
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System
Mariz Awad, Jailan Salah, Nabila Hamdi and Slim Abdennadher
Faculty of Media Engineering and Technology, German University in Cairo, New Cairo, Cairo, Egypt
Keywords:
Intelligent Tutoring Systems, Computer Adaptive Testing, Adaptive Item Selection, e-Learning, Expert
Systems, Item-based Learning.
Abstract:
Computer Adaptive Testing (CAT) methods have been widely used by test centres to assess examinees quickly.
These methods change question difficulty in response to the performance of the examinee. This work presents
a modified framework, which we call Computer Adaptive Learning (CAL). CAL uses the CAT principles to
improve exam-training efficiency rather than assessment efficiency. We applied the proposed method to a
learning platform and conducted a comparative experiment using 50 participants to investigate the effective-
ness of CAL. We evaluated the system in terms of knowledge gain, learning efficiency, and engagement by
comparing it to another adaptive method in which the game mechanics and UI adapt to the user’s emotional
state. Results confirm that the proposed CAL algorithm exposes the learner to questions more efficiently and
improves the learning gain when compared to traditional systems in which difficulty increases sequentially.
Engagement, however, did not differ across systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, there have been rising concerns over the
decline in the number of people pursuing pedagogical
degrees, shifting to careers in computer science and
technology. Meanwhile, the number of enrollments in
schools, especially in developing countries, has been
seeing a pronounced increase. This has been making
it increasingly difficult for teachers to provide individ-
ualised focus on the students’ different learning needs
and styles. In their book Poor Economics (Banerjee
and Duflo, 2011), economists Abhijit Banerjee and
Esther Duflo report the benefits of using computer-
assisted learning programs. These programs allowed
the students to learn at their own pace and helped
them achieve higher scores on their tests (Banerjee
et al., 2007). Today, AI has significantly enhanced
these programs by fully customising the learning con-
tent. AI-powered intelligent tutoring systems (Gian-
nandrea and Sansoni, 2013) are now able to assess
the student’s initial level in terms of both skill (Eggen,
2012) and knowledge (Doignon and Falmagne, 2012),
make use of data gathered about the student as well
as data collected from a multitude of other students,
and adapt the instructional content with the purpose
of optimizing the learning process. These platforms
have gained widespread attention especially during
the COVID-19 crisis situation.
A variety of other adaptivity techniques have pre-
viously been used in e-learning platforms and serious
games to aid the learning process. A growing body
of research in the field of Affective Computing (AC)
focused on reducing the learner’s cognitive burden by
adapting features in an e-learning system to the emo-
tional state of the learner (Solovey et al., 2011; Funk
et al., 2015; ElKomy et al., 2017). A study by (Salah
et al., 2018) in which the game mechanics and UI
adapted to the learner’s affective state showed a sig-
nificant improvement in the learning gain and engage-
ment level of students.
Meanwhile, systems that adapt the instructional
content for the learner have been criticized for not
enabling the student with the skills needed for long-
term independent learning. Nevertheless, during crit-
ical times before an exam item-based exam training
systems can help students identify practice questions
that most suit their level of mastery of a subject and
that quickly address gaps in their knowledge and un-
derstanding of a topic. This, in turn, saves them a lot
of valuable time. One research study (Linssen, 2011)
proposed an adaptive difficulty technique in the con-
text of a serious game, however in such games the
adaptivity feature would usually be confined to the
scenario and mechanics of the game which prevents
ICT-agnostic educators from building adaptive pro-
grams with their own educational content. Therefore,
in this research study our aim was to incorporate item-
based adaptive difficulty in a generic serious game
Awad, M., Salah, J., Hamdi, N. and Abdennadher, S.
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System.
DOI: 10.5220/0010996300003182
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2022) - Volume 1, pages 189-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-562-3; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
189

which allowed ICT-agnostic educators to furnish the
platform with their own question pools. The aim of
the adaptivity feature is to render questions which suit
and challenge the student’s ability for the purpose of
exam-training efficiency. Moreover, addressing the
lack of empirical research of AI systems in education
(Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019; Pedro et al., 2019), we
wanted to investigate the effectiveness and engage-
ment of this adaptivity feature when compared to that
in which the game mechanics and UI adapted to the
learner’s emotional state according to the methods de-
scribed in (Salah et al., 2018).
A well established methodology in the fields
of Psychometrics and Education, which features an
item-based adaptive difficulty mechanism is Comput-
erized Adaptive Testing (CAT). The main goal of a
CAT is to reduce the number of questions that an ex-
aminee has to answer in order to reach a reliable es-
timation of their ability. In effect, it has been proven
that adaptivity implemented in CATs improves testing
efficiency and reduces the test’s length by up to 50-
60% (Lord, 1980a; Freedle and Dur
´
an, 1987; Eggen,
2012).
Previous work shed some light on the potential
of using the CAT models for the purpose of learning
efficiency rather than assessment efficiency (Eggen,
2012; Wauters et al., 2010; Park et al., 2019; Pli-
akos et al., 2019; Pandarova et al., 2019). The key-
point which distinguishes the efficiency in the CAT’s
adaptivity is that questions are calibrated according
to extra parameters other than their level of difficulty,
such as how discriminating a question is between stu-
dents of different ability levels (see Section 3.2.1).
These parameters provide further insight into the abil-
ity level of the student and improves efficiency even
further. However, there are several problems under-
lying the use of such methods generically and demo-
cratically in learning environments, namely that they
require a large number of students to create a cali-
brated question pool dataset. Hence, in our work we
address these problems and propose our own modi-
fied framework named Computer Adaptive Learning
(CAL). The design focus of this framework is to be
more suited for educators to create their own small-
scale CAL programs.
The outline of the work can be listed as follows:
1. We describe our CAL framework building upon a
pre-extisting CAT model [3].
2. We apply the CAL system to a platform with an
editor which the educator can use to install and
calibrate their own question pool [4].
3. We build two versions of a serious games plat-
form rendering questions to the user: one with
the CAL adaptivity feature, and another one with
a different selection algorithm that increases the
difficulty sequentially, and in which the game me-
chanics and UI adapt to the user’s emotional state
[5.2].
4. Using a between subject study we compare both
versions to answer the following research ques-
tions [5.3]:
• (RQ1) Is there a significant difference between
the two versions on the learning gain of stu-
dents?
• (RQ2) Would the CAL’s adaptive selection
method expose students to questions more ef-
ficiently than the system in which the difficulty
increases sequentially?
• (RQ3) Is there a significant difference between
the two adaptivity methods of the two versions
on the engagement level of students?
5. We provide empirical evidence that the proposed
CAL system has significant influence on the learn-
ing experience [6] and discuss the results.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Related Work
A lot of recent research studies proposed different
adaptive algorithms that keep track of the learner’s
real-time ability change and render questions spe-
cific to their current ability. One research study
concerned with the cold start problem (Park et al.,
2019) explored supplementing the Elo Rating System
(ERS) with explanatory Item Response Theory (IRT)
to make the system more efficient and to reduce abil-
ity estimation issues. Other studies (Pliakos et al.,
2019; Pandarova et al., 2019) proposed using a hy-
brid approach of IRT combined with machine learn-
ing. The main investigative feature within these stud-
ies was to improve the ability estimation accuracy.
However, these models rely on large question pool
datasets which would be burdensome for an educator
to generate.
Another study explored item selection methods
traditionally developed for computer adaptive tests
(CATs) and proposed an alternative selection proce-
dure based on Kullback-Leibner information (Eggen,
2012). One of the strength points of this study is that
it draws the distinction between efficiency in testing
and efficiency in training, where the proposed selec-
tion algorithm is constantly monitoring the student’s
growth in ability, and selecting items that feed this
growth rather than items that test their ability. Simu-
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
190
lation studies comparing the different selection algo-
rithms showed that the differences between the CAT’s
Fisher information method and the KL information
method for item selection were small.
Nevertheless, this study alongside others (Wauters
et al., 2010) brings our attention to the potential use
of CAT models in adaptive training systems.
3 METHODS
3.1 The Problem with Large Numbers
Most CAT models are built on item response theory
(IRT), a powerful psychometrics paradigm invented
by Fredrick Lord through the years 1968 - 1980 (Birn-
baum et al., 1968; Lord, 1980b). The problem with
IRT however, is that a large number of examinees
(500-1000 in the 3PL-IRT model (Yoes, 1995)) are
needed to take the paper-based test in the calibration
phase in order to accurately estimate item parameters.
While this large number of examinees required
doesn’t pose a real problem for professional testing
agencies, it comes as a real roadblock for small scale
instructional programs that want to incorporate CATs.
For these kinds of programs, as (T. Frick, 1992)
puts it, “the IRT approach to adaptive testing can be
likened to the use of a cannon to kill a mosquito.“.
So instead, Frick proposed a discrete model,
termed EXSPRT(Frick, 1992). It views CATs as an
Expert system (Luk, 1991) with production rules, an
inference engine and an intelligent item selection al-
gorithm. We decided to use this model in our ap-
proach as it doesn’t need as many calibration students
(a minimum of 50) which makes it much less burden-
some for educators using the system.
In our CAL framework, we build upon Frick’s
EXSPRT model and extend it to classify the user into
A, B, or C grade categories, using the sequential prob-
ability ratio test (SPRT) (Spray, 1993) to serve for the
termination criterion. The main goal of the selection
algorithm is to select questions that are both compat-
ible with the user’s mastery level as well as challeng-
ing and time efficient.
Accordingly, our CAL is divided into two phases
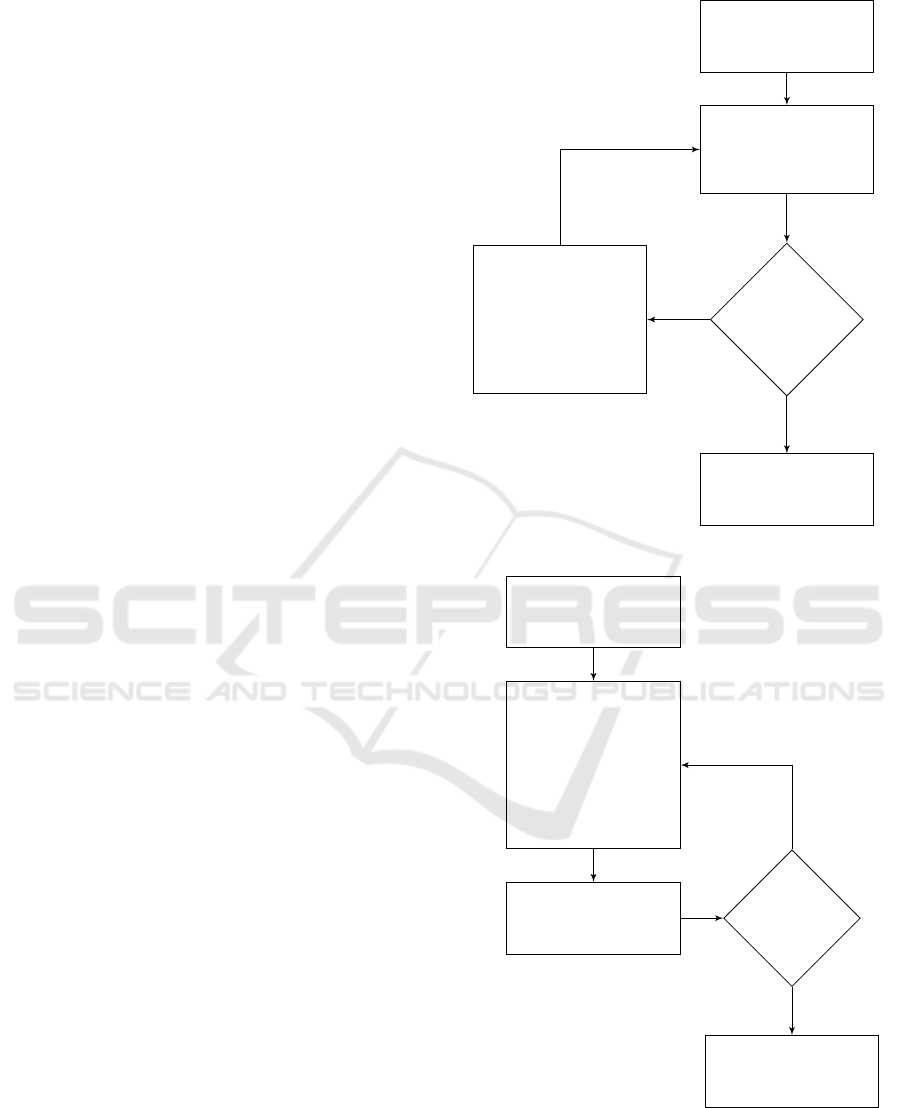
which render questions to the user (figure 1), Phase
I is a CAT expert system, which aims to classify the
user (as an examinee) as an A, B or C student, and
Phase II benefits from the user’s test result in Phase
I, along with the items’ information, pre-attained
through calibration, to further elect questions for the
user (as a trainee) that most challenge their current
estimated ability level.
Administer item of
median difficulty
Score response
by updating the
likelihood ratios and
the ability estimate
is the ter-
mination
criterion
met?
Select item which
is most efficient in
bringing the user to
a classification &
most compatible with
the user’s current
ability estimate
Classify the user
into A, B, or C and
proceed to Phase II
no
yes
(a) Phase I: A CAT Expert System.
Fix the rank-
ing utility
Select item which
is most efficient
in training the
user to the next
higher category &
most compatible
with the current
ability estimate
Score response
by updating the
ability estimate
Question
pool
depleted?
Stop
yes
no
(b) Phase II: From CAT to CAL.
Figure 1: Flow Chart of the CAL System.
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System
191

3.2 Phase I: An Extended CAT Expert
System
The system is divided in this phase into 3 engines:
1. Calibration Engine: Empirically calibrates the
question pool according to 3 item parameters: dif-
ficulty, discrimination, and utility. These parame-
ters are derived from a set of probability rules that
make up the ”knowledge base” of the expert sys-
tem.
2. Inference Engine: Uses the Bayesian method for
scoring (Frick, 1989; Schmitt, 1969) and the se-
quential probability ratio test (SPRT) (Kingsbury
and Weiss, 1983; Reckase, 1983; Wald, 1947) for
termination.
3. Intelligent Selection Engine: Continuously se-
lects questions that quicken classifying the user
into a master or non-master (or an A, B, or C stu-
dent).
3.2.1 Calibration Engine
In order to calibrate the item pool, the paper-based-
test must first be given to a representative sample
of examinees, whom we will name ”calibration stu-
dents”. The procedure is as follows:
1. Design a pool of MCQs of varying difficulties,
which covers a single instructional topic.
2. Give the paper-based-test to a representative sam-
ple of calibration students with varying compe-
tencies (ideally half are masters and half are non-
masters).
3. Choose a mastery cut-off score (eg. 85%).
4. Divide the calibration students into masters and
non-masters based on their test scores.
5. For each item in the question pool, calculate the
probabilities of correct and incorrect responses as
follows:
P(C
i
) = (#r
i
+ 1)/(#r
i
+ #w
i
+ 2) (1)
P(¬C
i
) = 1 −P(C
i
) (2)
P(C
i
| M) = (#T
im
+ 1)/(#T
im
+ #W
im
+ 2)
(3)
P(¬C
i
| M) = 1 − P(C
i
| M) (4)
P(C
i
| N) = (#T
in
+ 1)/(#T
in
+ #W
in
+ 2) (5)
P(¬C
i
| N) = 1 − P(C
i
| N) (6)
Such that, for an item i: P(C
i
), P(¬ C
i
), P(C
i
|
M), P(C
i
| N) is the correct answer probability, the
incorrect answer probability, the probability of a
correct answer by a master and the probability of
a correct answer by a non-master respectively.
This process and calculations is automated in our im-
plementation of the Editor which will be discussed in
4.
Subsequently, 3 parameters can be calculated for each
question in the question pool:
• Discrimination: Item discrimination is how dis-
criminating the item is between masters and non-
masters. It is calculated as follows:
D
i
= P(C
i
| M) − P(C
i
| N) (7)
A highly discriminating item is one of the ”golden
items” that only the master students were capable
of answering correctly and which subsequently
contributed to their high scores. This plays the
biggest role in test efficiency.
• Difficulty and Item/Examinee Incompatibility
Index: Not only do we want to render items of
high discrimination but we also want to render
items whose difficulty is compatible with the ex-
aminee’s current ability level estimate. An item’s
difficulty is the probability that this item is an-
swered incorrectly P(¬C
i
). The examinee’s ability
estimate E(θ
j
) is calculated to be comparable to
the items‘ difficulties. The incompatibility index
I
i j
is then the incompatibility between each item
difficulty and the examinee’s ability estimate.
E(θ
j
) = (#r
j
+ 1)/(#r
j
+ #w
j
+ 2) (8)
I
i j
= abs{(1 − P(C
i
)) − E(θ
j
)} (9)
• Utility: Finally, an item‘s utility parameter is es-
tablished, which is the ratio between discrimina-
tion and incompatibility index.
U
i j
= D
i
/(I
i j
+ 0.0000001) (10)
Extension to A,B, or C grade categories:
In order to extend the model to choose between 3 dis-
crete alternatives instead of 2, the students in the es-
timation sample would be divided into A, B, and C
students using 2 cut-off scores (A cut-off and B cut-
off) and the probabilities of correct and incorrect re-
sponses are incremented to accommodate A, B, and C
categories.
More importantly however, there will be three dis-
crimination parameters, and subsequently three util-
ity parameters instead of one, each discriminating be-
tween 2 of the 3 classification alternatives (D
i
{AB}),
(D
i
{BC}) and (D
i
{AC}). And thus utilities U
i j
{AB},
U
i j
{BC}, and U
i j
{AC}.
3.2.2 Inference Engine
After calibration is completed, the items are now
ready for the inference and selection engines. Here
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
192

is where the adaptivity function takes place. The CAT
continuously infers information about the user’s abil-
ity from their responses and accordingly selects ques-
tions for the user from the calibrated question pool.
The selected question always aims to classify the user
faster into one of the category levels and to match the
user’s estimated ability in real-time.
(i) The Scoring method in the CAT Expert System
follows a Bayesian process, where a likelihood
ratio (LR) is computed each time the user an-
swers a question:
LR =
P
om
∏
n
i=1
P(C
i
| M)
s
[1 − P(C
i
| M)]
f
P
on
∏
n
i=1
P(C
i
| N)
s
[1 − P(C
i
| N)]
f
(11)
For a numerical example of this Bayesian rea-
soning process, refer to (Frick, 1989).
(ii) The sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) then
determines the termination criterion by defining
the following 3 rules:
• Rule S1: if LR ≥ M
th.
, then stop and choose
master.
• Rule S2: if LR ≤ N
th.
, then stop and choose
non-master.
• Rule S3: if N
th.
< LR < M
th.
, then select an-
other item, update the LR, and apply the three
rules again.
Where, M
th.
is the mastery threshold and N
th.
is the non-mastery threshold, whose values are
calculated based on error rates established a-
priori (Wald, 1947).
Extension to A,B, or C grade categories:
To extend the scoring method, 3 likelihood ratios are
computed instead of 1. Each compares between 2 of
the 3 classification alternatives.
LR1 =
Prob(Examinee level is B)
Prob(Examinee level is C)
LR2 =
Prob(Examinee level is A)
Prob(Examinee level is B)
LR3 =
Prob(Examinee level is A)
Prob(Examinee level is C)
Then, for the termination criterion we define an
upper bound (UB) and a lower bound (LB) for each
likelihood ratio. For a user to be classified, for ex-
ample as a B student then LR1 must exceed its upper
bound UB1 and LR2 must be lower than the lower
bound LB2. This follows from Spray’s extension of
the SPRT (Spray, 1993).
• Rule S1: If (LR1 ≤ LB1) and (LR3 ≤ LB3), then
terminate and choose C student.
• Rule S2: If (LR1 ≥ U B1) and (LR2 ≤ LB2), then
terminate and choose B student.
• Rule S3: If (LR2 ≥ U B2) and (LR3 ≥ UB3), then
terminate and choose A student.
• Rule S4: Otherwise, select another question, up-
date the likelihood ratios and apply the 4 rules
again.
Where, LB1 and UB1 are the lower and upper bounds
for LR1 respectively, LB2 and UB2 for LR2 ..etc
In short, the CAT uses the likelihood ratios to con-
tinuously compare the alternatives of the user’s classi-
fication, and terminates when it has achieved enough
confidence that the user is more likely to be catego-
rized into one of the grade level categories as opposed
to all others.
3.2.3 Selection Engine
Selection in Frick’s EXSPRT model is based on max-
imum information search and select (MISS), in which
the user‘s achievement estimate E(j) is saved and con-
tinuously re-calculated each time they make a correct
or incorrect answer, as per equation 8, the item incom-
patibility index (Iij) is also continuously re-calculated
using equation 9. The selection algorithm then picks
the next selected item to be that of the greatest current
utility as per equation 10, which means that;
”It will be the remaining one which is most discrim-
inating between masters and non-masters, and least
incompatible with the examinee’s current ability level
estimate”.
In the extended model however, selection be-
comes a bit more challenging as there is no longer
one utility parameter but 3.
The selection engine uses the information pro-
vided by the inference engine and calculates 3 dis-
tance equations:
dA = (UB2 − LR2) + (UB2 − LR3). (12)
dB = (UB1 − LR1) + (LR2 − LB2). (13)
dC = (LR1 − LB1) + (LR3 − LB3). (14)
The minimum of the 3 distances is used to determine
which classification the user is closest to, each time
they make a correct or incorrect answer. Based on
this current information, it selects one of the 3 utility
parameters for ranking the items that quickens bring-
ing the user closer to their most likely classification.
3.3 Phase II: From CAT to CAL
With the ongoing adaptive difficulty feature at hand,
the CAT system works reasonably well on its own in
training the user. However, two important questions
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System
193

remain; what to do after the CAT test finishes and how
to benefit from its result. Accordingly, our proposed
technique serves as a continuation to the CAT test in
phase I. The approach was to use the test result along
with the information about the items to promote ques-
tions that most efficiently challenge the user’s estab-
lished ability. This is achieved by looking at the item
utility parameters from a different perspective.
During a CAT, after each user’s response, the re-
maining items are sorted according to one of the 3
item utilities U
i j
{AB}, U
i j
{BC}, and U
i j
{AC}, de-
pending on the classification to which the user is cur-
rently closest to. Hence, the sorting utility is different
each time they make an answer.
Alternatively, in Phase II the sorting utility is
fixed based on the CAT’s final classification re-
sult to be one of another set of 3 item utilities
{U
i j
{AB},U
i j
{BC},U
i j
{A}} for the remainder of the
session. Where U
i j
{A} is a 4th item utility parameter
which is calculated according to the following equa-
tion:
U
i j
{A} = P(¬C
i
| A)/I
i j
(15)
The following algorithm follows after the user has
been classified by the CAT:
• If the user is a C student, fix the ranking utility to
be U
i j
{CB}.
• If the user is a B student, fix the ranking utility to
be U
i j
{AB}.
• If the user is an A student, fix the ranking utility
to be U
i j
{A}.
By intuition, we consider the following compari-
son: On the one hand, from an assessment perspec-
tive, ranking items according to their U
i j
{AB} means
sorting them according to how useful they are in dis-
criminating between A and B level categories to speed
up the classification process. On the other hand,
from a training perspective, ranking items according
to U
i j
{AB} promotes the items whose likelihood of
an A student responding correctly is higher than the
likelihood of a B student responding correctly. And
thus could be viewed as sorting the items according
to how beneficial they are in efficiently training a B
student to become an A student.
The same goes for U
i j
{AB}. Moreover, if the user
is identified as an A student, then we do not have a
higher level to transition them to and so we target the
questions that A students answer incorrectly, by fixing
the ranking utility to be U
i j
{A}.
Summing up, the CAT in phase I aims to effi-
ciently classify the user (examinee) into an A, B, or
C student, and after it has terminated, phase II starts
in which we continue to update the user (trainee)’s
achievement estimate every time they make an an-
swer, as well as, the incompatibility index for each
item to maintain compatibility between the next
selected item’s difficulty and the user’s ongoing
achievement -ie. real-time adaptivity doesn’t stop.
Furthermore, item selection is fulfilled by using
the CAT’s result to fix the ranking parameter to be the
item utility that would efficiently transition the user
into the next higher level.
Hence, training could continue until all the ques-
tions have been rendered or until the user decides to
stop and restart the test.
4 SYSTEM APPLICATION
We applied the CAL system to a platform of serious
games designed to render MCQs to the user. The plat-
form was augmented with an ”Editor” to be used by
educators to supply the platform with different pools
of MCQs and set up their own adaptive training sys-
tem, making the system generic and democratic.
4.1 Editor
To create their own CAL system, the educator should
follow steps 1 and 2 listed in 3.2.1. Then, the edu-
cator uses the editor to supply the platform with the
collected information and set up a fully functioning
CAL system of their own question pool.
This is achieved in 3 stages: The first stage is
where the educator types the MCQs and their respec-
tive answer choices, and saves them for calibration. In
the second stage, the educator supplies the students’
responses from the paper-based tests to each of the
questions as in figure 2. This is needed to calculate
the probability equations 1 through 6. First the edu-
cator states the number of students that took part in
the paper-based tests, and then a list is created. For
each student, the educator should supply the response,
whether correct or incorrect, to each question in the
registered question pool, and using arrow keys they
could navigate through the questions.
A critical factor that determines how the CAL will
perform is choosing the A cut-off and the B cut-off.
If the test was well designed and the students were
carefully selected, ideally the students would be dis-
tributed evenly among the 3 grade categories, how-
ever this is not always the case. Therefore, the third
and final stage is designed to give the educator statis-
tics about the student distribution based on a chosen
cut-off score.
The following distribution scales are produced
that distribute the students in the estimation sample
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
194

(a) Stage 2
(b) Stage 3
Figure 2: The Editor.
into the 3 level categories according to their result
scores. By clicking one of the scales, the educator can
view the A and B cut-off scores that would be needed
to achieve that specific distribution. These scales are:
• The uniform scale, where the number of students
is uniformly distributed among the 3 level cate-
gories.
• The average scale, where most of the students are
categorized as B-level (average) students.
• The excellence scale, in which the higher the
level, the fewer the students that qualify for it.
• The extremity scale, in which there are more stu-
dents around the two extreme level-categories A
and C than there are in the middle level-category
B.
• The underdog scale, in which there more students
are classified as high achievers.
The educator then saves the chosen scores to fi-
nalize the 3 calibration stages and publish their fully
adaptive MCQ game.
5 TESTING AND
EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
5.1 Calibration Phase
To test the system, we asked a college professor to
provide us with an MCQ question pool that tests a
pathology topic. We further instructed the educator
to design and divide the question pool into 3 levels,
the first level consists of 13 very easy questions, the
second level consists of 13 questions of medium dif-
ficulty, and the third level consists of 20 very difficult
questions.
5.2 Two Versions
Figure 3.
Then, we created a games platform that rendered the
questions to the student. We created two separate ver-
sions of the platform summarized in the above tree
diagram, as part of a comparative study to evaluate
different learning parameters.
The first version uses the calibrated question pool
and operates the CAL system, while the game me-
chanics and user interface remain consistent through-
out all the games. The second version applies the
adaptivity feature proposed by (Salah et al., 2018)
where the game mechanics and UI adapt to the user’s
emotional state. The emotions are reported in be-
tween games using the Self Assessment Manikin
(SAM) described in (Salah et al., 2018) and the dif-
ferent game metrics are modified according to table
1.
Table 1: Mapping Emotion to Timer and Music.
Emotion / Metric Timer Music
Boredom Decrease time limit Play active music
Frustration Increase time limit Play relaxing music
Relaxed Decrease time limit No change
Table 2: Mapping Emotion to Theme Color and Scoring.
Emotion / Metric Theme Color Scoring Method
Boredom Red Increase penalty
Frustration Increase time limit Play relaxing music
Relaxed Decrease time limit No change
For the second version, we created another ran-
domized selection algorithm to be able to compare it
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System
195

to the CAL system. It selects a total of 21 questions
(less than half the question pool) from the 3 difficulty
levels designed by the educator: 7 questions randomly
selected from the easy difficulty level, followed by 7
questions randomly selected from the medium diffi-
culty level, and finally 7 questions randomly selected
from the high difficulty level.
In this way the randomized selection algorithm
has no bias towards any one level, and operates in
the conventional manner of increasing the difficulty
sequentially (non-adaptive). It doesn’t skip questions
the way the CAL system does if the user is perform-
ing well, and it is indifferent to the user’s skill level so
it can render questions that are too easy or too difficult
compared to the user’s ability.
Finally, with all things considered, we aligned
both systems to be as alike as possible wherever the
adaptivity features are not concerned. The user repet-
itively plays the games back to back until they finish
answering the 21 questions, after which, the session
abruptly ends.
5.3 Design and Procedure
We invited 50 students that were currently enrolled in
the Pathology course to take part in the experiment.
The age range was from 20 to 22. They were ran-
domly and evenly divided amongst the two versions
of the game so that 25 played in each one, however
they did not know which version they were assigned
to, and they all participated in the following 3 tests:
• Learning Gain: This test consists of a paper-
based pre-test and post-test taken before and af-
ter playing the game. The two tests were iden-
tical and consisted of the full set of 46 MCQs,
which was used in the computer systems. The dif-
ference between the student’s score on both tests
comprised their learning gain.
• Exposure Efficiency: This test was designed to
quantifiably compare the efficiency of the two se-
lection algorithms. It evaluates how many ques-
tions the algorithm was able to successfully target
and render out of all the questions that the student
answered incorrectly in their pre-test, within the
game’s ”21 Questions Period”.
This is achieved by first, marking the questions
that the student answered incorrectly on the pre-
test. Then, we log all the questions that are ren-
dered to the user during the game in a text file. Fi-
nally, we match and mark the questions rendered
to the user which they had answered incorrectly in
the pre-test, and calculate the exposure efficiency:
Exposure E f f iciency =
w
e
w
(16)
Where,
– w: number of questions answered incorrectly
on the pre-test.
– w
e
: number of questions answered incorrectly
on the pre-test and were rendered in the game.
• Engagement Level: This test is a standardized
questionnaire (Pearce et al., 2005) used to test
the engagement level of the student. The student
is asked to rate agreement to different questions
measuring their level of enjoyment and control
throughout the experience. The mean of their rat-
ings is finally calculated.
An independent t-test was used to analyze the
results of the comparative tests with a significance
threshold of p =< 0.05.
The CAL selection algorithm in version 1 is com-
pared to the randomized selection algorithm in ver-
sion 2 in terms of learning gain, and exposure effi-
ciency, where the learning gain describes what infor-
mation the student actually remembers. Whereas, ex-
posure efficiency describes the selection algorithm’s
efficiency in exposing the user to questions they
hadn’t already known.
The engagement of the CAL’s adaptive difficulty
in version 1 is compared against that of the emotional
adaptivity feature in version 2.
6 RESULTS
Table 3: Mean and Standard Deviation for the different
tests.
V1: CAL Adaptivity V2: UI Adaptivity
Learning Gain M=24.1 , SD=6.89 M=17.5 , SD=7.49
Exposure Efficiency M=0.494 , SD=0.092 M=0.411 , SD=0.066
Engagement M=2.17 , SD=0.451 M=2.05 , SD=0.565
Table 4: Test Results and Significance
(RQ1) Learning Gain CAL Group > UI Group
mean diff=6.6 , p=0.002
95% CI, 2.51 - 10.69
(RQ2) Exposure Efficiency CAL Group > UI Group
mean diff=0.083 , p < .001
95% CI, 0.038 - 0.129
(RQ3) Engagement No significant difference.
mean diff=0.116 , p=0.455
95% CI, -0.195 - 0.427
The results (tables 3 & 4) showed that both the learn-
ing gain (RQ1) and the exposure efficiency (RQ2)
for the group that used the CAL adaptive difficulty
version of the platform were significantly higher than
those for the group that was exposed to the version
were the game mechanics and UI adapted to user’s
emotional state and where the questions’ selection
was random (p=0.002, p < .001 respectively). How-
ever, there was no significant difference between both
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
196
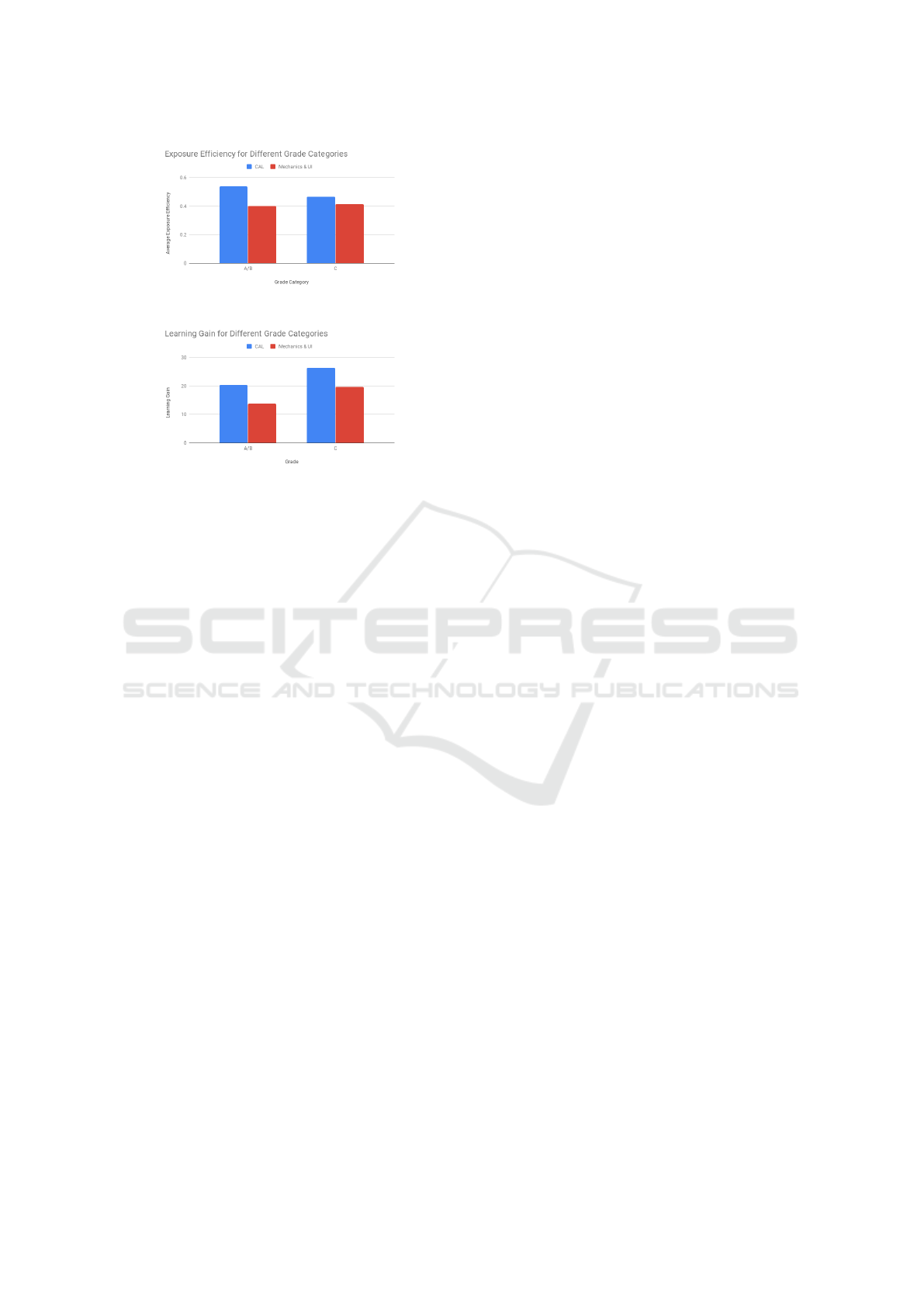
(a) Exposure efficiency for different grade cate-
gories.
(b) Learning gain for different grade categories.
Figure 4: Independent T-tests for different Grade Cate-
gories.
versions of the system on the engagement level of the
students (RQ3).
Furthermore, we divided the students from each of
the sample groups to those who scored higher than the
B cut-off on the pre-test and those who scored lower.
We ran separate t-tests for these faceted grade cate-
gories.
Results from the A/B students showed that expo-
sure efficiency resulting from the group that used the
CAL version was significantly higher than that of the
other group that used the Emotional adaptivity ver-
sion (p = 0.001) with a mean difference of 0.152.
On the other hand, results from the C students
showed that exposure efficiency resulting from the
group that used the CAL version was not significantly
higher than that of the other group that used the Emo-
tional adaptivity version(p = 0.069) with a mean dif-
ference of 0.044.
7 DISCUSSION
Our results showed that the proposed CAL system
was successful in improving the learning gain of the
students across all grade categories, as well as effi-
ciently training them with questions that challenged
their skill level.
Furthermore, amongst C students exposure effi-
ciency was not significantly higher for the CAL al-
gorithm when compared to that of the randomized se-
lection algorithm [figure 4a]. This proves the point
that the CAL’s efficiency is most effective with A and
B students as they are the ones who benefit from skip-
ping questions, while C students would make a lot of
mistakes and would thus benefit from any manner of
exposure. Nevertheless, the significant difference be-
tween the two systems’ learning gain results for C stu-
dents [figure 4b] proves that exposure does not equal
learning which reflects the benefit of the CAL’s com-
patibility index when dealing with C students.
On the other hand, there was no significant differ-
ence in the engagement level between the two adap-
tivity features.
Among the limitations, the students playing the
emotionally adaptive version of the game usually re-
ported they were feeling ”excited”. According to the
system’s implementation ”excitement” is a desirable
learning emotion, thus no noticeable changes were
made in the game. Another limitation was that the
session was fairly short with few switches between
game scenes, so the user did not get a chance to expe-
rience all the changes that correspond to the different
emotional reports. As a result, the emotional adaptiv-
ity feature might have been latent for several partici-
pants.
According to our study, the designed adaptive al-
gorithm effectively improves students’ learning, with
only 50 students needed to calibrate the question pool
dataset as opposed to 500 and 1000. This makes this
system much less burdensome for ICT-agnostic edu-
cators who wish to create their own adaptive learning
programs. Future work would be needed to test the
usability of the Editor (4.1) for different educators.
8 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we designed an item-based computer
adaptive learning/training system (CAL). It trains the
learner by rendering items that most efficiently transi-
tions them into a higher mastery category and whose
difficulty is compatible with the learner’s ability, esti-
mated from their ongoing performance. The designed
system also enables the educator to publish their own
adaptive learning program and to reuse it with differ-
ent question pools. A comparative experiment was
conducted on 2 adaptive versions of a learning plat-
form, version 1: operated the CAL adaptive difficulty
system, and version 2: adapted the game mechanics
and UI to the user’s emotions while increasing the
difficulty sequentially. Results showed that (RQ1)
version 1 significantly improves the learning gain of
students when compared to version 2, (RQ2) version
1 exposes students to questions more efficiently than
version 2, however (RQ3) engagement was found not
to differ between the two systems.
A-Learning: A Computerized Adaptive Learning Expert System
197

REFERENCES
Banerjee, A. V., Cole, S., Duflo, E., and Linden, L. (2007).
Remedying education: Evidence from two random-
ized experiments in india. The Quarterly Journal of
Economics, 122(3):1235–1264.
Banerjee, A. V. and Duflo, E. (2011). Poor economics : a
radical rethinking of the way to fight global poverty,
chapter 4 - Top of the Class, pages 188–196. Publi-
cAffairs.
Birnbaum, A., Lord, F., and Novick, M. (1968). Statistical
theories of mental test scores. Some latent trait mod-
els and their use in inferring an examinee’s ability.
Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
Doignon, J.-P. and Falmagne, J.-C. (2012). Knowledge
spaces. Springer Science & Business Media.
Eggen, T. J. (2012). Computerized adaptive testing item
selection in computerized adaptive learning systems.
Psychometrics in Practice at RCEC, page 11.
ElKomy, M., Abdelrahman, Y., Funk, M., Dingler, T.,
Schmidt, A., and Abdennadher, S. (2017). Abbas: an
adaptive bio-sensors based assistive system. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2017 CHI conference extended ab-
stracts on human factors in computing systems, pages
2543–2550.
Freedle, R. O. and Dur
´
an, R. P. (1987). Cognitive and
linguistic analyses of test performance, volume 22.
Ablex Pub.
Frick, T. W. (1989). Bayesian adaptation during
computer-based tests and computer-guided practice
exercises. Journal of Educational Computing Re-
search, 5(1):89–114.
Frick, T. W. (1992). Computerized adaptive mastery tests
as expert systems. Journal of Educational Computing
Research, 8(2):187–213.
Funk, M., Dingler, T., Cooper, J., and Schmidt, A. (2015).
Stop helping me-i’m bored! why assembly assistance
needs to be adaptive. In Adjunct Proceedings of the
2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Perva-
sive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of
the 2015 ACM International Symposium on Wearable
Computers, pages 1269–1273.
Giannandrea, L. and Sansoni, M. (2013). A literature re-
view on intelligent tutoring systems and on student
profiling. Learning & Teaching with Media & Tech-
nology, 287:287–294.
Kingsbury, G. G. and Weiss, D. J. (1983). A comparison
of irt-based adaptive mastery testing and a sequential
mastery testing procedure. In New horizons in testing,
pages 257–283. Elsevier.
Linssen, J. (2011). Adaptive learning in an educational
game–adapting game complexity to gameplay in-
creases efficiency of learning. Master’s thesis.
Lord, F. (1980a). Application of item response theory to
practical testing problems. first. Hilsdale, New Jersey,
EUA: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Lord, F. M. (1980b). Applications of item response theory
to practical testing problems. Routledge.
Luk, H. (1991). An empirical comparison of an expert sys-
tems approach and an irt approach to computer-based
adaptive mastery testing.
Pandarova, I., Schmidt, T., Hartig, J., Boubekki, A., Jones,
R. D., and Brefeld, U. (2019). Predicting the difficulty
of exercise items for dynamic difficulty adaptation in
adaptive language tutoring. International Journal of
Artificial Intelligence in Education, 29(3):342–367.
Park, J. Y., Joo, S.-H., Cornillie, F., van der Maas, H. L., and
Van den Noortgate, W. (2019). An explanatory item
response theory method for alleviating the cold-start
problem in adaptive learning environments. Behavior
research methods, 51(2):895–909.
Pearce, J. M., Ainley, M., and Howard, S. (2005). The ebb
and flow of online learning. Computers in human be-
havior, 21(5):745–771.
Pedro, F., Subosa, M., Rivas, A., and Valverde, P. (2019).
Artificial intelligence in education: Challenges and
opportunities for sustainable development.
Pliakos, K., Joo, S.-H., Park, J. Y., Cornillie, F., Vens, C.,
and Van den Noortgate, W. (2019). Integrating ma-
chine learning into item response theory for address-
ing the cold start problem in adaptive learning sys-
tems. Computers & Education, 137:91–103.
Reckase, M. D. (1983). A procedure for decision mak-
ing using tailored testing. In New horizons in testing,
pages 237–255. Elsevier.
Salah, J., Abdelrahman, Y., Dakrouni, A., and Abdennad-
her, S. (2018). Judged by the cover: Investigating the
effect of adaptive game interface on the learning expe-
rience. In Proceedings of the 17th International Con-
ference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Multimedia, pages
215–225. ACM.
Schmitt, S. A. (1969). Measuring uncertainty: An ele-
mentary introduction to Bayesian statistics. Addison-
Wesley.
Solovey, E. T., Lalooses, F., Chauncey, K., Weaver, D.,
Parasi, M., Scheutz, M., Sassaroli, A., Fantini, S.,
Schermerhorn, P., Girouard, A., et al. (2011). Sens-
ing cognitive multitasking for a brain-based adaptive
user interface. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages
383–392.
Spray, J. A. (1993). Multiple-category classification using
a sequential probability ratio test.
Wald, A. (1947). Sequential analysis, john wiley & sons.
New York, NY.
Wauters, K., Desmet, P., and Van Den Noortgate, W. (2010).
Adaptive item-based learning environments based on
the item response theory: Possibilities and challenges.
Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 26(6):549–
562.
Yoes, M. (1995). An updated comparison of micro-
computer based item parameter estimation procedures
used with the 3-parameter irt model. Saint Paul, MN:
Assessment Systems Corporation.
Zawacki-Richter, O., Mar
´
ın, V. I., Bond, M., and Gou-
verneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of re-
search on artificial intelligence applications in higher
education–where are the educators? International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Educa-
tion, 16(1):1–27.
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
198
