
Coordination Mechanisms with Misinformation
Constantinos Varsos
1,2
, Michail Fasoulakis
1
, Giorgos Flouris
1
and Marina Bitsaki
2
1
Institute of Computer Science, FORTH, Vasilika Vouton, Heraklion, Greece
2
Department of Computer Science, University of Crete, Heraklion, Greece
Keywords:
Game Theory, Misinformation Games, Mechanism Design, Coordination Mechanisms, Information in
Games, Non-atomic Congestion Games with Parallel Links.
Abstract:
We introduce a novel approach for coordination mechanisms in games, based on the idea of misinforming
players about the game formulation in order to steer them towards a behaviour that leads to an improved
outcome in terms of social welfare. As a use case, we study single-commodity non-atomic congestion games
with parallel links and affine cost functions. We propose a simple mechanism that provides to the players
the right incentives to adopt a socially optimal behaviour by misinforming them with regards to the latency
functions of the links, under various assumptions. We use a metric called the Price of Misinformation to
quantify the effect of misinformation on social welfare (compared to the optimum of the actual game), and
show that our mechanism can minimise this metric, resulting in values that are better than the Price of Anarchy
(i.e., the social outcome without any intervention from the designer).
1 INTRODUCTION
In games with selfish and rational players, the out-
come may be very inefficient in terms of social wel-
fare. The Price of Anarchy, introduced in (Koutsou-
pias and Papadimitriou, 1999), measures how far the
worst Nash equilibrium is from the social optimum.
In this paper, we investigate methods to lead play-
ers’ behaviour to a socially improved outcome. Co-
ordination mechanisms were introduced for this pur-
pose in (Christodoulou et al., 2009; Christodoulou
et al., 2014), in which a theoretical framework is pro-
posed where modifications of the game lead to a re-
duced fraction, compared to the Price of Anarchy, of
the worst Nash equilibrium in the modified game to
the social optimum of the original game. This has
been applied to many classes of games such as load
balancing and congestion games (Nisan et al., 2007).
A common assumption in game theory is that
players have complete information concerning the
game of interest, i.e., the set of players, the set of
strategies and the payoffs for each player is com-
mon knowledge among players. In (Varsos et al.,
2021), this assumption is dropped by studying situa-
tions where each player may have a different (and thus
incorrect) perception about the game being played,
while being unaware that she has only a subjective
view of the interaction. To that direction, (Varsos
et al., 2021) agglomerate the objective interaction
(called actual game) and the subjective views, in-
troducing the concept of misinformation games for
normal-form games. A key characteristic of misin-
formation games is that each player’s choices are dic-
tated by her view, whereas her payoff is provided by
the actual game. This leads to the introduction of
a new equilibrium concept, the natural misinformed
equilibrium, which is the set of strategic choices
where no player wants to deviate in her view.
Moreover, a metric, the Price of Misinformation
(PoM), was introduced to measure the impact of mis-
information in games, compared to the socially opti-
mum situation (Varsos et al., 2021). Clearly, misinfor-
mation could lead players to strategic choices that are
different from the ones they would make in the ab-
sence of misinformation. This includes choices that
are actually beneficial (from the perspective of social
welfare) for the players. Inspired by this observation,
we combine misinformation games and coordination
mechanisms to address the following question:
Is it possible for the designer of a game to misin-
form players regarding the game parameters, in order
to provide incentives for a better (or even optimal) be-
haviour in terms of social welfare?
We positively answer this question, and provide a
novel way for applying coordination mechanisms us-
ing the concept of misinformation, thereby establish-
Varsos, C., Fasoulakis, M., Flouris, G. and Bitsaki, M.
Coordination Mechanisms with Misinformation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010836100003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 1, pages 237-244
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
237

ing a connection between the classical coordination
mechanisms and misinformation games.
As in classical coordination mechanisms, where
the designer modifies the game in order to minimize
the ratio between the worst Nash equilibrium of the
modified game and the social optimum of the origi-
nal game, we propose a similar approach where the
designer misinforms players. Next, we compare the
worst natural misinformed equilibrium (i.e., the worst
result of misinformation) with the social optimum of
the actual game, that is Price of Misinformation. In-
terestingly, it could be less than the Price of Anarchy,
resulting in an improved behaviour (from the perspec-
tive of social welfare) of the players, compared to the
scenario without misinformation.
A key difference between classical coordination
mechanisms and coordination mechanisms with mis-
information is that in the first case the designer can
influence the actual interaction as a whole, whereas
in the latter the designer determines the subjective
views of the players, i.e., the misinformed views.
Thus, in the first case the designer modifies the ac-
tual game specification, whereas in the latter the de-
signer changes players’ (subjective) information, but
has no power over the actual game specification, In
this paper, we consider the setting where the designer
cannot impose a different game specification, but can
misinform players about the actual set up.
We consider the problem under assumptions about
the number of misinformed views that the designer
can spawn. In particular, the designer has bounded ca-
pabilities with regards to the number of different mis-
informed views that can be spawned (see Section 6).
As a real-life situation, consider the case where
two companies compete with each other in a market.
We can see one of them (say D) as the designer, and
the other (say P) as a group of divisions (P
1
,...,P
2
),
representing players. The designer D can use a coor-
dination mechanism with misinformation in order to
benefit from the (in-)efficiency of the rival company,
by misleading the divisions of P into actions that are
not optimal for P. Although this is a rather simplistic
scenario, in general, coordination mechanisms with
misinformation can be used in (among others) bar-
gaining, negotiation and conflict scenarios.
We apply the above ideas for single-commodity
non-atomic congestion games with n parallel links
and affine cost functions. We first adapt the concept
of misinformation to the class of non-atomic conges-
tion games (Section 4), and design a polynomial-time
algorithm for computing a pure Nash equilibrium in a
network (Section 5). Moreover, we describe a mecha-
nism for designing misinformation games with an op-
timal Price of Misinformation (and thus better social
outcomes) under various assumptions (Section 6).
2 RELATED WORK
The idea of designing mechanisms to improve coordi-
nation in multi-player systems with selfish players is
not new. One approach is to introduce taxes ((Fleis-
cher et al., 2004), (Fotakis and Spirakis, 2008), (Cara-
giannis et al., 2010), etc.); this has been applied in
congestion games, where players pay a toll for every
edge they use. In (Cole et al., 2003) it was shown that
there exist taxes that reduce the Price of Anarchy to
1. However, there are two issues for this approach:
i) taxes may be very high, and ii) if taxes are part of
the cost, then the Price of Anarchy is not improved.
Similarly, (Lavi and Swamy, 2007), (Seregina et al.,
2017), (Turrini, 2013) used rewards to improve coor-
dination. In (Monderer and Tennenholtz, 2003) the
game is extended by adding new strategies and en-
hanced monetary policies for the players, such that all
Nash equilibria of the new game involve strategies of
the original game exclusively. In that case, the Price
of Anarchy is decreased.
In this paper, we will use the concept of misinfor-
mation games (Varsos et al., 2021). This concept lies
in the area of games with misperceptions (see Chapter
12 in (Luce and Raiffa, 1957)), which studies games
where players have a subjective knowledge regard-
ing game specifications. Related ideas include: i) hy-
pergames ((Bennett, 1980; Sasaki and Kijima, 2012;
Bakker et al., 2021) etc.), ii) games with unaware-
ness/awareness ((Copic and Galeotti, 2006; Halpern
and R
ˆ
ego, 2014; Schipper, 2017; Feinberg, 2020)
etc.), and iii) other works ((Esponda and Pouzo, 2016;
Ozbay, 2007) etc.) where players may have misper-
ception. To the best of our knowledge, there has been
no study in this area regarding non-atomic congestion
games, and also none of these has been applied to im-
prove the social outcome of games.
Another approach dealing with unawareness is
that of incomplete information that is described by
Bayesian games. They were introduced by (Harsanyi,
1967) and have received a lot of attention by many
scholars ((Sz
´
ekely and Rizzo, 2007; Zamir, 2009;
Myerson, 2004), etc.). The main idea of this approach
is that players’ beliefs with regards to game specifica-
tions are represented by probability distributions.
There are several key differences between misin-
formation and Bayesian games. Firstly, in Bayesian
games, players are aware of the incompleteness of
their information (as represented by the probabil-
ity distributions), whereas in misinformation games
players are unaware of the fact that their game spec-
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
238

ification is wrong. Therefore, they will not consider
mitigating strategies “just in case” they have a wrong
specification. Moreover, the payoffs they get are dic-
tated by the actual game and may be radically differ-
ent from the ones specified in their own game.
Moreover, in the Bayesian approach the concept
of non-common knowledge is dealt indirectly through
the assignment of distributions over actions and be-
liefs, as opposed to misinformation games, where
we can directly deal with non-common knowledge
games, using subjective views. Consequently, the two
aforementioned approaches have different equilibria
concepts, namely Bayesian Nash equilibrium and nat-
ural misinformed equilibrium, respectively.
Another approach to cope with incomplete infor-
mation in non-atomic routing games was introduced
in the works of (Meir and Parkes, 2015a; Meir and
Parkes, 2015b; Meir and Parkes, 2018), where the au-
thors propose a model with player-specific costs. In
these studies, the authors suggest that players play a
modified game with cost functions potentially differ-
ent than the actual game, without considering either
misinformation or coordination mechanisms.
3 SINGLE COMMODITY
NON-ATOMIC CONGESTION
GAMES
We define single-commodity non-atomic congestion
games using an approach similar to that of (Meir and
Parkes, 2015b):
Definition 1. A single-commodity non-atomic con-
gestion game is a tuple Γ = hG,l, s,t,ri, where:
• G = (V,E) is a directed graph,
• l is the set of non-decreasing, continuous, and
non-negative latency cost functions with l
e
(x) :
R
≥0
→ R
≥0
(one for each edge e ∈ E), where x
is the flow,
• s ∈ V is the source,
• t ∈ V is the destination,
• r is the total mass of flow.
We consider that any player controls an infinitesi-
mal amount of flow r.
Let P be the set of total paths from s to t, then
we define as f (r) ∈ [0,r]
|P|×1
a feasible flow of the
players routing r units of flow on the paths. We define
as f
p
(r) the flow of players that follows the path p ∈
P. The flow of the players on the edge e ∈ E is f
e
(r).
The cost of following a path p is C
p
( f
p
(r)) =
∑
e∈p
l
e
( f
e
(r)) and the total Social Cost of the flow
f (r) is SC( f (r)) =
∑
e∈E
f
e
(r)l
e
( f
e
(r)). The so-
cially optimal flow is the feasible flow f (r) such that
SC( f (r)) is minimum. We define a pure Nash equi-
librium (also known as Wardrop equilibrium) in non-
atomic congestion games as follows:
Definition 2 (Pure Nash equilibrium (Nash,
1951)/Wardrop equilibrium (Wardrop, 1952)).
A pure Nash equilibrium is a feasible flow f
∗
(r) such
that for any p, ˆp ∈ P,
C
p
( f
∗
p
(r)) ≤ C
ˆp
( f
∗
ˆp
(r)),
in other words, a flow is an equilibrium if no player
has any incentive to deviate from her path.
Any non-atomic game has at least one equilibrium
(Schmeidler, 1973; Rosenthal, 1973).
Next, we present the specific class of single-
commodity non-atomic congestion games with n par-
allel links from s to t with r = 1. We consider that
the cost function of an edge/link k ∈ {1,2,...,n} is
an affine function, that is, l
k
(x
k
) = a
k
x
k
+ b
k
, with
a
k
,b
k
> 0 , and x
k
∈ [0,1] is the flow of link k, with
∑
n
k=1
x
k
= 1. Without loss of generality, we assume
that the links are sorted in an increasing order with
respect to b
k
, or in other words that if k ≤ p, then
b
k
≤ b
p
. Let x = (x
1
,...,x
n
) be an allocation of the
flow on the links. Here the cost on an edge k is
l
k
(x
k
), thus the total Social Cost of this allocation is
∑
n
k=1
x
k
l
k
(x
k
). We denote this game as Γ, see Figure 1.
s
t
x
1
x
2
x
n−1
.
.
.
x
n
Figure 1: Single-commodity non-atomic congestion game
with n parallel links.
In the case of non-atomic congestion games with
n parallel links, Definition 2 provides that an allo-
cation x
∗
= (x
∗
1
,...,x
∗
n
) of the flow on the links is a
pure Nash equilibrium if and only if, ∀ i ∈ {1,...,n},
and ∀ j ∈ {1,...,n}, l
i
(x
∗
i
) ≤ l
j
(x
∗
j
). Consequently,
x
∗
= (x
∗
1
,...,x
∗
n
) is a pure Nash equilibrium if and
only if, l
i
(x
∗
i
) = l
j
(x
∗
j
) for all i, j ∈ {1,...,n} with
x
∗
i
,x
∗
j
> 0. Moreover, all Nash equilibria result in the
same Social Cost (Chapter 18 of (Nisan et al., 2007)).
Coordination Mechanisms with Misinformation
239

4 MISINFORMATION
NON-ATOMIC CONGESTION
GAMES
Misinformation games were defined in (Varsos et al.,
2021) for the general class of normal-form games.
Under the definition of (Varsos et al., 2021), a misin-
formation game of N players consists of N + 1 game
specifications (mG = hG
0
,G
1
,...,G
N+1
i). The first
(G
0
) is the so-called actual game, which corresponds
to the game that the players actually play, whereas
each one of games G
i
corresponds to the subjective
view of the game from the perspective of player i, that
is the game that player i believes that is being played.
Note that this definition allows all types of mis-
information to occur (including, e.g., cases where
the players are misinformed regarding the available
strategies or players). However, in (Varsos et al.,
2021) a special form was considered, called canonical
misinformation games, where subjective views differ
only in the values of the elements of the payoff matri-
ces. It was shown that all non-canonical misinforma-
tion games can be transformed into canonical ones,
therefore we can, without loss of generality, restrict
our attention to canonical games.
In this Section, we use an analogous approach
to define misinformation games for the case of non-
atomic congestion games, where each player has a
subjective view about the game she plays, which may
be different from the others. Formally:
Definition 3 (Misinformation game). A misinforma-
tion non-atomic congestion game mΓ with θ splitting
is an (N + 1)-tuple mΓ = hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,...,Γ
N
i, where N is
the number of different views of the game that differ-
ent players may assume, Γ
0
= hG,l,s,t, ri is the ac-
tual game, Γ
j
= hG,l
j
,s,t, r
j
i are the different sub-
jective game specifications assumed by the players,
of which each player assumes only one, and θ =
hθ
1
,...,θ
N
i, where θ
i
is the portion of players that
experience view Γ
i
.
Here, we assume that the total mass of flow across
all Γ
j
(for j > 0) is equal to the respective mass in
Γ
0
, r
j
= r. Further, it must hold that
∑
i∈[N]
θ
i
= 1.
Thus, the players have the correct view of the graph
and the flow at hand, although they may assume dif-
ferent cost functions. In this case, we call the misin-
formation single commodity non-atomic congestion
games as canonical, similar to canonical misinforma-
tion games, as defined in (Varsos et al., 2021).
Definition 4 (Misinformed equilibrium strategy). A
misinformed strategy is a flow for portion θ
j
, that θ
j
with subjective view Γ
j
follows in a pure Nash equi-
librium strategy of its game view Γ
j
.
Definition 5 (Natural Misinformed equilibrium). A
natural misinformed equilibrium is a flow f such
that each portion θ
j
plays a misinformed equilibrium
strategy according to its game-specific view j.
Since any non-atomic congestion game has at least
one Nash equilibrium, then any misinformation game
of a non-atomic congestion game as defined above has
at least one natural misinformed equilibrium.
Having at hand the formal definition of the natural
misinformed equilibrium, we measure the deteriora-
tion/leverage in efficiency of a non-atomic congestion
game due to misinformation. For that, we adapt the
concept of Price of Misinformation (PoM), that was
defined in (Varsos et al., 2021), in the case of non-
atomic congestion games. Formally:
Definition 6 (Price of Misinformation). Given a mis-
information congestion game, the Price of Misinfor-
mation (PoM) is defined as
PoM =
max
f
NME
∈NME
SC( f
NME
)
SC( f
opt
)
, (1)
where f
opt
is the flow that minimizes the Social Cost
in the actual game Γ
0
and the nominator is the worst
(maximum) value of the Social Cost of the set NME
as computed with regards to the actual game.
We can show the following:
Proposition 1. For every misinformation non-atomic
congestion game, we have that:
1 ≤ PoM ≤ (r · max
p∈P
C
p
(r)) /opt (2)
Proof. In the worst case, all flow is routed through the
most costly routes, which leads to a Social Cost of r ·
max
p∈P
C
p
(r). Thus, PoM ≤ (r · max
p∈P
C
p
(r)) /opt.
Also, PoM ≥ 1 by definition.
Note that when Γ
0
= Γ
j
∀ j, then PoM coincides
with the Price of Anarchy (PoA). Using the definition
of PoA and (1), we can link these formulas as follows:
PoM = PoA ·
max
f
NME
∈NME
SC( f
NME
)
max
f
NE
∈NE
SC( f
NE
)
, (3)
where NE is the set of all Nash equilibria of Γ
0
.
Interesting results can be derived by comparing
the worst Nash equilibrium of Γ
0
(or PoA of Γ
0
) with
the worst natural misinformed equilibrium of mΓ (or
PoM of mΓ). If PoM < PoA, then misinformation has
a beneficial effect on the social outcome, as players
are inclined (due to their misinformation) to choose
socially better strategies. Otherwise (PoM > PoA),
misinformation leads to a worse outcome from the
perspective of social welfare. Next, we provide an
illustrative example of the above concepts.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
240

Example 1. We consider the non-atomic congestion
game as depicted in Figure 2a (known as Pigou net-
work (Pigou, 1933)), with latency functions l
1
(x) =
εx + 1, l
2
(x) = x + ε, r = 1 and x ∈ [0,1]. It is clear
that selfish players in a pure Nash equilibrium will all
choose route r
2
, resulting to a Social Cost equal to
1 + ε ≈ 1, for arbitrarily small ε > 0. On the other
hand, the social optimum is achieved by allocating
the flow as follows: ≈
1
/2 through route r
1
and ≈
1
/2
through route r
2
; so, SC( f
opt
) ≈
3
/4, and PoA ≈
4
/3.
Now, consider the actual game Γ
0
as depicted
in Figure 2a and the game Γ
1
as depicted in Fig-
ure 2b. Also, assume the misinformation game mΓ =
hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,Γ
2
i with θ splitting, where Γ
0
= hG,l,s,t,ri,
Γ
1
= hG,l
1
,s,t, r
1
i, Γ
2
= hG,l
2
,s,t, r
2
i, and θ =
hθ
1
,θ
2
i. Further, θ
1
=
2
/3 of the players have the
view Γ
1
, and the rest the view Γ
2
. In this example,
l
2
= l
0
= l, l
1
1
(x) = εx + 1, and l
1
2
(x) = x + 1. The
equilibrium for Γ
1
, Γ
2
is to choose the route r
1
, r
2
re-
spectively, leading to SC
NME
( f
NME
) ≈
7
/9 in the mΓ;
so PoM ≈
28
/27 < PoA. Thus, the social outcome is
improved, despite selfishness and misinformation.
A metric similar to PoM was introduced in (Meir
and Parkes, 2015b), called the Biased Price of Anar-
chy, which measures the ratio of the equilibrium un-
der biases in knowledge compared to the optimal out-
come. In this concept, all players play a game with
modified costs and, thus, (possibly) different than the
actual costs. In our concept, all players play a game
according to the misinformation that they assume that
is the same for anyone resulting to different outcomes,
so in general the two concepts PoM and Biased Price
of Anarchy are not equal. The following example clar-
ifies the differences between the two studies:
Example 2. Consider now the game as provided in
Figure 2a, where
1
/2 of the players knows the latency
functions: l
1
(x) = x and l
2
(x) =
1
/4, whereas the rest
knows l
1
(x) = x+1 and l
2
(x) = 1, for routes r
1
and r
2
respectively. The equilibrium point provided by (Meir
and Parkes, 2015a) is that the flow is splitted into two
equal halfs, each routed through different edge.
On the other hand, the misinformation non-
atomic game that is produced takes the form mΓ =
hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,Γ
2
i with θ splitting, θ = h
1
/2,
1
/2i. The flow
in Γ
1
has Nash equilibrium such that
1
/4 is routed
through r
1
, while
3
/4 is routed through r
2
. Similarly,
in Γ
2
, the Nash equilibrium is such that all the flow
is routed through r
2
. Therefore, the resulting natural
misinformed equilibrium is
1
/8 routed through r
1
, and
7
/8 routed through r
2
.
5 THE WATERFILLING
ALGORITHM
Here, we provide an algorithm that computes a pure
Nash equilibrium in a single-commodity non-atomic
congestion game with n parallel links, and affine la-
tency functions, inspired by the waterfilling theorem
of Information theory (Cover and Thomas, 2006; Fa-
soulakis et al., 2019). To our best knowledge, there is
not a similar approach in the literature.
One of the fundamental problems in wireless com-
munications is how to allocate a budget of power
in a constant number of different quality (different
noise levels) and independent wireless communica-
tion channels in order to maximize the sum of the
transmission rate. The optimal solution of this prob-
lem is given by the waterfilling theorem. Namely,
the algorithm fills with water (power) the channels
in a way that minimizes the maximum level of wa-
ter, where the level of water is the maximum value of
power plus noise in the channels that are used. By the
end of the algorithm, the noise plus the water in the
channels that are used is the same (see Figure 3)
Interestingly, this idea can be used to find a Nash
equilibrium flow allocation in a single-commodity
non-atomic congestion game with n parallel links and
affine latency functions.
Algorithm 1: Waterfilling approach algorithm for comput-
ing a pure Nash equilibrium in single-commodity non-
atomic congestion games with n parallel links and affine
latency functions.
Input: n parallel links with affine latency
functions a
k
x
k
+ b
k
, with a
k
,b
k
> 0,
∀ k ∈ {1,2,...,n}.
Output: A pure Nash equilibrium allocation.
Sort links in an increasing order based on b
k
.
for 1 ≤ i ≤ n do
Solve the Linear program (Algorithm 2), for
t = b
i+1
and j = i. If it returns a feasible
solution x
∗
, then STOP and return x
∗
.
By the definition of Nash equilibrium, we know
that there is at least one Nash equilibrium in which all
links that are used have the same latency, v = a
i
x
i
+b
i
,
and any link k that is not used has a latency no less
than v, or in other words a
k
· 0 + b
k
≥ v. However,
we do not know a priori the value of v, but we do
know that the possible values are between the inter-
vals of [b
1
,b
2
],(b
2
,b
3
],...,(b
n−1
,b
n
],(b
n
,+∞), since
b
i
s are sorted in an increasing order. Note that if
the optimal threshold is in interval [b
k−1
,b
k
], then in
the Nash equilibrium allocation we will have exactly
k −1 links. We exhaustively search the optimal values
Coordination Mechanisms with Misinformation
241
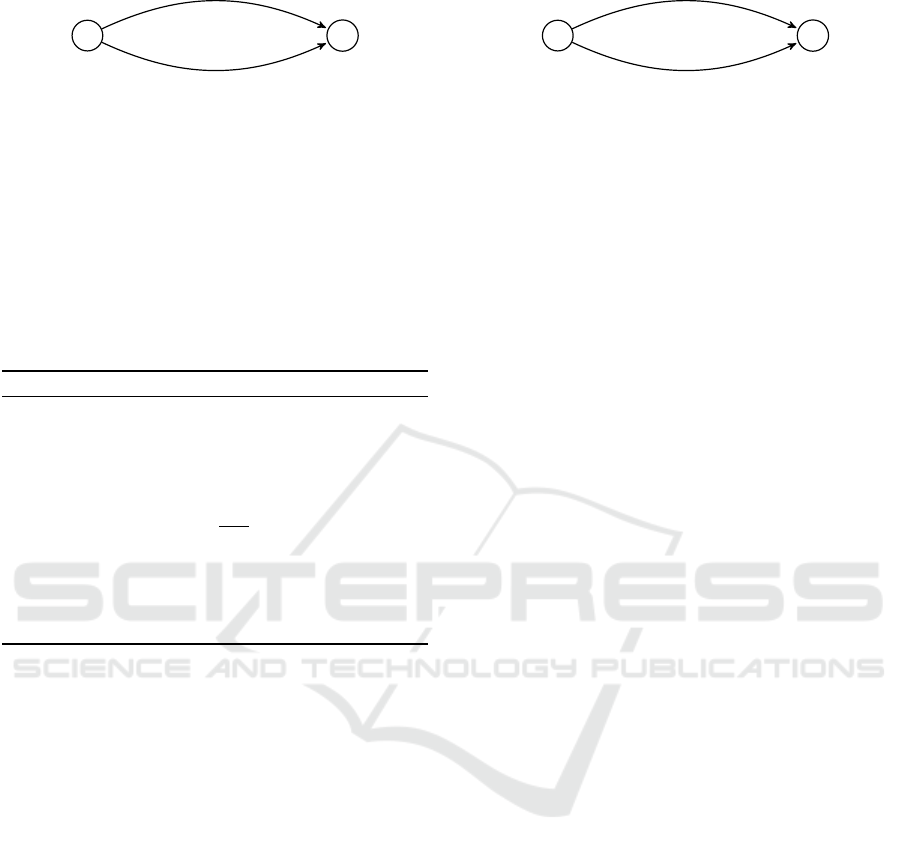
s
t
l
1
(x)
r
1
l
2
(x)
r
2
(a) Players without misinformation.
s
t
r
1
l
1
1
(x)
r
2
l
1
2
(x)
(b) Misinformed players.
Figure 2: Non-atomic congestion game with 2 parallel links.
in an increasing order for any possible interval, see
Algorithm 1. For any interval we solve a linear pro-
gram to check if there is an allocation with the Nash
equilibrium properties, if there is such an allocation
we return it. Since, we know the existence of such
an equilibrium, our algorithm always returns a feasi-
ble solution at the end. It is easy to see that the total
computational time of the algorithm is polynomial.
Algorithm 2: Linear program.
Input: A positive threshold t and an index j.
Output: x.
minimize v
s.t. x
i
=
v−b
i
a
i
, for i ≤ j.
∑
i∈[n]
x
i
= r.
x
i
≥ 0,v ≥ 0 and v ≤ t.
6 COORDINATION
MECHANISMS WITH
MISINFORMATION
Now we focus on single-commodity misinformation
non-atomic congestion games, where the actual game
has n parallel links and affine latency functions. We
restate the main question of the paper, that is how we
can use misinformation to improve the performance
of single-commodity non-atomic congestion games
with n parallel links in terms of Social Cost.
Specifically, note that if we properly change the
coefficients of the latency functions of the misin-
formed games then the flow according to the worst
natural misinformed equilibrium will change. To that
direction we choose to increase the coefficients of the
latency function from a
k
,b
k
to ˆa
j
k
,
ˆ
b
j
k
(one for each dif-
ferent subjective view Γ
j
respectively). Further, we
assume that the designer has the constraint that he can
provide a limited number of misinformed views.
We will show that it is always possible to find
a unique natural misinformed equilibrium that co-
incides with the optimal allocation, in terms of so-
cial welfare, by appropriately changing the coeffi-
cients. The constructed misinformation game mΓ =
hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,...,Γ
N
i, with θ splitting, described in the next
Subsection, has the following properties:
i) Γ
0
= Γ (the case of n parallel links),
ii) Γ
0
= hG, l,s,t,1i, Γ
j
= hG, l
j
,s,t, 1i, where
l
k
(x
k
) = a
k
x
k
+ b
k
, l
j
k
(x
k
) = ˆa
j
k
x
k
+
ˆ
b
j
k
.
iii) θ = hθ
1
,...,θ
N
i.
Next, we provide a methodology to construct a
misinformation game so that the unique natural mis-
informed equilibrium in the misinformation game is
an optimal allocation of the actual game. Forthwith,
we give an algorithm that takes as input a single-
commodity non-atomic congestion game Γ
0
, the op-
timal allocation in Γ
0
, and an arbitrary break down
(partition) of the links that are used in the optimal
flow. Let x
∗
= (x
∗
1
,x
∗
2
,...,x
∗
n
) be the optimal solution,
which we can easily find in polynomial time as a min-
imization of a convex function, and an abstract parti-
tion (k
1
,...,k
m
) of the allocation x
∗
over the parallel
links that are used; m is the number of misinformed
views that the designer provides to the players. E.g.,
if n = 3 with x
∗
i
> 0 ∀ i, then k
1
= {1,2}, k
3
= {3} is
a possible partition. With Algorithm 3 we construct a
misinformation game mΓ, where players perform op-
timally in terms of Social Cost.
To produce mΓ in Algorithm 3, we call Algo-
rithm 4 to compute the coefficients for the latency
functions for each Γ
i
separately. Afterwards, mΓ is
entailed easily.
At the beginning of Algorithm 4, we initialize v
by setting it equal to the maximum of the costs of the
latency functions over the links that are used in the
allocation y
∗
. Then, we increase the b
i
for the unused
links in y
∗
in order to make them no less than the cost
v. For any link i that is used in the allocation y
∗
we
can increase the b
i
in such a way that the cost of this
link with the allocation y
∗
i
is equal to the cost v. This
procedure can be done in polynomial-time by solving
a system of linear inequalities. For any y
∗
it is easy to
see that Algorithm 1 gives a unique pure Nash equi-
librium in the modified game for the players that have
this view. Taking the natural misinformed equilibrium
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
242

Transmitter
Noise
Figure 3: Two possible cases of waterfilling with different budget of power.
Algorithm 3: Coordination mechanism algorithm for
an abstract partition (k
1
,... ,k
m
) of n.
Input : An actual game Γ
0
= hG,l
j
,s,t, 1i
An optimal allocation x
∗
= (x
∗
1
,...,x
∗
n
)
A partition over the links, (k
1
,...,k
m
).
Output: A misinformation game mΓ.
A splitting θ.
while 1 ≤ i ≤ m do
New allocation y
∗
:
y
∗
j
=
(
x
∗
j
∑
t∈{k
i
}
x
∗
t
, j ∈ k
i
0, elsewhere
Apply Algorithm 4 for y
∗
to
construct the latency functions of Γ
i
.
θ
i
=
∑
j∈{k
i
}
x
∗
j
.
mΓ ← hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,...,Γ
m
i.
θ ← hθ
1
,...,θ
m
i.
Algorithm 4: Coordination mechanism algorithm.
Input : Coefficients a
i
,b
i
of latency functions
for any link i. The allocation y
∗
.
Output: New coefficients of latency
functions.
Put v = max
i:y
∗
i
>0
{a
i
y
∗
i
+ b
i
}.
Find
ˆ
b
i
, ∀ i,
s.t.
ˆ
b
i
≥ v, ∀ i such that y
∗
i
= 0,
a
i
y
∗
i
= v −
ˆ
b
i
, ∀ i such that y
∗
i
> 0,
ˆ
b
i
≥ b
i
, ∀ i.
return
ˆ
b.
we construct the allocation x
∗
, which is the optimal
allocation of the actual game, hence PoM = 1.
A similar mechanism can be used when the de-
signer can influence only some of the players, i.e.,
when she can construct a mechanism where the θ
1
portion gets misinformed, whereas the rest use the ac-
tual game. In this scenario, the resulting misinforma-
tion game would be of the form mΓ = hΓ
0
,Γ
1
,Γ
2
i,
where Γ
2
= Γ
0
, for the splitting θ = hθ
1
,θ
2
i.
To do so, we reconsider the optimal allocation for
the θ
1
fragment of the flow, taking into account the
fact that there is a fixed part of the players θ
2
who
will route according to Γ
2
, which has the same la-
tency functions as Γ
0
. We reconsider the coefficients
of the latency functions as they experience the addi-
tional cost of the Nash equilibrium flow of the unmis-
informed fragment θ
2
. Afterwards, we implement our
mechanism and get the desired mΓ. Note that, as we
can affect only some of the players, the rest would
route (maybe sub-optimally) according to the actual
specifications, so it may happen that PoM > 1.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we explored the use of misinforma-
tion as a novel method for coordination mechanisms.
We applied this idea in single-commodity non-atomic
congestion games with parallel links and affine la-
tency functions. Our goal was to steer players’ be-
haviour towards the socially optimum allocation, by
misinforming them with regards to the latency func-
tions of the network. Towards this, we provided two
polynomial-time algorithms. The first finds a Nash
equilibrium flow allocation in a single-commodity
non-atomic congestion game with n parallel links and
affine cost functions. The second takes as input an ab-
stract partition over the links that are used in the op-
timal allocation, and creates a misinformation game
whose subjective games follow the required specifi-
cation, and, thus, its natural misinformed equilibrium
is the optimum allocation in the actual game. Further,
we redefine misinformation games (originally pro-
posed for normal-form games (Varsos et al., 2021))
for non-atomic congestion games and recast all rele-
vant game-theoretic concepts for the new setting.
A future step is to design a mechanism for serial-
parallel networks and general latency functions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The second author was supported by the Stavros
Niarchos-FORTH postdoc fellowship for the project
ARCHERS.
Coordination Mechanisms with Misinformation
243

REFERENCES
Bakker, C., Bhattacharya, A., Chatterjee, S., and Vra-
bie, D. L. (2021). Metagames and hypergames for
deception-robust control. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys.
Syst., 5(3).
Bennett, P. G. (1980). Hypergames: Developing a model of
conflict. Futures, 12(6):489–507.
Caragiannis, I., Kaklamanis, C., and Kanellopoulos, P.
(2010). Taxes for linear atomic congestion games.
ACM Transactions on Algorithms, 7(1):13:1–13:31.
Christodoulou, G., Koutsoupias, E., and Nanavati, A.
(2009). Coordination mechanisms. Theoretical Com-
puter Science, 410(36):3327–3336.
Christodoulou, G., Mehlhorn, K., and Pyrga, E. (2014). Im-
proving the price of anarchy for selfish routing via
coordination mechanisms. Algorithmica, 69(3):619–
640.
Cole, R., Dodis, Y., and Roughgarden, T. (2003). Pric-
ing network edges for heterogeneous selfish users. In
STOC’03, pages 521–530.
Copic, J. and Galeotti, A. (2006). Awareness as an equilib-
rium notion: Normal-form games.
Cover, T. M. and Thomas, J. A. (2006). Elements of Infor-
mation Theory. John Wiley and Sons.
Esponda, I. and Pouzo, D. (2016). Berk–Nash equilibrium:
A framework for modeling agents with misspecified
models. Econometrica, 84(3):1093–1130.
Fasoulakis, M., Traganitis, A., and Ephremides, A. (2019).
Jamming in multiple independent Gaussian channels
as a game. In GameNets’19, volume 277, pages 3–8.
Feinberg, Y. (2020). Games with unawareness. The B.E.
Journal of Theoretical Economics.
Fleischer, L., Jain, K., and Mahdian, M. (2004). Tolls
for heterogeneous selfish users in multicommodity
networks and generalized congestion games. In
FOCS’04, pages 277–285.
Fotakis, D. and Spirakis, P. G. (2008). Cost-balancing tolls
for atomic network congestion games. Internet Math-
ematics, 5(4):343–363.
Halpern, J. Y. and R
ˆ
ego, L. C. (2014). Extensive games with
possibly unaware players. Math. Soc. Sci., 70:42–58.
Harsanyi, J. C. (1967). Games with incomplete information
played by “Bayesian” players, I–III Part I. The basic
model. Management Science, 14(3):159–182.
Koutsoupias, E. and Papadimitriou, C. (1999). Worst-case
equilibria. In STACS 99, pages 404–413.
Lavi, R. and Swamy, C. (2007). Truthful mechanism design
for multi-dimensional scheduling via cycle mono-
tonicity. In EC’07, pages 252–261.
Luce, R. D. and Raiffa, H. (1957). Games and Decisions:
Introduction and Critical Survey. John Wiley and
Sons, New York.
Meir, R. and Parkes, D. C. (2015a). Congestion games with
distance-based strict uncertainty. In AAAI’15, pages
986–992.
Meir, R. and Parkes, D. C. (2015b). Playing the wrong
game: Smoothness bounds for congestion games with
behavioral biases. SIGMETRICS’15, 43(3):67–70.
Meir, R. and Parkes, D. C. (2018). Playing the wrong
game: Bounding externalities in diverse populations
of agents. In AAMAS’17, pages 86–94.
Monderer, D. and Tennenholtz, M. (2003). k-
implementation. In EC’03, pages 19–28.
Myerson, R. B. (2004). Comments on ”games with incom-
plete information played by ’bayesian’ players, i-iii”:
Harsanyi’s games with incomplete information. Man-
agement Science, 50(12):1818–1824.
Nash, J. F. (1951). Non-cooperative games. The Annals of
Mathematics, 54(2):286–295.
Nisan, N., Roughgarden, T., Tardos, E., and Vazirani, V. V.
(2007). Algorithmic Game Theory. Cambridge Uni-
versity Press.
Ozbay, E. Y. (2007). Unawareness and strategic announce-
ments in games with uncertainty. In TARK’07, page
231–238.
Pigou, A. C. (1933). The Economics of Welfare. The Eco-
nomic Journal, 43(170):329–330.
Rosenthal, R. (1973). The network equilibrium problem in
integers. Networks, 3:53–59.
Sasaki, Y. and Kijima, K. (2012). Hypergames and bayesian
games: A theoretical comparison of the models of
games with incomplete information. Journal of Sys-
tems Science and Complexity, 25(4):720–735.
Schipper, B. C. (2017). Self-confirming games: Unaware-
ness, discovery, and equilibrium. In TARK’17.
Schmeidler, D. (1973). Equilibrium points of nonatomic
games. Journal of Statistical Physics, 7(4):295–300.
Seregina, T., Brun, O., Azouzi, R. E., and Prabhu, B. J.
(2017). On the design of a reward-based incentive
mechanism for delay tolerant networks. IEEE Trans-
actions on Mobile Computing, 16(2):453–465.
Sz
´
ekely, G. J. and Rizzo, M. L. (2007). The uncertainty
principle of game theory. The American Mathematical
Monthly, 114(8):688–702.
Turrini, P. (2013). Endogenous games with goals:
side-payments among goal-directed artificial agents.
CoRR, abs/1311.3088.
Varsos, C., Flouris, G., Bitsaki, M., and Fasoulakis, M.
(2021). A study of misinformation games. In PRI-
CAI’21, pages 76–87.
Wardrop, J. G. (1952). Some theoretical aspects of road
traffic research. In Proceedings of the Institute of Civil
Engineers, Part II, 1, pages 325–378.
Zamir, S. (2009). Bayesian Games: Games with Incomplete
Information, pages 426–441.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
244
