
DEVELOPMENT OF VOICE-BASED MULTIMODAL USER
INTERFACES
Claudia Pinto P. Sena
Universidade do Estado da Bahia, Salvador, 41.150-000, Bahia, Brasil
Celso A. S. Santos
Universidade do Salvador, Salvador, 41.950-275, Bahia, Brasil
Keywords: HCI, multimodality, voice recognition.
Abstract: In the last decades, the interface evolution made the visual interfaces popular as standard and the keyboard
and mouse as input device most used to the human-computer interaction. The integration of voice as an
input style to visual-only interfaces could overcome many of the limitations and problems of current human-
computer interaction. One of the major issues that remain is how to integrate voice input into a graphical
interface application. In this paper, we introduce a development method of multimodal interfaces combining
voice and visual input/output. In order to evaluate the proposed approach, a video application multimodal
interface was implemented and analysed.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Raskin (2000), the user’s interface
establishes the devices in which the user must
interact with a computing system and the way that
this system invites and answers user’s interaction.
This definition brings two important concepts to be
analyzed: the interface devices and the styles of
interaction available to the user.
The interface devices are parts of the computing
system in which the user has physical, perceptive
and conceptual contact. The interface involves a set
of necessary software and hardware to allow and
facilitate the communication and interaction
processes between the user and the application
(Carneiro, 2003). Interaction is a process that
involves user’s actions and interpretations about the
answers revealed by this interface (De Souza,1999).
Interaction styles involve the ways used by the
users to communicate or interact with an application
(Preece et al.,1994; Shneiderman, 1998). Natural
language, command languages, menus, WIMP
(Windows, icons, menus and pointers), form filling
in and direct manipulation are well-known examples
of user´s interaction styles (Shneiderman, 1998). In
general, as in a Graphical User Interface (GUI),
different styles can be supported by an application
interface.
The integration of voice as an input style to
visual-only interfaces could overcome many of the
limitations and problems of current user application
interaction. The problems related with the voice
interaction can be approached as a part of the natural
language processing style type, once they involve
the possibility of the computer and its applications to
understand and to respond to the actions using the
user’s language itself (Carvalho, 1994 e Siqueira,
2001). In this case, the natural language applications
are supposed to have a dictionary of words and
meanings restricted to the domain, requiring the
establishment of precise dialogs and restricting the
possibilities of the user’s pronunciation (Siqueira,
2001).
Another approach is to develop applications that
support the use of natural language with few
restrictions. In this case, the problems in natural
language processing, as vague and ambiguous
constructions with grammar mistakes need to be
solved. Finally, regardless of voice interaction is
treated, the speech must be considered as a possible
interaction style between the user and the computer,
that allows him to accomplish his tasks with more
efficiency and less effort.
310
Pinto P. Sena C. and A. S. Santos C. (2006).
DEVELOPMENT OF VOICE-BASED MULTIMODAL USER INTERFACES.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 310-316
DOI: 10.5220/0001573103100316
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Due to the overwhelming number of inputs and
outputs objects in direct manipulation interfaces,
users have simply many things to see or to do. Voice
inputs and outputs are a natural channel, available
and systematically under-utilized to improve the
communication between the user and the computer.
For these users, such interfaces added to the current
visual ones increase the feeling of direct
manipulation and enhance user’s understanding
(Mountford, 1990).
We consider “mode or modality” as an input
and output mechanism with the user’s interface
(Nunes and Akabane, 2004). Thus, multimodality is
defined as the combination of two or more input
modalities (such as speech, touch, gestures, head
movements and mouse) in a coordinate way with
different available outputs in a multimedia system
(Ovviat, 2002). Different from the multi-channel
access which makes possible to access data and
applications from different channels (such as
laptops, PDAs or cellular phones), multimodal
access allows the combination of multiple ways in
the same interaction or section (Srivasta, 2002).
According to Maybury (2001), machines
supporting multimodal inputs and generating
coordinated multimedia output can bring benefits,
including: more efficient interaction (less effort for
the task execution), more effective interaction (tasks
and dialogs regarded to the user’s context) and more
natural interaction (support to the combination of
speaking, writing and gestures as in the man-man
communication).
Within this context, this paper aims to present a
process for the development of multimodal user
interfaces with emphasis in the voice modality. The
focus here is to present an approach towards
integration of voice commands into traditional
mouse based interfaces.
This article is organized as follows: Section 2
reviews paradigms of graphical interfaces
interaction. Section 3 discusses voice features as an
input modality. Section 4 gives the reader details of
the voice interaction of the GUI and presents the
GRMMI environment. Section 5 introduces the
application of the proposed approach to the
development of a video manipulation interface. The
last section analyses the results and presents
conclusions.
2 INTERACTION PARADIGMS
The term paradigm is generally used to mean a
model of how something operates. An interaction
paradigm specifies a model of how an interface
operates (reacts) when the user executes an action on
it. It also indicates the order that elements are are
selected or activated by the user when he executes a
task. These paradigms can be grouped in two basic
styles (De Souza, 1999):
a) action + object interactions – the user
selects the action to be done, and then the
object on which it must interact.
b) object + action interactions – the user first
selects the object and then the operation
that wishes to do over it.
In a direct manipulation interface, the user
hopes the system to offer representations of objects
those interact like real objects themselves. These
objects must have associated tasks with meanings
like those of the real world. Because of this it is
common to imagine that the user’s interface use the
interaction “object + action” paradigm. However, as
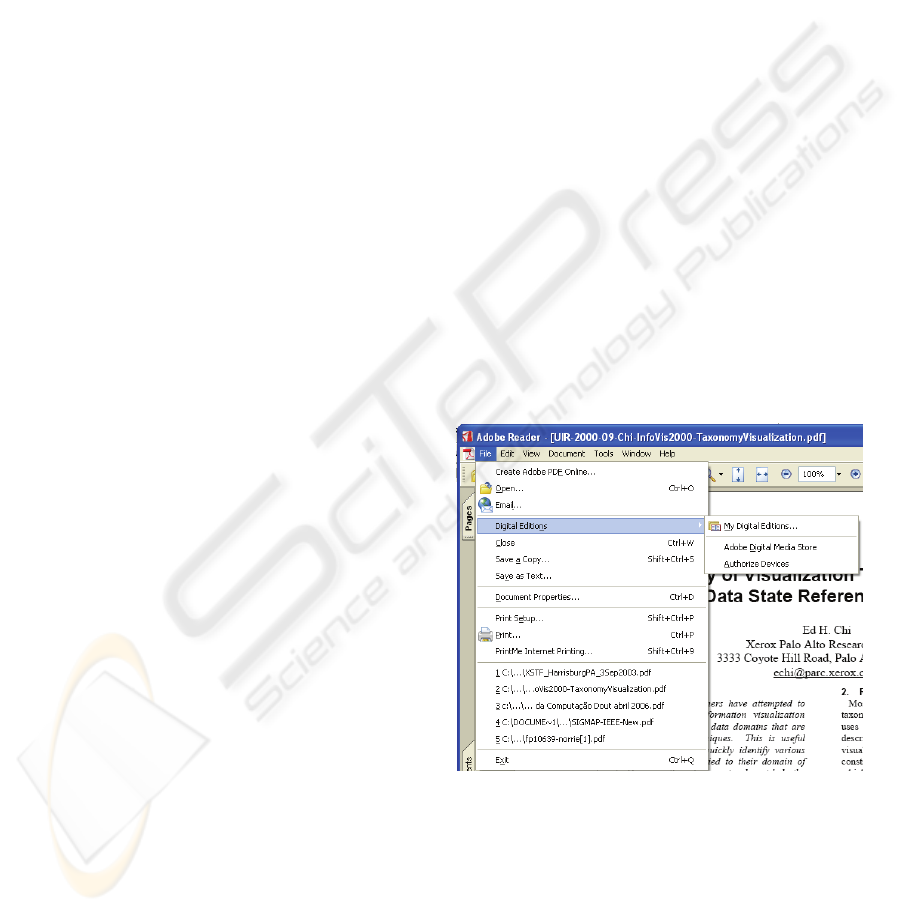
depicted in Figure 1, even in well-known interface
standards this paradigm is not always kept. In the
first level of the interface menu structure there are
elements that give us the idea of object
manipulation, as File and Tools, as well as the
elements which are related to the actions as Edit,
View and Help. Thus, one can say that menus apply
a paradigm modeled sometimes by the “action +
object”, sometimes by the “object + action”.
Figure 1: Adobe Reader main screen: an example of menu
interaction.
Another important point is that, it doesn’t matter
what interaction paradigm is adopted, the user
usually wait for a reaction of the system through the
graphical interface. In the example of Figure 1, after
some interactions, the different levels of the menu
are detached and presented.
DEVELOPMENT OF VOICE-BASED MULTIMODAL USER INTERFACES
311
From the previous observations, one can say
that some important problems must be solved to
allow the integration of the voice commands to the
GUI:
1. How to model the multimodality integration in a
graphical environment that applies different
interaction paradigms?
2. Which interface objects to which the natural
interaction must be done with the voice?
3. How do the graphical interfaces must react to
the user’s voice commands even when different
interaction paradigms are used?
3 THE VOICE AS AN INPUT
MODALITY
Each interaction modality has its own characteristic
that many times determinate its utilization. In
general, the tasks made by the users on the interface
are associated to the following actions (Damper,
1993):
− Selection: choose the items as in a menu.
− String: composition of a text characters
sequence.
− Quantification: numeric value specification as
in the case of the number of a text edition line.
− Orientation: angular quantification, as in the
case of a line segment orientation.
− Position: point specification in a bi-dimensional
space.
− Path: position and orientation sequence
resulting in a curve in the application space.
For each action there are more or less indicated
modalities. The speaking recognition (identification
of the spoken words and transcription to the written
text) is generally indicated to selecting and text
composition tasks (string) for it proportions a more
natural interaction between the user and the
application. On one hand, the selection of an action
through simple voice commands instead of a
considerable number of keys or clicks reduce the
time interaction between the user and the system. On
other hand, the quantification, positioning and
orientation actions become complicated, imprecise
and more vulnerable to mistakes if the voice
modality is used as input. Thus, these actions are
more appropriated to the use of devices such as
keyboard and mouse (Damper, 1993).
The input modality choice must consider some
circumstances and conditions to the application use
(Sun Microsystems, 1998: Hix, 1993). One can say
the voice input modality is indicated in the cases
where:
− The person who uses the application has the
hands or eyes occupied.
− Mobility is required.
− It is not possible to use the keyboard.
− Objects or actions within a great amount of
options or through a repetitive way must be
selected.
− The required commands are built in within a
great menu structure.
− The users have some physical deficiency,
especially visual problems.
Voice-based and direct manipulation interfaces have
complementary characteristics. This fact
collaborates and justify the use of many modalities
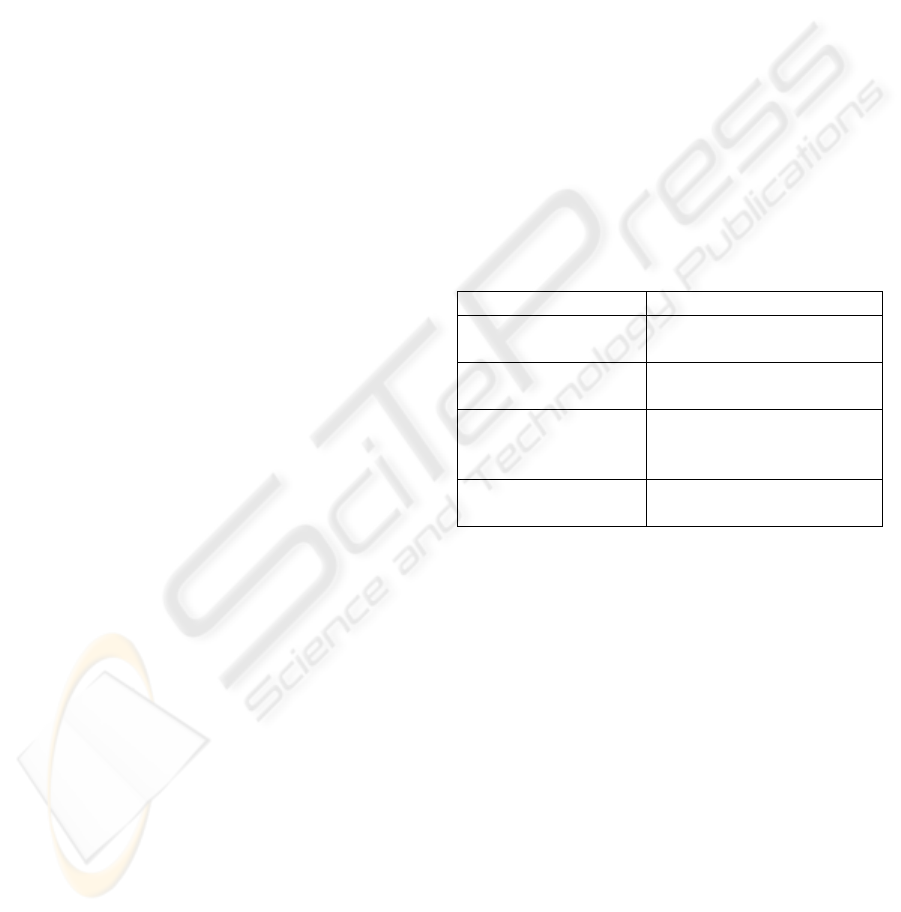
in a same interface (Grasso, 1996). Table 1 describes
these features.
Table 1: Complementary characteristics of the voice and
direct manipulation.
Direct Manipulation Voice Recognition
Direct use Operations without the use
of hands and/ or eyes
Simple and intuitive
actions
Possibility of complexes
actions
Consistent
appearance and
behavior
Reference independent of
the location
No ambiguity in the
reference
Multiple ways of relating
to entities
In IBM (2003) some considerations related to
the voice use associated to the graphical interface
are also presented. Some visual elements that need
the user’s input or action can be activated with the
voice. Buttons, text fields, links, list box and
checkbox are typical examples of this possibility,
while, graphics, tables and diagrams are better
presented and manipulated via graphic interface.
4 THE PROCESS OF INCLUDING
VOICE IN GRAPHICAL
INTERFACES
Starting from a naïve approach, the voice integration
to a graphical interface could be solved with the
simple association of voice commands to the objects
that compose such interface. However, that this is
not the most adequate way to deal with the problem.
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
312

Some tasks (e.g. a region or image marking) or
situations (e.g. noisy places) voice make difficult to
use as interface input modality.
It must be also observed that the use of some
input modalities integrated in a complementary or
simultaneous manner should be an imposed to a
specific task execution.
The voice integration to the graphical interface
can not just follow the graphical interface interaction
paradigm because they do not have a standard:
sometimes the paradigm is “action + object”,
sometimes it is “object + action”. In general, for
voice commands (e.g., “edit this Figure”), it is more
natural for the user to mention the action first and
complementing it with the object afterwards.
The problem of the interface feedback to the
user’s input action through the voice commands also
must be treated. In other words, it is necessary that
the interface allows the user to verify if the
command was effectively recognized and executed.
Then, the implemented solution must allow a narrow
link between the voice commands and the graphical
interface objects that execute similar actions. These
graphic objects will give the user a feedback through
reactions in the graphical interface. In Figure 1, for
instance, the user could start up an action directly in
the lowest Menu level (“Save As”) without being
necessary to pronounce the command that refer to
the highest level (“File”), in an “action + object”
style. However, the interface reaction would show
the user that the command was recognized with the
same resulting visual representation of an action
with the mouse according to the Menu hierarchy.
Thus, different input interactions (voice, mouse and
keyboard) to the same task performance (a Menu
option choice) must generate identical interface
responses.
The process of including voice in graphical
interfaces proposed here, are beyond the simple
voice rules association of the interface graphical
elements. This process intends to solve the problems
listed in section 2 and is based on the following
steps:
1. To indentify the use case associated to the
graphical interface as a whole or a part of it (i.e.
a module, a component etc.);
2. For each use case identified, to define the
interface actions and components that are part
of it;
3. To define the grammar rules that associate voice
commands to graphical components;
4. To create a file (XML) that defines the
pronunciation hierarchy from defined grammar
commands, if necessary;
5. To define the parameters associated to the voice
commands, if necessary;
6. To identify the situations of the activation and
deactivation of the grammar rules for each use
case;
7. To implement a method that produce the visual
feedback associated to the execution of the
voice commands in the interface.
The use cases from phase 1 allows the
identification of tasks to be executed with the
interface and the adequate functions to the voice
interaction. The action definition and the grammar
associated with voice interaction can be done in a
general way to any interface component and
independent of the adopted interaction paradigm.
The grammar rules define, consequently, the words
or sentences (tokens) that should be accepted by the
recognizer.
Another important point is the specification of a
precedence hierarchy between the voice commands.
This hierarchy avoid the user from pronouncing any
voice rule defined in a grammar in any order. This
approach has direct impact in the recognition system
performance. Furthermore, the hierarchy relates in a
clear way “what is possible to say now” (voice
interface) at the moment and “what is possible to do
now” (graphical interface), keeping the user
informed on the result of his/her interactions through
a visual interface feedback. It means that enabling
(disabling) a graphical component related to it and
vice-versa.
Once there is any treatment related to the
complementary and simultaneous multimodal
commands to the grammar rules (e.g. voice and
mouse use to zoom part of a digital image), it is
suggested to these commands to be identified and
modeled to the following way: L (location) – A
(action) – O (object) – P (parameters). The
“location” is given by the mouse position in this
case; “action” corresponds to the action of zooming;
“object” corresponds to the image and the
“parameters” to the complementary information
necessary to the action (how much the image must
be enlarged).
The steps 3, 4 and 5 are executed with help of a
environment called GRMMI (Grammar Rules for
MultiModal Interfaces). This environment supports
both voice grammars and hierarchies specification
and the execution of the multimodal application that
applies the specified grammars. The part of
environment related to the integration between what
was pronounced and the interface reactions is called
GRMMI engine. Hence, it is an intermediator
DEVELOPMENT OF VOICE-BASED MULTIMODAL USER INTERFACES
313

between voice and visual interfaces modes. GRMMI
engine is in charge of identifying the grammar rule
associated to the token (accepted word) pronounced
(uses the grammar rules), verifying if there is a
foreseeing precedence hierarchy for such token (it
uses the hierarchy file – XML) and then enable and
unable according to this hierarchy the adequate
grammar rules, as well as in maintaining the
harmony with the graphical objects. This means that
once enabled or disabled, the voice command, the
graphical object associated to it will also be enabled
or disabled, giving a visual response to the
application user.
The GRMMI engine offers many available
functions which can be used in applications with
graphical interfaces, as long they are created to the
grammar and XML files necessary to the definition
of the voice interface in steps 3 to 5 of the proposed
approach.
5 CASE STUDY
As an illustration of the proposed process, consider
the example of the interface from one of the
components of an interface for the annotation of
digital videos (player component) (Santos et. al.,
2004).
Two use cases are associated to this interface
component, as depicted in Figure 2:
(i) “watching video”
(ii) “describing video segment”.
Annotation
Controls
VCR
Controls
Figure 2: Player component interface.
The related actions to these use cases are
described bellow: for the use case “watching video”,
the associated actions are the typical controls from a
VCR. The associated actions to the use case
“describing video segment” allows the splitting up
of the video at a time (begin and start) and the
description of the created segment (add region, add
annotation).
1. To watch video: play, pause, stop, next,
forward, rewind and previous.
2. To describe video segment: start segment,
end segment, add region, add annotation.
Figure 3 illustrates the rules grammar for the
previous player component.
g
rammar player;
public <watch> = watch{watch};
public <describe> = describe{describe};
public <play> = play{play};
public <stop> = stop{stop};
public <pause> = pause {pause};
public <forward> = forward {forward};
public <rewind> = rewind {rewind};
public <next> = next {next};
public <previous> = previous {previous};
public <zoom> = zoom {zoom};
public <begin> = start segment {begin};
public <end> = end segment{end};
public <comment> = add annotation {comment}
public <region> = add region {region};
associated XML tag
recognized word / command
rule name
use
cases
actions
(tasks)
Figure 3: Player component grammar.
The following step is the creation of the
commands hierarchy. This hierarchy allows the
establishment of which interface components
(commands) must be enabled (disabled) when the
user performs a voice commands sequence.
Figure 4 illustrates an example of hierarchy for the
commands of the player component. In this
hierarchy, if the user pronounces the word “watch”
(use case “watch”), just the player VCR buttons will
be enabled. If the “play” command is pronounced,
all the buttons, except “stop” and “pause” will be
disabled (for the application of video annotation,
was defined that after the beginning of the video
presentation, the sole available actions for the user
would be the “pause” action or the “stop” action to
interrupt the presentation through a voice
command).
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
314

<?Xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<
WordList>
<UseCase tag="watch">watch
<FatherNode root="false" tag="play">play
<Child tag="pause">pause</Child>
<Child tag="stop">stop</Child>
</FatherNode>
<FatherNode root="true" tag="next">next
...
</FatherNode>
<FatherNode root="true" tag="forward">forward
...
</FatherNode>
...
<FatherNode root="false" tag="stop">stop
<Child tag="play">play</Child>
<Child tag="forward">forward</Child>
<Child tag="next">next</Child>
</FatherNode>
</UseCase>
<UseCase tag="describe">describe
<FatherNode root="true" tag="begin">start segment
<Child tag="end">end segment</Child>
<Child tag="region">add region</Child>
<Child tag="comment">add annotation</Child>
</FatherNode>
...
</UseCase>
<
WordList>
Figure 4: Extract from the hierarchy of commands.
One example of interface visual response to the
voice command sequence is illustrated on Figure 5.
After the initial stage linked to the “watch” case use
(Figure 5 (a)), the user pronounces the “play”
command and just the “pause” and “stop” buttons
get enabled. (Figure 5 (b)). In the sequence after the
“pause” command is pronounced, all the buttons,
except the “pause” one itself, get enabled. (Figure 5
(c)). Notice that the enabled (disabled) components
sequence follows exactly the grammar rules from
Figure 4. Observe as well that the graphical objects
associated to another use case (describes video
segment) also remain disabled. The use cases are
mutually exclusive, meaning that the manipulation
of one of them disables the others.
(a) Player interface: initial state.
(b) Player interface: after “play” command.
(c) Player interface: after “pause” command.
Figure 5: Interface reactions for some voice commands.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
The paper has proposed a new approach to
multimodal interface development with emphasis in
the use of voice. This implies in evaluate the
graphical interface in which voice will be integrated
and, beyond this, knowing the voice characteristics
while input modality. The major contributions of the
work are:
1. Proposal of a process that suggest which
activities must be followed to the voice
inclusion in a GUI;
2. Proposal of hierarchy problem solving of voice
command precedence through the use of XML
files associated to rules grammar;
3. XML file model as the result of the hierarchy
generation of voice commands precedence;
4. Proposal of a model parametrized multimode
commands treatment;
5. The GRMMI environment implementation, that
provides the solution and treatment for
pronounce maintenance problems among the
commands, as well as of a visual response to the
application user of what can be said or done.
The GRMMI environment, beyond making the
proposed inclusion process of the voice modality in
a graphical interface valid, facilitates the
implementation made by developers that wish to use
voice in their applications, since it makes available a
set of functions proper to input manipulation and
treatment by voice and grammar and hierarchy
automatic generation. The effort of development
becomes less if compared to this work’s. Using
GRMMI, it is only necessary for application
developers to identify the use cases, associated tasks
and then use the generation module and the GRMMI
engine in their applications (these are the steps of the
proposed method).
The search for more simple, natural and
intuitive human-computer interfaces has increased,
mainly with the intention to reduce the user’s
problems and anxiety when using the system. The
voice interface, once it is more natural to ht e human
being, minimizes a little these initial problems and
can facilitate and make the application learning
process rich, as well as make its use flexible, in the
meaning of allowing the access without using hands
and/or eyes, access in small devices, generating a
productivity gain. Besides, if the speech is
associated to other modality, as clicking or drawing
in digital images, the process can be a lot more
DEVELOPMENT OF VOICE-BASED MULTIMODAL USER INTERFACES
315

interesting, since one of the modalities become more
appropriated to tasks, often complementary.
From these considerations and obtained results,
one can suggest as future activities that will continue
this work: (i) submission to the multimode interface
proposal to the evaluation by the users in order to
measure the real gain relating to its use; (ii)
possibility of choosing the recognizer language, that
is currently only Portuguese; (iii) implementation of
a multimodal output, allowing audio, text and image
modalities integration; (iv) restriction of the possible
words from the dictate dictionary, making it more in
a context (e.g. if it is a medical application, a
dictionary with medical expressions makes the
recognition more precise and faster); (v) use of
another recognition system that does not depend on
training and (vi) implementation of treatment of the
parametrized multimode commands.
REFERENCES
Carneiro, M. 2003. Interfaces Assistidas para Deficientes
Visuais utilizando Dispositivos Reativos e
Transformadas de Distância. Rio de Janeiro. 162p.
Phd Thesis, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio
de Janeiro, Brazil.
Carvalho, J.O.F. 1994. Referenciais para Projetistas e
Usuários de Interfaces de Computadores Destinadas
aos Deficientes Visuais. MSc. Thesis, Univ. of
Campinas, Brazil.
Damper, R. I., 1993. Speech as an interface medium: how
can it best be used?, in Baber, C. and Noyes, J. M.,
Eds. Interactive Speech Technology: Human Factors
Issues in the Application of Speech Input/Output to
Computers, pages pp. 59-71. Taylor and Francis. UK.
DE Souza, C.S.; Leite, J.C.; Prates, R.O.; Barbosa, S.D.J.,
1999. Projeto de Interfaces de Usuário: perspectivas
cognitivas e semióticas. Jornada de Atualização em
Informática, Brazilian Symposium of Computing, Rio
de Janeiro, Brazil.
Gavaldà, M., 2000. La Investigación em Tecnologías de
La Lengua. Quark Ciencia, Medicina, Comunicación y
Cultura. N. 19, Jul-Dec. 2000, p. 20-25.
Grasso, M. A., 1996. Speech Input in Multimodal
Environments: A proposal to Study the Effects of
Reference Visibility, Reference Number, and Task
Integration. Technical Report TR CS-96-09, University
of Maryland, Baltimore Campus.
Hix, D.; Hartson, H. R., 1993. Developing User
Interfaces: Ensuring Usability Through Product &
Process. Caps 1, 2 e 3. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
IBM, 2003. Multimodal Application Design Issues. (URL:
ftp://ftp.software.ibm.com/software/pervasive/info/mu
ltimodal/multimodal_apps_design_issus.pdf, access on
03/07/2005)
Maybury, M., 2001. Coordination and Fusion in
Multimodal Interaction.
(URL:http://www.mitre.org/work/tech_papers/tech_pa
pers_01/maybury_coordination/maybury_coordination
.pdf).
Mountford, S. J.; Gaver, W. W., 1990. Talking and
listening to computers. In Laurel, B. (Ed.), The art of
human-computer interface design, 319-334. Reading,
MA: Addison-Wesley.
Nunes, L. C.; Akabane, G. K., 2004. A Convergência
Digital e seus Impactos nas Novas Formas de
Interação Humana. In Anais XI SIMPEP - Bauru, SP,
Brasil.
Oviatt, S., 2002. Multimodal Interfaces. Handbook of
Human-Computer Interaction, Lawrence Erlbaum:
New Jersey.
Preece, J. et al., 1994. Human-computer interaction. Great
Britain: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
Raskin, J., 2000. The Humane Interface: New Directions
for Designing Interactive Systems. ACM Press.
Santos, C.A.S.; Rehem Neto, A. N; Tavares, Tatiana
Aires. 2004. Um Ambiente para Anotação em Vídeos
Digitais com Aplicação em Telemedicina. In:
Webmedia & LA Web 2004, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil.
Shneiderman, B., 1998. Designing the User Interface
:
Strategies for Effective Human-Computer-Interaction.
3rd Ed. Addison-Wesley.
Siqueira, E. G., 2001. Estratégias e padrões para a
modelagem da interface humano-computador de
sistemas baseados na arquitetura softboard. São José
dos Campos: INPE.
SUN MICROSYSTEMS., 1998. Java Speech API
Programmer´s Guide. October, 26, 1998. 156 p.
(URL: http://java.sun.com/products/java-media/
speech/forDevelopers/jsapi- guide.pdf)
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
316
