
DISTRIBUTED BUSINESS PROCESSES IN OPEN AGENT
ENVIRONMENTS
Christine Reese, Kolja Markwardt, Sven Offermann and Daniel Moldt
Department of Informatics, University of Hamburg, Germany
Keywords:
Inter-organisational Business Processes, Agents, Reference Nets, Distribution, Agent Networks.
Abstract:
In the context of multi-agent systems, a general aim is the inter-operability of agents. One problem remaining
unsolved is the control of processes between agents. The need for workflow technology to support business
processes on the level of agents becomes obvious. We provide concepts for distributed WFMS where the dis-
tribution is realised within the architecture. Given the formal background of Petri nets, this work is innovative
regarding the interplay of agent and workflow technologies.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of multi-agent systems, a general aim
is the interoperability of agents. The standardisa-
tion committee FIPA as well as the European project
Agentcities and its successor openNet provide stan-
dards and de-facto standards. One problem remaining
unsolved is the control of processes between agents.
FIPA interaction protocols provide general interaction
patterns that are specialised in the specific case. An-
other level of support is provided with process de-
scription languages like BPEL or OWL-S. It is desir-
able to develop process-oriented applications. There-
fore the need for workflow technology on an agent
level to support Business Processes becomes obvious.
Conceptually, the techniques of agents and work-
flows are combined by using concepts of both for
the perception of a complex system. By this, vari-
ous characteristics of complex systems like control,
monitoring, autonomy, encapsulation and flexibility
are combined systematically. We envision to use a
common WFMS-Ontology.
In this paper we present our architecture: an
agent-based system for inter-organisational Business
Processes, which is based on reference nets.
2 BUSINESS PROCESSES
Today, organisations try to analyse and model their
business activities in a process-oriented way, focus-
ing on their core Business Processes, while explor-
ing possibilities to source out activities that could
be accomplished more efficiently by external part-
ners (Riedl, 2003). For this purpose business process
management (BPM) tools are necessary to design,
analyse, and execute these processes.
Inter-Organisational Business Processes It is de-
sirable that each organisation can use their own
WFMS for their internal processes and link it together
with the WFMSs of the partners’ organisation to form
a large, inter-organisational system, sharing only the
parts that need to be shared. It is thus necessary to
have a hierarchical form of inter-WFMS structure,
where encapsulated, autonomous parts represent the
participating organisations.
Petri Nets for Business Processes A common way
to model Business Processes is the use of Petri nets.
This formalism offers the notion of states and activi-
ties, a solid formal foundation in the field of concur-
rent processes as well as many tools to define, analyse
and execute the process definitions.
However, usually Petri net models focus mainly on
the process aspect of Business Processes, describing
the order in which activities are to be executed. Other
81
Reese C., Markwardt K., Offermann S. and Moldt D. (2006).
DISTRIBUTED BUSINESS PROCESSES IN OPEN AGENT ENVIRONMENTS.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - SAIC, pages 81-86
DOI: 10.5220/0002460900810086
Copyright
c
SciTePress

aspects like the definition of activities, the roles and
permissions involved and resources associated with
the business process are often ignored in these mod-
els. And so, for the actual execution of the process
in the productive context, other programs have to be
used, that offer a better integration into the business
context. This often means that instead of the actual
Petri net models derived forms are used for the execu-
tion as well as for modifications. These derived forms
cannot be formally verified, which later on might lead
to unsound processes.
This is where reference nets and the R
ENEW tool
can show their strengths
1
. Reference nets are a spe-
cial kind of high-level Petri nets, that allow the use
of references as tokens in the Petri net. These tokens
can be Java Objects and, more interestingly, other nets
that can be synchronised with each other. Jacob shows
in (Jacob, 2002) how reference nets can be used to
model a multi-layered workflow management system,
that integrates the different aspects mentioned above
into a workflow net.
Jacob’s plug-in for R
ENEW that we use as basis for
this architecture provides, besides the common fea-
tures of a workflow enactment service, roles and other
security and safety features. It is based on a persis-
tently working engine as introduced in (Jacob et al.,
2001).
Agent based BPM Agents and multi-agent systems
offer a software development paradigm, that focuses
on autonomous entities interacting with each other to
reach their goals.
A special characteristic of the applied agent frame-
work C
APA (“Concurrent Architecture for a Multi-
agent Platform”, see (Duvigneau et al., 2003)) is that
the platform is implemented as an agent itself. Such
a platform agent contains all agents. This concept is
used to develop the WFMS agents. The basic agent
in C
APA is modelled as a reference net which enables
basic agent features like sending and receiving mes-
sages and accessing a knowledge base. The behaviour
of an agent is defined on the one hand by protocol
nets which usually have workflow-like structure and
on the other hand by a decision component net which
encapsulates the complex knowledge of an agent.
3 OPEN AGENT ENVIRONMENTS
The standards of FIPA are “intended to promote the
interoperation of heterogeneous agents and the ser-
vices that they can represent” (FIPA, 2005). In
1
Reference nets published in (Kummer, 2002), detailed
introduction in (Kummer, 2001). R
ENEW software, user
guide, and literature freely available at (Renew, 2005).
this standardisation process there were test-beds and
experiments to connect heterogeneous but standard-
compliant agents to networks. Since 2000 this
was coordinated within a European research project,
Agentcities, and since 2004 within openNet, its suc-
cessor. “OpenNet is dedicated to facilitating collabo-
ration between research projects developing, applying
and above all deploying Agent, Semantic Web, Web
Service Grid and similar networked application tech-
nologies in large-scale open environments such as the
public Internet” (openNet, 2005).
The network services were increasing from the first
FIPA test network up to the openNet environment:
FIPA provided basic interaction standards, like a com-
munication language, FIPA agent management ontol-
ogy, and transport protocols; a reference model of
software agents as autonomous components commu-
nicating via messages; and specifications of basic di-
rectory services. Using these, Agentcities developed
a mechanism to provide centralised non-hierarchical
directory services for platforms, agents and services
provided by agents. The naming conventions for plat-
forms introduced by Agentcities were extended by the
successor openNet to have Internet-like hierarchical
domain names. openNet introduced a non-accessible
background platform where only top-level domains
can register to avoid the central bottleneck.
Each platform is represented within the network by
a platform service agent which is able to test other
platforms on a request. Network service agents gather
such information.
The services of Agentcities and openNet are com-
binable, since the access to network status data is not
specified separately by openNet, while the gathering
of such data is elaborated in openNet.
The aim of Scholz et al. in (Scholz et al., 2005)
is to enable the cooperation of heterogeneous agent
systems, on a methodological level: Their proposal
is to join several multi-agent systems (MASs) with
a design goal each using gateway agents that repre-
sent one MAS at a time. Interaction between these
gateway agents forms a logical MAS on top of other
MASs. The resulting system is called a Multi-MAS, a
Multi-Multi-Agent-System (called Agent.Enterprise).
Scholz et al. assume that each simple MAS is a closed
system and provide an example where a supply chain
application is realised by joining solutions for the dif-
ferent levels and systems.
This effort as well as several projects that where
hosted and supported within the Agentcities and
openNet projects aim at enabling the cooperation of
heterogeneous and autonomous components. This re-
quires syntactical and semantical standards as well
as process coordination. Syntactical aspects are ad-
dressed by FIPA-ACL, or by the more widespread al-
ternative SOAP. The problem of defining adequate se-
ICEIS 2006 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
82
mantics is only partly solved by ontology support, but
is not addressed here. We address the process coor-
dination by providing concepts to integrate workflow
technology with agent environments as openNet.
We can use the hierarchical infrastructure of open-
Net, the directories concepts provided by Agentcities.
What is needed is the control for processes. So, our
proposal is to supply openNet with an agent-based
WFMS. Special attention is given to the agent inter-
face: It should be possible to join WFMS parts of dif-
ferent providers within the network.
4 INFRASTRUCTURE
This section describes the structural elements of our
proposed system.
Relation between Workflows and Agents Usually,
the workflow itself exists as a data structure in the
WFMS. Wrapped by an agent, a workflow is concep-
tually only accessible via its message interface (we
do not discuss general security problems in the agent
area here) and thus a certain level of autonomy and
mobility is enabled within the architecture.
Workflows are represented by agents. In the usual
case of a “local” workflow, where “local” means in-
side a kind of closed system, this WF agent does not
hold much autonomy. It just provides access to its
process definition. In a more complicated case, the
WF agent interacts with the Workflow Engine.
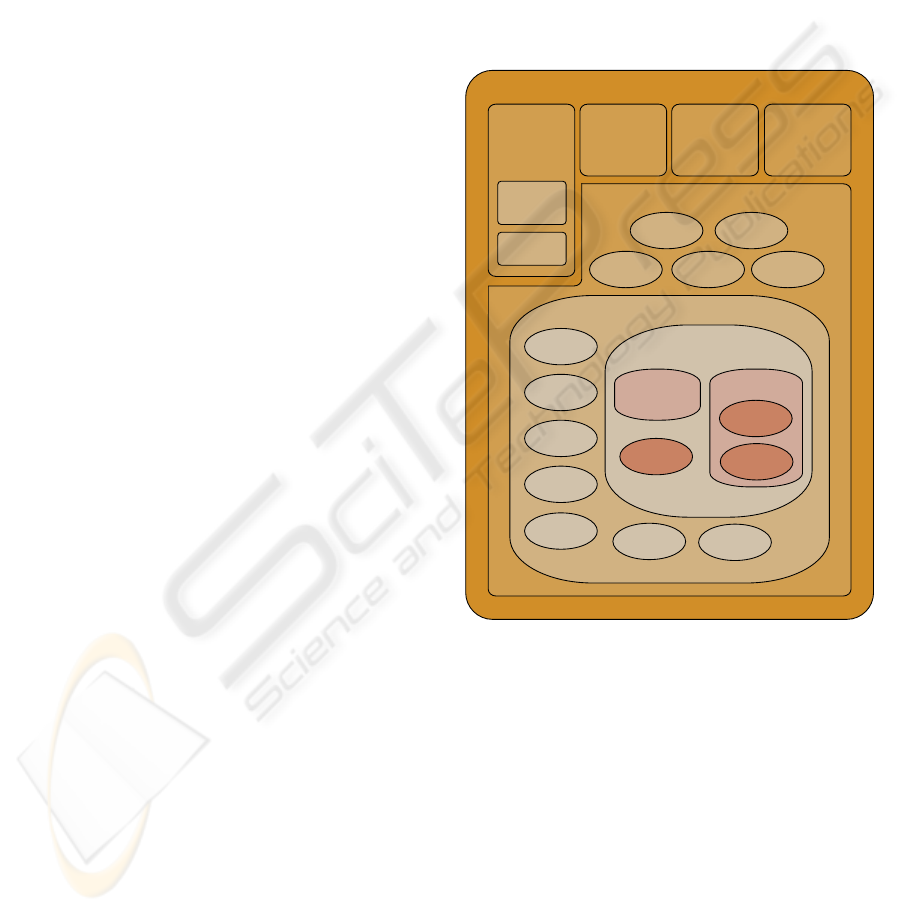
Agent Types Figure 1 shows all agent types that
belong to the WFMS. The runtime environment R
E-
NEW contains diverse plug-ins, including the basic
reference net editor, an AUML editor, a workflow
plug-in and the agent platform C
APA.CAPA con-
tains the Agent Management System (AMS), the Di-
rectory Facilitator (DF) as specified by the FIPA and
the C
APA platform agent. Plug-ins for CAPA may
add further agents as the Web Service gateway agent
(shown in Figure 1 near “other agents”). The WFMS
platform agent runs within C
APA and is provided by
a WFMS plug-in. It contains the Client Interaction
Agent, Administration Agent, Workflow Definition
Agent, Monitoring Agent, and Workflow Enactment
Service Platform Agent (WFES). These have a gate-
way functionality. They form the interface of the
WFMS, as described by the Workflow Management
Coalition (WfMC, 2005). They separate and connect
the agent WFMS with the basic local WFMS func-
tionality provided by the Workflow plug-in for R
E-
NEW and with any application domain components
not shown in the figure. The Workflow and Workflow
Fragment Agents (WF and WFF) as well as Workflow
Engine Platform Agents (WFE) and Task Agents are
dynamically instantiated during runtime as described
in Section 5. The agents Remote Communication and
Distribution Agent are explained there, also.
In the course of workflow execution different
pieces of information are collected, partly as control
data for the workflow, partly as case data for use in the
workflow tasks. This data is in the case of an unfrag-
mented workflow stored within the knowledge base
of the workflow agent. In the case of a fragmented
workflow, data is stored throughout all the workflow
fragment agents and the data needs to be shared be-
tween the fragments on synchronisation points.
reference net
editor
...further tools
integrated
within Renew
runtime environment Renew
WS
gateway
other
agents
AMS DF
platform
agent
agent platform CAPA
WF
definition
client
interaction
WFE 1
WFF b
(travelling)
WFES platform agent
WFMS platform agent
WFE 2
WFF a
WF 1
remote
commun.
task
agent
distribution
agent
monitoring
agent
admin
agent
workflow
management
tool, including:
tool for
workflow
definition
other
WFMS parts
AUML
diagramm tool
Figure 1: Components within each platform.
Workflow Management for Open Agent Networks
Within open agent networks, the described agent
types could be distributed using network services like
up-to-date directory services. Because the agent types
are interfaces and because for the data format for
these interfaces various agreed and spread standards
exist, parts of this WFMS can be distributed arbitrar-
ily across the network. In this way, the different func-
tions of a WFMS like definition of new workflows or
monitoring can be implemented externally and run at
the office they belong to. If one of the administrators
visits another company, he can log into the monitor-
ing system by searching within the current agent net-
DISTRIBUTED BUSINESS PROCESSES IN OPEN AGENT ENVIRONMENTS
83

work for an agent enabled monitoring service. This
means, he searches for a monitoring service that im-
plements the monitoring interface and either is able to
communicate these messages via ACL or a Web Ser-
vice gateway is available.
Within an open agent network, several providers of
the service “workflow administration” can be regis-
tered as well as several providers for “workflow mon-
itoring” or “workflow definition” etc. These take as
argument for their services contact information to the
desired WFMS together with the data content, which
they either help to create (by providing e.g. a GUI to
draw a workflow definition) or which they take from a
given source. These service providers contact the ap-
propriate interface agents within the desired WFMS
where the actual effect is produced, as described in
Section 5.
This is the “centralised WFES” view on our pro-
posed architecture, which is a translation and spe-
cialisation of the WfMC model to agent communica-
tion regarding interfaces number 1, 2, 3, and 5. Now
please regard Figure 2. This shows another view on
the system. Each of the coloured boxes represents
one agent within an agent network, as just described.
Some of these (i.e. the WF Engines) form a virtual
WFES, while the Workflow Fragment Agents form a
virtual WF Agent. So the objective is to implement an
agent using multiple agents within the network. The
virtual WFES acts as a distributed environment for
WFE agents which acts in whole like a central ser-
vice.
The WF agent sends a representative to be cre-
ated within the WFE platform and through this trusted
channel all communication that is necessary to solve
that workflow is routed. To save the autonomy of
the WF agent, it remains the possibility to use other
communication channels than through the WFE agent
(this is shown in Figure 2).
5 OPERATIONAL SEQUENCES
In the last chapter the structural elements of the agent-
based WFMS were described. Now we are going to
discuss in more detail the interactions between the
different agents that form the system.
In the following, typical events are described that
occur in the envisioned system.
These interactions do not refer to general services
within open agent networks like directory search, be-
cause this is not developed but taken for encapsulated
functionality provided by the agent network.
Explanatory note Each interaction with a user is
handled by the Client Interaction Agent. It provides
the users work list as well as functionality according
to the access rights of the user. Choosing the func-
tion “Define new Workflow” will cause the process
described in the next subsection to happen etc.
Each of the following subsections represents one
process within the WFMS which is triggered (in most
cases) by the Client Interaction agent and executed
until the system is “quiet” again and waiting for the
next event.
Each time the Client Interaction agent causes an-
other agent to invoke an application according to the
rights of the user, the user communicates logically di-
rectly with that application or agent. Practically this
communication is projected on a tunnelled and thus
trusted and secure communication (or the other way
round: the mediated communication can be projected
to direct communication). Please compare with Fig-
ure 2.
The following abbreviations are used:
CLI Client Interaction Agent
DEF Workflow Definition Agent
ADA Administration Agent
WFES Workflow Enactment Service Agent
DIS Distribution Agent
WFE Workflow Engine Agent
WF Workflow Agent
WFF Workflow Fragment Agent
TASK Task Agent
REM Remote Agent
MON Monitoring Agent
User or Role Definition CLI calls ADA (“I would
like to introduce a new User/Role”). ADA checks his
own knowledge base to verify that CLI has the rights
to do so. If successful, ADA invokes an application
with which CLI can specify the desired data, which
ADA then stores in its knowledge base.
Workflow Definition CLI calls DEF (“I would like
to define a new WF”). DEF asks ADA if CLI has
the rights to insert a new WF into the system. If yes,
DEF starts an application that provides file upload (for
previously defined process description) as well as the
possibility to launch the R
ENEW WF definition tool.
DEF then stores the process definition.
Workflow Execution
1. Instantiation
CLI calls WFES (“I would like to instantiate a
WF”). WFES asks ADA if CLI has the rights to
instantiate a new WF. If yes, WFES asks DEF for
ICEIS 2006 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
84

EPPO Workflow descriptions agent.
Holds all WFs of EPPO that are used
within this virtual WFMS. Also the example.
EPPO Client Agent.
Controls and Triggers Worfklow
execution by pushing, pulling, chosing,
rejecting or completing tasks.
EPPO Application Agent.
Provides Funcionality / Services that
are application specific.
EPPO WF Engine
IPM Workflow descriptions agent.
Holds all WFs of IPM that are used
within this virtual WFMS. Also the example.
IPM Client Agent.
Controls and Triggers Worfklow
execution by pushing, pulling, chosing,
rejecting or completing tasks.
IPB Application Agent.
Provides Funcionality / Services that
are application specific.
IPM WF Engine
HL Workflow descriptions agent.
Holds all WFs of HL that are used
within this virtual WFMS. Also the example.
HL Admin Agent.
Provides information
on users rights and
roles.
HL Client Agent.
Controls and Triggers Workflow
execution by pushing, pulling, choosing,
rejecting or completing tasks.
HL Application Agent.
Provides Funcionality / Services that
are application specific.
HL WF Engine
virtual WFES
EPPO
HL
IPM
virtual WF agent
virtual WF agent - Agent
representative
logical communication
Imagine the fantasy names EPPO,
IPM and HL to be short names for
internationally operating concerns
that want to cooperate within some
joint project.
Figure 2: Virtual WFES.
a summary of available process definitions. These
are forwarded to CLI. CLI chooses the desired
WF. WFES calls DIS to create WFE, WF and WFF
agents.
Any changes to available Tasks that arise from this
action are detected by step 2 in Section “Workflow
Execution”.
2. For each process step
WFE, WF and WFF agents interact with each other
and with possibly activated TASK agents, with the
result of further TASK agents being activated ac-
cording to the workflow (that means it is then in
the status of a work item). This may require re-
mote communication due to distributed workflows,
so REM is used as a gateway to other WFE, WF,
WFF agents. TASK calls appropriate applications
to solve the task. This may be an appropriate CLI to
tell about available tasks, or some other application
as specified.
3. End of a workflow
If the workflow termination criteria are reached,
WFE or WF contacts WFES which terminates
WFE and WF.
User Choosing a Task CLI calls the TASK (“I
would like to handle that task”). TASK asks ADA
if the CLI has the rights to handle the task. If yes,
TASK gets into the state of an activity and tries to pro-
vide information to complete the task by contacting
the WFES. TASK now either invokes the appropri-
ate application involving user interaction, or provides
CLI with information to invoke an application itself.
Any changes to available Tasks that arise from this
action are detected by step 2 in “Workflow Instantia-
tion”.
Terminating a Task CLI or the invoked application
calls TASK (“I am done with my work”, or “I cannot
do the work”). TASK asks ADA if CLI has the rights
to terminate the task. If yes, TASK takes termination
data (such as state or application data) from CLI and
forwards these to the appropriate WF, WFF, or WFE
agent.
Any changes to available Tasks that arise from this
action are detected by step 2 in Section “Workflow
Execution”.
Monitoring and Influencing Running Workflows
CLI calls MON (“I would like to view the status of
a workflow”, or “I would like to manually change the
state of a workflow”). MON asks ADA if CLI has
sufficient rights to do that. If yes, MON gathers the
information or requests the change by communicating
to the appropriate WFE, WF, or TASK agent.
Any changes to available Tasks that arise from this
action are detected by step 2 in Section “Workflow
Execution”.
DISTRIBUTED BUSINESS PROCESSES IN OPEN AGENT ENVIRONMENTS
85

6 CONCLUSION
This paper contributes to the process-oriented appli-
cation development with workflow technology on an
abstract level. We provide concepts for modelling and
implementation of distributed WFMS where the dis-
tribution is realised within the architecture. The tech-
nologies used and parts of the architecture are based
on existing work. This paper extends the work in
(Reese et al., 2005) in such a way that we embed our
distributed WFMS in open agent environments. It is
innovative regarding the interplay of technologies us-
ing the formal method of Petri nets.
Realisation The agent framework C
APA has been
used to develop complex, Petri net based agent sys-
tems for several years (e.g. (Offermann et al., 2005)).
This framework is supported by an efficient develop-
ment environment for Petri nets (Renew, 2005), which
provides plug-ins for code generation, monitoring,
logging, and debugging. The Petri net-based work-
flow engine from Jacob (Jacob, 2002) is able to con-
tinuously update data on available activities to client
PDAs. It was extended here for distributed systems
and implemented as a prototype in a student project.
The described system is meant to be used in open
agent environments, with special attention to auton-
omy, encapsulation, and flexibility as found in such
systems.
Outlook A general aim of our work is the devel-
opment of a collaborative integrated development en-
vironment (C
IDE) for which a prototype exists. The
next step is an evaluation of the prototype within
the openNet context, running a distributed change-
request-management application. To embed this
within the open agent environment community, a
FIPA-compliant ACL specification of the WfMC in-
terface for WFMSs has to be provided.
REFERENCES
Duvigneau, M., Moldt, D., and R
¨
olke, H. (2003). Con-
current architecture for a multi-agent platform. In
Giunchiglia, F., Odell, J., and Weiß, G., editors, AOSE
2002, Revised Papers and Invited Contributions, vol-
ume 2585 of LNCS, Berlin. Springer.
FIPA (2005). FIPA: Foundation for Intelligent Physical
Agents. Homepage. http://www.fipa.org.
Jacob, T. (2002). Implementierung einer sicheren und rol-
lenbasierten Workflowmanagement-Komponente f
¨
ur
ein Petrinetzwerkzeug. Diplomarbeit, University of
Hamburg, Department of Informatics.
Jacob, T., Kummer, O., and Moldt, D. (2001). Persistent
Petri Net Execution. Petri Net Newsletter, 61:18–26.
Kummer, O. (2001). Introduction to Petri nets and reference
nets. Sozionik Aktuell, 1:1–9. ISSN 1617-2477.
Kummer, O. (2002). Referenznetze. Logos, Berlin.
Loock, H. (2005). Umwandlung von Petrinetzen in OWL-
S Ontologien. Diplomarbeit, Universit
¨
at Hamburg,
Fachbereich Informatik.
Moldt, D., Offermann, S., and Ortmann, J. (2005). A
Petri Net-Based Architecture for Web Services. In
Cavedon, L., Kowalczyk, R., Maamar, Z., Martin, D.,
and M
¨
uller, I., editors, Workshop on Service-Oriented
Computing and Agent-Based Engineering, SOCABE
2005, Utrecht, Netherland, July 26, 2005. Proceed-
ings, pages 33–40.
Moldt, D. and Ortmann, J. (2004). DaGen: A Tool for Auto-
matic Translation from DAML-S to High-Level Petri
Nets. In Wermelinger, M. and Margaria-Steffen, T.,
editors, Fundamental Approaches to Software Engi-
neering: FASE 2004. Held as Part of ETAPS 2004,
Barcelona, Spain, 2004. Proceedings, volume 2984,
pages 209–213, Berlin. Springer.
Offermann, S., Ortmann, J., and Reese, C. (2005).
Agent Based Settler Game. Available at: http://x-
opennet.org/netdemo/Demos2005/
aamas2005
netdemo settler.pdf. Part of NETDEMO.
openNet (2005). openNet project. http://www.x-
opennet.org/.
Ortmann, J. (2003). Prozeß-Ontologien in Multiagentensys-
temen – Eine prototypische Umsetzung von DAML-S
Beschreibungen in Petrinetzen und ihre Verwendung
in Mulan. Diplomarbeit, University of Hamburg, De-
partment of Informatics.
Reese, C., Ortmann, J., Moldt, D., Offermann, S.,
Lehmann, K., and Carl, T. (2005). Architecture for
distributed agent-based workflows. In Henderson-
Sellers, B. and Winikoff, M., editors, Proceedings
of the Seventh International Bi-Conference Workshop
on Agent-Oriented Information Systems (AOIS-2005),
Utrecht, Netherlands, as part of AAMAS 2005 (Au-
tonomous Agents and Multi Agent Systems), July
2005, pages 42–49.
Renew (2005). R
ENEW – the reference net workshop home-
page. URL http://www.renew.de/.
Riedl, R. (2003). Begriffliche Grundlagen des Business
Process Outsourcing. Information Management &
Consulting, 18:6–10.
Scholz, T., Krempels, K.-H., Nimis, J., Schiemann, B.,
Woelk, P.-O., Braubach, L., and Pokahr, A. (2005).
www.AgentEnterprise.net – a MMAS-based web-
portal for supply chains managed by ASCML. In
openNet Networked Agents Demonstration for AA-
MAS 2005.
WfMC (2005). Workflow reference model. URL
http://www.wfmc.org/standards/model.htm.
ICEIS 2006 - SOFTWARE AGENTS AND INTERNET COMPUTING
86
