
TOWARDS MULTIAGENT INTERACTIVE ADAPTION
OF INDIVIDUAL MODELS FOR DECISION SUPPORT
∗
Tobias Warden, Thomas Wagner, Hagen Langer and Otthein Herzog
Center for Computing and Communication Technologies (tzi), Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany
Keywords:
Multiagent systems, Interaction protocols, Distributed knowledge management, Machine learning, Knowl-
edge exchange, Interactive learning.
Abstract:
Software agents in complex, dynamic environments need to update, adapt, and improve their knowledge mod-
els for decision making in order to achieve adequate results. Their individual adaption often relies on machine
learning from observational data. However, when data is not available in the required quantity and quality,
alternative approaches are required. We propose an interaction-based approach to individual model adaption
in multiagent systems, describe agent roles and interaction principles, and discuss how a goal-oriented transfer
of knowledge among agents can be integrated into an agent-based knowledge management framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Besides adequate access to decision-relevant informa-
tion and domain knowledge, access to tailored dy-
namic knowledge is a competitive advantage for the
performance of intelligent agents in complex task do-
mains such as health care, supply chain management,
electronic markets, or autonomous logistics. Refer-
ring to dynamic knowledge, we concur with Jennex
who defines knowledge as information, ”understood
such that it explains the how and the why about some-
thing” (Jennex, 2009), i.e., patterns applicable in sit-
uation assessment and prediction. Dynamic knowl-
edge subsumes several categories of integral knowl-
edge models for decision making, including decision
models, prediction models, or classification models.
Depending on the specific use case, the respective
models may be placed at an agent’s disposal on in-
stantiation. This means that the models have been ei-
ther learned offline from historic data or handcrafted
in a knowledge engineering process. In other cases,
the agents themselves may be equipped with the pre-
requisites for online learning of models, based on
individual experience or accessible data repositories.
We consider agents which not only compile and em-
ploy classification models in their primary domain
∗
This research has been supported by the German Re-
search Foundation (DFG) within the Collaborative Research
Centre 637 ”Autonomous Cooperating Logistic Processes
– A Paradigm Shift and its Limitations” at the Universität
Bremen, Germany.
roles but also possess the ability to assess the perfor-
mance of their models. This kind of meta-reasoning
in particular enables the agents to monitor their per-
formance over time and determine when an adaption
of momentarily operationalized classification models
is necessary.
However, left to its own devices, it is often not
possible for a deployed agent to effectuate the desired
model adoption. For instance, the necessity for adap-
tion may allude to a preset model, provided for use
by an external source such as a knowledge engineer.
Consequently, the agent may not have access to a rep-
resentative pool of data to address adaption by means
of individual re-learning on this data. In other cases,
the ability to relearn may exist but the costs of a new
learning sweep are prohibitive or it has become ev-
ident that available learning schemes cannot provide
an improved model. Thus, while self-assessment of
an agent reveals a necessity to adapt a decision sup-
port model, its skill set and/or resources inhibit a self-
sufficient adaption.
We claim that the multiagent environment pro-
vides the key to complement the individual adaption
capability of an agent. Within a persistent multiagent
system (MAS), there are often multiple agents with
kindred primary tasks and associated decision sup-
port models. These models may contain knowledge
that is both relevant and useful for an agent with an
adaption deficiency. We propose a knowledge man-
agement (KM) framework which allows agents to tap
that knowledge in a goal-oriented way. Our approach
553
Warden T., Wagner T., Langer H. and Herzog O..
TOWARDS MULTIAGENT INTERACTIVE ADAPTION OF INDIVIDUAL MODELS FOR DECISION SUPPORT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003886905530559
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (IWSI-2012), pages 553-559
ISBN: 978-989-8425-95-9
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

builds upon dedicated knowledge management func-
tions executed by both the agent seeking model adap-
tion and its supporters. It enables individual adaption
in knowledge networks. Specifically, it acknowledges
that dynamic knowledge may not be simply trans-
ferred among agents. Rather, interactive adaption as
we see it requires that the agents seeking adaption ac-
tively interpret and integrate advice from peers, thus
effectively re-constructing individual advisor knowl-
edge. Thus, our approach to address adaption defi-
ciencies through social interaction emulates, in spirit
rather than cognitive accuracy, human problem solv-
ing strategies. Also, instead of imposing a fixed orga-
nizational structure, the approach is fully distributed.
The framework builds upon and extends approaches
pursued in the machine learning (ML) community,
such as active learning or transfer learning.
The following section first provides a detailed
problem analysis and relates our methodology to ap-
proaches from the ML community. Section 3 then
adds a knowledge management and multiagent per-
spective. It introduces our framework that enables in-
teractive adaption of individual decision support mod-
els. Section 4 highlights related research, then con-
clude with a discussion and future work.
2 PROBLEM ANALYSIS
The minimal common prerequisites for agents that we
seek to support through interactive model adaption
are: 1) For competitive action in their primary domain
role, the agents rely on a classification model. We
make no assumptions as to the origin of this model,
although models learned by the agent itself are our
primary concern. 2) The agents actively monitor both
performance of their models and any self-sufficient
model adaption. Based on these prerequisites, a range
of scenarios for our approach can be spanned.
The first distinction refers the embedding of a
learning subsystem. Agents without this feature can-
not adapt their model through learning from training
data. For adaption, they are thus necessarily depen-
dent on external help. For agents with a learning sub-
system, a second distinction refers to whether indi-
vidual learning constitutes a feasible option alterna-
tive in the momentary context. Engaging in learn-
ing may be infeasible due to the following reasons:
1) Training data may not be accessible, at all, or be
insufficient. 2) The costs in terms of either com-
putation/memory resources or computation time in-
curred by (re-)learning a model may be prohibitive.
In both cases, self-sufficient learning is not practi-
cal as means to improve a model. Hence, agents in
these situations have an interest in enlisting external
help for a target-oriented direct model modification.
Even if (re-)learning was a feasible option in princi-
ple, agents may still have to face problems: The avail-
able data constitutes a skewed sampling of an under-
lying true distribution and is thus not representative
or data may only allow to learn a concept description
which does not comply with desired quality character-
istics. For classification, this would be objectives with
respect to acceptable precision and recall, or false-
positive/false-negative classifications. While learning
is possible in these cases, due to the input data it does
not provide a model which complies with preset per-
formance standards or which bests the currently op-
erationalized model. Therefore, agents in such situ-
ations may have an interest in enlisting external help
designed to either broaden their data basis or acquire
advice which essentially allows their machine learn-
ing scheme to derive additional value from an unvar-
ied data basis.
We have shown scenarios where agents can draw
a surplus from a flexible framework for interactive
adaption of their models. An additional important
finding is that the required complementary adaption
skill sets vary depending on the respective situation.
From a machine learner’s perspective, selected prob-
lem instances laid out in the problem analysis have
been addressed in the literature. Two strands of ML-
research with special relevance are transfer learning
from previous learning tasks an interactive learning
supported by other individuals.
Transfer learning addresses the specific problem
of an insufficient data basis to learn a model through
re-use of training data originally collected for related
learning tasks (for a survey on transfer learning for
classification problems, see (Pan and Yang, 2009)). A
broadening of the data basis is also a primary goal in
the area of active learning (Settles, 1995). The ap-
proach has been suggested amongst others for clas-
sification problems where the labeling of training in-
stances for learning is costly or time-consuming. Be-
ginning with a small pool of labeled training data,
the learning system iteratively learns a model and as-
sesses which additional data would provide the best
chance to optimize the hitherto learned model. This
data is then made available through intervention of a
human domain expert or acquired autonomously, e.g.,
through conduct of experiments.
Možina et al. have proposed argumentation based ma-
chine learning (ABML). This approach allows to at-
tain improvements in the performance of a learning
system which needs to solve a classification task by
a human domain expert as an interaction counter-
part (Možina et al., 2007). The learning system is
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
554

endowed with self-assessment capabilities in that it
monitors its own learning progress and, specifically,
identifies problem instances in the training data, that
are particularly ill-covered by its learned concept de-
scription. The learner then reaches out to its preset hu-
man interaction partner, presenting these instances as
queries. The expert then uses his domain knowledge
to provide a machine-readable explanation (called ar-
gumentation). These are accounted for in subsequent
learning phases.
ABML addresses what we consider the most chal-
lenging flavor of interactive model adaption in that it
tries to tap on the implicit domain expertise of an ad-
visor to augment the existing advisee training data,
thus enabling learning progress. However, the ap-
proach needs to be elevated to multiagent learning.
Here, other learning agents as artificial domain ex-
perts would then subsume the single human expert
involved in ABML. Since specific strengths of ABML
that have been highlighted by Možina et al. include
not only ”effective reconstruction of expert’s prior
knowledge” (Možina et al., 2007, p. 932) and favor-
able results even in situations where the human in-
teraction partner’s ”knowledge about the domain is
superficial (might be wrong occasionally)” (Možina
et al., 2007, p. 933), this approach seems promising.
3 A MULTIAGENT APPROACH
FOR INTERACTIVE ADAPTION
The methodical assessment of robust interactive adap-
tion and, in the process, transfer of individually
learned knowledge among cooperating agents in mul-
tiagent systems requires a suitable context from a
knowledge management point of view. We draw on
a framework for distributed knowledge management
that we have originally proposed for intelligent agents
jointly realizing control of autonomous logistic pro-
cesses (Langer et al., 2006). We will use and extend
this framework as a point of origin to derive necessary
knowledge management roles, means for interoper-
ability, and intra- as well as inter-agent organization
of multiagent adaption.
3.1 Role-based Distributed Knowledge
Management in MAS
This framework focusses on KM whose functions are
procured by software agents. More importantly, these
functions are also designed for use by agents as ar-
tificial decision-makers. In complex task environ-
ments, e.g., autonomous logistics, the availability of
diverse knowledge has been identified as a key factor
for an effective treatment of the primary agent roles in
the modeled processes with a desired quality of ser-
vice (Gehrke et al., 2010). Often, initial provision of
such default knowledge alone is not sufficient in order
to accommodate for the complexity and dynamics of
the task environment. It then becomes necessary to
design adaptive agents, capable of individual knowl-
edge revision and the compilation of tailored models
via learning. Over time, knowledge hence becomes
to an increasing degree tailored to its task context.
Thus, analogously to the situation with employees
within organizations, knowledge is spread rather than
accumulated in a centralized knowledge repository as
assumed in conventional knowledge management ap-
proaches.
This situation is specifically accounted for in
the KM framework through encapsulation of well-
differentiated knowledge management functions as
agent roles. Examples proposed in (Langer et al.,
2006) cover amongst others knowledge acquisition,
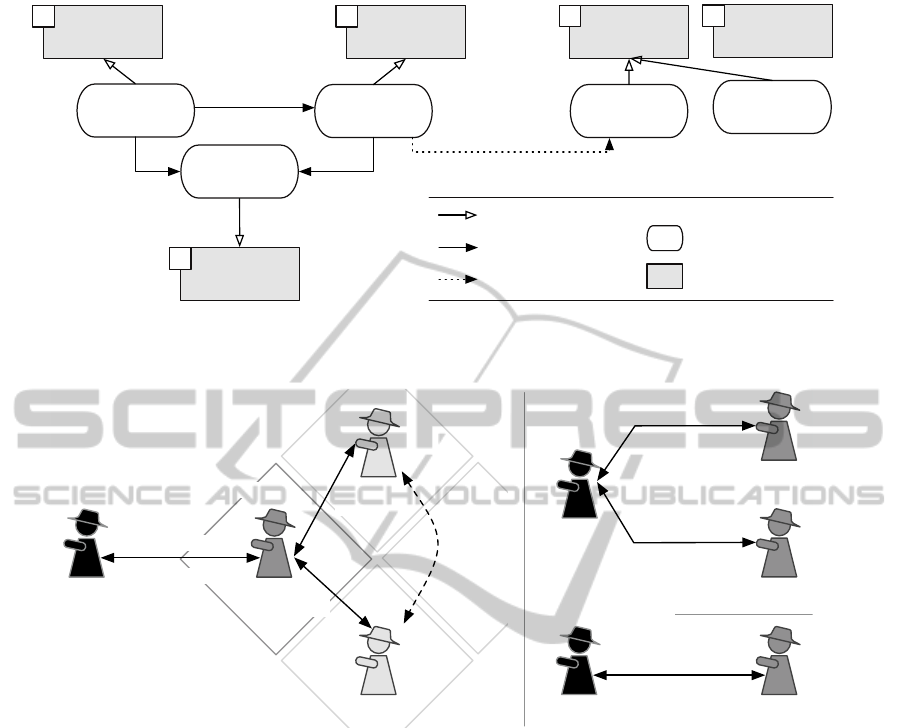
knowledge processing or brokerage (See Figure 1).
The strength and flexibility of the role abstraction is
that, in contrast to other approaches (Van Elst et al.,
2004), knowledge management-related abilities are
not restricted to highly-specialized dedicated agents.
Rather, any agent is free to assume a time-variant set
of knowledge management roles as deemed appropri-
ate in its situation context. These roles are understood
as auxiliary roles which complement domain-specific
primary roles such as the management of logistic pro-
cesses. The roles can be further categorized into inter-
nal and external roles. We adopt a notion of internal
roles where these are characterized 1) by reasoning
capabilities and 2) a deliberation pattern (i.e., a plan
to accomplish the knowledge management task). In-
ternal roles can be conducted self-sufficiently. Exter-
nal roles by contrast require interaction, structured by
one or more interaction protocols.
3.2 Knowledge Management Roles for
Interactive Adaption
Two complementary roles are involved in interactive
adaption, namely the advisee role played by an agent
seeking assistance in adaption and the advisor role
played by a temporary domain expert. In our mul-
tiagent environment, these roles are no longer tied to
specific types of actors. We now introduce additional
knowledge management roles and role aspects (See
Figure 1) which extend our framework for distributed
knowledge management (Langer et al., 2006).
The model acquisition role is a specialization of
the knowledge processing role, it presupposes access
TOWARDS MULTIAGENT INTERACTIVE ADAPTION OF INDIVIDUAL MODELS FOR DECISION SUPPORT
555
Knowledge
Consumer
Knowledge
Broker
Knowledge
Provider
Knowledge
Processing
Model
Acquisition
Knowledge
Acquisition
Advice
Integration
Advisor
Advisee
Advisory
Broker
Register Advisory
Service
Request Advisory
Service
Request advice for
learning problem
Role Specialization
Role Interaction
Task Delegation
Role Extensions
Basic KM Roles
E E
E
I
I
Figure 1: Adopted roles in the distributed KM framework by Langer et al. (Langer et al., 2006) (gray) and extensions for
interactive adaption of individual models.
...
P
P
P
Advisee
Advisor
1
Advisee
Advisor
n
Advisor
1
...
Advisee
Advisor
1
Advisor
n
Advisor
2
...
Advice
1
(P)
P
P,AdvList
Advice
1
(P)
Advice
n
(P)
Advice
2
(P)
Advice
n
(P)
Advice
*
(P)
1:1:(n-1)-Interaction
1:n-Interaction
P
1:1-Interaction
Figure 2: Overview of possible interaction patterns for knowledge transfer episodes.
to representative training data and an adequate ma-
chine learning scheme (e.g., a decision tree learner).
Contingent on the agents’ primary domain role(s), the
data used for machine learning may constitute indi-
vidual experience gathered through action in the task
domain. It may as well originate from a data reposi-
tory accessible to the learner. Once a model such as
a classifier has been learned successfully, we assume
that the role also exposes its inferential capabilities
for internal used by the agent.
The advisee role is a specialization of the knowl-
edge consumer role, elevated to the level of knowl-
edge rather than information. Any agent may as-
sume the advisee role when an assessment of its de-
cision support model has shown deficiencies in the
model performance that cannot be handled by inter-
nal means alone. Such a situation may arise due to
an insufficient access to representative training data
such that the prerequisites for the model acquisition
role cannot be met. If the agent is keen to improve
its model immediately rather than wait for new data
to become accessible, the advisee role offers a viable
action alternative. The agent then becomes an active
learner in that it actively seeks for and eventually ap-
proaches peers that assume the learning advisory role
introduced below. In the interaction associated with
these roles, advisors are presented with learning prob-
lems and asked to offer advice to address said problem
based on their models.
The advice integration role is a specialization of
the knowledge processing role. Advice integration is
understood as a subsidiary task to succeed with the
advisee role. We propose that the superordinate ad-
visee role delegates advice integration to this internal
role. One can conceive different feasible interpreta-
tions of this role. As a first option, the advice pro-
vided as input may be used to directly revise an ex-
isting model (e.g., by pruning or expanding branches
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
556

in a decision tree, or revision of a rule set). A sec-
ond option is to conceive the advice integration as a
specialization of the model acquisition role presented
above. In such a case, a new model is learned based
on the initial training data and the accumulated advice
as additional background knowledge to bias/focus the
operation of a learning scheme that is able to handle
the additional input.
The advisor role is the role complement to the
advisee role and a specialization of the knowledge
provider role. It may be played by any agent with ac-
cess to a particular decision support model if it wants
to provide an knowledge advisory service for agents
which need to learn and maintain similar models. The
advisor model constitutes a valuable asset in that it
captures relevant domain expertise for agents in sim-
ilar application contexts. The model which is used
as basis for the advisory service may be hand-crafted,
yet the probably more interesting use case involves
individually learned models. In order to play an ad-
visor role, it is necessary to interpret requests placed
by advisees and compile tailored advice to address the
communicated learning subproblem, based on the ad-
visor’s own model. The role abstracts from the par-
ticular type of decision support model used by an ad-
visor. While the adoption of an advisee role is an im-
mediate consequence of a concrete need, the comple-
mentary advisor role may be played persistently.
The advisory broker role is an external role. It
is devised as a specialization of the knowledge bro-
ker role. An agent in this role acts as a specialized
yellow pages service within the MAS. It administers
meta-information about knowledge advisory services
exposed by agents currently assuming one or more ad-
visor roles for specific learning problems. The meta-
information is deposited by the advisors. It specifies
amongst others the respectively handled learning task
(e.g., classification), any bias towards particular learn-
ing objectives (e.g., avoidance of false positive classi-
fications) and a meta-description of the learning do-
main. An advisory broker also accepts requests by
agents seeking advice for a learning problem. The
broker matches the request information against its ad-
visory portfolio in order to point the requesting agents
to suitable interaction partners.
3.3 Structuring Agent Interaction for
Knowledge Transfer Episodes
Further building blocks for our approach are means to
organize interactive adaption. To that end, we propose
a two-layer approach: On the lower layer, an interac-
tion protocol is used to structure the course of a single
knowledge transfer episode. Each such episode spans
the acquisition of a single piece of advice relating to
a specific learning subproblem. On the upper level,
agents need to structure their global interactive learn-
ing process which may involve multiple consecutive
lower-level transfer episodes. Each is thereby char-
acterized by a specific learning subproblem which is
brought up by an advisee. In the episode, the advisee
engages in direct interaction with one or more suitable
advisors which need to be known beforehand. Given
such a list of advisors, the advisee can then utilize
several interaction patterns as sketched in Figure 2.
Single-Tier 1:1 Interaction: As a first option, the
advisee may choose one advisor for exclusive inter-
action. As a result, the advisee will receive a single
piece of advice to resolve the learning subproblem ad-
dressed in the transfer episode. If the advisor refuses
to advise on the specified problem, the outcome may
also be a failure of the learning episode.
Single-Tier 1:n Interaction: In order to broaden
advice acquisition for the learning subproblem at
hand, and at the same time reduce to the failure po-
tential of the transfer episode, the agent may place the
same advisory request with a larger number of advi-
sors. As a result of this interaction pattern the ad-
visee may be able to receive multiple independently
compiled pieces of advice. As a consequence, it lies
within the responsibility of the advisee to perform ad-
vice integration. In case of complementary advice,
such an operation may be straightforward. However,
advice integration also involves conflict resolution for
contradictions. An interaction protocol for this inter-
action pattern is depicted in Figure 3.
Multi-Tier 1:1:n Interaction: The two interaction
patterns discussed so far are single-tier interactions
in which the advisee interacts directly with all advi-
sors involved in the transfer episode. An alternative is
a multi-tier interaction which again involves a group
of advisors. In contrast to the preceding interaction
patterns, the advisors appear as a holon
2
with a sin-
gle advisor acting as holon head. The advisory holon
is created dynamically upon request by the advisee.
Besides the learning subproblem that constitutes the
topic of the interaction, the advisee also communi-
cates to an initial advisor, acting as holon head, a set
of additional advisors. These then are to be consulted
while preparing a single, consolidated piece of advice.
The initial advisor uses this information about the ad-
ditional advisors to relay the learning problem. It is
also responsible for advice integration. The interac-
tion among the advisors can itself follow different in-
teraction patterns depending on the preferred method
2
In the categorization of holonic MAS by Fischer et
al. (Fischer et al., 2003), the organizational form of an mod-
erated association is adequate.
TOWARDS MULTIAGENT INTERACTIVE ADAPTION OF INDIVIDUAL MODELS FOR DECISION SUPPORT
557
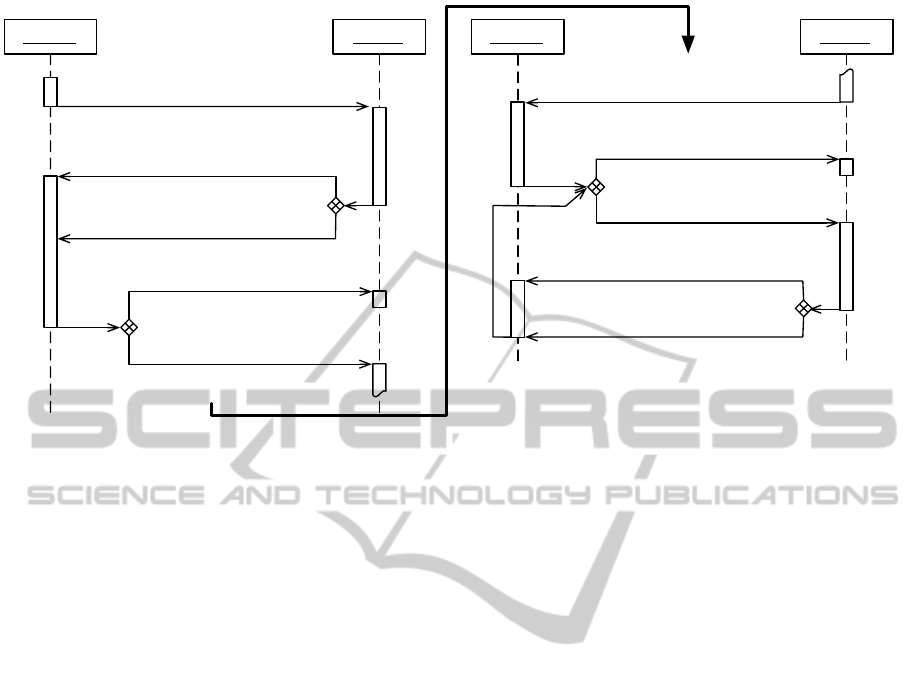
: Advisee : Advisor
inform-result: cannot_advise
inform-result : can_advise
(Learning Sub Problem P)
inform-done : inform
request: advice_on(P)
request: can_advise_on(P)
1 n
n
m
n-m
o
m-o
: Advisee : Advisor
inform-result: cannot_explain
inform-result: explanation(Adv)
request: explain_advice(Adv)
inform-done : inform
1 n
p ≤ o
inform-result : advise(P)
(Advice Adv)
Figure 3: Protocol for single-tier 1:n interaction in a knowledge transfer episode.
of advice integration.
A Single-Tier 1:n Interaction Protocol We now
present an interaction protocol for the single-tier 1:n
interaction pattern (See Figure 3). The protocol con-
sists of multiple stages. First, the advisor requests
from all potential advisors, whether or not they con-
sider themselves fit to provide advice for the learning
subproblem at hand. The advisee waits for the respec-
tive advisor responses. Based on this feedback, the
advisee can select the subset of advisors from which
it can then request actual advice. In case the advisors
do not only communicate a simple binary decision
with respect to their willingness to advise, but also
include information about their confidence to provide
’good’ advice, the advisee may choose to continue the
conversation with a selection of all capable advisors.
Those which are excluded are consequently informed
that their services are no longer required. The remain-
ing advisors receive requests to advise. The interac-
tion protocol in Figure 3 then envisages that the earlier
consent to advise enforces that each advisor actually
provides individual advice and does not back out at
this stage of the conversation. In case the communi-
cated advice proves to be comprehensible for the ad-
visee, the interaction with the respective advisor ends
here. If, however, the advisee cannot comprehend any
piece of advice directly, the interaction protocol pro-
vides for a continuation of the conversation to (repeat-
edly) request additional information to further under-
standing.
4 RELATED WORK
Interactive adaption of decision support models bears
a cross-sectional character with related work from
several research fields, namely machine learning (ML)
and multiagent systems (MAS). In Section 2, we in-
troduced related ML-research, most notably argument
based machine learning by Možina et al. (Možina
et al., 2007). While still restricted to adaption of rule-
based classification models (AB-CN2), the approach
has been embraced by Napierala and Stefanowski for
the MODLEM rule induction algorithm (Napierala and
Stefanowski, 2010). We consider these approaches
a vantage point to implement the advice integra-
tion role. Ontañón and Plaza propose an approach
to interactively resolve inconsistencies in individu-
ally learned concept descriptions based on computa-
tional argumentation (Ontañón and Plaza, 2010). As
their goal is the consolidation of individual models,
the approach is interesting when advice from mul-
tiple advisors must be consolidated to reach con-
sensus. Costantini and Tocchio propose an ap-
proach for learning by knowledge exchange in log-
ical agents (Costantini and Tocchio, 2005). The au-
thors concentrate on the exchange of agent beliefs and
rules encoding action recipes. They contemplate the
role of trust in exchanging knowledge and propose
strategies for graded operationalization of acquired
knowledge. Jakob et al. implement adaptability in
MAS by means of collaborative logic-based learning,
focussing on communication strategies for acquired
knowledge (Jakob et al., 2008). At the cross-section
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
558

of MAS, robotics, and reinforcement learning, the im-
plementation of social learning strategies have drawn
significant attention (see, for instance, (Noble and
Franks, 2003)).
5 DISCUSSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we have sketched an interaction-based
approach to the adaption of individual decision sup-
port models in MAS. It is desirable when software
agents in complex, dynamic environments need to up-
date, adapt, or improve their knowledge base for de-
cision making. Sometimes, this improvement process
can be based on machine learning from observational
data, alone. But when available data is insufficient
in quantity or quality, when data is too expensive, or
when the machine learning process turns out to be too
complex, alternative approaches are needed. There
are two basic components in our approach: 1) a set of
specific knowledge transfer roles which extends a set
of basic knowledge management roles, and 2) a col-
lection of interaction protocols for knowledge trans-
fer.
Ongoing work on the proposed multiagent frame-
work comprises a prototype implementation of the
KM roles and interaction patterns introduced in Sec-
tion 3. We focus first on the adaption of rule-based
classification models, relying, for advice integration,
on the ABML approach by Možina et al. In the pro-
cess, we will also elaborate the meta-control, used
by an advisee to guide its interactive adaption pro-
cess over multiple knowledge transfer episodes, as a
flavor of local search in a model space. The proto-
type is implemented based on the JADE agent devel-
opment environment. Evaluation will be performed
in the PlaSMA multiagent-based simulation environ-
ment (Warden et al., 2010). In the future, we also
seek to enable a more far-reaching interoperability be-
tween heterogeneous agents in the context of inter-
active model adaption. This includes support for di-
versity in employed models (e.g., rule-based for the
advisee and ANN-based for the advisor(s)). It also in-
cludes support for heterogeneity in the training data
(with respect to attributes), discretization of values in
individual learning, and the naming of attributes and
concept classes. These extensions specifically call for
the provision of additional KM roles, enabling, for in-
stance, semantic mediation.
REFERENCES
Costantini, S. and Tocchio, A. (2005). Learning by Knowl-
edge Exchange in Logical Agents. In WOA, pages 1–
8. Pitagora Editrice Bologna.
Fischer, K., Schillo, M., and Siekmann, J. (2003). Holonic
Multiagent Systems: A Foundation for the Organisa-
tion of Multiagent Systems. In Holonic and Multi-
Agent Systems for Manufacturing, pages 1083–1084.
Springer.
Gehrke, J., Herzog, O., Langer, H., Malaka, R., Porzel, R.,
and Warden, T. (2010). An Agent-Based Approach
to Autonomous Logistic Processes. Künstliche Intel-
ligenz, 24(2):137–141.
Jakob, M., Toži
ˇ
cka, J., and P
ˇ
echou
ˇ
cek, M. (2008). Collab-
orative Learning with Logic-Based Models. In Adap-
tive Agents and Multi-Agent Systems III. Adaptation
and Multi-Agent Learning, volume 4865 of LNCS,
pages 102–116. Springer.
Jennex, M. (2009). Re-Visiting the Knowledge Pyramid. In
Proceedings of the 42nd Hawaii Intl. Conference on
System Sciences, 2009., pages 1–7. IEEE.
Langer, H., Gehrke, J. D., Hammer, J., Lorenz, M., Timm,
I., and Herzog, O. (2006). A Framework for Dis-
tributed Knowledge Management in Autonomous Lo-
gistic Processes. Intl. Journal of Knowledge-Based &
Intelligent Engineering Systems, 10(4):277–290.
Možina, M., Zabkar, J., and Bratko, I. (2007). Argu-
ment Based Machine Learning. Artificial Intelligence,
171(10-15):922–937.
Napierala, K. and Stefanowski, J. (2010). Argument Based
Generalization of MODLEM Rule Induction Algo-
rithm. In Rough Sets and Current Trends in Comput-
ing, volume 6086 of LNCS, pages 138–147. Springer.
Noble, J. and Franks, D. W. (2003). Social Learning in
a Multi-Agent System. Computing and Informatics,
22(6):1001–1015.
Ontañón, S. and Plaza, E. (2010). Concept Convergence in
Empirical Domains. In Proceedings of the 13th Intl.
Conference on Discovery Science, pages 281 – 295.
Pan, S. and Yang, Q. (2009). A Survey on Transfer Learn-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data En-
gineering, pages 1345–1359.
Settles, B. (1995). Active Learning Literature Survey. Sci-
ence, 10(3):237–304.
Van Elst, L., Dignum, V., and Abecker, A., editors (2004).
Agent-Mediated Knowledge Management: Interna-
tional Symposium (AMKM ’03), Standford, CA, USA.
Springer. Revised and Invited Papers.
Warden, T., Porzel, R., Gehrke, J., Herzog, O., Langer, H.,
and Malaka, R. (2010). Towards Ontology-based Mul-
tiagent Simulations: The PlaSMA Approach. In Proc.
of the 24th European Conference on Modelling and
Simulation, pages 50–56.
TOWARDS MULTIAGENT INTERACTIVE ADAPTION OF INDIVIDUAL MODELS FOR DECISION SUPPORT
559
