
COMBINING TWO STRATEGIES FOR ONTOLOGY MAPPING
1
Ying Wang, Jianbin Gong, Zhe Wang, Yanchun Liang and Nan Lu
College of Computer Science, Key Laboratory of Symbol Computation
and Knowledge Engineering of the Ministry of Education,
Jilin University, Qianwei Street,Changchun 130012,P.R. China
Keywords: Ontology mapping.
Abstract: Ontologies are the key to the Semantic Web because they are the carriers of the meanings contained in the
Semantic Web (McGuinness, 2002). At the same time, ontology mappings can provide a channel from
which several ontologies could be accessed and hence could exchange information. Establishing such
mappings has been the focus of a variety of research originating from diverse communities. In this paper,
we propose an approach ACAOM (A Composite Approach for Ontology Mapping) for automatic ontology
mapping based on the combination of name and instance based strategies. ACAOM uses WordNet to
calculate similarities between concepts in two ontologies and also uses instances that include text
information to build vectors, and then computes similarities. The two similarity measures are then combined
to create the results of mapping. The experimental results and comparisons with related work indicate that
ACAOM can find mappings effectively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Semantic Web uses metadata with semantic
information to annotate resources on the web so that
machines can understand them (Berners-Lee, 1999
).
Ontologies are cores in the Semantic Web because
they are the carriers of the meaning contained in the
Semantic Web. However in many cases, different
domains define different ontologies containing the
same concepts. Even in the same domain, different
organizations construct different ontologies.
Therefore, it is necessary to find a flexible, practical
approach to establish semantic correspondences
between ontologies and implement the exchange of
data annotated by different ontologies.
So far, many different approaches have been
proposed with diverse range of mapping techniques.
For example, an integrated ontology mapping
approach (Ehrig, 2004) was proposed based on rules
and quick ontology mapping focuses on runtime of
the program.
The approach of semantic enrichment for
ontology mapping exploits text categorization to
automatically assign documents to the concept in the
ontology and use the documents to calculate the
similarities between concepts in ontologies (Su,
2004).
In ontology mapping, it is common to compute
semantic similarities between concepts in entities.
To achieve this, dictionaries and thesauri are needed,
such as WordNet. In this paper, ACAOM first uses
WordNet to calculate similarities between concepts
in two ontologies. It then uses instances that include
text information to build vectors in order to compute
similarities between entities’ concepts again. The
two similarity measures are then combined to create
the results of mapping.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 introduces the basic concepts in ontology
mapping. Section 3 describes the main ideas in our
approach and the mapping strategies used. Section 4
gives the background information about the
experiments and the results. Section 5 discusses
related work and analyzes the reasons why our
method cannot achieve 100% mapping result.
Section 6 concludes the paper with discussions on
future research.
1
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
under Grant No. 60433020, and the Key Laboratory for Symbol Computation
and Knowledge Engineering of the National Education Ministry of China.
Project985: supported by the creative platform of technology of computation
and software science. The authors would like to thank for the support from
European Commission under grant No. TH/Asia Link/010 (111084) linkman:
Chunguang Zhou email: cgzhou@jlu.edu.cn
381
Wang Y., Gong J., Wang Z., Liang Y. and Lu N. (2006).
COMBINING TWO STRATEGIES FOR ONTOLOGY MAPPING.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Internet Technology / Web
Interface and Applications, pages 381-386
DOI: 10.5220/0001247003810386
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 BASIC IN ONTOLOGY
MAPPING
This section introduces the basic definition of
ontology and ontology mapping.
Ontology: In philosophy, an ontology is a theory
about the nature of existence, of what types of things
exist. In 1993, Gruber presented the definition of
ontology which is used commonly today: “An
ontology is a formal, explicit specification of a
shared conceptualization.” (Gruber, 1993).
We use the following notation to formally
definite an ontology. An ontology O composes of
tuples:
O=(C, R, F, A, I)
where C is a set of concepts, R is a set of
relations, F is set of functions, A is a set of axioms
and I is set of instances. We only make a generic
introduction about the basic definition. In this paper
an entity is defined as follows: e
ij
are entities of O
i
with e
ij
∈ {C
i
,R
i
,I
i
},entity index j∈ N (Ehrig, 2004).
Ontology Mapping: The overall objective of
ontology mapping can be described as (): given two
ontologyies O
1
and O
2
, for each element in one
ontology O
1
, finding the corresponding
element(s),which has same or similar semantics in
ontology O
2
, and vice verse.
Formally an ontology mapping function can be
defined as:
z map
1
i
O →
2
i
O
denotes the mapping function between the two
ontologies
z map(
11
ij
e )=
22
ij
e
denotes the mapping of two entities
In this paper, we only consider the 1:1 mappings
between single entities and we don’t consider its
knowledge reasoning or complicate reasoning.
3 A COMPOSITE APPROACH
FOR ONTOLOGY MAPPING
(ACAOM)
In this section, we will clarify the main processes of
ACAOM.
3.1 The Main Steps in ACAOM
The ontologies used in this paper are constructed
with OWL. The main steps as follows:
Step 1. ACAOM uses WordNet to calculate
similarities between names and then uses name-
based strategy (see Sect. 3.2) to compute all of the
names of concept nodes in ontologies. Finally, we
get the name matching nodes.
Step 2. This step computes similarities between
concept nodes by semantic enrichment for
ontologies using vector space model.
Step 3. This step uses the combined similarity
values derived from the above two steps to calculate
the degrees of mappings between entities from two
ontologies, O
1
to O
2
.
3.2 Name-based Strategy
Name-based mapping strategy has been used in
many research papers (Tang, 2005). In this paper,
we use a semantic dictionary and add a method of
path in it. WordNet is a widely used semantic
network which is organized by synset. Each synset
may contain multiple words with similar meanings.
Between synsets there are some relationships, such
as hyponymy and meronymy. In this paper, we make
use of hyponymy between words, which means a
kind of relationship between words. A word may
have two parts of speech, noun and verb. We will
judge its part of speech first and then use its noun to
compare with other words’ noun and the same is to
its verb. It is pointless to compare a noun and a verb
because they belong to different hierarchy trees.
We use WordNet as auxiliary information to
calculate similarity values between concepts in the
two ontologies based on Lin’s approach (Lin, 1998)
which defines the similarity between two senses . In
this paper, sense denotes the word’s sense.
There are a number of measures to compute
semantic relatedness besides the method described
above and the easiest one is to use the path length
between concepts. It regards WordNet as a graph
and finds relatedness between senses by identifying
the shortest distance, e.g., the shorter the path from
one node to another, the more similar they are
(Resnik, 1995). We integrate the measure of path
length into our mapping approach based on Lin’s
method (Lin, 1998) to obtain the following revised
formula.
When we search for common hypernym of sense
s
1
and sense s
2
, we design a punishment
coefficient
1
2
l
α
, where α is a constant between 0 and
1 and is used to adjust the decrease of the degree of
similarity between two senses when the path length
between them is deepened, l expresses the longest
distance either sense s
1
or sense s
2
passes by in a
hierarchical hypernym structure. Because sense s
1
(
)
(
)
()
()
()
()
12
12
12
2log ,
1
(, )
2
log log
l
new
pss
sim s s
ps ps
α
=•
+
i
(1)
WEBIST 2006 - WEB INTERFACES AND APPLICATIONS
382

and sense s2 occupy one of the common branches,
this value has to be halved. For example, if we want
to compute the similarity of “apple” and “orange” by
using the method described above, we have the
following illustration:
Figure 1: Fragment of WordNet.
In this example, the path from “apple” to “edible
fruit” is 1 and the path from “orange” to “edible fruit
” is 2, so we will make l equal to 2.
In the formula (1), there are some details defined
as:
where formula (2)denotes the word count in
sense s and formula(3) expresses the probability that
sense s occurs in some synset. N is the total number
of words in WordNet. So p(s
1
,s
2
) is the probability
that the same hypernym of sense s
1
and sense s
2
occurs.
Word w
1
and word w
2
may contain many senses,
we use s(w
1
) and s(w
2
) to denote the set of senses of
word w
1
and word w
2
respectively, that is, s(w
1
)={s
1i
∣ i=1,2,……,m} , s(w2)={s
2j
︱ j=1,2,……,n}.
Assume that the amounts of senses that word w
1
and
word w
2
contain are m and n, we define the
similarity between them as:
When computing names of concept nodes which
compose of many words, for instance, College of
Arts and Sciences, we split the sentence and put the
individual words into a set like w={w
1
,w
2
,w3} and
then we deal with these words as follows:
1. Firstly, calculate similarities of every pair of
words from both sets by using Formula (4). If the
first set has n elements and the second has m, there
will be n×m similarity values.
2. Choose the largest similarity value from
the
above results and then match the two words of
the pair that has this similarity value in the two
corresponding sets. Delete the words in each pair
that is identified in the second step above from their
corresponding set of words.
3. Repeat the second and the third steps
above
until all of the matching words have been
deleted.
4. If there exist some free words, words
that have
no matching elements in another set of words, let
the free elements correspond to the vacancy.
5. Compute the final degree of similarity
using the
arithmetic average of similarities because it is
assumed that each word in its word set has equal
probability of occurrence. The result obtained is the
degree of similarity between word sets.
3.3 Instance-Based Strategy
This strategy exploits the vector space model to
denote documents and then finds mapping results
between entities. In this paper, we assume that the
documents have been associated with concept nodes
in ontologies. We establish feature vectors for each
document that belongs to the concept nodes and then
compute the feature vectors for each concept node.
1 In the pre-processing stage, we process
documents in order to perform the computation
described below. This process includes removing
html or other tags, removing stop words according to
a stop list, such as, a, the etc, and performing
prototypes extraction of words by using porter
stemming algorithm (PorterStemmer). Then we use
vectors to denote documents.
2 In a vector space model, we attach a weight to
each word to measure how important the word is in
the document. There are many approaches to
computing weights of words and we deploy the
method developed in Smart system (
Buckley, 1985).
The formulas used in the method are given below:
new_tf
i
expresses the computation of word
frequency. tfi(term frequency)is the number of
times that word i appear in document d.
()
() ()
nwordss
f
re
q
s count n
∈
=
∑
(2)
()
()
f
req s
ps
N
=
(3)
()
12 1,2(, ) max ( )ij
s
im w w sim s s= (4)
_0.50.5
max_
i
i
tf
new tf
tf
=+
(5)
lgi
t
N
id f
n
=
(6)
edible frui
t
apple orange
citrus
COMBINING TWO STRATEGIES FOR ONTOLOGY MAPPING
383

idf
i
expresses inverse document frequency and N is
the total number of documents in document set D, n
t
is the amount of documents containing word i.
wi is the weight of word i. It considers both the
frequency of the word appearing in a document and
the number of documents that contain the word. It
guarantees that a word, which has a high appearance
frequency coupled with a low number of documents
containing it, has a high weight.
3 We will construct feature vectors for the
concept nodes of ontologies. We differentiate
between leaf-nodes and non-leaf nodes in an
ontology and process them differently. For each
leaf-node, its feature vector is computed as an
average of the number of documents assigned to it.
Let C
K
be the feature vector of concept node K and
D
j
is the collection of documents that have been
assigned to it. w
ij
is the weight of word i in
document j. Then:
When a node is a non-leaf node, the construction
of its feature vector should begin with leaf-nodes
and go step by step upwards towards non-leaf nodes
recursively. The construction of the feature vector of
a non-leaf node is therefore recursively calculated
from its leaf-nodes. We put emphases on all the sub
nodes of non-leaf nodes. The vector of feature i is
thus constructed as follows:
C
i
sub
is the vector of feature i for a leaf-node that is
under node K and the vector of feature i of a non-
leaf node is defined as the sum of feature vectors
associated with its child-nodes.
4 In this step, we first calculate similarity by
using instance based strategy. The similarity of two
vectors is directly calculated as the cosine measure:
the less the angle is, the more similar the two vectors
are. However, this method only considers an angle
not the length of a vector. To overcome this
problem, authors in (Wang, 2000) proposed a new
approach to measuring the degree of similarity
between two vectors:
SIM is the degree of similarity between concept
nodes a and b. C
a
and C
b
are the feature vectors of a
and b respectively and n is the given counts of
feature vectors. The SIM approach takes into
account both the angle and the length of vectors.
When two vectors are equal, the value of SIM is 0. If
two vectors are orthogonal, the value of SIM is 1.
However, the results are opposite to the common
sense of people. So we modify the formula as
follows and use the modified vision in this paper:
3.4 Integrating the Two Strategies
We integrate the results that are computed by the
two mapping strategies described above in Sections
3.2 and 3.3. This paper uses a common
combination method:
where wk is the weight for individual strategy
and assigned by hand. For this method a fixed
constant a is taken as threshold value. If
sim(
11
ij
e ,
22
ij
e )>a, then it will be the correct
mapping.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Datasets and Experiment
Evaluation
We evaluated ACAOM using two data sets, whose
characteristics are shown in Table1 (Doan, 2004).
Both data sets describe courses at Cornell University
and Washington University.
Table1: Ontologies in the experiments.
For the performance of the algorithm, it lacks the
standard measure to evaluate the performance of
ontology integration and ontology mapping
algorithms, so like other papers we use information
retrieval metrics, Precision and Recall, to evaluate
our method. Precision describes the number of
correctly found mappings versus the number of all
_iiiw new tf idf= i
(7)
j
ij
DK
k
i
j
w
C
D
∈
=
∑
(8)
ksub
ii
CC=
∑
(9)
() ()
2
2
1
22
22
11
()
n
ab
ab
ii
i
nn
ab
ab
ii
ii
CC
CC
SIM
CC
CC
=
==
−
−
==
+
+
∑
∑∑
(10)
1newSIM SIM
=
−
(11)
11 2 2 11 2 2
2
,
,
1
() ( )
ij ij k k ij ij
k
sim e e w sim e e
=
=
∑
(12)
Ontologies Concepts
Number of
instances
Manual
mapping
Cornell 34 1526 34 Course
CatalogI
Washington 39 1912 37
Cornell 176 4360 54 Course
CatalogII
Washington 166 6975 50
WEBIST 2006 - WEB INTERFACES AND APPLICATIONS
384
mappings discovered by ACAOM. Recall measures
the number of correctly found mappings versus the
number of possible existing mappings discovered by
hand.
a
ma
m
mm
ecision
∩
=Pr
m
am
m
mm
call
∩
=Re
where m
a
and m
m
represent the mappings
discovered by ACAOM and by hand respectively.
4.2 Experiment Results
We run both our system and iMapper system on the
above dataset listed in Table 1. Although we use the
vector space model too, our method of constructing
the model and way to make of information in the
WordNet are different from that deployed in
iMapper. Since both iMapper and our ACAOM use
WordNet and the vector space models, we compare
the performances of these two systems here.
Table 2: Comparison of experiment results.
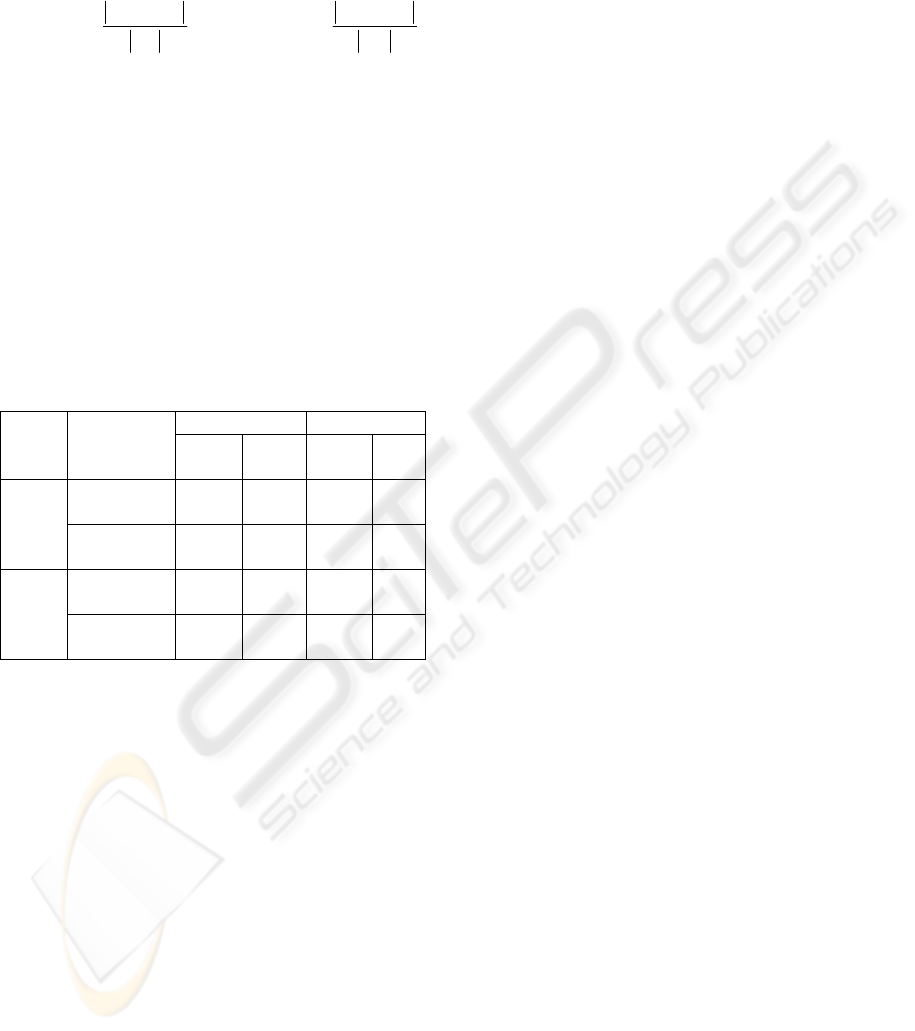
For Course Catalog I dataset, the two ontologies
have similar structures, we believe that it is why the
precision of our mapping for this dataset is better
than that of the other dataset. However, for Course
Catalog II dataset, they have larger ontologies with
less similar structures. This is the reason why the
precision of our mapping for this dataset is lower.
Furthermore, there are some nodes in ontologies
which should have larger degrees of similarities
but in reality they do not. One of the reasons is that
the amount of documents assigned to nodes has
great discrepancy and the other one reason is that
there are some disturbance words in instances. When
computing feature vectors, these factors will lead to
errors in the feature vectors and then affect the final
mapping results.
5 RELATED WORK AND
DISCUSSION
ONION(Mitra, 2002) system proposes a semi-
automated algorithm for resolving the terminological
heterogeneity among the ontologies and establishing
the articulation rules necessary for meaningful
interoperation.. The ONION system uses WordNet
to compute similarity between terms in ontologies.
But this method does not make full use of
information content of WordNet.
HCONE-merge (Vouros, 2005) proposes a
method for aligning the original ontologies with a
hidden intermediate ontology in a fully automated
way. Actually, the alignment is done by mapping
ontology concepts to WordNet senses. This is an
iterative method that in each iteration re-computes
concept mappings given the WordNet senses
associated to the concepts during the last iteration.
This approach is “unstable”, given that correct
mappings computed during an iteration may result to
non-correct mappings when recomputed in the next
iteration and so on. Therefore, this method does not
guarantee to converge to a set of concept mappings.
Some other methods exploit text categorization
to automatically assign documents to the concept in
the ontology and use the documents to calculate the
similarities between concepts in ontologies , such as
iMapper (Su, 2004). ACAOM is similar to iMapper,
but it has some additional functions. First, when
calculating feature vectors for documents, what
ACAOM emphases on is the leaf-nodes. Because it
is believed that leaf-nodes contain more information.
Second, computing similarities between two concept
nodes in ontologies, not only the angles between
vectors are considered but also the lengths of vectors
are considered too. However, iMapper only
considers using angles for measuring similarities
between entities. Third, ACAOM proposed an
approach which combines Lin’s probabilistic model
(Lin, 1998) with the path length to find the
similarities between concepts names, which iMapper
could not do. Therefore, ACAOM performs better
than iMapper.
Although ACAOM produces better result of
ontology mapping, there are several reasons that
prevent ACAOM from correctly matching the
remaining nodes. First, in the name-based strategy,
ACAOM does not consider the structures between
words and assumes that all the words are equally
important. However, different word in a name has
different degree of importance. For example, when
we compare the lessons Romance_Linguistics and
Latin, Romance is the modifier to Linguistics. So
Linguistics is a more important word than Romance.
Nevertheless, Latin and Romance are very similar
iMapper ACAOM Data
sets
Mapping
Preci-
sion
recall Preci-
sion
recall
Cornell to
Washington
82.4 82.4 85.3 85.3 Course
Catalog
I
Washington to
Cornell
82.4 75.7 84.8 75.7
Cornell to
Washington
66.1 57.4 72 66.7 Course
Catalog
II
Washington to
Cornell
68.8 62 72.9 70
COMBINING TWO STRATEGIES FOR ONTOLOGY MAPPING
385

after calculating the similarity between single words.
After using our name-based strategy, we obtained a
high degree of similarity between Romance
Linguistics and Latin. However, this is not the
results we want because they should have low
similarity value and should not be mapped. Second,
in the instance-based strategy, we only use word
frequencies to carry out the computation and do not
analyze the importance of words, such as, titles of
documents, key sentences in paragraphs, key words
having high weights in each sentence, etc.
Therefore, the comparison of vectors is not perfectly
precise.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed an ontology mapping
approach which combines two strategies. These two
strategies make use of name information and
instance information assigned to concept nodes
respectively to calculate similarities between
entities. Then an integrated approach is designed to
incorporate both strategies. The experimental results
show that ACAOM performs better than iMapper
and it improves the precision of iMapper from
+2.4% to 5.9%.
There are several aspects that can be improved in
our proposed system. (1) We could realize ontology
merging and integration in the same system.
ACAOM can be applied to other aspects of ontology
related issues, such as, queries based on distributed
ontology. (2) Our method can not support n:m
mappings at present, which are useful in many cases,
we will extend our method to deal with these cases
in the future during complex mappings.
REFERENCES
Berners-Lee, T., Fischetti,T., Francisco,M., 1999.
Weaving the web: The Original Design and Ultimate
Destiny of The World Wide Web by Its Inventor. The
publisher: Harper San Francisco USA, 1
st
edition, 240.
Buckley, C. & Lewit, A.F., 1985. Optimization of inverted
vector searches. In SIGIR’85, 8th Annual International
ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and
Development in Information Retrieval. SIGIR
Press,97-110.
Doan,anhai,2004
http://anhai.cs.uiuc.edu/archive/summary.type.html
Ehrig, M.& Sure, Y. (eds.) 2004. Ontology mapping - an
integrated approach. In ESWS’04, 1st European
Semantic Web Symposium. Proceedings of the 1st
ESWS. Lecture Notes in Computer Science., Springer-
Verlag, 76-91.
Ehrig, M. & Staab, S., 2004. QOM:Quick Ontology
Mapping. In ISWC’04, 3rd International Semantic
Web Conference. ISWC Press, 683-697.
Gruber, T.R., 1993. A translation approach to portable
ontologies. Knowledge Acquisition, 199-220.
Horrocks, 2002. DAML+OIL:a reason-able web ontology
language. Proc. EDBT. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Lin, Dekang., 1998. An information-theoretic definition of
similarity. In ICML’98, 15th International Conference
on Machine Learning. ICML Press, 296-304.
McGuinness,D.L., Fikes, R., Hendler, J. & Stein, L. A.,
2002. DAML+OIL: an ontology language for the
semantic web. IEEE Intelligent Systems.
Mitra,P. & Wiederhold, G., 2002. Resolving
terminological heterogeneity in ontologies. In
ECAI’02, 15th European Conference on Artificial
Intelligence. ECAI Press.
PorterStemmer,
http://www.tartarus.org/~martin/PorterStemmer/
Resnik,P., 1995. Using information content to evaluate
semantic similarity in a taxonomy. In IJCAI’95,
International Joint Conference on Articial
Intelligence.IJCAI Press, 448-453.
Su,Xiaomeng. & Gulla, J.A., 2004. Semantic enrichment
for ontology mapping. In NLDB’04, 9th International
Conference on Application of Natural Language to
Information Systems. NLDB Press,217-228.
Tang ,J., Liang Bangyong., & Li, Juanzi., 2005, Toward
detecting strategies for ontology mapping. In
WWW’05, Workshop on Semantic Computing in the
14th International World Wide Web Conference.
WWW Press.
Vouros, G.A., Kotis,K., 2005. Extending HCONE-Merge
by approximating the intended meaning of ontology
concepts iteratively. In ESWC’05, 2nd European
Semantic Web Conference. ESWC Press, 198-210.
Wang Jianyong, Xie Zhengmao, Lei Ming, & Li
Xiaoming: Research and Evaluation of Near-replicas
of Web Pages Detection Algorithms. Chinese Journal
of Electronics.
WEBIST 2006 - WEB INTERFACES AND APPLICATIONS
386
