
An Ontology Based Architecture for Integrating
Enterprise Applications
Razika Driouche
1
, Zizette Boufaїda
1
and Fabrice Kordon
2
1
Lire laboratory, Department of Computer Science, Mentouri University
of Constantine, 25000, Algeria
2
LIP6 Laboratory, Pierre & Marie Curie University, 4, Place
Jussieu, 75252, Paris Cedex 05 France
Abstract. Today, companies investigate various domains of collaborative busi-
ness-to-business e-commerce. They have to look inward to their applications
and processes. These applications must be able to cooperate dynamically. This
leads to a rise of cooperative business processes, which need the integration of
autonomous and heterogeneous applications. However, currently existing ap-
proaches for application integration lack an adequate specification of the se-
mantics of the terminology that leads to inconsistent interpretations. In this pa-
per, we propose a formal solution to the problem of application integration and
we reflect upon the suitability of the ontology as a candidate for solving the
problem of heterogeneity and ensure greater interoperability between applica-
tions.
1 Introduction
The integration of information, business processes, workflows and various applica-
tions across companies is seen as a viable solution in order to cross organisations and
market boundaries and hence enable application deployment in a wide variety of
domains, ranging from e-commerce to e-Science Grid projects. As the field of B2B
(Business-to-Business) e-commerce grows, we need the question on how enterprises
work with their suppliers, customers and other trading partners. This frequently en-
tails the building of new applications by coupling existing ones. This is known as
EAI (Enterprise Application Integration). EAI addresses the need to integrate both
intra and inter-organizational systems through functionalities from different applica-
tions. It supports an efficient incorporation of IS (Information Systems) into business
domain [1].
The problem of application integration is already complex due to diverse require-
ments and heterogeneity of data, processes and applications. Heterogeneity may ex-
hibit in the use of different programming languages, availability on different hard-
ware and operating system platforms. In addition, the heterogeneity emerges in the
use of various representations for the exchange of data the use of different approaches
Driouche R., BoufaÑ
˚
Uda Z. and Kordon F. (2006).
An Ontology Based Architecture for Integrating Enterprise Applications.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Modelling, Simulation, Verification and Validation of Enterprise Information Systems, pages 26-37
DOI: 10.5220/0002493000260037
Copyright
c
SciTePress

for modeling applications. However, these applications were not developed to be
integrated. They were created independently and thus; do not share the same seman-
tics for the terminology of their applications models. This lead to inconsistent inter-
pretations.
In our context, integration is the process of linking heterogeneous applications, to
make a unit complete and confers to it properties related to the interoperability and
the coherence of IS. Many attempts have been made to integrate different IS. In most
approaches, the remaining problems are still twofold. They are developed for specific
business sectors and they do not cope with the challenge of incorporating semantics
into applications [5][6][10]. An architecture based on an ontology is often seen as
new solution providing exchange facilities of semantically enriched information. It
supports mapping process for integrating local ontologies related to heterogeneous
and distributed applications. For us, ontologies should be used for two main reasons:
first, for modelling the application’s structure and behaviour in a precise and rigorous
way and second, for representing vocabularies and providing semantic rules of map-
ping in order to integrate enterprise applications [6].
In this paper, we propose an architecture for applications integration having two
levels: applicative and collaborative ones. This architecture is based on a mapping
approach to bridge applications ontologies. It supports several heterogeneous applica-
tions accessing multiple local ontologies. A component, named mapper, generates a
global ontology for managing the enterprise information heterogeneity based on the
semantic bridges concept. A semantic bridge encapsulates all required information to
translate instances of the source entity to instances of the target entity. So, the inte-
grated applications can successfully and efficiently communicate and exchange in-
formation as well as services.
The structure of the paper is as follows: section 2 presents some characteristics of
the EAI domain, interoperability and ontology. In section 3, we address some related
work. Section 4 shows more details on our architecture, gives a description of the
mapper for bridging the application ontology and its main components. Then, section
5 describes our application integration process based on UML class diagram and the
description logic formalism. Section 6 concludes our paper and sketches some future
work.
2 An Overview of EAI, Ontology and Semantic Bridge
Integration is now seen as a challenge of the information and communication tech-
nology field. It is a new research area and many related issues are still under investi-
gation. EAI is the process of adapting a system to make distributed and heterogene-
ous applications work together to carry out a common objective [2]. In companies,
the essential requirement for heterogeneous and distributed IS is to be able to ex-
change information and services with other ones in a semantically rich and sound
way. Thus, semantics should be captured, verified and used to validate reliable infor-
mation exchange. This is commonly referred to as the problem of interoperability.
Ontology is an appropriate way to enable interoperability. It includes an explicit de-
27

scription of both a domain structure and the related terms describing this domain. It
allows applications to agree on the terms they use when communicating.
The main purpose for building the application ontology is to capture information
about the application structure, behaviour and domain. This information will allow us
to elaborate a communication framework. The latter aims to support data interchange
and communication processes. One important step in this direction is the reuse of the
mapping information based on semantic bridge to enhance the system requirements.
Semantic bridges are appropriate and useful to represent ontology mapping. A se-
mantic bridge considers different dimensions, each one describing a particular aspect
[3]:
- Entity: this dimension reflects the type of ontology entities being bridged (e.g.
classes, properties and relations).
- Cardinality: this dimension reflects the number of ontology entities being bridged
(1:1, 1:n, n:m).
- Structural: this dimension reflects the way whose the elementary bridges may be
combined into more complex bridges (specialized, abstract, composed or alterna-
tive bridges).
- Constraint: this dimension reflects constraints applied during the execution phase
to instances from the source ontology.
- Transformation: this dimension reflects how the instances of source ontology are
translated during the mapping process.
In our work, it is still necessary to take into account the fact that the addition of a
new application will require a constant process of integration so that ontology re-
mains adapted to the enterprise evolution.
3 Related Work
Much research has been done in the area of ontology integration with specific focus
on the heterogeneity. Solving this problem in ontologies is therefore a desirable goal
for many integrating approaches. Heterogeneity can be broadly distinguished into
non-semantic (syntactic) and semantic. Syntactic heterogeneity denotes the difference
between the language primitives that are used to specify ontologies, while semantic
heterogeneity denotes differences in the way that the domain is conceptualised and
modeled. Mismatches caused by semantic heterogeneity occur when combining on-
tologies, which describe domains that partially overlap. Semantic heterogeneity oc-
curs when there is a disagreement about the meaning and the interpretation of the
information [7]:
− Different names for the same content (e.g. synonym, for instance client and cus-
tomer).
− Different value domains (for instance different measures of temperature Fahren-
heit/Celsius, hours/minutes).
− Different abstraction levels (e.g. generic terms vs. more specific ones, for instance
name vs. first name and last name).
− Different structures about the same contents (e.g. type or part of a type, for exam-
ple date vs. day, month and year).
28

Numerous approaches for ontologies integration can be identified [4], [5], [6],
[10], [12]. In the single ontology approach, a global one provides a shared global
ontology to specify the semantics. All information sources are related to the global
ontology i.e. they are unified. The global ontology can be a combination of modular-
ised sub ontologies [10]. This approach increases considerably the maintenance tasks
if there are modifications in the local ontologies. In the multiple ontology approach,
each information source has its own local ontology that can be developed independ-
ently. To integrate them, the ontologies must be brought together by finding a set of
mapping rules between them, alignment of concepts and relations to indicate equiva-
lence [4],[12] or by translating one ontology into another one [5]. In the hybrid ap-
proach, the basic features of the two other approaches are combined. The global on-
tology is obtained by merging the existing ontologies in a common one that includes
all aspects of the individual ontologies [6]. The only really realistic possibility is the
mapping approach because in this case the integrated ontologies are not affected.
4 Application Integration Architecture
In the system, we identify several types of legacy, client/server and Web applications,
developed using different programming languages. They work on different operating
system platforms and use various format for the exchange of data. By using applica-
tion ontologies, we enhance communication between applications, for the benifit of
integration. Hence, ontologies serve as stable basis for understanding the require-
ments for the user applications.
The integration system we propose aims at offering a support for integrating het-
erogeneous and distributed applications, accessing multiple ontologies (Fig. 1). It
provides a communication framework as a central service. It permits an appropriate
exchange of information between applications ontologies and generates the global
one. The introduced framework tries to enhance the ontology mapping which enables
the reuse of mapping information for managing heterogeneity. The integration proc-
ess is based on the semantic bridges to indicate the semantic equivalence of ontology
entities for assembling them. These applications are linked seamlessly to partners,
vendors and suppliers through a common interface.
Furthermore, we give an overview of the two-level approach for application inte-
gration, the applicative level and the collaborative one:
− Applicative level consists of heterogeneous and distributed applications. Each ap-
plication has its own local ontology. Our important direction is the development of a
communication framework for ontology mapping. In our architecture, we aim to
overcome the gap between local ontologies application, according to the semantic
relations. A special component, named mapper, is invoked to perform its tasks for
building the global ontology. The latter can be seen as an enterprise ontology and
permits the resolution of semantic conflicts in both concepts and attributes.
− Collaborative level takes place in the business process collaboration with partners.
Each company has a mobile agent selecting the best partner basing itself on criteria
(e.g., price limits, product configurations or delivery deadlines) and using its collabo-
ration scenario for achieving business process. The mobile agent permits to perform
29
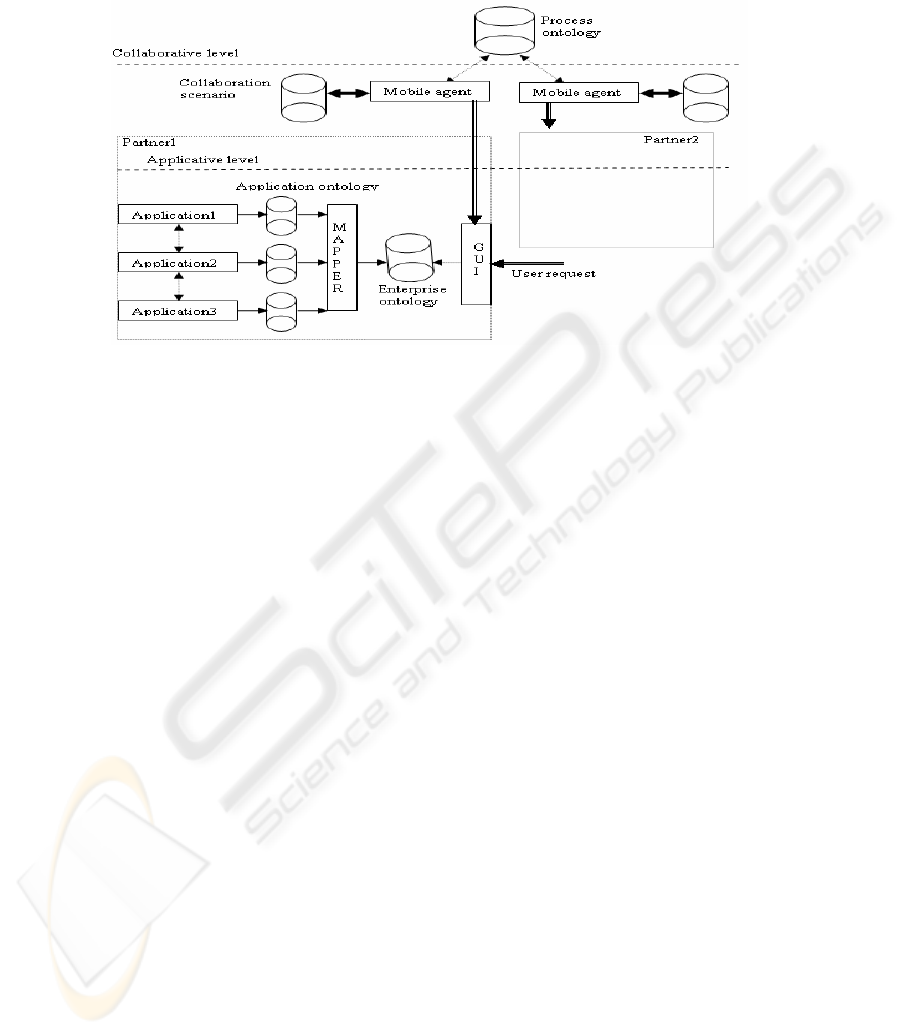
the integration tasks according to a process ontology and using an optimized itinerary.
The latter improves the performance of the system and reduces the response time.
Fig. 1. Integration system architecture.
Further components of the architecture are the collaboration scenario and the proc-
ess ontology. The latter includes information about the business processes, the organ-
izational constraints, the customer profile and the business constraints. Collaboration
scenario are inspired from the ebXML (electronic-business XML) [3] for providing
an interoperable framework.
The focus of this paper is on the applicative level as well as building and integra-
tion of the application ontologies. Additionally, an overview of the mapper compo-
nent is given in the following. The mapper component has four parts:
− The identifier is used to discover the related concepts or attributes of ontologies and
the relations between them. This can be done automatically or manually with the help
of domain experts. For instance, it can use lexical ontologies such as WordNet or
domain specific thesauri to define the synonym and the antonym relations [8].
− The adaptor is used to represent the identified equivalence relations between on-
tologies based on the semantic bridges. It combines many algorithms to measure the
similarity. It adopts a multi-strategy approach to calculate the concepts similarity in
various levels, such us lexical, properties (role and attributes), hierarchical and in-
stances similarities. Then, the adaptor checks domain and cardinality inclusion.
− The linker transforms instances from the source application ontology into instances
of the target application ontology by evaluating the equivalence relations defined
earlier by the adaptor. The missing mappings can be gained through inference
mechanism.
− The communicator is used to enhance the communication between global ontology
(enterprise ontology) and local ones (application ontologies). It is responsible for
information exchange to answer the user request using the appropriate mapping. It
translates the query sent by the user to an equivalent one. This is done by using the
30

mapping information in order to facilitate the query interpretation, according to the
concepts of the concerned application ontology.
5 Application Integration Process
Application integration process based on ontologies is a new approach that has rap-
idly been developed with the emergent Semantic Web [2]. This is mainly due to the
fact that ontology is the best way to enhance interoperability and integration of het-
erogeneous applications. We propose a process for integrating the applications that is
characterized by the iteration in order to consider the addition of a new application
and the evolution of company requirements and market criteria. The proposed process
is divided into four basic steps: capturing, building, integrating and exploiting.
The suggested process is doted by two sub-processes, essential for ontologies
building and integration. The first one is building the applications ontologies follow-
ing many steps, from meta-modeling to implementation. The second one is the inte-
gration of ontologies in order to better obtain the enterprise ontology. Our process is
complete, i.e., starting from collecting the applications needs and ending at a global
ontology.
5.1 Capturing Requirements
A company model is a computational representation of the structure, activities, proc-
esses, information, resources, people, behaviour, goals and constraints of the busi-
ness. This step consists of taking note of the field of integration while identifying the
applications behaviour as well as the relations which they maintain between them.
The purpose of this step is to capture the sets of applications of the enterprise, the
activities that they perform, the resources required by these activities, the manipulated
data and the messages invoked them. Then, we identify the flows of information, their
structure and the technical infrastructure to support them. To develop the correspond-
ing ontologies, we make this information available to the designers. This step is car-
ried out by the industrial specialists that are expert in the market domain.
5.2 Building the Application Ontology
A range of methods and techniques have been reported in the literature regarding
ontology building methodologies [15]. Mike Uschold’s methodology [16], Michael
Grüninger and Mark Fox’s methodology [17] and Methontology [18] are the most
representative. Grüninger methodology is only limited to ontologies using first-order-
logic languages [2]. Uschold’s and Methondology have a common that they start
from the identification of the ontology purpose and the need for domain knowledge
acquisition. Uschold proposes a codification of knowledge in a formal language. In
Methondology, a set of intermediate representations independent of the formal lan-
guage to be used is expressed. For our purpose, we have chosen the UML language
31
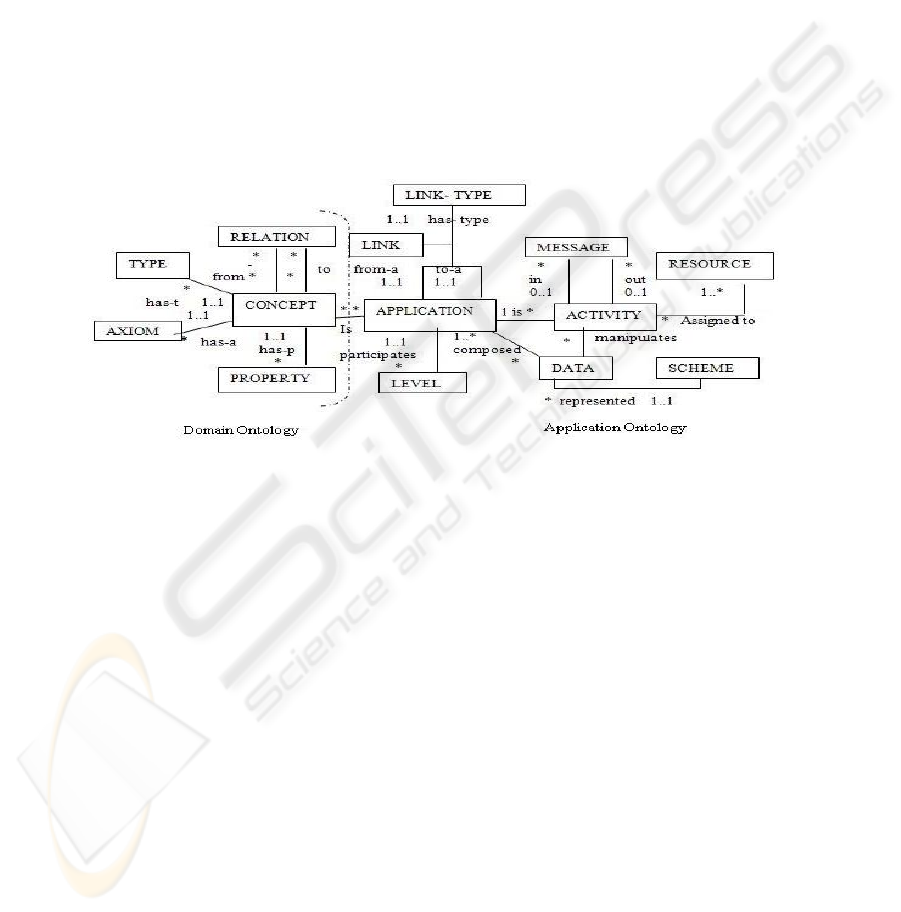
[3] to represent the concepts hierarchy and how they are related. So, the UML class
diagram is used as a meta-model of the application ontology.
Meta-Modeling Application. Let us notice that we retain the logical structure in
layers where each application is made up of data and the activities managed by a user
interface. The concepts of the application ontology are represented as a set of UML
[3] class diagram in Fig. 2. UML is a good and a powerful modeling language for
designing object oriented applications. Ontologies include class/subclass hierarchies,
relationships between classes, class attribute definitions and axioms that specify con-
straints. This information is usually modeled in class diagram, the reason why UML
is a promising notation for ontologies. Our ontology makes it possible to offer on the
one hand, a framework of meta-modeling the applications to be integrated and on the
other hand, an intelligent layer used to manage semantics related to the various con-
cepts used.
Fig. 2. Meta-model of application and domain ontologies.
The domain ontology gives a formal representation of concepts of the studied do-
main as well as their relations. However, the domain ontology cannot describe spe-
cific fonctionnality and the differences between different applications in a given do-
main. It attempts to find the set of concepts covering the domain. In our work, we are
considering business enterprises which provide products and services for partners and
potential customers. We identify two overlap domains, sale and purchase.
Let us give a description of the concepts of the application ontology (Ont):
Ont = (Link-type, Level, Activity, Data, Concept, Relation, Type, Axiom, Property,
Resource, Message, Scheme)
− Link-type. It is a concept that describes some characteristics of the application re-
lated to other applications. It includes partner collaboration, data sharing and service
exchanging.
− Level. This concept shows the level where application participates to answer cus-
tomer/partners needs, collaborative and/or applicative.
32

− Activity. This concept captures all functionalities that the application can do. It
contains the activity properties such as : message in / message out, pre-condition,
activity type, sub-activities, time-begin, time-end and resource assigned.
− Data. This concept includes the local/global data manipulated by the application,
like type, access right and schema.
Let us remark that starting from the diagram of class (Fig. 2.), the instantiation will
vary according to applications. In particular, each application can have its own activi-
ties, its data and the role to play in the company.
Formalization. The formalization implies the representation of the ontology in DL
(Description Logic) formalism [13]. We consider the SH [12] family of DL as
equivalent to the ALC DL [12], extended with transitive properties and property
hierarchy. The latter is important for OWL (Ontology Web Language) [12] as it is a
feature of RDFS ( Resource Description Framework Schema) [9]. Members of the SH
family include the SHOQ(D) DL. This language has the ability to define a class by
enumerating its instances and support for datatypes and values. Because OWL
includes datatypes, the semantics for OWL is very similar to that of DL that also
incorporate datatypes, in particular SHOQ(D). We use it to describe the concepts and
the roles represented in the UML diagram (Fig.3.). We illustrate in capital letter the
concepts and in minuscule the roles. For the SHOQ(D) constructors [24], atleast and
atmost show the min and max cardinality, inverse means the inverse role. We give
some rules related to the meta-model in Fig 2.
CONCEPT :< ( all has-a AXIOM)
AXIOM:< (all (inverse has-a ) CONCEPT)
CONCEPT :< ( all has-p PROPERTY)
PROPERTY:< (all (inverse has-p ) CONCEPT)
CONCEPT :< ( all has-t TYPE)
TYPE:< (all (inverse has-t ) CONCEPT)
CONCEPT :< ( all from RELATION)
RELATION:< ( all (inverse from) CONCEPT)
CONCEPT :< (all to RELATION)
RELATION:< ( all (inverse to ) CONCEPT)
APPLICATION:< (all (inverse is1 ) CONCEPT)
APPLICATION:< (all participates LEVEL)
LEVEL :< (all ( inverse participates ) APPLICATION)
APPLICATION:< (all composed DATA)
DATA :< (all(inverse composed ) APPLICATION)( atleast 1 (inverse composed))
APPLICATION:< (all is ACTIVITY)
ACTIVITY:< ( all ( inverse is) APPLICATION)
APPLICATION:< (
all from-a LINK-TYPE)
APPLICATION:< (all to-a LINK-TYPE)
LINK-TYPE :<(all (inverse has-type) LINK-TYPE)
Implementation and Test. The implementation deals with building a computable
model. The effort is concentrated on the suitability of the OWL DL [9] which is
33

equivalent to the SHOQ(D) [9]. For checking, we need to use the inference services
provided by many systems such as FACT [9], RACER [10] and DLP [9]. These sys-
tems have shown to work well in realistic applications and to be able to reason with
large ontologies. The use of the RACER system can make possible to read OWL file
and to convert it in the form of a DL knowledge bases. It can also provide inference
services. To manipulate the application ontology, PROTEGE-2000 [21] offers a con-
vivial graphical user interface.
Adaptation and Evolution. Ontologies may change over the time or may be adapted
for applications specific needs. Therefore, mechanisms which can discover changes
recognize different versions are required (e.g. PROMPT, [7]). Ontology versions may
not be compatible with each other. So, information must be available to facilitate
discovering changed ontologies. OWL provides some built-in constructs to mark
version compatibilities.
For managing the evolution of ontology, a classification takes place once a defini-
tion of concept is newly created. For this purpose, we propose the use of the DL clas-
sification algorithm.
5.3 Integration of Applications Ontologies
In order to achieve an ontology-based semantic integration, we propose a sub-process
that includes several main tasks: comparison, bridging and inference.
− Comparison consists of comparing each ontology concept A with each ontology
concept B and of determining a similarity metric. We adopt a multi-strategy process
[4] which computes similarities between ontology entities using different algorithms.
Using just one approach is unlikely to achieve as many good mapping candidates as
one we combine several approaches. The first one focuses on acquiring a lexical
similarity. The next step computes the so-called property similarity that is responsible
to acquire the similarity between concepts based on their properties, either attributes
or relations. Then, we propagate the similarity to other parts of the taxonomy, the
super and the sub-concepts. Then, we check domain and cardinality inclusion.
− Bridging is responsible to establish correspondence between entities based on the
similarities computed previously. Each instance represented according to the source
ontology is translated into the most similar instance described according to the target
ontology. It intends to associate a transformation procedure to the translation.
− Inference mechanism is used when the source concept has not a target concept,
which means the source concept has not a direct counterpart in the target ontology.
Example. Let us consider a small part of two different ontologies (cf. Fig 4). The first
ontology (O1) describes a sale application (Activity: receive order goods, check
availability, make payment; Data: customer, product, facture). The second one (O2)
characterizes a business application using a very simple approach (sale, purchase).
First, the mapping must define the two ontologies being mapped. We start with the
sale-marketing bridge.
< Mapping rdf : ID= “ mapping”>
34

<relatesSourceOntology rdf: resource=”&O1 ;”/>
< relatesTargetOntology rdf: resource=”&O2 ;”/>< has Bridge rdf: re-
source=”# Sale-Marketing”/>
</Mapping>
We present the semantic bridge between source concept, product and target con
cept, article:
<bridges: One2One ConceptBridge rdf : ID =”product- article”>
<bridges : relatesSourceEntity rdf: resource= “&so; product”/ >
<bridges : relatesTargetEntity rdf :resoure“&article”/>
<bridges: accordingToTransformation rdf : resource =”&serv; construct”>
<bridges : hasBridge rdf : resource=
“# productconcern-Marketingapplication_ in check local stock activity”/>
<bridges : hasBridge rdf : resource=
“# productconcern-Marketingapplication_ in delivery activity”/>
</bridges: One2One ConceptBridge>
Composition relation Semantic bridge link
Fig. 3. Example of two application ontologies.
Protégé [21] is an open source ontology development environment with functional-
ity for editing classes, slots (properties) and instances. The current version of Protégé
(3.1.1) is highly extensible and customizable. We have used it for developing the two
ontologies find in the example. Actually, we focus on the OWL build-in constructs to
build the global ontology. For the mapping process, the most interesting build-in of
OWL is owl: sameAs, which is used to specify that two entities identified by an URI,
refer to the same individual. Classes can be treated as instances, owl: sameAs, can
also be used to define class equality, thus indicating that two concepts are equivalent.
5.4 Exploitation
This step deals with the realization of the computational model of integration, which
makes it possible to link the enterprise applications. Once the system is deployed, it
remains us that to maintain the technical infrastructure of integration. Furthermore,
this step covers the exploitation of the integration system. This function is not limited
by time. It is necessary to address the evolutions of the enterprise (e.g. integration of
a new application) and to manage the ontology versions.
35

6 Conclusion and Perspectives
The problem dealing with heterogeneity, even semantic has been deeply investigated
in the field of ontology.
We proposed an ontological approach for integrating company applications. This
approach enhances application integration at both applicative and collaborative levels.
For the first one, we called upon the mapping process based on the semantic bridges
for integrating local ontologies. For the second one, we give more attention to the
partners’ collaboration using common process ontology and mobile agents for ensur-
ing interoperability. The important benefit of our work is that the communicator can
reuse the mapping information for managing interaction between applications.
We are currently developing local and global ontologies basing on the mapping
process and facilitating the exchange between them through the communication com-
ponent. We intend to design the process ontology and evaluate the approach in the e-
business domain.
Future work will focus on the development of the collaborative level. Our atten-
tion is related to the ebXML [3] collaboration scenario in order to offer an interoper-
able infrastructure for business collaboration. Furthermore, the ebXML collaboration
scenario will be extended by mobile agents in order to search the appropriate partners
and negotiate business parameters (product price, delivery time, …). For application
ontologies, we can address some perspectives: (i) experimentation to validate the
integration process; (ii) using the framework MAFRA [4] to support the application
integration; (iii) improving concepts and properties similarities basing on semantic
aspects.
References
1. Themistocleous, M., Irani, Z., Kuljis, J., Love, P.: Extending the information system life-
cycle through enterprise application integration: a case study experience. In: Pro. of the 37
th
International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii (2004)
2. Linthicum, D., S.,. (ed.): Next generation application integration. , Addison-Wesley, (2004)
3. Chauvet, J., (ed.) : Services Web avec SOAP, WSDL, UDDI, ebXML. Eyrolles (2002)
4. Maedche, A., Motik, B., Silva, N., Volz, R. : MAFREA : A MApping FRAmework for
Distributed Ontologies in the Semantic Web. In: Proc. Of the ECAI Workshop Knowledge
Transformation, Lyon, France (2002)
5. Chalupsky, H.: OntoMorph: A Translation System for Symbolic Knowledge. In: Pro of
the Seventh International Conference of Principles of Knowledge Representation and Rea-
soning, San Francisco, USA (2000)
6. Dou, D., Mcdermott, D., Qi, P.: Ontology Translation by Ontology Merging and Auto-
mated Reasoning. In: Pro. of the EKAW, Workshop on Ontologies for Multi-Agent Sys-
tems (OMAS), Spain (2002) 3-18
7. Gahleitner, E., Wob, W.: Enabling Distribution and Reuse of Ontology Mapping Informa-
tion for Semantically Enriched Communication Services. In: IEEE. Computer Society, of
the 15
th
International Workshp on Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA),
Zaragoza, Spain (2004)
8. Hailstone, R.: Integrations Strategies: The Start of Convergence. IDC (2003)
36

9. Horrocks, I., Patel-Schneider, P., F., Harmelen, F., V.: From SHIQ and RDF to OWL: The
making of a web ontology language http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/Webont/charter, (2003)
10. Haarslev, V., Möller, R.: RACER System Description. In: Pro. of IJCAR-01, (2001)
11. Omelayenko, B.: Integrating Vocabularies: Discovering and Representing Vocabulary
Maps. In: Pro. of the First International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC), Springer, Sar-
dinia (2002) 206-220
12. Calvanese, D., De Giacomo, G., Lenzerini, M.: Ontology of Integration and Integration of
Ontologies. (2001)
13. Knublauch, H., Mugen, M., Rector, A.: Editing description logic ontologies with protégé
OWL plugin. In: DL’04, Workshop on Description Logic, Canada. (2004)
14. Rodriguez M., A., Egenhofer, M., J.: Determining Semantic Similarity Among Entity Class
From Different Ontologies. In: IEEE, Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.
(2003)
15. Lopez, M., F., Perez, A., G, Overview and Analysis of Methodologies for Building On-
tologies. In: Knowledge Engineering Review, 17(2), (2002)
16. Uschold, M., Grüninger, M.: Ontologies Principles Methods and Applications. In: Knowl-
edge Engineering Review, 11(2), June (1996)
17. Grüninger, M., Fox, M., S.: Methodology for th Design and Evaluation of Ontologies. In:
Pro of IJCAI Workshop on Basic Ontological Issues in Knowledge Sharing, Montreal
(1995)
18. Fernandez, M., Gomez-Perez, A., Juristo, N.: Methontology From Ontological Art Toward
Ontological Engineering, In: Spring Symposium Series on Ontological Engineering, AAAI,
Stanford, USA (1997)
19. Gruber, R., T.: A Translation Approach to Portable Ontology Specification. In: Knowledge
Acquisition, (5), (1993) 199-220
20. Borgida, A., Serafini, L.: Distributed Description Logics Assimilating Information from
Peer Sources. In: Journal of Data Semantics, (2003) 153-184
21. Protégé OWL, version 3.1.1, (2005). http://protege.stanford.edu.
37
