning node on output
layer of ART
a
, and w
ab
J
is the corresponding weight
values vector on the map field . The index J of this
component is the number of the category in which
the input vector A has been classified. The use of the
map field is thus to associate a category number to
each neuron of ART
a
’s output layer. However, not
just the category that best fits an input is the only
result of the classifying process. The weight values
associated with this category may also be useful to
get ulterior information about the relationship
between the input vector and the categories learned
by the network in the training process.
3 WORKING MODEL
3.1 Training the Network
The data for this experiment were collected through
the Freeway Performance Measurement System
(PeMS) project, and could be obtained thanks to the
Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM) and Federal
Highway Administration (FHWA) web page at
http://ngsim.fhwa.dot.gov. PeMS project was
conducted by the Department of Electrical
Engineering and Computer Sciences at the
University of California, at Berkeley, with the
cooperation of California Department of
Transportation. Available data from 5 detector
stations on US 101 South for 11 days, from June 8 to
June 22, excluding the weekends, are provided in
this data set. Speed, volume and occupancy at each
detector for the 5-minute time step are presented at
each detector in each lane.
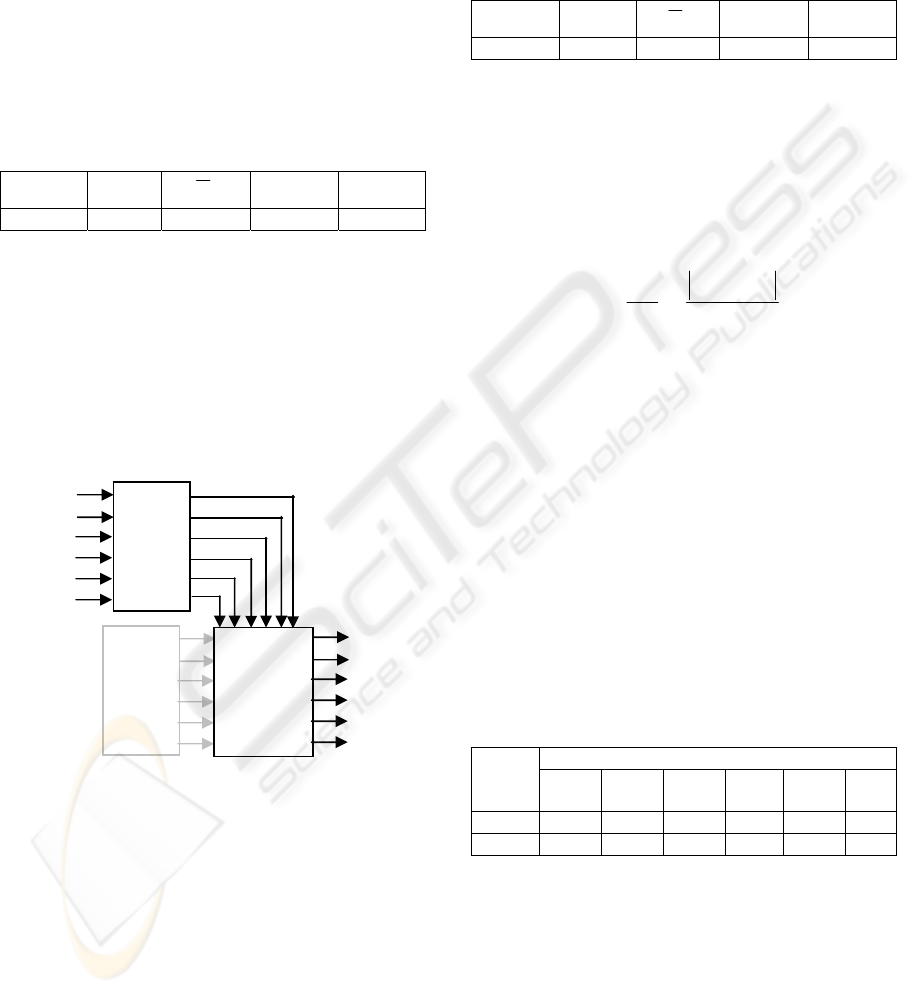
Figure 2: Fuzzy ARTMAP training structure. v
tr
(t):
training speed value at instant t; v
c
tr
(t): training speed
categorized value at instant t.
Average speed data from June 13 to June 17 (5
consecutive weekdays, making a total of 1440
samples) collected from two stations with different
traffic congestion levels (717486, light; 717489,
heavy), were employed to train the net. Figure 2
shows the structure of the Fuzzy ARTMAP during
this process
.
Table 1: Training cases.
Case
Input training
subsets time step
(min)
ART
a
input
nodes
ART
b
input
nodes
No. of
Categories
A 6*5 6 1 9
B 6*5 6 1 81
C 6*5 6 6 81
D 6*5 4 4 81
E 6*5 8 8 81
F 1*5 6 6 81
Six different structure model cases, shown in
Table 1, were considered with different number of
input and output nodes, categories and time step
between consecutive input training subsets. In Case
A, six ART
a
input nodes and one ART
b
input node
were used to associate six consecutive 5-min time
step normalized past speed values to one categorized
future speed value in the map field of the Fuzzy
ARTMAP, F
ab
. This categorized speed value is
calculated as the average of the six 5-min time step
speed values following the normalized speed values
presented to ART
a
, and categorized into one of 9
possible categories. Numerically, these categories
are linearly spaced and normalized speed values in
the range of 0-80 mph. In Case B, and following
ones, the number of categories were increased to 81.
In Case C, each six consecutive 5-min time step
normalized past speed values presented to ART
a
v
tr
(t
0
)
v
tr
(t
0
-5)
v
tr
(t
0
-10)
v
tr
(t
0
-15)
v
tr
(t
0
-20)
v
t
r
(
t
0
-25
)
ART
a
v
c
tr
(t
0
+5)
v
c
tr
(t
0
+10)
v
c
tr
(t
0
+15)
v
c
tr
(t
0
+20)
v
c
tr
(t
0
+25)
v
c
t
r
(
t
0
+30
)
ART
b
F
ab
NEURAL NETWORK MODEL BASED ON FUZZY ARTMAP FOR FORECASTING OF HIGHWAY TRAFFIC DATA
21
were associated to six consecutive 5-min time step
normalized future speed values presented to ART
b
.
In Case D and E the number of input nodes were
changed to 4 and 8 respectively. Finally in Case F,
with six input nodes anew, the consecutive sets of
values presented to the ART
a
and ART
b
were 5
minutes ahead of the former, instead of 30 minutes.
A one-shot stable learning configuration, as
shown in Table 2, has been adopted: conservative
limit (α≅0) and fast learning (β=1), holding for
fuzzy ART modules with constant vigilance
(Carpenter, G.A. et al., 1992).
Table 2: Training configuration network parameters.
α β
a
ρ
ρ
ab
ε
0.001 1 0 0.95 0.001
3.2 Testing the Network
Average speed data from June 20 to June 22 (3
consecutive weekdays following the training ones,
making a total of 864 samples) collected from the
same two stations that in the training process and
shown in
Figure 4.(a) and Figure 5.(a), were employed
to make a test of the speed forecasting net capability.
A test performance was made for each training case.
Figure 3: Fuzzy ARTMAP testing structure. vts(t): testing
speed value at instant t; vp(t): forecasting speed value for
instant t.
Figure
3 shows the structure of the Fuzzy ARTMAP
during this process. Sets of consecutive 5-min time
step normalized speed testing values were presented
to ART
a
. ART
b
in testing phase is not used. A
number of forecasting speed values, equals to the
number of input nodes in ART
b
in the training
phase, were obtained from each set. These
forecasting speed values were calculated from the
weight vectors of the map field F
ab
, w
ab
, multiplying
the selected weight vector, w
ab
J
, by the speed value
associated to the higher training category.
The fuzzy ARTMAP configuration for the testing
phase was similar to the one adopted in the training
phase but with the learning capability deactivated
(β=0), as shown in
Table 3.
Table 3: Testing configuration parameters.
α β
a
ρ
ρ
ab
ε
0.001 0 0 0.95 0.001
3.3 Forecasting Results
The Fuzzy ARTMAP model have been implemented
in MATLAB
®
Release 12 technical language on a
mobile AMD Athlon
™
XP 2000+ computer. In order
to measure the forecasting accuracy, an average
error term was defined in the following form:
()
[] []
[]
∑
=
−
=
N
t
t
pt
tv
tvtv
N
E
1
100
%
(5)
where N is the number of predicted speed values;
v
p
[t], the predicted speed value for moment t; v
t
[t],
the testing speed value measured by the station
detector at moment t.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the forecasting speed
(b) and the forecasting error (c) values over the
testing days time. The maximum error values occur
close to high traffic congestion situations in 717489
station, when vehicles speed changes too fast in the
5-min step time. This maximum error values are
dramatically high but are quickly reduced as the next
forecasting speed values are available. Hence, global
error performance keeps a satisfactory level. Table 4
shows the average error in forecasting speed for the
considered cases.
Table 4: Average error in forecasting speed.
E(%)
Station
Case
A
Case
B
Case
C
Case
D
Case
E
Case
F
717486 4.12 2.91 3.16 3.77 3.12 2.64
717489 14.78 13.95 10.96 9.67 15.84 7.78
v
ts
(t
0
)
v
ts
(t
0
-5)
v
ts
(t
0
-10)
v
ts
(t
0
-15)
v
ts
(t
0
-20)
v
ts
(t
0
-25)
ART
a
ART
b
v
p
(t
0
+5)
v
p
(t
0
+10)
v
p
(t
0
+15)
v
p
(t
0
+20)
v
p
(t
0
+25)
v
p
(
t
0
+30
)
F
ab
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
22

(a) 717486 station detector speed data
(b) 717486 station forecasting speed data
(c) 717486 station forecasting speed error
Figure 4: 717486 station data and forecasting results.
Case B improves Case A forecasting precision by
simply increasing the number of categories,
particularly with the 717486 station in which all
speed values concentrate in a range of 30 mph.
Forecasting precision for 717489 station, in
which speed values change quickly close to high
congestion situations, strongly improves in Case C
as more predicted speed values are given (six instead
(a) 717489 station detector speed data
(b) 717489 station forecasting speed data
(c) 717489 station forecasting speed error
Figure 5: 717489 station data and forecasting results.
of one) for the 30-min forecasting time interval
considered. Applying no interpolation rule, six is the
highest number of predicted values since detectors
present new data each 5 minutes.
The increase in the number of nodes in Case E
implies that both the time interval of past speed
values presented to the net and the time interval of
forecasting speed values are longer, since the
NEURAL NETWORK MODEL BASED ON FUZZY ARTMAP FOR FORECASTING OF HIGHWAY TRAFFIC DATA
23

number of nodes in ART
a
and ART
b
were equal in
the training process. For the 717489 station, with
speed values changing quickly close to high traffic
congestion situations, the longer the forecasting time
interval , the bigger the error will be. In Case D, the
opposite situation occurs but the processing time
increases substantially for the same forecasting time
interval. No significantly error variation for 717486
station in Cases D and E.
Figure 6: Case F model structure.v
ts
(t): testing speed value
at instant t; v
pi
(t): ith forecasting speed value for instant t;
v
p
(t): forecasting speed value for instant t.
The best error performance is achieved in Case F
in which several forecasting speed values (up to the
number of input nodes) are obtained for a particular
moment into the future (due to the time overlap of
the input set speed values). An average of them is
then made to get the final forecasting speed value.
Figure 6shows the model structure designed for this
particular case.
3.4 Comparative Results
The average errors in forecasting values presented in
(Dharia, A. and Adeli, H., 2003) for BP and CPN
models with the same duration of time step (5min)
and the same number of input and output nodes (6),
were slightly higher (11.5% and 10.9% respectively)
than the one achieved for the Case F (7.8% for the
station with the most congested traffic level) in the
Fuzzy ARTMAP model. However, speed travel
values, instead of travel time values, were predicted
in the model presented in this article and real traffic
data were used instead of simulated traffic data.
Case F did not take more than 10 seconds (a rough
measure was made) of processing time to carry out
both training and testing phases with the conditions
described above. BP and CPN models took 312.7
and 3.8 seconds respectively just for the training
process. Convergence behaviour of Fuzzy ARTMAP
networks are faster and more independent of the
initial weights than Back or Counter propagation
networks. Actually, training convergence can be
guaranteed as far as Fuzzy ART Stable Category
Learning Theorem (Carpenter, G.A. et al., 1992) is
satisfied.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The Fuzzy ARTMAP neural network model
described in this article provides an appropriated
forecasting travel cost mechanism, in terms of
average speed values for being integrated in travel
cost estimates systems supplied with traffic dynamic
parameters such as speed, occupancy or volume
data. Multiple training and working configurations
for the network are possible in order to match host
system requirements, all of them with a remarkable
time processing and forecasting error performance.
Forecasting test results obtained accuracy levels
under the 8% of precision from real congested
highway traffic data. A figure slightly lower than
previous neural network models developed for
highway traffic predictions. So it represents a
promising challenge in the evolution of neural
networks appliance to intelligent transportation
system (ITS).
ACKNOLEDGEMENTS
NGSIM Website - Home of the Next Generation
Simulation Community, at http://ngsim.camsys.com
- for the traffic data set.
REFERENCES
Adeli, H., 2002. “Automatic detection of traffic incidents
using data obtained from sensors embedded in
intelligent freeways ”. Sensor Review; Volume: 22
Issue: 2; 2002 Research paper.
Adeli, H., Hung, S.L., 1995. “Machine Learning-Neural
Networks, Genetic Algorithms, and Fuzzy Systems”.
Wiley, New York.
Adeli, H., Hung, S.L., 1994. “An adaptive conjugate
gradient learning algorithm for efficient training of
neural networks”. Applied Mathematics and
Computatio n 62 (1), 81–100.
Carpenter, G.A., 2003. “Default ARTMAP”. Neural
Networks, 2003. Proceedings of the International Joint
...
v
ts
(t
0
-5)
v
ts
(t
0
-10)
v
ts
(t
0
-15)
v
ts
(t
0
-20)
v
ts
(t
0
-25)
v
ts
(t
0
-30)
ART
a
ART
b
v
p6
(t
0
+5)
v
p5
(t
0
+10)
v
p4
(t
0
+15)
v
p3
(t
0
+20)
v
p2
(t
0
+25)
v
p1
(t
0
+30)
v
ts
(t
0
)
v
ts
(t
0
-5)
v
ts
(t
0
-10)
v
ts
(t
0
-15)
v
ts
(t
0
-20)
v
ts
(
t
0
-25
)
v
p6
(t
0
)
v
p5
(t
0
+5)
v
p4
(t
0
+10)
v
p3
(t
0
+15)
v
p2
(t
0
+20)
v
p1
(t
0
+25)
average
module
v
p
(t
0
+5)
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
24

Conference on Volume 2, 20-24 July 2003
Page(s):1396 – 1401 vol.2.
Carpenter, G.A., et al., 1992.”Fuzzy ARTMAP: A neural
network architecture for incremental supervised
learning of analog multidimensional maps”. Neural
Networks, IEEE Transactions on Volume 3, Issue 5,
Sept. 1992 Page(s):698 – 713.
Dharia, A. and Adeli, H., 2003. “Neural network model
for rapid forecasting of freeway link travel time”.
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,
Volume 16, Issues 7-8, October-December 2003,
Pages 607-613.
Jiang, G., et al., 2003. “The study on the application of
fuzzy clustering analysis in the dynamic identification
of road traffic state”. Intelligent Transportation
Systems, 2003. Proceedings. 2003 IEEE. Volume 1,
2003 Page(s):408 – 411 vol.1.
Park, D., Rilett, L.R., 1999. “Forecasting freeway link
travel times with a multilayer feedforward neural
network”. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure
Engineering 14 (5), 357–367.
Wang, X-H, Xiao, J.M.,2003.”A radial basis function
neural network approach to traffic flow forecasting”.
Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2003. Proceedings.
2003 IEEE. Volume 1, 2003 Page(s):614 – 617 vol.1.
NEURAL NETWORK MODEL BASED ON FUZZY ARTMAP FOR FORECASTING OF HIGHWAY TRAFFIC DATA
25
