
INFLUENCE OF NBMAX AND TABU LIST IN THE SCHEDULING
PROBLEM
Antonio Gabriel Rodrigues
Universidade do Vale do Rio dos Sinos
Av. Unisinos 950, S
˜
ao Leopoldo, RS, Brazil
Arthur T
´
orgo G
´
omez
Universidade do Vale do Rio dos Sinos
Av. Unisinos 950, S
˜
ao Leopoldo, RS, Brazil
Keywords:
Scheduling Problem, Part Selection Problem, Part Family, Tabu Search, Flexible Manufacturing Systems,
Cluster Identification, Keep Tool Needed Soonest approach.
Abstract:
Considering a Job Shop Scheduling Problems with tooling and due date constraints, experiments were made
with a computational model based in Cluster Analysis and Tabu Search. Two minimization policies can be
done in this model: swtiching instants and tardiness time. Previous experiments identify the conflict between
these policies, as the positive influence of variation of TS parameters. This paper presents experiments consid-
ering the influence of the variation of TS paramenters nbmax (number of non-improving iterations performed
by TS) and tabu list size.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Job Shop Scheduling Problem with tooling con-
straints (JST) can be defined as follows: there is a set
of machines and a collection of parts to be processed
on these machines. With each part type is associated a
specific process plan, which consists in a sequence of
operations. Each operation is defined by a machine
type on which it must be processed, its processing
time and the tools which are needed. A machine can
process only one part at a time and they are contin-
uosly avaliable. Each machine has a tool magazine
with limited capacity. All parts to be processed are
avaliable at processing time zero and each part can be
processed by only one machine at a time. No indi-
vidual operation can be pre-empted. Each operation
needs a number of tools, which never exceeds the ca-
pacity of tool magazine. The classical objective is to
minimize the makespan, the maximum of the comple-
tion times of all operations. Since the tool magazine
have limited capacity, tool changes are needed. When
a tool change occurs on a machine, some tools are
replaced by others required for the next parts of the
sequence on this machine. This time spent exchange
tools is called switching instant(Hertz and Widmer,
1996).
In this paper we refer a Job Shop Scheduling Prob-
lem applied to a Flexible Manufacturing Cell (FMC),
considering due dates and tooling constraints (refered
here as JSTD). A FMC is composed by one workas-
tation (CNC/DNC machine whith possesses a device
for tool storage with restricted capacity), a mater-
ial handling system and a computer center (Groover,
2001). We define a objective function z which per-
mits the managing of the importance of due dates
and switching instants in the Scheduling. A com-
putational model based on simple Tabu Search and
Cluster Analysis is used to generate a scheduling
which minimizes z. Experiments performed with
this model in previous works (Rodrigues and G
´
omez,
2005) showed the conflict between due dates and
switching instants minimization. In the present pa-
per, another experiments are made, in which the vari-
ation of TS parameters nbmax and tabu list size are
analyzed.
2 COMPUTATIONAL MODEL
Are considered, additionally to the JSTD constraints
(described in the previous item), the two assumptions:
(i) once processed, any part can return to the system;
(ii) the production turn is considered, so any part can
be processed after the finish of the turn; A batch is
considered a set of parts which can be processed in
the workstation with the same set of tools. Between
the processing of two batches, a switching instant is
required. A switching instant lasts α + βr time units,
217
Gabriel Rodrigues A. and Tórgo Gómez A. (2006).
INFLUENCE OF NBMAX AND TABU LIST IN THE SCHEDULING PROBLEM.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 217-220
DOI: 10.5220/0001216702170220
Copyright
c
SciTePress

where α is a fixed time due to removal of the tool
magazine for the machine and clean the workspace
area, β is a fixed time for each tool replacement and
r is the total number of tools which must be replaced.
In the presented model, it was used an approach sug-
gested by G
´
omez (G
´
omez, 1996) where α and βr are
considered two different decision variables in the ob-
jective function.
2.1 Techniques
To group parts into batches, Part Selection Problem
(PSP) is studied. In this problem a set of parts must
be grouped into subsets,called Part Families (PFs), ac-
cording to some similarity. The PSP is represented us-
ing matrix formulation, a classical approach of Group
Technology (TG). To solve this problem is used the
Cluster Identification Algorithm (CIA) modified by
G
´
omez (G
´
omez, 1996). Originally developed by Ku-
siak and Chow (Kusiak and Chow, 1987), the modi-
fied CIA organizes the rows and columns of the ma-
trix A, generating a matrix B with part-tools clusters,
where each cluster is a FP.
To solve the Job Shop Scheduling Problem, a Tabu
Search (TS) approach was proposed (Glover and La-
guna, 1997). TS is a meta-heuristic composed by a lo-
cal search procedure associated with a memory struc-
ture which constraints the search to visit regions in the
solution space already visited. This memory structure
intents to make the search avoid the local optimals,
performing a better exploration of the space.
2.2 Architecture
The computational model uses TS e modified CIA to
find the schedule such the objective function z is min-
imized. The z function has the following decision
varaiables:
• tardiness time (At): diference between due date
and date of the completion of the part, expressed
in minutes.
• tool replacement time (St): representing the
βr time in the switching instants, expressed in
minutes.
• tool removal time (Sp): representing the α time in
the switching instant, expressed in minutes.
The importance of these decision variables in the fi-
nal schedule can be managed through the assignment
of weights to them. The objective function was devel-
oped considering two dimensions: physical dimen-
sion (Part Families) and time dimension (scheduling).
Considering: N the total amount of parts; L the num-
ber of setups in s; U the number of switching tools in
s; Dv
i
the due date of part i; Ds
i
the completion date
of part i; T r the time to removal the tools e prepare
the workstation for new parts, in minutes; T e the time
to replace one tool in minutes.
Minimize
z(p, f ) = P
1
· At(p, f) + P
2
· Sp(p, f)
+ P
3
· St(p, f)
(1)
Where
At(p, f ) =
N
X
i=1
(Dv
i
− Ds
i
)
such (Dv
i
− Ds
i
) ≥ 0,
i ∈ {1, . . . , N}
(2)
Sp(p, f) = T r ·
L
X
i=1
Sp
i
such Sp
i
≥ 0, T r ≥ 0,
i ∈ {1, . . . , L}
(3)
St(p, f) = T e ·
U
X
i=1
St
i
such St
i
≥ 0, T e ≥ 0,
i ∈ {1, . . . , U}
(4)
P
1
≥ 0, P
2
≥ 0, P
3
≥ 0 (5)
The computational model was developed in four
modules: (i)Part generator, (ii) PF generator, (iii)
Initial Solution generator and (iv) TS-based mod-
ule. More datails about the computational model can
be seen in previous works (Rodrigues and G
´
omez,
2005).
3 EXPERIMENTS
The variation of weights of the objective function was
analyzed in previous papers (Rodrigues and G
´
omez,
2005). A summary of the results are replicated here.
Based on these results, new experiments were made,
considering the influence of nbmax and tabu list size
in the objective function.
3.1 Summary of Previous
Experiments
The previously performed experiments were made
with objective of the managing of the three decision
variables of the z function, presented in the item 2.
The parameters of the experiments performed were:
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
218

(i) a set of 10 parts and 9 tools; (ii) the magazine ca-
pacity is 4 tools; (iii) the time spend for each tool
replacement is 4 minutes; (iv) the time for tool re-
moval is 5 minutes; (v) the production period (turn)
is defined as 480 minutes; (vi) the tabu list initially
stores 10 forbidden moves; (vii) and nbmax number
is defined as 100 iterations. Initially was defined
a non-tendentious solution (NTS), in which all the
decision variables have the same contribution in z.
The values of the weights of decision variables are:
At = 17.27 · Sp and At = 9.89 · St.
Once defined the NTS solution, experiments with
variation of the weights of z were made. The
methodology used was: one of the three weights of
z were increased and the other two were made con-
stant with the values of the NTS solution. There
were made experiments which represents three dif-
ferent minimization policies (minimizing Sp, St and
At). The same behavior (reducing of St and increas-
ing of At) occurs when Sp is minimized. Using the
above TS parameters, the increasing of this weight did
not contribute to generating a schedule with less tar-
diness. Thus, other experiments were performed, in
which nbmax and tabu list size are varied. The results
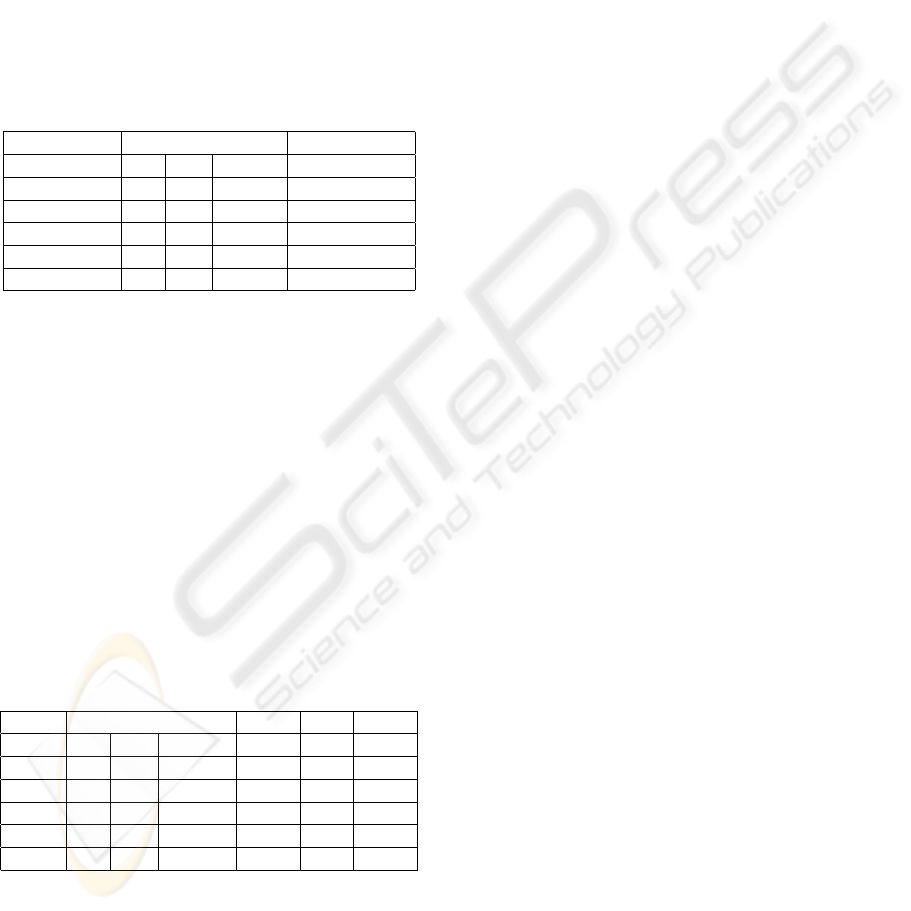
of this lasts experiments are showed in table 1.
Table 1: Tabu list size and nbmax variation for solution that
At = 10.
nbmax tabu list At St Sp
200 100 355 30 56
300 150 397 25 44
400 200 355 30 56
500 250 397 25 44
600 300 355 30 56
700 350 344 30 56
800 400 361 30 56
900 450 397 25 44
1000 500 397 25 44
As the values of At become smaller with the in-
creasing of TS parameters, the values of St and Sp
became high, confirming the conflict between switch-
ing instants and tardiness. New experiments are made
in a manner to determine better the influence of the
variation of these parameters in At minimization.
3.2 Experiments with Nbmax and
Tabu List Size
In the new experiments, the tabu list size and nbmax
size are varied one at each time. The initial solu-
tion was generated using Part Family rule (FAM) dis-
pacthing rule. The initial sequence of parts for these
experiments is {3, 4, 5, 1, 7, 9, 2, 6, 8, 10}. Other pa-
rameters are the same of the previous experiments.
The value (in minutes) of each decision variable using
the FAM rule is: St = 40, Sp = 20 and At = 1026.
The values of the weights used in the new exper-
iments are: At · 100, St · 10, Sp · 18. In the first
type of experiments, tabu list size was varied, while
nbmax = 1000. The best result was found at TS in-
teraction 1712, with At = 311, St = 56, Sp = 30
and tabu list with size = 500. In the figure 1 shows
the behavior of At in the experiment and the iteration
where it was found the better result.
Figure 1: Values of At considering variation of tabu list size
and iteration when it was found the best result.
A second type of experiment was performed, Using
the best value of tabu list size in the experiment pre-
sented above. In this experiment NBMAx was varied
and the same better solution was found in the TS iter-
ation 1712, with nbmax ≥ 900. Figure 2 shows At
and the best iteration behavior.
Figure 2: Values of At considering variation of nbmax and
iteration when it was found the best result.
Comparing the variation of two graphs, it can be
noticed that tabu list size determines the search reach
to the better results for At, considering a high nbmax
number. The increasing of these parameters reduces
de At value significantly, but increases the amount of
memory used by the model and the running time. In
INFLUENCE OF NBMAX AND TABU LIST IN THE SCHEDULING PROBLEM
219
the next item, comparsion is made between TS pa-
rameters of previous works and new TS parameters
used in the presented experiments.
3.3 Comparing Results
Table 2 shows a comparsion among initial FAM solu-
tion, NTS solution (At · 1, St · 10 and Sp · 18) and
the solutions obtained with 3 minimization policies
weights in previous works (Rodrigues and G
´
omez,
2005).
Table 2: Comparsion among initial solution and policies of
minimization considering nbmax = 100 and tabu list size
= 10.
Minimizing decision variables best iteration
St Sp At
St 28 20 891 7
Sp 32 20 709 7
At 56 30 451 16
NTS 32 20 709 7
FAM 40 20 1026 -
The initial solution (FAM) groups parts with same
PF, forming a sequence with minimum switching in-
stants time (20 minutes). The increasing of Sp can-
not improve z and the tool replacement time remains
the same. The St minimization results in less tool re-
placement time and a higher tardiness value, accord-
ing to the previous experiments. The At minimization
reduces 575 minutes the tardiness time (
∼
=
56%), in-
creasing the tool removal and tool replacement time.
Table 3 shows the impact of the variation of TS pa-
rameters in the decision variables of z, considering
the initial, solution, NTS solution and minimization
policies.
Table 3: Comparsion among initial solution and policies of
minimization. BI = best iteration; TL = tabu list size; NB =
nbmax.
Min Desision variables BI TL NB
St Sp At
St 28 20 891 7 50 500
Sp 32 20 624 70 50 100
At 56 30 311 1712 500 1000
NTS 32 20 397 43 50 100
FAM 40 20 1026 - - -
The increasing of tabu list size doesn’t contribute
for improvement of any decision variable in St min-
imization. Its influence is low in Sp minimization,
reducing the tardiness time in 85 minutes. With the
NTS solution, the variation results in a better At time,
while St and Sp remain the same value. It was needed
a higher variation of TS parameters to find a better re-
sult of At, when its minimization is considered.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The experiments presented in this paper has the ob-
jective of investigate the influence of TS paramenters
in a computational model developed to deal with Job
Shop Scheduling Problem with tooling and due date
constraints. This model allows to manage three deci-
sion variables of an objective function: tardiness, tool
replacement and tool removal. Previous experiments
shows a conflict between minimizing tool replace-
ment and tool removal versus tardiness. Those expri-
ments shows the positive influence of the increasing
of the tabu list size and nbmax number in minimiza-
tion of tardiness.
Experiments were made, where these TS parame-
ters were variated. In the initial experiments, tabu
list size was variated, and the increasing of this pa-
rameter results in better At time. It noticed that some
values assigned to tabu list size minimizes At more
than other values. In the second type of experiments,
nbmax was increased, considering the best value of
tabu list size. The reduction of At value obtained was
the same of the initial experiments. The tabu list size
parameter is the main factor in the diversification of
the search, determining the variation of At compo-
nent.
REFERENCES
Glover, F. and Laguna, M. (1997). Tabu Search. Kluwer
Academic Publishers.
G
´
omez, A. T. (1996). Modelo para o seq
¨
uenciamento de
partes e ferramentas em um sistema de manufatura
flex
´
ıvel com restric¸
˜
oes
`
as datas de vencimento e
`
a ca-
pacidade do magazine. PhD thesis, Instituto Nacional
de Pesquisas Espaciais, S
˜
ao Jos
´
e dos Campos, S
˜
ao
Paulo, Brasil.
Groover, M. P. (2001). Automation, production systems and
computer-integrated manufacturing. Prentice-Hall,
second edition.
Hertz, A. and Widmer, M. (1996). An improved tabu search
approach for solving the job shop scheduling problem
with tooling constraints. Discrete Applied Mathemat-
ics, 65:319–345.
Kusiak, A. and Chow, W. S. (1987). Efficient Solving of the
Group Techonology Problem.
Rodrigues, A. G. and G
´
omez, A. T. (2005). Production time
minimization strategies: a Tabu Search approach. In
Annals of the 2nd ICINCO - International Conference
on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics.
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
220
