
A Machine Learning based Study on Classical Arabic Authorship
Identification
Mohamed-Amine Boukhaled
Department of Computer Science, ESIEE-IT Engineering School, Pontoise, France
Keywords: Classical Arabic, Machine Learning, Authorship Identification, Style Marker, Syntactic Features,
Diachronic Corpus.
Abstract: Arabic is a widely spoken language with a rich and long written tradition spanning more than 14 centuries.
Due to its very peculiars linguistic properties, it constitutes a difficult challenge to some natural language
processing applications such as authorship identification, especially in its classical form. Authorship
identification works done on Arabic have mainly focused on the investigation of style markers derived from
either lexical or structural properties of the studied texts. Despite being effective to a certain degree, these
types of style markers have been shown to be unreliable in addressing authorship problems for such
language. In this contribution, we present a machine learning-based study on using different types of style
markers for classical Arabic. Our aim is to compare the effectiveness of machine learning authorship
identification using style markers that do not rely primarily on the lexical or structural dimension of
language. We used three types of style markers relying mostly on the syntactic information. By way of
illustration, we conducted a study and reported results of experiments done on a corpus of 700 books written
by 20 eminent classical Arabic authors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Arabic is a Semitic language with a rich and long
written tradition spanning more than 14 centuries.
Two different forms of Arabic have diachronically
emerged and co-exist nowadays, the Classical
Arabic (CA) is the historical form of the Arabic
language used in literary texts and applied mainly
for the formal academic and religious domains.
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) on the other hand is
the form used in contemporary written works as well
as in the media.
MSA does not essentially differ from CA in its
basic linguistics foundations (morphology or
syntax). However, most researchers on Arabic
Natural Language Processing (NLP) have
concentrated their efforts on MSA. Classical Arabic,
being much more rich and complex in its stylistic,
syntactic and lexical usages, is an interesting area of
linguistics research, as much as it is a challenging
form of language for existing NLP applications
because of its peculiar characteristics.
One of the NLP applications that have received
considerable attention lately is authorship
identification. The authorship identification problem
is the task of identifying the author of a given
document. This problem (known also as authorship
attribution
1
or authorship recognition) can typically
be formulated as follows: given a set of candidate
authors for whom samples of written text are
available, the task is to assign a newly unseen text of
unknown authorship to one of these candidate
authors (Stamatatos, 2009).
This task has been addressed traditionally in the
literature as a text categorization problem
(Sebastiani, 2002). Text categorization is indeed a
useful way to organize large document collections.
In this line of work, current authorship attribution
methods have two key steps. First, an indexing step
based on some style markers is performed on the
studied text using some natural language processing
techniques depending on the type of the desired style
features, such as tokenizing, tagging, parsing, and
morphological analysis; then an identification step is
applied subsequently using the indexed markers to
determine the most likely authorship.
1
Authorship identification and authorship attribution are
two terms used interchangeably in this document.
Boukhaled, M.
A Machine Learning based Study on Classical Arabic Authorship Identification.
DOI: 10.5220/0010969100003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 1, pages 489-495
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
489

The identification step usually involves using
machine learning algorithms or some other kind of
statistical and numerical analysis.
Authorship attribution works done on Arabic
have mainly focused on the investigation of style
markers derived from either the lexical or the
structural properties of the studied texts (e.g.
frequency of word forms, discourse markers, type
and length of sentences). Despite being effective to a
certain degree, these types of style markers have
been shown to be unreliable in addressing authorship
problems in Arabic (Omar and Hamouda, 2020).
This can be indeed attributed to the peculiar
linguistic properties of Arabic in general, and CA in
particular. Moreover, the majority of the work done
in Arabic authorship identification used MSA as text
resources, mainly due to its dominant usage in
journalistic and social media contents.
In this contribution, we present a comparative
study on using different types of style markers for
classical Arabic based on a machine learning
approach for authorship identification. Our aim is to
compare the effectiveness of using style markers that
do not rely primarily on the lexical or structural
dimensions of language, and hence are more prone
to be topic-independents. We used three types of
style markers relying mostly on the syntactical
information contained in the structure of the text:
Part of Speech-based features, Function Word
features, and Character-based features
By way of illustration, this study is done on a
corpus of 700 books written by 20 eminent classical
Arabic authors. To evaluate the effectiveness of our
approach, we conducted a machine learning
experiment based on three different algorithms
belonging to different statistical families and
reported their performances.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: we
first give in section 2 a brief review of related works
concerned with authorship identification in general
and in Arabic language in particular, and then we
describe our experimental setup in section 3. The
results of the comparative study are presented in
section 4. Finally, section 5 concludes this
contribution and gives our main prospects.
2 RELATED WORKS
Authorship attribution is a relatively old research
field. A first scientific approach to the problem was
proposed in the late 19th century, in the work of
Mendenhall in 1887, who studied the authorship of
texts attributed to Bacon, Marlowe and Shakespeare.
More recently, the problem of authorship attribution
gained greater importance due to new applications in
forensic analysis and humanities scholarship, as well
as in contemporary society and industry (Kestemont
et al., 2019).
The identification process involves using
methods that fall mainly into two categories: the first
category includes methods that are based on
statistical analysis, such as principal component
analysis (Jamak, Savatić and Can, 2012) or linear
discriminant analysis (Chaski, 2005); the second
category includes machine learning techniques, such
Support Vector Machine (SVM) (Stamatatos, 2008),
decision trees (Abbasi and Chen, 2005), K-Nearest
Neighbours (KNN) (Zamani et al., 2014) and neural
networks (Zheng et al., 2006).
To achieve high authorship attribution accuracy,
one should use features that are most likely to be
independent from the topic of the text. Many style
markers have been used for this task, from early
works based on simple features such as sentence
length and vocabulary richness (Yule, 1944), to
recent and relevant works based on function words
(Zhao and Zobel, 2005) (Boukhaled and Ganascia,
2015), punctuation marks (Martin-del-Campo-
Rodriguez et al., 2019), Part-of-Speech (POS) tags
(Pokou, Fournier-Viger and Moghrabi, 2016), parse
trees (Gamon, 2004) and character-based features
(Sapkota et al., 2015).
There is a consensus among different researchers
that function words are a highly reliable indicator of
authorship (Kestemont, 2014). There are two main
reasons for using function words in lieu of other
markers. First, because of their high frequency in a
written text, function words are very difficult to
consciously control by the author, which minimizes
the risk of false attribution. The second is that
function words, unlike content words, are more
independent from the topic or the genre of the text,
so one should not expect to find great differences of
frequencies across different texts written by the
same authors on different topics (Chung and
Pennebaker, 2007).
For the Arabic language, one can categorize
existing works into two categories based on the
extracted features (Al-Ayyoub, Alwajeeh and
Hmeidi, 2017). The first category includes the
lexical approach, where the feature vector for each
text is computed based on the occurrences of the
words within it. The second category is based on
more sophisticated style markers; it relies on
computing certain features by trying to capture more
relevant and deep linguistic traits. Finally, for a
more comprehensive coverage of the different works
NLPinAI 2022 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
490
and issues on Arabic authorship identification
problem, interested readers are referred to (El Bakly,
Darwish and Hefny, 2020)
3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
3.1 Data Set
For this comparative study, we constructed our data
set collection from the OpenITI corpus (Belinkov et
al., 2019). This choice was motivated by our special
interest in studying classical Arabic literature, which
has not benefited from as much attention as MSA
literature did in the community.
OpenITI corpus is a historical corpus of Arabic,
containing some 6 thousand titles and approximately
1 billion words.
The collection is based on edited manuscripts,
and each title (book) is represented by its full text
support.
The corpus is cleaned and organized with
metadata information. The Library of Congress
scheme in its simplified version is followed as rules
for coding author names and book titles. Moreover,
the entire corpus is processed with state-of-the-art
Arabic NLP tools (tokenizers and morpho-syntactic
analysers among other tools). The result is a full
analysis per word, including tokenization,
lemmatization, part-of-speech-tagging, and various
morphological features, which would be very helpful
in extracting style markers considered in our
analysis. The corpus contains the majority of the
famous titles in Arabic culture, and almost all genres
that played an important role in the development of
the Arabic written tradition are represented.
For our experiment, we collected books for the
twenty most represented authors in terms of works
in the OpenITI corpus, so that the total number of
books is 700. This author selection schema helps us
cover most of the classical Arabic time period, from
the 9
th
to the 15
th
century CE (which corresponds to
3
rd
and 9
th
centuries respectively in Islamic Hijri
calendar AH) (Ali and Ali, 1987).
The next step was to divide these books into
smaller pieces of texts in order to have enough data
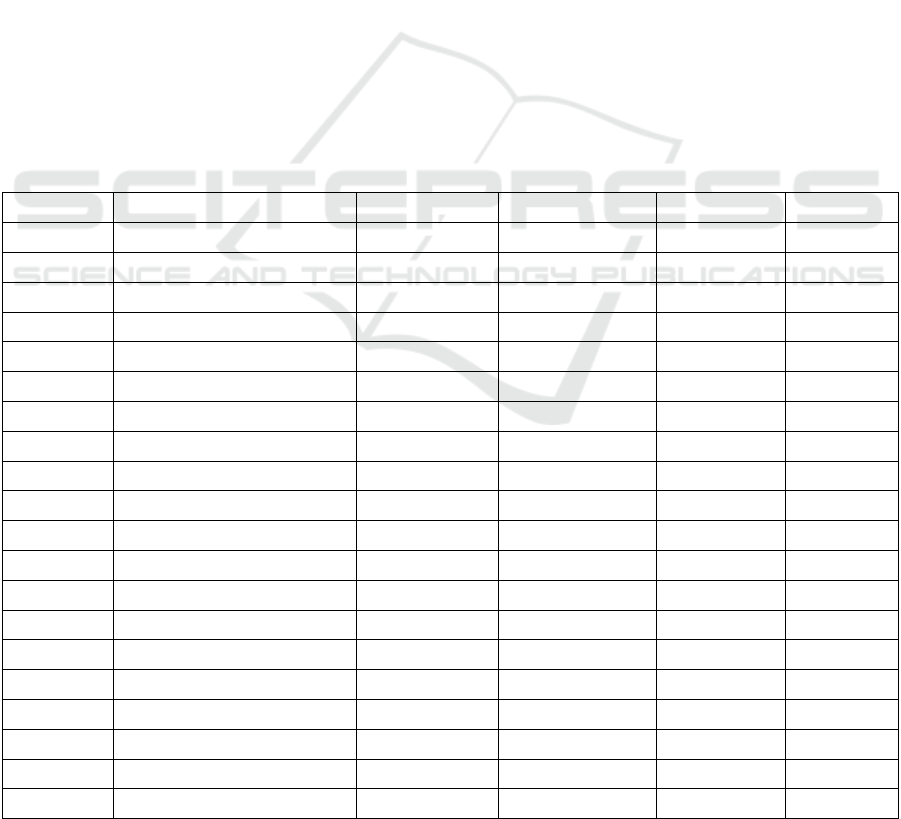
Table 1: Statistics for the data set used in our experiment, the first column represent the year of death of an author, taken as
time period indicator.
Year (AH) Author # Words # Sentences # Books # Texts
303 Nasai 1655894 36925 17 76
385 Daruqutni 1355617 51345 22 105
413 ShaykhMufid 1186846 56091 44 121
430 AbuNucaymIsbahani 2981145 89544 28 180
456 IbnHazm 3060549 82807 27 165
458 Bayhaqi 5270192 135144 23 255
463 KhatibBaghdadi 3096101 49427 26 104
505 Ghazali 2103712 51758 22 104
571 IbnCasakir 6649073 167963 24 319
576 IbnMuhammadSilafi 402677 11412 16 31
597 IbnJawzi 5356768 240757 50 462
600 CabdGhaniMuqaddasi 608623 25059 21 56
643 DiyaDinMuqaddasi 1155397 48541 25 102
676 Nawawi 4182033 124590 21 263
728 IbnTaymiyya 9191977 183184 89 378
748 Dhahabi 7659298 505507 42 953
751 IbnQayyimJawziyya 4492335 97880 40 196
795 IbnRajabHanbali 2063206 94798 22 184
852 IbnHajarCasqalani 14962764 577075 50 1070
911 Suyuti 10479550 647426 91 1216
A Machine Learning based Study on Classical Arabic Authorship Identification
491

instances to train the attribution algorithm.
Researchers working on authorship attribution
applied on literary texts have been using different
dividing strategies. For example, Hoover (2003)
decided to take just the first 10,000 words of each
book as a single text, while Argamon and Levitan
(2005) treated each chapter of each book as a
separate text.
As done in (Boukhaled and Ganascia, 2017) and
since we are considering sentence-split texts, in our
experiment we chose to slice books by the size of
the smallest one in the collection in terms of number
of sentences.
More information about the data set used in the
experiment is presented in Table1 above.
3.2 Style Markers (Features) and
Classification Scheme (Algorithms)
In our approach, we focus our comparative study on
using style markers that do not rely on the lexical or
structural dimension of classical Arabic. We used
three types of style markers relying mostly on the
syntactical information contained in the structure of
the text: Part of Speech features, Function Word
features, and Character-based features. More
precisely, each text in our data set is represented by
a vector of normalized
2
frequencies of occurrence of
these three types of stylistic markers: part-of-speech
tag n-grams, function words frequencies, character-
based n-grams (with n varying from 1 to 3).
Then we relied on a classification scheme based
on three different machine learning algorithms,
belongings to different statistical families, to derive
a discriminative model for our represented authors.
The three algorithms used in the experiments are:
The Logistic Regression Classifier, the Gaussian
Naïve Bayes Classifier, and K-Nearest-Neighbours
(KNN) Classifier.
To get a reasonable estimation of the expected
attribution performance (generalization), we used
common classification metrics: Precision (P), Recall
(R), and F1-score based on a 10-fold cross–
validation as follows:
𝑃=
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃 + 𝐹𝑃
(1)
𝑅=
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃 + 𝐹𝑁
(2)
2
The normalization of the frequencies vectors was done
based on the L1 normalization technique.
𝐹1 𝑠𝑜𝑐𝑟𝑒 =
2𝑃𝑅
𝑃+𝑅
(3)
Where TP, TF, FN and FP are respectively true
positive, true negative, false negative, and false
positive text-to-author attributions.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Results of measuring the attribution performance for
the different feature sets presented in our experiment
setup are summarized below in Table 2. These
results show in general a better performance when
using character-based features, which achieved a
very high attribution, over features based on part-of-
speech and function words features.
Our study here shows that the KNN classifier is
by far the best performing model in our experiment.
Combined with features extracted using Character n-
grams, it can achieve a high attribution performance
(That is, F1 = 91.5% for character based 3-grams).
To a certain limit, adding more grams increases the
attribution performance. These comparative
performance results suggests that a simple (lazy)
model does better than complex models such as
Logistic regression classifier in our classification
settings; we believe that is due to the relatively small
size of the training data.
By contrary to our expectation, function-word-
features did not perform well in our corpus, In fact,
they achieved at best a mitigated performance (F1 =
83,7%) when used with the TF-IDF heuristic. We
believe that this is due to the presence of some
peculiar linguistic properties related to classical
Arabic affecting the attribution process. These
properties, that need to be more deeply studied in
further works, depend on the linguistic character of
the text, such as the syntactic and the lexical
disparities between the different parts of one book,
and the time period in which it was written.
Despite the fact that function word-based
markers are state-of-the-art in many other languages,
they are basically relying on the bag-of-words
assumption, which stipulates that text is a set of
independent words. This approach completely
ignores the fact that there is a syntactic structure and
latent sequential information in the text. In fact,
De Roeck, Sarkar and Garthwaite (2004) have
shown that frequent words, including function
words, do not distribute homogeneously over a text.
NLPinAI 2022 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
492
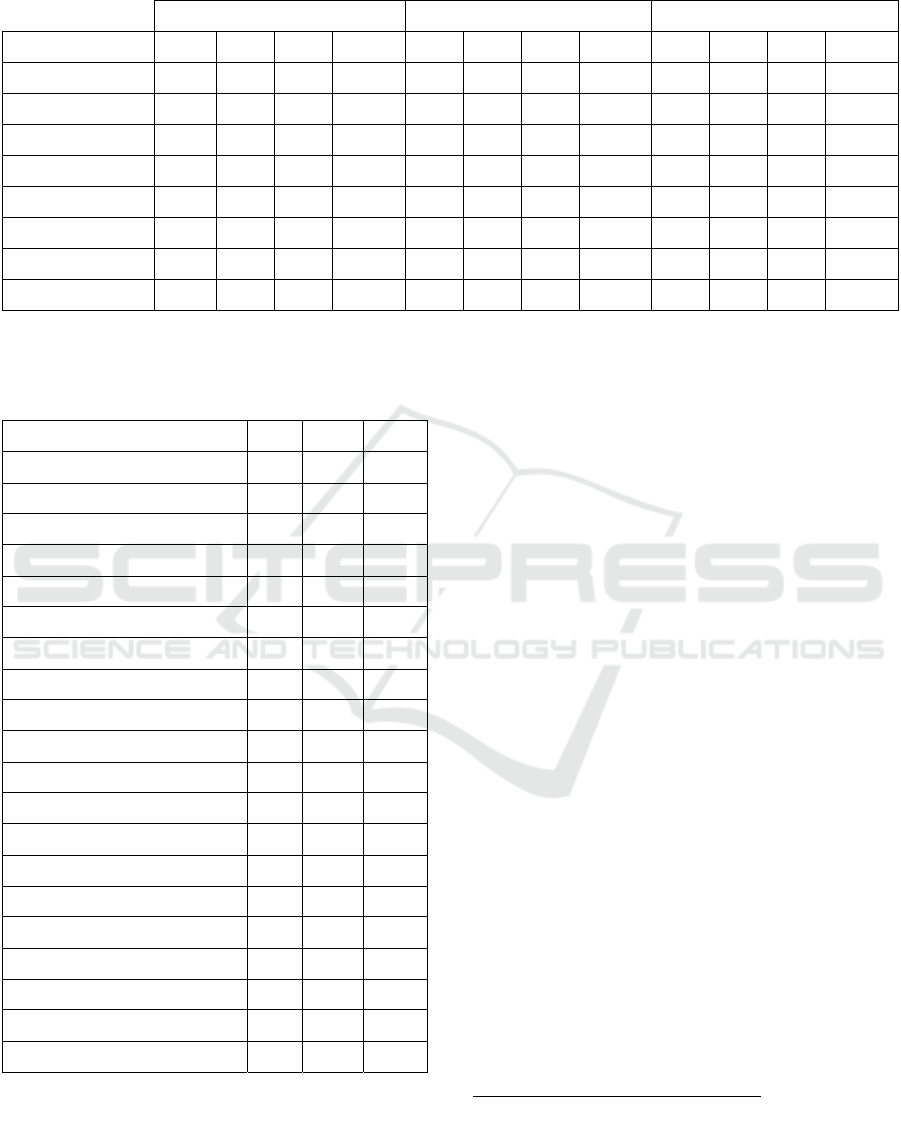
Table 2: 10-fold cross-validation results for the three models based on different types of style features. Precision (P), Recall
(R) and F1- score are shown in percentages; Time of execution is reported in seconds.
LogisticRegression GaussianNB KNeighborsClassifier
Style Markers P R F1 Time P R F1 Time P R F1 Time
CHAR_1_gram 25,9 37,4 26,1 16 63,1 55,4 56,2 6 86,6 86,2 86,1 12
CHAR_2_gram 25,1 38,1 26,9 189 67,2 62,0 62,4 27 91,5 91,0 90,9 171
CHAR_3_gram 25,3 34,9 22,8 979 81,1 80,3 79,9 118 91,0 91,6 91,5 684
FW 38,5 46,0 37,2 49 63,2 49,0 52,2 8 84,0 83,2 83,0 24
FW_TF-IDF 39,1 45,8 37,0 46 63,2 44,2 48,2 9 84,7 83,9 83,7 23
POS_1_gram 33,3 45,8 36,7 22 58,9 48,4 49,3 8 85,5 84,8 84,7 10
POS_2_gram 27,3 43,4 31,9 85 63,8 55,9 57,9 13 90,2 89,6 89,6 27
POS_3_gram 25,9 41,6 29,6 312 74,1 72,5 72,0 37 91,2 90,6 90,6 151
Table 3: Individual attribution results for each author in
the data set, produced by the best performing model KNN
classifier with character 3-gram.
Year-Author P R F1
0303-Nasai 0.89 1.00 0.94
0385-Daruqutni 1.00 0.69 0.81
0413-ShaykhMufid 0.88 1.00 0.93
0430-AbuNucaymIsbahani 1.00 0.95 0.97
0456-IbnHazm 1.00 0.94 0.97
0458-Bayhaqi 1.00 1.00 1.00
0463-KhatibBaghdadi 1.00 0.78 0.88
0505-Ghazali 0.78 1.00 0.88
0571-IbnCasakir 0.97 0.95 0.96
0576-IbnMuhammadSilafi 0.67 0.67 0.67
0597-IbnJawzi 0.83 0.98 0.90
0600-CabdGhaniMuqaddasi 0.20 0.25 0.22
0643-DiyaDinMuqaddasi 1.00 0.80 0.89
0676-Nawawi 0.79 0.90 0.84
0728-IbnTaymiyya 0.86 0.91 0.88
0748-Dhahabi 0.94 0.97 0.96
0751-IbnQayyimJawziyya 0.81 0.81 0.81
0795-bnRajabHanbali 0.87 0.93 0.90
0852-IbnHajarCasqalani 0.97 0.95 0.96
0911-Suyuti 0.97 0.92 0.95
Therefore, these results can provides evidence for
the fact that the bag-of-words assumption is not
valid for Classical Arabic as well.
By looking at the individual performances for
each author based on the best model (KNN
3
classifier with character 3-gram, see Table 3), we
can notice that there are no clear patterns that
emerge. Some authors have a very distinguishable
writing style such as Bayhaqi
4
which have a perfect
attribution performance, or IbnHazm
5
which have
high attribution performance (F1=97% and
P=100%), others have less distinguishable text such
as CabdGhaniMuqaddasi
6
(F1=22%). These
individual results do not seem to neither show any
correlation between the attribution performances and
the authors time period on the one hand, nor the
qualities of text that we had for each of them on the
other hand.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study addressed the authorship identification
problem for classical Arabic based on a machine
learning approach. Despite being shown unreliable
in addressing the authorship identification problems
for Arabic, works done traditionally on this language
have mainly focused on the investigation of style
markers derived from either lexical or structural
properties of the studied texts. In light of this
argument, we presented a comparative study on
3
With K=3
4
(994 – 1066 CE)
5
(994 – 1064 CE)
6
(1146 – 1203 CE)
A Machine Learning based Study on Classical Arabic Authorship Identification
493

using different types of style markers for classical
Arabic. Our aim was to compare the effectiveness of
using style markers that do not rely primarily on the
lexical or structural dimensions of language. We
used three types of style markers based mostly on
the syntactical information contained in the structure
of the text: part of speech based features, function
word features and character-based features. To
evaluate the effectiveness of these markers, we
conducted an experiment on a diachronic classical
Arabic corpus comprising more than 700 books. Our
results show that these markers can indeed be very
effective stylistic features, achieving high
performance in authorship attribution results.
REFERENCES
Abbasi, A. and Chen, H. (2005) ‘Applying authorship
analysis to extremist-group web forum messages’,
IEEE Intelligent Systems. IEEE, 20(5), pp. 67–75.
Al-Ayyoub, M., Alwajeeh, A. and Hmeidi, I. (2017) ‘An
extensive study of authorship authentication of arabic
articles’, International Journal of Web Information
Systems. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Ali, A. S. M. and Ali, A. S. (1987) A linguistic study of the
development of scientific vocabulary in Standard
Arabic. Routledge.
Argamon, S. and Levitan, S. (2005) ‘Measuring the
usefulness of function words for authorship
attribution’, in Proceedings of the Joint Conference of
the Association for Computers and the Humanities and
the Association for Literary and Linguistic Computing.
El Bakly, A. H., Darwish, N. R. and Hefny, H. A. (2020)
‘A Survey on Authorship Attribution Issues of Arabic
Text’, International Journal of Artificial Intelligent
Systems and Machine Learning, 2, pp. 86–92.
Belinkov, Y. et al. (2019) ‘Studying the history of the
Arabic language: language technology and a large-
scale historical corpus’, Language Resources and
Evaluation. Springer, 53(4), pp. 771–805.
Boukhaled, M. A. and Ganascia, J.-G. (2015) ‘Using
function words for authorship attribution: Bag-of-
words vs. sequential rules’, in Natural Language
Processing and Cognitive Science. De Gruyter, pp.
115–122.
Boukhaled, M. A. and Ganascia, J.-G. (2017) ‘Stylistic
Features Based on Sequential Rule Mining for
Authorship Attribution’, in Cognitive Approach to
Natural Language Processing. Elsevier, pp. 159–175.
Chaski, C. E. (2005) ‘Who’s at the keyboard? Authorship
attribution in digital evidence investigations’,
International journal of digital evidence. Citeseer,
4(1), pp. 1–13.
Chung, C. and Pennebaker, J. W. (2007) ‘The
psychological functions of function words’, Social
communication, pp. 343–359.
Gamon, M. (2004) ‘Linguistic correlates of style:
authorship classification with deep linguistic analysis
features’, in Proceedings of the 20th international
conference on Computational Linguistics, p. 611.
Hoover, D. L. (2003) ‘Frequent collocations and authorial
style’, Literary and Linguistic Computing. ALLC,
18(3), pp. 261–286.
Jamak, A., Savatić, A. and Can, M. (2012) ‘Principal
component analysis for authorship attribution’,
Business Systems Research: International journal of
the Society for Advancing Innovation and Research in
Economy. Udruga za promicanje poslovne
informatike, 3(2), pp. 49–56.
Kestemont, M. (2014) ‘Function words in authorship
attribution. From black magic to theory?’, in
Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Computational
Linguistics for Literature (CLFL), pp. 59–66.
Kestemont, M. et al. (2019) ‘Overview of the Cross-
domain Authorship Attribution Task at PAN 2019.’, in
CLEF (Working Notes).
Martin-del-Campo-Rodriguez, C. et al. (2019)
‘Authorship Attribution through Punctuation n-grams
and Averaged Combination of SVM’.
Omar, A. and Hamouda, W. I. (2020) ‘The effectiveness
of stemming in the stylometric authorship attribution
in arabic’,
International Journal of Advanced
Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 11(1),
pp. 116–121.
Pokou, Y. J. M., Fournier-Viger, P. and Moghrabi, C.
(2016) ‘Authorship Attribution using Variable Length
Part-of-Speech Patterns.’, in ICAART (2), pp. 354–
361.
De Roeck, A., Sarkar, A. and Garthwaite, P. H. (2004)
‘Defeating the homogeneity assumption’, in
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on the
Statistical Analysis of Textual Data (JADT), pp. 282–
294.
Sapkota, U. et al. (2015) ‘Not all character n-grams are
created equal: A study in authorship attribution’, in
Proceedings of the 2015 conference of the North
American chapter of the association for computational
linguistics: Human language technologies, pp. 93–
102.
Sebastiani, F. (2002) ‘Machine learning in automated text
categorization’, ACM computing surveys (CSUR).
ACM, 34(1), pp. 1–47.
Stamatatos, E. (2008) ‘Author identification: Using text
sampling to handle the class imbalance problem’,
Information Processing & Management. Elsevier,
44(2), pp. 790–799.
Stamatatos, E. (2009) ‘A survey of modern authorship
attribution methods’, Journal of the American Society
for information Science and Technology. Wiley Online
Library, 60(3), pp. 538–556.
Yule, G. U. (1944) The statistical study of literary
vocabulary. CUP Archive.
Zamani, H. et al. (2014) ‘Authorship identification using
dynamic selection of features from probabilistic
feature set’, in International Conference of the Cross-
NLPinAI 2022 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
494

Language Evaluation Forum for European
Languages, pp. 128–140.
Zhao, Y. and Zobel, J. (2005) ‘Effective and scalable
authorship attribution using function words’, in
Information Retrieval Technology. Springer, pp. 174–
189.
Zheng, R. et al. (2006) ‘A framework for authorship
identification of online messages: Writing-style
features and classification techniques’, Journal of the
American Society for Information Science and
Technology. Wiley Online Library, 57(3), pp. 378–
393.
A Machine Learning based Study on Classical Arabic Authorship Identification
495
