
PROTOTYPE OF CHINESE MACROECONOMIC
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
Junpeng Wei, Xinyou Li
National Information Center, No.58 Sanlihe Road, Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Keywords: e-Government, macroeconomic management, information system.
Abstract: Chinese Macroeconomic Management Information System is one of the most important e-Government
projects, which collects economic information from government departments, establishes the database and
data warehouse, and makes economic analysis reports for government departments to make decisions about
great economic policies. In this paper we introduce a prototype which can experiment some critical
technologies involved in this system, such as information services using a portal website, query and
management of large scale database and data warehouse, data analysis and presentation, and the
unstructured information management in the remote literature warehouse.
1 INTRODUCTION
Macroeconomic management is a kind of
systematic, synthetic, general directions and
regulations, which requires that the country and the
central government follow the natural and the
economical rules, and use economical, legal and
necessary administrant methods. With the effective
macroeconomic management, Chinese economy has
got a high-speed development. The Macroeconomic
Management Information System is an important
project of the national e-Government construction in
China. It integrates the operational applications, data
services and data analysis to achieve the
interconnection of the departments on
macroeconomic management, by organizing the
information resources and building the shared
information platform. It can improve the
informational levels, management efficiency and
working qualities through the consummation and
construction of the operational applications. The
Macroeconomic Management Information System
can enhance the power of macroeconomic
regulations.
The construction of the Macroeconomic
Management Information System includes:
organizing the information resource, building the
shared database, establishing the shared information
platform, consummating and building the
applications for the operations of macroeconomic
management, and constructing the macroeconomic
decision support system. The whole system involves
eight national departments on macroeconomic
management, with the data in the range of terabytes.
The implementation of the whole system depends on
a great deal of technology in many fields. So, we
push forward a research about the prototype system
to validate the key technology in the
Macroeconomic Management Information System.
And we try to meet the users’ demands through the
implementation and iteration of the prototype
system.
Information sharing is the most important part of
the Macroeconomic Management Information
System. The shared information platform is an
Internet Data Center in fact, which implement the
interconnection of the departments on
macroeconomic management. And the platform
fulfils some functions such as: data exchange,
information services and decision support. This
paper studies the prototype system on the key
assignment of the Macroeconomic Management
Information System. We establish an experimental
environment of the prototype system, and build a
shared information platform to simulate the
experiment. We implement the information services
in the shared information platform, and validate the
implementation feasibility of the shared information
platform.
45
Wei J. and Li X. (2006).
PROTOTYPE OF CHINESE MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Society, e-Business and
e-Government / e-Learning, pages 45-50
DOI: 10.5220/0001251000450050
Copyright
c
SciTePress
2 TASKS OF PROTOTYPE
SYSTEM
The task of the prototype system is to build an
experimental environment, with moderate scale and
complete types, and develop the prototype system.
We want to implement the information exchange,
information services and decision support through a
portal website of platform service in the prototype
system. The concrete tasks of the prototype system
are as follows:
1. Create a portal website, and provide a serial of
service columns that can reflect the operations of
data maintenance and the functions of data sharing,
such as user management, information searches and
data presentation.
2. Select some representative data to create the
shared database of the prototype system. Choose
several economical indexes to show the process of
data query, index generation and chart presentation.
Besides, form a Data Center in the website.
3. Construct data warehouse based on the shared
database, establish the models of data warehouse
and datamart by economical subjects and application
fields, implement the function of OLAP (On-Line
Analytical Processing) and data mining, and
engender an Analysis Center to present the
information of data analysis in multi-ways by front-
end tools that are integrated in the portal website.
4. Implement the classifying, clustering, searches
and customization of literature data in the remote
literature warehouse through Internet, and set up a
Literature Center.
3 DESIGN OF PROTOTYPE
SYSTEM
3.1 Design of Experimental
Environments
The mission of the prototype system is to construct a
shared information platform, create shared database
and data warehouse, and implement the information
services in the shared information platform. The
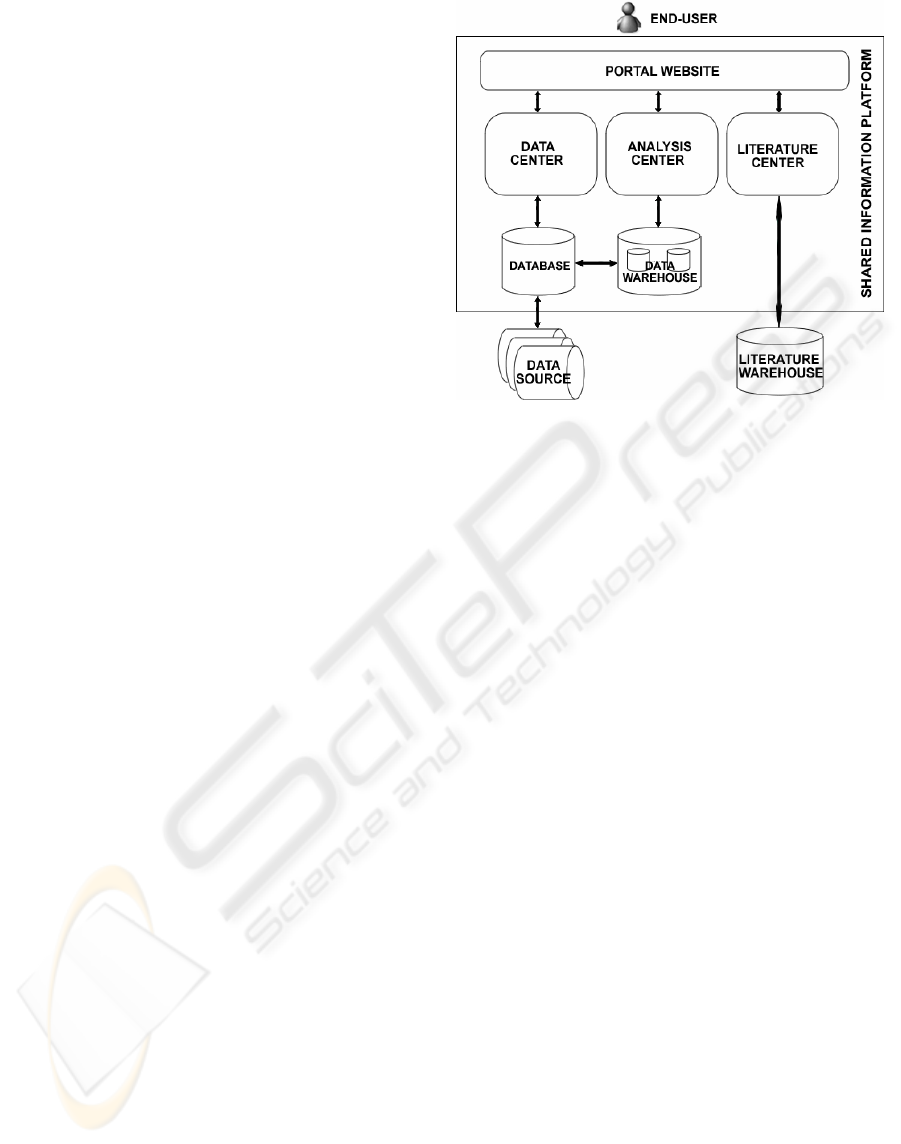
architecture of the prototype system has been
showed in figure 1.
So, we should deploy several high-performance
servers and plenty of applications. An experimental
environment composed by servers is established.
The network environments of the prototype system
are showed in figure 2.
There are five high-performance servers in the
prototype system. Each server runs a pivotal service,
such as database service, portal service, application
service, analysis service, and file service. All these
servers build up the shared information platform,
which includes the shared platform database. The
remote literature warehouse becomes the sub-note
shared database. The platform connects the remote
literature warehouse through the Internet. All of
these servers compose the hardware environment of
the prototype system.
We install a lot of software in these servers, such
as DBMS (database management system), data
warehouse system, ETL (Extract, Transform and
Load) tools, OLAP tools, data mining tools,
middleware, Web service tools etc. So, all of this
software engenders the software environment of the
prototype system together, and achieve the general
information services of the shared information
platform.
The prototype system is a universal, open and
extensible system. It can not only load more
hardware and software to take a larger experiment,
but also expand the prototype to the shared
information platform by using this developing
pattern.
Figure 1: The architecture of the prototype.
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
46

Figure 2: The network environments of the prototype.
3.2 DESIGN OF PORTAL
WEBSITE
We can implement the information services in the
prototype system through the common service portal
website in the platform. Users can gain the services
of data or literature in the platform by using this
portal website. The website has a universal logon
page; only by passing the authentication can the
users enter the main page of the website. And then,
they can view the pages which hold plenty of
information. There are three columns in the main
page: Data Center, Analysis Center and Literature
Center. We link up the shared database to analyze
the index data in the Data Center, link up the data
warehouse to run subject analysis, and connect the
remote literature warehouse to manage the literature
data through Internet. All of these analytic results
are presented in the portal website by multifarious
patterns.
During the design of the portal website, the
primary characters are as follows (Heller, 2003):
1. Personalization
Personalization provides every user a work
platform which suits for his habits and interests. It
can make users acquire information more
expediently, and take decisions more accurately and
quickly. The personalized services include the
content personalization and interface style
personalization in the prototype system.
2. Single sign on
Single sign on allows users to enter an application
with the access approach to other applications, and
the users can visit any other applications without
passing the process of logging on. In other words,
single sign on is a scheme that can reflect one main
logging on to other applications for the same user.
We establish a relationship between the user of the
portal website and the user of the applications in
background, and implement a logging on
management system about user database based on
the portal website. As long as a user enters the portal
website, he can visit the corresponding content by
the authorization.
3. Content aggregation
Content of different sources is aggregated into a
database with a standard format for users’
convenience. All of the shareable and repeatable
information resource can interconnect each others in
different systems by the criterion and standard. We
build the bottom architecture to every disparate
systems, applications and sources. And then, we
integrate them to the portal website in the platform
to present the function of data information services.
4 IMPLEMENTATION OF
PROTOTYPE SYSTEM
4.1 Database Analysis
DBMS is the body of the information resource layer
in the Macroeconomic Management Information
PROTOTYPE OF CHINESE MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
47

System. The data in the database follows the
classified organization of the shared database index
system in the Macroeconomic Management
Information System. We implement the framework
of the index system by using classifying tables, and
expand the index system in the fields of
consumptions and prices. Concurrently, the database
system provides the source data to the decision
support system (Silberschatz et al., 2002).
In the prototype system, the prototype database
management system of consumptive statistics and
important commodity prices that we establish
surrounds two subjects, CONSUMPTIONS and
PRICES, and loads the source data to the shared
database for the requirement of the data warehouse,
datamart, data analysis, and data presentation. The
source data is different in many ways, such as
relation database, excel file, text file, newspapers
and magazines. So, we must conform to the source
data by hand or using programming before loading
these data to the shared database.
There are more than 13,000 indexes in the index
system of the Macroeconomic Management
Information System. These indexes are divided into
31 primary sorts, for example GDP (Gross Domestic
Product) calculation, industrial statistics, agricultural
statistics, important commodity prices, and so on.
We use arborescence architecture to show these
indexes in the prototype system. The primary sorts
are displayed in the web page initially. When users
want to expand one sort, the system will load all
indexes in this sort automatically. So it can avoid the
slow system reflections caused by loading the initial
vast index data.
The Data Center in the portal website implements
the function of data analysis. Data analysis is to link
up the database and search the index related to the
data resource.
There are three functions in the Data Center: the
index querying, the graphic presentation, and the
literature interoperability. The index querying is a
standard SQL (Structured Query Language)
querying based on the index name, the time and the
region scope. All the querying results are displayed
to the table in the web page. The graphic
presentation is to use some pattern form to show the
index data, such as bar chart, pie chart, line chart,
point chart, area chart, and so on (Hanbin et al.,
2005). The literature interoperability is to list some
interrelated literature based on the keyword search in
remote literature warehouse by using the selected
index to match a serial of keywords.
4.2 Data Warehouse Analysis
The purpose of the Macroeconomic Management
Information System is to enhance the level of
scientific decision. So, we need to establish a
decision support system on macroeconomic
management, and implement it by deploying OLAP
tools and data mining tools.
The Analysis Center is a decision support system
which aims at shared database in the prototype
system. It is a three-layer architecture, which include
the data layer, the analysis layer and the access layer.
The data layer is to generate the data warehouse and
datamart by using the ETL tools to gain data from
the shared database. The analysis layer is the
applications of the data warehouse or datamart, such
as OLAP, data mining and statistic analysis. The
access layer is the portal of the decision support
system, which can present all the applications in web
pages.
We use the technology of data warehouse to
organize the dispersed information of the shared
database into the data warehouse, which has subject-
oriented, integrated, nonvolatile, time-variant
collections of data in decision support of
macroeconomic management (Inmon, 2002). And
we set up a serial of shared datamart according to
operational subjects and applied fields based on the
data warehouse (Eckerson, 1997).
We use the star schema during the design of the
data warehouse. In the star schema, we use a fact
table of subject and several dimension tables of
unmoral description to execute the decision querying.
During the data organization in the data warehouse,
we associate the related dimension tables around a
fact table, and make most of the query finish by
using this structure. And we can accelerate the
querying speed and efficiency. We divide the whole
data models into several sub-models around the core
of the fact table, which generated several datamart.
The source data must pass through the processes
of extracting, transforming, cleaning and loading
before we load the data to the data warehouse. All
these operations need to use the ETL tools. We
design the data flow in these tools, and deployed
them into servers to achieve the data loading.
The main purpose of the data warehouse and
datamart is to implement the decision support
system. And OLAP is a common decision support
method. It is a technology of online data access and
analysis about some special problems. It can make
the analyzers observe the data in multi-views, and
acquire embedded knowledge. The basic operations
of the OLAP are as follows: slice, dice, rotate and
thrill (including thrill down and roll up) (Bolloju et
al., 2002). And the analyzers can analyze the data in
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
48

multi-views and multi-sides. So, we need to build
the data cubes in the data warehouse following the
operational subject, and create quantity of middle
data files to fasten the querying speed and report
generating. Finally, we present the multi-data into
the web pages by multiple formats, such as tables,
charts, reports, KPI (Key Performance Index)
monitor, dashboard, balanced scorecard, and so on.
Data mining is to estimate and evaluate the new
data by using the rules and patterns which are found
by statistics and artificial neural network. The
essence is to discover the relationship between the
actual data and the latent rules, and turn the feelings
into the facts (Roiger et al., 2003). Because the
prototype system is established by Browse/Server
architecture, we only provide a small quantity of
functions on online data mining. Furthermore, we
develop a presentation on complicated analytic
reports. After the analyzers take an advanced
analysis on one subject and write a complicated
report, they can upload the report to the appointed
FTP server. And then, we can enter the portal
website, view the analytic report by its URL, and
download it when necessary.
4.3 Unstructured Information
Management
The unstructured information of the Macroeconomic
Management Information System is the sources of
macroeconomic management decision, too. It is the
literature, such as newspapers, periodicals,
conference records, policies, rules, research reports,
and so on. The literature warehouse is built on the
catalogue system of the shared information platform.
We use unstructured information management
system to manage the literature warehouse. The
platform connects the remote literature warehouse
by Internet in the prototype system. The Literature
Center is a prototype of the unstructured information
management system. The management of the
literature is querying, analyzing, managing and
processing of the unstructured information.
In the unstructured information management
system, we use content understanding and pattern
matching to extract the files’ elements. And we
identify the files’ conception based on Bayesian
Probabilistic and Shanon Information. By doing
these, we can implement the automatic operation to
the files.
We use the Dynamic Reasoning Engine,
Classification Server and User Agent Server to
provide the unstructured information services. The
Dynamic Reasoning Engine can implements context
summarization, query summary, concept
highlighting, hyper linking, and nature language
retrieval by using pattern identifying and the
technology of probabilistic. The Classification
Server can implement categorization, clustering,
taxonomy generation, and spectrographic analysis
by using Dynamic Reasoning Engine. The User
Agent Server can provide a serial of wide and strong
individuation services, such as profiling,
collaboration, and alerting.
We finish the functions of literature management
in the portal website of the prototype system. The
concrete functions are as follows: categorization,
recommendation, keywords retrieval, intelligence
retrieval, hotspot literature clustering, and
individuation services. The categorization is a search
in the arborescence architecture literature catalog
trimmed by the context of the literature. The
recommendation is to recommend some related
literature by the concept matching in the current
literature. The keywords retrieval is a Boolean
retrieval with the logic symbols of AND, OR, NOT.
The intelligence retrieval is a search based on nature
language understanding and semantic analyzing. The
hotspot literature clustering is to gather the related
information by comparing content to each other. The
entire cluster has a common conception, and we can
find their hotpots and developing trends after
clustering. Additionally, the Literature Center
provides individuation services for the taste and
interest.
5 CONCLUSION
The prototype system of the Macroeconomic
Management Information System is an elementary
experimental environment based on the feasibility
report of the Macroeconomic Management
Information System. It validates the technical
feasibilities of the system design scheme by the
study and implementation of the prototype system,
and establishes a foundation of interconnection and
information sharing to each department on
macroeconomic management.
REFERENCES
Thorsten Heller, 2003. Logical Portal Architecture,
CommITment Whitepaper.
Abraham Silberschatz, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan,
2002. Database System Concepts, China Machine
Press, Beijing.
PROTOTYPE OF CHINESE MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
49

Gan Hanbin, Li Zhixin, Peng Bin, 2005. Data description
model of victor graphics editing system on SVG,
Computer Engineering and Design.
W. H. Inmon, 2002. Building the Data Warehouse, John
Wiley & Sons, Inc., CANADA.
Wayne W. Eckerson, 1997. The Case for the Datamart,
Database and Network Journal.
Narasimha Bolloju, Mohamed Khalifa, Efraim Turban,
2002. Integrating knowledge management into
enterprise environments for the next generation
decision support. Decision Support System.
Richard J. Roiger, Michael W. Geatz, 2003. Data Mining:
A Tutorial Based Primer, Tsinghua University Press,
Beijing.
WEBIST 2006 - SOCIETY, E-BUSINESS AND E-GOVERNMENT
50
