
Allocation Considering Agent Importance
in Constrained Robust Multi-Team Formation
Ryo Terazawa and Katsuhide Fujita
a
Graduate School of Engineering, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Team Formation, Robustness, Multi-objective Constraint Optimization.
Abstract:
Forming a team to accomplish a given mission is a significant challenge in multi-agent systems. The mission-
oriented team formation problem is selecting agents with a set of skills to accomplish a mission. Each mission
can be accomplished by assigning a team with the necessary skills. Furthermore, the team needs to accomplish
the mission, even if an agent fails in an environment where agents are lost between missions. In addition, other
aspects besides the ability to accomplish the mission are considered in team formation.
In this paper, we focus on the mission-oriented constrained robust multi-team formation problem. We define a
framework, decision, and several optimization problems. Then, we propose an algorithm for the optimization
problem with fixed robustness. In our experiments, we confirmed the search efficiency by changing the order
in which agents are searched. The results show that a short runtime is obtained in searching for agents with
high importance when the ratio of solutions to the search space is large. Furthermore, the runtime is minimized
in searching for easily pruned agents when the ratio of solutions to the search space is small.
1 INTRODUCTION
The mission-oriented team formation prob-
lem(Liemhetcharat and Veloso, 2012; Nair and
Tambe, 2005a) is the problem of forming the best
possible team to accomplish an interactive mission
given a limited set of resources. The team formation
problem can be applied to many problems, including
those related to multi-agent collaboration, such
as RoboCup rescue teams(Parker et al., 2016),
unmanned aerial vehicle operations(George et al.,
2010), and online soccer prediction games(Matthews
et al., 2012). However, multiple factors should be
considered when trying to apply the team formation
problem to real-world problems(Moz and Pato,
2004). For example, robustness (i.e., the ability of
the team to continue the mission) is crucial in a
dynamic environment, where an agent may be lost
during a mission, such as when an agent is injured
in the formation of a rescue team. In addition, it
may be prohibited to assign robots from competing
companies to the same team if different companies
provide the robots used in the rescue team.
(Demirovic et al., 2018), a study on recoverability,
and (Schwind et al., 2021), a study on partial robust-
ness, are representative of works that generalize the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7867-4281
ability of a mission to achieve its goals. These works
are valid because of the potentially huge costs in en-
suring robustness. However, this paper focuses on the
influence of factors other than mission accomplish-
ment ability on team formation, aiming at forming a
robust multi-team with constraints. The constraint
means that an agent may be lost during a mission,
where robots from competing companies are prohib-
ited from being assigned to the same team. How-
ever, a mission-oriented robust multi-team formation
considering constraints has not been studied. In ad-
dition, efficient algorithms have not been proposed.
Compared to some existing works(Okimoto et al.,
2016), this paper considers the robustness and cost of
each team simultaneously (i.e., bi-objective optimiza-
tion) with the problem constraints.
In this paper, we define a new framework called
mission-oriented constrained robust multi-team for-
mation (MOCRMTF). MOCRMTF considers the de-
cision problem and some optimization problems. A
team is considered k-robust (for a given non-negative
integer k) if k agents can be removed from the team
and the team can accomplish the given mission. The
decision problem is whether a team can be formed or
not for a given cost x and robustness k if all teams
under cost x satisfy k-robust, and multi-teams satisfy
the constraints. We can also consider the optimiza-
Terazawa, R. and Fujita, K.
Allocation Considering Agent Importance in Constrained Robust Multi-Team Formation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010774300003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 1, pages 131-138
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
131

tion problem of fixing the robustness of teams and
finding the least-cost team that satisfies the robust-
ness. As another optimization problem, we can con-
sider MOCRMTF as a multi-objective constraint op-
timization problem (MO-COP) (i.e., optimizing both
the cost and robustness of a team). Compared to the
existing works(Okimoto et al., 2016), the goal of this
paper is to form a robust multi-team with constraints.
We clarify classes to which MOCRMTF belongs
in the theory of computational complexity. From a
computational perspective, the mission-oriented team
formation problem is similar to a well-known NP-
complete decision problem (e.g., SET COVER prob-
lem). An existing work(Okimoto et al., 2016) on task-
oriented robust team formation (TORTF) shows the
decision problem with NP-complete. In MOCRMTF,
we need to consider constraints and multiple teams,
unlike TORTF. We prove that MOCRMTF belongs to
NP-complete and its computational class is the same
as TORTF’s. We also propose an algorithm for the op-
timization problem of finding the least-cost team that
satisfies the robustness goal. The experiments show
that the runtime varies, depending on the order of the
search. We also show that the value of robustness
is significantly limited by the number of agents and
teams in MOCRMTF.
The remainder of the study is organized as fol-
lows. First, we describe MOCRMTF. Next, we
propose the optimization algorithm for MOCRMTF
and prove MOCRMTF’s computational complexity.
Then, we demonstrate the experimental simulation re-
sults and discussions. Finally, we conclude this study.
2 RELATED WORK
The problem of forming teams has been the subject
of much research. Classically, a set of tasks and a set
of agents are provided, and each agent has some costs
and skills to accomplish each task. The performance
of a team is often evaluated by the set of capabilities
of its members chosen from a limited set of resources.
(Nair and Tambe, 2005b) addressed the team for-
mation problem to maximize expectations so that
teams have the necessary skills for irregular missions.
There are also several studies on team formation
problems, where agents are assumed to be lost. Ro-
bustness was proposed by (Okimoto et al., 2015) as
the most robust concept for agent loss.
(Demirovic et al., 2018) proposed recoverability
as a generalization of the ability to accomplish a mis-
sion. Recoverability allows a team to function in the
event of an agent loss by employing an additional
agent with a smaller cost and capability.
(Schwind et al., 2021) proposes partial robustness,
which guarantees that a team will function to some
extent in the event of an agent loss. However, the for-
mation of a team may consider factors other than the
ability to accomplish the mission. For example, gen-
der balance, and assignment of robots from compet-
ing companies.
To the best of our knowledge, no team formation
problem simultaneously considers agent losses and
non-skill factors.
3 MISSION-ORIENTED
CONSTRAINED ROBUST
MULTI-TEAM FORMATION
(MOCRMTF)
MOCRMTF is defined on the basis of (Okimoto et al.,
2016).
Definition 1 (Constrained Multi-Team Formation
Problem (CMTF))
A constrained multi-team formation problem is
defined by a tuple CMT F = hA,S, M, cost, skill,
constrainti. where A = {a
1
,a
2
,..., a
n
} is a set of
all agents, S = {s
1
,s
2
,..., s
t
} is a set of all skills of
agents, M = {m
1
,m
2
,..., m
g
} is a set of missions, and
m
i
⊆ 2
S
for 1 ≤ i ≤ g. In addition, cost : 2
A
× M → N
is the cost function, skill is a map of A → 2
S
, and
constraint is a mapping of A → C. C = {c
1
,c
2
,..., c
n
}
is a set of constraints for each agent, and c
i
⊆ A for
1 ≤ i ≤ n. The function cost computes a team’s cost,
the map skill outputs an agent’s skill, and the map
constraint is used to manage the constraint state of
the team. Note that n,t,i,g ∈ N. The set of agents
T ⊆ A is called the team, and the pair (T, m) is called
the mission team, m ∈ M.
Afterward, we assume CMT F = hA,S, M,cost, skill,
constrainti, a constrained multi-team formation prob-
lem given a mission team (T, m).
Definition 2 (Mission Team Cost)
A non-negative integer x, (T, m) is called x-costly if
the cost of (T,m) is less than x: cost(T,m) ≤ x. For
simplicity in this paper, it is assumed that the cost of
a team are given by the sum of the costs of each agent
a
i
of team T , that is, cost(T,m) =
∑
a
i
∈T
cost(a
i
,m).
In this paper, we conduct experiments, where the cost
is unaffected by the mission content, but we define the
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
132

framework as one in which the cost can be affected by
the mission for the general problem of MOCRMTF.
Definition 3 (Mission Team Validity)
(T, m) is said to be valid if (T, m) can accomplish m:
m ⊆
S
a
i
∈T
skill(a
i
).
Definition 4 (Mission Team Robustness)
Given a non-negative integer k, (T, m) is called k-
robust if the following conditions are met: (T \T
0
,m)
is valid for any T
0
(T
0
⊆ Tand|T
0
| ≤ k).
We define the team constraints introduced in this
study to consider points other than the ability to per-
form a mission in the mission-oriented team forma-
tion problem.
Definition 5 (Mission Team Constraints)
Because (T, m) satisfies a constraint, the following
equation holds: T ∩
S
a
i
∈T
constraint(a
i
) =
/
0. This
constraint prohibits an agent a
i
from being classified
into the same team with an agent that is an element
of the set obtained by the mapping constraint and de-
fines an arbitrary pair of agents that cannot be paired.
We define a mission multi-team and its associated
cost, robustness, and constraints.
Definition 6 (Mission Multi-Team)
A set consisting of mission teams is called a mission
multi-team (MMT ): MMT = {(T
i
,m
i
)|T
i
⊆ A, m
i
∈
M, T
i
∩ T
j
=
/
0,1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ g}
Definition 7 (Mission Multi-Team Cost)
Given a non-negative integer x
M
, MMT is called
x
M
-costly if the sum of the costs of an element
(T
i
,m
i
) of MMT is less than or equal to x
M
:
∑
1≤i≤g
cost(T
i
,m
i
) ≤ x
M
. If
∑
1≤i≤g
cost(T
i
,m
i
) = x
M
,
the cost of that multi-team is x
M
.
Definition 8 (Mission Multi-Team Validity)
MMT is regarded as valid if each mission team
(T
i
,m
i
) of MMT is valid (1 ≤ i ≤ g).
Definition 9 (Mission Multi-Team Robustness)
MMT and a non-negative integer k
M
, MMT is k
m
-
robust if k
M
≤ min(k
i
|1 ≤ i ≤ g). If min(k
i
|1 ≤ i ≤
g) = k
M
, the robustness of that multi-team is k
M
.
Definition 10 (Mission Multi-Team Constraint)
MMT satisfies a constraint if all mission teams
(T
i
,m
i
) of MMT satisfy the constraint.
In this paper, we assume that a multi-team is sim-
ply a set of multiple teams and that the effects of
inter-team relationships are not considered. In ad-
dition, robustness and constraints do not change the
complexity of the team formation problem. There-
fore, the computational class of MOCRMTF is the
same as mission-oriented team formation. There-
fore, the decision problem of MOCRMTF is NP-
complete(Okimoto et al., 2015).
Definition 11 (Decision Problem)
Input: CMT F = hA,S, M, cost, skill, constrainti,
maximum cost x, robust goal k(x,k ∈ N).
Output: MMT that satisfies the constraints and is
x-costly and k-robust.
Considering the cost and robustness of mission multi-
teams simultaneously, multi-team formation is con-
sidered a bi-objective optimization problem. Because
there is a tradeoff between the two objectives in this
problem, no ideal mission multi-team that minimizes
cost c
M
and maximizes robustness k
M
exists. There-
fore, the “optimal” mission multi-team for this prob-
lem is defined as Pareto optimization.
Definition 12 (Dominance)
Considering two mission multi-teams MMT and
MMT
0
that satisfy the constraints, the cost of MMT
is c
M
and its robustness is k
M
, whereas the cost of
MMT
0
is c
0
M
and its robustness is k
0
M
. The dominance
of MMT over MMT
0
means that (c
M
≤ c
0
M
and k
M
>
k
0
M
) or (c
M
< c
0
M
and k
M
≥ k
0
M
)
Definition 13 (Pareto Optimality)
If no constraint-satisfying multi-team MMT
0
dom-
inates the constraint-satisfying multi-team MMT ,
MMT is said to be a Pareto optimal mission multi-
team.
Definition 14 (Bi-objective Optimization Problem)
Input: CMT F = hA, S,M, cost,skill,constrainti
Output: All Pareto optimal mission multi-teams
(T, m) satisfying the constraints. A typical MO-
COP(Marinescu, 2010; Rollon and Larrosa, 2006) is
Pareto optimal in the worst case for all possible as-
signments.
Allocation Considering Agent Importance in Constrained Robust Multi-Team Formation
133

At this time, we can consider the optimization
problem of MOCRMTF, where the robustness goal is
fixed and the goal is to minimize the cost.
Definition 15 (Optimization Problem with Fixed
Robustness)
Input: CMT F = hA, S, M, cost,skill,constrainti and
robust goal k(x,k ∈ N).
Output: Pareto optimal mission multi-team that sat-
isfies constraints and has robustness k.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Algorithm of MOCRMTF
An algorithm for the optimization problem with fixed
robustness is based on the branch-and-bound method
(Lawler and Wood, 1966), which guarantees to output
a mission multi-team with the lowest cost among mis-
sion multi-teams satisfying constraints with the same
robustness as the robust goal. Algorithm 1 illustrates
the initialization procedure. First, S and As are initial-
ized to be empty. No agent is assigned to any team in
the pre-search phase, so each mission multi-team is an
empty set (line 6). R
As
stores the robustness of the cur-
rent partial team assignment As (line 7) and is used to
determine whether the robustness objective has been
achieved. Note that the algorithm assumes that the or-
der of agents is given lexicographically to create the
search tree. The search for the solution starts from
the root node of the search technique, which is the
first agent in the agent order (line 9).
Algorithm 2 shows the pseudocode that demon-
strates the solution details. It takes an integer N as
a parameter and attempts to assign an agent in the
Nth of A to each mission team (T, m) (lines 10,11). If
the agent does not have any skills related to the mis-
sion of m and cannot contribute to the team, the as-
signment to this mission team (T, m) is ignored (lines
15-17). Next, the agent’s constraints are evaluated,
and if there is already an opponent in (T, m) who is
prohibited from being assigned to the same team, the
assignment is ignored as well (lines 18-20). If both
skills and constraints are satisfied, the agent is added
to the team T of (T, m) ∈ As (line 21). Then, if the
cost of As exceeds the cost of the current solution by
adding the agent to T , the agent’s assignment is can-
celed (T ← T \ {a}) and the search continues with
the next team assignment (lines 23-26). Finally, the
robustness of As is evaluated (lines 26-36). The ba-
sic idea of this part is to detect the possibility of the
current partial team assignment As not resulting in a
Algorithm 1: Constrained Multi-Teams Formation Target
Robustness.
Input: A multi-team formation problem CMT F =
hA,P,M, cost, skill, constrainti
Output: Mission multi-team S
1: S: a MMT //Current solution
2: S ←
/
0
3: As: a MMT //Current assignments
4: As ←
/
0
5: for each mission m of M do
6: As ← As ∪ {(
/
0,m)} //All missions are added to
As
7: end for
8: R
As
:a robustness of As //Current assignments’ ro-
bustness
9: R
As
← 0
10: target-resolve (1,R
As
,As,S,CMT F)
11: return S
mission multi-team that satisfies the robustness goal.
At least t agents are required to increase the robust-
ness of t mission teams. Therefore, the minimum
number of agents required to obtain an effective mis-
sion multi-team can be calculated for the remaining
mission teams (lines 27-32). If the number of remain-
ing unallocated agents is less than this minimum num-
ber, it means that no valid mission multi-team can be
found. Simultaneously, the robustness of the current
mission multi-team by storing the minimum robust-
ness value of each mission team is computed (line
33). (|A| − N) is the maximum number of agents that
can still be added to As. If this number is less than
the minimum agents required MinAgent, it is point-
less to continue with the current partial team alloca-
tion As. Therefore, the agent assignment is canceled,
and we continue the search with the next team assign-
ment (lines 34-36). By evaluating skills, constraints,
costs, and robustness, pruning reduces branching and
the search space. If the current assignment passes
all evaluations, the search continues with the next
agent (line 38). We also need to cover and search
for branches that do not assign agent a to all teams
(line 41). If As satisfies the robustness target, i.e.,
R
As
≥ targetRobust, cost(As) ≤ cost(S) is guaranteed
because the cost is checked when making the assign-
ment. Therefore, As is the dominant solution for S.
Therefore, S is set to As and solutionCost is updated
(lines 1-5). Finally, it backtracks and continues the
search (lines 5, 42). The case, where the allocation is
completed without satisfying the robust goal needs to
be handled at this time (line 8).
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
134

Algorithm 2: target-resolve(N,R
As
,As,S,CMT F).
Input: An integer N,R
As
, a MMT As, S and
a multi-team formation problem CMT F =
hA,P,M,cost,skill, constrainti.
1: //1)Judge if As is an appropriate solution
2: if R
As
≥ targetRobust then
3: S ← As
4: solutionCost ← cost(As)//Initial value of
solutionCost is ∞
5: return
6: end if
7: //All agents have been assigned
8: if N > |A| then
9: return
10: end if
11: a:the N
th
agent of A
12: //2)Assign agent N to a mission
13: for each(T, m) of As do
14: //3)Check the T robustness
15: if T ’s robustness k ≥ targetRobust then
16: continue
17: end if
18: //4)Check if a can accomplish a task of m
19: if skill(a) ∩ m ==
/
0 then
20: continue
21: end if
22: //5)Check a constraint
23: if constraint(a) ∩ T 6=
/
0 then
24: continue
25: end if
26: T ← T ∪ {a}
27: //6)Check the cost bound
28: if cost(As) > solutionCost then
29: T ← T \ {a}
30: continue
31: end if
32: //7)Check multi-team robustness
33: MinAgent :← 0
34: for each pair(T
i
,m
i
) of As do
35: if T
i
is not valid w.r.t. m then
36: MinAgent ← MinAgent +targetRobust + 1
37: end if
38: if T
i
’s robustness is k w.r.t. m and k <
targetRobust then
39: MinAgent ← MinAgent + (targetRobust − k)
40: R
As
← min(R
As
,k)
41: end if
42: end for
43: if (|A| − N) < MinAgent then
44: T ← T \ {a}
45: continue
46: end if
47: //8-1)Continue the search with the next agent
48: target-resolve(N + 1, R
As
,As,S,CMT F)
49: T ← T \ {a}
50: end for
51: //8-2)Continue the search with the next agent
52: target-resolve(N + 1, R
As
,As,S,CMT F)
53: return
4.2 Computational Complexity of
MOCRMTF
The computational complexity of MOCRMTF is
given by the following proposition, where m repre-
sents the number of missions, n represents the num-
ber of agents, s represents the total number of skills,
and the number of agents is sufficiently larger than the
total number of skills and missions.
Proposition: The worst-case space complexity
of our proposed MOCRMTF algorithm is O(n(m +
1)
n
) and the worst-case time complexity is O(n(m +
1)
n+1
).
Proof of Space Complexity: From the number of mis-
sions m and the number of agents n, the number of
patterns in the allocation of all agents is (m + 1)
n
,
which is the number of mission multi-teams that need
to be saved in the worst case. Mission multi-teams
can be expressed in terms of allocation, constraints,
robustness, and cost. Since an agent can only belong
to one mission team, the allocation can be represented
as a vector of integers of size n, where each com-
ponent represents a team of one agent. The team’s
constraints can be represented by a vector of integers
of size n since it can be denoted by the sum of the
constraints of each agent. It is sufficient to store the
number of agents corresponding to a mission so that
it can be characterized as a vector of integers of size
s to calculate robustness for each mission team (T, m)
in As. The cost calculation can be performed with
constant memory. Therefore, the amount of spatial
computation is limited by O ((n+n +s)×(m+1)
n
) =
O(n(m + 1)
n
).
Proof of time complexity: Let ST be the total num-
ber of partial assignments and j be a non-negative in-
teger (1 ≤ j ≤ n). Considering that only one agent
can change mission teams at a given time, there are
(m + 1)
j
possible assignments for the first j agents
in the sequence when no pruning occurs, so the total
number of partial assignments ST is given by
N
∑
j=1
(m + 1)
j
=
(m + 1)
n+1
− 1
m + 1 − 1
−1 =
(m + 1)
n+1
− 1
m
−1
This value is bounded by O((m + 1)
n+1
). Assigning
a new agent a to a mission team (T
0
,m
0
) with partial
allocation As requires the following summary calcu-
lations.
• Checking (skill(a) ∩ m
0
6=
/
0) if the agent a can
achieve m
0
. This operation is linear (i.e., in the
worst case, (T
0
,m
0
) possesses a vector of the num-
ber of agents corresponding to the mission), so we
only need to check the skills of a, and the compu-
tational complexity is bounded by the number of
skills s.
Allocation Considering Agent Importance in Constrained Robust Multi-Team Formation
135

• Checking (constraint(a) ∩ T 6=
/
0) if (T
0
,m
0
) sat-
isfies the constraints. This operation is linear, i.e.,
in the worst case, we only need to check all con-
straints on a and all agents assigned to T , so the
computational complexity is bounded by n + n.
• Updating the robustness of (T
0
,m
0
). As men-
tioned earlier, (T
0
,m
0
) possesses a vector of the
number of agents corresponding to the mission, so
the maximum computational complexity is lim-
ited by the number of elements in the vector s.
• Checking the robustness of As. This operation
checks all m mission teams if the robustness
of each mission team before the assignment is
known. Alternatively, the computation can be per-
formed when updating the robustness of the team
that assigned A, so the computational complexity
is limited by m + s.
Thus, the computational complexity of the entire op-
eration is O(2n + s + s + m)=O (n). In addition, the
cost computation does not affect the overall compu-
tational complexity because it can be performed in a
constant number of operations, just adding the agent’s
cost to the known cost before the assignment. If
pruning does not occur, ST times operations occur,
and this computational complexity is O((m + 1)
n+1
×
n)=O(n(m + 1)
n+1
). Finally, the algorithm checks
if As is dominated by the current solution if As is a
complete assignment. However, this operation only
needs to compare the known values of cost and ro-
bustness with all solutions, and since the number of
solutions is at most (m +1)
n
, as mentioned earlier, the
computational complexity is limited to O((m + 1)
n
).
Therefore, the overall computational complexity is
O((n(m + 1)
n+1
+ (m + 1)
n
)=O(n(m + 1)
n+1
).
5 EVALUATIONS
5.1 Experimental Setup
In this experiment, the agent cost is fixed (i.e., the cost
is the same, regardless of which team is assigned to
the mission multi-team). Thus, this is not a problem
of minimizing agents and destinations but minimiz-
ing the purchasing agent cost. In our experiments, we
change the number of constraints, robustness, and the
order in which agents are assigned.
The basic parameters are as follows:
• Number of agents is 18.
• Number of mission teams is 2.
• Cost of agents is chosen uniformly at random
from a range of [10,11,..., 100].
Table 1: Average runtime of an experiment to change the
number of teams in the optimization problem with fixed ro-
bustness (unit: s).
] of teams Average runtime
2 14.34
3 527.59
• Number of missions per team is three. No two
teams can have the same mission, and no two
teams can have the same mission.
• Agent skill is determined uniformly at random,
but the number is subject to the next section. Each
agent’s number of skills is determined randomly
in a range of [1,2,.. . , (number o f teams×3)−1].
The breakdown is as close to the same as possible.
• The number of constraints is 10.
• The number of robust goals is two.
• The number of constraints was changed in a range
of [1,2,..., 20]
• Robustness was changed in a range of [1,2,3].
There are seven assignment orders for agents,
which are summarized as follows: Random, As-
cending order of agent cost, Descending order of
agent cost, Ascending order of agent skills, De-
scending order of agent skills, Ascending order
of agent constraints, meaning that the number of
agents prohibited to be paired, and Descending or-
der of agent constraints.
• Each simulation was performed 100 times under
the same conditions.
5.2 Experimental Results
Table 1 shows the average runtime of an experiment
to change the number of mission teams. In the ex-
periment of changing the number of mission teams,
the average runtime was shorter than that of the bi-
objective optimization problem. Especially, it was
very short in three mission teams. This is because
the effect of pruning of robustness is large. Fur-
thermore, more efficient exploration is possible under
many mission teams since at least m + 1 agents are
required when the robustness is m in a mission team.
Table 2 lists the average runtime of an experiment
to change the number of constraints. In changing the
number of constraints, the average runtime tends to
decrease as the number of constraints increases, espe-
cially when agents are assigned in descending order
of the number of constraints.
Table 3 shows the average runtime of an experi-
ment to change the robustness. In changing the ro-
bustness goal, the larger the goal, the longer the run-
time. This is because the larger the goal, the more
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
136
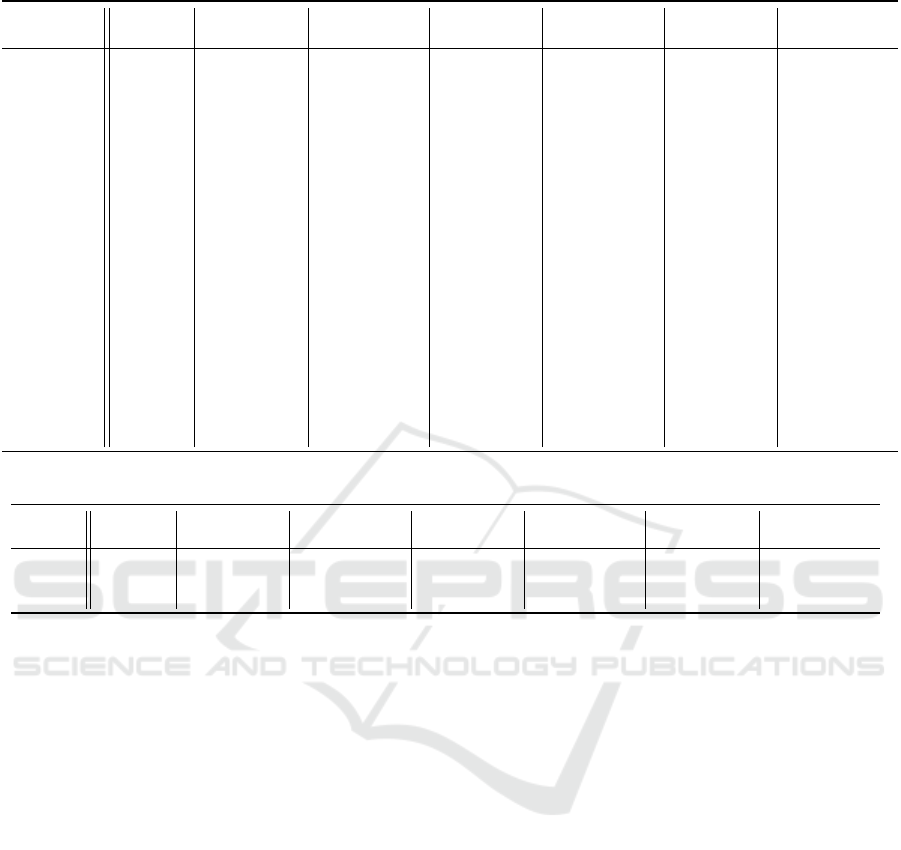
Table 2: Average runtime of an experiment to change the number of constraints (unit: s).
] of
constraints Random
Cost
(Ascending)
Cost
(Descending)
Skill
(Ascending)
Skill
(Descending)
Constraint
(Ascending)
Constraint
(Descending)
1 16.73 24.48 16.64 18.32 21.98 20.04 17.94
2 17.55 25.22 13.75 17.52 21.52 17.90 16.87
3 16.87 20.79 14.94 19.03 18.12 18.07 14.50
4 16.46 21.31 15.36 16.06 19.27 18.57 11.70
5 14.29 21.17 12.60 13.86 17.08 21.02 10.83
6 14.64 18.02 10.67 16.30 15.33 19.00 10.65
7 15.23 17.22 10.08 14.34 17.25 20.23 10.97
8 13.54 18.01 12.30 14.15 16.18 16.09 8.95
9 11.55 15.65 9.42 12.71 15.17 16.37 9.85
10 14.34 17.57 10.13 11.60 15.22 16.74 9.25
11 11.00 16.38 11.41 11.37 14.79 15.23 8.46
12 10.19 13.59 9.13 11.57 14.76 15.94 7.72
13 11.77 13.76 9.30 11.33 13.63 15.02 6.90
14 10.23 12.91 8.72 10.47 13.44 13.37 6.61
15 10.41 13.08 8.04 8.89 13.34 14.33 6.62
16 8.39 10.01 8.64 8.88 12.16 13.31 6.38
17 9.13 10.44 8.90 8.82 13.20 12.13 6.06
18 7.34 10.50 8.31 7.55 12.60 12.39 5.19
19 7.81 9.98 7.01 7.99 11.25 14.46 4.43
20 7.90 8.84 7.41 7.06 10.74 13.38 4.67
Table 3: Average runtime of an experiment to change the robust goal (unit: s).
Robust
goal Random
Cost
(Ascending)
Cost
(Descending)
Skill
(Ascending)
Skill
(Descending)
Constraint
(Ascending)
Constraint
(Descending)
1 1.11 1.35 1.02 1.34 0.96 1.16 0.90
2 14.34 17.57 10.13 11.60 15.22 16.74 9.25
3 24.44 26.34 22.39 12.92 43.87 37.58 12.46
agents are assigned to the team that solves the prob-
lem, and the search tree is sufficiently deep to sat-
isfy the goal. When the goal is small, the runtime is
shorter when the number of skills is assigned in de-
scending order, but when the goal is large, the run-
time is shorter when the number of skills is assigned
in ascending order.
The substantial difference in runtime of skill or-
der, depending on the robustness goal, is related to
the agent’s importance. The smaller the goal, the
smaller the number of agents required. Thus, the ratio
of patterns satisfying robustness becomes larger with
respect to the number of patterns in the allocation. As
a result, the smaller the goal, the easier it is to find
patterns satisfying the condition. Agents with higher
skills are important because they are more likely to
contribute to the goal than other agents with lower
skills. When the number of robustness is small, the
condition can be satisfied through a greedy approach,
by assigning the most important agent with the high-
est number of skills. As a result, cost pruning works
early in the search. When the number of goals is large,
the number of patterns that satisfy the goal is small.
Therefore, satisfying the condition is challenging un-
less the search is sufficiently conducted in advance.
When agents are assigned in ascending order of
the number of skills and descending order of the num-
ber of constraints, the runtime becomes shorter be-
cause the pruning in each check has a higher prob-
ability close to the root node. When the number of
constraints increases, agents are assigned in descend-
ing order of the number of constraints.
6 CONCLUSION
Mission-oriented team formation to accomplish a
given set of missions is an important problem in
multi-agent systems. This study introduced a frame-
work for an MOCRMTF problem. The objective of
this problem was to satisfy the constraint that compet-
ing agents cannot belong to the same team while en-
suring robustness, which is the ability to accomplish a
given mission, even if some agents fail, thereby min-
imizing the cost of the team. We proposed an algo-
rithm for the optimization problem with a fixed ro-
bustness goal to solve this problem and investigated
the computational classes and their complexity.
In our experiments, we showed that the runtime
varies, depending on the search order of agents. If the
Allocation Considering Agent Importance in Constrained Robust Multi-Team Formation
137

condition was easy to satisfy, the pruning of costs was
effective in the early stage of the search by allocating
agents with high importance. Alternatively, when the
condition was not easily satisfied, it helped increase
the pruning of the search space by allocating agents
that were more likely to be pruned, such as agents
with fewer skills or more constraints.
The possible future work is as follows. In this ex-
periment, the cost was set to be the same, regardless of
the agent’s team, and the cost’s value was determined
randomly. However, the problem may change signif-
icantly by changing the cost setting. As a change in
the framework, the robustness of multi-teams was as-
sumed to be the minimum value of the team to which
it belongs, but the robustness of multi-teams can be
generalized by allowing each team to set its own ro-
bustness goal, thereby making the model more sim-
ilar to a real-world environment. In this case, it is
expected that the complexity of robustness results in
more Pareto optimal solutions, so it is necessary to
develop a fast algorithm for finding an approximate
solution.
REFERENCES
Demirovic, E., Schwind, N., Okimoto, T., and Inoue, K.
(2018). Recoverable team formation: Building teams
resilient to change. In Andr
´
e, E., Koenig, S., Dastani,
M., and Sukthankar, G., editors, Proceedings of the
17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents
and MultiAgent Systems, AAMAS 2018, Stockholm,
Sweden, July 10-15, 2018, pages 1362–1370. Interna-
tional Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multi-
agent Systems Richland, SC, USA / ACM.
George, J. M., Pinto, J., Sujit, P. B., and Sousa, J. B.
(2010). Multiple UAV coalition formation strategies.
In van der Hoek, W., Kaminka, G. A., Lesp
´
erance, Y.,
Luck, M., and Sen, S., editors, 9th International Con-
ference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Sys-
tems (AAMAS 2010), Toronto, Canada, May 10-14,
2010, Volume 1-3, pages 1503–1504. IFAAMAS.
Lawler, E. L. and Wood, D. E. (1966). Branch-and-bound
methods: A survey. Oper. Res., 14(4):699–719.
Liemhetcharat, S. and Veloso, M. M. (2012). Modeling
and learning synergy for team formation with het-
erogeneous agents. In van der Hoek, W., Padgham,
L., Conitzer, V., and Winikoff, M., editors, Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-
agent Systems, AAMAS 2012, Valencia, Spain, June
4-8, 2012 (3 Volumes), pages 365–374. IFAAMAS.
Marinescu, R. (2010). Best-first vs. depth-first AND/OR
search for multi-objective constraint optimization. In
22nd IEEE International Conference on Tools with
Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI 2010, Arras, France, 27-
29 October 2010 - Volume 1, pages 439–446. IEEE
Computer Society.
Matthews, T., Ramchurn, S. D., and Chalkiadakis, G.
(2012). Competing with humans at fantasy football:
Team formation in large partially-observable domains.
In Hoffmann, J. and Selman, B., editors, Proceed-
ings of the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, July 22-26, 2012, Toronto, Ontario,
Canada. AAAI Press.
Moz, M. and Pato, M. V. (2004). Solving the problem
of rerostering nurse schedules with hard constraints:
New multicommodity flow models. Ann. Oper. Res.,
128(1-4):179–197.
Nair, R. and Tambe, M. (2005a). Hybrid BDI-POMDP
framework for multiagent teaming. J. Artif. Intell.
Res., 23:367–420.
Nair, R. and Tambe, M. (2005b). Hybrid bdi-pomdp frame-
work for multiagent teaming. Journal of Artificial In-
telligence Research, 23:367–420.
Okimoto, T., Ribeiro, T., Bouchabou, D., and Inoue, K.
(2016). Mission oriented robust multi-team forma-
tion and its application to robot rescue simulation. In
Kambhampati, S., editor, Proceedings of the Twenty-
Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, IJCAI 2016, New York, NY, USA, 9-15 July
2016, pages 454–460. IJCAI/AAAI Press.
Okimoto, T., Schwind, N., Clement, M., Ribeiro, T., In-
oue, K., and Marquis, P. (2015). How to form a task-
oriented robust team. In Weiss, G., Yolum, P., Bordini,
R. H., and Elkind, E., editors, Proceedings of the 2015
International Conference on Autonomous Agents and
Multiagent Systems, AAMAS 2015, Istanbul, Turkey,
May 4-8, 2015, pages 395–403. ACM.
Parker, J., Nunes, E., Godoy, J., and Gini, M. L. (2016).
Exploiting spatial locality and heterogeneity of agents
for search and rescue teamwork. J. Field Robotics,
33(7):877–900.
Rollon, E. and Larrosa, J. (2006). Bucket elimination for
multiobjective optimization problems. J. Heuristics,
12(4-5):307–328.
Schwind, N., Demirovic, E., Inoue, K., and Lagniez, J.
(2021). Partial robustness in team formation: Bridging
the gap between robustness and resilience. In Dignum,
F., Lomuscio, A., Endriss, U., and Now
´
e, A., edi-
tors, AAMAS ’21: 20th International Conference on
Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Virtual
Event, United Kingdom, May 3-7, 2021, pages 1154–
1162. ACM.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
138
