
MATCHING OF ENHANCED XML SCHEMAS WITH A
MEASURE OF STRUCTURAL-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
Amar Zerdazi and Myriam Lamolle
LINC – University of Paris VIII, IUT of Montreuil – 140, rue de la Nouvelle France, 93100 – Montreuil, France
Keywords: Heterogeneity, schema matching, semantic integration, XML schema.
Abstract: Schema matching is a critical step in integration of heterogeneous data sources. Recent integration work has
mainly focused on developing matching techniques to find equivalent elements among the different XML
sources. In this paper we propose a new approach to structural similarity measure based on the notion of
context, between entities of the Enhanced XML Schemas, called EXS. In our approach, the set of the EXS
schemas, are considered like a federation of XML schemas descended of different heterogeneous sources
schemas (relational, object, XML, etc.) and enriched by the semantic metaknowledge. We present here the
major problems bound to this crucial task, notably with regard to the semantic of schemas. So, we propose a
structural matching algorithm. The algorithm takes two schema graphs as input, and produces as output a
mapping between corresponding nodes of the schema graphs. After our algorithm runs, we expect a human
tolcheckiandiadjustitheiresults.
1 INTRODUCTION
Schema matching is a schema manipulation process
that takes as input two heterogeneous schemas and
possibly some auxiliary information, and returns a
set of dependencies, so called mappings that identify
semantically related schema elements (Rahm et
Bernstein, 2001). In practice, schema matching is
done manually by domain experts (Miller and al.,
2000), and it is time consuming and error prone. As
a result, much effort has been done toward
automating schema matching process. This is
challenging for many fundamental reasons.
According to (Drew et al., 1993), schema elements
are matched based on their semantics. Semantics can
be embodied within few information sources
including designers, schemas, and data instances.
Hence schema matching process typically relies on
purely structure in schema and data instances (Doan
and al., 2001). Schemas developed for different
applications are heterogeneous in nature i.e.
although the data they describe are semantically
similar, the structure and the employed syntax may
differ significantly (Abiteboul et al., 1997). To
resolve schematic and semantic conflicts, schema
matching often relies on element names, element
datatypes, structure definitions, integrity constraints,
and data values. However, such clues are often
unreliable and incomplete. Schema matching cannot
be fully automated and thus requires user
intervention, it is important that the matching
process not only do as much as possible
automatically but also identify when user input is
necessary and maximally used (Boukottaya et al.,
2004).
Consequently, a lot of work on schema matching
tried to automate this process. The main goal of this
paper is to propose a novel approach for structural
matching based on the notion of structural node
context. We propose a structural algorithm that can
be used for matching of Enhanced XML Schema,
called EXS. The EXS schemas, are considered like a
federation of XML schemas descended of different
heterogeneous schema sources (relational, object,
XML, etc.) and enriched by the set of semantic
metaknowledge. The algorithm that we suggest to
128
Zerdazi A. and Lamolle M. (2007).
MATCHING OF ENHANCED XML SCHEMAS WITH A MEASURE OF STRUCTURAL-CONTEXT SIMILARITY.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Internet Technology, pages 128-133
DOI: 10.5220/0001263801280133
Copyright
c
SciTePress

perform structural matching is based on the
following idea. The first step assigns for each node
in source and target schema a context. After what,
such context is compared to produce a node
similarity coefficient that reflects structural
similarity between schema nodes. The second one
uses produced node similarity to derive a set of
mappings.
The rest of paper is organized as follows. In
section 2, we summarize some examples of recent
schema matching algorithms that incorporate XML
structural matching. Section 3 gives a brief overview
of the Enhanced XML Schema (EXS), with his
schema graph (EXS graph). This graph is used in the
matching process for the measure of node context
similarity. Section 4 presents and discuses our
algorithms for structural contexts. Section 5
concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Schema matching is not a recent problem for the
community of databases. (Castano and De
Antonellis, 1999) developed the ARTEMIS system
employ rules that compute the similarity between
schemas as a weighted sum of similarities of
elements names, data types, and structural position.
With the growing use of XML, several matching
tools take into consideration the hierarchical and
deal essentially with DTDs. In the following, we
present some examples of recent schema matching
algorithms that incorporate XML structural
matching.
We do not present here of exhaustive manner all
existing systems for schema matching, but those that
appeared us interesting for the problematic that they
raise or for the considered solutions.
2.1 Cupid
Cupid is a hybrid matcher combining several
matching methods (Madhavan et al., 2001). It is
intended to be generic across data models and has
been applied to XML and relational data sources.
Cupid is based on schema comparison without the
use of instances. Despite these extensions, Cupid
does not exploit all XML schema features such as
substitution groups, abstract types, etc that could
give a significant clue in solving XML schema
matching problem.
2.2 LSD
The LSD (Learning Source Description) system
(Doan et al., 2001) uses machine-learning
techniques to match a new data source against a
previously defined global schema. LSD is based on
the combination of several match result obtained by
independent learners. This approach presents several
limitations since it does not fully exploit XML
structure. Besides, the only structural relationship
considered within the LSD system is the parent-
child relationship, which is not sufficient to describe
the context of elements to matcher.
2.3 Similarity Flooding
In (Melnik et al., 2002), authors present a structure
matching algorithm called Similarity Flooding (SF).
The SF algorithm is implemented as part of a
generic schema manipulation tool that supports, in
addition to structural SF matcher, a name matcher,
schema converters and a number of filters of
choosing the best match candidates from the list of
ranked map pairs returned by the SF algorithm. SF
ignores all type of constraints while performing
structural matching. Constraints like typing and
integrity constraints are used at the end of the
process to filter mapping pairs with the help of user.
2.4 SemInt
SemInt (Li and Clifton, 1994), (Li and Clifton,
2000) represents a hybrid approach exploiting both
schema and instance information to identify
corresponding attributes between relational
schemas. The schema-level constraints, such as data
type and key constraints are derived from the DBMS
catalog. Instance data are exploited to obtain further
information, such as actual value distributions,
numerical averages, etc. For each attribute, SemInt
determines a signature consisting of values in the
interval [0,1] for all involved matching criteria. The
signatures are used first to cluster similar attributes
from the first schema and then to find the best
matching cluster for attributes from the second
schema. The clustering and classification process is
performed using neural networks with an automatic
training, hereby limiting pre-match effort. The
match result consists of clusters of similar attributes
from both input schemas, leading to m:n local and
global match cardinality.
MATCHING OF ENHANCED XML SCHEMAS WITH A MEASURE OF STRUCTURAL-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
129
3 OUR SCHEMA
3.1 Enhanced XML Schema
The objective of our approach is to provide a
flexible integration model, capable to federate
different heterogeneous data sources while holding
in account the structural and semantic dimensions of
schema sources. For it, the definition of our model
must include a minimal number of entities to
manipulate but sufficient to translate schemas
(Lamolle and Mellouli, 2003), (Lamolle and
Zerdazi, 2005). We defined rules of extraction that
homogenise the representation of the different
schema sources to integrate while expressing them
under shape of XML-Schemas (XML-Schema,
2001). This phase is called structural modelling.
Once this transformation made, the semantic part of
the XSDi created is refined by the addition of
metaknowledge (Semantic modelling) (Zerdazi and
Lamolle, 2005), which are deducted (for instance,
the catalogue of data in the case of relational
databases), or are specified by the expert of the
domain.
3.1.1 Structural Modelling
The enhanced XML schema (noted EXS) as it is
modelled at the time of the first phase (structural
modelling) is composed of three types of entity.
Concept: a concept in the EXS schema is
equivalent to the notion of entity in an ER diagram,
a class in an object-oriented diagram or an element
in the semi-structured data model. He can generate
properties and/or include other concepts and having
relations with some concepts.
Relation: two concepts are connected via a
relationship. A relationship in EXS schema
represents a nesting relationship. Each relationship
has a degree and some constraints, and possesses
also a predefined category and other
metaknowledge.
Property: a property in the EXS schema is
equivalent to the notion of attribute in the relational,
object-oriented or the semi-structured data model. A
property can be a property of a concept or property
of a relationship.
3.1.2 Semantic Modelling
The semantic enrichment phase follows the phase of
structural modelling of the EXS schemas. The
semantic dimension of entities (concepts, relations,
and properties) is enriched by the contribution of
metaknowledge at the time of a survey more
deepened of the entity state (structure, completeness,
level of encapsulation, type of association,
constraints on properties, cardinality, etc.). These
metaknowledge are used at the time of the
integration phase in order to get more precise
correspondences between EXS schema. The
semantic enrichment consists in spreading the
structure of entities (concepts, relations, properties)
via attributes and facets.
3.2 EXS Schema Graph
We model an EXS schema as a directed labelled
graph with constraint sets. An EXS schema graph
consists of series of nodes that are connected to each
other through directed labelled links. In addition,
constraints can be defined over nodes and links
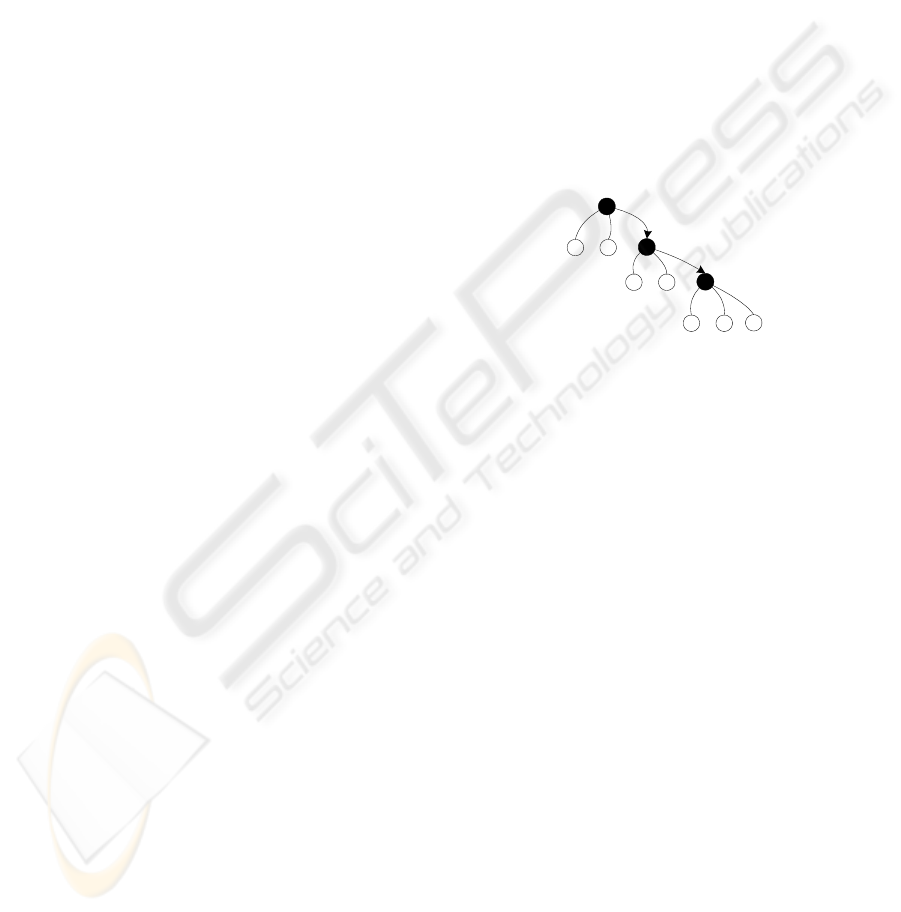
(Zerdazi and Lamolle, 2006). Figure 1 illustrates a
schema graph example.
Figure 1: An EXS schema graph example.
4 STRUCTURAL MATCHING
ALGORITHMS
In this paper, we focus on understanding, modelling
and formalizing the problem of structural XML
schema matching. The scope of this paper, in the
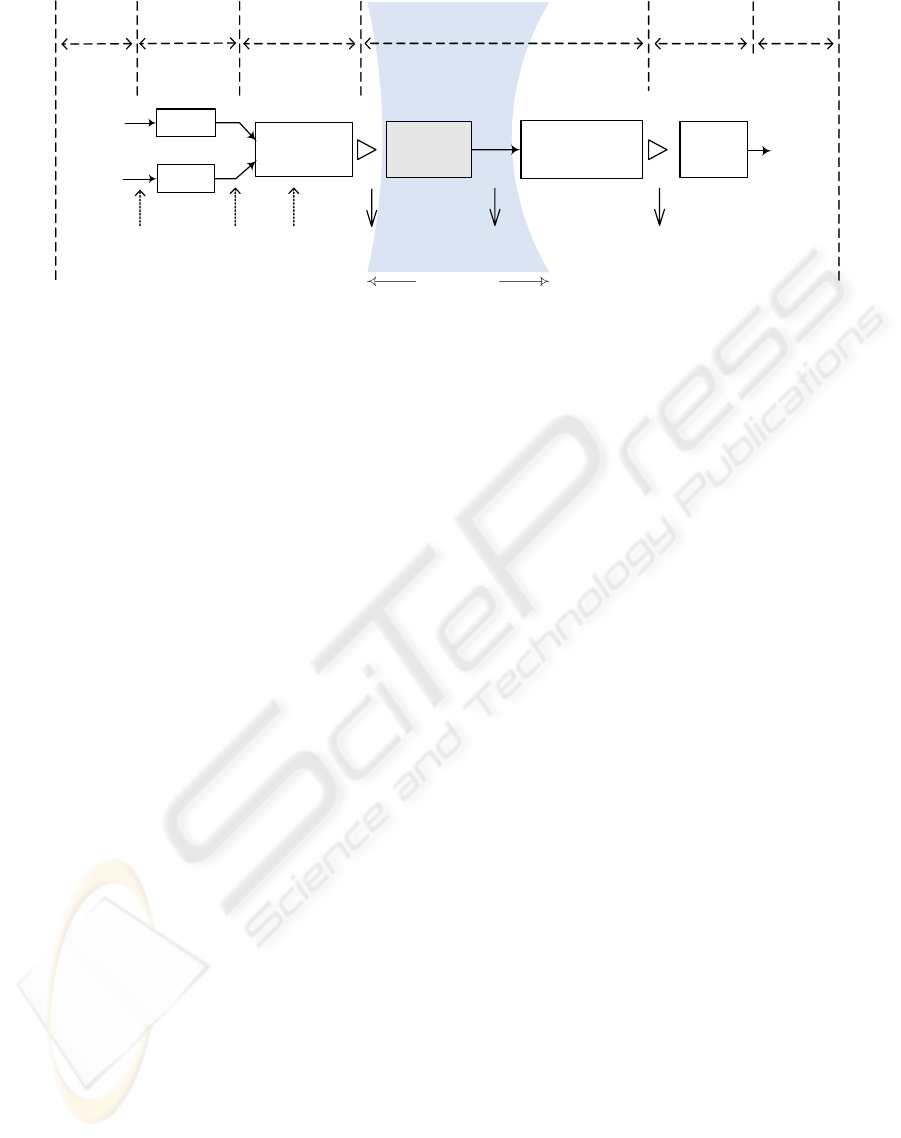
context of our research, is indicated in figure 2.
The first phase of our matching process concerns
the terminological matching (T.M). The aim of
this phase is to compute the similarity between
schema nodes based on the similarity of their labels.
The proposed matching method takes as input a
matrix of terminological similarity coefficients
(ranging in [0,1]) between source and target nodes
as well as semantic relationships. Terminological
similarity uses WordNet (Miller, 1995), (Miller et
al., 2000) as auxiliary information.
Techniques of terminological matching compare
only nodes between a source schema and target
schema. These matching techniques may provide
incorrect match candidates. Structural matching is
used to correct such match candidates based on their
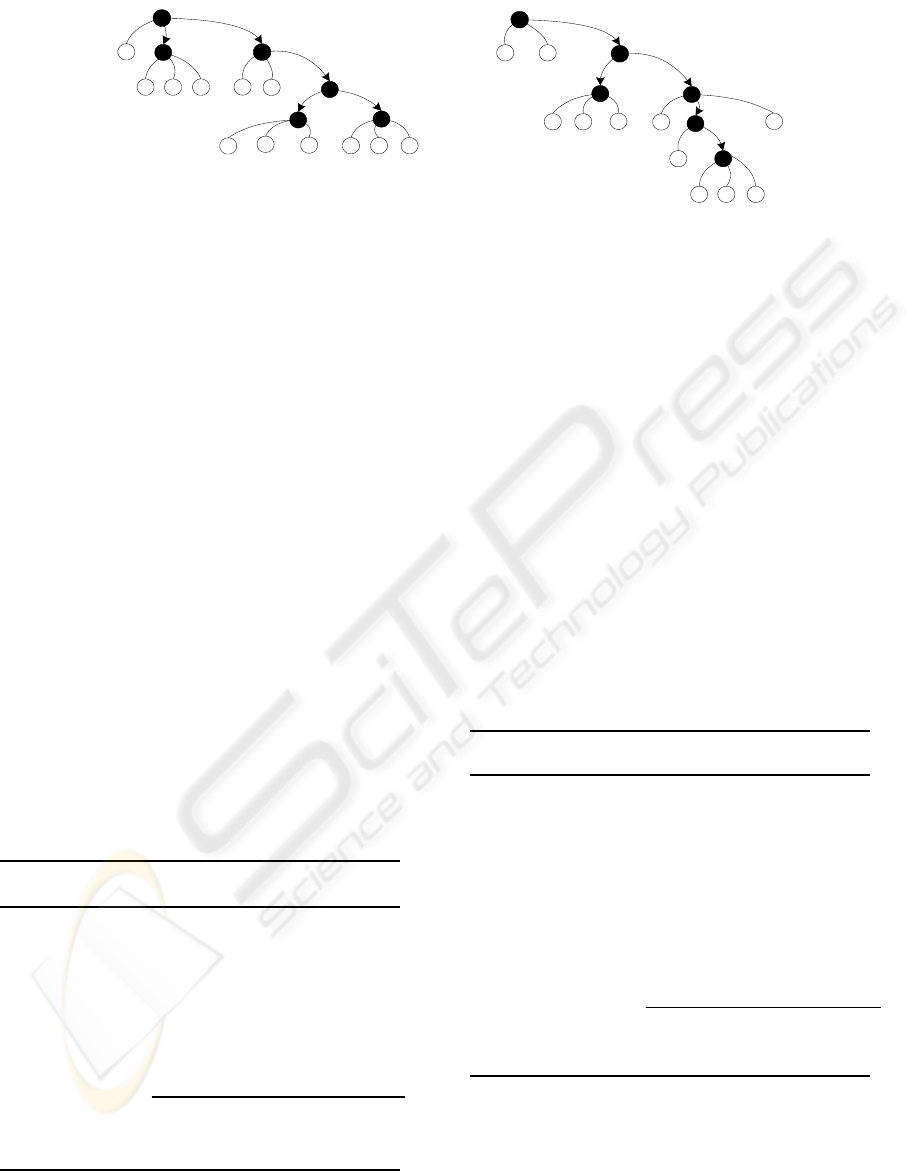
structural context. For example, assume that we let
the schema graph in figure 3 be the source schema
title
number
statute
name
title
publication
membre
desc.
laboratory
year
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
130
graph, denoted G
source
and the target schema graph,
denoted G
target
.
Based on the two terminological matching and
datatype compatibility techniques, we obtain a
match between node laboratory/address (of G
source
)
and node Author/Address (of G
target
), while the first
is a laboratory address and the second is an author
address. The structural matching (following phase in
the matching process) compares the contexts in
which nodes appear and can deduce that the two
nodes address do not match, instead the node
address in the source schema match the node
location in the target schema and source relationship
between laboratory and address match target
relationship between laboratory and location. In this
paper we only present our structural matching relies
on the notion of node context.
4.1 Node Context Definition
The aim of structural matching is the comparison of
the structural contexts in which nodes in the schema
graph appear. Thus, we need a precise definition on
what we mean by node context. We distinguish
three kinds of node contexts depending on its
position in the schema graph.
The root-context: A root context of a node n
i
is
defined by the root path having n
i
as its ending node
and the root of the schema tree as its starting node.
For instance, the root-context of node publication in
figure 3(a) is given by the path
laboratory/member/publication which describes the
publications of a member belonging to a laboratory.
If the root-context of the root node is empty, it is
assigned a null value.
The intermediate-context: An intermediate-
context of node n
i
includes its immediate subnodes.
The intermediate-context of node reflects its basic
structure and its local composition. For instance, the
intermediate-context of node Laboratory of figure
3(a) is given by (name, address, and member). The
intermediate-context of an atomic node is assigned a
null value.
The leaf-context: Leaves in the XML tree
represent the atomic data that the schema describes.
The leaf-context of node n
i
includes the leaves of the
subtree rooted at n
i
. For instance, the leaf-context of
node Publication in the schema graph of figure 3(a)
is given by the set (title, abstract, volume, title,
price, and publisher). The leaf-context of an atomic
node is assigned a null value.
Finally, the context of a node is defined as
theunion of its root-context, its intermediate-context
and its leaf-context. Two nodes are structurally
similar if they have similar contexts. The notion of
context similarity has been used in Cupid and SF;
however none of them relies on the three kinds of
contexts. To measure the structural similarity
between two nodes, we compute respectively the
similarity of their root, intermediate and leaf
contexts. In the following we describe the basis
needed to compute such similarity.
4.2 Node Context Similarity
4.2.1 Root-Context Similarity
The root context similarity, root_ctxSim captures the
similarity between two nodes based on their root
context. Since the root context of a given node n
i
is
described by the root path (the path from the root to
n
i
), computing root contexts similarity is equivalent
to comparing two paths. The root_ctxSim between
Figure 2: The matching process.
Gsource
Gtarget
Starget
Starget
Ssource
Ssource
Terminological
Matching
Node context
similarity
Discovery of nodes
and edges matches
User
validation
Modelling
Terminological
matching
Structural matching Mappings
Name similarity
WordNetXML JAVA API
Terminological
similarity coefficients
Node
similarity
Structural similarity
Direct and
complex mappings
Schema similarity
Input
EXS Schema Schema graph
Output
Final
mapping
result
Root, intermediate
and leaf context
Datatype
compatibility
Matching
algorithm
Scope of this paper
MATCHING OF ENHANCED XML SCHEMAS WITH A MEASURE OF STRUCTURAL-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
131
two nodes n
1
and n
2
is given by the path
resemblance measure between the two paths (root
1
,
n
1
) and (root
2
, n
2
) weighted by the terminological
similarity (TSim) between n
1
and n
2
.
root_ctxSim (n
1
, n
2
)← pathSim
((root
1
, n
1
),(root
2,
n
2
))× TSim(n
1
, n
2
)
4.2.2 Intermediate-Context Similarity
The intermediate-context similarity (inter_ctxSim) is
obtained by comparing nodes immediate
descendents (children) sets including subtree. Given
a node n
1
having m immediate children represented
by the set (n
11
,…n
1m
) and node n
2
having k
immediate children represented by (n
21
, …n
2k
). To
compute the similarity between these two sets, we
(i) compute the terminological similarity between
each pair of children in the two sets, (ii) select the
matching pairs with maximum similarity values and
(iii) take the average of best similarity values.
Algorithm 1 illustrates how we compute the
intermediate-context similarity.
Algorithm 1 – INTERMEDIATE-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
1. Input: n
1
, n
2
, TSimMat
// having respectively
// m and k children
2. Output: Inter_ctxSim
3. Begin
4. inter_sim ←
MAX
i∈[1, m], j∈[1, k]
{(n
1i
, n
2j
, TSim) ∈
TSimMat}
5. sim_pairs ← (n
1i
, n
2j
, Sim_Inter)
6. inter_ctxSim ← ∑
(n1i, n2j, inter_sim)∈sim-pairs
(inter_sim)
MAX (m, k)
7. return inter_ctxSim
8. End.
4.2.3 Leaf-Context Similarity
Since the effective content of a node is often
captured by the leaf nodes of the subtree rooted at
that node, we compute leaf context similarity of two
nodes n
1
and n
2
by comparing their respective leaves
sets, n
1
{leaves} and n
2
{leaves}. Thus to compute the
similarity between two leaves l
1
∈
n
1
{leaves} and l
2
∈
n
2
{leaves}, we propose to compare the contexts in
which these leaves appear. If a leaf node l
∈
n
1
{leaves}, then the context of l is given by the path
from n
1
to l. The context similarity of two leaves is
then obtained by comparing such paths, and the
similarity between two leaf nodes is obtained by
comparing their context similarities and their
terminological similarity. Algorithm 2 illustrates
how we compute the leaf-context similarity.
Algorithm 2 – LEAF-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
1. Input: n
1
, n
2
// having respectively m and k leaves
2. Output: leaf_ctxSim
3. Begin
4. for each l
1i
∈ n
1
{leaves}
5. for each l
2j
∈ n
2
{leaves}
6. leaf_sim (l
1i
, l
2j
) ← pathSim((n
1
, l
1i
), (n
2
, l
2j
) ×
TSim(l
1i
, l
2j
)
7. temp_sim ←
MAX
i∈[1,m], j∈[1,k]
(l
1i
, l
2j
, leaf_sim}
8. sim_pairs ← (n
fk
, n
fh
, temp_Sim)
9. leaf_ctxSim ← ∑
(l1i, l2j, leaf_sim)∈sim-pairs
(leaf_sim)
MAX (m, k)
10. return leaf_ctxSim
11. End.
The goal of this measure of structural-context
similarity, it easier to optimize and to automatically
generate transformation scripts expressed in XSL
language between EXS schemas.
laboratory
article
address
author
title
publisher
price
volumeabstract
article
publication
membre
name
address
laboratory
street
city
zip
name
address
book
title
title
publisher
uri
author
library
name location
book
title
name
street city
zip
(a) A schema graph source (Gsource)
(b) A schema graph target (Gcible)
Figure 3: An EXS schema graph (source and target).
WEBIST 2007 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
132

5 CONCLUSION
In this paper we have interested on schema
matching, and focused on structural context
matching for enhanced XML schemas. We began by
an analysis of problems involved in the matching,
and we proposed a new solution taking into account
of heterogeneity of the schema sources. For the
structural similarity measure, we recovered a matrix
of terminological similarity coefficients between
schema nodes based on the similarity of their labels.
We outlined the limitations of current solutions
through the study of Cupid and Similarity Flooding
systems. Then we proposed a structural matching
technique that considers the context of schemas
nodes (defined by their roots, intermediates and
leafs contexts in schema graph). By the way, we
suggest a simple structural algorithm based on the
previous ideas and exploit the three types of
contexts. We refer to the result produced by the
algorithm as a mapping. The user validates this
mapping in order to produce a final mapping result
that serves to generate transformation scripts.
For future work, we would like to improve the
matching process, while taking into account the
optimisation of the process in order to determine a
set of semantic equivalences between schemas
(source and target). That will facilitate the
generation of operators based on the primitive of
transformations between entities of EXS schemas.
The second axis to land concerns the efficiency and
the time of human interaction. The key is then to
discover how to minimize ser interaction but
maximizing the impact of the feedback.
REFERENCES
Abiteboul, S., Cluet, S., Milo, T., 1997. Correspondence
and Translation for heterogeneous data. In Proceeding
of The international Conference on Database Theory
(ICDT). 351-363.
Boukottaya, A., Vanoirbeek, C., Paganelli, F., Abou-
Khaled, O., 2004. Automating XML documents
transformations: a conceptual modelling based
approach. In Proceedings of the first Asian-Pacific
conference on Conceptual modelling. ACM, 81-90.
Castano, S. and De Antonellis, V., 1999. A schema
analysis and Reconciliation Tool Environment For
Heterogeneous Databases. In Proceedings of
International Database Engineering and Applications
Symposium.
Doan, A., Madhavan, J., Domingos, P., Halevey, A., 2001.
Reconciling schemas of disparate data sources: A
machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings ACM
SIGMOD conference. 509-520.
Drew, P., King, R., McLeod, D., Rusinkiewicz, M.,
Silberschatz, A., 1993. Report of the Workshop on
Semantic Heterogeneity and Interoperation in
Multidatabase Systems. In Proceedings ACM
SIGMOD record, 47-56.
Fellbum, C., 1998. WordNet: An Electronic Lexical
Database. MIT press.
Lamolle, M. and Mellouli, N., 2003. Intégration de bases
de données hétérogènes via XML.EGC’2003.
Lamolle, M. and Zerdazi, A., 2005. Intégration de Bases
de données hétérogènes par une modélisation
conceptuelle XML, COSI’05. 216-227.
Li, W.S. and Clifton, C., 1994, Semantic Integration in
Heterogeneous Databases Using Neural Networks.
VLDB.
Li, W.S. and Clifton C., 2000, SemInt: A Tool for
Identifying Attribute Correspondences in
Heterogeneous Databases Using Neural Network. Data
and Knowledge Engineering. 49-84.
Madhavan, J., Bernstein, P., Rahm, E., 2001. Generic
schema matching with cupid. VLDB.
Melnik, S., Garcia-Molina, H., Rahm, E., 2002. Similarity
Flooding: A versatile Graph Matching and its
Application to Schema Matching. Data Engineering.
Miller, A.G., 1995. WordNet: A lexical Database for
English. ACM. 39-41.
Miller, A.G., Hass, L., Hernandez, M.A., 2000. Schema
mapping as query discovery. VLDB. 77-88.
Rahm, E. and Bernstein, P., 2001 A survey of approaches
to automatic schema matching. In VLDB Journal.
334-350.
XML Schema, W3C Recommendation, 2001. XML-
Schema Primer, W3 Consortium, 2001. Available at
http://www.w3.org/TR /xmlschema-0.
Zerdazi, A. and Lamolle, M., 2005. Modélisation des
schémas XML par adjonction de métaconnaissances
sémantiques. ASTI’05. 29-32.
Zerdazi, A. and Lamolle, M., 2006. Intégration de sources
hétérogènes par matching semi-automatique de
schémas XML étendus. INFORSID’2006. 991-1006.
MATCHING OF ENHANCED XML SCHEMAS WITH A MEASURE OF STRUCTURAL-CONTEXT SIMILARITY
133
