
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using
Feedback-based Price Discrimination
∗
Alexandre Martins
1
, Hung-Yu Wei
2
and Karl-Erik
˚
Arz
´
en
3
1
Axis Communications and Department of Automatic Control, Lund University, Sweden
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taiwan
3
Department of Automatic Control, Lund University, Sweden
Keywords:
Camera Systems, Automatic Control, Resource Allocation, Price Discrimination, Video Sensors.
Abstract:
Camera sensor networks, mainly with surveillance cameras, are growing in size and complexity. Storage
space is the prime resource in such systems but current surveillance setups are still very much centralized and
limited in resources due to cost and security constraints. Allocating the correct amount of storage to each
camera sensor considering their large difference in characteristics and video content is challenging. In this
paper we propose a framework using feedback-based price discrimination of storage resources in order to
guarantee a uniform quality level of the videos in camera sensor networks, regardless of the specific camera
sensor parameters. We designed a lightweight solution using simple video quality metrics, cascade control
and PI (Proportional and Integral) controllers to define the optimal price of resources per camera.
1 INTRODUCTION
The number and size of camera sensor systems used,
e.g., in different types of public spaces with surveil-
lance cameras, are growing due to the Internet of
Things (IoT) trend and they are currently one of the
major storage and bandwidth consumers. With grow-
ing demands on high resolution, high frame rate and
level of detail, the amount of storage needed to re-
tain these videos is a growing problem. Surveillance
installations are usually critical installations and are
mostly running on dedicated infrastructures, storing
video in trusted servers owned by systems administra-
tors. Newer installations are usually large scale (com-
monly hundreds of cameras), heterogeneous and have
large differences in resource requirement. (IPVM,
2021).
In this paper we propose a lightweight solution
using the price discrimination principle from micro-
economics, (Armstrong, 2008), to allocate storage re-
sources while separating the resource providers (i.e.,
the storage units) from the resource buyers (i.e., the
camera sensors). The buyers have private information
on the amount of resources needed and act accord-
ingly to maximize their utility (here the desire to mini-
∗
This work has been partially funded by the Wallenberg
AI, Autonomous Systems and Software Program (WASP),
the ELLIIT strategic research area on IT and mobile com-
munications, and the Nordforsk university hub on Industrial
IoT (HI2OT).
mize the compression of their own video stream). The
utility represents the goal the buyers want to achieve.
The storage units enforce the constraint on resource
availability through the use of pricing.
The focus in this paper is H.264 video cam-
eras, the dominating system on the market today.
H.264 is a video compression standard based on
block-oriented, motion-compensated coding (ITU-T,
2010). A model of the bandwidth needed/generated
by a H.264 surveillance camera was presented in our
earlier work (Edpalm et al., 2018a; Edpalm et al.,
2018b). This model provides an estimate of the band-
width needs for a H.264 video given current scene
conditions and specific sensor parameters and allows
to calculate the long term resource needs for the cam-
era as long as it maintains the current parameters.
For a video surveillance system operator, the most
important metric is the video quality. As such they
want to have the best possible system-wide video
quality given the current (mostly cost) constraints
without knowledge of the prior or current character-
istics of each camera sensor. The video compression
level of H.264 videos, qp, determines the quality of
each frame. The lower the qp value, the less com-
pression is applied to the frame, the better the qual-
ity but the higher the frame size. The qp value and
its variation over time have a direct impact on the
perceived video quality (using mean opinion score
testing) according to (Xue et al., 2010; Xue et al.,
2013; Lin et al., 2012), i.e., the lower and less vary-
34
Martins, A., Wei, H. and Årzén, K.
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination.
DOI: 10.5220/0010858500003118
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS 2022), pages 34-44
ISBN: 978-989-758-551-7; ISSN: 2184-4380
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ing the compression parameter qp is, the better the
perceived quality will be. Our aim is thus to have all
video cameras in the system to deliver videos with
the same compression parameter values without hav-
ing specific information about them.
The contributions of the paper are:
• A new flexible framework for facilitating resource
allocation in medium- and large-size camera sen-
sor networks.
• The use of cascade control to decide the price of
resource per camera (price discrimination) so that
the storage usage is maximized.
• A proposed utility measure for camera sensor net-
works based on the compression value (qp) and
its deviation from a nominal value.
2 RELATED WORK
Price discrimination is a known profit optimization
method in economics, (Armstrong, 2008), but it has
been mostly used for revenue maximization. A study
of different pricing schemes for maximizing rev-
enue from selling cloud resources can be found in
(Xu and Li, 2013). (Li et al., 2009) studied the
maximum revenue achievable by a monopolistic ser-
vice provider under complete network information.
Revenue maximization using price discrimination for
communication network service providers was stud-
ied in (Shakkottai et al., 2008). Price discrimination
was used in order to distribute energy between sen-
sors in (Edalat et al., 2009). In (Tsakalozos et al.,
2011) the same technique was used to optimally allo-
cate virtual machines in a cloud service infrastructure.
But, to the best of the authors knowledge, however,
no prior work has used price discrimination in cam-
era sensor networks for visual quality maximization.
Some centralized bandwidth allocation techniques
optimizing the system’s compression level have been
proposed in (Seetanadi et al., 2018) and (Silvestre-
Blanes et al., 2011). Centralized task allocation for
collaborative radar sensors based on resource avail-
ability and Quality of Service are proposed in (Yan
et al., 2021) and (Giannecchini et al., 2004). An al-
ternative but related distributed approach to assign re-
sources are auctions, thus second price auctions have
been applied to video surveillance systems to opti-
mize specific applications such as area overage (Ding
et al., 2012; Konda et al., 2016; Dieber et al., 2011),
sensor placement (Elhamifar and Vidal, 2009; Ermis
et al., 2010) and object tracking (Qureshi and Ter-
zopoulos, ; Sankaranarayanan et al., ). Auction theory
has also been used to minimize content delivery delay
and caching cost for large mobile networks involving
multiple stakeholders as reported in (Li et al., 2016)
or (Ghosh et al., 2004) or to allocate tasks between
radar sensors as in (Ostwald et al., 2005).
3 ARCHITECTURE, VALUATION
& FRAMEWORK
We consider a simplified camera sensor network with
one storage unit (Network Attached Storage, Cloud
storage or other) and I IP video cameras, each having
a camera sensor, indexed with i: {C
1
, C
2
, ...C
I
}. An
overview of the system with I = 4 is shown in Fig-
ure 1. Typically a video surveillance camera system
is owned by a security department, which buys/rents
storage from an IT department or cloud provider
at a fixed rate. In our system, viewing quality is
most important. The main system goal is to maxi-
mize the overall global video quality given the cur-
rent system constraints: running cost and video stor-
age size. The shared information between the de-
vices and the system load should be as low as pos-
sible. We therefore use the video compression fac-
tor as a computation-free and simple way to mea-
sure the video quality. The direct correlation between
the perceived video quality and the compression fac-
tor and its oscillation over time was studied in (Xue
et al., 2013) and (Xue et al., 2010). In H.264 videos,
the compression factor is defined by the quantization
parameter, qp ∈ {0, 1, . . . , 51} with 0 being lossless
and 51 being the highest compression level (ITU-T,
2010). The quantization controlled by the qp value
is the only non-reversible step in the H.264 com-
pression/decompression process impacting the visual
quality.
Every predefined period k, e.g., an hour, a day, or a
week, the cameras need to buy storage from the seller
to save the video they generate, using the money at
their disposal. If the cameras run out of storage they
need to wait until the next period to buy more. At
the beginning of each period, k, the cameras obtain an
amount of money, m, that they can use at their discre-
tion to buy resources. The amount they receive de-
pends on the cost of running the system. Each camera
sensor has a virtual account holding the money it may
use. Any remaining money can be saved for future
periods. The amount of money available for camera
C
i
to buy storage at the beginning of each period k is:
m
i
(k) = m
i
(k − 1) + m. We do not enforce a limit to
the amount of money a camera can retain if unused.
How the money is distributed and enforced is not in-
vestigated in this paper.
It is assumed that all camera sensors in the net-
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination
35
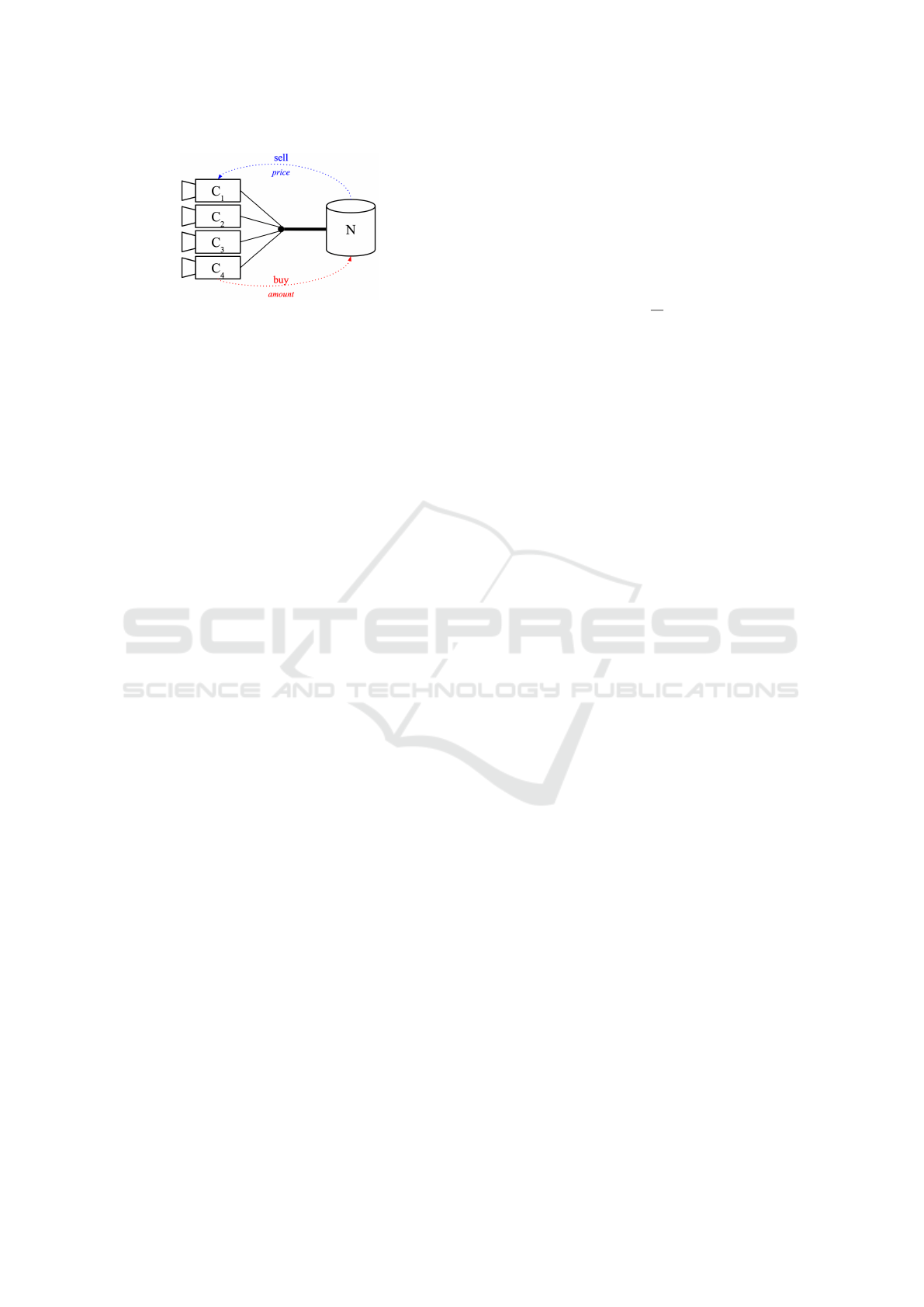
Figure 1: System with four cameras and one storage unit.
work can communicate with the seller and they could,
e.g., be part of the same virtual network. The total
quantity of storage available by the storage provider
is s and the storage space allocated to camera C
i
is
s
i
. The corresponding expected quantities are anno-
tated with a
∗
superscript, e.g. the expected allocated
storage s
i
to camera C
i
is denoted s
∗
i
. Only the stor-
age unit has storage space, i.e., the cameras are not
storage providers.
3.1 Price and Valuation of Resources
3.1.1 Storage Providers
The running price of each storage unit (Tbyte, Gbyte,
etc.) is determined by the storage provider. The
most common approach is to use marginal pricing,
i.e., the price is defined as the running cost plus a rev-
enue margin. The storage provider will then charge
p
0
= p
min
0
+ ε where p
min
0
is the running cost and ε
the revenue margin. If p
0
≤ p
min
0
the storage provider
would sell at a loss. We can calculate p
min
0
from the
physical cost of hard disks, e.g., a 8Tb hard disc costs
around 400$, thus p
min
0
= 0.05 $ per Gb of storage.
By adding a 20% margin, we would have p
0
= 0, 06$.
In our approach, the seller will instead set different
(or discriminate) prices per buyer based on the quality
of the video stored by the buyer. We define the dis-
criminate price of camera i at time k as p
i
(k) ≥ p
min
0
We denote with R(k) the revenue of the seller at
time k:
R(k) =
I
∑
i=1
s
i
(k) · p
i
(k) (1)
where p
i
(k) is the price set by the seller and s
i
(k) is
the amount of storage bought by camera i at time k.
The seller wants to maximize the camera’s video
quality given the current system constraints and to ad-
just the price to reflect the storage limitations without
sacrificing the revenue.
The compression level, i.e., qp, of H.264 videos
is part of the headers of the received videos. Hence,
in each transaction period the storage provider has ac-
cess to the qp of the received videos.
The discriminate prices are set with the help of PI
controllers (one per camera) which compute the off-
set ∆ p
i
(k) to the running price p
0
, i.e., the discrim-
inate price is p
i
(k) = p
0
+ ∆ p
i
(k). Proportional and
Integral (PI) control is the most widely used control
scheme in industry (Wittenmark et al., 2003). The
equation for a continuous-time PI controller is given
by
u(t) = K
e(t) +
1
T
I
Z
t
e(s) ds
, (2)
where u(t) is the control signal, e(t) the error between
the desired value (or setpoint) of the measured signal
and the actual value of the measured signal, and K and
T
I
are constant parameters. The storage provider has
one controller per camera. It uses the current com-
pression level, qp, of the video as the measured sig-
nal. The setpoint is determined by a single outer-loop
probing controller which monitors the amount of stor-
age allocated. The goal of the probing controller is
to compute the desired compression level for all the
cameras so that the storage usage is maximized. Prob-
ing control is a simple version of extremum-seeking
control that is commonly used in process control, e.g.,
(Akesson and Hagander, 2000) and (Dochain et al.,
2011). The probing controller adjusts its output signal
gradually until it reaches a good enough value, prob-
ing a new value at regular intervals to check if the new
optimal value has changed.
Here the output of the probing controller is the de-
sired system compression level which is used as the
setpoint of the inner-loop PI controllers. The output
of the PI controllers, i.e., the control signal, is the dis-
criminate price offset ∆ p
i
(k). In order to maximize
the used storage the compression level should be as
small as possible. Hence, the probing controller will
decrease the desired compression level until the re-
quested storage is at or above the maximum storage
available. Then it will increase the desired compres-
sion level until the requested storage is within a safety
margin and then keep it constant. It is kept constant
until either (1) the requested storage is again at or
above the maximum storage available, in which case
it will start to increase the desired compression level
again, or (2) a time-out event occurs, in which case it
will again start to gradually decrease the desired com-
pression level.
The cascade architecture with n cameras is shown
in Figure 2 and the state machine of the probing con-
troller is shown in Figure 3. The sampling period of
the controllers is the transaction period and they are
executed at the beginning of each period.
The effect of the feedback-based price discrimi-
nation is that the compression levels, qp, of the cam-
eras will converge to the setpoint value of the PI con-
SENSORNETS 2022 - 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks
36
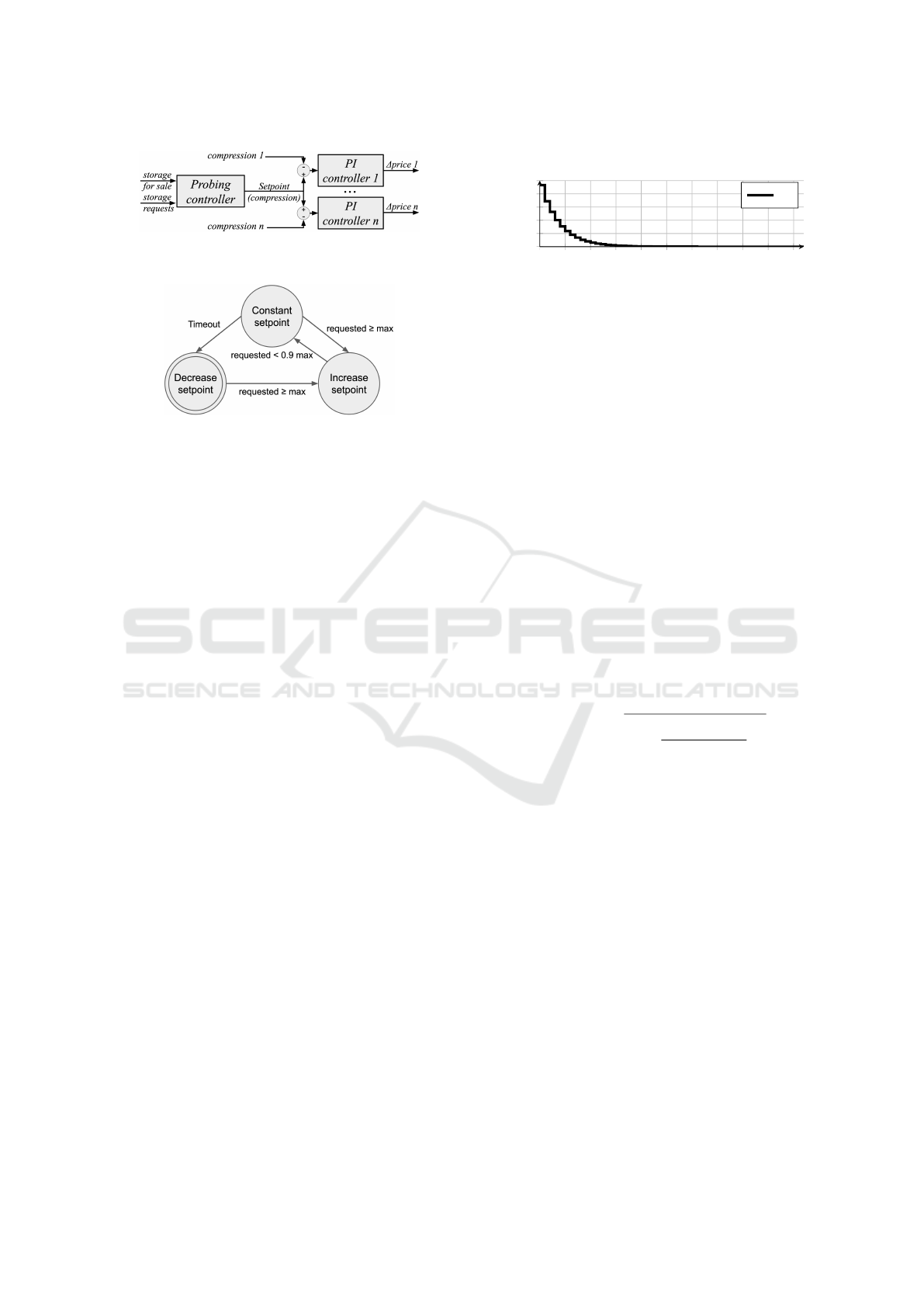
Figure 2: Cascade control structure, one probing controller
decides the setpoint of the price controllers.
Figure 3: Probing controller state machine. The double bor-
der indicates that this is the initial state. The margin avoids
rapid state changes close to the maximum storage amount.
The Timeout event occurs when the Constant setpoint state
has been active longer that a specified interval.
trollers, i.e., the value set by the outer probing con-
troller.
If the total amount of storage requested by the
cameras exceeds the total amount of available storage
for sale, the storage provide will provide each cam-
era C
i
with an amount of storage s
i
proportional to its
demand compared to that of the other cameras.
3.1.2 Cameras
In order to decide how much storage a camera C
i
wants to buy it needs to know how much storage it
needs to store a video of a certain quality. An esti-
mate of the storage needed for each qp is obtained us-
ing the frame size estimation model provided in (Ed-
palm et al., 2018b). This model is based on empiri-
cal values from multiple real surveillance videos. We
denote the estimated storage at the period k for cam-
era i, s
∗
i,k
(qp), it provides for each qp the expected
amount of storage necessary for a video with the cur-
rent parameters (e.g., motion in the scene, light level,
amount of nature) and settings of the specific camera
sensor (e.g., frame rate, group of picture length). An
example of s
∗
i,k
(qp) is shown in Figure 4. The higher
the qp is, the smaller the amount of storage needed
and the lower the visual quality of the video.
At the beginning of each transaction period k, each
camera C
i
calculates s
∗
i,k
(qp), i.e., an estimate of the
storage need for each qp ∈ {0, 1, . . . , 51} given the ac-
tual scene and camera sensor parameters which are
assumed to be measured or estimated by the cam-
era. The s
∗
i,k
(qp) functions differ from camera to cam-
era and over time because each camera sensor which
equips camera C
i
has different settings and overlooks
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45 50
0
20
40
60
80
100
QP (compression)
Gb
Expected storage for different qp values
s
∗
i
Figure 4: s
∗
i,k
example.
a different non-constant scene.
Camera C
i
uses the actual curve to decide how
much storage it should buy with its available money
m
i
(k), see Section 3.1.3. We do not impose any lim-
itation on the saved funds of cameras and unused
money could be saved indefinitely.
3.1.3 Camera Utility
The more storage the camera has, the lower qp it can
use to compress its video and therefore the better the
video quality (Xue et al., 2010) will be. Oscillations
between qp values have a large impact on the visual
quality of the video because of the visible jumps in
visual quality (Xue et al., 2013).
The valuation function θ
i
of buyer C
i
designed to
embody the system objective, i.e., to retain videos of
the highest possible quality in the system, where qual-
ity is measured by the video compression level, qp
i
,
and how much it varies. It is defined by the ellipse
equation
θ
i
(qp
i
, m
i
) = m
i
·
s
1 −
qp
i
+ σ
n
(qp
i
)
2 · 51
2
, (3)
where m
i
is the money available for the camera C
i
, qp
i
the compression value corresponding to the received
amount s
i
, and σ
n
(x) is the standard deviation of x
over the n last periods.
The equation of an ellipse has an interesting char-
acteristic around its vertexes. The derivative of the
ellipse is low when approaching the co-vertex (low
qp and low σ(qp)), while it is high when close to the
vertex (high qp and high σ(qp)). It is valued more
(high derivative) to move away from the high qp and
high σ(qp) values (vertex) than it is to get closer to
the low qp and low σ(qp) values (co-vertex).
The utility u
i
of buyer C
i
is then given by
u
i
(qp
i
, m
i
, p
i
) = θ
i
(qp
i
, m
i
) − p
i
(4)
where p
i
is the price paid to obtain the amount of stor-
age s
i
. The smaller the compression level and the vari-
ation of the compression level the higher the camera
utility will be. An example of the utility is shown in
Fig 5. We use the last 10 qp values from previous
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination
37
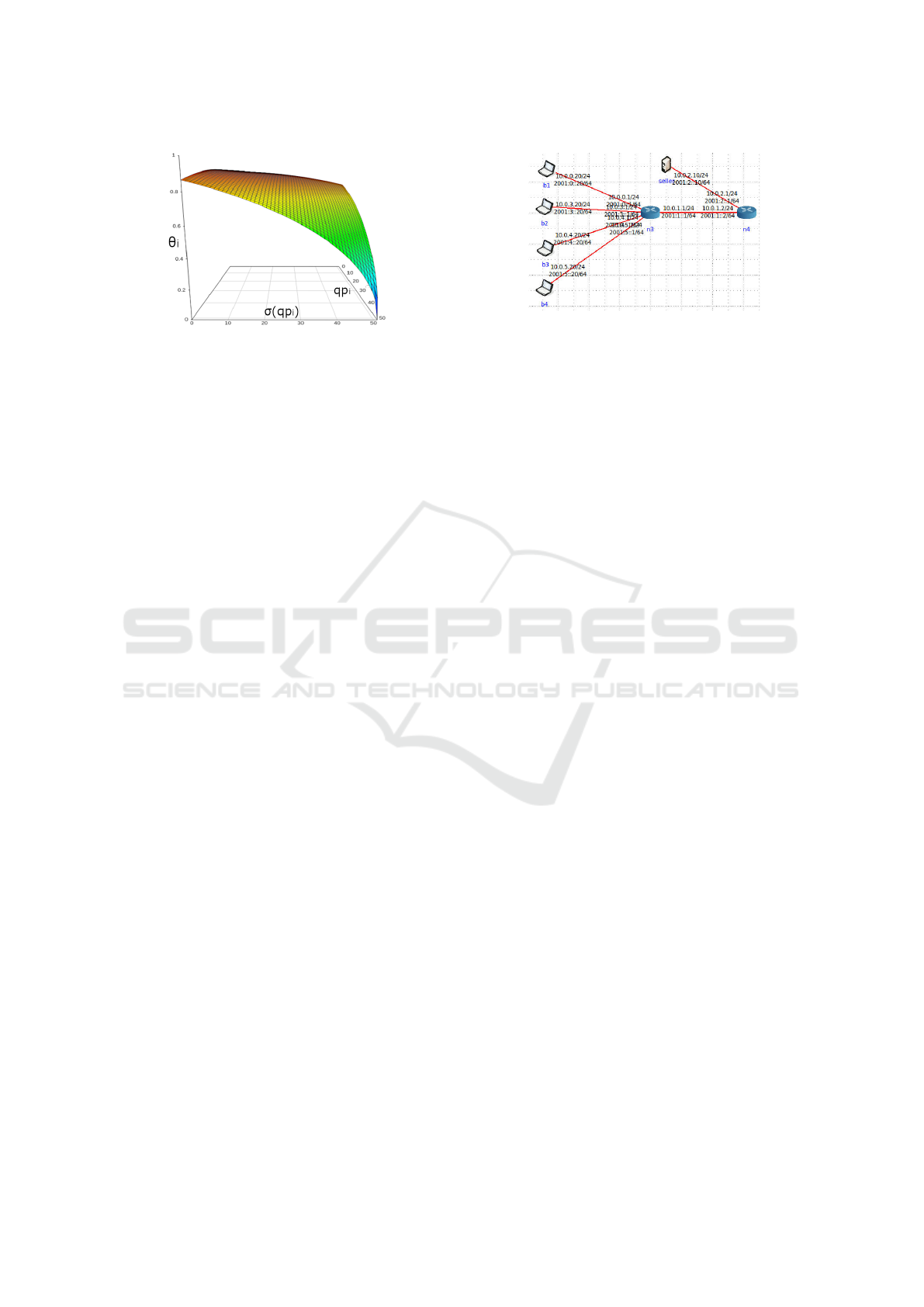
Figure 5: An illustration of how the valuation of resources,
θ
i
, depends on the compression and its variation.
transactions to calculate the standard deviation. The
longer this history, the longer a deviation in qp will
affect the utility.
At the beginning of each transaction period k, af-
ter calculating the expected storage amount of storage
s
∗
i,k
(qp) (see Section 3.1.2), the camera calculates the
expected utility u
∗
i
assuming that it gets the associ-
ated storage s
∗
i,k
given the available money m
i
(k) and
the announced unit price p
i
(k).
Different cameras can have different strategies for
buying storage. Here we consider two possible strate-
gies:
1. At each period k, the camera buys the amount of
storage s
∗
i,k
which maximizes the expected utility
u
∗
i
(k) given the money m
i
(k) available.
2. The camera keeps all the money until an event oc-
curs. When the event occurs it acts according to
Strategy 1 (above).
3.2 Transaction Steps
We use a transaction mechanism inspired by the
closed bid transaction mechanism used in auctions
(Reck, 1997). A transaction is defined by the step
described below. At the beginning of each transaction
period k:
1. Camera C
i
gets an amount of money, m, for the
new period k. The money available to the camera
is m
i
(k) = m
i
(k − 1) + m.
2. The storage provider, n, announces the total
amount of storage for sale, s(k), and the unit price
of camera C
i
: p
i
(k).
3. Camera C
i
decides how much it buys based on the
expected storage usage s
∗
i,k
(qp), p
i
(k) and m
i
(k).
It sends to n the amount from s
∗
i,k
(qp) maximizing
its expected utility u
∗
i
(k) (see Section 3.1.3).
4. Storage provider n decides the storage allocation
and sends to C
i
the amount of storage it is allowed
to buy, s
i
.
Figure 6: CORE network emulator setup.
5. Camera C
i
pays the storage provider n the price
s
i
· p
i
, deduces this amount from the money it has,
i.e., m
i
(k) = m
i
(k) − s
i
· p
i
, and starts streaming
video data up to the provided amount s
i
allocated.
6. Storage n extracts the compression level from the
received videos, qp
i
(k), and uses it to decide the
price for the next transaction p
i
(k + 1) using the
PI controllers. It also calculates the total amount
of storage allocated,
∑
i
s
i
(k), and uses it to adjust
the desired compression level using the probing
controller so that the storage usage is maximized,
see 3.1.1.
4 RESULTS
To validate the price discrimination approach we run
multiple simulations using a python framework with
independent players (seller and buyers) communicat-
ing via queues as well as simulations using the CORE
real time network emulator (Ahrenholz et al., 2008).
Each simulation uses random unit prices, p
0
, and ran-
dom camera parameters (resolution and motion level).
The storage needs of the cameras are determined us-
ing the model described in (Edpalm et al., 2018b).
The cameras will have a computation horizon of 10
periods to calculate their utility.
In the simulations we compare three different
cases:
1. The storage uses marginal pricing, i.e., it defines
the running cost and adds a margin to it (see Sec-
tion 3.1.1).
2. The storage uses the price discrimination scheme
described in Section 3 with a fixed system quality
setpoint, i.e., without any probing controller.
3. The storage uses the price discrimination scheme
described in Section 3 with the probing controller
selecting the system quality setpoint.
The camera utility is given by Equation (4). We
also define a seller utility U(k) to visualise how ef-
ficiently the proposed approach reduces the standard
SENSORNETS 2022 - 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks
38

deviation of the sum of the compression levels. It is
given by
U (k) =
1
σ
n
∑
I
i
qp
i
(k)
(5)
The simulations use four cameras in Fig 7 and Fig-
ure 9 and ten cameras in Figure 8. The storage price
p
0
is set randomly at simulation start. In the simula-
tions in Figure 7 and Figure 9, C
1
is a 4K camera and
as such requires the largest storage amount, C
2
and C
3
are 1080p cameras with different scene characteristics
(C
2
’s video is more noisy and has more motion) and
C
4
is a 720p camera. In Figure 8, camera parameters
are randomly selected at simulation start. During the
simulations the camera parameters are constant (reso-
lution and motion levels are fixed) but uniform noise
of amplitude up to 25% of the frame sizes was added
to reflect a real scenario where noise from the sensor
and small changes in the scene would create changing
frame sizes. All cameras receive the same amount of
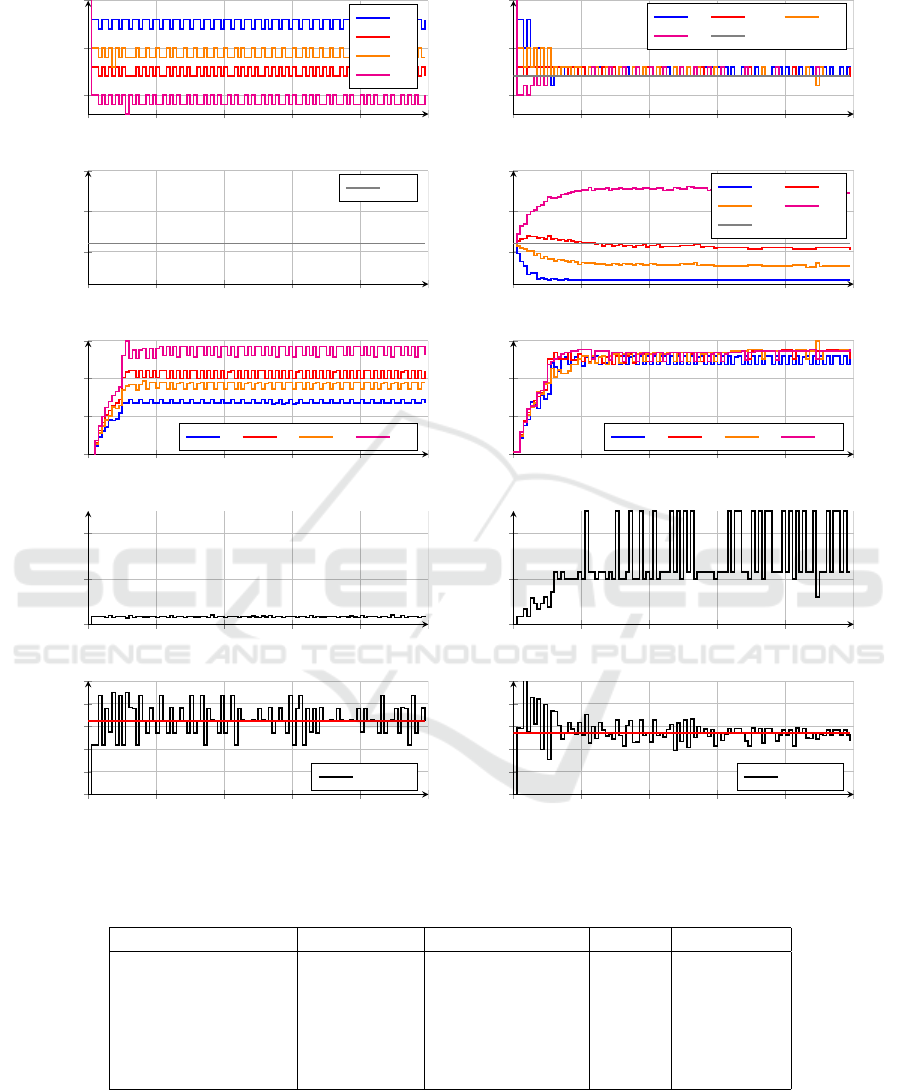
money m at each period k. Figure 7 shows the sim-
ulation results of case 1 and case 2. The left column
contains the results using marginal pricing scenario
(case 1) and the right column contain the results us-
ing price discrimination with PI control but without
probing controller, i.e., with a fixed setpoint (case 2).
The uppermost plots contain the qp values of the
cameras (remember that a higher qp means a lower
video quality), the ones below are the prices set by
the storage provider (gray for the base price, colored
for discriminate prices). The third row is the camera
utility and the final two rows show the seller utility
(defined in 1) and the revenue from selling storage to
the cameras (see 3.1.1). Note that in the utility plots
the maximum utility has been limited to 5 for easier
plotting and calculations (as the utility of an infinites-
imal standard deviation tends to infinity).
In the right column of Figure 7, we can see that the
PI controllers change the unit prices p
i
to allow the
video compression qp
i
to converge towards a com-
mon qp value (first row). The seller utility U (fourth
row) in the price discrimination case (case 2, right
column) is clearly higher than in the fixed price case
(case 1, left column) while the seller revenues R are
very close to each other (fifth row), i.e., the price dis-
crimination policy allows the total system to run in
a better state than using marginal price policy. Be-
cause of the seller utility definition, the utility value
will tend to infinity when the standard deviation of
the camera qp is zero, leading to the jumps we can
see in Figure 7.
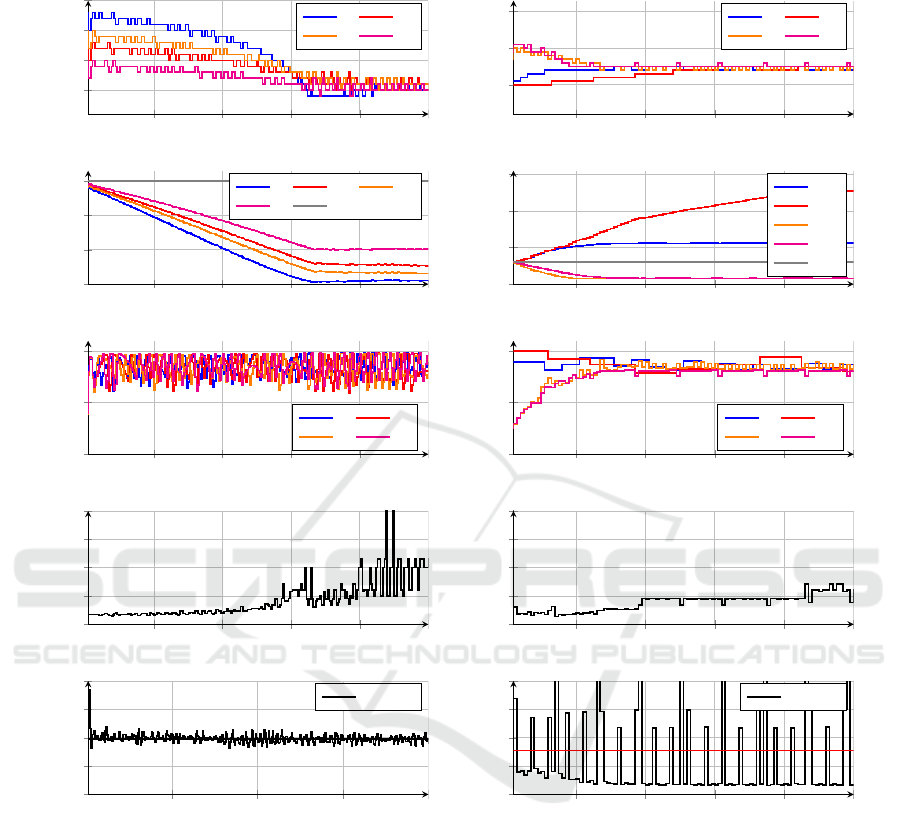
In the simulations in Figure 9 price discrimina-
tion with probing controller (case 3) is used in both
columns. The camera parameters (apart for the video
resolution) are selected randomly at simulation start.
The results in the left and right column are from two
different runs. In the left column, cameras are buy-
ing storage at each period k, the simulation being run
for 400 periods. In the right column the simulation
is done with 4 cameras over 100 periods, cameras C
3
and C
4
are buying at each time period but C
1
and C
2
only buy every 5 and 12 periods respectively. The
simulations were done using the same code and mod-
els as the python framework but the seller and buy-
ers were running in virtual machines communicat-
ing through sockets in the CORE real time network
emulator (Ahrenholz et al., 2008). A screenshot of
the used system can be seen in Figure 6. With the
CORE simulator we can simulate multiple machines
communicating over different network architectures
and simulate different network conditions. We used
the CORE simulator to ensure communication was
not sequential and reflected a real-world setup with-
out having to deploy such a setup. The focus of the
python framework is to simulate the system sequen-
tially with a focus on the global system behavior.
In the right part of Figure 9 the seller revenues os-
cillate because of the less frequent storage buy from
cameras C
1
and C
2
, but the average revenue is com-
parable and the different strategies does not prevent
the system from converging to a common compres-
sion level. In the left part of Figure 9, we can observe
the effect of the probing controller adjusting gradu-
ally the setpoint compression level down in order to
maximize the storage usage, leading to a stable sys-
tem value with qp = 20. We can also see that the
prices set follows the same trend in order to converge
to the system setpoint set by the probing controller but
also each discriminate prices diverge in order for the
compression of each camera to converge to a common
value thanks to the price discrimination PI controllers.
Figure 8 shows simulations with 10 cameras and
same selected parameters (randomly chosen once for
both simulations) and we visualize the most interest-
ing 250 periods. In this figure, the left side has only
the price discrimination PI controllers (case 2) run-
ning with a manually fixed global quality setpoint of
qp = 25 (which is the optimal setpoint for this spe-
cific system). The right side of the figure shows the
same parameters with the setpoint controller (case
3) converging autonomously to the optimal value of
qp = 25. In the left column (case 2) we can see that
all cameras converge slowly to the defined setpoint
while on the right (case 3) they converge faster and
autonomously to the desired quality levels.
Finally, to test the robustness of the proposed ap-
proach, we run 100 simulations of 500 transactions
period k each with price discrimination (case 3) and
100 others with marginal pricing (case 1) where all
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination
39
20
25
30
qp
QP values per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
20
25
30
qp
QP values per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
Target
5
10
15
p
0
Price per transactions
Base
5
10
15
p
i
Price per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
Base
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
u
i
Cameras utilities
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
u
i
Cameras utilities
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
0
2
4
U
Storage utility
0
2
4
U
Storage utility
0 20 40
60
80 100
10
12
14
16
18
20
k
R
Storage revenue
Average R
0 20 40
60
80 100
10
12
14
16
18
20
k
R
Storage revenue
Average R
Figure 7: Fixed price (left) and discriminate price (right) with fixed system setpoint (no probing controller) for 4 cameras.
Table 1: Multiple simulations results.
Discriminate Discriminate+rnd Margin Margin+rnd
Seller utilities mean 1.68 0.56 0.33 0.27
Seller revenue mean 19.8 20 20 20
Buyer 1 utility mean 0.87 0.82 0.81 0.78
Buyer 2 utility mean 0.86 0.82 0.8 0.75
Buyer 3 utility mean 0.86 0.82 0.83 0.79
Buyer 4 utility mean 0.86 0.83 0.82 0.8
cameras were buying at each period k. We also run
simulations with random uniform distributed video
parameters changing from frame to frame. In real-
ity this is highly unlikely to happen, but demonstrate
a hypothetical worst case scenario. This is denoted
with ”+rnd” in Table 1.
A global summary of the simulation runs can be
found in Table 1. The seller utilities U are on average
SENSORNETS 2022 - 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks
40
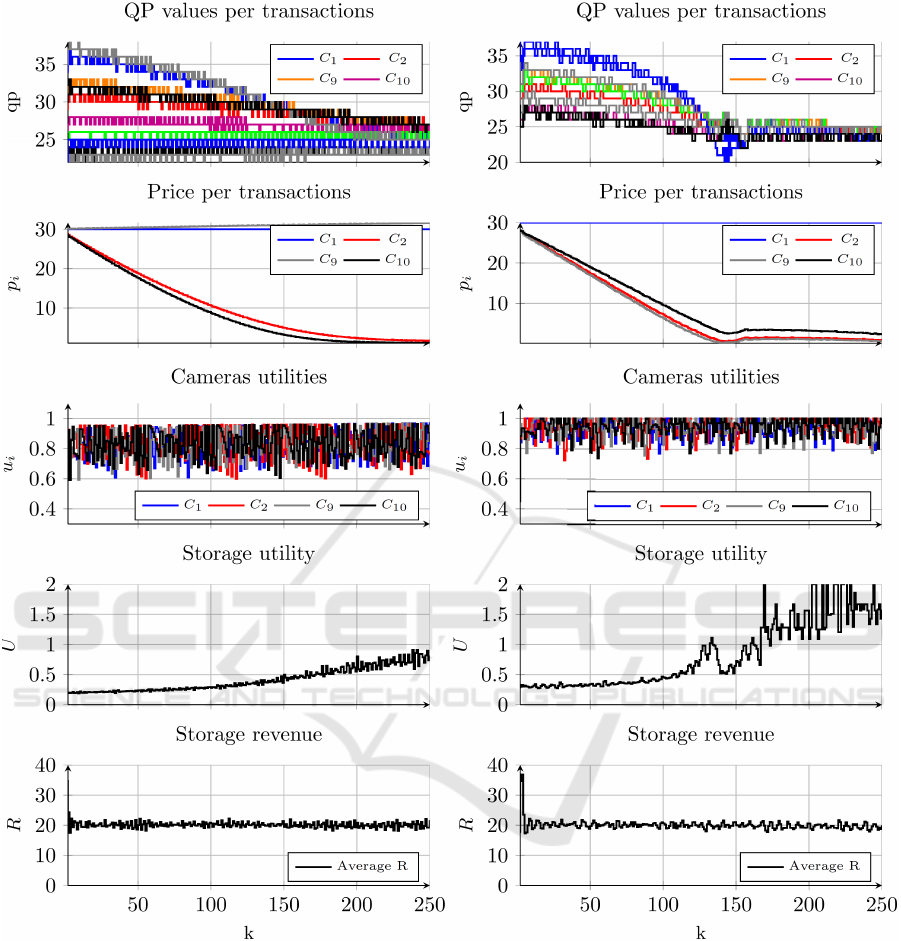
Figure 8: Discriminate price with fixed setpoint (left) and with probing controller (right) for 10 cameras.
(mean) higher in the discriminate pricing (1.68 and
0.56) than for the marginal pricing (0.33 and 0.27).
Note that the utility difference between the random
and non-random case in Table. 1 comes from the util-
ity being based on σ
n
(qp). With randomly chang-
ing video parameters, the optimal qp value will rarely
stay equal to the system setpoint qp value, thus lead-
ing to a lower utility value for the storage than in a
more stable environment. The revenue R remains very
close at 19.8 and 20 for the discriminate pricing ver-
sus 20 for the margin pricing indicating no noticeable
loss in revenue for the seller. The buyer utilities u
i
have higher values with price discrimination than with
the marginal pricing because of the visual quality uni-
formity enforced by the storage provider.
5 CONCLUSIONS & FUTURE
WORK
In this work we proposed a method based on price
discrimination of storage costs for system-level op-
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination
41
20
25
30
35
qp
QP values per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
10
20
30
qp
QP values per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
0
10
20
30
p
i
Price per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
Base
0
10
20
30
p
i
Price per transactions
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
Base
0
0.5
1
u
i
Cameras utilities
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
0
0.5
1
u
i
Cameras utilities
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
0
1
2
3
4
U
Storage utility
0
1
2
3
4
U
Storage utility
100 200 300 400
0
10
20
30
40
k
R
Storage revenue
Average R
20 40
60
80 100
0
10
20
30
40
k
R
Storage revenue
Average R
Figure 9: Discriminate price with setpoint probing controller for continuous buyers only (left) or continuous and event buyers
(right) for 4 cameras.
timization of video quality, which to the best of the
authors knowledge is a novel approach to solve video
storage allocation. The approach is lightweight and
requires limited system knowledge and computation
requirements. The results in terms of system-wide
video quality are encouraging and do not lead to sig-
nificant revenue loss for the storage sellers but im-
proves the overall system video quality. The simpli-
fied approach also lays the ground for future develop-
ment of game theory approaches using the same trans-
action framework.
A logical extension of this paper would be to han-
dle multiple storage providers and develop more com-
plex utility functions for both cameras and storage
sellers which would take into account different con-
straints such as network latency and bandwidth. We
could also use a different convergence method which
would optimize the storage usage more by allowing
the compression levels to slightly deviate for some
cameras. Instead of having the probing controller in-
creasing or decreasing the compression level for all
the cameras it could increase/decrease the compres-
sion level of the cameras one at a time, ensuring that
SENSORNETS 2022 - 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks
42

at all times the cameras have setpoints that maximally
differ with one compression level value. This would
increase the storage utilization.
A limitation of this work is that we expect the stor-
age provider to be able to access the received videos
in order to get access to the qp values in order to de-
cide on a discriminate price. If the video is stored in
an encrypted format this technique could not be used.
Video quality is here considered as correlated to the
video compression. An alternative approach would be
to use an application specific metric or a recognized
quality metric such as the structural similarity index
measure (SSIM), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR)
or other metrics enumerated in (Yang, 2007), but at
the expense of additional computation costs.
REFERENCES
Ahrenholz, J., Danilov, C., Henderson, T. R., and Kim,
J. H. (2008). Core: A real-time network emulator. In
MILCOM 2008-2008 IEEE Military Communications
Conference, pages 1–7. IEEE.
Akesson, M. and Hagander, P. (2000). A simplified prob-
ing controller for glucose feeding in escherichia coli
cultivations. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Confer-
ence on Decision and Control (Cat. No.00CH37187),
volume 5, pages 4520–4525 vol.5.
Armstrong, M. (2008). Price discrimination. MIT Press.
Bernhard Dieber, Christian Micheloni, and Bernhard Rin-
ner. ”Resource-aware coverage and task assignment
in visual sensor networks”. In: IEEE Transactions
on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 21.10
(2011), pp. 1424–1437.
Chong Ding et al. ”Collaborative Sensing in a Distributed
PTZ Camera Network”. In: IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing 21 (July 2012), pp. 3282–3295.
Dochain, D., Perrier, M., and Guay, M. (2011). Extremum
seeking control and its application to process and re-
action systems: A survey. Mathematics and Comput-
ers in Simulation, 82(3):369–380. 6th Vienna Interna-
tional Conference on Mathematical Modelling.
Edalat, N., Xiao, W., Tham, C.-K., Keikha, E., and Ong,
L.-L. (2009). A price-based adaptive task allocation
for wireless sensor network. In 2009 IEEE 6th In-
ternational Conference on Mobile Adhoc and Sensor
Systems.
Edpalm, V., Martins, A.,
˚
Arz
´
en, K.-E., and Maggio, M.
(2018a). Camera networks dimensioning and schedul-
ing with quasi worst-case transmission time.
Edpalm, V., Martins, A., Maggio, M., and
˚
Arz
´
en, K.-E.
(2018b). H.264 Video Frame Size Estimation.
Ehsan Elhamifar and Ren Vidal. ”Distributed calibra-
tion of camera sensor networks”. In: 2009 3rd
ACM/IEEE Int. Conference on Distributed Smart
Cameras, ICDSC 2009 (2009).
Erhan Baki Ermis et al. ”Activity based matching in dis-
tributed camera networks”. In: IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing
Ghosh, P., Roy, N., Das, S. K., and Basu, K. (2004). A
game theory based pricing strategy for job allocation
in mobile grids. In 18th Int. Parallel and Distributed
Processing Symp., 2004. Proceedings., pages 82–.
Giannecchini, S., Caccamo, M., and Shih, C.-S. (2004).
Collaborative resource allocation in wireless sensor
networks. In Proceedings. 16th Euromicro Confer-
ence on Real-Time Systems, 2004. ECRTS 2004.
IPVM. Top 5 Problems in Video Surveillance Stor-
age. url: https://ipvm.com/reports/problems-video-
surveillance-storage (visited on 08/18/2021).
ITU-T (2010). H.264 standard documentation.
Krishna Reddy Konda, Nicola Conci, and Frnacesco De
Natale. ”Global coverage maximization in PTZ cam-
era networks based on visual quality assessment”. In:
IEEE Sensors Journal (2016).
Li, J., Sun, J., Qian, Y., Shu, F., Xiao, M., and Xiang,
W. (2016). A commercial video-caching system for
small-cell cellular networks using game theory. IEEE
Access, 4:7519–7531.
Li, S., Huang, J., and Li, S.-Y. R. (2009). Revenue max-
imization for communication networks with usage-
based pricing. In GLOBECOM 2009-2009 IEEE
Global Telecommunications Conference, pages 1–6.
IEEE.
Lin, X., Ma, H., Luo, L., and Chen, Y. (2012). No-
reference video quality assessment in the compressed
domain. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics,
58(2):505–512.
Ostwald, J., Lesser, V., and Abdallah, S. (2005). Combina-
torial auctions for resource allocation in a distributed
sensor network. In 26th IEEE International Real-Time
Systems Symposium (RTSS’05).
Qureshi, F. Z. and Terzopoulos, D. In 2009 Third
ACM/IEEE Int. Conference on Distributed Smart
Cameras (ICDSC).
Reck, M. (1997). Trading-process characteristics of elec-
tronic auctions. Electronic Markets, 7(4):17–23.
Sankaranarayanan, A., Veeraraghavan, A., and Chellappa,
R.
Seetanadi, G. N., Oliveira, L., Almeida, L., Arz
´
en, K.-
E., and Maggio, M. (2018). Game-theoretic network
bandwidth distribution for self-adaptive cameras.
Shakkottai, S., Srikant, R., Ozdaglar, A., and Acemoglu,
D. (2008). The price of simplicity. IEEE Journal on
Selected Areas in Communications, 26(7):1269–1276.
Silvestre-Blanes, J., Almeida, L., Marau, R., and Pedreiras,
P. (2011). Online qos management for multimedia
real-time transmission in industrial networks. IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 58(3):1061–
1071.
Tsakalozos, K., Kllapi, H., Sitaridi, E., Roussopoulos, M.,
Paparas, D., and Delis, A. (2011). Flexible use of
cloud resources through profit maximization and price
discrimination. In 2011 IEEE 27th International Con-
ference on Data Engineering, pages 75–86. IEEE.
Wittenmark, B.,
˚
Astr
¨
om, K., and
˚
Arz
´
en, K.-E. (2003).
Computer control: An overview. Technical report, De-
partment of Automatic Control, Lund University.
Storage Allocation for Camera Sensor Networks using Feedback-based Price Discrimination
43

Xu, H. and Li, B. (2013). A study of pricing for cloud re-
sources. ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation
Review, 40(4):3–12.
Xue, Y., Ou, Y.-F., Ma, Z., and Wang, Y. (2010). Perceptual
video quality assessment on a mobile platform con-
sidering both spatial resolution and quantization arti-
facts. In 2010 18th International Packet Video Work-
shop, pages 201–208. IEEE.
Xue, Y., Song, Y., Ou, Y.-F., and Wang, Y. (2013). Video
adaptation considering the impact of temporal varia-
tion on quantization stepsize and frame rate on per-
ceptual quality. In International workshop on video
processing and quality metrics for consumer electron-
ics, pages 70–74.
Yan, J., Dai, J., Pu, W., Zhou, S., Liu, H., and Bao, Z.
(2021). Quality of service constrained-resource al-
location scheme for multiple target tracking in radar
sensor network. IEEE Systems Journal.
Yang, K.-C. (2007). Perceptual quality assessment for com-
pressed video. PhD thesis, UC San Diego.
SENSORNETS 2022 - 11th International Conference on Sensor Networks
44
