
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Wael Korani and Malek Mouhoub
a
University of Regina, 3737 Wascana Parkway, Regina, Canada
Keywords:
Constraint Satisfaction, Swarm Intelligence, Nature Inspired Techniques, Metaheuristics.
Abstract:
The Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) is a powerful framework for a wide variety of combinatorial prob-
lems. The CSP is known to be NP-complete, and many algorithms have been developed to tackle this challenge
in practice. These algorithms include the backtracking technique, improved with constraint propagation and
variable ordering heuristics. Despite its success, backtracking still suffers from its exponential time cost, es-
pecially for large to solve problems. Metaheuristics, including local search and nature-inspired methods, can
be an alternative that trades running time for the quality of the solution. Indeed, these techniques do not
guarantee to return a complete solution, nor can they prove the inconsistency of the problem. They are, how-
ever time-efficient, thanks to their polynomial running time. In particular, nature-inspired techniques can be
very effective if designed with a good exploitation/exploration balance during the search. To solve CSPs, we
propose two discrete variants of two known nature-inspired algorithms. The first one is an adaptation of the
Mother Tree Optimization (MTO). In contrast, the second is an extension of the Particle Swarm Optimization
(PSO) with a new operator that we propose. Both variants rely on a heuristic that gathers information about
constraints violations during the search. The latter will then be used to update candidate solutions, follow-
ing a given topology for MTO, and position/velocity equations for PSO. To assess the performance of both
methods, we conducted several comparative experiments, considering other known systematic methods and
metaheuristics. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of both methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many combinatorial problems are known to be NP-
hard and require powerful solving models and tech-
niques. In this regard, the Constraint Satisfaction
Problems (CSPs) (Dechter et al., 2003; Carbonnel
and Cooper, 2016; Gutin and Yeo, 2012; Apt, 2003)
has been proposed to tackle a wide variety of deci-
sion problems. The CSP is the cornerstone of many
industrial real-world and academic applications such
planning (Do and Kambhampati, 2001), scheduling
(Apt, 2003), vehicle routing and timetabling (Hmer
and Mouhoub, 2016; Roos et al., 2000).
More formally, a CSP consists of a triplet
(V,D,C). V is the set of variables, V = {v
1
,...,v
n
}.
Each variable V
i
is defined on a domain D
i
=
{d
1
,...,dm} (D
i
∈ D). C is the set of constraints, C =
{c
1
,...,c
k
}, restricting the values that variables can
take (Ruttkay, 1998). A solution to a CSP is a com-
plete assignment of values to all variables such that all
constraints are satisfied. CSPs are NP-complete, and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7381-1064
many systematic and stochastic methods have been
developed to tackle this challenge in practice. Sys-
tematic search methods guarantee to find a solution,
if any, or detect the inconsistency of the CSP. They
do, however, suffer from their exponential time cost.
In order to overcome this difficulty in practice, back-
tracking methods improved through constraint propa-
gation and variable ordering heuristics have been pro-
posed (Dechter et al., 2003). Despite these improve-
ments, backtracking does have limitations, especially
for some hard and large CSP instances. In this regard,
nature-inspired and local search techniques have been
proposed to trade the quality of the solution returned
for time efficiency (Minton et al., 1992a; Galinier
and Hao, 1997; Blum and Roli, 2003; Glover and
Kochenberger, 2006; Talbi, 2009; Shil et al., 2013;
Korani and Mouhoub, 2021). More precisely, these
stochastic search methods can find the solution faster,
thanks to their polynomial running time, but this is
not always guaranteed (Kumar, 1992). Moreover,
stochastic search methods cannot prove the inconsis-
tency of the CSP. Note that recent works combining
234
Korani, W. and Mouhoub, M.
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for Constraint Satisfaction Problems.
DOI: 10.5220/0010803100003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 3, pages 234-241
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

both systematic and local search methods have been
proposed in order to take advantage of each tech-
nique (Zhang and Zhang, 1996; Jussien and Lhomme,
2002; Mouhoub and Jafari, 2011; Blum and Roli,
2003; Talbi, 2009). Nature-inspired algorithms have
been used to solve CSPs. These techniques include
Genetic Algorithms (GAs), Ant Colony Optimiza-
tion (ACO), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and
Honey Bee Algorithm (HBA). In (Tsang et al., 1999),
Tsang et al. introduced a Guided Genetic Algorithm
(GGA) that combines GA and Guided Local Search
to solve CSPs. The results show that GGA is more
efficient than GAs (Mitchell, 1996). In (Mouhoub
and Jafari, 2011), we introduced the ACO along with
Hill Climbing (HC) to come up with good variable or-
dering heuristics for solving CSPs. The results show
that the proposed method achieves better results, es-
pecially in the case of random hard problem instances.
In (Othman and Bouamama, 2019), the authors in-
troduced a method based on Honey Bee algorithm
to solve Max-CSPs. The results show that the pro-
posed method outperforms other Honey Bee-based al-
gorithms.
In (Korani et al., 2019), we proposed the Mother
Tree Optimization (MTO) algorithm to solve continu-
ous optimization problems based on a fixed-offspring
topology. The results of several comparative exper-
iments show that MTO outperforms different Parti-
cle Swarm Optimization (PSO) variants. In (Korani
and Mouhoub, 2020), we developed a discrete version
of MTO, which we called Discrete MTO (DMTO),
to solve the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). The
results of the experiments we conducted on TSP in-
stances demonstrate the efficiency of DMTO com-
pared to variants of PSO. DMTO is based on a swap
operator that is well suited for TSPs.
In this paper, we propose a variant of DMTO
adapted to CSPs. The new technique, which we call
DMTO-CSP, relies on gathering constraint violations
(Minton et al., 1992b; Mouhoub and Jafari, 2011;
Mouhoub, 2004; Yong and Mouhoub, 2018) for each
variable and recording this information in a data struc-
ture that we call Recommendation Pool (RP). In ad-
dition, we propose a variant of a PSO algorithm that
we developed for solving dynamic CSPs (Bidar and
Mouhoub, 2019a). This variant, which we call Muta-
tion PSO (MPSO), is also based on RP. In both meth-
ods (DMTO-CSP and MPSO), the main role of RP is
to update candidate solutions, respectively following
the MTO topology, in the case of DMTO-CSP, and the
position and velocity equations in the case of MPSO.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 presents an overview of constraint problems
and the related nature-inspired solving techniques. In
section 3, the basic concept of MTO algorithm and
its adaptation, DMTO-CSP, is discussed. In section 4,
we present MPSO. In section 5, we report on the ex-
periments for evaluating the performance of DMTO-
CSP and MPSO. Finally, section 6 lists concluding
remarks and ideas for future works.
2 RELATED WORK
In (Goradia, 2013), Goradia introduced Limited-
Memory Ant-Solver to solve CSPs. In the Ant-Solver,
ants have limited memory, where variables’ value re-
call partial assignments from their previous iteration.
The results show that the proposed method has the
same performance as Ant-Solver with respect to sev-
eral performance criteria. The authors combine their
proposed method along with a local search technique.
The results show that the proposed method along with
local search outperforms Ant-solver, along with local
search, especially for solving large CSPs. In (Liang
et al., 2017), Liang et al. introduced a method that
is built on the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algo-
rithm, called improved ABC (I-ABC) algorithm to
solve constraints optimization problems. In I-ABC
algorithm, the authors proposed a new selection strat-
egy based on rank selection and a search mechanism
using the information of the best so far solution to
balance exploration and exploitation processes(Blum
and Roli, 2003; Glover and Kochenberger, 2006;
Talbi, 2009; Korani and Mouhoub, 2021). In ad-
dition, the authors used the periodic boundary han-
dling model to repair invalid solutions. The authors
conducted extensive experiments to demonstrate the
efficiency of their proposed algorithm. In (Zouita
et al., 2019), Zouita et al. introduced a new CSP
solving technique based on arc consistency and ge-
netic algorithms (GAs). Here, a candidate solution
is represented as a chromosome where variables cor-
respond to genes and values represent alleles. Con-
straint propagation, through arc consistency, is used
to remove some inconsistent values, which will make
the remaining search task easier for the GA method.
In (Bidar and Mouhoub, 2019a), we introduced a dis-
crete variant of PSO to solve Dynamic CSPs (DC-
SPs). A DCSP is a dynamic variant of a CSP, where
constraints are added dynamically. In this regard, the
main goal of the proposed PSO is to solve the CSP
in an incremental way anytime new constraints are
added. In addition, the new solution obtained should
be as close possible to the old one. To evaluate the
performance of our proposed PSO, we conducted sev-
eral experiments on CSP instances randomly gener-
ated using the model RB. The results show that our
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for Constraint Satisfaction Problems
235

PSO outperforms other exact and stochastic search
algorithms. In (Mouhoub and Jafari, 2011), we pro-
posed two new variable and value ordering heuristics
respectively based on Hill Climbing (HC) and Ant
Colony Optimization (ACO). The goal of these two
heuristics is to provide a good variable and value or-
dering to a backtrack search algorithm. Experimen-
tal evaluation demonstrates the good performance of
backtracking when using our ordering heuristics.
3 DMTO-CSP
The MTO algorithm is based on a fixed-offspring
topology (Korani et al., 2019), where agents (repre-
senting potential solutions) update their positions in
the search space according to the group to which they
belong. MTO is inspired by the symbiotic relation-
ship between Douglas fir trees and mycorrhizal fungi
networks. The population is a set of Active Food
Sources (AFSs) whose size is denoted as N
T
. Follow-
ing the fixed-offspring topology, the MTO population
is divided into three groups: the TMT (the agent re-
ceiving nutrients from a random source), the Partially
Connected Trees (PCTs) group that has N
PCTs
agents,
and the Fully Connected Trees (FCTs) group that has
N
FCTs
agents. In addition, the PCTs group is divided
into the First Partially Connected Trees (FPCTs) sub-
group that has N
FPCTs
agents and the Last Partially
Connected Trees (LPCTs) sub-group that has N
LPCTs
agents. The FPCTs group has
N
T
2
− 2 agents in range
[ 2
nd
:
N
T
2
− 1]. The LPCTs group has
N
T
2
− 2 agents
in range [
N
T
2
+ 3 : N
T
] and ends at the last agent in
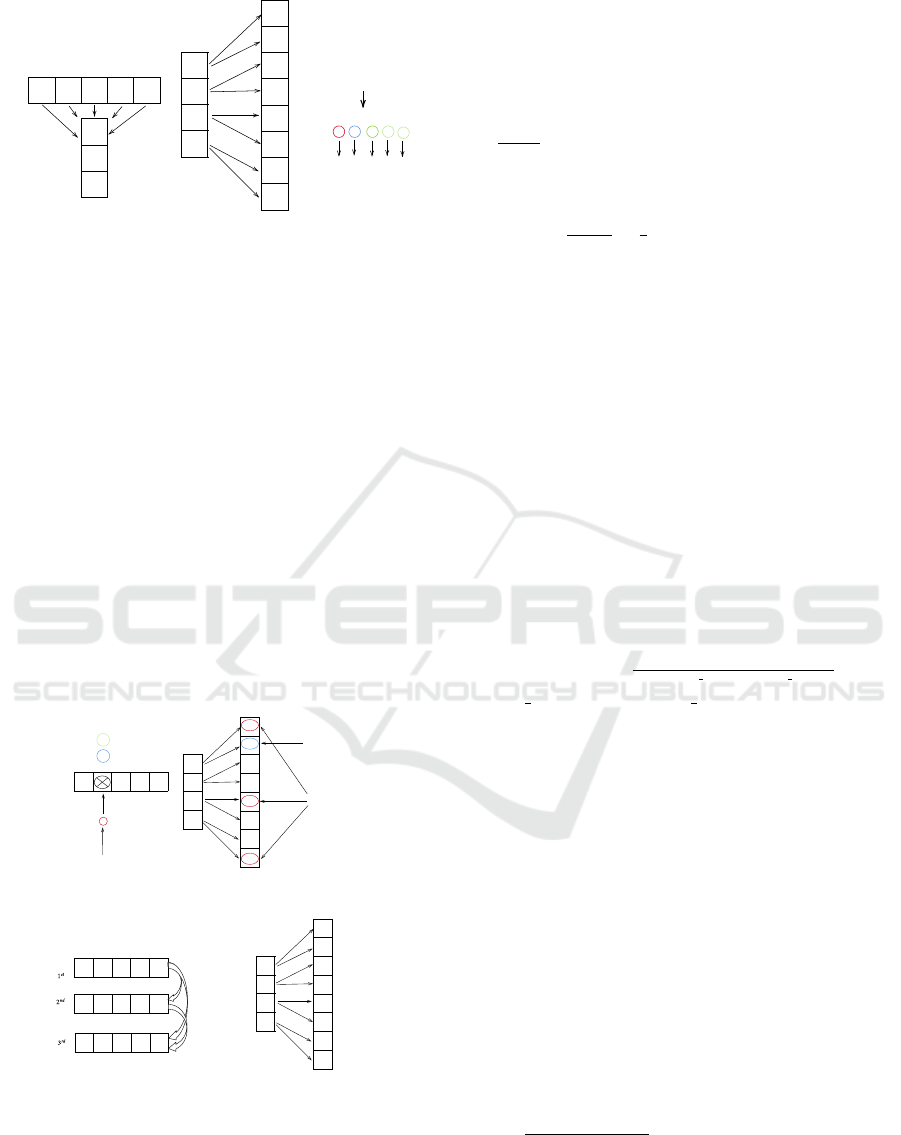
the population. Figure 1 shows the different groups
of candidates, following the fixed-offspring topology.
Here, agents are arranged (top down) in descending
order of their fitness value.
Figure 1: MTO Topology.
In (Korani and Mouhoub, 2020), we proposed the
DMTO algorithm to solve the Traveling Salesman
Problem (TSP). DMTO is based on a swap opera-
tor that is well suited for TSPs. In order to adapt
DMTO to CSPs, we propose a new technique that we
call the recommendation pool (RP). RP main goal is
to help the search converge quickly towards the solu-
tion. Moreover, we define a recheck operator (r) for
selecting the best candidate from RP. Our proposed
technique is inspired by the hill climbing heuristic
(Minton et al., 1992b; Mouhoub, 2004). Basically, at
each iteration of the DMTO-CSP algorithm, we im-
prove candidate solutions in each of the three groups
(TMT, PCT, and FCT) as done in hill climbing. More
precisely, for each potential solution, we select the
variable involved in most conflicts and replace its
value with the one that minimizes the number of con-
flicts. In order to prevent the algorithm from being
trapped in a local optimum, we balance this exploita-
tion strategy with exploration. For this latter, we se-
lect the value randomly for a chosen variable. In the
following, we define the details of the DMTO-CSP
components.
3.1 Solution Representation, Fitness
Function and Recommendation Pool
(RP)
Following on our past work, (Bidar and Mouhoub,
2019a), each candidate solution (or agent) in the pop-
ulation corresponds to a vector of size n, where n is
the total number of CSP variables. Each vector entry
corresponds to a variable value. The fitness function
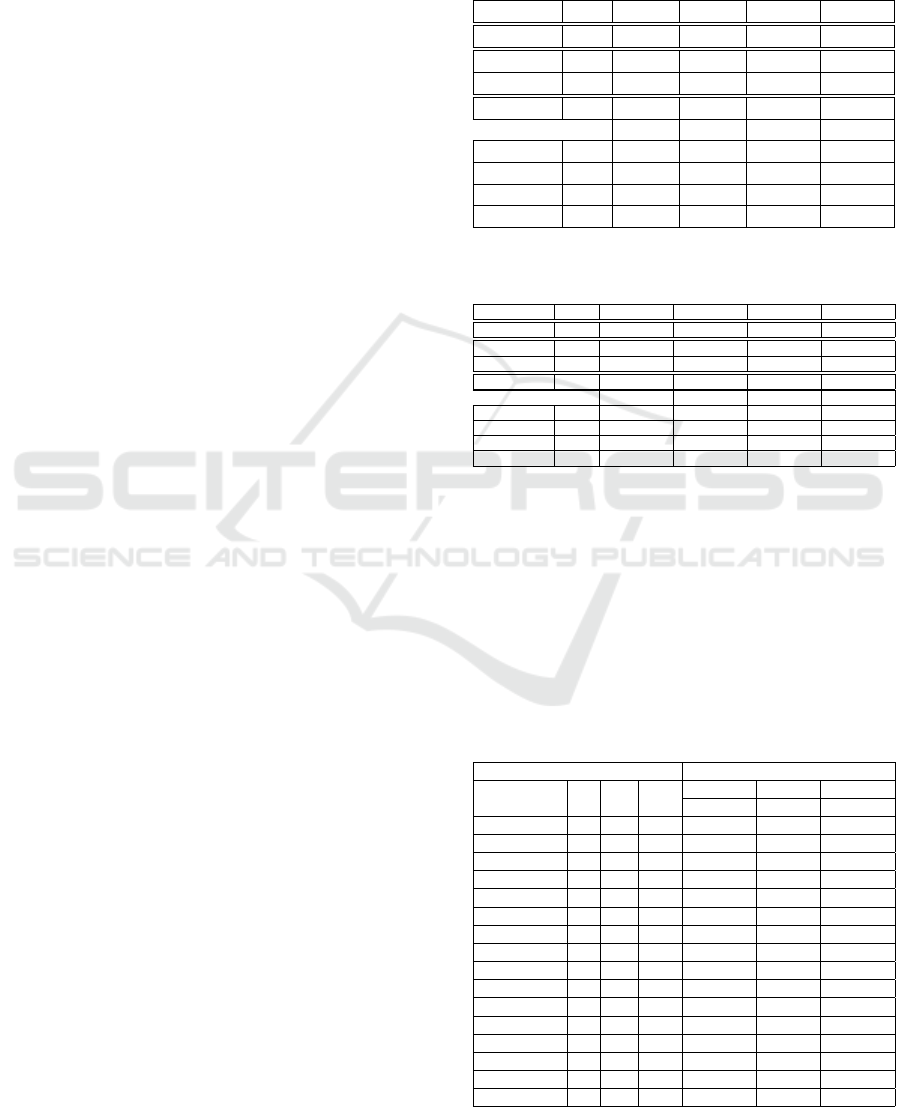
is defined as the number of violated constraints. Fig-
ure 2 shows a candidate solution corresponding to a
CSP with five variables, each defined on a domain
with three values, {a, b, c}. The candidate solution
listed has a fitness value of 4 (corresponding to four
constraint violations). RP is a list containing all the
CSP variables ranked in descending order of the con-
straint violations they are involved in. RP is produced
from, another list that we call the Violation Pool (VP).
VP contains all variables occurring in each constraint
violation. Figure 2 shows both lists. Variable Var
1
is involved in most conflicts (3), followed by variable
Var
4
(2 conflicts),..., Etc.
3.2 Updating the Top Mother Tree
(TMT) and Other Candidate
Solutions
At each iteration of the DMTO-CSP algorithm, can-
didate solutions are rearranged in descending order
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
236
Solution
Domain
Constrains
Incompatible tuples
a
b
c
a
a
bcb
(1, 0)
(4, 3)
(4, 1)
(1, 2)
Var 1 Var 2
Var 3 Var 4Var 0
(c, b)
(b, b)
(a, a)
(a, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
{ 1, 0, 4, 3, 4, 1, 1, 2}
Violation Pool
{
Recommendation Pool
Number of variables occurance
3
2
1
1
1,
4,
0,
3, }
2
1
Figure 2: A CSP with five variables and domain of three
values. There are 4 constrains and a total of 8 incompatible
tuples.
of their fitness value. TMT (ranked 1
st
) is the best
candidate solution (candidate with the lowest fitness
value). The RP of TMT is called Super Recommen-
dation Pool (SRP). Inspired by the root signal level
and mycorrhizal fungi network (MFN) level (Korani
et al., 2019), TMT balances exploitation and explo-
ration as follows. Exploitation is conducted as shown
in Figure 3. First, we select the first variable in SRP
(Var
1
, the variable involved in the largest number of
conflicts). Then, we select the value that minimizes
the number of conflicts (value a, which reduces the
number of conflicts for Var
1
to 0). If there is no better
value, the algorithm switches to exploration by choos-
ing a random value for the second or the third variable
in SRP. This process will ensure diversification as the
algorithm will explore more promising areas.
Constrains
Incompatible tuples
a
a
b
c
b
(1, 0)
(4, 3)
(4, 1)
(1, 2)
Var 1 Var 2
Var 3
Var 4
Var 0
(c, b)
(b, b)
(a, a)
(a, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
{
SRP
1, 0,
4,
3
}
TMT
Violations var 1 = c
b
a
Violations var 1 = b
Violations var 1 = a
winner value
first variable in the super
recommendation pool
a
c
bb
Var 1 Var 2 Var 3
Var 4
Var 0
a
a
bb
Var 1
Var 2
Var 3 Var 4
Var 0
TMT
Assume we have 6 agents and Nos = 2
feeder
feedee
a
b
Constrains
Incompatible tuples
(1, 0)
(4, 3)
(4, 1)
(1, 2)
(c, b)
(b, b)
(a, a)
(a, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
(a, c)
(c, b)
{
FRP12
var1 = a,
var3 = a
}
when var 1 = a
CVs = 0
when var3 = a
CVs = 2
CVs = 1
a
c
bb
Var 1 Var 2 Var 3
Var 4
Var 0
b
Figure 3: Updating the TMT (left) and the second agent in
the population (right).
Unlike TMT which is updated through exploita-
tion and exploration following a hill climbing heuris-
tic, candidate solutions in PCT and FCT groups are
updated according to the influence (feeding process)
their parents have on them. This process is guided
by a fixed-offspring topology. More precisely, par-
ticles are influenced and updated according to their
parents in the topology, with a given probability. This
probability (also called weight of the parent) is equal
to
1
n−i+1
where n is the position of the agent, and i
is the position of its parent. The right illustration of
3 illustrates this procedure for the second best agent.
This latter is influenced by its parent (the TMT), with
probability
1
2−1+1
=
1
2
, and is updated as follows. The
RP of this second agent, called Feeder Recommended
Pool (FRP), is filled with all the variable assignments
of the feeder (TMT) that are different from those of
the receiver (the second agent). In our example, this
will result in the following FRP for the second agent
that is influenced by the first one: FRP12 = {Var
1
= a, Var
3
= a}. Then, the assignment that mini-
mizes the fitness function of the receiver is selected.
If such assignment does not exist, then the algorithm
switches to exploration and random values will be as-
signed to the variables in FRP. In our case, assign-
ing a to Var
1
will reduce the fitness function of the
second agent to 0 (as shown in Figure 3). This is a
particular case where the algorithm will find and re-
turn a complete solution (given that the fitness value
is equal to 0). In case random assignments are per-
formed, the algorithm will compute the following sig-
moid function value in order to decide if the agent will
be updated: Sig =
1
(1−e
f itness updated− f itness current
)
. Here,
fitness updated and fitness current represent the fit-
ness of the updated and initial agent, respectively. If
the sigmoid value is greater than the weight of the
parent agent then the agent will not be updated. Fig-
ure 3 shows that agent ranked second receives nu-
trients from only the TMT, and the FRP12 = {Var
1
= a, Var
3
= a}. All recommended variables’ value
in the FRP12 are evaluated on the current receiver
and the best variable value that achieve lowest num-
ber of violations is selected, and then updated the re-
ceiver solution. Figure 3 shows that when the value
of Var
1
of the second solution is changed to a as
recommended in the FRP12 the number of CVs de-
creases to zero violation, which is the global solu-
tion. If no variable value could achieve better solu-
tion, then the 1
st
and 2
nd
variables’ value in the FRP12
update their values in a random way. Then, the sig-
moid value of the difference between the updated fit-
ness and the current fitness is calculated as follows:
Sig =
1
(1−e
updated−current
)
. Each feeder has an associated
weight according to our offspring topology (Korani
et al., 2019). If the returned sigmoid value is greater
than the weight of this feeder, then the updating of
this feeder is taken place and the current solution is
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for Constraint Satisfaction Problems
237

updated. This feeding process (depicted in Figure 1)
is repeated for all the agents in each group.
3.3 DMTO-CSP Climate Change
The climate change is a diversification operation that
helps DMTO-CSP to explore more promising areas
in the hope of finding the solution to the CSP. The
number of climate change events is denoted by Cl
and each climate change happens once every cycle (a
given number maxCl of iterations). More precisely,
the climate change operation works as follows. The
best updated solution is recorded in a queue called a
Best Solution Pool (BSP) that has a length equal to
the population size. At each climate change event, we
apply a distortion process on all solutions in BSP. The
distortion process consists of randomly changing the
values for rv randomly selected variables. Prelimi-
nary experiments that we conducted show that 10 and
2 are the best values for maxCl and rv, respectively.
4 MPSO
PSO is a very popular nature inspired algorithm that
has been used to tackle challenging continuous and
discrete optimization problems (Kennedy and Eber-
hart, 1995; Fornarelli, 2012). PSO is a population-
based nature inspired algorithm, where candidate so-
lutions (called particles) search for a given solution,
following velocity and position equations. In (Bidar
and Mouhoub, 2019a), we have introduced a variant
of PSO that we call Discrete PSO (DPSO) for solving
dynamic CSPs. In this regard, we have defined the
following equations for position and velocity, in the
case of CSPs.
X
t+1
i
= X
t
i
+V
t+1
i
(1)
V
t+1
i
= ω ⊗V
t
i
| {z }
exploration
+c
1
r
1
⊗ [X
t
lb
X
t
i
] + c
2
r
2
⊗ [X
t
gb
X
t
i
]
| {z }
exploitation
(2)
In the above equations, V
t
i
and X
t
i
are respectively
the velocity and position of particle i (a given candi-
date solution), at time t. ω is the inertia coefficient, c
1
and c
2
are acceleration coefficients in range [0,1], and
r
1
and r
2
are random values in range [0,1]. Equation 2
balances exploration and exploitation as follows. Ex-
ploration is expressed by the first part (ω ⊗V
t
i
) where
the particle moves at random, depending on the in-
ertial coefficient ω. Exploitation is guided by the
rest of the equation, where the particle respectively
moves towards its local best (X
lb
), and to the global
best (X
lb
), according to the acceleration coefficients
and random values. The operator corresponds to
changing some of the particle (X
i
) variables values so
it moves closer to its local or global best, respectively.
This is done by having both particles sharing more
identical values. The operator ⊗ decides on how close
should the particle be to its local and global best re-
spectively (according to to the initial coefficients and
random parameters). Similarly, in the case of explo-
ration, ⊗ decides on the level on randomness to apply,
according to the parameter ω.
Our proposed MPSO follows the same individual
representation and fitness function of DPSO, as de-
scribed in Section 3.1. MPSO also follows the same
equations 1 and 2. The difference resides in the way
the operators ⊗ and are implemented. Like in
DMTO-CSP, we use recommendation pools to per-
form exploration and exploitation, through these two
operators. Similarly to the Feeder Recommended
Pool (FRP), we defined in Section 3.2, we use a Local
RP (LRP) and (respectively a Global RP (GRP)), that
contains all the variables assignments of the local best
(respectively the global best) that are different from
the current particle. Then, we select the assignments
that minimize the number of conflicts. The number
of the selected assignments depend on the inertia co-
efficients (respectively the random values). The cor-
responding variables in the current particle will then
be mutated accordingly. Exploration is performed by
randomly mutating a fraction (corresponding to ω) of
the particle variables.
5 EXPERIMENTATION
In order to evaluate the performance of our DMTO-
CSP and MPSO, we conducted several comparative
experiments that we report in this section. The exper-
iments are performed on random as well as real-world
instances. Random instances are generated using the
model RB (Xu and Li, 2000). This model is an vari-
ant of the standard Model B, and is capable of pro-
ducing hard to solve instances (those that are close
to the phase transition). Instances are randomly gen-
erated based on four parameters: the number of vari-
ables (n), the constraint tightness (0 < p < 1), and two
positive constants, α and r, (0 < α,r < 1). The con-
straint tightness is defined as the number of incompat-
ible tuples over the Cartesian product of the variables
domain. Given these four parameters, RB instances
are generated as follows.
1. Select rn ln n distinct random constraints. Each
random constraint is formed by selecting 2 of n
variables.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
238
2. For each constraint, we uniformly select pd
2
dis-
tinct incompatible pairs of values, where d = n
α
is the domain size of each variable.
3. All the variables have the same domain corre-
sponding to the first d natural numbers (0 ...d −
1).
In the above, the number of constraints, and the
number of incompatible tuples should be rounded to
the nearest integer. According to (Xu and Li, 2000),
the phase transition pt is calculated as follows: pt =
1 − e
−α/r
. Solvable problems are therefore generated
with p < pt.
For real-world problems, we use the Driverlog, the
Quasi Completion Problem (QCP) and the balanced
Quasigroup with holes (BQWH) problems (Rous-
sel and Lecoutre, 2009). The Driverlog is a logis-
tic planning problem with four parameters: drivers,
trucks, packages, and locations. Drivers drive trucks
that carry packages to specific locations. The main
goal here is to find a solution for transporting a subset
of packages, by drivers and trucks, to certain loca-
tions. The number of CSP variables is ranging in [71
: 650], and the number of constraints is ranging in
[217 : 17447]. The Quasi-group Completion Prob-
lem (QCP) consists of completing a partially filled
Latin square. A Quasi-group can be seen as a mul-
tiplication table, with n rows and n columns, defin-
ing a Latin square. Each row and column of the ta-
ble must be filled with a unique integer value. QCP
instances are used to bridge the gap between ran-
dom instances (such as those represented by the RB
model) and structured problems (Rossi et al., 2006).
These problems have many relevant real-world ap-
plications including resource allocation, timetabling,
statistical design and error correction codes. Quasi-
group with Holes (QWH) are generated by starting
with a complete Latin square (corresponding to a
complete Quasi-group). Some entries are then re-
moved. BQWH are generated such that the distri-
bution of the holes is balanced. In this regard, the
number of unassigned cells is approximately the same
across the different rows and columns.
Tables 1 and 2 list comparative results, in terms
of Number of Constraint Check (NCC), for CSP in-
stances with 100 and 200 variables, respectively. Our
algorithms are compared to our previous implemen-
tations of DPSO (Bidar and Mouhoub, 2019a) and
the discrete Firefly algorithm (DFA) for CSPs (Bidar
and Mouhoub, 2019b). The results for Table 1 show
that MPSO is outperforming all the other methods for
tightness values ranging from 0.25 to 0.4, excluding
p = 0.35 where DMTO-CSP is the winner. For tight-
ness ranging from 0.45 to 0.6 (corresponding to the
hardest problems to solve) DPSO is the best method.
However, for 200 variables, MPSO is the best method
for all the tightness values, as demonstrated in Table
2.
Table 1: Experimentation results on CSPs with 100 vari-
ables with different tightness.
Algorithm factor p=0.25 p=0.3 p=0.35 p=0.4
DMTO-CSP NCC 2209297 1477767 2127931 5445792
FA NCC 4016487 4939168 4940176 5567451
DPSO NCC 1815428 1915214 2216247 3230127
MPSO NCC 929979 1196615 2146649 2432194
p=0.45 p=0.5 p=0.55 p=0.6
DMTO-CSP NCC 8879399 9076893 11499728 10577580
FA NCC 5671379 5973192 6881238 7120192
DPSO NCC 3846671 5171136 5383012 5928431
MPSO NCC 4311061 5369965 6002175 7085718
Table 2: Comparative results for CSP instances with 200
variables.
Algorithm factor p=0.25 p=0.3 p=0.35 p=0.4
DMTO-CSP NCC 40475600 61233920 74535560 89581360
FA NCC 31217848 63102648 89742144 66245760
DPSO NCC 26114584 56745192 57585984 59538080
MPSO NCC 13807200 22245960 33345400 43709160
p=0.45 p=0.5 p=0.55 p=0.6
DMTO-CSP NCC 86075000 119251440 109129680 141961160
FA NCC 132845190 148474200 13975843 217817280
DPSO NCC 71021584 122029320 135748912 131999680
MPSO NCC 56173480 63899000 72359320 88160600
In order to assess the quality of the solutions re-
turned when solving the Driverlog instances (Rous-
sel and Lecoutre, 2009), we conducted experiments
comparing our two methods to the backtrack search
algorithm with dom/wdeg* variable ordering heuris-
tic (Yong and Mouhoub, 2018). This latter heuristic
consists of ordering variables starting with the most
constraining one. More precisely, variables are or-
dered according to the ratio dom/wdeg, where dom
Table 3: Comparative results for the Driverlog, BQWH and
QCP instances.
Instance Algorihtms
No. V R C
DMTO-CSP MPSO dom/wdeg*
# cck # cck # cck
01c 71 14 217 1.05M 1.2M 0.026M
08c 408 648 9321 1003.5M 2862.56M 67.233M
08cc 408 649 9321 1046.26M 3408.71M 75.787M
09 650 1639 17447 3955.9M 4392.02M Not reported
bqwh-15-106-0 106 155 644 .862M 0.069M 5.355M
bqwh-15-106-5 106 135 644 1.335M 0.245M 0.347M
bqwh-15-106-9 106 149 644 2.73M 0.49M 2.870M
bqwh-18-141-0 141 236 966 2.075M 0.104M 26.935M
bqwh-18-141-06 141 229 966 25.27M 0.245M 12.357M
bqwh-18-141-22 141 263 966 3.75M 0.057M 1.941M
qcp-10-67-0 100 12 900 3.1M 1.65M 0.133M
qcp-10-67-7 100 11 900 3.8M 1.31M 1.452M
qcp-10-67-14 100 12 900 6.6M 9.2M 0.089M
qcp-15-120-0 225 17 3150 28.35M 4.6M 12.835M
qcp-10-67-8 225 17 3150 77.68M 24.48M 38.085M
qcp-10-67-14 225 17 3150 28.64M 1.09M 1.565M
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for Constraint Satisfaction Problems
239

is the domain size of the variable while wdeg is the
weighted degree of the corresponding node. This
weight is equal to the sum of the weights of the con-
straints associated the variable. The weight of a con-
straint is computed based on the conflict and sup-
port counts gathered by a look-ahead method during
search. Given that dom/wdeg* returns a complete so-
lution, we had to let our two methods run for 1000
iterations and only report those results where com-
plete solutions are returned. Table 3 (first 4 rows),
lists the results of this experimentation. As we can
notice, dom/wdeg* outperforms our methods for the
first three problem instances. For the last and hardest
instance however (No 9), dom/wdeg* was not able to
return the solution while our methods where success-
ful. This is a promising result that will motivate us to
conduct further improvements for both DMTO-CSP
and MPSO.
Table 3 (from the 5th row) lists the number of con-
straint checks when solving BQWH and QCP prob-
lem instances. Here again, DMTP-CSP and MPSO
are compared to the backtrack search algorithm with
dom/wdeg* variable ordering heuristic. As we can
notice from the results, MPSO is the winner in most
of the problem instances. The dom/wdeg* method
was the best in only two problem instances. More-
over, some instances show that DMTO-CSP is also
better than dom/wdeg*. These results favoring our
two methods might be due to the fact that QCP and
BQWH inherit properties from both the random and
the structured problems.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We propose an adaptation of DMTO (Korani and
Mouhoub, 2020) and DPSO (Bidar and Mouhoub,
2019a) for solving CSPs. Our variants are respec-
tively called DMTO-CSP and MPSO and are guided
by a hill climbing heuristic. Indeed, both meth-
ods gather the information regarding those variables
in conflict (Mouhoub and Jafari, 2011; Yong and
Mouhoub, 2018), and use it to update their popula-
tion through the MTO topology and PSO position and
velocity equations, respectively. To assess the practi-
cal performance of our proposed techniques, we con-
ducted several comparative tests on randomly gen-
erated as well as real-world instances. Random in-
stances are generated using the known RB model
(Xu and Li, 2000) which can generate hard-to-solve
instances. Real-world instances are taken from the
XCSP library (Roussel and Lecoutre, 2009) and cor-
respond to the Driverlog, the balanced Quasigroup
with holes (BQWH) and the Quasi Completion Prob-
lem (QCP) instances. Our methods were compared
to other nature-inspired techniques (DPSO (Bidar and
Mouhoub, 2019a) and DFA (Bidar and Mouhoub,
2019b)) and backtrack search using variable ordering
heuristics, dom/wdeg* (Yong and Mouhoub, 2018).
Overall, the results are promising and show the su-
periority of our techniques for both random, BQWH,
and QCP instances. For the Driverlog problems, al-
though dom/wdeg* is the winner for most of the in-
stances, our two methods were the only ones capa-
ble of solving the hardest instance. These results
motivated us to conduct further research on improv-
ing both techniques by considering other information
gathering heuristics and a good balance between ex-
ploration and exploitation. We also plan to general-
ize the idea of learning the hardness of constraints
during the search to other nature-inspired techniques
we developed in the past for solving CSPs (Abbasian
and Mouhoub, 2016; Bidar et al., 2018; Bidar and
Mouhoub, 2019c). We will also tackle the case of
variants of CSPs, including dynamic CSPs (Bidar
and Mouhoub, 2019a) and weighted CSPs (Bidar and
Mouhoub, 2019c).
REFERENCES
Abbasian, R. and Mouhoub, M. (2016). A new paral-
lel ga-based method for constraint satisfaction prob-
lems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl., 15(3):1650017:1–
1650017:22.
Apt, K. (2003). Principles of constraint programming.
Cambridge university press.
Bidar, M., Kanan, H. R., Mouhoub, M., and Sadaoui, S.
(2018). Mushroom reproduction optimization (MRO):
A novel nature-inspired evolutionary algorithm. In
2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation,
CEC 2018, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, July 8-13, 2018,
pages 1–10. IEEE.
Bidar, M. and Mouhoub, M. (2019a). Discrete particle
swarm optimization algorithm for dynamic constraint
satisfaction with minimal perturbation. In 2019 IEEE
International Conference on Systems, Man and Cy-
bernetics (SMC), pages 4353–4360. IEEE.
Bidar, M. and Mouhoub, M. (2019b). Self-adaptive discrete
firefly algorithm for minimal perturbation in dynamic
constraint satisfaction problems. In IEEE Congress
on Evolutionary Computation, CEC 2019, Wellington,
New Zealand, June 10-13, 2019, pages 2620–2627.
IEEE.
Bidar, M. and Mouhoub, M. (2019c). Solving weighted
constraint satisfaction problems using a new self-
adaptive discrete firefly algorithm. In 2019 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Systems, Man and Cyber-
netics, SMC 2019, Bari, Italy, October 6-9, 2019,
pages 2198–2205. IEEE.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
240

Blum, C. and Roli, A. (2003). Metaheuristics in combi-
natorial optimization: Overview and conceptual com-
parison. ACM computing surveys (CSUR), 35(3):268–
308.
Carbonnel, C. and Cooper, M. C. (2016). Tractability
in constraint satisfaction problems: a survey. Con-
straints, 21(2):115–144.
Dechter, R., Cohen, D., et al. (2003). Constraint processing.
Morgan Kaufmann.
Do, M. B. and Kambhampati, S. (2001). Planning as
constraint satisfaction: Solving the planning graph
by compiling it into csp. Artificial Intelligence,
132(2):151–182.
Fornarelli, G. (2012). Swarm intelligence for electric and
electronic engineering. IGI Global.
Galinier, P. and Hao, J. (1997). Tabu search for maximal
constraint satisfaction problems. In Smolka, G., ed-
itor, Principles and Practice of Constraint Program-
ming - CP97, Third International Conference, Linz,
Austria, October 29 - November 1, 1997, Proceedings,
volume 1330 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 196–208. Springer.
Glover, F. W. and Kochenberger, G. A. (2006). Handbook of
metaheuristics, volume 57. Springer Science & Busi-
ness Media.
Goradia, H. J. (2013). Ants with limited memory for solv-
ing constraint satisfaction problems. In 2013 IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pages 1884–
1891. IEEE.
Gutin, G. and Yeo, A. (2012). Constraint satisfaction prob-
lems parameterized above or below tight bounds: A
survey. In The Multivariate Algorithmic Revolution
and Beyond, pages 257–286. Springer.
Hmer, A. and Mouhoub, M. (2016). A multi-phase hybrid
metaheuristics approach for the exam timetabling.
Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl., 15(4):1650023:1–
1650023:22.
Jussien, N. and Lhomme, O. (2002). Local search with con-
straint propagation and conflict-based heuristics. Ar-
tificial Intelligence, 139(1):21–45.
Kennedy, J. and Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm opti-
mization. In Proc. IEEE Intl. Con on Neural Networks
(Perth, Australia), pages 1942–1948. IEEE.
Korani, W. and Mouhoub, M. (2020). Discrete mother tree
optimization for the traveling salesman problem. In
International Conference on Neural Information Pro-
cessing, pages 25–37. Springer.
Korani, W. and Mouhoub, M. (2021). Review on Nature-
Inspired Algorithms. SN Operations Research Forum,
2(3):1–26.
Korani, W., Mouhoub, M., and Spiteri, R. J. (2019). Mother
tree optimization. In 2019 IEEE International Confer-
ence on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), pages
2206–2213. IEEE.
Kumar, V. (1992). Algorithms for constraint-satisfaction
problems: A survey. AI magazine, 13(1):32–32.
Liang, Y., Wan, Z., and Fang, D. (2017). An improved ar-
tificial bee colony algorithm for solving constrained
optimization problems. International Journal of Ma-
chine Learning and Cybernetics, 8(3):739–754.
Minton, S., Johnston, M. D., Philips, A. B., and Laird,
P. (1992a). Minimizing conflicts: a heuristic re-
pair method for constraint satisfaction and scheduling
problems. Artificial intelligence, 58(1-3):161–205.
Minton, S., Johnston, M. D., Philips, A. B., and Laird,
P. (1992b). Minimizing conflicts: a heuristic re-
pair method for constraint satisfaction and scheduling
problems. Artificial Intelligence, 58(1):161–205.
Mitchell, M. (1996). An introduction to genetic algorithms
mit press. Cambridge, Massachusetts. London, Eng-
land, 1996.
Mouhoub, M. (2004). Systematic versus non systematic
techniques for solving temporal constraints in a dy-
namic environment. AI Commun., 17(4):201–211.
Mouhoub, M. and Jafari, B. (2011). Heuristic techniques for
variable and value ordering in csps. In Proceedings of
the 13th annual conference on Genetic and evolution-
ary computation, pages 457–464.
Othman, H. B. and Bouamama, S. (2019). A new template
concept guided honey bee optimization for max-csps.
Procedia Computer Science, 159:2154–2161.
Roos, N., Ran, Y., and Van Den Herik, J. (2000). Com-
bining local search and constraint propagation to find
a minimal change solution for a dynamic csp. In
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence:
Methodology, Systems, and Applications, pages 272–
282. Springer.
Rossi, F., van Beek, P., and Walsh, T., editors (2006). Hand-
book of Constraint Programming. Elsevier.
Roussel, O. and Lecoutre, C. (2009). Xml representation of
constraint networks: Format xcsp 2.1. arXiv preprint
arXiv:0902.2362.
Ruttkay, Z. (1998). Constraint satisfaction-a survey. CWI
Quarterly, 11(2&3):123–162.
Shil, S. K., Mouhoub, M., and Sadaoui, S. (2013). Win-
ner determination in combinatorial reverse auctions.
In Contemporary challenges and solutions in applied
artificial intelligence, pages 35–40. Springer.
Talbi, E.-G. (2009). Metaheuristics: from design to imple-
mentation, volume 74. John Wiley & Sons.
Tsang, E. P., Wang, C. J., Davenport, A., Voudouris, C., and
Lau, T. L. (1999). A family of stochastic methods for
constraint satisfaction and optimization. In The First
International Conference on the Practical Application
of Constraint Technologies and Logic Programming
(PACLP), London, pages 359–383.
Xu, K. and Li, W. (2000). Exact phase transitions in random
constraint satisfaction problems. Journal of Artificial
Intelligence Research, 12:93–103.
Yong, K. W. and Mouhoub, M. (2018). Using conflict and
support counts for variable and value ordering in csps.
Appl. Intell., 48(8):2487–2500.
Zhang, J. and Zhang, H. (1996). Combining local search
and backtracking techniques for constraint satisfac-
tion. In AAAI/IAAI, Vol. 1, pages 369–374.
Zouita, M., Bouamama, S., and Barkaoui, K. (2019). Im-
proving genetic algorithm using arc consistency tech-
nic. Procedia Computer Science, 159:1387–1396.
Discrete Mother Tree Optimization and Swarm Intelligence for Constraint Satisfaction Problems
241
