
FACIAL EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS AND RECOGNITION WITH
INTENSITY ALIGNMENT
Hao Wang
System Research Center Beijing, Nokia Research Center,No. 11 He Ping Li Dong Jie,100013, Beijing, China
Keywords: Facial expression, synthesis, recognition, intensity alignment, SLPP.
Abstract: This paper proposes a novel approach for facial expression synthesis that can generate arbitrary expressions
for a new person with natural expression details. This approach is based on local geometry preserving
between the input face image and the target expression image. In order to generate expressions with
arbitrary intensity for a new person with unknown expression, this paper also develops an expression
recognition scheme based on Supervised Locality Preserving Projections (SLPP), which aligns different
subjects and different intensities on one generalized expression manifold. Experimental results clearly
demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Realistic facial expression synthesis has attracted
considerable attention in recent years. In order to
design a more human-like, effective and efficient
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) system, the
capability of affective computing, which includes
automatic facial expression analysis and synthesis,
has to be addressed. There has been much research
in this area, and expression mapping had become a
popular method for generating facial animations. As
pointed out in (Zhang, 2006), this method is a kind
of warping-based approaches, which requires
accurate labeling of feature positions of a subject’s
neutral face and another face of the same person
with target expression. Because it considers shape
changes only, the texture variations on the face are
ignored, consequently it does not generate
expression details such as wrinkles due to skin
deformations. An alternative approach uses a large
amount of sample views and applies morphing
between them. The drawback of this method is that
it is difficult to generate expressions for a new
person who is not included in the training set.
Chandrasiri et al. proposed Personal Facial
Expression Space (PFES) to recognize person-
specific, primary facial expression image sequences
(Chandrasiri, 2004). On PFES, facial expression
parameters are processed to synthesize an
expressional face image by using a generic
wireframe face model. The benefit of their system is
that mixed expressions with varying intensities can
be synthesized by interpolation of the face models
while at the same time blending corresponding
textures. However, it is not capable to process a new
face under the framework. Wang and Ahuja
proposed an approach for facial expression
decomposition with Higher-Order Singular Value
Decomposition (HOSVD) that can model the
mapping between persons and expressions, used for
facial expression synthesis for a new person (Wang,
2003). One problem is that the global linearity
assumption of expression variations introduces some
artifacts and blurring while synthesizing expressions
for a new person who is not in the training set. Du
and Lin used PCA and linear mapping based on
relative parameters as emotional function (Du,
2002). They encountered the similar problem as
using HOSVD that large amount of training samples
are demanded to well represent the variations of
expressions for different subjects.
Kouzani reported a Quadtree PCA (QPCA) to
implement a global-local decomposition for
approximating face images using a limited set of
examples (Kouzani, 1999). Computation complexity
is certainly increased by QPCA, and the results do
not look very good for human observation. Zhang et
al. developed a geometry-driven facial expression
synthesis system (Zhang, 2006). They subdivide the
face into a number of subregions in order to deal
with the limited space of all possible convex
combinations of expression examples. The synthesis
results look realistic and desirable. However, the
45
Wang H. (2007).
FACIAL EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS AND RECOGNITION WITH INTENSITY ALIGNMENT.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 45-52
DOI: 10.5220/0002132400450052
Copyright
c
SciTePress
blending along the subregion boundaries requires
further efforts to avoid image discontinuities, and
the registration of the large amount of feature points
is a challenging task.
Generally, a system that is intended to design
facial expression synthesis should be capable to
fulfill the following tasks. First, it is required to
obtain realistic visual effects rather than only
generating cartoon-like animations. Secondly, the
system must be able to synthesize facial appearance
for a new person, not limited to particular subjects
within the training set. Finally, an efficient method
is needed to synthesize arbitrary facial expressions
with any desired intensities.
Let I
P
represent a face image, and I
E
be an
expression image of this face. The procedure of
expression synthesis is equivalent to setting up a
mapping relation M between a face and its
expression,
)(
PE
IMI =
, where M is supposed to be
a complex nonlinear mapping. In this paper, a local
geometry preserving based nonlinear method is
proposed to approximate the mapping function M.
This method is inspired by Locally Linear
Embedding (LLE) (Roweis, 2000). It is assumed that
small image patches in the face image and the
expression image form manifold with similar local
geometry in two different image spaces, and
expression synthesis can be performed by giving
training face-expression pair samples based on local
nearest neighbors reconstruction. Another
component of the proposed system is expression
recognition, i.e., identifying the expression type and
the intensity level of the input face image. A
Supervised Locality Preserving Projections (SLPP)
is developed to align different subjects and different
intensities on one generalized expression manifold
so that corresponding pair samples with aligned
expression intensity are used to synthesize
expressions of any desired intensity level.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,
the principle of the expression synthesis approach is
presented. Section 3 describes the expression
recognition scheme with intensity alignment.
Section 4 gives a brief extension on expression
synthesis with arbitrary intensity. In Section 5 the
experiments are presented and discussed. Finally,
conclusions are presented in Section 6.
2 SYNTHESIS OF BASIC
EXPRESSIONS
Facial expressions of a new person can be
synthesized under the assumption that similar
persons have similar expression appearance and
shape (Wang, 2003). However, all PCA based
methods further assume that expression synthesis
can be approximated by a linear combination of
training face-expression pair samples. Due to the
complexity of face structure, adopting this globally-
linear assumption is not accurate when training
samples are limited or there are big shape
deformations of expressions.
Promising manifold learning methods such as
LLE provide hints on this problem. The principle of
LLE is to compute neighbor-preserving mapping
between an original high-dimensional data space and
a low-dimensional feature space, based on the
simple geometric intuition that each data point and
its neighbors lie on or close to a locally linear patch
of the manifold (Roweis, 2000). It is reasonable to
adopt a local geometry preserving scheme to
compute the mapping between the original face
image space and the expression image space. To
solve the problem of limited samples and
deformable expression structure, a patch-based
strategy is applied as in (Liu, 2005).
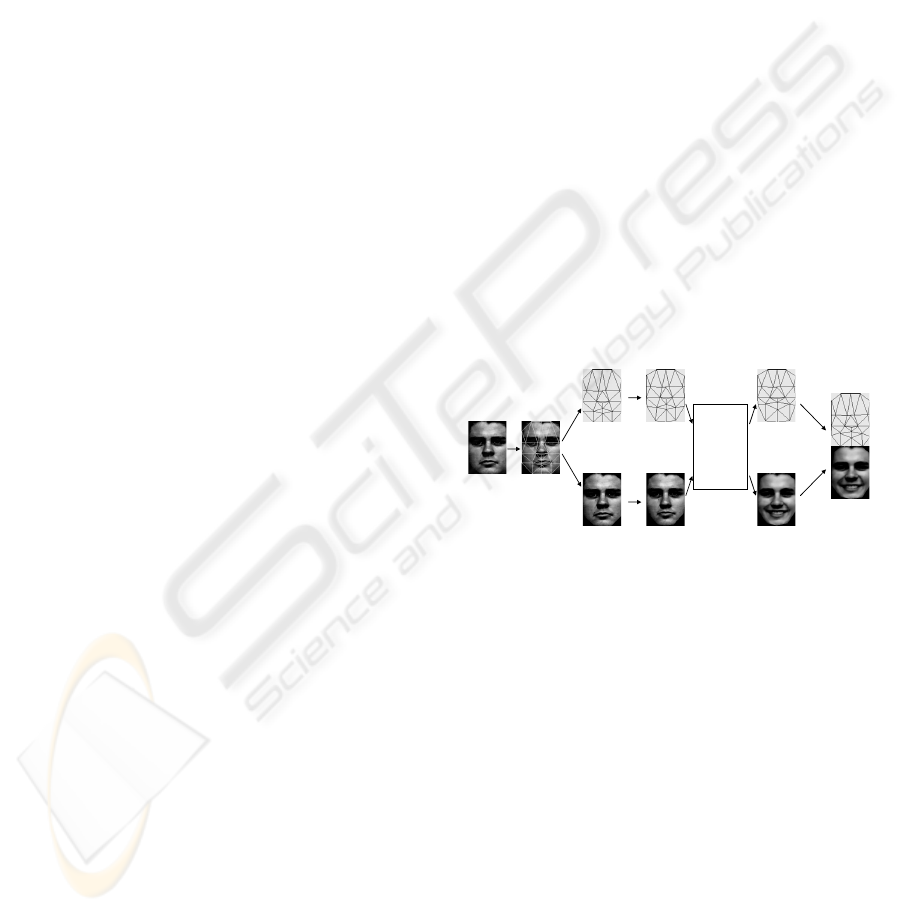
2.1 Expression Synthesis Framework
P
Graph
matching
I
P
S
P
G
G
S’=G(S
P
)
I’=G(I
P
)
Expression
Transform-
ation
G
-1
G
-1
S
E
’
I
E
’
I
E
=G
-1
(I
E
’)
Figure 1: Framework of the expression synthesis system.
Basic facial expressions typically recognized by
psychologists are happiness, anger, fear, disgust,
sadness and surprise. For convenience, ‘neutral’ is
considered to be a seventh basic expression in this
paper. This section presents the algorithm to
synthesize one of the basic facial expressions by
given a neutral face from the frontal view. As can be
seen later, mapping between any two basic
expressions with any intensity will be easily
implemented in the same framework.
To take different geometrical shapes of faces into
account, an average shape of faces is created from
all training samples of each basic facial expression,
as called mean shape. In the training stage, all the
samples are aligned by warping the face images to
the mean shape of the corresponding expression
category using affine interpolation based on a set of
triangles. At runtime, the expression synthesis can
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
46

be implemented as following steps, as shown in
Figure 1:
y For a given neutral face P, locate all the fiducial
points on the face graph model to extract shape
information.
y Apply geometric transformation by warping
the face image to a mean shape derived from the
training set to separate the texture I
P
and shape S
P
:
))(),(()','(
PP
SGIGSI =
.
y Employ expression transformation to obtain
texture I
E
’and shape S
E
’ for the expression.
y Compute the final expression image I
E
from the
inverse geometric transformation:
)'(
1
EE
IGI
−
=
.
2.2 Expression Transformation
The adoption of a patch-based strategy is driven by
two factors. First, the probability distribution of a
pixel and its neighbors in an image is assumed to be
independent of the rest of the image. Secondly, the
linear assumption of face reconstruction is more
intent to be satisfied for small areas rather than the
entire image especially when training samples are
limited. Thus with the principle of local geometry
preserving, the global non-linear variations of facial
expressions can be approximated by locally-linear
combination.
In this paper, both of the neutral face image and
the basic expression image are divided into N small
overlapping image patches in the same way. Let
j
n
p
and
j
e
p
(
Nj ,...,2,1=
) denote the image patches of
the neutral image and the expression image
respectively, corresponding neutral and expression
image patches form manifolds with similar local
geometry in two different image spaces. Similar to
LLE, each neutral image patch
j
n
p
is fitted with its
K nearest neighbors from training samples
j
n
T
, and
the reconstruction weights are calculated. Then its
corresponding expression image patch
j
e
p
can be
approximated from training samples
j
e
T
by
preserving the local geometry. The expression
transformation algorithm is summarized as follows:
1) For a neutral image patch
j
n
p
,
Nj ,...,2,1=
,
find its K nearest neighbors
Kkp
j
n
j
kn
,...,2,1,
ˆ
,
=∈T
.
2) Compute the reconstruction weights of the
neighbors,
Kkw
j
kn
,...,2,1,
,
=
.
3) Based on local geometry preserving, composite
its expression image patch
j
e
p
using corresponding
expression image patches
j
e
j
ke
p T∈
,
ˆ
of the K nearest
neighbors
j
kn
p
,
ˆ
and the reconstruction weights
Kkw
j
kn
,...,2,1,
,
=
:
∑
=
=
K
k
j
ke
j
kn
j
e
pwp
1
,,
ˆ
(1)
In step 1, local search with small search window
is employed to find the best match between two
image patches in order to deal with slight
geometrical mis-alignments that may exist even after
warping the images to the mean shape. In step 2, the
reconstruction weights can be achieved by
minimizing
2
1
,,
ˆ
)(
∑
=
−=
K
k
j
kn
j
kn
j
n
j
pwpw
ε
, (2)
Subject to:
Kkww
j
kn
K
k
j
kn
,...,2,1,0,1
,
1
,
=≥=
∑
=
.
This is a constrained least square problem and the
close-form solution can be found in (Liu, 2005).
In this paper, another simpler method is applied to
compute the reconstruction weights of the neighbors,
called Heat Kernel that is inspired by LPP (He,
2003), as follows:
Kkew
t
pp
j
kn
j
kn
j
n
,...,2,1,
~
2
,
ˆ
,
==
−
−
, (3)
where the final weights are normalized as
Kkwww
K
k
j
kn
j
kn
j
kn
,...,2,1,
~
/
~
1
,,,
==
∑
=
. (4)
To avoid image discontinuities along the
boundaries of image patches, a simple averaging
process is adopted for overlapped regions in the final
reconstructed expression image. There are three
parameters that might have effects on the synthesis
results: the number of nearest neighbors K, the patch
size, and the degree of overlapping between adjacent
patches. Experiments show that the overlapping
parameter does not have obvious effects.
(
a
)
(
b
)
(
c
)
Figure 2: Comparison of synthesis with different patch
sizes: (a) 5×5, (b) 9×9, (c) 13×13. First row: using Heat
Kernel weights. Second row: using weights of error-
minimizing method.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 illustrate the comparisons of
synthesized expression images with different patch sizes
and different numbers of nearest neighbors respectively.
Selection of the patch size is a trade-off between losing
small details if the size is too large, and bringing noise
when the size is too small. Similarly, if the number of
nearest neighbors K is too small, noise will appear, and it
is over-smooth if K is too large. It is also noted that using
Heat Kernel weights instead of using error-minimizing
FACIAL EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS AND RECOGNITION WITH INTENSITY ALIGNMENT
47

method in formula (2) will have less sensitivity to the
changes of parameters. Thus in the following experiments
the Heat Kernel weights are applied and the parameters
are selected as K=5 and patch size with 9×9.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 3: Comparison of synthesis with different neighbor
sizes: (a) K=5, (b) K=15, (c) K=25. First row: using Heat
Kernel weights. Second row: using weights of error-
minimizing method.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 4: Comparison of synthesis with proposed method
and eigentransformation: (a) original face, (b) proposed
method without shape alignment, (c) eigentransformation
without shape alignment.
Figure 4 shows the advantage of the proposed
method comparing with eigentransformation (Tang,
2003) regarding face image reconstruction.
Sometimes the fiducial feature points on the face can
not be obtained accurately so that the shape
alignment is unavailable. Then the reconstructed
face image using eigentransformation will have
some artifacts and often look unlike the original face
because it approximated the face using a global-
linear process. The proposed method achieves better
result even without shape alignment. The reason is
that the ‘double locality preserving’ scheme - both
locality with image patchs in the spatial domain and
locality with geometrical structure of manifold - is
capable to approximate the global-nonlinear
structure more efficiently.
3 INTENSITY ALIGNMENT
Generally, an expression synthesis system should be
able to transform a face with any expression and
intensity to a target expression and intensity, not
particular to only convert a neutral face to one of the
basic expressions. It can be implemented under the
same framework presented above if two
requirements are satisfied: first, the training database
is aligned in a generalized structure for different
subjects, expressions and intensities; secondly, the
system can recognize the expression category of the
input face image and identify the intensity. Then
corresponding training subset will be used for
reconstruction of the target expression image. This
section presents a SLPP based expression
recognition algorithm with intensity alignment.
3.1 Related Work
Development of an automatic facial expression
analyzer has attracted great attention in these
decades, and the reader is referred to (Pantic,, 2000)
for an excellent survey. Tian et al. developed an
Automatic Face Analysis (AFA) system to analyze
facial expressions based on both permanent facial
features (brows, eyes, mouth) and transient facial
features (deepening of facial furrows). The AFA
system recognizes fine-grained changes in facial
expression into action units (AUs) of the Facial
Action Coding System (FACS), instead of a few
prototypic expressions. However, the AFA system
requires accurate locations of the facial features, and
further efforts are demanded to implement a
corresponding model-driven facial expression
synthesis system under the framework of AFA. In
(Yeasin, 2006) they used a subjective measurement
of the intensity of basic expressions by associating a
coefficient for the intensity by the relative image
number in the expression image sequence. Though
simple and effective for their application, this
method does not align expression intensities of
different.
In recent years manifold learning methods are
used for facial expression analysis, which is based
on the fact that variations of face images can be
represented as low dimensional manifolds embedded
in the high dimensional image space. Chang et al.
(Chang, 2003) made first attempt to apply two types
of embedding, LLE and Lipschitz embedding, to
learn the structure of the expression manifold. In
(Hu, 2004), they further proposed an approach for
facial expression tracking and recognition based on
Isomap embedding. One problem of these methods
is that they learned the expression manifold in the
feature space described by a large set of landmarks,
which requires complex extracting or tracking
scheme and is not easy to be obtained accurately,
additionally, the number of such landmark points is
far beyond the number of fiducial points used in
expression synthesis stage. Another potential risk is
that the research was conducted on data sets
containing only several subjects, the efficiency on a
large number of subjects was not verified. Shan et al.
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
48

(Shan, 2005) first investigated an appearance
manifold of facial expression based on a novel
alignment method to keep the semantic similarity of
facial expression from different subjects on one
generalized manifold. Based on their work, a further
attempt to enhance the resolution of the intensity of
expressions from different subjects is proposed in
this paper.
3.2 Supervised LPP (SLPP)
LPP is a linear approximation of Laplacian
Eigenmap. It seeks a transformation P to project
high-dimensional input data
],...,,[
21 n
xxx=X
into a
low-dimensional subspace
],...,,[
21 n
yyy=Y
in
which the local structure of the input data is be
preserved. The linear transformation P can be
obtained by minimizing the following objective
function:
∑
=
−
n
ji
ijji
Wyy
1,
2
min
P
, (5)
where
ii
xy
T
P=
, the weight matrix W is
constructed through the adjacency graph with k
nearest neighbors or ε-neighborhoods. The
minimization problem can be converted to solving a
generalized eigenvalue problem as
PXDXPXLX
TT
λ
=
, (6)
where
∑
=
j
ijii
WD
is a diagonal matrix, and
WDL −=
.
When class information is available, LPP can be
performed in a supervised manner (Ridder, 2003)
(Cheng,, 2004) (Shan, 2005). The basic idea is to
encode class information in the embedding when
constructing the neighborhood graph, so that the
local neighborhood of a sample x
i
from class c
should be composed of samples belonging to class c
only. This can be achieved by increasing the
distances between samples belonging to different
classes, as the following definition
ijijij
MSup
δ
α
+Δ=Δ
]1,0[∈
α
, (7)
where
ij
Δ
denotes the distance between x
i
and
x
j
,
ij
SupΔ
denotes the distance after incorporating class
information, and
ijji
M Δ=
,
max
,
0=
ij
δ
if x
i
and
x
j
belong to the same class, and 1 otherwise. The
parameter
α
represents the degree of supervision.
When
0=
α
, one obtains unsupervised LPP; when
1=
α
, the result is fully supervised LPP.
By applying SLPP to the data set of image
sequences of basic expressions, a subspace is
derived, in which different expression classes are
well clustered and separated (Shan, 2005). However,
there are two questions to be considered further.
First, neutral faces are not processed separately,
which introduced noise in their recognition.
Secondly, intensity of expressions is not taken into
account in formula (7).
In this paper an extended definition of the
incorporated distance is proposed as
)')1((
ijijijijij
MSup
δ
β
δ
β
α
Δ−+
+
Δ
=
Δ
, (8)
where
),1[],1,0[
+
∞
∈
∈
β
α
. The principle is to
construct the neighborhood graph to enable that
expressions with similar intensity but from different
subjects are closer than those of different intensities
but from the same subject, thus the local
neighborhood of a sample x
i
with intensity i from
class c should be composed of samples belonging to
class c, and with similar intensity i from different
subjects. This is achieved by introducing a within-
class distance component
')1(
ijij
δ
β
Δ−
:
1' =
ij
δ
if x
i
and
x
j
belong to the same subject within an
expression class (excluding neutral), and 0
otherwise. The parameter
β
controls the scale of
intensity resolution, and
1=
β
will regress to (7).
The within-class distance component is not applied
for neutral expression so that the neutral class can be
clustered more closely and the boundary between
neutral face and the expression of a sequence will be
clearer.
3.3 Facial Expression Recognition
Following (Shan, 2005) and (Chang, 2003), a k
Nearest Neighbor method is applied to classify the
basic expressions on the aligned expression
manifold. For intensity identification of an input
sample x, the mean of its nearest neighbors from the
same expression class c on the aligned manifold is
calculated, and then the intensity scale is normalized
by the maximum intensity value of this class, as
following
max
/ DDi
xx
=
, (9)
where
x
i
denotes the intensity of sample x, which
ranges between [0,1].
x
D
represents the distance
between the center of the neutral expression class
and the mean of nearest neighbors of sample x.
4 SYNTHESIS FOR ARBITRARY
INTENSITY
After facial expression recognition and intensity
identification, an input face image can be labeled
FACIAL EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS AND RECOGNITION WITH INTENSITY ALIGNMENT
49

with expression type c and intensity value i. To
synthesize a face image of target expression c
t
with
target intensity i
t
, an intuitive way is to apply
corresponding training subsets during the expression
transformation. Let
),( icT
denotes the training
subsets with expression type c and intensity range
),(
ε
ε
+− ii
, which contains M samples from
different subjects, and the corresponding subset
),(
tt
icT
contains M samples of expression type c
t
and intensity range
),(
ξ
ξ
+−
tt
ii
, from different
subjects. The expression transformation can be
performed by using
),( icT
to compute the
reconstructing weights of image patches, and using
),(
tt
icT
to reconstruct the target expression image.
5 EXPERIMENTS
According to (Shan, 2005), the optimal data set for
expression manifold learning should contain O(10
2
)
subjects, and each subject has O(10
3
) images that
cover basic expressions. However, there is no such
database available until now. In this paper,
experiments are conducted on the Cohn-Kanade
database (Kanade, 2000) which consists of 96
subjects and each of them has several tens frames of
basic expressions. Both in expression synthesis and
recognition, 82 subjects are used for training and the
rests for testing.
5.1 Basic Expression Synthesis
Figure 5 shows the result of basic expression
synthesis for one subject based on local geometry
preserving, and comparison with the real expression
samples of this subject. The synthesis shown in the
first row of Figure 5 utilizes the samples of different
expressions from this subject as training samples,
whereas the second row shows the results generated
by leaving those samples out, and almost no
degradation is introduced. Because not all the
subjects in the training set has samples of all basic
expressions, the numbers of image samples for basic
expression synthesis are 82, 36, 34, 47, 72, 52, and
48 for neutral, anger, disgust, fear, happiness,
sadness, and surprise respectively. It can be seen that
the effects of synthesis are not highly depended on
the number of training samples to be used. Some
noises exist in the regions of hair. This is because
variations in these regions are highly nonlinear and
can not be represented well even with local linear
preserving.
Figure 5: Synthesized facial expression images of one
subject (from left to right: neutral, anger, disgust, fear,
happiness, sadness, surprise). First row: there are sample
images of the same person in the data set. Second row: the
samples are left out from the data set. Third row: samples
of the same subject with different expressions.
Figure 6 shows the synthesis results of a new
person who is not included in the training set, and
comparison with the results obtained by the
eigentransformation method and directly warping.
Though improved by separating shape and texture,
the eigentransformation tends to reconstruct the
faces that do not look very alike to the original face
of the same person, basically because it regards the
mapping between neutral and expressions as a linear
process. Direct warping fails to generate natural
expressions, e.g., the artificial warping can not
produce an open mouth if the mouth is closed in the
origin. Obviously the proposed algorithm obtains
better results than the other methods. And as
illustrated in Section 2, the proposed algorithm is not
sensitive to the accuracy of the locations of fiducial
points on the face graph model, which enhances the
robustness for variant use cases.
To evaluate the expression synthesis, a
subjective measurement is introduced that 15
volunteers are involved in this test. First ‘person
verification’ is performed: a series of synthesized
expressional face images are presented to the
participants, and they are required to identify the
original neutral face from a given set. Then
‘expression identification’ is carried out by given the
real samples of expressions as reference. Finally
each participant gives an overall score of the
synthesis quality of each image, i.e., 5 for very good
identification and realistic effects, 4 for good, 3 for
fair, 2 for poor and 1 for ugly. Table 1 shows the
evaluation result, which is very desirable from
subjective observation.
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
50
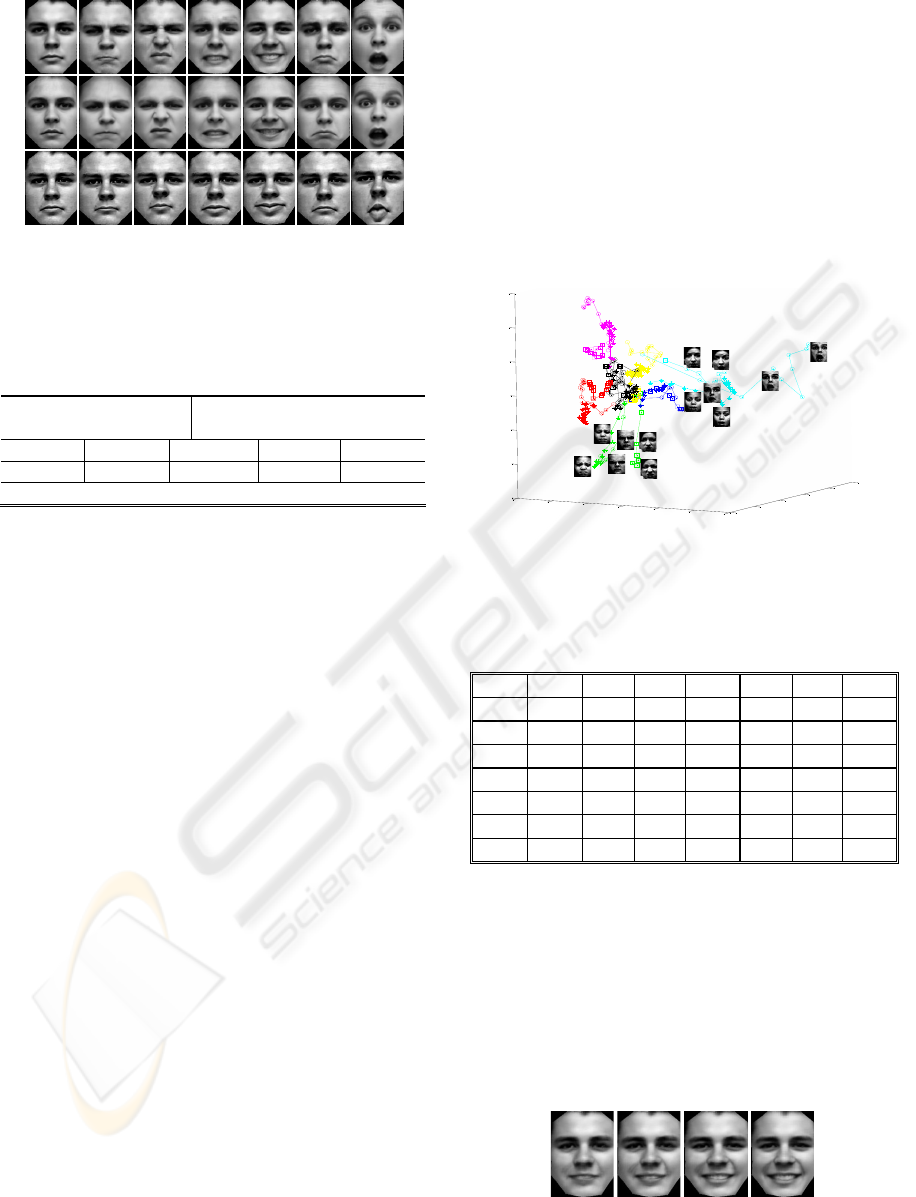
Figure 6: Synthesized facial expression images of a new
person (from left to right: neutral, anger, disgust, fear,
happiness, sadness, surprise). First row: proposed method.
Second row: eigentransformation with shape alignment.
Third row: direct warping of the original face.
Table 1: Subjective evaluation result.
person verification:
95.6%
expression identification:
98.1%
5 4 3 2 1
54% 38% 7% 1% 0%
overall performance factor: 4.56
5.2 Appearance Manifold of Facial
Expressions
In the experiments, 379 image sequences consisting
of totally 4,643 images of the seven basic
expressions were selected from the database, which
come from 82 subjects. Raw image data is used as
the appearance feature. For computational
efficiency, the face images are down-sampled to
60×80 pixels with calibration of the eyes locations.
The 3-D visualization of the aligned manifold of 3
subjects is shown in Figure 7. It is observed that
neutral faces are clustered within a super-sphere, and
every expression sequence is mapped to a curve on
the manifold that begins near from the neutral face
and extends in distinctive direction with varying
intensity of expression. Expression images from
different subjects but with similar intensity are
mapped closely, which well represents the intensity
resolution of the generalized manifold. It is noted
that each curve is not aligned strictly along a linear
direction, basically because the adopted appearance
feature does not remove the variations of
illumination and pose changes, and the basic
expressions are not fully independent.
To test the performance of facial expression
recognition, 35 image sequences (437 images in
total) from the rest 14 subjects are selected for the
experiment. Unlike just using peak frames of each
sequence in (Shan, 2006), images of expressions
with weak intensity are also included in the testing
set. The overall rate is 86.7% for 7-class recognition.
The confusion matrix shown in Table 2 confirms
that some expressions are harder to differentiate than
others, partially because there are inter-dependences
existing among the basic expressions and it is
difficult to collect pure expression samples even in
the stage of database creation. Most confusion
occurs among anger, sadness, and neutral, however,
these mistakes will not affect much for the facial
expression synthesis because they have low intensity
and can be approximated with neutral without losing
necessary accuracy.
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
Figure 7: The aligned manifold of 3 subjects with intensity
resolution. Different colors represent different
expressions: red-anger, green-disgust, blue-fear, yellow-
happiness, magenta-sadness, cyan-surprise, black-neutral.
Table 2: 7-Class expression recognition.
Ang. Dis. Fear Hap. Sad. Sur. Neu.
Ang. 71.4 0 7.1 0 0 0 21.5
Dis. 16.1 83.9 0 0 0 0 0
Fear 0 1.7 89.6 1.7 0 1.7 5.3
Hap. 0.9 0 4.3 92.2 0.9 0 1.7
Sad. 8.8 1.5 0 0 75.0 2.9 11.8
Sur. 0.9 0 1.9 3.8 1.9 90.6 0.9
Neu. 2.1 0 4.3 6.4 2.1 0 85.1
5.3 Arbitrary Expression Synthesis
Figure 8 gives an example of synthesizing an
expression with different intensities for a new person
by the proposed method. As described above, direct
warping-based method can not produce the details
that are not presented in the input face image,
whereas the proposed method achieves good results
by intensity alignment of the training set.
Figure 8: Synthesis of happiness with accrescent
intensities.
FACIAL EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS AND RECOGNITION WITH INTENSITY ALIGNMENT
51

Figure 9 exhibits the capability of the proposed
method to synthesize different expressions with
diverse input-output modes. The input face image
contains arbitrary expression with unknown intensity
for a new person, and the output image is for any
target expression with any target intensity. The
experimental results further prove the effectiveness
of the unified framework of the proposed algorithm.
(a1) (a2) (b1) (b2)
(c1) (c2) (d1) (d2)
Figure 9: Synthesis results of arbitrary input-output pairs.
(a1)(b1)(c1)(d1): input faces with sadness, anger, fear, and
happiness respectively; (a2)(b2)(c2)(d2): synthesized
expressions of happiness, disgust, anger, and surprise.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a novel facial expression synthesis and
recognition scheme is proposed under a general
framework. With intensity alignment, automatic
facial expression recognition and intensity
identification are performed by using Supervised
Locality Preserving Projections (SLPP), and facial
expression synthesis is implemented based on local
geometry preserving. Extensive experiments on the
Cohn-Kanade database illustrate the effectiveness of
the proposed method.
Future work may address the following aspects.
The first extension is to create an objective
evaluation of the facial expression synthesis. A
Gradient Mean Square Error (GMSE) is introduced
(Wang, 2003) to evaluate the synthesized face
image, however, the criteria is not in accord with the
subjective human observation, and will be failed if
the real expression image is not available. Another
focus is to explore more efficient appearance
features, which can deal with the illumination and
pose variations, for creating the generalized
expression manifold. And then synthesis of mixed
expressions needs to be considered so that any
natural expressions can be generated rather than only
creating a few basic expressions. Due to the inter-
dependence among basic expressions, the current
framework might need to be extended by dividing
the face into several relative-independent
subregions, consequently the reconstructions in each
subregion can be performed by the current approach
without changes, and spatial combinations of the
subregions will produce mixed effects of any
possible expressions.
REFERENCES
Roweis, S.T., Saul, L.K., 2000, Nonlinear Dimensionality
Reduction by Locally Linear Embedding, Science,
290, 2323-2326.
He, X., Niyogi, P., 2003, Locality Preserving Projections,
NIPS.
Ridder, D., et al., 2003, Supervised locally linear
embedding, Proc. of Artificial Neural Networks and
Neural Information Processing, ICANN/ICONIP.
Cheng, J., et al., 2005, Supervised kernel locality
preserving projections for face recognition,
Neurocomputing 67, 443-449.
Shan, C., et al., 2005, Appearance Manifold of Facial
Expression, ICCV workshop on HCI.
Hu, C., et al., 2004, Manifold based analysis of facial
expression, CVPRW on Face Processing in Video.
Chang, Y., et al., 2003, Manifold of Facial Expression,
Int. Workshop on AMFG.
Wang, H., Ahuja, N., 2003, Facial expression
decomposition, ICCV.
Tian, Y. , et al., 2001, Recognizing Action Units for Facial
Expression Analysis, IEEE Trans. on PAMI, 23, 97-
115.
Chandrasiri, N.P., et al., 2004, Interactive Analysis and
Synthesis of Facial Expressions based on Personal
Facial Expression Space, FGR.
Pantic, M., 2000, Automatic Analysis of Facial
Expressions: The State of the Art, IEEE Trans. on
PAMI, 22, 1424-1445.
Yeasin, M., et al., 2006, Recognition of Facial
Expressions and Measurement of Levels of Interest
From Video, IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, 8, 500-508.
Zhang, Q., et al., 2006, Geometry-Driven Photorealistic
Facial Expression Synthesis, IEEE Trans. on
Visualization and Computer Graphics, 12, 48-60.
Du, Y., Lin, X., 2002, Mapping Emotional Status to Facial
Expressions, ICPR.
Liu, Q., et al., 2005, A nonlinear approach for face sketch
synthesis and recognition, CVPR.
Tang, X., Wang, X., 2003, Face sketch synthesis and
recognition, ICCV.
Kanade, T.,
et al., 2000, Comprehensive Database for
Facial Expression Analysis, FGR.
Shan, C., et al., 2006, A Comprehensive Empirical Study
on Linear Subspace Methods for Facial Expression
Analysis, CVPRW.
Kouzani, A.Z., 1999, Facial Expression Synthesis, ICIP.
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
52
