ON COLOUR SPACES AND ON COLOUR PERCEPTION
Independence between uniques and chromatic circularity
Alfredo Restrepo Palacios
Laboratorio de Señales, Dpt. Ing. Eléctrica y Electrónica, Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia
Keywords: Colour space, unique colour, spectral colour, independence of uniques, chromatic circularity.
Abstract: The colour space one uses has a bearing on the type of colour image processing tasks one does. As we
approach the stage of colour processing in image processing, new colour spaces may be needed. In
particular, colour spaces that model properties of our perception of colour may be useful. We propose two
nonlinear, tridimensional transformations of the variables of the RGB (or LMS) colour space. In the
resulting spaces pure S, or pure M input, does not imply the presence of yellow. Since there is evidence of S
input to the parvocelular system, we use a dimension called violet minus green; in the resulting space, as the
wavelength variable sweeps the visible spectrum, a circle is obtained, making explicit a circularity of
chromaticity for spectral colours.
1 INTRODUCTION
While experimenting with a technique for colour
contrast enhancement (Restrepo et al, 2002),
(Restrepo and Vega, 2005), for which colour space
is triangulated with tetrahedra and points (colours)
within each tetrahedron are expanded, it became
clear that the technique performs better in some
colour spaces than in others. In particular, for the
detection of malaria parasites in thin blood films, the
colour space called here Hering-2 is better than
traditional RGB space (Ortiz et al, 2005).
We are particularly interested in perceptually
good colour spaces. In RGB space, the corners of
the cube although geometrically equivalent, play
different roles perceptually: cyan and violet are
binary colours, black and white are achromatic
colours while red, green, blue and yellow are unique
colours. We say that a colour space is perceptually
better than another if it geometrically makes
conspicuous perceptual aspects and does not
geometrically differentiate between aspects that
perceptually are of the same type. The terminology
used here and that includes the terms unique colour
and binary colour is the one used by researchers
such as Pridmore, in (Pridmore, 1999).
Trichromacy, although a fundamental link
between the wavelength and the perceptual aspects
of colour, is also a source of misunderstanding,
partially because it is valid both at the receptoral
(e.g. in the human retina or in a colour camera) and
at the stimulus (MacAdam, 1985) (e.g. in a colour
projector or a computer screen) levels. At a
receptoral level, it is convenient to call the response
variables of the human visual system large, medium
and small, rather than red, green and blue, the terms
red, green and blue being misleading there.
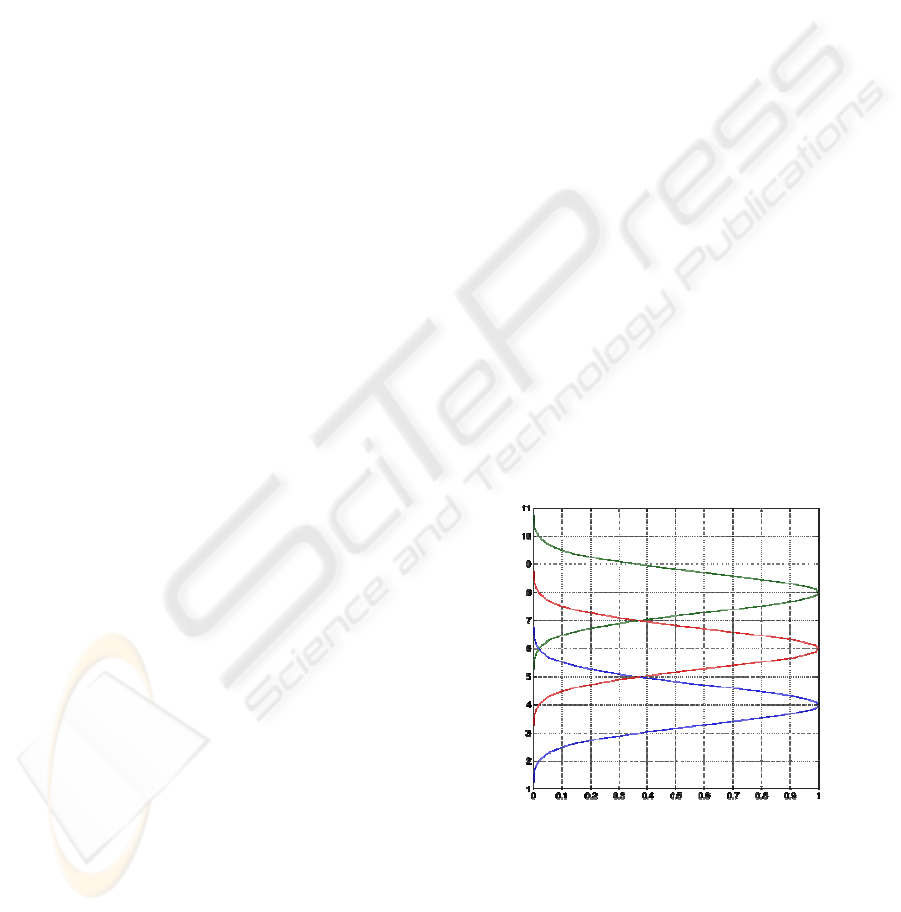
Figure 1: Assumed R, G and B functions. For the purpose
of a schematic illustration of the ideas presented here, for
the R, G and B functions, we use the shown bell shaped
curves, on an artificial wavelength scale from 0 to 12,
rather than real curves based on psychophysical data.
Likewise, in image processing, RGB is an
ambiguous term, partly because of the phenomenon
of metamerism. Interpreted as an input code for
image processing, RGB refers to the broadband and
183
Restrepo Palacios A. (2006).
ON COLOUR SPACES AND ON COLOUR PERCEPTION - Independence between uniques and chromatic circularity.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 183-187
DOI: 10.5220/0001361201830187
Copyright
c
SciTePress

overlapping functions R(λ) (a high-pass filter at
approximately 600 nm) G(λ) (a band-pass between
approx. 500 and 575 nm) and B(λ) (a low-pass at
approx. 500 nm), of the wavelength variable λ,
which are the spectral transmittance functions of the
3 filters used in colour cameras. As an output code,
RGB may refer to the relative intensities of three
light sources of narrow spectrum (e.g. a Blue Violet
LED at 430 nm, a Super Red LED at 633 nm and a
Pure Green LED at 555 nm) which when combined
evoke the corresponding same RGB readings in a
colour camera; these narrowband lights do not
usually have the colours we speak of as red, blue and
green. Unique red is not a spectral colour, in fact,
unique red, a red that does not appear neither
yellowish nor bluish must include both long and
short wavelengths [4]. When displaying colours on
the screen of the computer, RGB values given by 1
0 0, 1 1 0, 0 1 0 and 0 0 1 correspond to “pure” red,
yellow, green and blue, respectively, and if we want
pure and unique coincide, the stimulus
corresponding to red cannot be narrow band.
The NCS (Natural Colour Space) is inspired in
Hering´s colour theory of opposite colour pairs
(Hering, 1964), advanced towards the end of the
nineteenth century and rechampioned by Hurvich
and Jameson (Hurvich and Jameson, 1957). The
dimensions in NCS space are red versus green or
RG, yellow versus blue or YB and lightness or
Bk&Wt. As a system inspired in the opposing colour
theory, the four chromatic basic components given
by [RG, YB, Bk&Wt] = [1, 0, 1/3], [-1, 0, 1/3], [0, 1,
1/3] and [0, -1, 1/3], should correspond to unique
colours. An interesting asymmetry should be noted
here: the two chromatic and opposing processes RG
and YB differ in that a mixture of green and red is
likely to produce a yellow, which lies in the
chromatic YB dimension, while a mixture of blue
and yellow is likely to produce a grey, in the Bk&Wt
dimension, with no chromatic RG or YB component.
(A mixture of binaries cyan and violet is likely to
produce a grey, though.) Also, the chromatic RG and
YB processes are opposing from the perceptual point
of view, while the achromatic Bk&Wt process is a
cooperative process: greys are perceptually
intermediate colours between black and white.
At the perceptual level there is an independence
between the uniques green, red, yellow and blue; the
four “true colours” proposed by Alberti in 1435
(www.colorsystems.com, 2005). (Also interesting,
perceptually, there are four chromatic binaries, and
no “ternary” chromatic combinations.) We would
like a colour system that allowed such an orthogonal
quality between uniques, and have the possibility of
zeroing e.g. the RG channel but not the YB channel.
(Clearly, there should be no way of silencing the
achromatic, magnocelular system.) Such an
independence does not exist for the dimensions of
the RGB system as the response curves overlap.
Even though the NCS system is perceptually a better
model than RGB space, granting that the NCS and
RGB systems are linearly related as RG = R-G, YB
= 0.5(R+G)-B and Bk&Wt = (1/3)(R+G+B), NCS
space has the apparent drawback that from pure red
and from pure green, a nonzero yellow results: YB =
0.5. This is a source of confusion since we might
expect an independence between the Y part of the
YB dimension of the NCS colour system and the RG
dimension, all of the involved colours red, green,
yellow and blue being uniques.
The workings of a color camera model the
responses of the human L, M and S channels, at the
receptoral level. Pioneered by Young, polished
during the nineteenth century by Maxwell and
Grassmann and finally published in complete form
by Helmholtz (Helmholtz, 2005), the Young-
Helmholtz trichromacy theory served as an
inspiration for the color TV camera. However, the
perceptual uniques red, yellow, green and blue,
result from (possibly multiple, accounting for
metamerism,) specific combinations of the L, M and
S responses, and not from only one of these channels
responding at a time. Not even at the ganglionar
level, where Hering´s theories found biological
grounds, are the uniques made explicit (as Marr
would say (Marr, 1980)) by a unique channel system
of firing neurons. The NCS system and the
architecture of the human visual system correlate at
the ganglionar level like this: the RG dimension
corresponds to the parvo system of the human visual
system, the YB dimension to the konio system and
the Bk&Wt dimension to the magno system. It is
perhaps not until cortical area V4 that a 1-1
correspondence between our colour experience and
the responses of specific neurons is found (Zeki,
1993).
It will be probably necessary to go beyond the
RGB and NCS colour systems to do meaningful
colour processing of images. At any rate, this path
roughly follows the course of the visual system in
frugivorous primates; RGB correlates with the
receptoral layer of the retina while NCS correlates
with the ganglionar layer.
In this paper, guided by the search of
mathematical models of the circular perception of
chromaticity and of the independence of the uniques
red and green and the unique yellow, we propose
two colour systems; the starting point being the
RGB system
.
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
184

2 THE TRIDIMENSIONALITY OF
COLOUR PERCEPTION
Aristotle´s model of colour is linear (Aristotle,
2001), (Aristotle, 2002), as it is da Vinci’s (da Vinci,
2002). Although Acuilonius in the fifteenth century
proposed a model that is not linear and includes
black and white as extrema, the first circular model
of (chromatic) colour is Newton´s circle of colours,
which appears in his work Optiks in 1704. In 1810,
Otto Runge published his sphere of colours, the first
tridimensional colour space, from a geometric point
of view (www.colorsystem.com, 2005). The
mathematization of trichromaticity by Grassmann
gave the algebraic tridimensionality to trichromatic
colour space. Hering´s opposing colour theory is
also tridimensional; likewise, colour space HSI
(Hue, Saturation, Intensity) is tridimensional.
Granting that a colour space should be
tridimensional and even if in all currently accepted
cases, topologically the space is a 3-ball, the fact
remains that there are many possible tridimensional
manifolds. And it is not clear whether they should
have a boundary: no matter how white a region in a
scene looks, it is possible to make another region
look whiter. Also, other mathematical structures
(such as orbifolds), besides manifolds could turn out
to be more appropriate.
Besides the geometric and topological properties
of a colour space, there should be also algebraic
structures modelling of colour mixtures and colour
independence. We are well behind such
expectations; consider for example that the RGB
cube is not closed under the operation of standard
vector addition
.
3 INDEPENDENCE BETWEEN
RED, GREEN AND YELLOW
In the NCS space, both pure yellow (RGB=110) and
pure blue (RGB=001) result in a zero valued RG
channel; not so for pure red and pure green when
considering the YB channel. We propose a
modification of the YB dimension of the NCS
consisting in modulating it with the factor (R*G –
B), which we interpret as red and green, or blue.
This makes the new variable Y\B zero, for pure red
and for pure green; we call the resulting
transformation Hering-1
:
RG = R – G
Y\B = (R*G + B)(0.5[R + G] - B) (1)
Bk&Wt = (1/3)(R + G + B)
The resulting image of the RGB cube, under
transformation (2), is shown in Fig. 2.
E.g. for R= 0, the equation for the surface image
of the plane G-B is given by
:
Y\B = [3/2]*(Bk&Wt)
3
– (3/8)*RG
2
*Bk&Wt
For the computation of the inverse of
Transformation 2, we must first solve the cubic
polynomial in the variable B
B
3
+ (4 – 7*Bk&Wt)*B
2
+ (15*Bk&Wt
2
– 4*Bk&Wt-RG
2
)*B
+ Bk&Wt*RG
2
– 9*Bk&Wt + (3/8)*YB = 0
and then solve for R and G
Figure 2: The image of the RGB cube under
Transformation (2).
R = 0.5(3*Bk&Wt + RG – B)
G = 0.5(3*Bk&Wt – RG – B).
Several researchers have remarked on the need
for nonlinear models of the L, M and S variables for
colour perception. (Larrimer, 1974), (Elzinga and
de Weert, 1984); so, it is not unreasonable to use
nonlinear transformations for colour spaces in image
processing
.
4 CIRCULARITY
Let us remind ourselves that there are non spectral
colours; that is, colours that are not metameric to
any narrowband spectral light, among them we have
the greys, browns (which result mainly in contrast)
and unique red (in fact, the whole line of purples of
CIE space).
As the wavelength of a hypothetical single-
wavelength light (a spectral light) sweeps the visible
ON COLOUR SPACES AND ON COLOUR PERCEPTION - Independence between uniques and chromatic circularity
185

spectrum, the resulting point in RGB space (using
the functions in Fig. 1) describes a curve as the one
shown in Fig. 3, that starts at the origin (pure black),
parallel to the B axis and ends at the origin, parallel
to the R axis. On the other hand, since unique red is
not a spectral colour, a curve of visible λ’s in a
hypothetical perceptual colour space would not be a
simple closed curve (i.e. a topological circle), there
would be a gap between spectral colours
corresponding to large wavelengths which we
perceive as reddish oranges and those of small
wavelengths which we perceive as purples. Our aim
here is to have a colour space where such a curve
corresponding to spectral lights is closed and closes
itself at a point where the variables R and B are
small valued but not yet zero. (It is probably
incorrect to assume that an electromagnetic radiation
with spectral contents off the
visible spectrum gives
rise to black; invisible would be a more appropriate
term.)
Figure 3: The image of the wavelength interval [2, 10]
with respect to the functions R, G and B of Figure 1
.
In order to speak of a curve in a hypothetical
colour perception space we need the mathematical
concept of continuity. The perceptual correlate of
such a continuity is grounded in MacAdams´ ellipses
(MacAdam, 1999). His finding gives geometrical
meaning to the fact that a small enough change in
the spectral contents of a light goes unnoticed; it
gives fuzziness to the concept of equivalence in
colour space.
A new transformation, called Hering-2 is
obtained by further transforming the variables Y\B
and RG of the Hering-1 colour space. As has been
pointed out (Stromeyer et al, 1998), there may well
be an input from the S channel to the parvo channel;
thus, instead of a red-versus-green process, we
propose a violet. versus. green process given by
V~G= 0.5(R+B) – G
In addition, modulating the YB variable of the
NCS system with red or blue, and green, we also get
zero for pure green and for pure red, in a new
variable called Y~B. We get circularity for spectral
colours in this way.
Y~B = 10G(R+B)(0.5[R + G] - B)
A factor of 10 has been added to make clearer
the resulting circularity in a plot. Thus, we have the
transformation Hering-2 given by
:
V~G= 0.5(R+B) – G
Y~B = 10G(R+B)(0.5[R + G] - B) (2)
Bk&Wt = (1/3)(R + G + B)
Figure 4: The image in the V~G – Y~B plane of the
wavelength interval [0, 12] with respect to the functions R,
G and B of Figure 1
.
Under this transformation, in the V~G – Y~B
plane, the curve corresponding to the spectral lights,
for the interval λ∈[0, 12], is as shown in Fig. 4; a
closed curve is obtained. The curve in Fig. 4 is not
meant to include black, (the origin) as the curve
closes on itself before the three variates R, G and B
are all zero.
To invert (3), we obtain B, using a rational
function, then we find R and G, as shown below.
B=
3
10
*YB − 9*Bk &Wt
3
+ 2*VG
2
* Bk &Wt + 30 * VG * Bk &Wt
2
3*VG * Bk &W
t
−
9Bk &W
t
2
+ 2VG
2
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
186

R= 3*Bk&Wt + (2/3)*VG – B
G= Bk&Wt – (2/3)*VG
.
6 CONCLUSION
Two transformations of the R, G, B data, intended to
model the perceptual independence between unique
colours, and the perceptual circularity of our colour
perception, up to spectral colours, are given. As the
perceptual properties are surely advantageous to
frugivory primates, it is probable that the given
implementations will be of use in computer vision,
they have shown to be useful in the detection of
malaria in images from thin blood films. We have
explored colour standardization by triangulating
colour space and expanding colours within each
tetrahedron (Restrepo et al, 2002), for the
recognition of malaria (Ortiz et al, 2005), we had
that Hering-2 is a more meaningful space.
Regarding the perceptual independence between
reds and greens on the one side and yellows on the
other, it probably has advantages regarding the
detection of mature fruits. It is difficult to speculate
as to the ways and advantages in which circular
chromaticity is achieved in the human visual system;
for one thing, it is probably not convenient to have
to close a chromatic circle using black; a symmetry
in the way the L, M and S channels are treated by
the neural circuits of the visual system may
represent savings ins genetic code and neural wiring.
Unlike NCS space, in RGB space the achromatic
line is not geometrically conspicuous in the cube and
it is hard to speak of the circularity of the chromatic
colours.
Colour, as a perceptual entity is meant to give us
information about the surfaces of the objects in a
scene and, as such, is largely independent of the
spectral contents of the illuminant. Even though
mathematically, pointwise, colour is a vector
statistic of a spectral density, it is a very
sophisticated measure when taken in the context of
the surrounding colours in a scene. We can only try
and speculate about the adavantages brought about
by the workings of our visual perception.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers of
a cruder version of this paper for their patience and
much valuable comments
.
REFERENCES
Restrepo, A., Nieto, A., Ardila, S. and Vega., J., 2002. An
approximation to color standardization. In Procs. 4
th
IASTED Signal and Image Processing Int. Conf.
Kawai, 609-614.
Restrepo, A. and Vega, J., 2005. A Tool for Color
Contrast Enhancement. In Memorias del X Simposio
de Tratamiento de Imagenes, Señales y Visión
Artificial, Cali, Colombia.
http://senales.univalle.edu.co.
Ortiz, M.V., Pimentel, M.A. y Restrepo, A., 2005.
Metodología para el reconocimiento automático de la
malaria basado en color. In Memorias del X Simposio
de Tratamiento de Imagenes, Señales y Visión
Artificial, Cali, Colombia.
http://senales.univalle.edu.co
Pridmore, R.W., 1999. Unique and binary hues as
functions of luminance and illuminant color
temperature, and relations with invariant hues. Vision
Research, 39, 3892-3908.
MacAdam. D.L., 1985. Color Measurement, Theme and
variations, Springer, Berlin, 2
nd
edition.
Hering, E., 1964 Outlines of a Theory of the Light Sense.
Tr. by L. M. Hurvich and D. Jameson, Harvard
University Press, Cambridge.
Hurvich, L.M. and Jameson, D., 1957 An pponent-process
theory of color vision Psychological Review, 64, 6,
385-403.
www.colorsystem.com, 2005
Helmholtz, von H., 2005. Treatise on Physiological
Optics,. Dover, Mineola.
Marr, D., 1980. Vision. Freeman, San Francisco.
Zeki, S., 1993. A Vision of the Brain. Blackwell, Oxford.
Aristotele, 2001. Anima. Bompiani, Milano.
Aristotele, 2002. L’anima e il corpo. Parva Naturalia.
Bompiani, Milano.
da Vinci, L., 2002. Trattato della pittura. Rusconi, Roma.
Larimer, J., 1974. “Opponent-process additivity -I:
Red/Green equilibria. Vision Research, 14, 1127-
1140.
Elzinga, C.H. and de Weert, C.M.M., 1984. Nonlinear
codes for the yellow/blue mechanism. Vision
Research, 24, 911-922.
Macadam, D.L, 1999. Role of luminance increments in
small color differences. In Color Metrics, J.J. Vos,
L.F.C. Friele and P.L. Walraven, eds., 160-167.
C.F. Stromeyer, C.F., Chaparro, A., Rodriguez, C., Chen.
D., Hu, E. and R.E. Kronauer, R.E., 1998. Short-wave
cone signal in th Red-Green Detection Mechanism.
Vision Research 38, 813-826.
www.microbackup.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/lightandcolor/le
dsintro.html, 2005.
ON COLOUR SPACES AND ON COLOUR PERCEPTION - Independence between uniques and chromatic circularity
187
