
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES
AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY OPERATION CENTER
Abdoul Karim Ganame, Julien Bourgeois, Renaud Bidou, Francois Spies
LIFC, Universite de Franche Comte
4, place Tharradin, 25211 Montbeliard, France
Keywords:
IDS, SOC, Distributed intrusion detection, Network security, Graphical cartography center.
Abstract:
Detecting all kinds of intrusions efficiently requires a global view of the monitored network. We have devel-
oped a security operation center which is able to detect coordinated attacks that are not detected by traditional
IDS. In this article, we present several methods used to test the accuracy and the performance of our security
operation center. A real ISP network have been used as well as experiments in our lab.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ensuring network security requires two modules:
protection and supervision. Protection is composed
of hardware, software and a security policy that
must be followed. Even the best protection is always
vulnerable to attacks due to unknown security bugs.
Besides, the network configuration is subject to
constant changes and possibly adds security holes.
That is why the network supervision is an essential
part of the security process and is realized by security
experts.
In order to help the supervisors, Intrusion Detection
Systems (IDS) have been developed (Anderson,
1980), but these systems have several flaws. First of
all, IDSs have an insufficient rate of detection: either
too many intrusions are detected or missed (Cuppens,
2001). Furthermore, simple IDSs have no sufficient
information to detect coordinated attacks. Other types
of IDS have been created and tested like distributed
one (Neumann and Porras, 1999). Cooperation of
IDSs is still ongoing work (Yu et al., 2005).
We have proposed a completely integrated Security
Operation Center (SOC), called SOCBox
1
, in order
to overcome the limitations of IDS. The SOCBox
gathers data from a wide range of sources (IDS,
firewall, router, workstation, etc.) and therefore has
a global view of the network. Its analysis engine
can then correlate all messages generated by all the
1
This project was partially funded by a CAPM, CRFC,
government and EU programme under the STIC pole.
network components and find patterns of intrusion.
For more details about the SOCBox please see (Bidou
et al., 2003).
To measure the detection capabilities and perfor-
mance of the SOCBox, an evaluation has been
performed with Snort 2.4.3 (Snort, 2005) as a base-
line. This evaluation has taken place in two different
but complementary environments: a real Internet
Service Provider network and our laboratory.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: Sec-
tion 2 designs the global architecture of the SOCBox.
In Section 3, we focus on the SOCBox evaluation and
we provide details about the experimentation. Section
4 presents some work related to intrusion detection
system evaluations. Section 5 summarizes the main
results and presents our conclusions.
2 THE SOCBOX GLOBAL
ARCHITECTURE
The SOCBox implements the different box types de-
fined for network intrusion detection system (North-
cutt and Novak, 2002). However, beside the pure
technical aspects involved in such implementation, it
is necessary to consider the supervision of an IT in-
frastructure as a full operational project. We will thus
follow the functional steps of such a project in order
to describe both the purpose and the concepts of se-
lected parts of the architecture described in Figure 1.
48
Karim Ganame A., Bourgeois J., Bidou R. and Spies F. (2006).
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY OPERATION CENTER.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 48-55
DOI: 10.5220/0002101900480055
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Figure 1: Global architecture of the SOCBox.
2.1 Data Acquisition
Before setting up sensors and designing any correla-
tion or analysis rule, it is necessary to evaluate the
overall security level of the IT infrastructure to be su-
pervised. This will make it possible to determine if an
intrusion path may effectively lead to an intrusion into
the target system and the criticality associated with
such an intrusion attempt.
Another point to be defined is the security policy,
mostly in terms of access rights, permitted operations,
etc.
2.1.1 Vulnerability Database
The vulnerability database holds information about
security breaches and insecure behavior that would
either impact the overall security level or that could
be exploited by an attacker in order to perform an
intrusion. The database format must make it possi-
ble to include three types of vulnerability: structural
vulnerability, functional vulnerability and topology-
based vulnerability.
2.1.2 Security Policy
The next step of the supervised system inventory is an
organizational one and, more specifically, a review of
security policy aspects that would impact either event
generation and/or the reaction-reporting processes.
It is clear that the two major aspects of security
policy that need to be reviewed are authorization and
testing/audit procedures. These two aspects will pro-
vide information concerning behavior that sensors
would detect. Events generated (administrator login,
portscans, etc.) will then be marked as matching se-
curity policy criteria. Others will be analyzed as pos-
sible part of an intrusion attempt. This information is
stored in the Knowledge Base.
2.2 Data Analysis
The main operations performed to generate alerts are
the following: correlation, structural analysis, intru-
sion path analysis and behavior analysis. Correla-
tion is a stand-alone operation leading to the creation
of contexts in which further analysis will be made,
in order to check if they match the characteristics
of an intrusion attempt. Structural analysis may be
compared to an advanced pattern matching process,
used to determine if events stored within a certain
context lead to a known intrusion path or to an at-
tack tree (Schneier, 1999). Intrusion path analysis is
the next step whose output provides the intrusion at-
tempt detected with information about the exposure
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY
OPERATION CENTER
49

of the target system. Then, the behavior analysis in-
tegrates elements from the security policy in order to
determine if the intrusion attempt is allowed or not.
The purpose of such operations is to generate alerts
that do not only match the structural path of intrusion
(i.e. scan, fingerprinting, exploiting, backdooring and
cleaning), but also take care of the security policy de-
fined, as well as the criticality of target systems.
3 EVALUATION
In this section, we evaluate the intrusion detection ca-
pabilities of the SOCBox and its performance. The
SOCBox evaluation consists in running it in a real
ISP network and to verify its capacity to manage
events coming from heterogeneous platforms (routers
and access servers, hardware and software firewalls,
unix and linux servers, windows workstations, web
and mail servers, an AAA server and other ISP ap-
plications). This test has taken place for a week.
After that, some exploits were executed against the
network to check the capacity of the SOCBox to de-
tect various classes of intrusions. Then, the ability of
the SOCBox to detect distributed intrusions is evalu-
ated. After that, the clarity and the relevance of the
SOCBox reports are studied. Finally, performance
evaluation take place in comparison with Snort.
3.1 The Evaluation Network Design
The SOCBox is evaluated in a real ISP network (Fig-
ure 2) which manages more than 50000 subscribers.
This ISP network is composed by a core sub-net and
several regional sub-nets.
3.2 Detection Capabilities
3.2.1 Capabilities to Manage Heterogeneous
Platform Events
For the SOCBox be able to manage data coming from
sensors, it is necessary to install log redirection to-
wards it on sensors. To verify the SOCBox capabili-
ties to manage heterogeneous platform events, we run
it in a real situation on a ISP network for a week.
This showed multiple attempts at intrusion into the
network servers (including the SOCBox), in partic-
ular port scans, authentication attempts, brute force
attacks, sql attacks, mail relay attempts, etc. These
attacks are carried out on sensors running Solaris, Hp
ux, Linux, Windows 2000, Cisco IOS, Pix OS and ap-
plications such as Bind, Tacacs+, Apache, etc.
3.2.2 Intrusions Detection Capability
In this part, some classes of attacks are launched
against some critical sensors and the SOCBox itself.
The goal is to verify the intrusion detection capability
of the SOCBox. Some of the tests carried out are
presented below :
Flood an pollution at-
tacks
Detection Comment
Flooding the SOCBox
with Harpoon (Som-
mers, 2005) followed
by a brute force
attack (with THC-
Hydra (THC, 2006)) on
a Cisco access server
(Victim 3).
YES
The SOCBox
detects multiple
”authentication
failed” against
the access
server.
Flooding and polluting
the SOCBox with a ran-
dom MAC address gen-
erator (Macof (Song,
2001b)) followed by
a brute force attack
(with THC-Hydra) on a
router (Victim 3).
YES
The SOCBox
detects the
brute force
attack on the
access server
(multiple ”au-
thentication
failed”).
Scan and sniff Detection Comment
Scanning the network
with nmap.
YES
The SOCBox
detects the
scan (data were
collected by
the firewall
sensor).
Sniffing the network
with Dsniff (Song,
2001a).
NO
the SOCBox is
unable to detect
the attack be-
cause it can not
sniff on a net-
work.
Fragmentation, inser-
tion and camouflage
attack
Detection Comment
Fragrouter (Ptacek and
Newsham, 1998) attack
on the backbone router
(Victim 5) from a re-
mote host.
YES
The intrusion is
detected by the
SOCBox.
nmap with DECOY op-
tion (source IP camou-
flage).
YES
the SOCBox
detects the
attack.
Web attack Detection Comment
A Whisker (Puppy,
2003) attack on a web
server running Solaris
and Apache 2 on the
ISP site.
YES
The SOCBox
generates
”target iden-
tification”
alerts.
SECRYPT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SECURITY AND CRYPTOGRAPHY
50
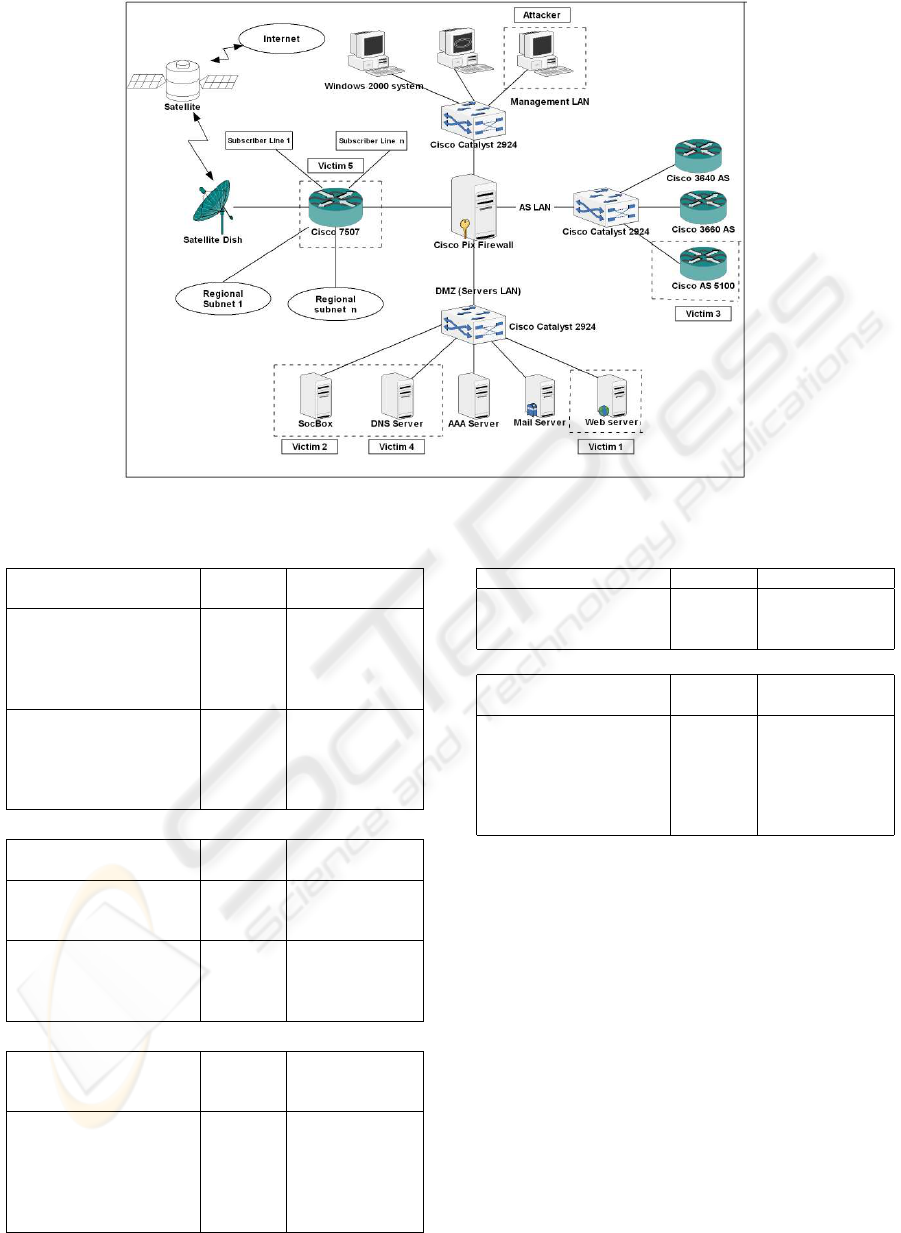
Figure 2: The ISP network used for the SOCBox evaluation.
Attack against filtered
ports and services
Detection Comment
Executing a brute force
attack with THC-Hydra
on a router (Victim
5) having ssh, telnet,
rlogin and rsh filtered.
YES
The intrusion
is ignored by
the SOCBox
because it can
never succeed.
Executing a web server
attack on the DNS
server (Victim 4, which
does not run a web
server).
YES
The intrusion
is ignored by
the SOCBox
because it can
never succeed.
Brute force and pass-
word cracking attack
Detection Comment
Brute force attack
against a router with
THC-Hydra
YES
The attack is
detected.
Attempt to crack pass-
word by John the Rip-
per (Openwall-Project,
2006)
YES
the attack is de-
tected.
Anomaly behavior in-
trusion detection evalu-
ation
Detection Comment
Attempt to connection
at 9 pm to a win-
dows 2000 server with
a username authorized
to connect only be-
tween 7 am and 8 pm.
YES
The SOCBox
generates a
”suspicious
behavior”
alarm.
Multi steps attacks Detection Comment
Lpr attack (lpr file1 (big
file); rm file1; ln -s
/etc/shadow file1)
YES
The intrusion is
detected by the
SOCBox.
Offline detection capa-
bility
Detection Comment
Replaying in the
ISP site the DARPA
2000 (Zissman, 2002)
DDOS attack data set
with TcpReplay (Aaron
and Matt, 2005).
YES
The SOCBox
generates alerts
about the
DDOS attacks.
As we can see, the SOCBox is able to detect
various classes of intrusions, suspicious behavior
(defined by the security manager) and it can ignore
events which generate useless alerts (attacks against
non-vulnerable systems). It also appears that the
more sensors send their logs to the SOCBox, the
better its detection capability is. Online exploits
executions and the replay of DARPA 2000 data sets
show that the SOCBox can detect online and offline
intrusions.
In summary, we can say that the SOCBox has proved
its efficiency in detecting intrusions and in presenting
the network security status clearly by using graphical
representations.
3.2.3 Detection of Distributed Intrusions
The evaluation of the aptitude of the SOCBox for de-
tecting distributed intrusions is described on Figure 3.
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY
OPERATION CENTER
51

The scenario of this attack is the following:
An attacker wants to hack a host (Victim) located on
the ISP core sub-net and hosting information about
subscribers. His idea is to gain access to Victim by
brute force attack and to steal data about subscribers.
Victim is secured and can be accessed only from spe-
cial hosts in the Management LAN and in some re-
gional sub-nets (for maintenance purpose). The at-
tacker tries to compromise Victim and unfortunately
for him, all his actions are refused. After further
thought, he thinks that it would be easier for him to
try to hack Victim from hosts located on the ISP net-
work. He uses social engineering technique to know
the name of the administrators of the ISP core and re-
gional sub-nets; this can help to improve the username
database of the brute forte attack tool. After several
attempts at intrusion, he compromises three less se-
cured hosts on the ISP network (one in the Manage-
ment LAN and two in regional sub-nets). From these
hosts, he initiates the attack, composed of the follow-
ing actions:
• From Attacker 1 located in a regional sub-net, he
launches a quick scan (with nmap) to detect opened
ports on Victim. He sees that ssh and mysql are
opened on Victim.
• From Attacker 2 located in the ISP core sub-net, he
executes an OS Fingerprinting with Xprobe2. He
see that Victim runs Solaris 8.
• From Attacker 3 located in another regional sub-
net, he launches a brute force attack (with THC-
Hydra) against Victim to gain access to the mysql
database.
This test shows that the SOCBox can gather events
and alerts coming from different sensors (Cisco Pix
Firewall sensor detects the quick scan, Snort sensor
detects the OS Fingerprinting, and logs of Victim per-
mit to detect the brute force attack). Because these
events have the same target and they take place ap-
proximatively in the same time, the SOCBox matches
them with the same context and generates a suspicious
behavior alert. An alarm is also sent to the security
manager for advanced investigation on Attacker 1, At-
tacker 2 and Attacker 3. Investigation on these hosts
shows that Attacker acceded them. Then, the secu-
rity manager concludes that Victim is attacked by At-
tacker.
Without correlation of alerts, it would be impossible
to detect this attack. The SOCBox is thus able to
correlate alerts coming from divers sources (firewalls,
IDS, hosts, etc.) to generate a single alert.
3.3 Performance Evaluation
At this stage, we check the aptitude of the SOCBox
to handle high bandwidth traffic and its ability to de-
tect intrusions when a massive attack occurs. We
use D-ITG (Avallone et al., 2004) and IP-Traffic (Zti-
Telecom, 2005) to generate traffic in this test. The
same tests are apply to Snort for comparison pur-
pose. In spite of the fact that Snort isn’t a Soc and the
SOCBox isn’t an NIDS (the SOCBox is much more
than an NIDS because it has a global view of a net-
work security), the comparison between Snort and the
SOCBox is justified in this test: Both monitor the se-
curity of a unique host and they generate alerts only
about attacks on this host.
3.3.1 Evaluation of the SOCBox Maximum
Processing Capacity
A victim host (which sends its log to the SOCBox via
syslog) is flooded and attacked (Figure 7(a)). Then,
we observe the SOCBox behavior. The SOCBox
host characteristics are: Pentium III, 450 MHz,
256MB of RAM. The same tests are carried out
with Snort installed on a host which have the same
characteristics (Figure 7(b)). The tests are summed
up in the following tables:
Action The SOCBox
reaction
Snort reaction
Launching a
Whisker attack on
a victim running
Apache.
The SOCBox
generates
”Target iden-
tification”
alerts.
Snort
generates
”WEB-MISC
whisker”
alerts.
Flooding the
SOCBox and
Snort with 10
6
packets of 10
bytes each sec-
ond for 15mins
followed by a
Whisker attack.
The SOCBox
runs slowly
and it detects
the Whisker
attack (the
SOCBox host
uses more than
245 MB of
RAM).
Snort detects
the Whisker
attack and
it runs
too slowly
(around 250
MB of RAM
is used).
Flooding the
SOCBox and
Snort with
1, 2 ∗ 10
6
pack-
ets of 10 bytes
each second for
15mins followed
by a Whisker
attack.
The SOCBox
detects the
Whisker at-
tack (around
250MB of
RAM is
used by the
SOCBox
host). It runs
slowly.
Snort host has
not enough
memory to
continue (all
the memory is
used up).
Flooding the
SOCBox and
Snort with
1, 4 ∗ 10
6
pack-
ets of 10 bytes
each second for
15mins followed
by a Whisker
attack.
The SOCBox
host has not
enough mem-
ory.
SECRYPT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SECURITY AND CRYPTOGRAPHY
52
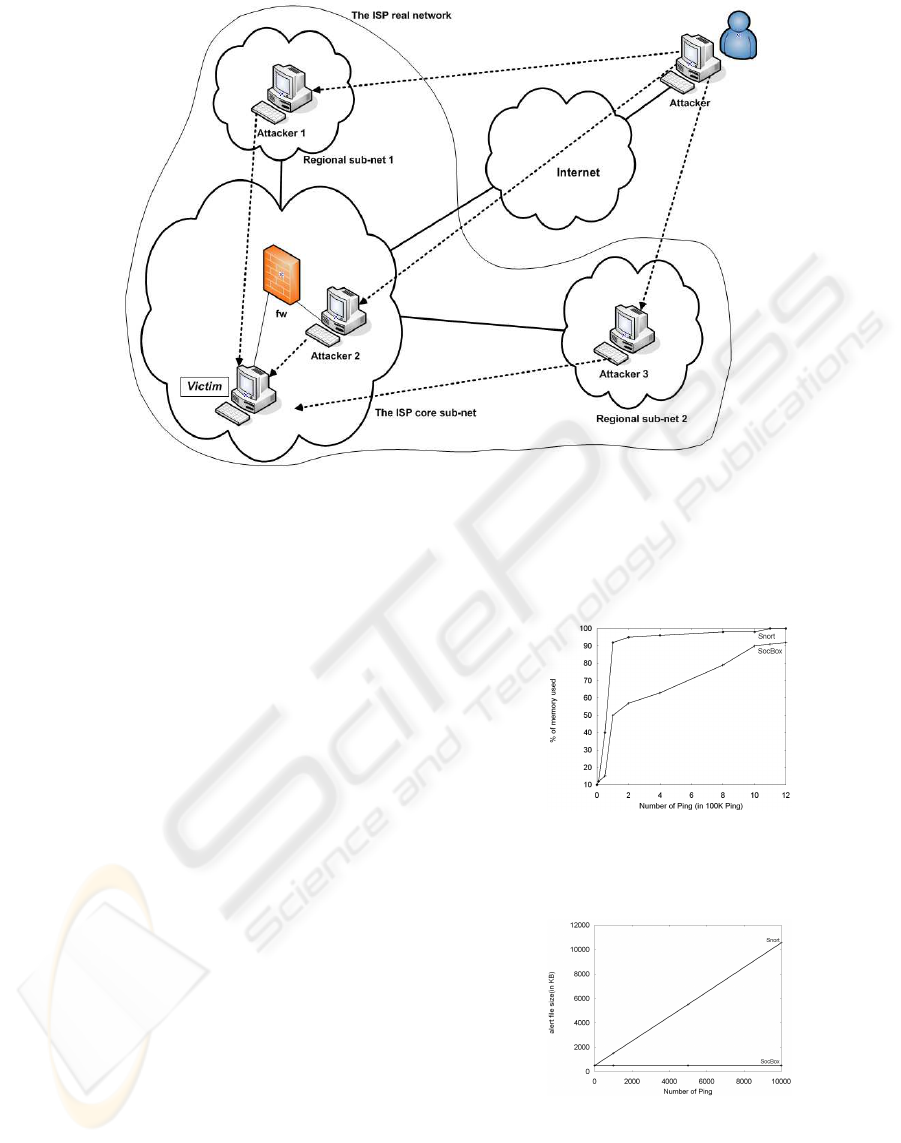
Figure 3: Evaluation of the SOCBox aptitude for detecting distributed intrusions.
After that, ping with large packet flood is carried
out against both the SOCBox and Snort, followed by
a Whisker attack against the victim host. The goal
is to observe the behavior of the SOCBox and Snort
under a strong attack. The victim host characteristics
are: Pentium III, 450 MHz, 256 MB of RAM.
• Action: Sending 20 millions (2 ∗ 10
7
) Ping with
50000 bytes each one (time between 2 Pings = 0)
to the Victim host (via IP-Traffic), followed by a
Whisker attack.
• The SOCBox behavior: Up to 1, 8 ∗ 10
6
Ping, the
SOCBox is able to detect the Whisker attack. At
1, 9 ∗ 10
6
Ping the SOCBox host is broken down
and is unable to detect the Whisker attack.
• Snort behavior: Snort generates too many alerts
about the Ping (10
5
Ping generate 100576 alerts,
including 50283 Large ICMP packets detected). At
10
6
Ping, Snort generates 4GB of dumped data and
is unable to generate alerts.
3.3.2 Comments
This test shows that the SOCBox is able to detect in-
trusions under a high traffic or under a massive at-
tack. Under a massive attack the SOCBox uses less
resources than Snort and has better performance. It
also generates far fewer alerts than Snort and is able
to compact similar alerts to generate one only. More-
over, the SOCBox only records events that match se-
curity rules defined by the security manager.
The SOCBox and Snort performance, memory usage
and hard disk usage during the Ping test are shown on
Figures 4, 5 and 6.
Figure 4: Snort and the SOCBox memory usage during Ping
test.
Figure 5: Snort and SOCBox alert file (in KB) during the
Ping test.
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY
OPERATION CENTER
53

0
20
40
60
80
100
120
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Number of generated alarms
Number of Ping (in 100K Ping)
(a) SOCBox Ping test result
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
0 2 4 6 8 10
Number of generated alarms (in 100K alarms)
Number of Ping (in 100K Ping)
(b) Snort Ping test result
Figure 6: The SOCBox and Snort behavior during the Ping test.
(a) The SOCBox performance evaluation (b) Snort performance evaluation
Figure 7: The SOCBox and Snort performance evaluation networks.
4 RELATED WORK
Various papers coming from both academy and indus-
try laboratories and related to intrusion detection sys-
tem evaluation have been published. Some industrial
evaluations are biased because the tests are not always
done in an objective way; the behavior of IDSs are
adapted to the data sets and some tests are carried out
without baseline. In this section, we will present some
well-known intrusion detection systems evaluations,
coming primarily from academy laboratories.
4.1 Mit Lincoln Labs Evaluation
Sponsored by DARPA in 2000, this evaluation (Lipp-
man et al., 2000) is one of the best-known intrusion
detection tests. This evaluation uses a testbed which
generates live background traffic containing hundreds
of users and thousands of hosts. More than 200 in-
stances of 58 attack types are embedded in 7 weeks’
training data and 2 weeks’ test data. The goal is
to evaluate the efficiency for more than 18 research
IDSs to detect unknown attacks without first train-
ing on instances of these attacks. Automated at-
tacks are launched against a router and hosts running
Unix/Linux and Windows NT. Attacks include Dos,
user to root, probe, remote to local attacks. The draw-
back of this evaluation is the lack of baseline.
4.2 The UCAD Evaluation
In this evaluation (Puketza et al., 1997), automated
attacks using TELNET, FTP and RLOGIN sessions
were executed to evaluate a NIDS called Network
Security Monitor (NSM) (Heberlein et al., 1990).
Scripts of normal and intrusion sessions were exe-
cuted to verify the ability of the NSM to distinguish
between suspicious behavior and normal one. Its abil-
ity to handle high bandwidth traffic was also evalu-
ated. This evaluation has shown that NSM was unable
to detect intrusions under high CPU load. A similar
IDS evaluation (Debar et al., 1998) was performed by
IBM Zurich in 1998 to improve IDS systems designed
to detect intrusions into FTP servers.
4.3 The NSS Group Evaluation
In this evaluation (NSS-Group, 2001), 15 commercial
IDS and Snort were compared using 18 or 66 com-
monly available exploits such as Dos, DDos, ports
scan, Trojans, FTP, HTTP or IDS evasion technique
attacks. These systems were evaluated according to
the following criteria: their ease of installation and
configuration, their architecture, the type of reports
and analysis provided. Only attacks reported in ”as
straightforward and clear a manner as possible” were
supposed to be detected. In this evaluation, attack de-
tection rates are difficult to compare with the other
IDS evaluations because the simple detection of an
SECRYPT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SECURITY AND CRYPTOGRAPHY
54

intrusion is not sufficient; each generated alert must
be clearly labeled to be taken into account.
5 CONCLUSION
Intrusions are clearly taking place and thus there is a
need for operational supervision systems today. Ex-
perience shows that a pragmatic approach needs to be
taken in order to implement a professional SOC that
can provide reliable results. The SOCBox is our re-
sponse to these new threats.
During its evaluation, the SOCBox proved that it
is a powerful tool giving the cartography of network
security in a graphical and ergonomic way. It gen-
erates clear reports including graphs for helping the
security managers better and has an interface for se-
curity alert consulting. It also has the ability to com-
pact similar alerts to facilitate the legibility of the gen-
erated reports; this can be a great advantage during a
troubleshooting operation for example. Moreover, the
SOCBox does not need a powerful host: its detection
performance is closely linked to the capacity of the
sensors to send it their logs.
REFERENCES
Aaron, T. and Matt, B. (2005). Tcpreplay tool (2.3).
http://tcpreplay.sourceforge.net.
Anderson, J. (1980). Computer security threat monitoring
and surveillance. Technical report.
Avallone, S., Guadagno, S., Emma, D., Pescape, A., and
Ventre, G. (2004). D-itg distributed internet traffic
generator.
Bidou, R., Bourgeois, J., and Spies, F. (2003). Towards
a global security architecture for intrusion detection
and reaction management. In 4th Int. workshop on
information security applications, pages 111–123.
Cuppens, F. (2001). Managing alerts in a multi-intrusion
detection environment. In 17th Annual Computer Se-
curity Applications Conference, New-Orleans.
Debar, H., Morin, D., and Wespi, A. (1998). Reference au-
dit information generation for intrusion detection sys-
tems. In Proceedings of IFIPSEC 98, pages 405–417.
Heberlein, T., Dias, V., Levitt, K., Mukherjee, B., Wood,
J., and Wolber, D. (1990). A network security moni-
tor. In IEEE Symposium on Research in Security and
Privacy, pages 296–304.
Lippman, R., Haines, J. W., Fried, D. J., Korba, J., and Ku-
mar, D. (2000). Analysis and results of the 1999 darpa
off-line intrusion detection evaluation. In 3th sympo-
sium on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection 2000,
pages 162–182.
Neumann, P. G. and Porras, P. A. (1999). Experience with
EMERALD to date. In First USENIX Workshop on
Intrusion Detection and Network Monitoring, pages
73–80, Santa Clara, California.
Northcutt, S. and Novak, J. (2002). Network Intrusion De-
tection. ISBN: 0-73571-265-4. New Riders, third edi-
tion edition. September.
NSS-Group (2001). Intrusion detection systems group tests
(edition 2). http://www.nss.co.uk/ids.
Openwall-Project (2006). John the ripper password cracker
(1.7). http://www.openwall.com/john/.
Ptacek, T. H. and Newsham, T. (1998). Insertion, evasion,
and denial of service: Eluding network intrusion de-
tection. Technical report, Secure Networks, Inc.
Puketza, N., Chung, M., Olsson, R., and Mukherjee, B.
(1997). A software platform for testing intrusion de-
tection systems. IEEE Software, 14(5):43–51.
Puppy, R. F. (2003). A look at whisker’s anti-ids tactics.
http://www.wiretrip.net/rfp/txt/whiskerids.html.
Schneier, B. (1999). Attacks trees. Dr. Dobb.
Snort (2005). Snort (2.4.3) lightweight intrusion detection
for networks http://www.snort.org/dl.
Sommers, J. (2005). Harpoon: A flow-level traffic generator
http://www.cs.wisc.edu/ jsommers/harpoon/.
Song, D. (2001a). Dsniff 2.3: A collection of
tools for network auditing and penetration testing
http://www.monkey.org/ dugsong/dsniff/.
Song, D. (2001b). Macof - flood a
switched lan with random mac addresses
http://www.groar.org/trad/dsniff/dsniff-2.3/english-
txt/macof.8.txt.
THC (2006). The hacker’s choice, thc releases, thc-hydra
v5.2. http://www.thc.org/releases.php.
Yu, J., Reddy, Y. V., Selliah, S., Reddy, S., Bharadwaj,
V., and Kankanahalli, S. (2005). TRINETR: An ar-
chitecture for collaborative intrusion detection and
knowledge-based alert evaluation. Advanced Engi-
neering Informatics, 19(2):93–101.
Zissman, M. (2002). Darpa intrusion detection evaluation
data sets. http://www.ll.mit.edu/ist/ideval/.
Zti-Telecom (2005). Ip traffic (2.3), a test and mesure tool.
http://www.zti-telecom.com/fr/pages/iptraffic-test-
measure.htm.
EVALUATION OF THE INTRUSION DETECTION CAPABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE OF A SECURITY
OPERATION CENTER
55
