
DESIGN OF A MEDICAL DATABASE TRANSFORMATION
ALGORITHM
Karine Abbas
(1)
, Christine Verdier
(2)
, André Flory
(1)
Lyon Research Center for Images and Intelligent Information System
UMR 5205 CNRS/ INSA of Lyon
(1)
, University Claude Bernard Lyon1, University Lumière Lyon 2
(2)
,
Ecole Centrale of Lyon Bat. Nautibus, 43 bld du 11 Novembre 1918, F 69622 Villeurbanne cedex
Keywords: Medical record structure, database reverse engineering, database transformation algorithm.
Abstract: The aim of this article is to create a unique medical record structure from the metabase of any medical
record. The work proposes the design of transformation algorithms which consists in translating the legacy
relational database (RDB) into a unique medical record structure by analysing the correlation between the
legacy RDB keys and the classification of the relations into four types : base relation, dependent relation,
inheritance relation and composite relation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The medical record consists in collecting health
events corresponding to patient’s lifelong. Medical
data are of different types: laboratory test results,
radiology reports, diseases, etc. These data come
from many places: physician practices, hospitals,
nursing facilities, etc. Consequently, for each type
of data and care place, a medical information
system can have its own medical record structure.
Dealing with various record structures requires
much effort and time. Creating a unique medical
record structure becomes a primordial requirement.
In this context, our approach proposes to transform
any medical record towards a unique medical record
structure.
Thus, the aim of our research is the design of a
technique that ensures facility to extract hidden
semantics embedded within database relations and
efficiently to rebuild medical record’s structure.
This paper proposes the design of a medical
database transformation algorithm. This
methodology allows for
- Restructuring the physical schema by using the
data dictionary (métabase).
- Extracting a semantic description in each
relation.
- Analysing of the correlation between primary
keys and foreign keys.
This article is organized as follows. Section 2
presents related works. Section 3 describes the
principle of our reengineering technique by outlining
the database transformation algorithm. Finally,
section 5 concludes with our future work.
2 RELATED WORK
Many database reverse engineering works have been
proposed. (Chiang 1994) proposed an approach
which determines the regular and weak entities,
derives many-to-many and one-to-many
relationships, establishes generalisation hierarchies
and proceeds to the classification of relations,
attributes and their inclusion dependences.
Other works (Anderson 1994), (Petit 1995) based
on query/view analysis have been investigated. These
approaches analyse query language statements.
The method MERCI (Lammari 2001) suggests a
technique in three stages: 1) extract the physical
schema by using the data dictionary 2) design a
conceptual schema in the entity / relation form by
identifying entities, relationships, generalizations,
etc. 3) research hidden semantics embedded within
programs and data.
(Tari 1997) proposes a method which identifies
the relational schema in three categories: base,
dependent and composite relations, and translates
these relations into object-oriented schema by
analyzing the degree of correlation between the keys
of relations and the degree of correlation between the
tuples of the relations.
335
Abbas K., Verdier C. and Flory A. (2006).
DESIGN OF A MEDICAL DATABASE TRANSFORMATION ALGORITHM.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - DISI, pages 335-339
DOI: 10.5220/0002466703350339
Copyright
c
SciTePress

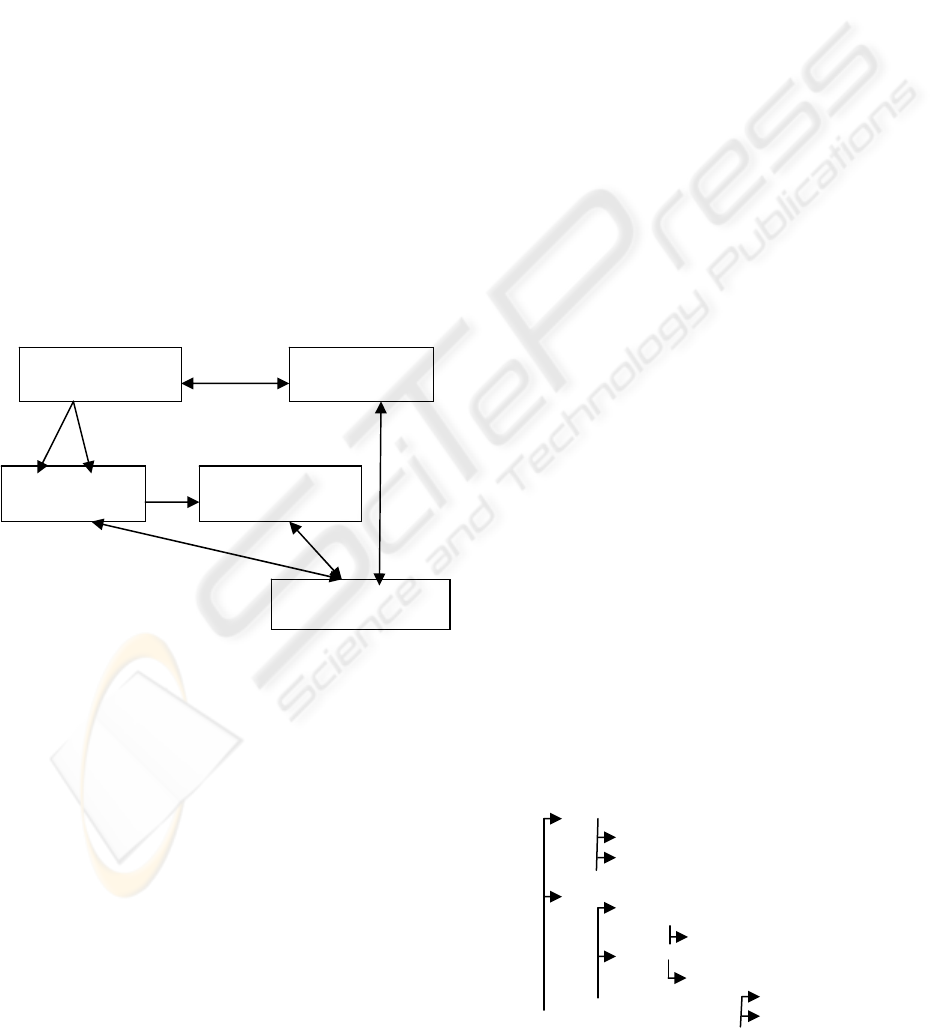
Figure 1: Medical record structure.
3 DESIGN OF THE UNIQUE
MEDICAL RECORD
STRUCTURE
A medical record contains information about an
individual’s lifetime health care. All medical
information about a patient is confidential and
accessible only for authorized persons (doctors,
nurses, etc.) involved in the care of the patient.
Defining access rules for medical data protection is
an important aspect. However, with the different
medical record structures, designing an access
policies system is a difficult process. That’s why
having a unique medical record’s structure becomes
an essential requirement. In this context, we propose
a transformation algorithm of any medical record
towards a unique medical record structure. This
algorithm restores the database physical schema and
generates a unique medical record’s structure.
3.1 Unique Medical Record
Structure Description
The medical record’s structure can be represented in
an oriented graph. Nodes contain medical terms and
arcs represent relationships between terms. Figure 1
represents the medical record architecture. The first
level manages four medical terms: administrative
record, medical record, nursing record and
emergency record. These terms are fixed. However,
the terms inserted into the nodes starting from level
2 are modifiable and depend on information
contained in the database schema.
3.2 Medical Reference Model
A medical reference model represents the most
elements used in the care places. This includes
concepts and terms for medical record components.
The terms of the reference model are used to be
compared with data retrieved from the database
physical schema.
In level 1, This medical record model is
composed as follows: A) Administrative record, B)
Medical record, C) Nursing care, D) Emergency
A list of similar or synonymic words
corresponding to each element of the medical record
is proposed. For generating this list, we use ontology
systems as UMLS, HL7, CEN TC 215. For example
the term ”surgery visit” can be represented by
“surgery consultation”, etc.
3.3 Design Technique of the Unique
Medical Record Structure
We propose a technique which consists in analysing
the information embedded within a relational
database. The physical schema is generated across
different relational databases’ data. Then, relations
are classified in four types: base relations, dependent
relations, composite relations and inheritance
relations.
Our technique mainly consists in two stages : I)
The first one analyzes the correlation between
relation keys. II) The second stage generates the
record structure.
3.3.1 Key Correlation Analysis
In the section, we analyse the correlation between
primary and foreign keys of the relations. Three
cases are identified: 1) relation does not contain
foreign keys, 2) foreign key is a component or not of
a composite primary key, 3) foreign key is equal to
the primary key.
This section describes key correlation analysis
stages:
1) The program retrieves all relations of the
relational database. This operation uses SQL which
interrogates the data dictionary and return back the
names of tables, primary keys and foreign keys.
2) Then, we fetch the relations which concern the
patient’s care.
A
:A
dministrative record
B : Medical record
C : Nursin
g
recor
d
A1 : name
B11 :medical histor
y
B21 : visit
B22 : disease
B1 : medical data
B2 : medical follow u
p
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
336

data dictionary
Analyzing the correlation
between PK et FK
Figure 2: Key correlation analysis.
- Look for the relation that identifies the patient.
This stage can be executed by comparing the names
of relations with the "Patient" word or its synonyms.
The relation “Patient” will be the starting point
- Traverse the physical schema : i) We analyze the
correlation between the primary keys and the foreign
keys of the relations.ii) We classify the relations in
two groups: composite and dependent relations
The stop point is a relation of the type n-m. We
explain this by giving a example:
visit (num, #num_patient, #num_med_resp)
prescript ( #num_visit, #num_drug
)
drug (num, #num_ther_class)
therapeutic_class (num)
The relation between “visit” and “Patient” is
represented with binary association. Thus, we take in
consideration the relation ”visit”.
The relation between “visit” and “drug” is
represented with n-area association. Thus we do not
take in consideration the relation “drug” and we stop
our processing because if we do, we take in
consideration the relation “therapeutic_class”. This
relation contains data that not provide any
information about the patient.
The algorithm1 proposes to realize the two
previous stages. The dependent relations are
expressed as follows : {visit} for th erelation
“Visit”. But for the composite relation
“Prescriptions”, this is represented in this way:
{prescriptions: visit + Medicine}.
Algorithm 1
Input : L_Tab : relations with primary
and foreign keys
Output : L1 : composite relations,
L : dependent relations
T = table_patient(L_Tab)
L = L ∪ T
For L_tab ∈ L do
For Tab ∈ L_Tab do
if FK of Tab ⊆ PK of L_tab then
if Pk of Tab ⊄ FK || PK of Tab
then L_ent=L_ent∪{Tab(L_tab)}
L = L ∪ {Tab}
If PK of Tab ⊆ FK of Tab then
L_assoc = L_assoc ∪ {Tab}
End for
End for
Example 1 : We propose a example of relational
schema. After the application of SQL queries on the
data dictionary, we obtain this information.
Person (num)
Patient (#num , #num_doctor)
Visit (num, #num_patient, #num_doct)
doctor (num)
Prescriptions ( #num_visit, #num_drug)
Drug (num, #num_thera_class)
Disease (num)
Disease_profile (#num_visit
, #num_disease)
After applying the algorithm1, we have
List_entit = {visit}
List_assoc = {
disease_profile = Visit+Disease,
Prescriptions=
Visit +Drug }
3.3.1.1 Patient’s Relation Analysis
Here, we analyze the relation “Patient”. Two data of
the relation “patient” are to be taken in
consideration: 1) non key attributes 2) foreign keys.
1) The non key attributes are added into the
administrative record of the medical record’s
structure.
2) The second case provides information from the
tables which depend of the relation “Patient ”. In the
phase, we test two possibilities: 1) If the primary key
is also a foreing key 2) If there are foreign keys
other than the primary key
.
- The first possibility allows to find the superclass
of the relation “Patient”.
- In the second possibility, we retrieve the names
of relations that depend on the relation “Patient”.
Algorithm 2
Input :relation « Patient »
Output:L_pat :depend of patient L_inh :
superclass relations
FK = Analyser (Patient).
For X ∈ FK do
if X est PK then
L_inh=L_inh ∪ {name_superclasse}
database
Relations with
PK et FK
Dependent
relations
Relationship
relations
DESIGN OF A MEDICAL DATABASE TRANSFORMATION ALGORITHM
337
Else
L_Pat=L_pat∪{name_FK : name_table)
End for
Example 2:
In the relation
Patient (#num, #num_doctor), we have :
PK = num. and FK = num_doctor.
Thus
List_Pat = {num_doctor : doctor}
The attribut “num” is also FK of the relation
“Person”. Result
list_inh = {Person}.
3.3.2 Constitution of the Structure
After building the two lists (dependent list and
composite list), we start inserting the elements of
these two lists in the medical record structure. We
begin with the dependent relations. The first point to
be realized is to compare every element of this list
with the data of the reference model of the patient’s
record. If the element is found, it is added to the
structure. Otherwise a synonym for this word is
proposed. If it is found, we insert the element into
the structure. Otherwise, we add it in the list of the
unclassified words to classify them later manually.
to compare
NO YES
NO YES
Figure 3: Reconstitution of the structure.
Now, we deal with the list of composite
relations. We remind that every element is
represented as follows: A= B+C (A represents the
name of the relationship relation, B and C the base
relations). We begin first by comparing “A” to the
list of elements constituting the reference model of
the medical record. If it is found, we insert “A” into
the structure. If not, we look for a synonym for “A”.
If it is found, we insert this synonym into the
structure. Otherwise we compare B and C. If it is
found, the synonym is inserted into the structure.
Algorithm 3
Input :L_entit : dependent relations,
L_assoc : composite relations
L_Pat : depend Relation patient
L_inh : patient relation
inherite
Output :unique medical record structure
// dependent relations
For L_ent ∈ L_entit do
L_ent = Tab (tab_dep)
If tab ∈ Modèle()
Inser(tab)
Else L_no_find = l_no_find ∪ Tab
End do
// composite relations
For L_ass ∈ L_assoc do
L_ass = attribA = tableB+tableC
If attribA ∈ Modèle()
Insert(attribA, tableB)
Else if
Attribn = Rech_syno(tableB,tableC)
Insert (attribn, tableB)
Else L_no_find = l_no_find ∪ L_assos
End do
// liste Liste_pat
For L_pati ∈ L_Pat do
L_pati = attrib:name_tab
If attrib ∈ Modèle()
Insert(attrib)
Else if
Attribu = Rech_syno (Name_tab)
Insert (attribu)
Else L_no_find = l_no_find ∪ L_pat
End do
// inheritance relations
For L_inher ∈ L_inh do
Insert(Find_attribute(L_inher))
End do
Example 3: We have four lists
L_entit = {visit (patient)}
L_assoc = { Disease_profile = Visit+Disease,
Prescriptions= Visit +Drug }
L_Pat = {num_doctor : doctor}
L_inh = {Person}
After applying the algorithm3, we have the
following structure :
Administrative record
Name
Address
Medical record
Medical data
Responsible doctor
Medical follow up
visit
disease_profile
Prescriptions
List of the
dependent relations
List of the composite
relations
Medical
Reference model
Unique medical
record structure
List to classify
manually
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
338

4 CONCLUSION
In this article, we have presented a technique which
creates a unique medical record’s structure. This
technique proposes algorithms which be developed
in JAVA. The unique medical structure record’s
structure is represented in XML language. This
structure will be used later in our future works for
managing access control in a medical system.
REFERENCES
Anderson M., 1994, Extracting an Entity-
Relationship Schema from a Relational Database
through Reverse Engineering, Proc. Of the Int. Conf.
On the Entity-Relationship Approach (ERA),
Manchester, pp 403-419.
Chiang R.H.L, Barron T.M, Storey V.C, 1994,
Reverse Engineering of Relational Databases:
Extraction of an EER Model from a Relational
Database. Data Knowl. Eng., 12(2): 107-142.
Lammari N., Si-Said S., Comyn-Wattiau I. Et
AkokaJ., 2001, Extracting Generalization
/specialization Hierarchies from Relational Databases:
a Reverse Engineering Approach . Rapport
scientifique CEDRIC, version 1.
Petit J-M, Toumani F., Kouloumdjian J., 1995,
Relational Database Reverse Engineering: A Method
Based on Query Analysis. Int. J. Cooperative Inf. Syst.
4(2-3): 287-316
Tari Z., Bukhres O., Stokes J., Hammoudi S., 1998,
"The Reengineering of Relational Databases Based on
Key and Data Correlations," Proc. Seventh Conf.
Database Semantics (DS-7), Chapman&Hall, pp. 40-
52.
DESIGN OF A MEDICAL DATABASE TRANSFORMATION ALGORITHM
339
