
DATA FLOW FORMALIZATION
Thouraya Bouabana-Tebibel
Institut National d’Informatique BP 68M, Oued-Smar 16270, Algiers, Algeria
Keywords: UML, OCL, Petri nets, temporal logics, verification, validation.
Abstract: The Object Constraint Language OCL is an extension of the UML notation for the expression of restrictions
on diagrams. We propose to take advantage of its all expression capabilities for validating the UML system
properties. For this purpose, we develop an approach to support the OCL invariant verification on the
colored Petri nets derived from the UML modeling. A case study is given throughout the paper to illustrate
the approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
UML (OMG, 2003) suffers from ceaseless critics on
the precision of its semantics when the verification
of modeling correctness has become a key issue.
UML 2.0 (OMG, 2004) brings more precision on its
semantics, but it remains informal and lacks tools for
automatic analysis and validation. We presented in
(Bouabana-Tebibel, 2004) a methodology to
automatically derive UML modeling in colored Petri
nets (Jensen, 1992) which are supported by lots of
tools to verifying them. In the present paper, we
carry on with this work by developing a technique to
deal with the verification process.
The Petri nets resulting from the derivation
processes, are analyzed by means of PROD (PROD,
2004), a model checker tool for predicate/transition
nets. Model checking is classified as the most
appropriate technique for verifying operational UML
models (Beato, 2004), (Ober, 2003). It allows a fast
and simple way to check whether the property holds
or not. To avoid the high cost learning of the model
checker, the designer can specify the system
properties in OCL, the Object Constraint Language
(OMG, 2003) which permits to formulate
restrictions over UML models, in particular,
invariants. The latter can be after, automatically
translated to temporal logic properties in order to be
verified by PROD during the Petri net analysis.
Translating OCL invariants into LTL and CTL
properties remains insufficient for validating the
properties. Indeed, OCL expressions refer to
classifiers to evaluate their association ends. The
association ends values are updated (created,
modified or read) on the object life cycle by means
of the link actions. So, in addition to the OCL
invariant translation in LTL and CTL properties, we
propose an approach to translate the link actions in
Petri nets, to achieve the systematic formal
verification of the OCL constraints.
The remainder of the paper starts with a brief expose
on the UML modeling derivation to Petri nets, this,
constituting the background of the present work. The
proposed approach is then presented and the
techniques upon which it is based are developed.
These techniques are illustrated in a case study. We
conclude with some observations on the obtained
results and recommendations on future research
direction.
2 BACKGROUND
We summarize in this section, the work that we
present in (Bouabana-Tebibel, 2004) to derive UML
statecharts to colored Petri nets. This work supports
the approach that we develop in the present paper.
2.1 Statecharts
A statechart describes the behavior of a class in
terms of states and exchanged messages with other
classes’ statecharts. A state is composed of two
atomic actions (at its entry and its exit) and one
activity. The states are linked by means of
transitions annotated with the event that triggers the
transition (event trigger) and atomic actions
148
Bouabana-Tebibel T. (2006).
DATA FLOW FORMALIZATION.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 148-153
DOI: 10.5220/0001219501480153
Copyright
c
SciTePress
produced by the triggered transition. Due to their
atomicity, the entry, exit and transit actions are in
fact, generated events respectively called: entry, exit
or transit events, see figure 1.
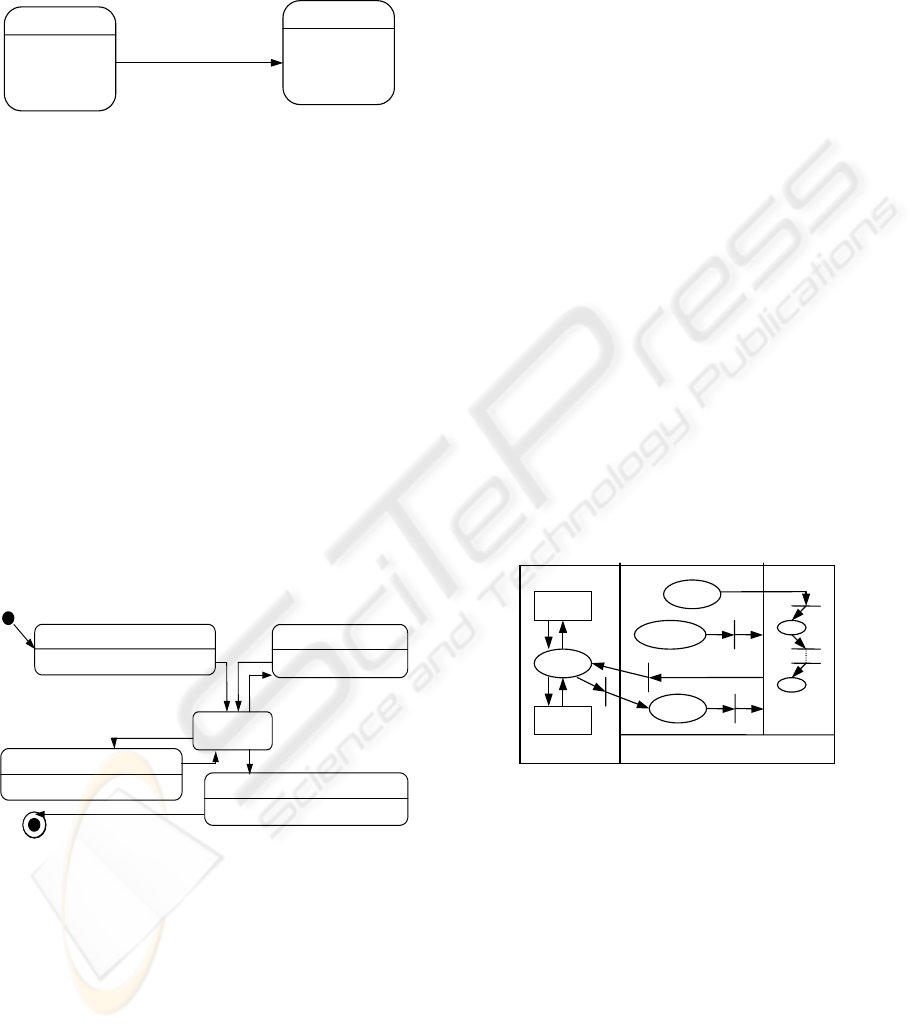
State 2
entry: event
do: activity
exit: event
trigger / transit event
State 1
entry: event
do: activity
exit: event
Figure 1. Statechart’s events and activity
The event is of two types: send event or call event.
These events are mentioned on the statechart as
follows: «send» class(), «call» operation().
Examples of these events are given in the case study
of figure 2.
We illustrate our study through a message server
application where the main role of the server is to
manage the communication between the connected
stations. All the exchanged messages must go
through this server, to be forwarded to the receivers.
Figure 2 represents the statechart of a station which
can, at all times, connect itself from the server. Its
connection request is realized using the «send»
connection event. The server confirms the station
connection using the «send» okconnection events.
When connected, a station can notify a message,
receive a message or disconnect itself. It notifies by
means of the «send» notification event.
entry : «send» connection()
connecte
d
entry : «send» disconnection()
disconnection
connection
«send» okconnection()
/ «create» notification()
«
sen
d
»
okdisconnection
()
rece
p
tion
exit : «call» save()
«send» forward()
entry : «send» notification()
notification
Figure 2. Statechart of the station class
After receiving a forwarded message from the server
by means of the «send» forward trigger, it saves it
using the «call» save event. Its disconnection is
requested by the «send» disconnection event and
confirmed by the «send» okdisconnection event.
2.2 Petri Nets
Petri nets have been presented in several works
(Baresi, 2002) as a suitable formalism for translating
the UML dynamic models. We used them in
(Bouabana-Tebibel, 2004) to derive the statechart
and collaboration diagrams. We defined them by the
7-tuple <P, T, A, C, Pre, Post, M
0
,> where:
- P = {p
1
, p
2
, …, p
n
} is a set of places.
- T = {t
1
, t
2
, …, t
n
} is a set of transitions.
- A ⊆ P × T ∪ T × P, is a set of arcs.
- C = {C
1
, C
2
, …, C
n
} is a set of colors where C
i
=
{<c
1
, c
2
,
,
…, c
k
>} and c
j
is a variable or a constant.
- Pre : P
×
T → P(C) is a precondition function to
the transition firing such that Pre(p
i
, t
i
) = {C
1
, C
2
, …,
C
k
}.
- Post : P
×
T → P(C) is a postcondition function to
the transition firing such that Post(p
i
, t
i
) = {C
1
, C
2
,
…, C
k
}.
M
o
: P → C is the initial marking function, such that
M
o
(p
i
) = ∑
k=1,K
C
k
.
2.3 Derivation Approach
The derivation process is based onto an object-
oriented approach. Each statechart modeling an
interactive class behaviour is transformed to an
object subnet called Dynamic Model or DM (see
figure 3). To construct the DM, each state s
∈
S is
converted to a place p
∈
P and each transition tr
∈
Tr is converted to a transition t
∈
T.
The classes interact through the Link place which
receives the events generated by the DMs and then
dispatches them to the destination DMs. The
forwarding is relayed by the Input place which
constitutes an input interface of the DM. The events
are modeled by tokens of event type
To deal with Petri net simulation, we tackle the Petri
net initial marking which may be of two types: static
or dynamic. The static initial marking provides the
class instances and their attribute values. These
instances are extracted from the object diagram to
initialize the Object place with tokens of object type
of the form <obj, attrib>. The dynamic initial
OPN
Link
OPN
OPN
DM
Input
Object
Scenario
Figure 3. Petri nets interconnection architecture
Figure 1: Statechart’s events and activity.
Figure 2: Statechart of the station class.
Figure 3: Petri nets interconnection architecture.
DATA FLOW FORMALIZATION
149

marking provides the exchanged messages among
the interactive objects. These messages are extracted
from the sequence diagram to initialize the Scenario
place with tokens of event type. The event tokens
have the form <srce, targ, op/xobj, attrib> where
Srce and targ are respectively the source object’s
identity and the target object’s identity. The
component op/xobj gives the called operation if a
call event and the exchanged object’s identity if a
send event. As for attrib, it designates the set
{attrib
1
, …, attrib
k
}of the exchanged object’s
attributes if a send event, the operation attributes if a
call event.
Thus, each generated event on the statechart is
converted to an arc from the Scenario place to the
transition to which it is related. It is after converted
to an arc from this transition to the Link place. As
for the event trigger, it is converted to an arc from
the Input place to the transition on which it occurs.
Figure 4 represents the Petri net resulting from the
conversion of the statechart of the station class.
3 ANALYSIS AND
VERIFICATION
The verification by model checking as treated in
PROD, is based on the state space generation and
the verification of safety and liveness system’s
properties on this space. The properties may be
basic, about the correctness of the model
construction or specific, written by the modeler to
ensure the faithfulness of the system modeling. For
each of these approaches, given a property, a
positive or negative reply is obtained. If the property
is not satisfied, it generates a trace showing a case
where it is not verified.
3.1 Generic Property Verification
The basic properties are verified according to on-
the-fly tester approach or the reachability graph
inspection approach. The on-the-fly verification of a
property means that the property is verified during
the state space generation which is automatically
stopped as soon as the property fails, in contrary to
the traditional approach where properties are
verified on the reachability graph, after its
generation.
The on-the-fly tester approach detects deadlock,
livelock and reject states. The deadlock verification
ensures that there exists no reachable marking where
no transition is enabled. In other words, that means
that there is no UML states that prevent any activity
to be invoked eventually. The livelock detection
informs about loops of actions on the graph. As for
the reject state checking, it detects undesirable
markings in critical places which is equivalent in
UML, to rejecting undesirable objects at given
states. These three properties are systematically
verified, without intervention of the designer.
The reachability inspection approach permits the
verification of some other properties such as quasi-
liveness, boundedness or reinitializability. These
properties are automatically verified.
The quasi-liveness property is weaker than the
deadlock. It guaranties that each transition is enabled
at least once, i.e., each UML activity can be invoked
eventually.
The boundedness is formulated to require an upper
bound to the number of objects that can be present,
in a state at a given time or in an association end,
according to the UML specification using the
multiplicity construct. Since objects correspond to
tokens, this property upper-bounds the number of
tokens.
The reinitializability property checks the possibility
for a system of restarting from any state, i.e., the
initial marking should be reachable from any
marking of the net. This is realized by a systematic
computation of the net strongly connected
components which must be equal to 1, so that the net
can be reinitializable.
3.2 Specific Property Verification
For a more precise validation, system’s specific
properties can be written by the designer in LTL or
CTL logics and then, verified by PROD. Since the
connectio
n
Input
notification
disconnection
reception
connected
Lin
k
Scenario Object
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
Figure 4. OPN of the station class
Figure 4: OPN of the station class.
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
150
main motivation of this work is that the UML
designer may reach a valid modeling without needs
for knowledge of formal techniques, it is only
reasonable that the properties are expressed by the
modeler in the OCL language and are after,
automatically translated in LTL and CTL logics.
Many works have investigated the OCL invariant
translation in other formalisms such as Object-Z
(Roe, 2003), B (Marcano, 2002), first-order
predicate logic (Beckert, 2002) or object-based
temporal logic (Distefano, 2000). Other works
tackled OCL invariant extension with temporal
operations (Cengarle, 2002), (Flake, 2004). The
relevance of such a mapping is of a practical nature.
It presents the merit of providing a specific
translation that takes the target tool’s (PROD)
characteristics into account. Due to the paper length,
this translation is presented in another work.
OCL is mainly based on collection handling in order
to specify object invariants. As these collections
correspond to association ends, the latter must
appear on Petri net specification so that the
translated LTL and CTL properties (whose
expression is essentially made of these constructs),
can be verified. This lead us to the necessity of
introducing the association end modeling onto the
statecharts in order to get after transformation, the
equivalent Petri net constructs. This object flow
modeling is realized by means of the link actions.
However, the usefulness of the link actions does not
concern explicitly the modeling of the object life
cycle. When constructing his diagrams, the designer
does not necessarily think to modeling these
concepts which are rather specific to the link and
end object updates. For example, for connecting a
station to the server, the connection request and
connection confirmation actions are naturally and
systematically modeled by the designer, but the
addition of the connected station to the association
end is usually omitted from the modelling, see
figures 2 & 5. That is why we recommend to the
designer to specify the link actions on the statechart
so that the OCL invariants can be verified. But, we
release him from this modeling on the sequence
diagram and take in charge the treatments related to
the initialization of these actions.
UML action semantics was defined in (OMG, 2001)
for model execution and transformation. It is a
practical framework for formal descriptions. For this
work, we are particularly interested in the create link
and destroy link. The create link action permits to
add a new end object in the association end. The
destroy link action removes an end object from the
association end. These actions will be represented on
the statechart as tagged values of the form
{linkAction(associationEnd)}, following the event
which provokes the association end update.
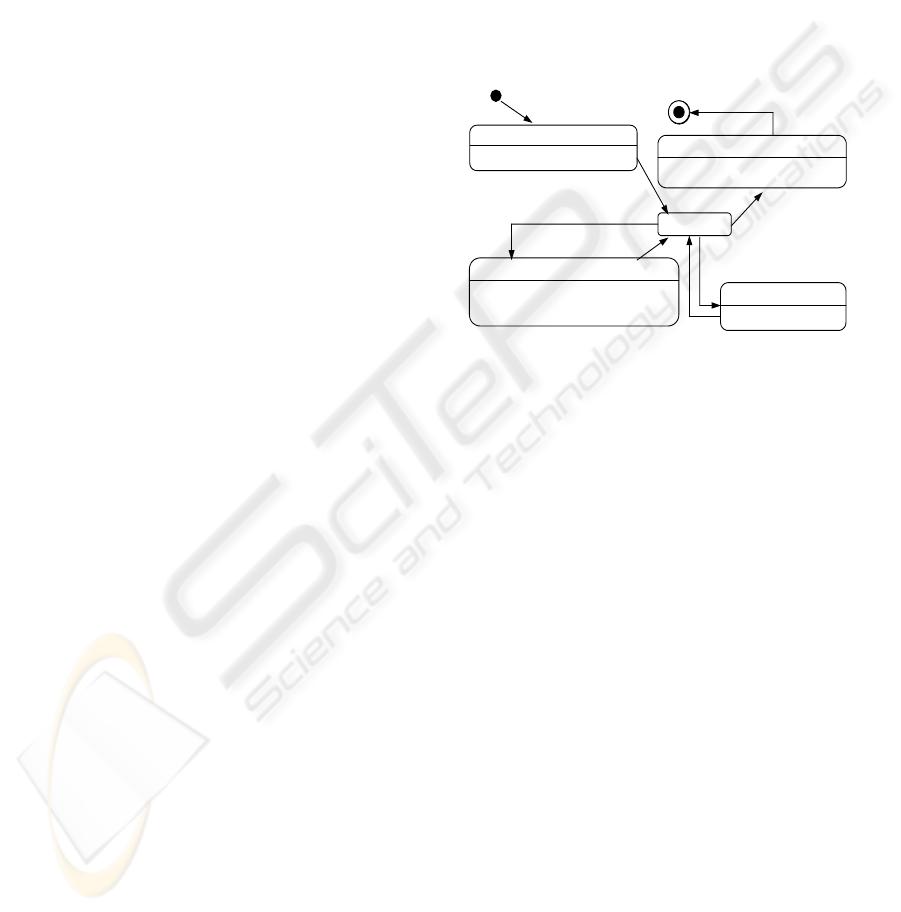
On figure 5, after confirmation of its connection or
disconnection («send» okconnection or «send»
okdisconnection), the station adds or removes itself
from the association end connectedStation, using
respectively, {createLink(connectedStation)} or
{destroyLink(connectedStation)}. It adds a notifed or
received message with {createLink
(transmittedMessage)} or
{createLink(receivedMessage)}, respectively.
The link actions may concern an active (interactive)
or passive (exchanged) end object. The object-
oriented approach, on which both UML and Object
Petri nets rely, is based on modularity and
encapsulation principles. To deal with modularity, a
given association end should appear and be
manipulated in only one statechart. In Petri nets, the
association end is translated in a place of role type.
This place holds the name of the association end and
belongs to the DM translating the statechart.
Furthermore, an association end regrouping active
objects must be updated within the statechart of
these objects’ class, in order to comply with the
encapsulation concept. Indeed, since the end object
is saved in the role place with its attributes, these
attributes must be accessible when updating the
association end. The exchanged objects are usually
manipulated by the interactive objects and are not
specified by dynamic models. So, the association
end representing them could be updated in the
statechart of the class that is at the opposite end. As
more than one opposite end can be linked, the
selected class is the one affecting the association
end. For exchanged objects, the encapsulation
constraint is lifted given that the exchanged object’s
entry : «send» connection()
connecte
d
entry : «send» disconnection()
disconnection
connection
«send» okconnection()
{createLink(connectedStation)}
/ «create» notification()
«send» okdisconnection()
{destroyLink(connectedStation)}
receptio
n
exit : «call» save()
«send» forward()
{createLink(receivedMessage)}
entry : «send» notification()
{createLink(transmittedMessage)}
notification
Figure 5. Statechart of the station class with link action specification
Figure 5: Statechart of the station class with link action
specification.
DATA FLOW FORMALIZATION
151

attributes are transmitted within the message and so,
accessible by the interactive objects.
In Petri nets, the create link action is semantically
equivalent to an arc from the transition related to the
association end update towards the place specifying
the association end, adding an object within. The
destroy link action is semantically equivalent to an
arc from the association end place to the transition
corresponding to the link action, removing an object,
see figure 6.
The object to be added to / removed from the
association end is extracted from the components of
the token (whose global form is <srce, targ, op/xobj,
attrib>) corresponding to the event that provokes the
association end update. This token is situated in the
Scenario place if the event is generated. It is located
in the Link place if the event occurs. The
added/removed object may be the source object (src)
or the exchanged object (xobj) if the link action
follows a generated event. It is the target object
(targ) or the exchanged object (xobj) if the link
action follows an event trigger.
In Petri nets, the association end objects are colored
tokens of role type They are of the form <assoc, obj,
attrib>, where obj is the object to be added to or
removed from the association end and assoc is the
object at the opposite end.
We propose in what follows, to express a property
extracted from the server message application. This
property is first expressed into a paraphrased
(textual) form. It is after, specified as OCL
invariants and finally translated into LTL properties.
Property 1
The number of connected stations is limited to
maxStation.
Property 1 expression in OCL
context s:Server inv: s.connectedStation→size <=
Server.maxStation
Property 1 expression in PROD
For each server s and for each place of its DM
*
write
the property:
# verify henceforth (card(connectedStation : field[0]
== s) <= (place
DM*server
: field[2]))
where:
- connectedStation: field[0] designates the first
component (assoc) of the connectedStation’s tokens,
- place
DM*server
: field[2] designates the third
component (attrib
2
= maxStation) of the tokens of
DM* of the server,
- DM* designates a DM excluding the places of role
type.
4 CONCLUSION AND FURTHER
WORK
Formalization of UML statechart semantics (Kuske,
2001), (Truong, 2005), (Varro, 2002) and integration
in the statecharts of formal languages state-oriented
(Attiogbé 2003), (Meyer, 2001) or property-oriented
(Attiogbé 2003), (Royer, 2003) were widely
investigated in the research area. The OCL language
has also been used in various works in particular,
those of Flake (Flake, 03), (Flake, 04) who extends
it with temporal logics to express properties over
time. However, through our multiple investigations,
we have never encountered works that tackle the
integration of the end associations on the statecharts
to formalize the object flow dynamics.
This paper presents an approach to systematically
validate the UML modeling without need for the
user to know formal checking techniques. The
verification concerns both the correctness of the
model construction and the faithfulness of the
modeling. The latter is allowed thanks to the system
awaited properties which are expressed by the
modeler in OCL language and then translated into
LTL and CTL properties. To efficiently deal with
their validation, we propose to introduce an object
flow specification into the object’s control flow
model (statechart), using predefined actions on the
association ends.
An extension of this work concerns the automatic
translation of the OCL invariants to LTL and CTL
properties according to PROD syntax and features.
This work is actually under review. Another
prospect of this paper is the analysis of the
validation/verification results and their feedback to
the user are explored. These results must be
presented to the designer in an interpreted form,
where the error in modeling is simply and clearly
pointed out. Since the methodology calls for UML
Statechart constructs Petri net constructs
{
CreateLink(role)}
role
derivation
derivation
role
{
DestroyLink(role)}
Figura 6. Translation of the link actions
Figure 6: Translation of the link actions.
ICINCO 2006 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
152

designer to provide the input specifications, it is only
reasonable for the output results to be meaningful to
that user.
REFERENCES
Attiogbé, C., Poizat, P., Salaun, G., 2003. Integration of
Formal Datatypes within State Diagrams, In M. Pezze
éds. Fundamental Approaches to Software
Engineering FASE’2003, LNCS, vol. 2621, pp. 341-
355, Springer.
Baresi, L., 2002. Some Premilinary Hints on Formalizing
UML with Object Petri Nets, Proc. of the 6th World
Conference on Integrated Design & Process
Technology, Pasadena, USA.
Beato, M. E., Barrio-Solorzano, M., Cuesta, C. E., 2004.
UML Automatic Verification Tool (TABU), In proc.
12
th
ACM SIGSOFT Symposium on the Foundations
of Software Engineering, October/November.
Beckert, B., Keller, U., Schmitt, P., 2002. Translating the
Object Constraints Language into First-order Predicate
Logic, Proc. Verify, Workshop at Federated Logic
Conferences, Copenhagen.
Bouabana-Tebibel, T., Belmesk, M., 2004. From UML
towards Petri nets to specify and verify, Proc. ICINCO
2004, 1
st
International Conference on Informatics in
Control, Automation & Robotics, Portugal.
Cengarle, JM., Knapp, A., 2002. Towards OCL/RT, In L.-
H. Eriksson and P. Lindsay, eds., Formal Methods –
Getting IT Right, LNCS, vol 2391, Springer, July, pp.
389-408.
Distefano, D., Katoen, J-P., Rensink, A., 2000. On a
Temporal Logic for Object-Based Systems, Proc.
Fourth International Conference on Formal Methods
for Open Object-Based Distributed System”,
FMOODs 2000, Stanford, California, USA,
September.
Flake, S., Mueller, W., 2004. Past- and Future-Oriented
Temporal Time-Bounded Properties with OCL, Proc.
2nd Int. Conf. on Software Engineering and Formal
Methods, China, ©IEEE. Computer Society Press, ,
pp. 154-163.
Flake, S., 2003. UML-Based Specification of State-
oriented Real-time Properties, PhD thesis, Faculty of
Computer Science, Electrical Engineering and
Mathematics, Paderborn University, Shaker Verlag,
Aachen, Germany.
Jensen, K., 1992. Coloured Petri nets, Vol 1: Basic
Concepts, Springer.
Kuske, S., 2001. A formal semantics of UML state
machines based on structured graph transformation,
M. Gogolla and C. Kobryn, ed. UML: The Unified
Modeling Language. Modeling Languages, Concepts
and Tools, LNCS vol. 2185, pp. 241-256.
Marcano, R., Lévy, N. 2002. Transformation rules of OCL
Constraints into B Formal Expressions, In University
of Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines eds.
Meyer, E., 2001. Développements formels par objets :
utilisation conjointe de B et d’UML, PhD thesis,
LORIA, University of Nancy 2, France.
Ober, I., Graf, S., Ober, I., 2003. Validating Timed UML
Models by Simulation and Verification, Proc.
International Workshop SVERTS: Specification and
Validation of UML Models for Real Time and
Embedded Systems, Fort Mason Center, San
Francisco, California, USA.
Object Modeling Group, 2004. UML 2.0 Superstructure
Specification.
Object Modeling Group, 2003. OMG Unified Modeling
Language Specification, version 1.5.
Object Modeling Group, 2003. Object Management
Group. UML 2.0 OCL Specification.
Object Modeling Group, 2001. The UML Action
Semantics.
PROD 3.4, 2004. An advanced tool for efficient
reachability analysis, Laboratory for Theoretical
Computer Science, Helsinki University of
Technology, Espoo, Finland.
Roe, D., Broda, K., Russo, A., Mapping UML Models
incorporating OCL Constraints into Object-Z, Imperial
College Technical Report N°2003/9, 2003.
Royer,. J.-C., 2003. Temporal Logic Verifications for
UML, The Vending Machine Example. RSTI -
L'objet, 4
th
Rigorous Object-Oriented Methods
Workshop, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 73-92.
Truong, N., Souquières, J., 2005. Verification of
behavioral elements of UML models using B. In
proceeding of 20th Annual ACM Symposium on
Applied Computing –SAC’05. New Mexico, USA.
Varro, D., 2002. A Formal Semantics of UML Statecharts
by Model Transition Systems, Proceedings of the 1st
International Conference on Graph Transformation,
Spain.
DATA FLOW FORMALIZATION
153
