
DEVELOPING A CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT MODEL
FOR USE IN THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY
Fergal McCaffery
Lero – The Irish Software Engineering Research Centre, University of Limerick, Ireland
Rory O’Connor
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Gerry Coleman
Department of Computing, Dundalk Institute of Technology, Dundalk, Ireland
Keywords: Configuration Management, Medical device, Software Process Improvement, CMMI.
Abstract: This paper outlines the development of a Configuration Management model
for the MEDical device
software industry (CMMED). The paper details how medical device regulations associated with
Configuration Management (CM) may be satisfied by adopting less than half of the practices from the CM
process area of the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI). It also investigates how the CMMI CM
process area may be extended with additional practices that are outside the remit of the CMMI, but are
required in order to satisfy medical device regulatory guidelines.
1 INTRODUCTION
Software is becoming an increasingly important
aspect of medical devices and medical device
regulation. Medical devices can only be marketed if
compliance and approval from the appropriate
regulatory bodies of the Food and Drug
Administration (FDA Regulations, 2002), and the
European Commission under its Medical Device
Directives (European Council Directive, 1993) is
achieved. Medical device companies must produce a
design history file detailing the software components
and processes undertaken in the development of
their medical devices. Due to the safety-critical
nature of medical device software it is important that
a highly efficient CM process is in place within
medical device companies.
CM is the discipline of c
oordinating software
development and controlling the change and
evolution of software products and components
(Ghezzi et al, 2003). It involves the ‘unique
identification, controlled storage, change control,
and status reporting of selected intermediate work
products, product components and products during
the life of a system’ (Jonassen-Hass, 2002). Such
CM procedures are needed to manage the vast
number of elements (source code, documentation,
change requests, etc) that are created and updated
over the lifetime of a software system.
For many software companies, who report CM
p
roblems, CM is the first major process weakness
that they are required to address. For example, as the
company expands, it must fulfil the task of acquiring
new customers whilst satisfying the demands of
existing customers. Often these demands include
product customisations which many young
companies, lacking reliable revenue streams, do not
feel they can ignore. In many situations this results
in companies having to support multiple code bases
and product versions with very limited resources.
Ultimately, a detailed CM process is the only way
this problem can be solved.
A study of a small Danish software firm shows
ho
w it was forced to review the number of products
it developed, and the amount of work it accepted,
because of CM difficulties (Baskerville and Pries-
Heje, 1999). But CM is equally important in large
software companies as a case study of Netscape and
81
McCaffery F., O’Connor R. and Coleman G. (2006).
DEVELOPING A CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 81-88
DOI: 10.5220/0001311900810088
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Microsoft’s development practices shows
(Cusumano and Yoffie, 1999). Therefore, in a
software company or department without CM to
control product development, there is no process to
assess and no basis for measurement (Fayad and
Laitinen, 1997). To succeed in this area Humphrey
(2000) proposes that a CM plan be developed in
conjunction with the establishment of a
configuration control board to manage changes to all
of the baseline configuration items and to ensure that
configuration control procedures are followed.
A number of ‘best practice’ software process
improvement (SPI) models such as ISO/IEC 15504
(also known as ‘SPICE’) and Capability Maturity
Model Integration (CMMI) have been designed to
help companies manage their software development
activity. For example, CMMI is an SPI improvement
model which specifies recommended practices in
specific process areas – including CM - that have
been shown to enhance software development and
maintenance capability (Chrissis et al., 1991).
This paper will investigate how thorough current
medical device regulations are in relation to
specifying what CM practices medical device
companies should adopt when developing software.
This will be achieved through comparing current
medical device regulations and guidelines for CM
against the formally documented software
engineering ‘best practices’ of the CMMI for the
CM process area.
2 MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY
Medical device companies have to adhere to medical
device regulations in relation to CM. Therefore the
main area of concern for medical device companies
in relation to CM is to ensure that the checklist of
CM elements required by Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) are in place rather than trying
to improve their overall CM practices. GAMP
(2001) details CM practices that medical device
companies may adopt in order to comply with
medical device regulations, however no
documentation exists within the medical device
domain in relation to how such practices could be
improved by incorporating practices from formal
software engineering SPI models for CM.
However, if we investigate other regulated
industries such as the automotive and space
industries we realise that these domains are not
content with satisfying regulatory standards, but
have proactively developed SPI models specifically
for their domain so that they may continuously
improve the development of their information
systems to achieve higher levels of safety, greater
efficiency, and a faster time to market, whilst
seamlessly satisfying regulatory quality
requirements.
The major process improvement frameworks that
currently exist, namely ISO/IEC 15504 and CMMI,
do not address the regulatory requirements of either
the medical device, automotive or space industries.
Therefore, a new SPI model (Automotive SIG,
2005) was developed specifically for the automotive
industry, this model was based upon ISO/IEC15504
(ISO, 2003) and is referred to as ‘Automotive
SPICE’. Likewise, a new ISO/IEC15504 based SPI
model was developed specifically for the space
industry, this model is known as SPiCE for SPACE
(Cass and Volcker, 2000). Both of these models
contain reference and assessment information in
relation to how companies may improve their
configuration management practices within their
domain.
This paper will not address the issue of
developing an entire SPI model for the medical
device industry (see McCaffery et al, 2004 for full
discussion), but shall instead focus upon the
individual process area of CM. This work addresses
an opportunity to integrate the regulatory issues and
SPI mechanisms to achieve improvements that are
critical to the CM of software for medical devices.
3 CMMED DEVELOPMENT
The CMMED (Configuration Management model
for the MEDical device software industry) was
initiated by work that one of the authors performed
whilst performing research for the Centre for
Software Process Technologies at the University of
Ulster, Northern Ireland. This work is now
progressing with Lero – the Irish Software
Engineering Research Centre. The initial research
work was assisted by the involvement of a steering
group with a pilot of 5 medical device companies
and a notified standards body (all based in Northern
Ireland). Each of the five companies expressed a
desire to have access to a CM model that would
incorporate software process improvement practices
and could fulfil the relevant medical device
regulatory requirements. However, this work is now
being extended to include medical device companies
in the Republic of Ireland.
The CMMED may be defined as a set of
activities that if performed at a base level will satisfy
the CM guidelines specified in the medical device
standards. However, CMMED also enables medical
device companies to follow a SPI path to achieving
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
82

CMMI certification. The CMMED will be flexible
in that relevant elements of the model may be
adopted as required to provide the most significant
benefit to the business. The model is based on the
CMMI, however another model is also being
developed that is based upon ISO/IEC15504. The
regulations used to extend the CMMI framework
will be those of the FDA and the ANSI/AAMI
SW68:2001 (SW68) standard (Medical device
software – Software life cycle processes).
The CMMED will provide a means of assessing
the software engineering capability for the
configuration management process area in relation
to software embedded in medical devices
(FDA/CDRH, 1997, 1999, 2005). The CMMED is
being developed to promote SPI practices into the
CM process adopted by medical device companies.
This is an attempt to improve the effectiveness and
efficiency of CM within medical device companies
through investigating the mapping of medical device
regulatory guidelines against the CMMI CM process
area.
The mappings between the medical device
standards and the CMMI specific practices for the
CM process result in the CMMED being composed
of a number of goals, practices and activities. The
CMMED determines what parts of the CMMI CM
process area are required to satisfy medical device
regulations. It also investigates the possibility of
extending the CMMI process areas with additional
practices that are outside the remit of CMMI, but are
required in order to satisfy medical device regulatory
guidelines.
The following section will detail a mapping of
existing software development and regulatory
guidelines for the medical device industry against
the CMMI for the CM process area.
4 GUIDELINE MAPPING
The FDA provides little insight into how CM should
be performed other than to state that a CM plan
should exist and that this should be adopted to
manage configuration items for medical device
software. Therefore in order to gain a greater
understanding of the CM guidelines that medical
device companies follow in order to achieve
regulatory compliance we referred to the medical
device software life cycle processes (SW68)
standard. This standard was drafted for use in the
medical device sector based on the lifecycle
requirements of ISO/IEC 12207 (ISO, 1995). This
section illustrates the CMMED structure for the CM
process area. In order to achieve this, FDA
regulations & SW68 guidelines (for the rest of the
paper we refer to these together as medical device
standards) were mapped against the goals and
practices of the CMMI CM process area.
This mapping is presented as follows: Firstly, we
identify the goals that exist within the CMMI CM
process area. Next the CMMI CM practices are
identified within each CM goal. Then the CM
activities (associated with the current practice) that
have to be performed in order to comply with
medical device regulations are listed. We then
identify the activities that have to performed in order
in to adhere to the CMMI in relation to the current
practice. Finally we lists the CMMI CM activities
that are required in order to meet the medical device
regulatory requirements associated with the current
practice. The composition of the resulting CMMED
is illustrated in figure 1.
CMMI CM practices
Medical device
regulations for CM
Non-CMMI practices
that are required for
medical device
standards
CMMI
practices
that are
required for
medical
device
standards
Non-required
CMMI practices
with potential
benefit to medical
device software
CMMI practices not
required for medical
device standards
CMMI CM practices
Medical device
regulations for CM
Non-CMMI practices
that are required for
medical device
standards
CMMI
practices
that are
required for
medical
device
standards
Non-required
CMMI practices
with potential
benefit to medical
device software
CMMI practices not
required for medical
device standards
Figure 1: Composition of the CMMED.
It should be noted however, in some instances the
CMMI CM activities associated with the current
practice may not provide full coverage of the
medical device standards and therefore these
additional activities have to be added in order to
achieve the full list of activities required to fulfil the
objectives of CMMED.
The CMMED has three goals: Goal 1: Establish
Baselines, Goal 2: Track and Control Changes and
Goal 3: Establish Integrity. To meet each of these
goals it is necessary for a number of practices and
activities to be performed. Each of the following
sub-sections will present the CM activities required
for each of the 3 goals.
4.1 Goal 1: Establish Baselines
In order to fulfil Goal 1 Establish Baselines the
following practices have to be performed: Identify
Configuration Items, Establish a CM System and
Create or Release Baselines.
DEVELOPING A CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY
83

4.1.1 Identify Configuration Items
The 4 activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to
identifying configuration items are:
1. Select the configuration items and the work
products that compose them based on
documented criteria
2. Assign unique identifiers to configuration items
3. Specify when each configuration item is placed
under CM
4. Identify Off the Shelf Components
The 5 activities that have to be performed in order to
satisfy the CMMI practice for identifying
configuration items are:
1. Select the configuration items and the work
products that compose them based on
documented criteria
2. Assign unique identifiers to configuration items
3. Specify the important characteristics of each
configuration
4. Specify when each configuration item is placed
under CM
5. Identify the owner responsible for each
configuration item
The 3 activities that are common to both the CMMI
and the medical device standards for identifying
configuration items are:
1. Select the configuration items and the work
products that compose them based on
documented criteria
2. Assign unique identifiers to configuration items
3. Specify when each item is placed under CM
Therefore, in order to adhere to the medical device
standards only 3 out of the 5 activities required for
the CMMI in relation to identifying configuration
items are necessary. However an additional activity
is required in order to identify Off-the-Shelf (OTS)
components as this is not included in the CMMI.
Therefore 4 CMMED activities are required for
identifying configuration items are:
1. Select the configuration items and the work
products that compose them based on
documented criteria
2. Assign unique identifiers to configuration items
3. Specify when each configuration item is placed
under CM
4. Identify Off the Shelf Components. Note: this
activity is not present in the CMMI but is
required in order to fulfil the requirements
specified in the medical device standards.
4.1.2 Establish a CM System
The 2 activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to
establishing a configuration management system
(CMS) are:
1. Store and retrieve configuration items in the
CM system
2. Store, update, and retrieve CM records
The 8 sub-practices that have to be performed in
order to satisfy the CMMI practice for establishing a
CMS are:
1. Establish a mechanism to manage multiple
control levels of CM
2. Store / retrieve configuration items in the CMS
3. Share and transfer configuration items between
control levels within the CMS
4. Store and recover archived versions of
configuration items
5. Store, update, and retrieve CM records
6. Create CM reports from the CMS
7. Preserve the contents of the CMS
8. Revise the CM structure as necessary
There are 2 activities that are common to both the
CMMI and the medical device standards for
establishing a CMS. Therefore, in order to adhere to
the medical device standards, only 2 of the 8
activities required by the CMMI for establishing a
CMS are necessary. The main differences are that
CMMI requests the usage of multiple control levels
of CM, as well as archiving and restoration
procedures to be in place. The 2 CMMED activities
for establishing a CMS are:
1. Store and retrieve configuration items in the
CM system
2. Store, update, and retrieve CM records
4.1.3 Create or Release Baseline
There is only a single activity that has to be
performed in order to adhere to the medical device
standards in relation to creating or releasing
baselines - Document the set of configuration items
that are contained in a baseline. Whereas there are 4
activities that have to be performed in order to
satisfy the CMMI practice for creating or releasing
baselines:
1. Obtain authorisation from the CCB before
creating or releasing baselines of configuration
items
2. Create or release baselines only from
configuration items in the CM system
3. Document the set of configuration items that are
contained in a baseline
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
84
4. Make the current set of baselines readily
available
There is only single CMMED activity that is
common to both the CMMI and medical device
standards for creating or releasing baselines.
Therefore, in order to adhere to the medical device
standards only one of the 4 activities - Document the
set of configuration items that are contained in a
baseline – is required for the associated CMMI
practice is necessary.
4.1.4 Summary of CMMED Goal 1
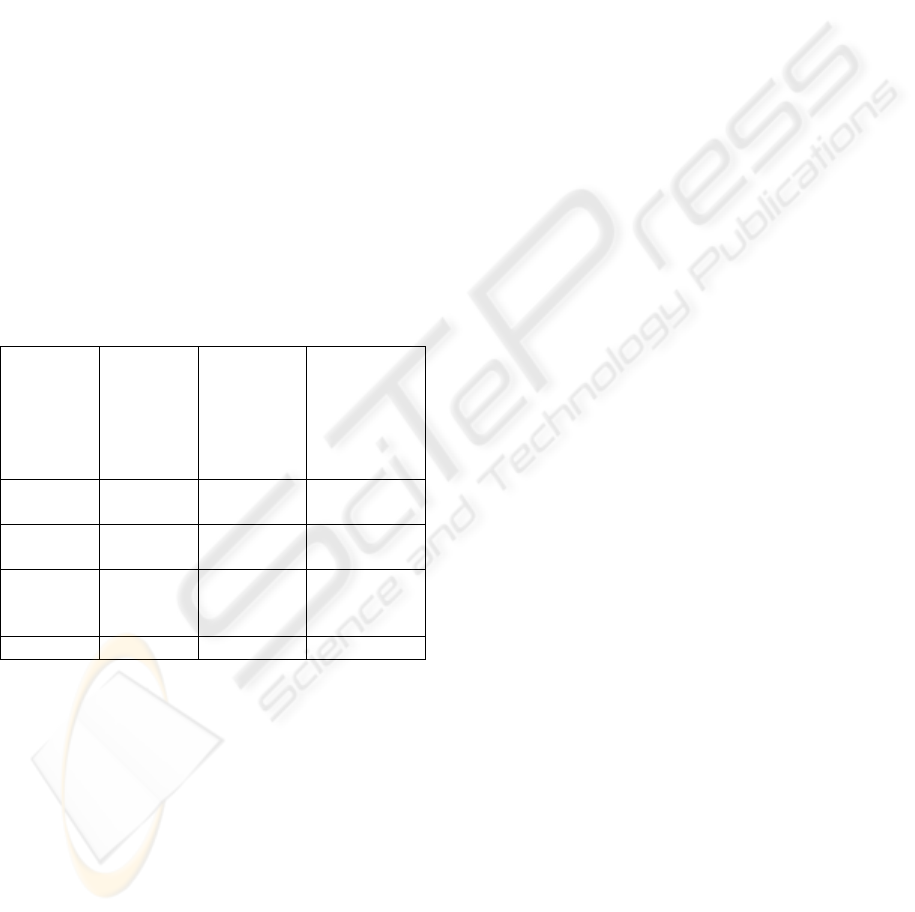
Table 1 summarises goal 1 of CMMED (Establish
Baselines). It may be observed from table 1 that not
all of activities of the CMMI have to be performed
in order to satisfy the medical device regulations (in
fact only 6 of the 17 CMMI activities have to be
performed). However, in order to satisfy the
objectives of the CMMED 1 additional (medical
device specific) activity had to be added (i.e. to
satisfy goal 1 of the CMMED).
Table 1: Summary of CMMED Goal 1.
Practice CMMI
activities
CMMI
activities to
meet
medical
device
standards
Additional
activities to
meet medical
device
standards
Identify
CM items
5 3 1
Establish
a CMS
8 2 0
Create or
delete
Baselines
4 1 0
Total 17 6 1
4.2 Goal 2: Track and Control
Changes
In order to adhere to the CMMED goal 2 of tracking
and controlling changes, the following specific
practices have to be performed: Track Change
Requests and Control Configuration Items.
4.2.1 Track Change Requests
The 5 activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to tracking
change requests:
1. Initiate and record change requests in the
change request database
2. Analyse the impact of changes and fixes
proposed in the change requests.
3. Review change requests that will be addressed
in the next baseline with those who will be
affected by the changes and get their agreement.
4. Track the status of change requests to closure.
5. Each upgrade, bug fix, or patch for OTS
software shall be evaluated, and the evaluation
shall be documented
There are 4 activities that have to be performed in
order to satisfy the CMMI practice for tracking
change requests:
1. Initiate and record change requests in the
change request database
2. Analyse the impact of changes and fixes
proposed in the change requests.
3. Review change requests that will be addressed
in the next baseline with those who will be
affected by the changes and get their agreement.
4. Track the status of change requests to closure.
There are 4 activities that are common to both the
CMMI and the medical device standards for tracking
change requests:
1. Initiate and record change requests in the
change request database
2. Analyse the impact of changes and fixes
proposed in the change requests.
3. Review change requests that will be addressed
in the next baseline with those who will be
affected by the changes and get their agreement.
4. Track the status of change requests to closure.
Therefore, in order to adhere to the medical device
standards all of the activities required for this CMMI
practice are necessary, but not always to the same
level of detail. However an additional practice is
required in order to ensure that each upgrade, bug
fix, or patch for OTS software is identified and
evaluated, and that the evaluation is documented, as
this is not included in the associated CMMI practice.
The CMMED activities for tracking change
requests are:
1. Initiate and record change requests in the
change request database
2. Analyse the impact of changes and fixes
proposed in the change requests.
3. Review change requests that will be addressed
in the next baseline with those who will be
affected by the changes and get their agreement.
4. Track the status of change requests to closure.
5. Each upgrade, bug fix, or patch for OTS
software shall be evaluated, and the evaluation
shall be documented. Note: this activity is not
present in the CMMI but is required in order to
DEVELOPING A CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY
85

fulfil the requirements specified in the medical
device standards.
4.2.2 Control Configuration Items
The 4 activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to
controlling configuration items are:
1. Control changes to configuration items
throughout the life of the product
2. Obtain appropriate authorisation before changed
configuration items are entered into the CM
system
3. Perform reviews to ensure that changes have not
caused unintended effects on the baselines
4. Record changes to configuration items and the
reasons for the changes as appropriate
The 5 activities that have to be performed in order to
satisfy the CMMI practice to control configuration
items are:
1. Control changes to configuration items
throughout the life of the product
2. Obtain appropriate authorisation before changed
configuration items are entered into the CM
system
3. Check in and check out configuration items
from the CM system for incorporation of
changes in a manner that maintains the
correctness and integrity of the configuration
items
4. Perform reviews to ensure that changes have not
caused unitended effects on the baselines
5. Record changes to configuration items and the
reasons for the changes as appropriate
As the control of configuration items is very
important in terms of ensuring the integrity of
medical device software it is no surprise that 4 of the
5 activities required for this CMMI practice are
necessary in order to adhere to the medical device
standards.
The following list shows the mapping of the
medical device standards against each of the
activities required by the CMMI practice for
controlling configuration items:
1. Control changes to configuration items
throughout the life of the product
2. Obtain appropriate authorisation before changed
configuration items are entered into the CM
system
3. Perform reviews to ensure that changes have not
caused unitended effects on the configuration
baselines
4. Record changes to configuration items and the
reasons for the changes as appropriate
4.2.3 Summary of CMMED Goal 2
Table 2, summarises goal 2 of the CMMED (Track
and Control Changes). It may be observed that
almost all of the activities of this CMMI goal will
have to be performed in order to satisfy the medical
device standards (in fact 8 of the 9 CMMI sub-
practices will have to be performed). However, in
order to satisfy the objectives of CMMED 1
additional sub-practice had to be added.
Table 2: Summary of CMMED Goal 2.
Practice CMMI
activities
CMMI
activities to
meet
medical
device
standards
Additional
activities to
meet
medical
device
standards
Track
change
requests
4 4 1
Control
Config
items
5 4 0
Total 9 8 1
4.3 Goal 3: Establish Integrity
In order to fulfil CMMED goal 3: Establish Integrity
the following specific practices have to be
performed: Establish CM Records and Perform
Configuration Audits.
4.3.1 Establish CM Records
The 3 activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to
establishing CM records are:
1. Record CM actions in sufficient detail so the
content and status of each configuration item is
known and previous versions can be recovered
2. Identify the version of the configuration items
that constitute a particular baseline.
3. Revise the status and history of the
configuration item as necessary
The 6 activities that have to be performed in order to
satisfy the CMMI practice for establishing CM
records are:
1. Record CM actions in sufficient detail so the
content and status of each configuration item is
known and previous versions can be recovered
2. Ensure that relevant stakeholders have access to
and knowledge of the configuration items
3. Specify the latest version of the baseline.
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
86

4. Identify the version of the configuration items
that constitute a particular baseline.
5. Describe the differences between successive
baselines
6. Revise the status and history of the
configuration item as necessary
The process of establishing CM records is very
important in terms of providing the traceability
evidence that is required to meet the regulatory
requirements associated with medical device
software. Half of the activities (3 out of 6) required
for this CMMI practice are necessary in order to
adhere to the medical device standards and are
therefore included in CMMED.
The CMMED activities for establishing CM
records are:
1. Record CM actions in sufficient detail so the
content and status of each configuration item is
known and previous versions can be recovered
2. Identify the version of the configuration items
that constitute a particular baseline.
3. Revise the status and history of the
configuration item as necessary
4.3.2 Perform Configuration Audits
The medical device standards do not specify any
activities that have to be performed in order to
achieve regulatory compliance in relation to
performing configuration audits. The list of the sub-
activities that have to be performed in order to
satisfy the CMMI practice for performing
configuration audits are:
1. Assess the integrity of the baselines
2. Confirm configuration records correctly identify
the configuration of the configuration items
3. Review the structure and integrity of the items
in the CM system
4. Confirm the completeness and correctness of
the items in the CM system
5. Confirm compliance with applicable CM
standards and procedures
6. Track action items from the audit to closure
This practice in CMMI has no equivalent practice
within the medical device regulations. The medical
device regulations do not specify any need for
auditing the CM processes and activities. Therefore
CMMED contains no activities, as a result of
mapping the regulatory medical device requirements
for CM against each of the activities required for the
CMMI practice relating to performing configuration
audits.
4.3.3 Summary of CMMED Goal 3
Table 3 summaries goal 3 of the CMMED (Establish
Integrity). It may now be determined that in order to
satisfy medical device standards that not all of
activities of this CMMI goal have to be performed
(in fact only 3 of the 12 CMMI activities have to be
performed. Additionally, no additional (medical
device specific) activities have to be added in order
to satisfy the objectives of CMMED.
Table 3: Summary of CMMED Goal 3.
Practice CMMI
activities
CMMI
activities to
meet
medical
device
standards
Additional
activities to
meet
medical
device
standards
Establish
CM records
6 3 0
Perform
configurati
on
audits
6 0 0
Total 12 3 0
5 PRELIMINARY FEEDBACK
In order to assist with preliminary feedback, the CM
process outlined by this paper has been compared
against the existing practices within an Irish medical
device company. A high level summary of their
comments are included below.
They liked the structure of the CMMED and in
particular how it enabled them to create a list of all
the CM practices that they should adopt in order to
adhere to the medical device standards. They also
made positive comments in relation to CMMED
providing additional information in relation to how
their existing CM practices could be improved by
incorporating guidance from the CM CMMI process
area in relation how mandatory medical device
activities may be performed.
Upon further consultation with the authors it has
also been decided that in order to assist with SPI
within the company that a process diagram shall be
created, this will provide a graphical representation
of the logical flow of the practices within their CM
process.
DEVELOPING A CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT MODEL FOR USE IN THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY
87
6 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
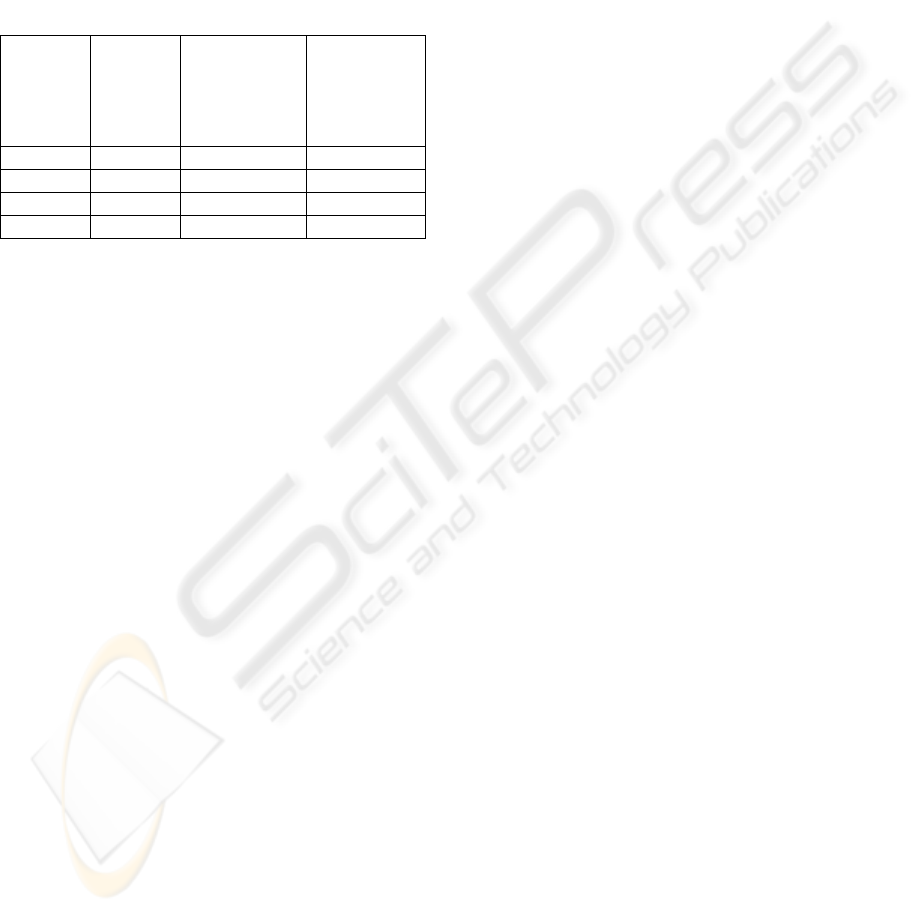
Table 4 provides a summary of the 3 goals within
CMMED. There are 40 activities required by
CMMED, consisting of 38 CMMI and 2 medical
device specific activities. In order to satisfy the
mandatory medical device CM requirements, 19 of
these activities have to be adhered to (17 CMMI and
2 medical device specific activities).
Table 4: Summary of CMMED Goals.
CMMED
goal
CMMI
activities
CMMI
activities to
meet medical
device
requirements
Additional
activities to
meet medical
device
requirements
Goal 1 17 6 1
Goal 2 9 8 1
Goal 3 12 3 0
Total 38 17 2
It is clear that following the guidelines specified in
the medical device regulations will at best, only
partially meet the specific goals of this CMMI
process area (this would only fulfil 17 of the 38
activities required by CMMI). Since failure to
perform any specific practice implies failure to meet
the specific goal, with respect to CMMI, it is clear,
that the goals of CM cannot be obtained by
satisfying medical device regulations and guidelines
during software development. But is the opposite
true, can meeting the CMMI goals for CM
successfully meet FDA and SW68 guidelines? With
the exception of 2 sub-practices, performing the
CMMI specific practices for CM would in general
more than meet the FDA and SW68 guidelines for
this area.
If a medical device company follows the CMMI
guidelines for CM (with the exception of 2
activities), this will more than fulfil the CM
requirements specified in the medical device
regulations. However, only a fraction of the CMMI
guidelines for CM will be satisfied by adhering to
the medical device regulations for CM
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by the Science
Foundation Ireland (SFI) funded project, Global
Software Development in Small to Medium Sized
Enterprises as part of Lero - the Irish Software
Engineering Research Centre (http://www.lero.ie).
REFERENCES
Automotive SIG, The SPICE User Group Automotive
Special Interest Group, Automotive SPICE Process
Reference Model, 2005.
Baskerville R. and Pries-Heje J., Knowledge Capability
and Maturity in Software Management, in The Data
Base for Advances in Information Systems, Spring
1999, Vol. 30, No. 2, 26-43.
Cass, A. and Volcker C., SpiCE for SPACE: A method of
Process Assessment for Space Projects, SPICE 2000
Conference Proceedings, http://www.synspace.com
Chrissis, M.B., Konrad, M. & Shrum, S., CMMI:
Guidelines for Process Integration and Product
Improvement, Addison Wesley, 2003
Cusumano M. and Yoffie D., Software Development on
Internet Time, IEEE Computer, Vol. 32, No. 10, Oct.
1999, 60-69.
European Council Directive 93/42/EEC Concerning
Medical Devices, 14 June 1993.
Fayad M. and Laitinen M., Process Assessment
Considered Wasteful, Communications of the ACM,
Vol. 40, No. 11, 1997, 125-128.
FDA Regulations, Code of Federal Regulations 21 CFR
Part 820, Food and Drug Administration, June 1997.
FDA/CDRH Guidance Document, General Principles of
Software Validation, FDA, June 1997.
FDA/CDRH Guidance Document, Guidance for Off-the-
Shelf Software Use in Medical Devices, FDA,
September 1999
FDA/CDRH Guidance Document, Guidance for the
Content of Premarket Submissions for Software
Contained in Medical Devices, FDA, May 2005.
GAMP, Guide for Validation of Automated Systems
(GAMP 4), International Society for Pharmaceutical
Engineering, December 2001
Ghezzi C., Jazayeri M. and Mandrioli D., Fundamentals of
Software Engineering, Prentice Hall, 2003.
Humphrey W., Introduction to the Team Software
Process, Addison Wesley, 2000.
ISO/IEC 15504, Information Technology – Process
Assessment – Part 5: An exemplar Process Assessment
Model, ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7, October 2003.
ISO/IEC 12207, Information technology - Software
lifecycle processes Amendment 2, International
Standards Organisation, 1995.
Jonassen-Hass M.E., Configuration Management
Principles and Practice, Addison Wesley, 2002.
Medical device software life cycle processes, American
National Standard / Association for the Advancement
of Medical Instrumentation, SW68, 2001.
McCaffery F., Donnelly P., Dorling A. and Wilkie G., A
Software Process Development, Assessment and
Improvement Framework for the Medical Device
Industry, Proceedings Fourth International SPICE
Conference on Process Assessment and Improvement,
Lisbon, Portugal, April 2004.
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
88
