
A Good Index, Prerequisite for Easy Access
of Information Stored in a Dictionary
Michael Zock
Laboratoire d'Informatique Fondamentale (LIF), CNRS, UMR 6166
Parc scientifique et technologique de Luminy, Case 901 - 163 Avenue de Luminy
F-13288 Marseille Cedex 9
Abstract. A good dictionary contains not only many entries and a lot of infor-
mation concerning each one of them, but also adequate means to reveal the
stored information. Information access depends crucially on the quality of the
index(es). I will present here some ideas of how a dictionary could be enhanced
to support a speaker/writer to find the word s/he is looking for. To this end I
suggest to add to an existing electronic resource an index based on the notion of
association.
1 Introduction
We spend a large amount of our lifetime searching : ideas, names, documents, and
“you just name it”. I will be concerned here with the problem of words, or rather,
how to find them (word access) in the place where they are stored: the brain, or an
external resource.
Obviously, a good dictionary is a well-structured repository with a lot of informa-
tion concerning words. Yet, what counts is not only the coverage, i.e. number of
entries or the quality of the information associated with it, but also access support.
Because, what is information good for, if one cannot access it when needed?
I will present here some ideas of how to enhance an existing electronic dictionary,
in order to help the user to find the word he is looking for. Before doing so I will take
a look at various solutions offered for different production modes, spontaneous, de-
liberate and automatic language production, to see their qualities and shortcomings.
Let me start with the latter.
2 Related Work in the Area of Natural-language Generation
A lot of work has been devoted to lexical issues during the last fifteen years. For
excellent surveys see Robin (1990), Stede (1995), Wanner (1996), or Cumming
(1986) for some earlier work. Two approaches that have been particularly successful
were discrimination nets (Goldmann, 1975) and graph-rewriting, i.e. pattern-
matching (Nogier & Zock, 1992, Bateman & Zock, 2003). The former can be seen as
Zock M. (2006).
A Good Index, Prerequisite for Easy Access of Information Stored in a Dictionary.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Natural Language Understanding and Cognitive Science, pages 37-46
DOI: 10.5220/0002473400370046
Copyright
c
SciTePress
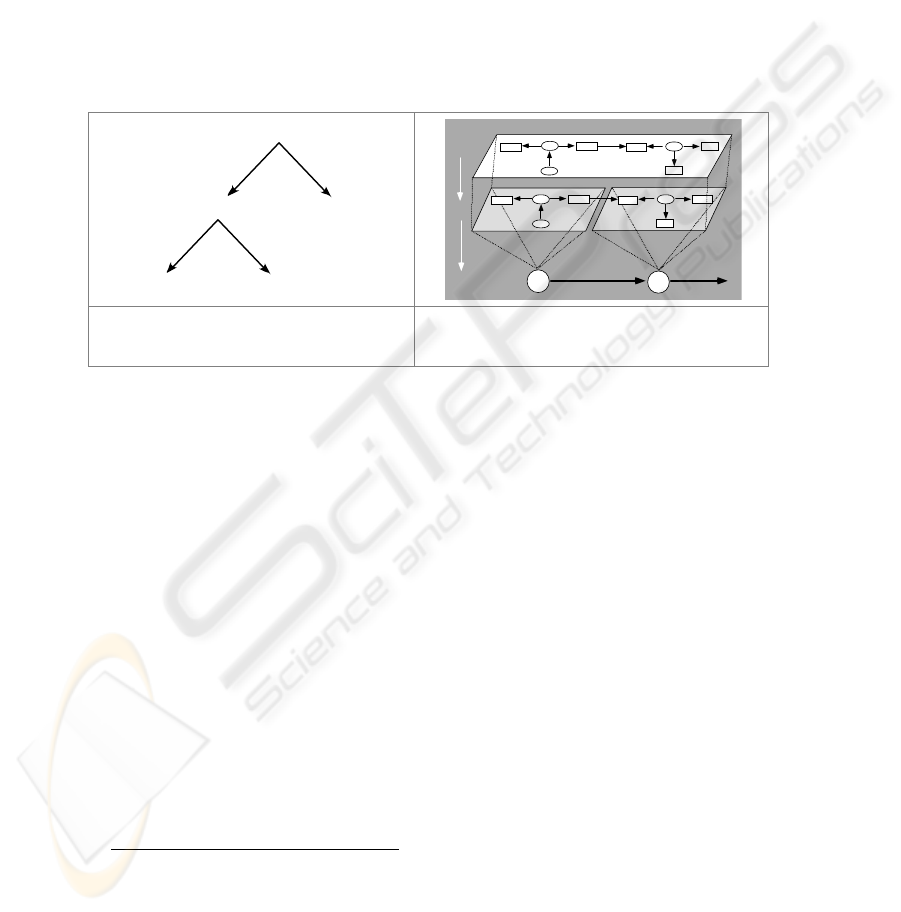
a hierarchically ordered set of tests whose outcome determine the word to be chosen.
Since the tests are hierarchically ordered, we have, formally speaking, a tree, whose
nodes are the conditions (tests) and the leaves the outcome, i.e. words (see figure 1a).
Yet, words are meant to express meanings, which, taken together form messages.
And since the input to the lexicalization component are messages, i.e. meanings
words are supposed to express, it is natural to represent both of them, messages and
the words’ underlying meaning, by the same formalism, for example, semantic net-
works. According to this view, lexicalization amounts to pattern-matching. Lexical
items are selected, provided that their underlying content covers parts of the concep-
tual input (Figure 1b). This being so, the goal is to find sufficient, mutually compati-
ble lexical items so as to completely cover the input with minimal unwanted addi-
tional information.
FT
action: INGEST
FT
object: FLUID
eat
drink
CL
LL
WL
W
1
W
2
Fig. 1a. Discrimination nets, or, the
check list approach.
Fig. 1b. Pattern matching with fully specified
conceptual input
1
.
Unfortunately there are several shortcomings with these two approaches:
• concerning the checklist approach: Apart from the fact that discrimination
nets have never been developed at a large scale (i.e. for a subset of a lexi-
con), it remains to be seen that this technique is well suited for all types of
lexical items. Also, the sum of the information given during the tests does
not amount to a full specification of the meaning of the word towards which
the tests converge, even if the underlying message is taken into account.
• concerning the pattern matching approach: this approach hinges on the as-
sumption that the message is completely planned in all its details prior to
verbalization, which, of course, is hardly ever the case. Yet, what shall we
do in case of incomplete conceptual input?
Of course, one could claim, as I’ve done elsewhere (Zock, 1996), that the input,
i.e. message to be expressed, is incomplete prior to lexicalization, and the role of the
lexicon is not only to express the message, but also to help refining its underspecified
parts. The speaker (or writer) starts with a skeleton plan (gist, or rough outline),
which he fleshes out with details little by little. For example, instead of saying “
X
meets
Y”, he provides further information concerning the referents X and Y, to pro-
duce “(
X: The young woman) met (Y: her husband)”.
1
CL : conceptual level (message); LL: lemma level (word meaning); WL: word level (expres-
sive form)
38

It is interesting to note, that in none of these works the issue of word access is ad-
dressed at all. As a matter of fact, from a strict computational linguistic point of view,
the whole matter may be a non-issue,
2
and as such it is natural that it would not ap-
pear neither in Ward’s list of problems to be addressed (Ward, 1988), nor in Cahill &
Reape’s paper (1999) ‘Lexicalisation in applied NLG systems’. However, if we ad-
dress the problem of lexicalisation from a psycholinguistic or man-machine interac-
tion point of view (spontaneous discourse or writing on a computer), things are quite
different. There is definitely more to lexicalisation than just choosing words: one has
to find them to begin with. No matter how rich a lexical database may be, it is of little
use if one cannot access the relevant information in time. Access is probably
THE
major problem that we are confronted with when trying to produce language, be it in
real-time (oral form) or consecutive mode (written form). As we shall see, this is
precisely a point where computers can be of considerable help. Before doing so, let’s
take a look at what psychologists have to say.
3 Related Work in Psychology and Psycholinguistics
There is an enormous amount of research in psycholinguistics regarding this issue: a
collection of papers edited by (Marslen-Wilson, 1989 and Levelt, 1992), several
monographs (Stemberger, 1985; Aitchinson, 2003), and an overwhelming amount of
empirical studies, to begin with Brown & Mc Neill’s landmark work on the tip-of-the
tongue phenomenon (1966), but also (Kempen & Huijbers, 1983; Roelofs, 1992) to
name just those. While all these papers take up the issue, they do not consider the use
of computers for helping people in their task. Yet this is precisely a point I am par-
ticularly interested in. Still, the work being done by psychologists and the results
obtained are truly impressive and very important.
The dominant psycholinguistic theories of word production are all activation-
based, multilayered network models. Most of them are implemented, and their focus
lies on modelling human performance: speech errors or the time course (latencies) as
observed during the access of the mental lexicon. The two best-known models are
those of Dell (Dell, 1986) and Levelt (Levelt, Roelofs, & Meyer, 1999), which take
opposing views concerning conceptual input (conceptual primitives vs. holistic lexi-
calized concepts) and activation flow (one-directional vs. bi-directional).
The Dell model is an interactive-activation-based theory that, starting from a set
of features, generates a string of phonemes. Information flow is bi-directional, that is,
lower level units can feed back to higher-level components, which may lead to errors.
For example, the system might produce rat instead of the intended cat. Indeed, both
words share certain components. Hence, both of them are prone to be activated. At
the conceptual level (from the top) they share the feature animal, while at the phono-
logical level (from the bottom) they share two phonemes. When the word node for cat
is active, the following segments are activated: /k/, /æ/, and /t/. The latter two pho-
2
Most programs running serially, there is no such thing as competition. Hence, problems like
interference, confusion or forgetting do not occur. Furthermore, computers having a perfect
memory, stored information can generally be accessed. Obviously, the situation is quite dif-
ferent for people.
39

nemes may feed back, leading to rat, which may already be primed and be above
baseline due to some information coming from a higher-level component. The model
can account for various other kinds of speech errors like preservations (e.g., beef
needle soup), anticipations (e.g., cuff of coffee), etc.
Based on the distribution of word errors, Dell argues that some aspects of speech
generation rely on retrieval (phrases, phonological features, etc), while many others
(word/phoneme and possibly morpheme combinations) rely on synthesis. Since gen-
eration is a productive task, it is prone to swapping or reuse of elements.
WEAVER++ (Word Encoding by Activation and VERification) is also a computa-
tional model. It has been designed to explain how speakers plan and control the pro-
duction of spoken words (Levelt et al., 1999). The model is "hybrid" as it combines a
declarative associative network and procedural rules with spreading activation and
activation-based rule triggering. Words are synthesized by weaving together various
kinds of information.
While
WEAVER++ is also activation-based, information flow is only one-
directional, top-down. Processing is staged in a strictly feed-forward fashion. Starting
from lexicalized concepts (concepts for which a language has words) it proceeds
sequentially to lemma selection, morphological, phonological and phonetic encoding,
to finish off with a motor plan, necessary for articulation. Unlike the previous model,
WEAVER++ accounts primarily for reaction time data. Actually, it was developed on
the basis of such data collected during the task of picture naming. However, more
recently the program managed to parallel a number of findings obtained in psycholin-
guistics where other techniques (chronometry, eye tracking, electrophysiological and
neuro-imaging) have been used.
Apart from work on the time course of lexical access, there is a large body of
work on memory and speech errors, providing the foundations for the above de-
scribed models. Work on memory has shown that access depends crucially on the
way information is organized (Collins & Quillian, 1969; Smith et al. 1974, Baddeley,
1982). From speech error literature (Fromkin 1973; Cutler, 1982) we learn, that ease
of access depends not only on meaning relations, — (word bridges, i.e. associations)
or the structure of the lexicon, i.e. the way words are organized in our mind, — but
also on linguistic form (similarity at the different levels). Researchers collecting
speech errors have offered countless examples of phonological errors in which seg-
ments (phonemes, syllables or words) are added, deleted, anticipated or exchanged.
Reversals like /aminal/ instead of /animal/, or /carpsihord/ instead of /harpsichord/
are not random at all, they are highly systematic and can be explained. Examples like
the one below (Fromkin 1973) clearly show that knowing the meaning of a word does
not guarantee its access (table 1).
Table 1. Various kinds of speech errors.
Anticipations
take my bike bake my bike
Preservations
pulled a tantrum pulled a pantrum
Reversals
Katz and Fodor Fats and Kodor
Misderivations
an intervening mode an intervenient mode
Word substitutions
before the place opens before the place closes
Blends
grisly + ghastly grastly
40

While all the work discussed so far started from a conceptual input, let’s take a
look at a tool, designed to contact (enter) the dictionary and to navigate in it by using
words. Actually, this kind of information retrieval or access is the one we are most
familiar with. Yet, WordNet (WN) the resource we will discuss in the next section is
quite different from conventional dictionaries, and as such, it is a great step forward:
rather than multiplying the number of dictionaries (one for each use or link: defini-
tion, synonyms, antonyms, etc.). WN has been built as a single resource (a database)
allowing for multiple accesses by following different links (Miller 1990, Fellbaum,
1998).
4 Related Work in the Area of Electronic Dictionaries: From
Word to Word
Despite the fact that there are many lexical resources available in electronic form
(http://www.ilc.cnr.it/EAGLES96/rep2/node1.html), I will discuss here only one,
WordNet. WN has been built on the basis of psychological mechanisms and organi-
zation principles like association, hierarchies, and semantic fields...
The way information is structured is quite different from conventional dictionar-
ies. Lexical entries are organized around linked synonym sets. There are basically two
kinds of links: lexical and semantic. The former hold between word forms, whereas
the latter connect word meanings. Set inclusion, i.e. hypernymy/ hyponymy (gen-
eral/specific), antonymy (opposite), entailment, and meronymy/ holonymy (part of)
are typical links. Different parts of speech are organized differently. For example,
nouns and verbs are organized into hierarchies, whereas adjectives are arranged in
clusters, each cluster being organized around antonymous pairs. Since adverbs are
often derived from adjectives, they may have antonyms.
While there is no doubt that WN is a major step in the right direction, it is not per-
fect, and its authors are very well aware of it. Let me mention just some of its short-
comings.
3
(1) The ‘tennis-problem’: words normally co-occurring together, hence naturally
associated (tennis, umpire, racket, court, backhand), are not linked in WN; (2) the
poverty of syntagmatic relations: "WordNet provides a good account of paradigmatic
associations, but contains very few syntagmatic links.".... If we knew how to add to
each noun a distinctive representation of the contexts in which it is used... WordNet
would be much more useful." (Miller, in Fellbaum 1998: 33-34). One can’t but agree
more. For a proposal going in this direction see Zock & Bilac (2004). (3) Incomplete-
ness of links. For a given synset there is no link between its elements apart from the
synonym link. Yet, each element might trigger a different association. Take for ex-
ample ‘rubbish’ and ‘garbage’. While the former may remind you of a ‘rabbit’ or
(horse)-‘radish’, the latter may evoke the word ‘cabbage’. (4) The problem of mean-
ing. WN’s underlying structure is a lexical matrix whose columns and rows are re-
spectively meanings and words. While the idea sounds perfect as it seems to model
the two major access or communication modes (meaning/forms, i.e. comprehen-
3
For other criticisms, see Hanks & Pustejovsky (2005), Sharoff, S. (2005).
41

sion/expression), it is not fully operational as meanings are equated with synsets only.
Hence, WN expects words rather than meanings (or meaning elements) as input. Yet
this sounds unreasonable, both for producing language in your mother tongue, and
even more so when speaking a foreign language.
5 Discussion
I have presented and commented on Fthree approaches dealing with the problem of
the lexicon. One would expect complementarities in the quest of achieving a unified
view, yet this is far from obvious. The goals and the methods being simply too differ-
ent. All of them capture something relevant, but none of them gives us a unified view.
Concerning the work done in the domain of “natural language generation”, next to
nothing can be used in the context of electronic dictionaries: the issue of word access
simply does not arise. The assumption being that what is stored in the machine can
naturally be accessed. In addition, most of this work is based on very small dictionar-
ies, tailored to the engineer’s specific needs, and the issue of macrostructure (organi-
zation) is not addressed at all.
As for the work carried out by psychologists, there are several problems: (a) the
size of their dictionaries is extremely small (around 100 entries); (b) the specificities
of the macrostructure are not spelled out at all; (c) the models being connectionist, the
links cannot be interpreted by human beings: all we get are weighted links; (d) the
notion of lemma is problematic as in computational linguistics, a lemma is a concrete
form for a given meaning (let say “walk”, in order to express some kind of move-
ment), we are nearly empty handed in the case of the mental lexicon. A lemma in this
framework means nothing more than a semantic-syntactic specification (part of
speech, and a set of features), but nothing coming close to a concrete word form, as
this is being taken care of by the phonological component, which determines the
lexeme.
By looking at this work one gets the impression that people don’t have words at
all in their mind. Notions like “words, dictionary, memory” etc. are but metaphors.
What we seem to have in our brains is a set of highly abstract information, distributed
all over. By propagating energy rather than data or information
(as there is no message
passing, transformation or accumulation of information, there is only activation spreading, that
is, changes of energy levels, call it weights, electronic impulses, or whatever)
, we propagate
signals, activating ultimately certain peripherical organs (larynx, tongue, mouth, lips)
in such a way as to produce sounds, that, not knowing better, we call words. Another
way of putting things is to say that our mind is a word fabric rather than a storehouse,
words being synthesized rather than retrieved.
Yet, we are concerned here with word access. In this respect, WN has the best po-
tential among the presented candidates. Even though it does not have the power or
flexibility of a mental lexicon—
for one it lacks too many of the links known to exist in our
mind (see all the work done on „word association“), and secondly, the links are not quantified
and context-sensitive.
— it could be improved in such a way as to get close to our ideal
lexicon. I will show in the remainder of this paper a line of research I am pursing in
order to remedy some of the shortcomings mentioned here above. The guidelines of
this work are the natural conditions and practical needs of a speaker or writer looking
42

for a word. Before doing so, let’s take a look at the speaker’s goals and knowledge at
the onset of initiating search.
6 Word Access on the Basis of Associations
There are at least two things that people usually know before opening a dictionary
4
:
the word’s meaning, or at least part of it (i.e. part of the definition) and its relation to
other words or concepts: x is more general than y, x is the equivalent of y, x is the
opposite of y (in other words, x being the hypernyme/synonyme or antonym of y),
etc. where x could be the source word (the one coming to one’s mind) and y the
target word (the word one is looking for). This is basically conceptual knowledge.
Yet, people seem also to know a lot of things concerning the lexical form (lexeme):
number of syllables, beginning/ending of the target word, its part of speech (noun,
verb, adjective, etc.), and sometimes even the gender (Brown et McNeill, 1966;
Burke et al. 1991; Vigliocco et al., 1997). While, in principal all this information
could be used to constrain the search search space, hence, the ideal would be multiple
indexes, I will deal here only with the conceptual part (meaning, i.e. partial definition,
and the words’ relations to other concepts or words).
The yet to-be-built (or to-be-enhanced) resource is based on the age-old notion of
association: every idea, concept or word is connected. In other words, I assume that
people have a highly connected conceptual-lexical network in their mind. Finding a
word amounts thus to entering the network at any point by giving the word or concept
coming to their mind (source word) and to follow then the links (associations) leading
to the word they are looking for (target word). In other words, look-up amounts to
navigation in a huge lexical-conceptual space and is not necessarily a one-shot proc-
ess.
Suppose, you were looking for a word expressing the following ideas: superior
dark coffee made from beans from Arabia, and that you knew that the target word
was neither espresso nor cappuccino. While none of this would lead you directly to
the intended word, mocha, the information at hand, i.e. the word’s definition or some
of its elements, could certainly be used. In addition, people draw on knowledge con-
cerning the role a concept (or word) plays in language and in real world, i.e. the asso-
ciations it evokes. For example, they may know that they are looking for a noun
standing for a beverage that people take under certain circumstances, that the liquid
has certain properties, etc. In sum, people have in their mind an encyclopedia: all
words, concepts or ideas being highly connected. Hence, any one of them has the
potential to evoke the others. The likelihood for this to happen depends, of course, on
factors such as frequency (associative strength), distance (direct vs. indirect access),
prominence (saliency), etc.
How is this supposed to work for a dictionary user? Suppose you wanted to find
the word mocha (target word), yet the only token coming to your mind was Java
(source word). Starting from this input the system would build internally a graph with
Java at the center and all the words connected to it at the periphery. The graph would
4
Bear in mind that I am dealing here only with the productive side of language : speak-
ing/writing.
43

be built dynamically depending on the demand. If the list contains the target word,
search stops, otherwise navigation continues, taking either one of the proposed candi-
dates as the new starting point or a completely new token.
Of course, one could also have several associations (quasi) simultaneously, e.g.,
‘black, delicious, strong, coffee, beverage, cappuccino, espresso, Vienna, Starbucks,
espresso...’ in which case the system would build a graph representing the intersec-
tion of the associations (at distance 1) of the mentioned words.
Obviously, the greater the number of words entered and associated to a source
word, the more complex the graph will be. As graphs tend to become complex, they
are not optimal for navigation. There are at least two factors impeding readability:
high connectivity (great number of links or associations emanating from each word),
and distribution (conceptually related nodes, that is, nodes activated by the same kind
of association, do not necessarily occur next to each other, which is quite confusing
for the user). This being so, I suggest to display by category (chunks) all the words
linked to the source word. Hence, rather than displaying all the connected words as a
huge flat list, I suggest to present the words in hierarchically organized clusters, the
links of the graph, becoming the nodes of the tree. This kind of presentation seems
clearer and less overwhelming for the user, allowing for categorical search, which is a
lot faster than search in a huge bag of words, provided that the user knows which
category a word belongs to.
7 Discussion and Conclusion
Obviously, in order to allow for this kind of access, the resource has to be built ac-
cordingly. Hence several problems have to be solved: (a) words have to be indexed
by the associations they evoke, (b) the most frequent/useful associations have to iden-
tified and labeled; (c) the strength of the links must be quantified.
5
This is precisely
my goal. Actually, I propose to build an associative network by enriching an existing
electronic dictionary (essentially) with an index based on (syntagmatic) associations
retrieved from a corpus, representing the average citizen's shared, basic knowledge of
the world (encyclopedia). To this end, I suggest to run a collocation extractor on a
well-balanced corpus.
As we can see, associations are very general and powerful mechanisms, and if the
very notion is age-old,
6
its use to support word access via computer is clearly new.
While we have shown elsewhere (Zock & Fournier, 1991) how words can be ac-
cessed on the basis of their spoken or written form, we have tried to deal here with
word access based on syntagmatic links, a neglected feature in WN. More details
concerning the envisaged strategies and the problems likely to arise when building
semi-automatically the associative network can be found in (Zock & Bilac, 2004).
Even though the work presented here is still at a very early stage and confined to a
5
Ideally, the weight should be (re-)computed on the fly to take into account contextual varia-
tions. The same word (Java) may evoke quite different associations depending on the context
(coffee vs. programming).
6
It amounts at least to Aristotle, 350 before JC.
44

very specific task, it has the potential to go well beyond word access: information
access by and large, brainstorming and subliminal communication, to name just these.
A dictionary is a vital component for any system processing language, be it natural
or artificial. There is hardly any task that we can do without it. Yet, what for an out-
sider seems to be one and the same object, turns out to be something very different
viewed by an insider. Indeed, the content, structure (organization) and navigational
properties of the resource, i.e. dictionary, vary considerably with the task (analysis vs.
synthesis), time constraints (spontaneous, speech production; written text production),
the nature of the information processor (man vs. machine) and the material support of
the data (brain, paper, computer). The goals of this paper were twofold: (a) to show
how different the resource (and its usage) can be depending on the way language is
produced: automatic generation by computer, spontaneous discourse production (the
speaker relying on his mental lexicon), or planned text-production, i.e. writing: an
author making use of an existing electronic resource; (b) to illustrate how an existing
electronic dictionary could be enhanced by adding an association-based index to
assist the language producer (writer).
I have looked at the dictionary only from the language producer’s point of view
for two reasons: space constraints and practical concern. People searching for infor-
mation regarding meanings or spelling are generally quite well served with alphabeti-
cally organized dictionaries, in particular if the resource is electronic, as it alleviates
the problem of misspelling. The way a dictionary is built depends, of course, crucially
on its ultimate usage; yet, this latter has to be anticipated. It seems to me that we have
missed a chance by not taking care to look over the dictionary users’ shoulders for
insights. Doing so would certainly be beneficial not only for the builders of the re-
source, but also for psychologists, as it shows them in slow motion what people are
doing and looking for. What can we ask for more?
References
1. Aitchinson, J.; (2003): Words in the Mind: an Introduction to the Mental Lexicon. Oxford,
Blackwell.
2. Baddeley, A. (1982) Your memory: A user's guide. Penguin
3. Bateman, J. ; Zock ; M. (2003) Natural Language Generation. In: R. Mitkov (Ed.) Hand-
book of Computational Linguistics, Oxford University Press. 284-304
4. Brown R.; McNeill, D. (1996). The tip of the tonuge phenomenon. In: Journal of Verbal
Learning and Verbal Behaviour, 5:325-337.
5. Burke, D.M.; MacKay, D.G.; Worthley, J. S.; Wade, E. (1991): «On the Tip of the Tongue:
What Causes Word Finding Failures in Young and Older Adults?». In: Journal of Memory
and Language 30, 542-579.
6. Cahill, L.; Reape, M. (1999). Lexicalisation in applied NLG systems. Brighton, ITRI: 9.
7. Collins, A.; Quillian, L. (1969) Retrieval time from semantic memory. Journal of Verbal
Learning and Verbal Behavior, 8, 240-247
8. Cumming, S. (1986). The Lexicon in Text Generation, ISI: 86-168.
9. Cutler, A. (Ed.) (1982). Slips of the Tongue and Language Production. Amsterdam: Mou-
ton
10. Dell, G.S. (1986): A spreading-activation theory of retrieval in sentence production. Psy-
chological Review, 93, 283-321.
45

11. Fellbaum, C. (1998). WordNet: An Electronic Lexical Database and some of its Applica-
tions. MIT Press.
12. Fromkin, V. (ed.) (1973): Speech errors as linguistic evidence. The Hague: Mouton Pub-
lishers.
13. Goldman N. (1975). Conceptual Generation, in Schank, R. (ed.): Conceptual Information
Processing, North Holland.
14. Hanks, P.; J. Pustejovsky. (2005). ‘A Pattern Dictionary for Natural Language Processing’
in Revue française de linguistique appliquée 10 (2)
15. Kempen, G.; Huijbers, P. (1983): The lexicalization process in sentence production and
naming: Indirect election of words. Cognition, 14, 185–209.
16. Levelt, W. (1992). Accessing Words in Speech Production: Stages, Processes and Repre-
sentations. Cognition 42: 1-22.
17. Levelt, W.J.M., Roelofs, A., Meyer, A.S. (1999): A theory of lexical access in speech
production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22, 1-75.
18. Marslen-Taylor, W. (Ed.) (1979) Lexical Representation and Process, Bradford book, MIT
Press, Cambridge, Mass.
19. Mel’čuk I., Clas A., Polguère A. (1995) : Introduction à la lexicologie explicative et com-
binatoire. Louvain, Duculot.
20. Miller, G.A. (ed.) (1990): WordNet: An On-Line Lexical Database. International Journal of
Lexicography, 3(4), 235-244.
21. Nogier, J.F.; Zock, M. (1992). Lexical choice by pattern matching. In Knowledge Based
Systems, 5 (3), pp. 200 - 212
22. Quillian, R. (1968). Semantic memory. In M. Minsky (ed.) Semantic Information Process-
ing, The MIT Press. Cambridge, MA., 216–270.
23. Robin, J. (1990). A Survey of Lexical Choice in Natural Language Generation, Technical
Report CUCS 040-90, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Columbia
24. Roelofs, A. (1992). “A spreading-activation theory of lemma retrieval in speaking.” Levelt,
W. (ed.) Special issue on the lexicon, Cognition, 42: 107-142.
25. Sharoff, S. (2005). The communicative potential of verbs of ‘away-from’ motion in English
and Russian. Functions of Language, 12:2, 203-238.
26. Smith, E., Shoben, E. & Rips, L. (1974) Structure and process in semantic memory: a
featural model for semantic decisions. Psychological Review, 81, 214-241
27. Stede, M. (1995). Lexicalization in Natural Language Generation: a survey. Artificial
Intelligence Review 8. pp. 309-336
28. Stemberger, N. (1985) The Lexicon in a Model of Speech Production. Garland, New York.
29.
Vigliocco, G.; Antonini, T.; Garrett, M. F. (1997): Grammatical gender is on the tip of
Italian tongues. Psychological Science, 8, 314-317.
30. Wanner, L. (1996). Lexical Choice in Text Generation and Machine Translation. Special
Issue on Lexical Choice. Machine Translation. L. W. (ed.). Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic
Publishers. 11: 3-35.
31. Ward, N. (1988). Issues in Word Choice. COLING-88, Budapest.
32. Zock, M. (1996): The Power of Words in Message Planning, COLING, Copenhagen, 990-
5, http://acl.ldc. upenn.edu/C/C96/C96-2167.pdf
33. Zock, M.; Fournier, J.P. (2001). How can computers help the writer/speaker expe-riencing
the tip-of-the-tongue problem ? In: Proc. of RANLP, 300-302.
34. Zock, M; Bilac, S. (2004). Word lookup on the basis of associations: from an idea to a
roadmap. Proc. of Coling workshop: Enhancing and using dictionaries, Geneva, 29-35.
46
