
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent
Systems Controllability
Mohamed Sedik Chebout
1a
, Farid Mokhati
1b
and Mourad Badri
2c
1
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, ReLa(CS)2 Laboratory, University of Oum el Bouaghi,
Oum el Bouaghi, Algeria
2
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Software Engineering Research Laboratory, University of Quebec,
Trois-Rivières, Canada
Keywords: Controllability, Norms, Open Multi-Agent Systems, AGR Model, JAVA Expert System Shell,
Aspect-Oriented Programming.
Abstract: Normative Open Multi-Agent Systems (NOMAS) are systems in which norms play a crucial role for
organizing, coordinating, controlling agents’ behaviours and interactions. In addition, heterogeneous agents,
in Open Multi-Agent Systems (OMAS), can work in similar or different ends. This might deviate the target
system state and lead to a chaotic behaviour. A particular kind of OMAS is implemented based on AGR
(Agent/Group/Role) model. This paper proposes a novel Norms-based Controllability approach for AGR-
based OMAS (NC4OMAS). Mainly, the proposed approach is divided into two phases: monitoring and
controlling. Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) technique is used for norm monitoring compliance. Also,
JAVA Expert System Shell (JESS) is used for norm specification, norm modification and for making
inference over norms at runtime. In order to address limitations and advantages of our approach, we
summarise the most relevant works on norms-based control according to some comparison criteria we
proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Open MAS (OMAS) are characterized, mainly, by the
heterogeneity of their participants (Criado et al., 2013),
the member agents are developed by different parties
and serve different, often competing interests (Artikis
et al., 2016). Unlike classical MASs, agents in OMAS
can freely join and leave systems at any time by
requesting and/or leaving roles. Accordingly, hetero-
geneous agents playing their roles in such systems
increase the risk to lead to non-desired situations,
unanticipated interactions and expand the gap between
the system observed
behaviour and the expected one
(Hewitt, 1991). To avoid that risk, it is necessary to
define control mechanisms to lead the system
behaviour from any unpredictable situation to a
predefined target state. As stated in (Hewitt, 1991):
“openness without control may lead to a chaotic
behaviour”.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5373-4495
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4311-342X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9034-9713
Roughly, the concept of controllability denotes
the ability to move a system state with its entire
current configuration using only certain potential
manipulations (Liberty, 1972) (Sontag, 1998).
Controllability and observability are dual aspects of
the same problem. Observe (i.e., monitor) a given
system consists to delegate another system (a
monitor), which runs concurrently with the monitored
one, for providing detailed information about the
execution of the other program (ISO/IEC/IEEE,
2017) (Hammoud et al., 2016).
A special kind of OMAS is implemented using
AGR (Agent/group/role) model in which the internal
agent structure is not specified (i.e., agent
heterogeneity). Also, groups in AGR model are
considered as black boxes where what happens in a
group cannot be seen from agents that do not belong
to that group (Ferber & Gutknecht, 1998).
164
Chebout, M., Mokhati, F. and Badri, M.
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent Systems Controllability.
DOI: 10.5220/0010793600003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 1, pages 164-171
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

This study is devoted to addressing the issue of
AGR-based OMAS controllability by proposing a
novel approach called NC4OMAS for Norms-based
Controllability for Open Multi-Agent Systems. In
NC4OMAS, norms specify the behaviours that agents
should follow to achieve the objectives of the OMAS.
JAVA Expert System Shell (JESS) (Friedman-Hill,
2008) is proposed, in the context of this paper, for
norm specification, norm updating and for making
inference over norms. Likewise, Aspect-Oriented
Programming (AOP) is used, in NC4OMAS, in order
to implement norm monitoring process. An initial
synthesis of OMAS control problem has been
introduced and investigated in (Chebout et al., 2016)
followed by an implementation of a dedicated
software tool for monitoring AGR-based OMAS in
(Chebout et al., 2019).
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 provides some related works about norms-
based control for OMAS. Section 3 outlines the main
preliminaries we used in our approach. Section 4
presents the proposed approach. Section 5 discusses
our proposal in light of comparisons made with some
relevant works. Finally, section 6 draws some
conclusions and gives some future work directions.
2 STATE OF THE ART
In the last two decades, several research works have
been published in which norms-based control related
concepts have been treated.
In (Criado et al., 2013), a distributed architecture
for enforcing norms in OMAS has been proposed
under the name of MaNEA (Magentix2 Norm-
Enforcing Architecture). The main aim of MaNEA is
to overcome problems of existing proposals on norm
enforcement. Also, MaNEA supports the creation and
deletion of norms on-line as well as the dynamic
activation and expiration of instances. MaNEA shows
good performance result in terms of: number of
instantiations, number of agents, number of roles,
number of norms, number of iterations and number of
actions compared to (Modgil et al., 2009).
In (Mahmoud et al., 2014), a literature review of
normative MAS has been established. That review
work classifies norms into two main categories:
conventional and essential norms. This latter,
encompasses three norm types: constitutive,
regulative, and procedural norms. A new norm type
has been proposed under the term: recommendation
norm. Authors contribute, also, with a norm lifecycle
process that summaries the different stages that affect
the norm from creation to removal.
In (Alechina et al., 2018), the problem of
detecting norm violations in OMAS is considered. In
that work, the MAS does not need to bear the cost of
paying for monitoring, as assumed in (Fagundes et al.,
2014). Agents are not always rewarded after they
monitor, but only if they discover a violation. A key
issue for that approach is how to incentivize the
agents to monitor the actions of other agents.
In (Fagundes et al., 2014), an approach for
analysing the trade-off between norm enforcement
efficiency and its cost has been proposed.
Furthermore, the cost is associated with norm
enforcement. For that, a simulation-based method to
calculate trade-offs involved in enforcement
mechanisms has been developed and experimented.
In that work, authors confirm that norm designers,
based on information provided by their simulation,
are able to analyse the trade-off between efficiency
and cost of norm enforcement.
In (Marir et al., 2019), an extension of JADE
agent platform (Bellifemine et al., 2007) named
Normative JADE (NorJADE) has been proposed to
support different aspects related to MAS normativity.
The proposed extension consists in providing JADE
developers with a normative framework in which
norm representation, norm enforcement, and norm
monitoring techniques are specified. Also, NorJADE
implements several norm related mechanisms using
AspectJ.
Although these works have considerably
forwarded the control issue in OMAS by proposing
novel approaches for each norm subareas (i.e., norm
lifecycle, conflict resolution between norms, norm
enforcement, and norm implementation), they did not
take into account the specificities of AGR-based
OMASs and they did not discuss, in a clear way, how
operationally norm compliance is monitored. It
should be pointed out that norm synthesis aspect is
not considered in this paper nor in the studied
literature. Although the enormous works in such
domain, using a rule-based system for expressing
norms is limited to a particular kind of system (i.e.,
electronic institutions). Norm enforcement proposed
architectures, in existing literature, are almost
centralized. However, a distributed architecture is
strongly preconized in order to avoid drawbacks
related to centralized ones (i.e., communication
overhead, etc.).
Existing works on norm monitoring in MAS,
except (Criado et al., 2013), delegate an agent for
monitoring norm compliance (second- and third-
party observability). Putting a particular agent in
charge for observing other agent’s behaviour is a
good solution in the design level. However,
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent Systems Controllability
165
interaction between monitor agent and other agents
implied in control process will increase the amount of
communication and affect considerably the
performances of controlled system. To the best of our
knowledge, this work is the first that uses AOP
techniques to provide support for norm monitoring.
Also, norm modification issue was not treated as well.
3 PRELIMINARIES
In what follows, we introduce the main materials we
used to support our proposal.
3.1 Normative Open Multi-Agent
System
According to (Boella et al., 2008), a normative MAS
“is a multi-agent system organized by means of
mechanisms to represent, communicate, distribute,
detect, create, modify, and enforce norms, and
mechanisms to deliberate about norms and detect
norm violation and fulfilment”. Also, norms have
been incorporated into OMAS to express the expected
behaviour of agents.
In Normative OMAS (NOMAS) literature, most
used norms are those who use deontic logic operators
(i.e., regulative norms): obligations, prohibitions, and
permissions (von Wright, 2021) (Woleński, 2016). In
our work, the focus is on a special type of norms in
which temporal constraints are considered (i.e.,
conditional norms). Obligations, prohibitions, and
permissions are submitted to temporal constraints:
start time and deadline. For instance, obligation start
time describes the moment when the norm is
instantiated. However, obligation deadline means that
obligation does not produce any effects after this
time. The period between obligation start time and
deadline expresses the fact when obligation is in
force. In AGR-based OMAS, norms will be activated
when agent requests a role. This means that norms are
addressed to roles played by agents. In contrast, norm
is deactivated when an agent leaves a role whatever
norm is fulfilled or violated.
To address the norms-based control process in
OMAS, norms should be communicated to agents
newly integrated in the system and, as a consequence,
agents may decide not to comply with the norms
(Criado et al., 2013) (Mahmoud et al., 2014). In order
to deal with agent autonomy in which agents can
work toward similar or different goals, the step of
agent decision related to comply or not with norms
will be bypassed in this work.
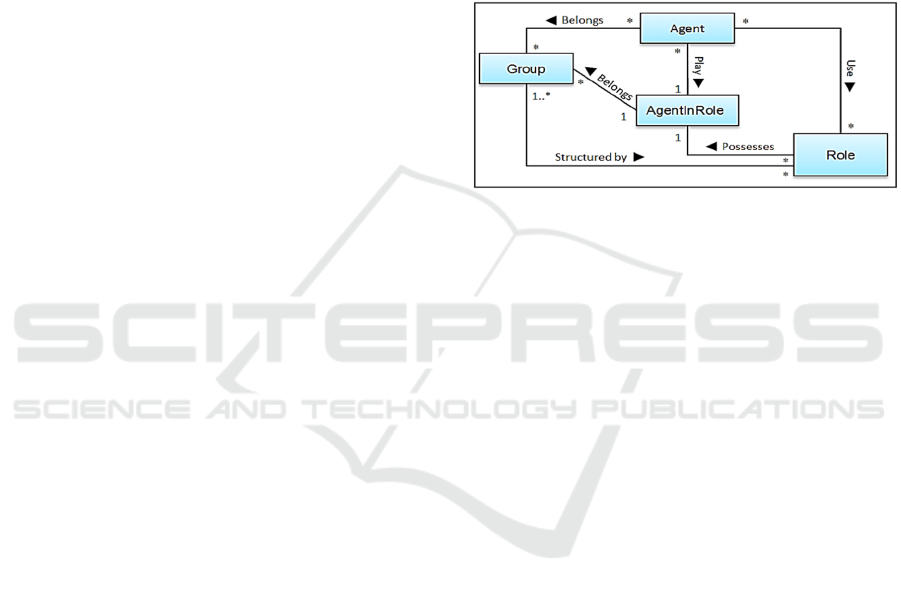
3.2 AGR Model
Agent, Group and Role (AGR) Model, is a generic
organizational model of multi-agent systems.
According to (Ferber et al., 2003), an agent is an
active, communicating entity playing roles within
groups, a group is used as a context for a pattern of
activities. Also, a group is defined as a set of agents
sharing some common characteristics. A role is the
abstract representation of a functional position of an
agent in a group. An agent must play a role in a group,
but an agent may play several roles (figure 1).
Figure 1: AGR core model (Ferber & Gutknecht, 1998).
Therefore, MaDKit (Multi-agent Development Kit)
platform (Gutknecht & Ferber, 2001) consists of an
operationalization of the AGR model and is selected
in this work for proposed approach implementation
purposes. Under MaDKit, an agent that wants to get
in the system, should pass an explicit request via
requestRole primitive. In contrast, agents that want to
go out from the system use leaveRole primitive.
3.3 JESS
Java Expert System Shell (JESS) is an editor of expert
systems and scripting language from Sandia National
Laboratories, written entirely in JAVA and using a
Lisp-like notation (Friedman-Hill, 2008). JESS
supports the development of rule-based systems that
can be tightly coupled to code written in JAVA
(Garcia-Camino et al., 2005). There are three ways to
represent knowledge in JESS: rules, functions and
Object-Oriented Programming (Friedman-Hill,
2003). Also, JESS uses backward chaining inference
method. A typical rule-based system has, at least,
three basic components: fact-list (i.e., instance-list),
knowledge-base (i.e., rule-base) and inference
engine. By using JESS, JAVA functions may be
called from JESS code, extending JESS by writing
JAVA code and embedding JESS in JAVA
Application (Friedman-Hill, 2008).
This feature adds more flexibility to the code.
JESS is used, in the context of this work, for
specifying and making inference over norms.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
166
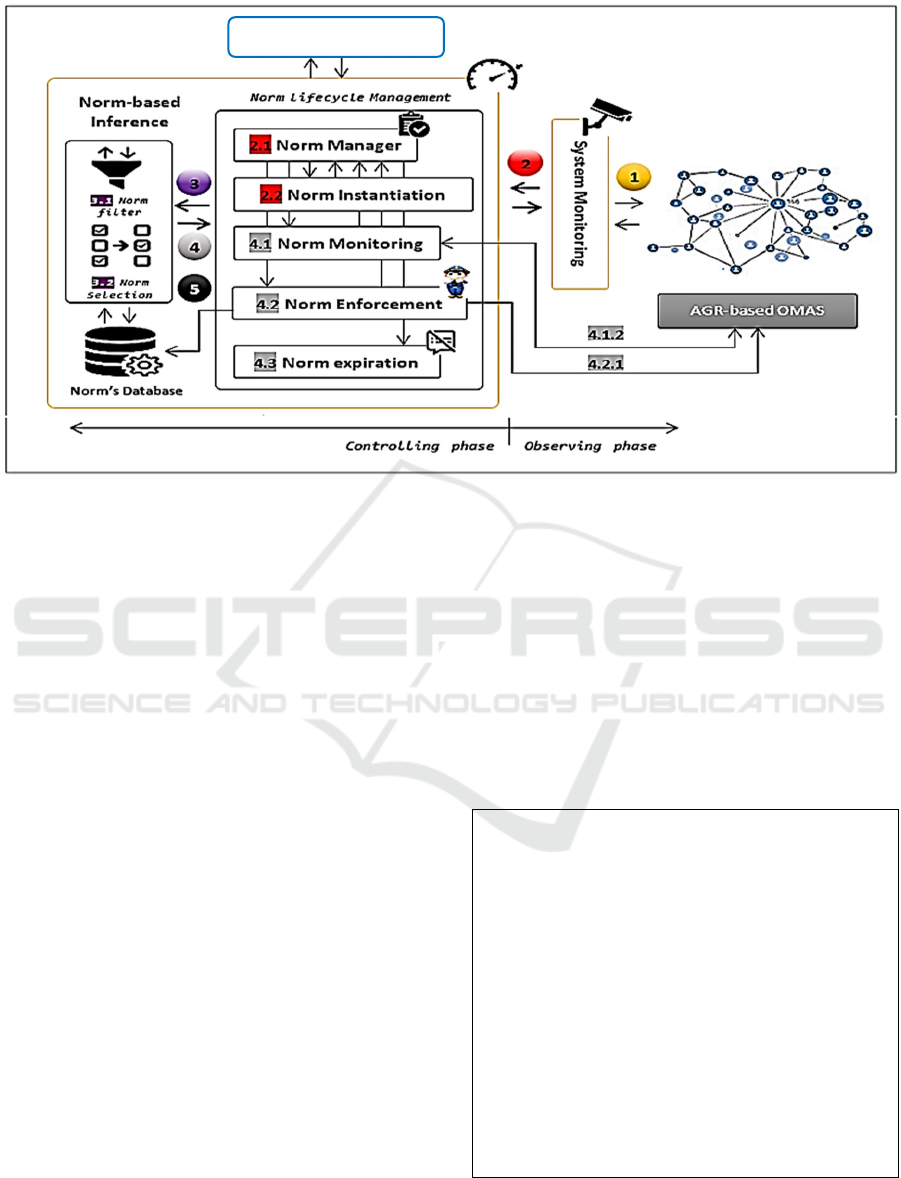
Figure 2: NC4OMAS architecture.
3.4 AspectJ
AspectJ is the most common AOP implementation for
JAVA (Kiczales et al., 2001). AspectJ supports the
definition of aspects, advices, join points, and
pointcuts. An advice is a special method-like
construct attached to join points. Join points are well-
defined points in the structure and dynamic execution
of a system. Examples of join points are method calls,
method executions, etc. Pointcuts are collections of
join points and are used in advice definitions. An
aspect defines sets of pointcuts and advices (Kiczales
et al., 2001). AspectJ provides an effective way for
monitoring agent movements and norm compliance.
4 PROPOSED APPROACH
The main purpose of Norms-based Controllability for
Open Multi-Agent Systems (NC4OMAS) is to
control AGR-based OMASs in order to guide, based
on a norm-driven process, their behaviour for
achieving expected states. To this end, NC4OMAS
approach is divided into two main phases (figure 2):
observing (i.e., monitoring) phase and controlling
phase.
4.1 Observing Phase
The monitoring phase consists of tracking and
gathering AGR related information. System
monitoring module in NC4OMAS architecture is
implemented as a set of AspectJ aspects. Based on
AspectJ pointcuts, system monitoring tracks agent’s
entrance, departure and performed actions. Snippet 1
shows a piece of code of system monitoring aspect in
which a pointcut named observeRequiredRole
intercepts all calls to requestRole primitive. After
that, a particular list named activatedRequested
RoleList will be updated. activatedRequested
RoleList encompasses information about agentID and
assigned roles.
pointcut observeRequiredRole(String
communityName, String groupName, String
roleName, Object passKey) :
call(ReturnCode *.requestRole(..)) &&
args(communityName, groupName, roleName,
passKey);
after (String communityName, String
groupName, String roleName, Object
passkey) returning (Returncode r) :
observeRequiredRole(communityName,
groupName, roleName, passKey){
AbstractAgent ag = (AbstractAgent)
thisJoinPoint.getTarget();
//
…
if (r.equals(ReturnCode. SUCCESS)){
activatedRequestedRolelist.put(agAd.getN
etworkID(), roleName);}
}
Snippet 1: Monitoring the agent requested roles.
NC4OMAS GUI
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent Systems Controllability
167

4.2 Controlling Phase
The purpose of NC4OMAS controlling phase is to
delegate a third-party MAS in order to ensure, for
OMAS, the achievement of expected state. Also,
delegated MAS is composed by a set of agents in
which their tasks are related to norm lifecycle. In this
work, four essential norm lifecycle phases have been
adopted: norm creation, norm instantiation, norm
monitoring, and norm enforcement. In Norm creation
step, a set of domain dependent norms will be created
and saved in norm database before launching the
controlled system (i.e., offline norm design). Norm
instantiation and norm enforcement steps are
delegated to specific agents named: norm instantiator
and norm enforcer respectively. Also, norms
monitoring step is implemented by a specific agent
that uses AspectJ constructors for observing norm
compliance. A particular agent type called norm
manager consists of supervising several norm related
tasks assigned to norm instantiator and norm
enforcer. Delegated MAS entities are dispatched over
groups of agents of the OMAS submitted to control.
Likewise, norm manager, norm instantiator, and norm
enforcer agents should pass, every one, an explicit
request for performing norm management, norm
instantiation and norm enforcement roles respectively
in each created group.
In contrast, norm instantiation consists of making
a copy of created norm (i.e., from norm database) that
corresponds to requested role using JESS pattern
matching mechanism. Instantiated norm for a given
role is taken based on JESS inference engine
following two successive steps: selection and
filtering which will be proceeded based on JESS
built-in RETE algorithm (Forgy, 1982). Once norm is
instantiated (i.e., in force), it will be inserted in a
particular list named instantiatedNormList.
Conversely, norm expiration process consists of
removing instantiated norms from the enforcement
process when a given agent gets out of the system.
For that, a specific list named desactivatedNormList
is maintained.
In NC4OMAS, a norm is specified as JESS rule.
This latter is similar to an IF-THEN statement. Rules
have two parts a left-hand side (LHS) and a right-
hand side (RHS) separated by the connective (=>).
The LHS is employed for matching fact patterns
based on RETE algorithm. Snippet 2 shows a
prohibition norm named AuthorProhibitionRule
related to paper submission in the context of
Conference Review System (CRS). Also, an author is
prohibited to submit a paper after submission
deadline.
(deftemplate AuthorPaperSubmission
(slot agentid)(slot group)(slot role)
(slot status (type STRING)))
(deftemplate SubmissionProhibition
(slot agentid)(slot group)(slot role)
(slot status (type STRING)))
(deftemplate rdPS
(slot submissionDeadline (type LONG)))
(defglobal ?*currentdate* = (System.
currentTimeMillis))
; check if currentDate > SubmissionDeadline
(defrule AuthorProhibitionRule
(AuthorPaperSubmission
(agentid ?author)(group ?gr)
(role ?role)(status ?s))
(rdPS (submissionDeadline ?sdl))
(test (> ?*currentdate* ?sdl))
(test (= ?s "preregistred"))
=>
(assert (SubmissionProhibition
(agentid ?author) (group ?gr)
(role ?role) (status "LeavingSystem")))
(printout t "Author " ?author " is
Prohibited to submit a paper " crlf))
Snippet 2: Prohibition norm for author paper submission.
Norm modification process consists of dynamically
modifying norms’ temporal constraints in order to
give more time to agents to adapt their behaviours
with normative ones. Hence, norm modification will
take place mainly after checking the non-achievement
of the expected system state. JESS provides support
for updating norm related facts by using constructs
like: defquery, modify, assert.
In norm enforcement process, norm monitoring
module observes, permanently, each change made on
instantiatedNormList and check which norm is
currently in force. In the case of obligation norms,
norms monitoring tracks if current performed action
by a given agent is submitted to an obligation and
check if the obligation deadline is reached. Norm
instantiator agent asserts, consequently, the
obligation related fact in the Working Memory
(WM). This means that action performed by a given
agent has been submitted to an obligation. Also,
asserted fact encompasses a set of agents’ relevant
information such as: agentID, agentRole,
agentGroup, and currentAgentStatus. In order to
determine fulfilled or violated obligations, norm
monitoring gets, after deadline expiration, asserted
obligation facts from the WM. By formulating a set
of JESS queries to the WM. An obligation is
considered as fulfilled, if current agent status matches
with status indicated in the obligation. Conversely,
obligation is considered as violated. A particular list
named: normStatusList is maintained by norm
manager for updating obligation enforcement-related
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
168
information.As far as normStatusList is dynamically
modified, norm manager informs norm enforcer to
proceed to punish or reward agent in question.
Punishments and rewards are domain dependent. In
the context of NC4OMAS, multiple lists are
maintained for managing rewarded and punished
agents (i.e., rewardedAgentList and
punishedAgentList respectively). Also, putting
rewarded or punished agents in such list is the
simplest way to behave with. Agent manager informs,
at runtime, sanctioned agents by the result of
enforcement process. In the case of prohibition, an
agent will be rewarded if its status does not much with
one indicated in the norm.
5 DISCUSSION
NC4OMAS is proposed mainly in order to control
AGR-based OMAS using a norms-based control
process. JESS is used to deal with norm specification
and modification issues thanks to its flexibility in
which JESS can be tightly coupled to JAVA code.
AspectJ is used, basically, for monitoring purposes.
However, AspectJ coding needs a particular attention
when manipulating data structures like, HashMap,
ArrayList, etc. These data structures are accessed by
both aspects for putting or updating data and
NC4OMAS agents for getting specific information
like activatedRequestedRoleList, instantiatedNorm
List, desactivatedNormList, etc. Therefore, data
structures with multiple access need a particular
control in order to avoid JAVA exceptions like
ConcurrentModificationException. To avoid such
exception, ConcurrentHashMap is opted instead
HashMap and CopyOnWriteArrayList instead
ArrayList and so on.
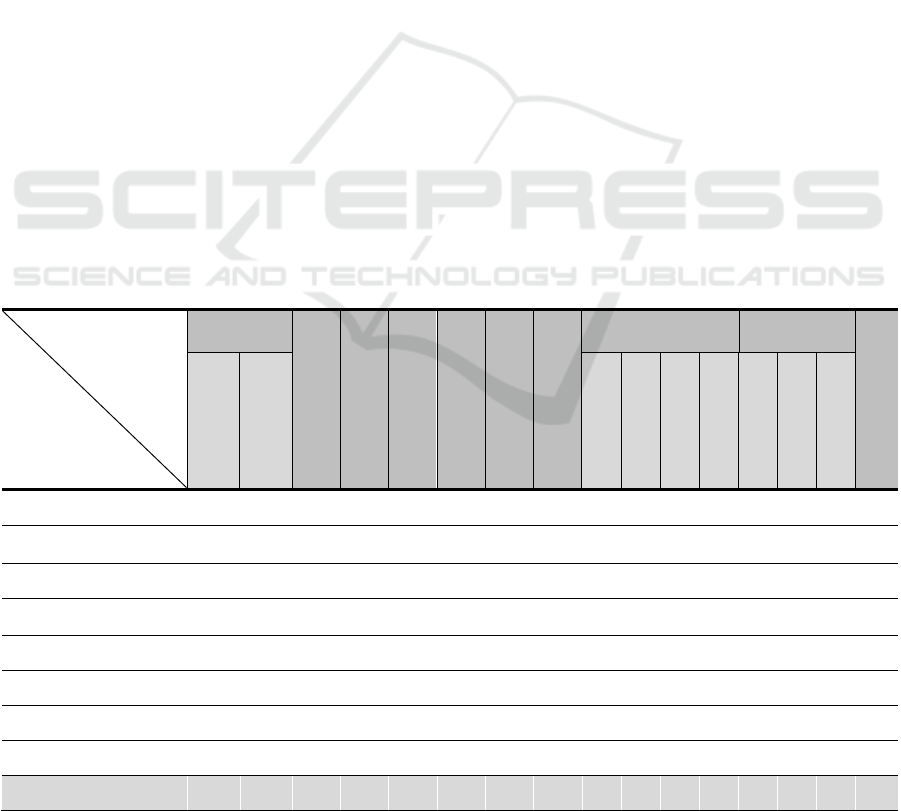
In order to address limitations and advantages of
our approach, Table 1 summaries the most relevant
works on norms-based control according to some
comparison criteria we proposed. Norm enforcement
(i.e., rewards and penalties). Norm modifications
means the ability of dynamically updating some norm
settings (i.e., temporal constraints). Distributed
enforcement architecture consists of the way for
doing enforcement mechanism (i.e., centralised or
distributed). Performed actions mean the possibility
of monitoring actions performed by agents. Norm
lifecycle investigates the evolutionary process of
norm’s lifecycle developed over several phases:
creation, instantiation, emergence, adoption,
internalization, and norm removal. Exchanged
messages underline the way in which agents
implicated in control process communicate with.
Norm representation indicates which formalism is
used to represent norm either rule-based systems,
deontic logic, binary strings or game theory. As a
MAS is constituted of environments, organizations,
Table 1: Summary of norms-based control proposals.
Criteria
Proposals
Norm
Enforcement
Norm Modification
Distributed enforcement
architecture
Performed actions
Norm lifecycle
Exchanged messages
Norm Representation
Deontic Concepts Context
Conflict resolution
Punishment
Reward
Permission
Obligation
Interdiction
Recommendation
Interaction
Environment
Organization
(Felicíssimo et al., 2008)
√ √ √ √
(Garcia-Camino et al.,
2005)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
(Ahmad et al., 2016)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
(Dastani & van der Torre,
2004)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
(Criado et al., 2013)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
(Mahmoud et al., 2014)
√ √ √ √
(Alechina et al., 2018)
√ √ √ √ √
(Marir et al., 2019)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
NC4OMAS √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent Systems Controllability
169

and agents interacting and playing roles, context
criterion is chosen for specifying which issue is
addressed by proposed normative approaches.
Finally, conflict resolution denotes the fact that
proposals are endowed with capabilities for applying
conflicts resolution techniques between norms. A
normative conflict arises when a given agent is
prohibited and obliged to perform the same action at
the same time (Belchior et al., 2018).
In light of these comparison results described in
Table 1, NC4OMAS takes a remarkable place
between existing proposals. Our proposal joins the
majority of proposed approaches in the enforcement
process, performed actions, norm representation,
deontic concepts in terms of permission, obligation,
and prohibition. Also, our work joins (Criado et al.,
2013) and (Alechina et al., 2018) in the distributed
enforcement architecture criteria in which we adopt
AGR model for implementing OMAS. Also, AGR
model allows decomposition over groups of roles.
With regards to norm lifecycle, our approach joins
proposals of (Criado et al., 2013) (Mahmoud et al.,
2014) and (Dastani & van der Torre, 2004) in which
norms are submitted to several phases starting with
creation, instantiation, enforcement, and finally
removal. In contrast, norm conflict resolution and
normative environment are excluded in NC4OMAS.
In our approach, there is no need to impose any
constraints (i.e., norms) on agent entrance and/or
departure and required capabilities for an agent for
doing a requested role. The purpose of norm
modification allows a dynamic update of norm
settings expressed in terms of temporal constraints.
This latter makes the behaviour specified in the norm
more flexible and gives, as a result, an opportunity for
agents to adapt their behaviour with normative one.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper, a Norms-based Controllability approach
for Open Multi-Agent systems (NC4OMAS) was
proposed. The idea of NC4OMAS consists of
delegating a third-party MAS in order to manage
norm related issues (i.e., norm instantiation, norm
monitoring, and norm enforcement). Delegated MAS
is designed in a distributed way in which agents
implied in control process are dynamically dispatched
over system groups. The originality of our
proposition is the runtime control by considering its
current system state and the target one using AspectJ
for norm monitoring compliance and JESS for
specifying, updating and making inference over
norms. Currently, a software tool called NC4OMAS
tool is being developed in order to demonstrate the
feasibility of our approach. NC4OMAS tool is
designed as a middleware and will be executed
concurrently with the system submitted to control in
order to maximize compatibility with any type of
AGR-based platform.
REFERENCES
Ahmad, A., Ahmed, M., Mohd Yusof, M. Z., Ahmad,
Mohd. S., & Mustapha, A. (2016). Resolving Conflicts
between Personal and Normative Goals in Normative
Agent Systems. Journal of IT in Asia, 4(1).
https://doi.org/10.33736/jita.43.2014.
Alechina, N., Halpern, J. Y., Kash, I. A., & Logan, B.
(2018). Incentive-compatible mechanisms for norm
monitoring in open multi-agent systems. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence Research, 62. https://doi.org/
10.1613/jair.1.11214.
Artikis, A., Sergot, M., Pitt, J., Busquets, D., & Riveret, R.
(2016). Specifying and Executing Open Multi-Agent
Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33570-
4_10.
Belchior, M., dos Santos, J. S., & da Silva, V. T. (2018).
Strategies for resolving normative conflict that depends
on execution order of runtime events in multi-agent
systems. ICAART 2018 - Proceedings of the 10th
International Conference on Agents and Artificial
Intelligence, https://doi.org/10.5220/00065932021602
23.
Bellifemine, F., Caire, G., & Greenwood, D. (2007).
Developing Multi-Agent Systems with JADE. In
Developing Multi-Agent Systems with JADE.
https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470058411.
Boella, G., van der Torre, L., & Verhagen, H. (2008).
Introduction to the special issue on normative
multiagent systems. Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10458-
008-9047-8.
Chebout, M. S., Mokhati, F., Badri, M., & Babahenini, M.
C. (2016). Towards preventive control for open MAS:
An aspect-based approach. ICINCO 2016 - Proceedings
of the 13th International Conference on Informatics in
Control, Automation and Robotics.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0006005602690274.
Chebout, M. S., Mokhati, F., Badri, M., & Babahenini, M.
C. (2019). Monitoring open multi-Agent systems: An
aspect-oriented programming-based approach.
Multiagent and Grid Systems. https://doi.org/10.3233/
MGS-190307.
Criado, N., Argente, E., Noriega, P., & Botti, V. (2013).
MaNEA: A distributed architecture for enforcing norms
in open MAS. Engineering Applications of Artificial
Intelligence, 26(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.
2012.08.007.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
170

Dastani, M., & van der Torre, L. (2004). Programming
BOID-Plan Agents deliberating about conflicts among
defeasible mental attitudes and plans. Proceedings of
the Third International Joint Conference on
Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, AAMAS
2004, 2.
Fagundes, M. S., Ossowski, S., & Meneguzzi, F. (2014).
Analyzing the tradeoff between efficiency and cost of
norm enforcement in stochastic environments.
Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications,
263. https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-61499-419-0-1003.
Felicíssimo, C., Chopinaud, C., Briot, J. P., Seghrouchni,
A. E. F., & Lucena, C. (2008). Contextualizing
normative open multi-agent systems. Proceedings of
the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing.
https://doi.org/10.1145/1363686.1363703.
Ferber, J., & Gutknecht, O. (1998). A meta-model for the
analysis and design of organizations in multi-agent
systems. Proceedings - International Conference on
Multi Agent Systems, ICMAS 1998. https://doi.org/
10.1109/ICMAS.1998.699041.
Ferber, J., Gutknecht, O., & Michel, F. (2003). From agents
to organizations: An organizational view of multi-agent
systems. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including
Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and
Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 2935.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24620-6_15.
Forgy, C. L. (1982). Rete: A fast algorithm for the many
pattern/many object pattern match problem. Artificial
Intelligence, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-3702
(82)90020-0.
Friedman-Hill, E. (2003). Jess in action. Rule-Based
systems in java. In Jess in action: rule-based systems in
Java.
Friedman-Hill, E. (2008). Jess The rule engine for Java
Platform. In Sandia National Laboratories.
Garcia-Camino, A., Noriega, P., & Rodríguez-Aguilar, J.
A. (2005). Implementing norms in electronic
institutions. Proceedings of the International
Conference on Autonomous Agents. https://doi.org/
10.1145/1082473.1082575.
Gutknecht, O., & Ferber, J. (2001). The MadKit agent
platform architecture. Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence (Subseries of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-47772-1_5.
Hammoud, M., Tang, A. Y. C., & Ahmad, A. (2016).
Negative norms detection technique in open normative
multi-agent systems. ICAART 2016 - Proceedings of
the 8th International Conference on Agents and
Artificial Intelligence, 2. https://doi.org/10.5220/000
5654502410249.
Hewitt, C. (1991). Open Information Systems Semantics
for distributed artificial intelligence. Artificial
Intelligence, 47(1–3). https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-
3702(91)90051-K.
ISO/IEC/IEEE. (2017). Systems and software engineering:
Vocabulary. ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2017(E), 2017.
Kiczales, G., Hilsdale, E., Hugunin, J., Kersten, M., Palm,
J., & Griswold, W. G. (2001). An overview of AspectJ.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including
Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and
Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). https://doi.org/
10.1007/3-540-45337-7_18.
Liberty, S. (1972). Modern control engineering. IEEE
Transactions on Automatic Control, 17(3).
https://doi.org/10.1109/tac.1972.1100013.
Mahmoud, M. A., Ahmad, M. S., Mohd Yusoff, M. Z., &
Mustapha, A. (2014). A review of norms and normative
multiagent systems. In Scientific World Journal (Vol.
2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/684587.
Marir, T., Silem, A. E. H., Mokhati, F., Gherbi, A., & Bali,
A. (2019). NorJADE. International Journal of Open
Source Software and Processes. https://doi.org
/10.4018/ ijossp.2019040101.
Modgil, S., Faci, N., Meneguzzi, F., Oren, N., Miles, S., &
Luck, M. (2009). A framework for monitoring agent-
based normative systems. Proceedings of the
International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents
and Multiagent Systems, AAMAS, 1.
Sontag, E. (1998). Mathematical control theory:
deterministic finite dimensional systems. In Texts in
applied mathematics: Vol. 2nd ed.
von Wright, G. H. (2021). A New System of Deontic Logic.
Danish Yearbook of Philosophy, 1(1).
https://doi.org/10.1163/24689300-00101017.
Woleński, J. (2016). How deontic logic contributes to the
analysis of legal systems. Revus, 29. https://doi.org/
10.4000/revus.3518.
NC4OMAS: A Norms-based Approach for Open Multi-Agent Systems Controllability
171
