
e-SENSE
Capturing Ambient Intelligence for Mobile Communications through Wireless
Sensor Networks
Mirko Presser, Alexander Gluhak, Derek Babb, Rahim Tafazolli
University of Surrey, Centre for Communication Systems Research , Mobile Communications Research Group, Guildford,
GU14DL, United Kingdom
Laurent Hérault
CEA-LETI, 17 rue des Martyrs, 38054 Grenoble Cedex 9, France
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, Body Sensor Networks, Context Awareness, Ambient Intelligence.
Abstract: This paper provides an overview of the e-SENSE Integrated Project, highlighting its strategic importance
with respect to other projects in Mobile and Wireless Systems and Platforms Beyond 3G (B3G). The main
focus of the project is to capture context through the use of wireless sensor networks and further integrate
the context information through an open gateway architecture into B3G. The motivation behind this is to
provide real context information for the concept of Ambient Intelligence that is a focal element in many
current next generation communication systems, applications and services. e-SENSE approaches this by
researching efficient and light weight wireless sensor communication systems including the physical layer
up to the transport layer and a distributed processing middleware including distributed services and
distributed data processing in a toolbox approach. Further, components of the toolbox are optimised
according to sensor network architectures, addressing several or very specific context capturing mechanisms
and sensor network applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Creating the Ambient Intelligent World is the
principal focus for FP6 Information Society
Technologies research in Europe. Key to Ambient
Intelligent systems is to “know” itself, its
environment and the context surrounding its use and
act accordingly (The Vision Book ).
The aim of e-SENSE is to enable Ambient
Intelligence in Beyond 3G Systems, i.e., using
wireless multi-sensor networks for making context-
rich information (e.g. about the user, his/her social
setting, or the environment) available to applications
and services. While today’s information systems
require cumbersome human input or computer-
generated data, future systems will be built on
continuous streams of real-world physical data
provided by numerous sensors linked together. They
will perform their tasks in an unobtrusive and
intelligent way enhancing the user experience,
gathering refined and accurate data, simplifying
tasks, increasing communication efficiency and
enabling a plethora of novel applications and
services and thus increasing the usability, efficiency
and value of day to day life as well as business and
scientific achievements. The envisaged e-SENSE
architecture has the capability to observe and
interact with physical phenomena in real time, and
with a fidelity that was previously unobtainable.
Figure 1: Basic e-SENSE.
341
Presser M., Gluhak A., Babb D., Tafazolli R. and Hérault L. (2006).
e-SENSE - Capturing Ambient Intelligence for Mobile Communications through Wireless Sensor Networks.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems, pages 341-346
DOI: 10.5220/0002093903410346
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The following sections provide an overview of the
project’s objective and motivation as well as give an
insight into the technical approach of the project.
2 e-SENSE OBJECTIVES
The main objective of the project is to contribute to
the evolution and definition of the future Ambient
Intelligent Mobile Systems and Platforms Beyond
3G by integrating ubiquitous Wireless Sensor
Networks (WSNs) in B3G mobile systems.
The richness of information that is required to fully
capture Ambient Intelligence demands a multitude
of multi-sensory information. To obtain this
information potentially a large variety as well as a
large number of sensors is required. The sensors
may communicate among themselves or via
gateways with other systems and networks (e.g.
other sensor networks, Cellular, WLAN, PAN, or
the core network). Even though the majority of the
sensors in these areas will be wireless (mainly for
ease of deployment and convenience), device
integrated sensors and hardwired sensors are of
importance to also be considered. Wireless sensors
are expected to operate in harsh environments such
as close body proximity communications, operate
over a long period of time and coexist with other
wireless networks. High power, bandwidth
efficiency and robustness to interference as well as
achieving small physical size are major focus of e-
SENSE.
Due to the ubiquitous nature as well as the quantity
and spread of sensors within such a system, key
requirements for e-SENSE are ultra low power
operation (in particular for communications but also
for local processing of sensor information) and
multidimensional scalability with respect to
mobility, number of sensors, diversity of sensor
classes, sensor network types and sensor payload
types. Also presenting captured information to
Ambient Intelligent Systems, achieving transparency
with respect to underlying sensor systems is of
importance. Key to these are:
o energy efficiency with respect to wireless
sensor node architectures
o Ultra low power and bandwidth efficient
air-interfaces and data transport and
networking protocols for wireless sensors,
clusters and gateways through cross-layer
optimisation
o distributed resource management for
wireless sensors
o co-existence with other radio interference /
signals
o distributed data processing and
collaborative aggregation
o intelligent data centric interface
o self growing, robust, and scalable wireless
sensor networks
o self organising sensor networks in mobile
and dynamic heterogeneous wireless sensor
systems
o self learning and intelligent interfaces for
transparent integration of new information
sources
o security framework
o privacy for personal or sensitive
information.
3 MOTIVATION
Addressing these issues, e-SENSE will be able to
capture information from phenomena and signals
from the real physical environments, transport and
pre-process the information. And thus provide the
information to other mobile/wireless devices or to
sensor applications and services in other networks
and most importantly provide information to service
platforms and subsequently service providers,
effectively enabling Ambient Intelligence.
The e-SENSE project is investigating a new
paradigm for bringing the flexibility of information
technology to bear in every aspect of daily life. It
foresees that people will be surrounded by
sensorised environments that provide easily
accessible yet unobtrusive support for an open-
ended range of novel applications and services, to
enrich daily life and to increase productivity at work.
This presents a paradigm shift from personal
computing to ubiquitous computing, challenging the
research community to investigate new building
blocks and integrated infrastructures, as well as
emerging applications and interaction styles.
Relevant knowledge areas include mobile and
wireless communications, distributed data
processing, data and knowledge modelling,
application platforms, human-computer interaction,
security, trust and privacy, as well as application
research in different settings and sectors. Such a
wide variety of topics can only be covered through
an Integrated Project which consists of
complementary expertise from industry and research
institutes from different disciplines which have been
brought together to address these issue.
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
342

The main reasons for undertaking the proposed
research are:
o The research has a real potential for
significant socio-economic impact: The
shift from personal computing to
ubiquitous, ambient intelligent systems is a
motor for innovation expected to transform
IST business over the next 10 years.
Infrastructure research will give rise to new
products, services and applications,
creating economic opportunities as well as
addressing societal concerns such as
accessibility, e-inclusion, health, safety,
learning and quality of life.
o The research is very timely: recent
advances have provided crucial enabling
technologies (embedded components,
sensors, ad hoc networks, location
technologies, etc) but there is still a
significant gap between these basic
building blocks and the potential
applications of sensorised environments.
o The research is highly innovative: it
develops new technology concepts ranging
from cross-layer energy-efficient design to
distributed services and data processing,
explores novel applications ranging from
smart maintenance to health, fitness and
well-being, and investigates the
fundamental architectures required as
foundation for fully integrated sensorised
environments to capture context in an end-
to-end system approach.
4 e-SENSE APPROACH
The e-SENSE approach organises itself into five
work areas that address:
o Scenarios, Requirements and Socio-
Economic Impact
o System Architecture and Concept
o Efficient and Light Weight Wireless Sensor
Communications
o Distributed Processing Middleware
o Test Bed Implementation and Validation
through Show Cases
The main technical approaches are detailed in the
following four subsections (omitting the area of
scenarios, requirements and socio-economic
impact).
4.1 System Architecture
The system architecture supports heterogeneous
networking, provides connectivity for a wide range
of sensor nodes, while managing mobility and
limited bandwidth and power resources. It also
includes issues related to the node architecture,
network topology, interconnection of heterogeneous
networks and node discovery. In addition, security
components have to be incorporated into the system
concept.
The overall architectural design will be based on
system components (air-interfaces, protocols) that
are already specified in various standardisation
organisations/industry alliances (e.g. 802.15.4,
ZigBee (ZigBee Alliance website)), are available in
the short term (e.g. 802.15.4a) or can be provided by
consortium partners. The goal of this task is to select
a set of common requirements leading to an efficient
architectural design of a wireless sensor system.
Sensor Node Architecture
Based on the functional requirements for wireless
sensor systems and the corresponding technical
communication requirements, the overall
architecture of the sensor nodes including hardware
and software aspects will be defined. The hardware
architecture of the node, including sensors and
actuators and their interfaces, will comprise
memory, processor, communications, RF, baseband
processing, network protocol stack, antenna, and
energy and security management blocks. The
software architecture will take into account the
numerous software elements embedded within the
nodes, such as application or communication
software.
Sensor Network Architecture
The objective of this activity is to develop the
architecture of the e-SENSE wireless sensor
network. The network comprises low-cost sensor
nodes, smart control nodes (e.g. cluster heads), as
well as access points (e.g. gateways) that provide
connectivity with the backbone core networks, the
Internet, and other mobile communication systems
including cellular, WLANs, and WPANs. It will
enable powerful connectivity between personal
devices and heterogeneous sensor networks that are
owned by the user or are part of the ubiquitous
sensor-enabled environment, or connectivity
between a potentially large numbers of sensors with
a back-bone network based application for
processing environmental data or performing asset
monitoring functions.
Distributed Processing Middleware and Service
Architecture
e-SENSE - Capturing Ambient Intelligence for Mobile Communications through Wireless Sensor Networks
343
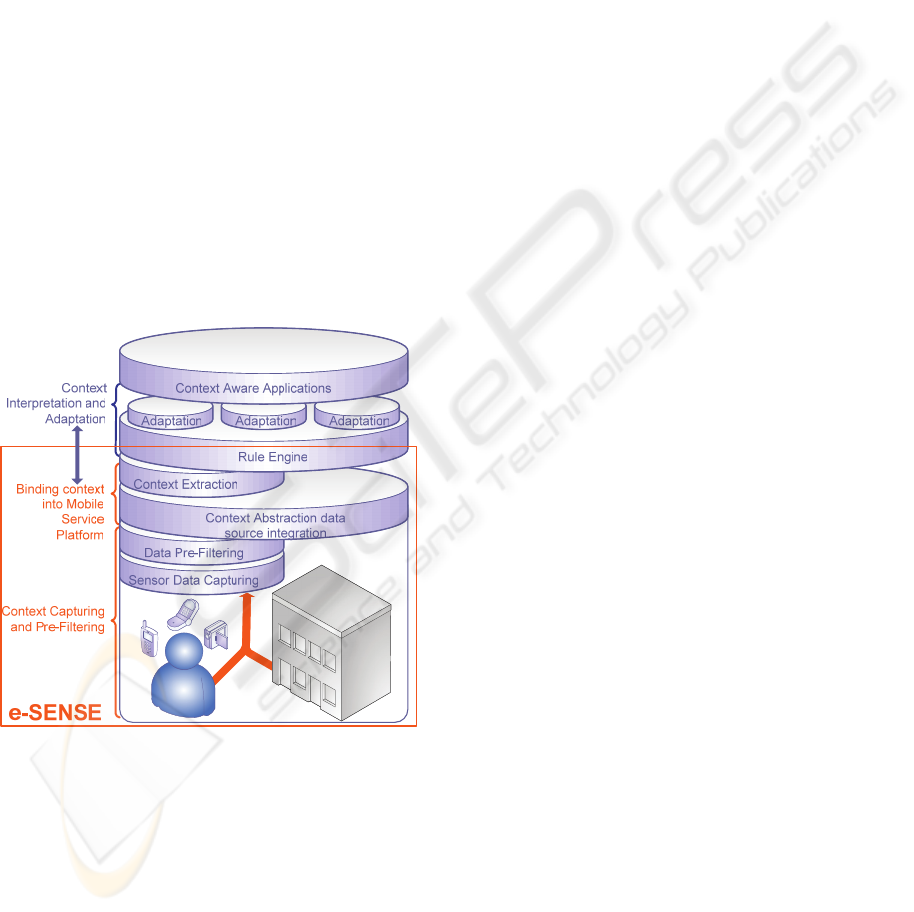
The distributed processing middleware and service
architecture combines the functionalities provided
through localisation, timing and synchronisation and
service discovery and provides means of intelligent
management of resources (e.g. outsourcing of
complex functionalities such as service discovery),
distributed signal and data processing. The interface
to the network architecture will be provided through
an intelligent data centric API. Further, the
distributed resource management configures the
reconfigurable e-SENSE communications
framework according to dynamics with respect to
tasks and resource availability.
4.2 Efficient and Light Weight
Wireless Sensor Communication
Systems
The objective is to design a set of algorithms
spanning from the physical to the transport layer in a
toolbox format and subsequently aimed at increasing
the system efficiency in terms of energy savings and
application performance through optimisation.
Figure 2: Information Processing Chain and link to
Service Platform.
The proposed solution will be based on a cross-layer
approach, where the schemes working at different
layers of the protocol stack will be sharing common
information in order to drive the system towards
globally optimal solutions. In particular, this
efficiency refers to system-wide aspects and is not
just meant to improve the quality of a single radio
link.
With these objectives in mind, the first optimisation
will be performed on RF hardware. Design
methodologies for greatly reducing the energy
efficiency of air interfaces will be studied and
validated. Novel RF sensing techniques will be
studied to, e.g., localise and estimate the distances of
devices. These novel physical layer algorithms will
enable the devices to access topology related
information that, in turn, will be exploited by any
other layer of the protocol stack according to a
cross-layer philosophy. That is, physical, medium
access control, routing and transport solutions, will
be considered in a coordinated fashion with the aim
of creating a re-configurable solution (depending on
application requirements) and aimed at increasing
system efficiency through topology awareness,
cross-layer design and cooperation among nodes.
4.3 Distributed Processing
Middleware
A defining characteristic of nodes in sensor
networks is that computing and communications
resources are a scarce and valuable commodity. This
is particularly true in scenarios with heterogeneous
sensors, as is the case in e-SENSE, where some
sensors may have almost no resources, while others
are relatively better off. Currently this leads to
centralised architectures where sensor data is
transported to a single point where a resource-rich
platform performs all the data processing. However,
the increasing deployment of sensors on the body
and in the environment offers an opportunity to
distribute much of this data processing to the sensor
nodes themselves. This has the advantage of
providing more scalable and resilient solutions,
while reducing or eliminating the need for
centralised nodes. However, for these advantages to
be realised, it is necessary to develop a number of
middleware support mechanisms to facilitate the
development of distributed sensor-based
applications.
Many of the applications that are typical for e-
SENSE are collaborative in nature: the nodes share
data among each other, transform data, thereby
essentially performing the task that is required. This
approach is essentially different from using a
traditional centralised approach, where all
transformations on and decisions based on data is
performed by a single entity, and based on a
complete set of data. The challenge involved in
employing a collaborative approach to data
transformation and decision making is twofold. One
is the co-ordination between the entities involved in
performing the task at hand is non-trivial, and will
e-SENSE
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
344
become more complex as increasing pervasiveness
of sensors increases the potential number of
collaborators. The other is caused by the fact that all
the operations on the data will have to be made with
the availability of only a subset of the data.
Besides challenges, this distributed approach to data
transformation and decision making brings
opportunities. The most important one is
performance. The costs associated with the transport
of sensor data are high, in relation to the energy
budget of most sensor nodes. Localising the data
processing and decision making task produces a
rather small set of result data and decisions and
reduces the communication needs. Instead of the raw
data, partial results will be communicated.
In scenarios with sensors distributed across an
extended geographical area, the transport of all this
data is generally too expensive, and processing all
this data in real time at a central computer might be
impossible or infeasible.
e-SENSE has categorised the functions required for
a Distributed Processing Middleware for sensor
networks into:
o Distributed services, which addresses
common services such as timing and
synchronisation, service discovery, etc.
o Distributed Data Processing, which
addresses mechanisms to enable
collaborative processing, context awareness
support, etc.
o Data Centric Resource Management, which
aims to optimise computing and
communications resources in a data-centric
network.
4.4 Testbed Implementation and
Validation through Show Cases
e-SENSE aims to implement and validate the
concepts and protocols of the sensor networks
developed within the project as well as provide a
limited set of show cases. For this purpose the
deployment of the developed concepts and protocols
on two independent testbeds is envisioned.
The first of the testbeds will be based on body
sensor network concepts, and mainly concerned with
the collection of physiological data, e.g. ECG,
breathing rate, body temperature, skin conductance
levels, voice. The second, a campus wide
environment sensor network tesbed, will mainly
focus on sensing physical data of a user space, e.g.
office space.
Key features of the sensor networking technologies
being developed and that are to be validated in this
project include:
o Throughout energy efficient
communication and operation
o Distributed data processing, and services
o Context availability (and potentially its uses
within a confined system)
o Context capturing mechanisms
To show these key features as well as the added
benefit of sensor information regarding context
awareness a limited number of concept validations
and subsequently show cases will be developed. A
particular challenge for the show cases will be the
integration of biometric sensor data with
environmental sensor data to provide context and
assist in determining user mood.
5 PROJECT DETAILS AND
CONSORTIUM
Acronym e-SENSE
Title of the
project
Capturing Ambient Intelligence for
Mobile Communications through
Wireless Sensor Networks
Proposal
number
IST-4-027227
Contract
number
027227
Starting date
End date
01/01/2006
31/12/2007
Duration 24 months
Project
Officer(s)
Paulo DE SOUSA
Logo
Website www.ist-e-sense.org
REFERENCES
The Vision Book by DG Information Society – European
Commission
e-SENSE website, http://www.ist-e-sense.org/
ZigBee Alliance website, http://www.zigbee.org/
N.B.: The content of this paper originates from the IST-e-
SENSE project which is partially funded by the EU within
FP6. The authors would like to acknowledge the work and
input from all partners. The paper is partly a reprint from
the IST-Summit 2006 in Mykonos.
e-SENSE - Capturing Ambient Intelligence for Mobile Communications through Wireless Sensor Networks
345

e-SENSE – Capturing Ambient Intelligence for Mobile
Communications through Wireless Sensor Networks – is a
R&D project within Mobile and Wireless Systems and
Platforms beyond 3G. e-SENSE will introduce new
technologies in the domain of wireless sensor networks to
provide context information for Ambient Intelligent
Systems. The project consists of 23 highly acknowledged
industrial and academic partners from 11 European
countries.
WINSYS 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS INFORMATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS
346
