
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE
SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO
Atsushi Ohnishi
Department of Computer Science, Ritsumeikan University, Shiga 525-8577, Japan
Keywords: Requirements elicitation, scenario analysis, alternative scenario.
Abstract: A generation method of alternative scenarios using a normal scenario written with the scenario language
SLAF is proposed. This method includes (1) generation of alternative plans and (2) generation of alternative
scenario by a user’s selection of these plans. Our method enables to lessen the omission of the possible
alternative scenarios in the early stages of development and contributes to improve the correctness and
effectiveness of the software development.
1 INTRODUCTION
Scenarios are important in software development,
particularly in requirements engineering, by
providing concrete system description
(Weidenhaupt et al., 1998). Especially, scenarios are
useful in defining system behaviors by system
developers and validating the requirements by
customers. In many cases, scenarios are foundation
for system development. Incorrect scenarios will
have a negative impact on the overall system
development process. However scenarios are
informal and it is difficult to verify the correctness
of scenarios. The errors in incorrect scenarios may
include:
1. Vague representations,
2. Lack of necessary events,
3. Extra events,
4. Wrong sequence among events.
The author has developed a scenario language
for describing scenarios in which simple action
traces are embellished to include typed frames
based on a simple case grammar of actions and for
describing the sequence among events (Ohnishi et
al. 2001, Ohnishi et al. 2002). Since this language is
a controlled language, the vagueness of the scenario
written with this language can be reduced.
Furthermore, the scenario with this language can be
transformed into internal representation. In the
transformation, both the lack of cases and the illegal
usage of noun types can be detected, and concrete
words will be assigned to pronouns and omitted
indispensable cases (Ohnishi et al., 1996, Ohnishi et
al., 2002). As a result, the scenario with this
language can avoid the errors typed 1 previously
mentioned.
Scenarios can be classified into (1) normal
scenario, (2) alternative scenario, and (3)
exceptional scenario. A normal scenario represents
the normal and typical behavior of the target system,
while an alternative scenario represents normal but
untypical behavior of the system and an exceptional
scenario represents abnormal behavior of the system.
In order to grasp whole behaviors of the system, not
only normal scenarios, but also alternative/
exceptional scenarios should be specified. However
it is difficult to hit upon alternative scenarios and
exceptional scenarios, whereas it is easy to think of
normal scenarios.
This paper focuses on how to generate
alternative scenarios from a normal scenario. We
adopt our scenario language for writing scenarios,
because our scenario language is a control language
and it is easy to analysis scenarios with our scenario
language.
The rest of this paper is organized into 5 sections.
Section 2 introduces the outline of the scenario
language, and gives a scenario example. Section 3
describes a generation method of alternative
scenarios from a normal scenario with examples. In
section 4, evaluation of the method is briefly
described. In section 5, a discussion of related
works is presented. Finally, in section 6 we provide
some concluding remarks and point out
our future
110
Ohnishi A. (2006).
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 110-117
DOI: 10.5220/0002442801100117
Copyright
c
SciTePress
works.
2 SCENARIO LANGUAGE
2.1 Outline
The scenario language has already been introduced
(Ohnishi et al., 2001, Ohnishi et al., 2002, Zhang et
al., 2004). In this paper, a brief description of this
language will be given for convenience.
A scenario can be regarded as a sequence of
events. Events are behaviors employed by users or
the system for accomplishing their goals. We
assume that each event has just one verb, and that
each verb has its own case structure (Fillmore,
1968). The scenario language has been developed
based on this concept. Verbs and their own case
structures depend on problem domains, but the roles
of cases are independent of problem domains. The
roles include agent, object, recipient, instrument,
source, etc. (Fillmore, 1968, Ohnishi, 1996).
We provide requirements frames (Ohnishi, 1996)
in which verbs and their own case structures are
specified. The requirements frame depends on
problem domains. Each action has its case structure,
and each event can be automatically transformed
into internal representation based on the frame. In
the transformation, concrete words will be assigned
to pronouns and omitted indispensable cases. With
Requirements Frame, we can detect both the lack of
cases and the illegal usage of noun types (Ohnishi,
1996).
We assume four kinds of time sequences among
events: 1) sequence, 2) selection, 3) iteration, and 4)
parallelism. Actually most events are sequential
events.
Our scenario language defines the semantic of
verbs with their case structure. For example, data
flow verb has source, goal, agent, and instrument
cases. Since such case structure can define the
abstraction level, scenario with our scenario
language becomes the almost same level of the
abstraction.
2.2 Scenario Example
We consider a scenario of train ticket reservation of
a railway company. Figure 1 shows a scenario of
customer’s purchasing a ticket of express train at a
service center of a railway company. This scenario
is written with our scenario language based on a
video that records behaviors of both a user and a
staff at a service center of a railway company
(Railway Information System, 2001).
A title of the scenario is given at the first line of
the scenario in Fig.1. Viewpoints of the scenario are
specified at the third line. In this paper, viewpoints
mean active objects such as human, system
appearing in the scenario. There exist two
viewpoints, namely staff, and customer. The order
of the specified viewpoints means the priority. In
this example, the first prior object is staff, and the
second is customer. In such a case, the prior object
becomes the subject of an event
.
In this scenario, almost all events are sequential,
except for just one selective event (the 9
th
event).
Selection can be expressed with if-then syntax like
program languages. Actually, event number is for
reader’s convenience and not necessary.
[Title: A customer purchases a train ticket of
reservation seat]
[Viewpoints: Staff, customer]
1. A staff asks a customer about leaving station and
destination as customer’s request.
2. He sends the customer’s request to reservation
center via private line.
3. He retrieves available trains with the request.
4. He informs the customer of a list of available
trains.
5. The customer selects a train that he/she will get.
6. The staff retrieves available seats of the train.
7. He shows a list of available seats of the train.
8. The customer selects a seat of the train.
9. If (there exists a seat selected by the customer)
then the staff reserves the seat with the terminal.
10. He gets a permission to issue a ticket of the seat
from the center.
11. The customer paid for the ticket by cash.
12. He gives the ticket to the customer.
Figure 1: Scenario example.
2.3 Analysis of Events
Each of events is transformed into internal
representation. For example, the 2
nd
event “He
sends the customer’s request to reservation center
via private line” can be transformed into internal
representation shown in Table 1.
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO
111

Table 1: Internal representation of the 2
nd
event.
Concept: Data Flow
source goal object instrument
Staff Reservation
center
Customer
’s request
Private line
In this event, the verb “send” corresponds to the
concept “data flow.” The data flow concept has its
own case structure with four cases, namely to say,
source case, goal case, object case and instrument
case. Sender corresponds to the source case and
receiver corresponds to the goal case. Data
transferred from source case to goal case
corresponds to the object case. Device for sending
data corresponds to the instrument case. In this
event, “customer’s request” corresponds to the
object case. Since the pronoun “he” in the event
should be “staff,” concrete noun “staff” is assigned
in the source case.
The internal representation is independent of
surface representation of an event. Suppose other
representations of event, “Customer’s request is
sent from staff to reservation center via private line”
and “reservation center receives customer’s request
from staff via private line.” These events are
syntactically different but semantically same as the
2
nd
event. These two events can be transformed into
the same internal representations.
The advantages of SLAF as a scenario language
are as follows.
1) Since SLAF is a control language, it is
relatively easy to analyze a scenario written
with SLAF.
2) Since SLAF is a control language, verbs
and nouns are restricted. This means that
the abstraction level of scenario with SLAF
can be controlled.
3) Although expressions of events are
different, same meaning events are
transformed into same internal expressions.
4) It is easy to transform a scenario written
with SLAF into standard documents such
as sequence diagrams of UML.
3 GENERATION OF
ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS
When a customer buys a ticket, there exist several
alternatives of payment, such as pay with cash,
credit card, personal check, banking card, money
order, and so on. When data is transmitted, there
exist several alternatives, such as sending via e-mail,
postal mail, FAX, FTP, and so on. These
alternatives arise from the diversity of methods. As
for the first case, the diversity of payment method
causes the alternatives. As for the second case, the
diversity of sending method causes the alternatives.
These alternatives appear in a certain case of the
case structure of a concept. For example, the
diversity of sending method appears in the
instrument case of the cases structure of data flow
concept. In case of payment with cash, there exist
alternatives (1) credit card, (2) personal check, (3)
banking card, and (4) money order.
We provide users with such alternatives using a
database whose contents are (a) pairs of an ordinary
method and its alternative methods and (b) event
sequences for the alternative methods as scenario
templates. We call this database “alternative
scenario DB.”
Users first specify a normal scenario, then
possible alternatives are provided to the users. By
users’ selecting alternatives, alternative event
sequence will be generated. By replacing the
original event sequence with the alternative event
sequence, an alternative scenario will be
automatically generated.
3.1 Generation Method of Alternative
Scenarios
Our generation method of alternative scenarios is
shown as follows. We assume that a normal
scenario is written with our scenario language in
advance as shown in step 0.
Step 0: Scenario writer describes a normal scenario
with our scenario language.
Step 1: The normal scenario is transformed into
internal representation. In this step each events is
transformed into internal representation based on
requirements frame. When the concept of the
internal representation is data flow and there exists
a noun corresponding to the instrument case, we
find alternatives for the instrument case. For
example, when the concept of the internal
representation is payment, we can find alternatives
for the payment methods.
Step 2: Alternative methods are automatically
generated and provided to the scenario writer.
He/she selects appropriate alternatives. The
describer can select one or more alternatives, or no
alternatives.
Step 3: Scenario templates can be derived from
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
112
alternative scenario DB in accordance with the
selected alternatives. There exist several lacks of
cases in the scenario template, but the lacked cases
are automatically compensated using the internal
representation of the event. Details of compensation
are in (Ohnishi, 1996).
Step 4: Alternative scenarios are provided to the
scenario writer. He/she can revise or customize
them.
3.2 Example of Generating Alternative
Scenario
The above 4 steps are illustrated with the example
shown in Fig. 1. In the step1, two events are
selected as alternative events. The 2
nd
event, “ He
sends the customer’s request to reservation center
via private line” can be transformed into internal
representation shown in table 1. Since the concept
of the event is data flow, and its instrument case is
“private line,” so there exist several alternative
events. The 11
th
event, “The customer paid for the
ticket by cash.” Can be transformed into an internal
representation shown as Table 2. There is no noun
for the goal case in this event, but analyzer
compensates a noun, “staff” as the goal case object.
Table 2: Internal representation of the 11
th
event.
Concept: Payment
agent object instrument goal
customer ticket cash staff
Since the concept of the event is payment, there
exist several alternatives for this event.
In the step 2, alternatives are shown with
alternative scenario DB. In case of sending data via
private line, there exist alternatives, such as
(1) public line,
(2) FAX,
(3) e-mail,
(4) postal mail, and
(5) FTP.
A describer can
select one or more alternatives. If
he/she cannot find any appropriate alternatives,
he/she may not select any alternatives.
Here, we assume that no alternatives are selected.
In case of payment with cash, there exist
alternatives, such as
(1) credit card,
(2) personal check,
(3) banking card, and
(4) money order.
Here, we assume credit card is selected as
alternative payment.
In the step 3, a scenario template for the payment
with credit card is derived from the alternative
scenario DB. This template is shown in Figure 2.
[Title: Payment with a credit card]
[Viewpoints: (Agent), (Goal)]
1. (Agent) passes a credit card to (Goal).
2. (Goal) enters the credit card and amount of
payment with a terminal.
3. (Goal) confirms that the card is authenticated.
4. (Goal) gets receipt and bill via terminal.
5. (Agent) gets the receipt and bill from (Goal).
6. (Agent) autographs the bill.
7. (Agent) passes the bill to (Goal)
8. (Goal) passes both the card and the receipt to
(Agent).
Figure 2: Scenario template of the payment with credit
card.
In this template, the goal case and the agent case
are not specified. Since the goal case of the 11
th
event and the agent case of the event are “staff” and
“customer” respectively, both the goal case and the
agent case in the template will be “staff” and
“customer” respectively. By compensating these
two nouns, the scenario becomes as follows.
[Title: Payment with a credit card]
[Viewpoints: customer, staff]
1. Customer passes a credit card to staff.
2. Staff enters the credit card and amount of
payment with a terminal.
3. Staff confirms that the card is authenticated.
4. Staff gets the receipt and bill via terminal.
5. Customer gets the receipt and bill from staff.
6. Customer autographs the bill.
7. Customer passes the bill to staff.
8. Staff passes both the card and the receipt to
customer.
Figure 3: Compensated scenario template of the payment
with credit card.
In the step 4, alternative scenario shown in Figure
4 is provided to the scenario writer. The 11
th
event
of normal scenario in Figure 1 is expanded with the
compensated scenario template of Figure 3.
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO
113

[Title: A customer purchases a train ticket of
reservation seat]
[Viewpoints: Staff, customer]
1. A staff asks a customer about leaving station
and destination as customer’s request.
2. He sends the customer’s request to reservation
center via private line.
3. He retrieves available trains with the request.
4. He informs the customer of a list of available
trains.
5. The customer selects a train that he/she will get.
6. The staff retrieves available seats of the train.
7. He shows a list of available seats of the train.
8. The customer selects a seat of the train.
9. If (there exists a seat selected by the customer)
then the staff reserves the seat with the terminal.
10. He gets a permission to issue a ticket of the
seat from the center.
11. Customer passes a credit card to staff.
12. Staff enters the credit card and amount of
payment with a terminal.
13. Staff confirms that the card is authenticated.
14. Staff gets the receipt and bill via terminal.
15. Customer gets the receipt and bill from staff.
16. Customer autographs the bill.
17. Customer passes the bill to staff.
18. Staff passes both the card and the receipt to
customer.
19. He gives the ticket to the customer
Figure 4: Alternative scenario for the normal scenario in
Figure 1.
Last, the scenario writer checks the alternative
scenario and revises it if needed.
3.3 Supporting Tool for Making
Alternative Scenario
We have developed a supporting tool based on our
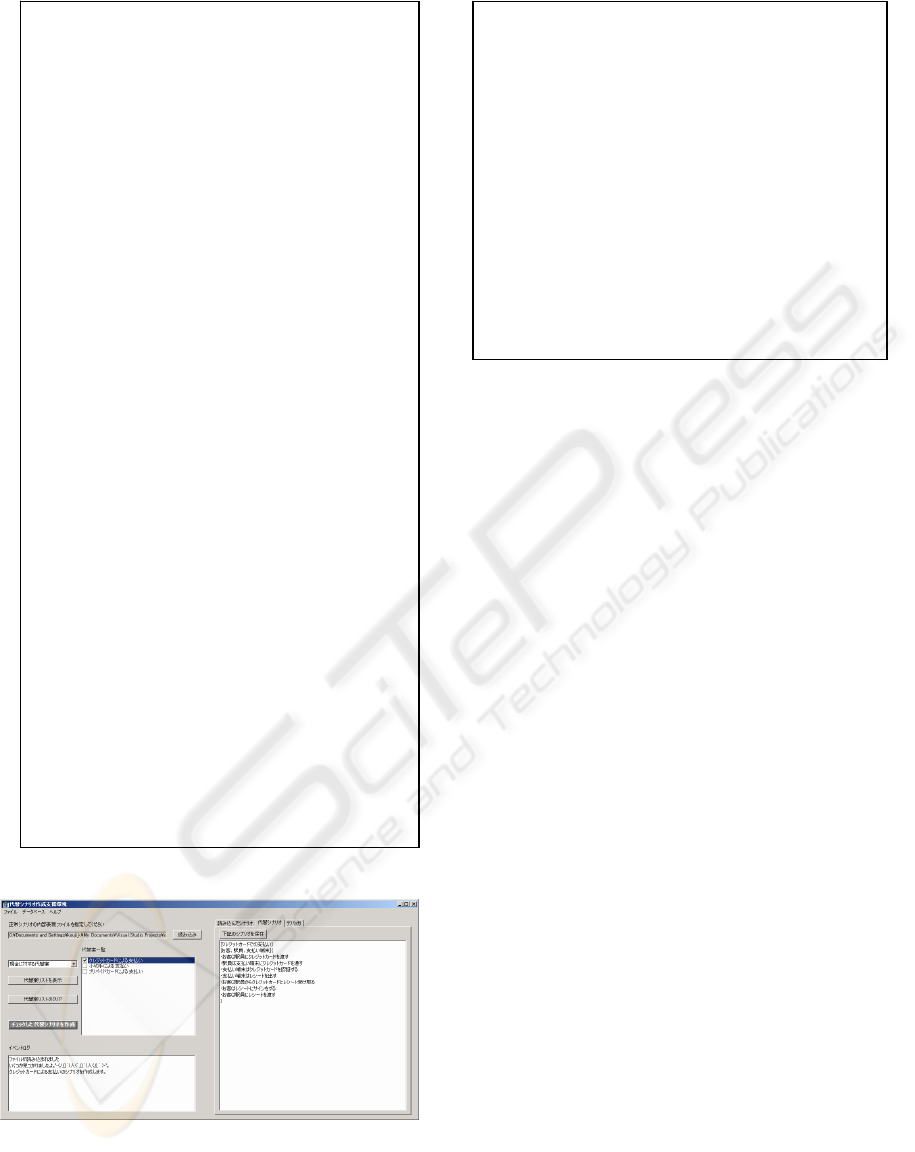
method with VisulaBasic.NET 2003. Figure 5(a)
shows display image of the tool. The left side of
Figure 5(a) shows alternatives of payment methods.
Figure 5(b) shows the list of alternatives of payment
in English. The right side of Figure 5(a) shows a
normal scenario. Figure 5(c) shows a normal
scenario in English. Figure 5(d) shows a part of
normal scenario with XML format.
We use a transformer from scenario with SLAF
to scenario with XML format. Our system accepts a
scenario with XML format.
Figure 5(a): Original normal scenario and list of
alternatives.
Payment with credit card
Payment with check
Payment with prepaid card
Figure 5(b): List of alternative methods of the payment.
1. A customer sends his order to a staff.
2. The staff sends the order to system.
3. The system displays available seats of the
train.
4. The staff selects a seat and enters the seat id
to the system.
5. A ticket of the seat is issued.
6. The staff notifies the customer of the total
amount fee.
7. The customer pays the fee with cash.
8. The staff hands out the ticket of the reserved
seat.
Figure 5(c): original normal scenario.
In the left side of Figure 6 (a), user selected the
first payment method. This method is payment
with credit card. The right side of Figure 6(a)
shows an alternative event sequence generated by
compensating scenario template with the
payment method using credit card.
Figure 6(b) shows the alternative event
sequence in English. Since Figure 3 shows
alternative events for payment with credit card,
Figure 3 and Figure 6(b) are mostly same. The
difference between them is system’s viewpoint is
included in the scenario or not. In Figure 6(b), 3
rd
and 4
th
events that state system’s behavior are
included. By replacing the 7
th
event of Figure
5(c) with the events in Figure 6(b), an alternative
scenario can be automatically generated.
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
114
<title>Reservation of seats </title>
<view>customer staff system </view>
<statement>
<event id="0">
<verb crd="DFLOW" >send </verb>
<object>
<noun type="DATA">order</noun>
</object>
<source>
<noun type="HUMAN"> customer</noun>
</source>
<goal>
<noun type="HUMAN"> staff</noun>
</goal>
</event>
<event id="1">
<verb crd="DFLOW" >send</verb>
<object>
<noun type="DATA">order</noun>
</object>
<source>
<noun type="HUMAN"> staff</noun>
</source>
<goal>
<noun type="FUNC">system</noun>
</goal>
</event>
<event id="2">
<verb crd="
DISPLAY">display</verb>
<object>
<noun type="DATA">available seats of the
train</noun>
</object>
<source>
<noun type="HUMAN">system</noun>
</source>
<goal>
<noun type="DEV">terminal</noun>
</goal>
</event>
Figure 5(d): A part of original scenario in XML.
Figure 6(a): Compensated scenario template of the
selected payment method.
[Payment with credit card]
[customer, staff, system]
1. The customer passes his credit card to the
staff.
2. The staff enters the credit card and amount of
payment with a terminal.
3. The system authenticates the card.
4. The system issues a bill and receipt.
5. The staff gets the receipt and bill via terminal.
6. The customer gets the receipt and bill from
the staff.
7. The customer autographs the bill.
8. The customer passes the bill to staff.
9. The staff passes both the card and the receipt
to customer.
Figure 6(b): Alternative events for payment with credit
card.
4 EVALUATION
In order to evaluate our method, the following
experiment was performed. We adopted a scenario
based software project of developing a bill
management system of an insurance company. In
this project, analysts wrote not only a normal
scenario for each projects, but also other scenarios,
that is, alternative scenarios and exceptional
scenarios. We applied our method to the normal
scenarios and got alternative scenarios. Then we
compared alternative scenarios that developed at the
projects with automatically generated scenarios.
Since original normal scenarios are written with
natural language, we rewrote the normal scenarios
with our scenario language prior to the experiments.
In this project, one normal scenario, 4 alternative
scenarios, and 5 exceptional scenarios are specified.
By applying our method of generating alternative
scenarios, we could get 5 alternative scenarios. By
comparing original alternative scenarios with
generated scenarios, we found that 3 scenarios are
same respectively, 2 scenarios are newly generated
and effective, and 1 scenario is not generated. Table
6 shows the above result. The not generated
scenario is regarded as an alternative scenario at the
project, but it should be categorized into a normal
scenario, because this scenario specifies normal
behavior of the bill management system.
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO
115

Table 6: Result of alternative scenarios of the project.
Total Same New Not
generated
Original 4 3 - 1
Method 5 3 2 -
5 RELATED WORKS
Ben Achour proposed guidance for correcting
scenarios, based on a set of rules (Achour, 1998).
These rules aim at the clarification, completion and
conceptualization of scenarios, and help the
scenario author to improve the scenarios until an
acceptable level in terms of the scenario models.
Ben Achour's rules can only check whether the
scenarios are well written according to the scenario
models. We propose generation methods of
exceptional scenarios and alternative scenarios from
a normal scenario.
Derek Cramp claimed the importance of
alternative scenarios. He proposed a model to create
alternative scenarios (Cramp et al., 1995). However,
his model strongly depends on a specific domain.
Our approach for generating alternative scenarios is
independent of a domain.
Ian Alexander proposed a scenario-driven search
method to find more exceptions (Alexander, 2000).
In his approach, a model answer was prepared with
knowledge of all exception cases identified by
stakeholders. For each event, related exceptions are
listed as a model answer. His model answer,
however, strongly depends on a specific domain.
Neil Maiden et al. proposed classes of
exceptions for use cases (Maiden et al, 1998).
These classes are generic exceptions,
permutations exceptions, permutation options,
and problem exceptions. With these classes,
alternative courses are generated. For
communication actions, 5 problem exceptions are
prepared, that is, human agents, machine agents,
human-machine interactions, human-human
communication, and machine-machine
communication. They proposed a generation
method of alternative paths for each normal
sequence from exception types for events and
generic requirements with abnormal patterns
(Sutcliff et al., 1998). We focus on generation of
alternative scenarios by providing more precise
model based on both case structure of actions and
actor types.
In the author’s previous work (Ohnishi, 1996),
we proposed to build software requirements from
textual requirements in Japanese, based on a
typology of concepts very similar to the semantic
roles of the case grammar (Fillmore, 1968). Another
related work is Ben Achour's use of case grammar
in scenario analysis (Achour, 1997, Achour, 1998).
Ben Achour focuses on how textual scenarios could
be integrated into different existing methods, and
proposes guidance for writing scenarios. He
provides style and content guidelines referring to
conceptual and linguistic model of scenarios, based
on the case grammar. These works demonstrate that
the case grammar is suitable to the semantic
characterization of any design models as well as the
semantic characterization of any natural language
sentence.
6 CONCLUSION
The author has proposed a generating method of
alternative scenario. We provide alternative events
and their templates with an alternative scenario DB.
By compensating the templates, we can
automatically get alternative scenarios. Our method
contributes to lessen developers’ work of making
several scenarios and to improve the quality of
scenarios.
The proposed method was demonstrated by the
example and was evaluated. The evaluation results
show that our method is valid in software
development.
The quality of the generated alternative scenario
depends on the alternative scenario DB. So, we
have a plan to derive alternative methods from
software documents. We will evaluate and improve
our method and system by applying them to several
scenario-based software system developments.
These are left as future works.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank to Mr. Koji Kitamoto (currently at NTT
Data co.), Dr. Hiroya Itoga, Mr. Taishi Yamamoto
and other members of Software Engineering
laboratory, Department of Computer Science,
Ritsumeikan University, Japan. This research is
partly supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific
Research (C)(2)(17500026), Ministry of Education,
Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
116

REFERENCES
Achour, C. B., 1997: Linguistic Instruments for the
Integration of Scenarios in Requirements Engineering,
Proc. of the Third International Workshop on
Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software
Quality (REFSQ'97), Barcelona, Spain, pp. 93-106.
Achour, C. B., 1998: Guiding Scenario Authoring, Proc. of
the Eight European-Japanese Conference on
Information Modeling and Knowledge Bases, Vamala,
Finland, May 25-29, pp.181-200.
Alexander, I., 2000: Scenario-Driven Search Finds More
Exceptions, Proc. 11
th
International Workshop on
Database and Expert Systems Applications, London,
U.K., Sep. 4-8, pp.991-994.
Cockburn, A., 2001: Writing Effective Use Cases,
Addison-Wesley, USA.
Cramp, D.G., Carson E.R., 1995: Assessing Health Policy
Strategies: A Model-Based Approach to Decision
Support, Proc. International Conference on System,
Man and Cybernetics, Vol.3, pp.69-73.
Fillmore, C.J., 1968: The Case for Case, in Universals in
Linguistic Theory, Bach and Harms, Chicago, Eds
Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Jackson, M., 1995: Problems and requirements, Proc. 2nd
International Symposium on Requirements
Engineering (RE’95), IEEE Computer Soc., York,
England, March 27-29, pp.2-8.
Leite, J.C.S.P., Rossi, G., Balaguer, F., Maiorana, V.,
Kaplan, G., Hadad, G., Oloveros, A., 1997: Enhancing
a requirements Baseline with Scenarios, Proc. of the
3rd IEEE International Symposium on Requirements
Engineering (RE’97), Annapolis, U.S.A., Jan. 6-10,
pp.44-53.
Maiden, N.A.M., Manning’ M.K., Ryan M., 1998:
CREWS-SAVRE: Systematic Scenarios Generation
and Use, Proc. 3
rd
International Conference on
Requirements Engineering (ICRE’98), Colorado
Springs, U.S.A., April 6-10, pp.148-155.
Maiden, N.A.M., Hare, M., 1998: Problem Domain
Categories in Requirements Engineering, International
Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 49, pp.281-304.
Ohnishi, A., 1996: Software Requirements Specification
Database Based on Requirements Frame Model, Proc.
of the IEEE second International Conference on
Requirements Engineering (ICRE'96), Colorado
Springs, U.S.A., April 15-18, pp.221-228.
Ohnishi, A., Potts, C., 2001: Grounding Scenarios in
Frame-Based Action Semantics, Proc. of 7th
International Workshop on Requirements Engineering:
Foundation for Software Quality (REFSQ’01),
Interlaken, Switzerland, June 4-5, pp.177-182.
Ohnishi, A., Zhang, H., Fujimoto, and H., 2002:
Transformation and Integration Method of Scenarios,
Proc. of 26th Annual International Computer Software
& Applications Conference (compsac02), Oxford,
England, pp.224-229.
Railway Information System Co., Ltd., 2001: JR System,
http://www.jrs.co.jp/keiki/en/index_main.html.
Ridao, M., Doorn, J., Leite, J.C.S.P., 2001: Domain
Independent Regularities in Scenarios, Proc. of the
Fifth IEEE International Symposium on Requirements
Engineering (RE’01), Toronto, Canada, August 27-31,
pp.120-127.
Sutcliffe, A.G., Ryan, M., 1998: Experience with SCRAM,
a Scenario Requirements Analysis Method, Proc. of
the 3rd International Conference on Requirements
Engineering (ICRE’98), Colorado Springs, U.S.A.,
April 6-10, pp.164-171.
Sutcliffe, A. G., Maiden, N. A. M., Minocha S., Manuel D.,
1998: Supporting Scenario-Based Requirements
Engineering, IEEE Trans. Software Engineering,
Vol.24, No.12, pp.1072-1088.
Weidenhaupt, K., Pohl, K., Jarke, M., Haumer, P., 1998:
Scenarios in System Development: Current Practice,
IEEE Software, March, pp.34-45.
Zhang, H., Ohnishi, A., 2004: Transformation Method of
Scenarios from Different Viewpoints, Proc. of the 11th
Asia Pacific Software Engineering Conference
(APSEC2004), Busan, Korea, Nov. 30-Dec. 3, pp.492-
501.
SUPPORTING METHODS OF GENERATING ALTERNATIVE SCENARIOS FROM A NORMAL SCENARIO
117
