
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS
USING ISDL
Boris Shishkov
Department of Computer Science, University of Twente, 5 Drienerlolaan, Enschede, The Netherlands
Dick Quartel
Department of Computer Science, University of Twente, 5 Drienerlolaan, Enschede, The Netherlands
Keywords: Business process modelling, Refinement, SDBC, ISDL.
Abstract: Aiming at aligning business process modeling and software specification, the SDBC approach considers a
multi-viewpoint modeling where static, dynamic, and data business process aspect models have to be
mapped adequately to corresponding static, dynamic, and data software specification aspect models. Next to
that, the approach considers also a business process modeling viewpoint which concerns real-life
communication and coordination issues, such as meanings, intentions, negotiations, commitments, and
obligations. Hence, in order to adequately align communication and dynamic aspect models, SDBC should
use at least two modeling techniques. However, the transformation between two techniques unnecessarily
complicates the modeling process. Next to that, different techniques use different modeling formalisms
whose reflection sometimes causes limitations. For this reason, we explore in the current paper the value
which the (modeling) language ISDL could bring to SDBC in the alignment of communication and
behavioral (dynamic) business process aspect models; ISDL can usefully refine dynamic process models.
Thus, it is feasible to expect that ISDL can complement the SDBC approach, allowing refinement of
dynamic business process aspect models, by adding communication and coordination actions. Furthermore,
SDBC could benefit from ISDL-related methods assessing whether a realized refinement conforms to the
original process model. Our studies in the paper are supported by an illustrative example.
1 INTRODUCTION
A number of software development approaches have
failed because of being insufficiently capable to
grasp and utilize the original business information.
As argued in (Shishkov & Dietz, 2004-1), the
specification of software and the analysis (and
modeling) of its corresponding business processes,
should be considered as one integrated task.
The SDBC (‘SDBC’ stands for S
oftware Derived
from B
usiness Components) approach (Shishkov,
2005; Shishkov & Dietz, 2005) addresses this
challenge, by allowing for a sound mapping between
a business process model and a software
specification model. They both consist of
corresponding aspect models which relate to
particular viewpoints. Hence, achieving consistency
in such a multi-viewpoint modeling is claimed to be
crucial (Dijkman, 2006).
SDBC considers three essential modeling
viewpoints: Structural viewpoint (about the statics),
Behavioral viewpoint (about the dynamics), and
Informational viewpoint (about the data).
Further, the approach considers also a business
process modeling viewpoint concerning real-life
communication/coordination issues: even though
software systems are usually well-structured and
rules-driven, the business systems which they are to
support, are more complex, driven by real-life
communication. Thus, the Communication
viewpoint plays a role in SDBC, with respect to
semantic and pragmatic real-life aspects. Such
aspects concern meanings, intentions, negotiations,
commitments, and obligations (Shishkov et al.,
2006).
In SDBC, the Communication and Behavioral
viewpoints are considered in combination, as
complementing each other. For example, it is usual
61
Shishkov B. and Quartel D. (2006).
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING ISDL.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 61-69
DOI: 10.5220/0002462200610069
Copyright
c
SciTePress
in SDBC that we address (using the DEMO Process
Step Model (Dietz, 1999), for instance) the
Communication viewpoint, by extending a structural
business process aspect model. Then we reflect this
in a behavioral business process aspect model (using
Petri Nets (Aalst & Best, 2003), for instance).
Hence, in order to adequately align
communication and behavioral aspect models,
SDBC should use at least two modeling techniques.
However, the transformation between two
techniques unnecessarily complicates the modeling
process. Next to that, different techniques use
different modeling formalisms whose reflection
sometimes may cause limitations.
The (modeling) language ISDL (ISDL; Quartel
et al., 2005) - ‘ISDL’ stands for I
nteraction Systems
Design Language, is powerful as concerns the
refinement of dynamic process models and
corresponding assessment for correctness. Thus, it is
feasible to expect that ISDL can usefully
complement the SDBC approach, allowing
refinement of dynamic business process aspect
models, by adding communication and coordination
actions.
This has motivated our studying potentials for
combining SDBC and an integrated modeling
facility based on ISDL. In particular, we explore in
this paper the value which ISDL could bring to
SDBC in the alignment of communication and
dynamic business process aspect models.
The existence of ISDL-related methods allowing
assessment whether a refinement conforms to the
original process model, further justifies the claim
that ISDL can be useful for refining dynamic
business process models in SDBC. ISDL could also
add value in the SDBC-driven mapping of such
models towards software specification, particularly
in the context of the design of software services
(Quartel et al., 2004), since a mapping mechanisms
exist
between ISDL and BPEL/WSDL specifications.
The outline of this paper is as follows: Section 2
considers SDBC, paying attention particularly to
concepts that concern the Communication and
Dynamic viewpoints (discussed before). Then we
present in Section 3 an illustrative example to be
used in our further studies. On this basis, we discuss
in Section 4 how ISDL could support SDBC in the
alignment of communication and dynamic business
process aspect models. Section 5 analyzes then the
value of applying SDBC and ISDL in combination.
And finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions.
2 SDBC
The approach SDBC supports software design, by
providing a business process modeling output that is
useful for the specification of the software system-
to-be.
Introducing the approach in detail is beyond the
scope of this paper; for information about SDBC,
interested readers are referred to (Shishkov, 2005).
However, the actual problem which we address
(in the paper) is the consistency in aligning
communication and dynamic aspect models that
concern business process modeling and related
software specification. As mentioned before,
reaching such a consistency requires appropriate
refinement of such models.
That’s why, after briefly presenting essential
relevant features of SDBC in the following sub-
section, we will particularly consider, in Sub-section
2.2, concepts that concern the problem mentioned
above.
2.1 Relevant Features
Next to the mentioned reference (Shishkov, 2005) to
exhaustive information about SDBC, readers could
find a general outline of the approach in the current
Proceedings (Shishkov et al., 2006). As for SDBC’s
features that are relevant to the problem addressed in
this paper, they will be briefly summarized below,
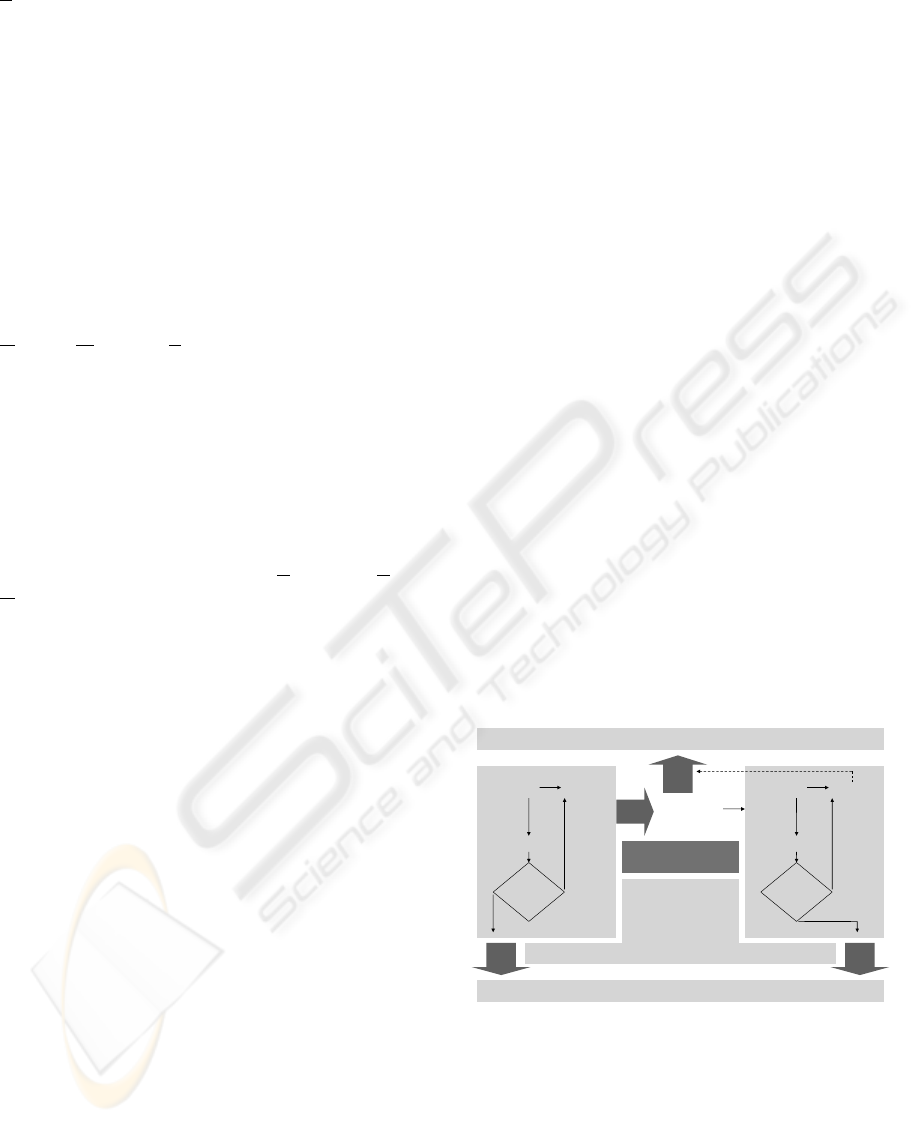
with the help of Figure 1.
business
p
rocess
modelin
g
based
on the theories o
f
LAP and OS
software
specification
consistent with
the UML
component-based
business-software
alignment
re-use of
modeling
constructs
S D B C
Figure 1: Essential features of SDBC.
As seen from the figure, fundamental values of
the approach are: 1) its capability of grasping
essential real-life aspects, with regard to a business
process modeling task, supported by the theories of
LAP and OS; 2) its UML-consistent software
specification output; 3) its allowing for a sound
business-software alignment, driven by the CBD
Paradigm; 4) its re-use potentials regarding
business/software modeling constructs. These issues
will be (briefly) discussed below:
By applying the L
anguage-Action Perspective –
LAP (Winograd & Flores, 1986) and O
rganizational
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
62
S
emiotics – OS (Liu, 2000), the SDBC approach is
capable of capturing the essential aspects (including
semantic and pragmatic aspects) that concern an
approached business reality – as studied in
(Shishkov et al., 2006). SDBC not only provides a
modeling framework suitable for such a LAP-OS
incorporation but also supports the mapping of a
LAP-OS-driven business process modeling output to
a software specification model. In this way, the
SDBC approach guarantees that the software
application-to-be would be adequately operational in
the business environment in which it would have to
function.
As for its software specification output, SDBC
guarantees the consistency of this output with the
U
nified Modeling Language – UML (Rational,
2005) and other de facto software design standards,
supported by a use case derivation procedure
(Shishkov & Dietz, 2004-2). Use case models are
derived and then reflected in UML Class diagrams,
Activity diagrams, and so on. Hence, such a
software specification output is straightforwardly
usable by other methods and tools.
The business-software alignment itself (in
SDBC) is component-based, founded in the CBD
Paradigm – ‘CBD’ stands for C
omponent-Based
Development (Shishkov, 2005). Such an alignment
allows for a good traceability between business and
software modeling constructs.
Further, the component-based business-software
alignment in SDBC allows for re-using modeling
constructs. This essentially improves the modeling
process since building new models includes re-using
previously built modeling constructs.
2.2 Essential Concepts
SDBC addresses the Communication viewpoint, by
applying the LAP theory which has been mentioned
above (readers can find information about it in the
current Proceedings (Shishkov et al., 2006)). Crucial
in this respect is the SDBC interpretation of the
LAP-driven Transaction concept.
The generic process of a Transaction is depicted
in Figure 2. If everything goes smoothly, a request is
followed by a promise, which is followed by a
statement (which is preceded by a non-
communicative production act), which is followed
by the acceptance of the production fact. However,
an actor could also enter discussions (negotiations).
For example, if Mary asks for a pizza, it might
happen that the sales person (Paul) says that the shop
is closing soon and only hamburgers could be
offered – so, this is the discussion, Mary could
accept this or not. If she accepts, Paul states a
promise regarding this updated request. If she does
not like the hamburger, when Paul states it is ready –
again they enter a discussion (whether another
hamburger should be delivered, for example). It is to
be noted that, depending on the outcome of such
discussions, a Transaction could reach failure and no
production fact would then have appeared.
That is why Figure 2 presents three layers. The
F-Layer concerns situations in which, as a result of
negotiations, a Transaction has reached failure. In
such a situation, no production fact has appeared in
the business system/environment. The S-Layer
concerns situations in which a Transaction has been
completed and thus a production fact has appeared.
In between these layers is the C-Layer that concerns
the process of communication and coordination
which determines the ultimate outcome of a
Transaction.
Hence, we have four possible communication
outcomes, as shown on the figure: 1(2) – agreement
is (not) reached and the Executor will (not) realize a
production act; 3(4) – the Initiator has (not) accepted
the delivered result and a Transaction has (not)
appeared.
The three layers discussed above as well as these
communication outcomes are of particular
importance for the current study. They are depicted
on Figure 2, in contrast to a simpler figure (to be
found in the current Proceedings (Shishkov et al.,
2006)) presenting also the Transaction concept.
C-LAYER: c o m m u n i c a t i o n a n d c o o r d i n a t i o n
communication patterns:
request (r)
promise (p)
state (s)
accept (a)
decline (d)
r (Initiator) p (Executor)
d (Executor)
Y
esNo
compromise
found?
s (Executor) a (Initiator)
d (Initiator)
Y
es
No
compromise
found?
2 4
1
production-act
3
F-LAYER: f a I l u r e - the transaction has not been realized
S-LAYER: s u c c e s s - the transaction has been realized
the
Transaction
concept
in
SDBC
Figure 2: The Transaction concept in SDBC.
Therefore, the elementary business process
modeling building blocks in SDBC are Transactions.
Further, we consider the communication patterns
(discussed above), namely: request, promise, state,
accept, and decline, needed for the elaboration of a
Transaction. And finally, by adopting a subjectivist
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING ISDL
63
philosophical stance, SDBC acknowledges that
nothing exists without a perceiving/acting agent
(Liu, 2000). Hence, we need to address the entities
related to corresponding Transactions. However,
instead of considering the particular agent (entity)
involved (human/artificial), SDBC adopts the actor-
role (Role) concept (Dietz, 1999). This allows for a
sound and flexible modeling – imagine a manager
sending a fax, this is not a typical activity for a
manager and would therefore make the modeling of
such thing complex and confusing, however if we
look at this as a role, we could easily model it by
introducing the role ‘Secretary’ (sending a fax is a
competence of this role; decision making is a
competence of the role ‘Manager’).
BUSINESS SYSTEM
composition structure
environment
concept
role
behavior
*
transaction …
communication pattern
request promise state accept decline
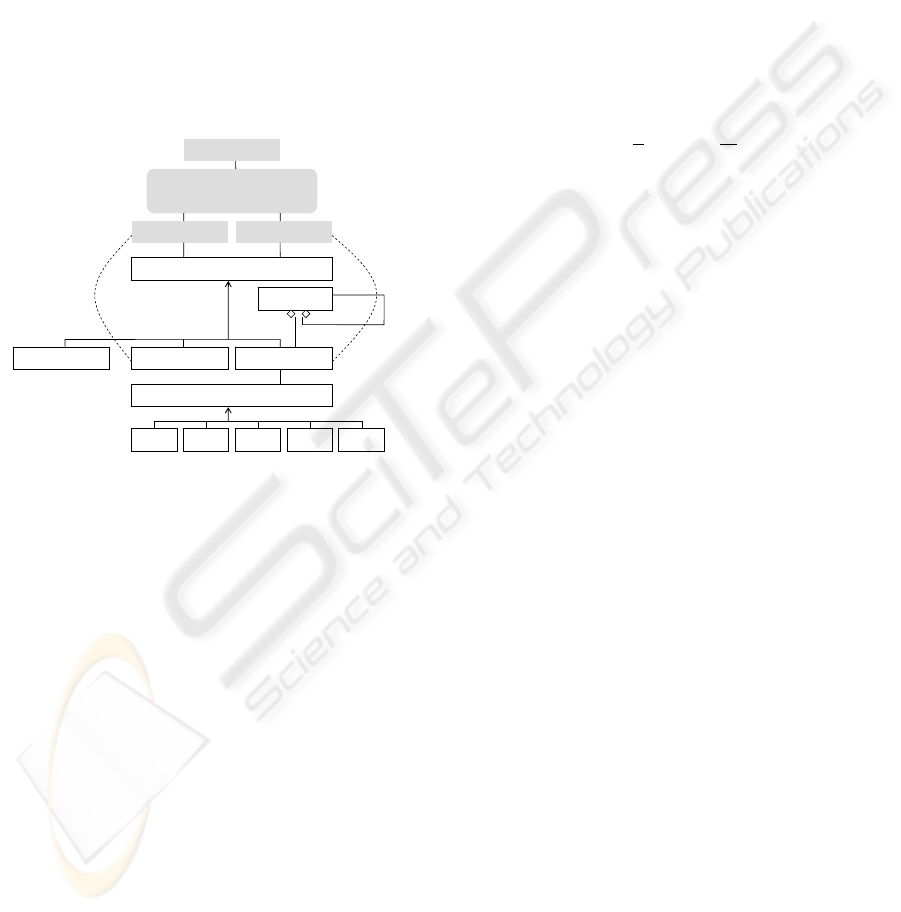
Figure 3: SDBC concepts.
We have depicted the mentioned SDBC concepts
in Figure 3. In positioning the concepts, we follow
the classical views of Bunge (1979), according to
which: a (business) system is characterized by
composition (it consists of some entities), structure
(the entities relate to each other), and environment
(entities and relationships outside the system). As
seen from the dashed lines, we consider Roles as
composition-related concepts, and Transactions as
structure-related concepts. The five communication
patterns are about the elaboration of a Transaction.
SDBC expresses multi-transaction structures via
Petri Nets (Aalst & Best, 2003), elaborating
Transactions via DEMO. This is to be adequately
reflected in a UML Activity Diagram.
By applying ISDL here, we expect to reach a
simpler and smoother representation, benefiting
from ISDL’s capability to model and refine a broad
range of dynamic patterns (Quartel et al, 2005).
In Section 3, we will introduce an illustrative
example and partially approach it with SDBC. Then,
ISDL will be introduced and applied to the example,
in modeling communication aspects (Section 4).
Based on this, we will analyze ISDL’s strengths and
limitations, in the context of the business-process-
modeling-driven specification of software in SDBC.
3 THE FM EXAMPLE
The illustrative example that we address in this
section, namely the FM example, concerns the
Icomp Case. Information about the case can be
found in the current Proceedings (Shishkov et al.,
2006), and for further elaboration, readers are
referred to (Shishkov, 2005).
‘FM’ stands for F
inancial Mediator. The FM
facilitates insurance companies, in the context of the
mentioned case. In order to use the mediator, a
company should subscribe (registering for its
service).
The support provided by FM to registered
companies includes advice and product delivery to
their customers:
* a customer can ask FM’s advice on which of the
companies’ products best satisfies a need;
* a customer can also ask FM to deliver a product,
on behalf of the particular company.
We will focus on advice delivery only.
To receive advice from FM, the customer should
firstly position his(her) request, making it clear
whether it is about a health insurance, car insurance,
and so on. Secondly, the customer has to specify the
particular demand – for instance: to insure a car
against theft with the highest possible coverage.
Based on this, a Request Processing Unit within the
FM generates a standardized specification regarding
the customer’s request, which is delivered to a
Match-making Unit (again within FM). The Match-
making Unit realizes then a match, supporting in this
way the FM in its advice delivery. This match is
driven by a particular criterion that is chosen by the
customer. For instance: a preference for the cheapest
or the most reliable product available. In order to
deliver such a criterion-driven match, the Match-
making Unit uses a data bank that contains relevant
rules and procedures. Besides the Request
Processing Unit’s specification, the Match-making
Unit needs as well an input from a Data Search and
Processing Unit within FM, in order to realize the
match. The Data Search and Processing Unit
searches through the information that concerns
registered companies, and applies procedures to this
information. This allows for a precise identification
of candidate-matches, relevant to the particular
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
64
customer’s request. Thus, the Match-making Unit
puts the candidate-matches list (delivered by the
Data Search and Processing Unit) against the
standardized request specification (delivered by the
Request Processing Unit), and realizes a match, by
applying rules and procedures, as above mentioned.
All this information, concerning the current
example, is partial and we only use it for illustrative
purpose.
In applying the SDBC approach to this example,
we should start from initial information structuring,
identification of role types, and so on (Shishkov,
2005). However, we overlook all initial SDBC
analysis and modeling steps and ‘arrive’ directly at a
constructed structural (static) business process
aspect model – Figure 4. For more information on
these initial modeling steps, readers are referred to
(Shishkov, 2005; Shishkov et al., 2006). As for the
mentioned model, we have constructed it, using the
notations of DEMO (Dietz, 1999). The model
concerns the two essential SDBC concepts: Roles
and Transactions (as they are depicted in Figure 3).
S02
Customer
T4
T3
T1
deliver advice
generate candidate-matches
generate c. specifications
perform match-making
A02
Match-
maker
T2
A01
Advisor
S01 FM
A03
Request
Processin
g
Unit
A04
Data Search
&
Processing
Unit
Figure 4: Static (structural) aspect model in SDBC.
As seen from Figure 4, an external role type is
modeled (Customer) as well as four internal role
types (Advisor, Match-Maker, Request Processing
Unit, and Data Search and Processing Unit) and four
transaction types (Deliver advice; Perform match-
making; Generate customer’s information
specification; Generate candidate-matches). The
rounded rectangle indicates the boundary of our
system. The black boxes indicate which role holds
the responsibility for a Transaction.
Now our task is to proceed to communication and
dynamic aspect modeling. This is to include
elaboration of the modeled Transactions in terms of
communicative acts and coordination (staying
consistent with the Transaction notion - Figure 2),
and also modeling of the flows of production facts.
This is addressed in Section 4. It will explore the
value which ISDL could bring to SDBC. As
mentioned, we envision potentials for a useful ISDL
support to SDBC in the alignment of communication
and dynamic business process aspect models.
4 APPLYING ISDL
The strengths of ISDL, which are envisioned with
regard to the considered research challenges, will be
demonstrated in this section, after we briefly
introduce the language.
ISDL is aimed at system modeling at higher
abstraction levels. In particular, the language is used
for business process modeling and application
design (Quartel et al., 2005; Quartel et al., 1997).
ISDL provides a small, but expressive set of
basic and generic concepts for behavior modeling,
aimed at modeling the behavior of systems from
varying domains and at successive abstraction
levels. The semantics of ISDL has been defined
formally, and a method for conformance assessment
has been defined. Furthermore, an integrated editor
and simulator is available, and tools supporting
conformance assessment and model-to-model (code)
transformations are being developed.
4.1 Concepts and Notation
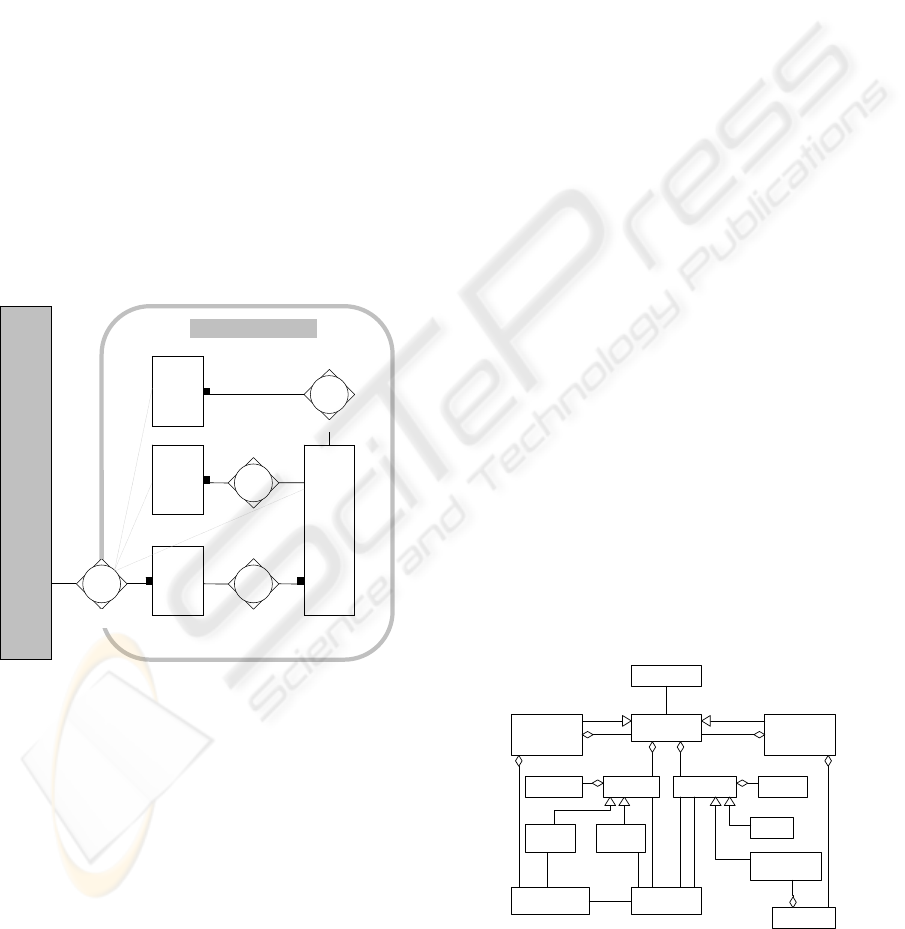
Figure 5 depicts part of the behavior conceptual
model of ISDL, including the entity concept. Figure
6 shows how these concepts are represented.
Entity
Behaviour
*
+performs
1
Constraint-
oriented
composition
Action
Activity
Interaction
Interaction
contribution
Attribute
Causality
condition
*
*
*
2..*
*
*
1
+refers
1
*
*
1
+has
Causality-
oriented
composition
Point
Entry
point
Exit
point
Parameter
Entry point
dependency
1
1
1+has
+refers
*
*
+refers
+has
11
*
*
*
Figure 5: ISDL concepts.
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING ISDL
65
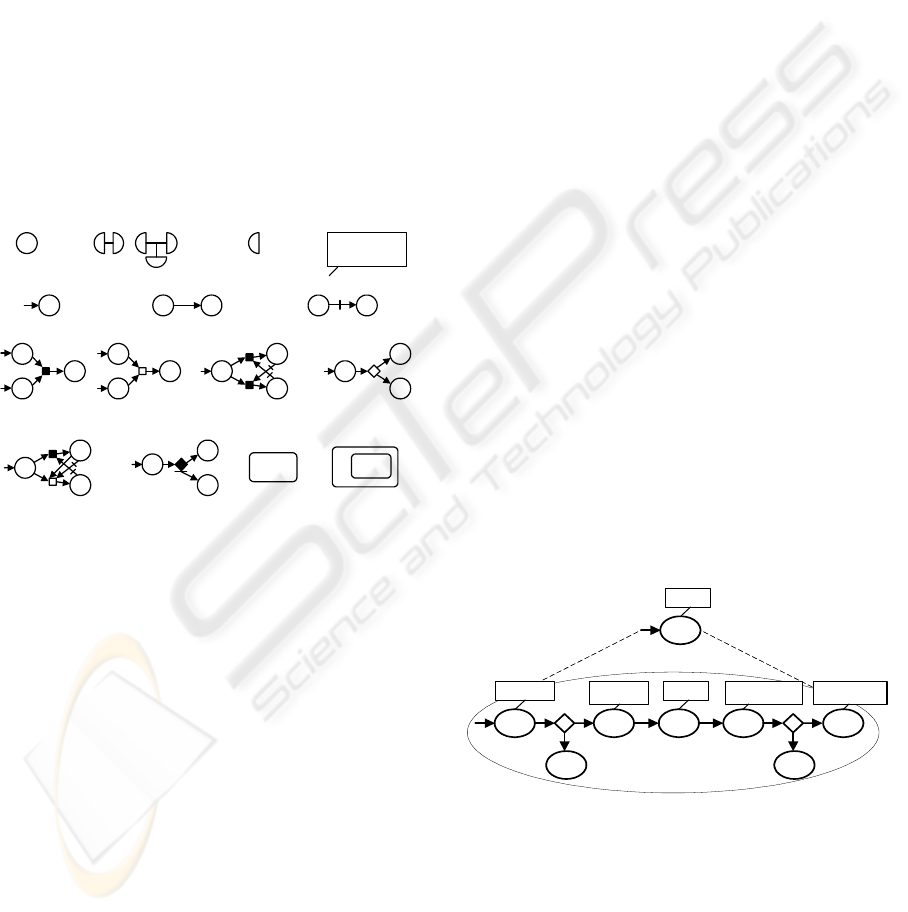
The entity concept represents a system part that
can perform some behavior. A behavior is
essentially a set of causally related activities. An
activity represents some unit of behavior that is
atomic, i.e., cannot be split at the abstraction level at
which it is defined. Further, an activity either
happens, in which case reference can be made to its
result, or does not happen at all, in which case no
reference can be made to any result, not even to
partial results. We distinguish three types of
activities. An action is performed by a single
behavior (entity). Actions are graphically expressed
by ovals (or circles). An interaction is performed by
two or more behaviors in cooperation. An
interaction is expressed as two or more connected
interaction contributions which represent the
participation of the involved behaviors. Interaction
contributions are expressed by oval (or circle)
segments.
a ab ab
(v) start condition of a (vi) enabling condition b of a (vii) disabling condition b of a
b
c
a
b
c
a
a
b
c
a
b
c
(viii) a depends on
the occurrences of
b and c
(ix) a depends on the
occurrence of b or c
(x) choice between a and b: a
depends on the occurrence of c
and the non-occurrence of b
(xi) shorthand for
choice relation
between a and b
B
a
(i) action a
a a
(iii) interaction
contribution a
a
(ii) interactions a and b
b b
b
Information i; Time t;
Location l
“[“ constraints “]”
(iv) attributes
(xii) disabling relation between
a and b: either b occurs and
disables a, or b occurs after a
a
b
c
a
b
c
(xiii) shorthand for
disabling relation
between a and b
(xiv) behaviour
B1
B2 b2
(xvi) behaviour
instantiation
Figure 6: ISDL language elements.
An activity can have attributes to represent the
relevant characteristics of the occurrence of the
modeled real-world activity. Predefined attributes
are the information, time and location attribute (see
Figure 6 (iv)), representing the activity result (e.g.,
some information or product), the time of
occurrence at which the result is available, and the
location where the result is available, respectively.
Constraints can be defined on the possible attribute
values. The constraints also specify the relation
between attribute values established in causally
dependent activities. ISDL does not prescribe a
language for defining attribute types and constraints,
but provides bindings to existing languages that can
be used for that purpose. Currently, bindings to Z,
Java and Q exist.
Relations between activities are modeled by
causality conditions. Each activity has a causality
condition, which defines how this activity causally
depends on other activities. An activity is enabled,
i.e., allowed to occur, if its causality condition is
satisfied. Three types of basic causality conditions
are identified as illustrated in Figure 6: (v) the start
condition represents that activity
a is enabled from
the beginning of some behavior and independent of
any other activity, (vi) enabling condition
b
represents that activity
b must have occurred before
a can occur, and (vii) disabling condition
¬
b
represents that activity
b must not have occurred
before nor simultaneously with a to enable the
occurrence of
b. These elementary conditions can be
combined using the and- and or-operator to
represent more complex conditions. Figure 6 depicts
also some simple examples.
Containment of one behavior by another (the
composite), is represented by behavior instantiation.
A behavior instantiation represents that some
behavior instance is created in the context of the
behavior that contains the instantiation.
4.2 Activity Refinement
An activity cannot be split at the abstraction level at
which it is considered. A more detailed model of an
activity can be obtained by decomposing this
activity into multiple sub-activities and their
relationships. The relevant characteristics of these
sub-activities can be modeled again by the activity
concept (i.e., actions, interactions or interaction
contributions). Therefore, the activity concept is
independent of the abstraction level or granularity at
which specific activities are modeled.
T
Tr
I
Tp
E
Td
E
Ts
E
Pa Ta
I
Td
I
Request r
Request r
[r = Tr
l
.r]
Pfact f
Statement s
[s = St(Pa.f)]
Statement s
[s = Ts
E
.s]
Pfact f
T= Transaction
P = Production act
r = request
p = promise
d = decline
s = statement
a = accept
I = Initiator
E = Executor
Data types
Request represents the request
Pfact represents the production fact
Statement represents the statement
St(..) function rendering
statement of some
production fact
Figure 7: The ISDL Transaction models.
In the context of SDBC, the activity concept is
used to model Transactions as well their
corresponding communication patterns. Figure 7
reflects the generic process of a Transaction, is
modeled at two different abstraction levels. At the
highest level, the Transaction is represented by a
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
66
single action, which models the production fact that
is established. Characteristics of the production fact
are modeled using action attributes. At a lower
abstraction level, the Transaction’s communication
aspects are modeled, conforming to Figure 2.
Separate actions are used to model the Transaction’s
request, promise, state, accept, and decline, and the
production act. Observe that actions
Td
E
and Td
I
correspond to the decline of a Transaction followed
by an unsuccessful negotiation (see Figure 2); and
actions
Tp
E
and Ta
I
represent the promise and
acceptance, respectively, which are possibly
preceded by an ‘initial decline’ followed by a
successful negotiation.
The result of the Transaction behavior at the
lower abstraction level should conform to the result
of the Transaction as modeled at the higher
abstraction level. In this case, the result of the
Transaction behavior is either the occurrence of
action
Ta
I
, which corresponds to the occurrence of T,
or the occurrence of
Td
E
or Td
I
, which corresponds to
the non-occurrence of T. Consequently, to assess
conformance one should assess whether the results
as modeled by actions
Ta
I
and T are equivalent.
A method has been defined for ISDL to assess
the conformance of any abstract behavior to a
concrete behavior that refines the abstract behavior.
The example in Figure 8 represents a special case of
this method. For a detailed explanation of the
method, refer to (Quartel et al, 2002).
T1
Advice a
T1r T1p T1sP1a T1aT3
T4
T2
T1r T1p T1sP1a T1a
T2r T3
T4
P2aT2p T2s T2a
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Figure 8: ISDL models of the FM behaviour.
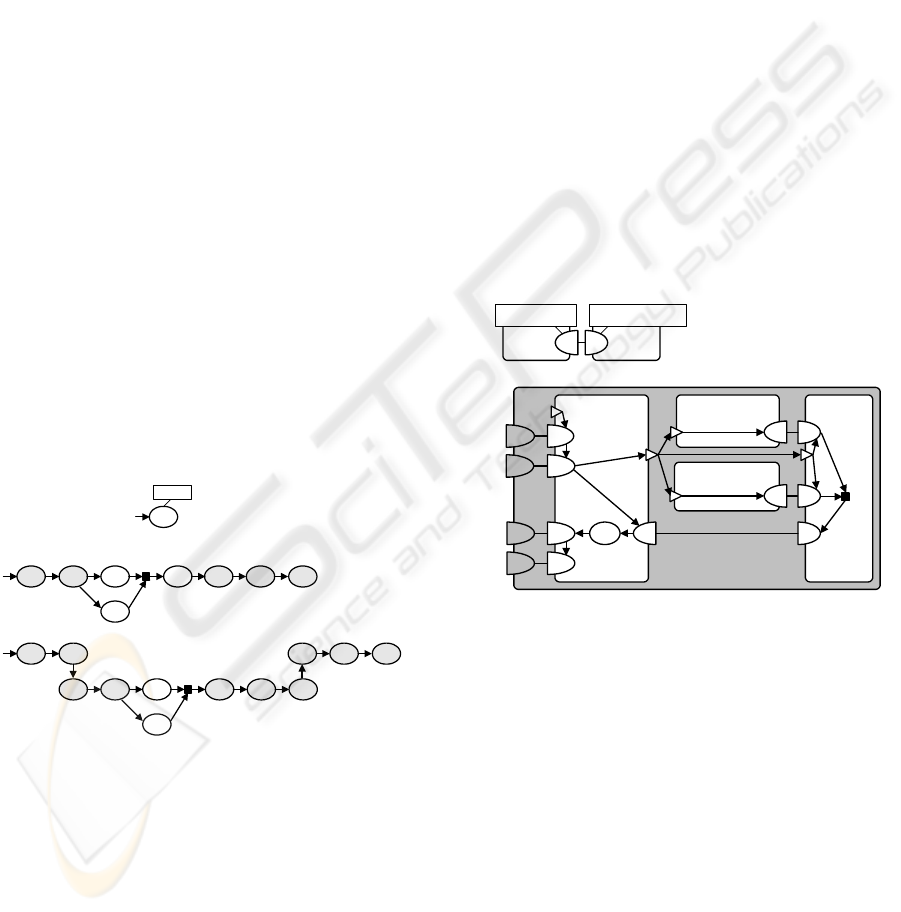
4.3 Modeling the FM Example
Using the ISDL Transaction models presented in
Sub-section 4.2, Figure 8 depicts the modeling of the
FM example (Section 3) at three successive
abstraction levels. At level (ii), some detail is added
on how the advice is delivered, eliciting part of the
internal behavior of the FM: in this case the
communication aspects of
T1 and the use of
Transactions
T2, T3 and T4. More detail is added in
(iii), by elaborating the communication aspects of
T2. A similar elaboration can be made for T3 and
T4, but has been omitted for brevity. For the same
reason, action attributes are not modeled and it is
assumed that Transactions will not be declined. To
clearly distinguish between the abstraction levels at
which a Transaction is modeled, the communication
patterns of a Transaction are indicated in grey.
The ISDL models presented so far do not
consider the Roles involved in each Transaction.
This aspect can be modeled explicitly using the
interaction concept. For example, Figure 9 (i)
models Transaction
T1 as an interaction between the
role type Customer and FM, where Roles are
represented by ISDL behaviors. The interaction
concept allows one to model the constraints each
Role may have on the possible results (production
facts) of the interaction. For example, a customer
may restrict the advices (s)he is interested in to car
insurances, whereas FM may only consider
insurances from particular companies.
FM
Customer FM
T1 T1
Advice a
[Achmea(a) or AXA(a)]
Advice a
[CarInsurance(a)]
Advisor Matchmaker
Request Processing
Unit
Data Search and
Processing Unit
T2
T3
T4
T1p
T4
P1a
T1r
T1s
T1a
T2
T3
(i)
(ii)
T1r
T1p
T1s
T1a
Figure 9: ISDL models of the FM behaviour.
Figure 9 (ii) presents the ISDL model
corresponding to the SDBC model depicted in
Figure 4; it is elicited which Roles are involved in
which Transactions. In this case the behavior of FM
is represented as a composite behavior (indicated in
grey). Behaviors in a composite behavior can be
related using: (i) constraint-oriented composition:
interactions that relate the interaction contributions
of the component behaviors; and/or (ii) causality-
oriented composition: entry and exit points that
represent a causality condition entering a behavior or
a causality condition exiting a behavior,
respectively. The condition that an entry point
represents is associated to it via an entry point
dependency. Entry and exit points are represented by
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING ISDL
67

triangles that point into or out of a behavior,
respectively. Interaction contributions of a
component behavior can contribute to interactions of
their composite behavior. This is represented by
drawing a line between the interaction contributions
of the component and interaction contributions of
the
composite (having the same name in the example).
5 ANALYSIS
As stated in Section 1, our study on the SDBC-ISDL
combination is to be the basis for an analysis (to be
conducted in the current section) on the suitability
and adequacy of combining the SDBC approach and
the ISDL language.
Our fundamental conclusion is that the essential
value of combining SDBC and ISDL concerns the
possibility to adequately grasp (driven by SDBC) a
business reality (addressing not only structural,
dynamic, and informational but also communication
aspects) and map this towards software
specification, facilitated by a powerful language
instrumentarium (ISDL), which allows one to align
communication and dynamic aspect views, and also
add precision in the reflection towards software
specification – particularly in the context of service
design (Quartel, 2005). Applying the powerful
graphical notations of ISDL makes it possible
therefore to combine communication and dynamic
aspect models, presenting them in a coherent whole
(and expressing complex behavior patterns) – ISDL
can be used at different abstraction levels and its
method for conformance assessment allows one to
relate successive abstraction levels. In all this, only a
single formalism is needed.
As we have studied, the concepts of ISDL (such
as the activity concept) correspond naturally to the
behavioral concepts of SDBC (such as the
Transaction concept), i.e., ISDL can represent the
properties modeled by SDBC concepts. Thus, one
can smoothly apply ISDL in the context of the
SDBC approach.
Further, complementing SDBC by ISDL, allows
for a consideration of the notions of Role and
Transaction – these are essential for a business
process modeling driven by SDBC (Shishkov &
Dietz, 2005). The interaction concept in ISDL
allows one to model transactions between different
roles. Furthermore, the transactions, modeled in such
a way, can be defined at a high level of abstraction
in contrast to e.g. modeling languages using message
passing as the basic interaction concept. When using
message passing, one is often forced to define
transactions closer to implementation level, since
one may need multiple messages to exchange the
information that is required to establish the desired
transaction result. Instead, the interaction concept in
ISDL allows each involved role to define its
constraints on the possible interaction result, while
abstracting from how these constraints are
implemented (e.g. through message exchange).
This strong point of ISDL can add value in the
context of the SDBC approach. It allows one to
decompose a transaction into transaction
contributions, defining the responsibility of each role
in the transaction (but still at an abstract level).
When defining a transaction as an action, one
abstracts from the contribution/responsibility of each
role in the transaction.
And finally, ISDL can be used to represent both
business process concepts and software application
concepts (Quartel et al., 2005); nevertheless, the
mapping towards software specification is beyond
the scope of this paper. Anyway, a
mapping/transformation is (being) defined from
ISDL to BPEL/WSDL, which should facilitate the
implementation of business process models using
the Service-Oriented Paradigm (Dirgahayu, 2005).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we report studies that concern the
actual challenge of achieving an adequate alignment
between the development of software and the
capturing of the business environment in which this
software would have to operate. In particular, we
have considered the SDBC approach which is
capable of realizing such an alignment, by mapping
business process aspect models to software
specification aspect models. Nevertheless, achieving
consistency in such a multi-viewpoint modeling is
believed to be crucial. This holds not only for the
business-software alignment task but also for the
business process modeling itself. It is critical that all
business process aspect models in SDBC are
consistent with each other.
The SDBC-driven business process modeling
concerns not only static, dynamic, and data business
process aspect models (as in many current methods)
but also a business process modeling viewpoint
which is about real-life communication and
coordination issues, such as meanings, intentions,
negotiations, commitments, and obligations. Thus, it
is essential that the SDBC approach allows for a
sound alignment between communication and
dynamic business process aspect models. However,
ICEIS 2006 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
68

currently the approach uses at least two modeling
techniques in order to achieve such an alignment.
The transformation among two techniques
unnecessarily complicates the modeling process and
causes limitations.
Therefore, if we apply within SDBC an
integrated language facility based on one formalism
and possessing powerful modeling expressiveness,
we could improve the alignment between
communication and dynamic business process aspect
models.
We have identified ISDL as a good candidate in
the mentioned context, given its refinement and
conformance assessment capabilities as well as
powerful graphical notations. In the course of the
current study, we have justified this choice, by
finding evidence of particular relevant strengths of
ISDL. Next to that, we have demonstrated those
strengths (and the value of the SDBC-ISDL
combination), by means of an illustrative example.
The powerful graphical notations of ISDL,
driven by one formalism, proved to work usefully in
the context of the SDBC approach. The mentioned
notations can support the approach in the alignment
of communication and dynamic aspect models,
presenting them in a coherent whole. Next to that,
ISDL could be used for refinement at different
abstraction levels, as demonstrated in Section 4,
supported by mechanisms allowing assessment
whether a refinement conforms to the original
process model. And finally, with regard to service-
oriented platforms, ISDL could support the business-
software alignment in SDBC (we have not studied
this issue in the current paper), applying an existing
mapping facility between ISDL and BPEL/WSDL.
To further this research, we plan to conduct a
real-life case study in order to bring practical
evidence in support of our findings. Next to that, we
will explore further the SDBC-ISDL combination,
particularly from the perspective of aligning static
and dynamic business process aspect models, and
we will study possibilities for simulation-driven
validation in SDBC of ISDL models.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is part of the Freeband AWARENESS
and A-MUSE projects (http://awareness.freeband.nl;
http://a-muse.freeband.nl). Freeband is sponsored by
the Dutch government under contract BSIK 03025.
REFERENCES
Aalst, W.V.D. and E. Best, 2003. Applications and theory
of Petri Nets, Springer, LNCS 2679.
Bunge, M.A., 1979. A world of systems, Treatise on basic
philosophy, Vol. 4, Reidel Publ. Company. Dordrecht.
Dietz, J.L.G., 1999. Understanding and modeling business
processes with DEMO. In ER’99, 18
th
International
Conference on Conceptual Modeling. Springer LNCS
1728.
Dijkman, R., 2006. Consistency in multi-viewpoint
architectural design, Universal Press. Enschede.
Dirgahayu, T., 2005. Model-driven engineering of web
service compositions: a transformation from ISDL to
BPEL, University of Twente – UT Press. Enschede.
ISDL home, http://isdl.ctit.utwente.nl, n.d.
Liu, K., 2000. Semiotics in information systems
engineering, Cambridge University Press. Cambridge.
Quartel, D.; R. Dijkman; M. van Sinderen, 2005. An
approach to relate business and application services
using ISDL. In EDOC’05, 9
th
IEEE International
EDOC Enterprise Computing Conference.
Quartel, D.; R. Dijkman; M. van Sinderen, 2004.
Methodological support for service-oriented design
with ISDL. In 2
nd
International Conference on Service
Oriented Computing.
Quartel, D.; L. Ferreira Pires; M. van Sinderen, 2002. On
architectural support for behaviour refinement in
distributed systems design. In Journal of Integrated
Design and Process Science, 6(1).
Quartel, D.; L. Ferreira Pires; M. van Sinderen; H.M.
Franken, 1997. On the role of basic design concepts in
behaviour structuring. In Computer Networks and
ISDN Systems.
Rational, 2005. UML Resource Center
(http://www.rational.com). USA.
Shishkov, B., 2005. Software specification based on re-
usable business components, Sieca Repro. Delft.
Shishkov, B.; J.L.G. Dietz; K. Liu, 2006. Bridging the
Language-Action Perspective and Organizational
Semiotics in SDBC. In ICEIS’06, 8
th
Int. Conference
on Enterprise Information Systems. ICEIS Press.
Shishkov B. and J.L.G. Dietz, 2005. Applying component-
based UML-driven conceptual modeling in SDBC. In
ICEIS’05, 7
th
International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems. ICEIS Press.
Shishkov B. and J.L.G. Dietz, 2004-1. Aligning business
process modeling and software specification in a
component-based way, the advantages of SDBC. In
ICEIS’04, 6
th
International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems. ICEIS Press.
Shishkov B. and J.L.G. Dietz, 2004-2. Deriving Use Cases
from business processes, The advantages of DEMO.
Enterprise Information Systems V, Ed: O. Camp,
J.B.L. Filipe, S. Hammoudi, M. Piattini, Kluwer
Academic Publisher. Dordrecht/Boston/London.
Winograd, T. and F. Flores, 1986. Understanding
computers and cognition: a foundation for design,
Ablex, Norwood, NJ.
REFINEMENT OF SDBC BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING ISDL
69
