
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture
Iraklis Katsaris
a
, Ilias Logothetis, Konstantinos Katsios and Nikolaos Vidakis
b
Department of electrical and Computer Engineering, Hellenic Mediterranean University, Stauromenos, Heraklion, Greece
Keywords: Blended Learning, Adaptive Learning, Platform’s Architecture, Education, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Developing
4Cs.
Abstract: In recent years institutions try to adapt their courses based on the students' needs. Research is focused on what
data to extract from students and how to use them to provide personalized learning material. This article
introduces the architecture of an Adaptive Blended Learning Platform that aims to help students develop 4Cs.
The suggested platform is based on the principles of Bloom’s Taxonomy, the Felder-Silverman Learning
Styles Model and Blended Learning. A simple interface is provided to the teacher to create and manage
courses and classroom material. Additionally, through the platform personalized worksheets for a selected
course are created. For the creation of such worksheets an algorithm acts as an assistant to the teacher that
suggests which learning objects suit each student better. Finally, the materials available to students consist of
digital and non-digital tools to make them more active and to stimulate their interest, such as activities,
exercises and games that can be practiced both at classroom and at home.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional methods of teaching in schools need to be
modernized and adapted to the context of 21st-
century society. Adaptive and Blended learning
methods are some of the modern approaches in the
field of education. Research shows that the use of
different educational methods combined with
technology creates a more positive attitude towards
the learning process and at the same time motivates
students to increase their grades (Abdul Latif &
Lajiman, 2011). The curriculum often consists of a
sole textbook that teachers are required to consult
although many times this does not suffice to
correspond to the diversity of a classroom. Nowadays
we move away from the norm "one size fits all" and
attempt to create courses compatible with the needs
and preferences of each student.
As Kolb (1984) states, each person learns
differently, so it is not appropriate to follow a specific
learning sequence. Adaptive learning is characterized
by the educational process of receiving data on the
knowledge, learning style, learning tools, and of
assessing each student. According to these data, this
learning method tries to adapt the educational process
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1410-0822
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0726-8627
to the needs and preferences of each student (Morze
et al., 2021). Teachers can contribute to the
integration of educational theories and give directions
for a more personalized learning process in order to
improve the content and the quality of a lesson. The
evolution of technology has enabled the creation of
many adaptive e-learning platforms that support
Learning Styles for the personalization of the learning
process (Katsaris & Vidakis, 2021). A learning
system tailored to each student's needs and learning
style provides additional motivation to help them
reach their full potential (Popescu et al., 2009).
Besides the educational theories, there are
cognitive theories that can be incorporated in the
learning process. Such a theory is the Revised
Bloom’s Taxonomy (RBT) that describes a
framework for the classification of learning
objectives (Krathwohl, 2002). This framework
provides six cognitive levels which are used for the
learning session design and guides students from
lower order (remembering, understanding) to higher
order (applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating)
thinking skills.
For the development of the aforementioned higher
order thinking skills the widely known 4Cs of 21st-
Katsaris, I., Logothetis, I., Katsios, K. and Vidakis, N.
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture.
DOI: 10.5220/0010998700003182
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2022) - Volume 2, pages 251-259
ISBN: 978-989-758-562-3; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
251

century skills can be of assistance. These skills
include:
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: In this
process, students discover hypothetical solutions to a
problem and by processing those solutions they
culminate in the most effective (Butler, 2012).
Communication: Communication constitutes an
individual's ability to understand, share, and
communicate thoughts, ideas, questions and solutions
through written or oral speech (Pheeraphan, 2013).
Collaboration: It is an individual's ability to
respect and cooperate with other individuals
(Pheeraphan, 2013). Students work on a project
towards achieving a goal while creating new
knowledge through this process (Sharratt, L. &
Planche, 2016).
Creativity: Creative thinking enables humans to
be able to produce a variety of ideas, have flexibility,
and be able to provide solutions to various daily life
problems (Yuliati & Lestari, 2018).
According to the ‘Partnership for 21st Century
Skills’ (P21, 2015b), every child in America, in order
to succeed as an effective citizen, employee, or even
a leader, should be equipped with the skills of the 21st
century.
Pedagogical methods nowadays use technology to
improve the learning process, combining both
traditional methods and software and aiming at the
involvement of students to a great extent (Nikolaos
Vidakis et al., 2017). Blended learning consists of two
main “components”: face-to-face instruction and
computer-mediated instruction to create a
personalized educational process which will facilitate
students' learning (Horn & Staker, 2011). The
blended learning method provides several advantages
such as increased flexibility in student learning and
increased student control in their learning
environment (Horn & Fisher, 2017). This can result
in students becoming more actively involved in the
lesson, more efficient, and discovering the teaching
method that suits them best (Liu et al., 2016; Zaharah
Hussin et al., 2015). An implementation of blended
learning is the flipped classroom method that incites
a student to study at home and solve questions and
exercise the studied content in the classroom (Huang
& Hong, 2016).
In a previous study about Adaptive e-learning
systems through learning styles (Katsaris & Vidakis,
2021) we observed that most Adaptive systems do not
follow a pedagogical theory and the majority of
research is conducted in higher education. As a result
and based on the main principles of the IOLAOS’
architecture (Vidakis et al., 2015) we developed an
educational platform incorporating the principles of
Bloom’s Taxonomy, the Felder-Silverman Learning
Styles Model and Blended Learning in order to
maturate the 4Cs of students, aiming to support the
lower levels of education (primary school).
2 RESEARCH BACKGROUND
An important element of Blended learning is
personalized education. As the teacher has
acknowledged the difficulties and weaknesses of the
students, he/she is capable of providing them with
appropriate assistance through targeted exercises.
The main goal of this method is to allocate
personalized education to the students by means of
home learning. Regarding the systems that will
support the adaptive blended learning platform, many
research proposals differ significantly from each
other, but all of them offer personalized learning
opportunities to the students and direct information to
the teacher.
Modern blended learning platforms offer the
ability to personalize education through targeted
exercises and activities such as that of Mohamed &
Lamia, (2018) which is focused on mathematics and
logic subjects/lessons. The use of the flipped
classroom enabled students to use their time at home
to study key concepts and then the teacher managed
to focus on developing 4Cs through the problem-
based learning method. As a result, students
performed better, needed less time and less mental
effort to find solutions to problems.
In another attempt at higher education
(Kakosimos, 2015) micro-adaptive instruction
methodology was applied using behavioural data,
self-assessment and performance information of
students. Accordingly, the students demonstrated an
increasing efficiency in the fields of perception,
engagement, motivation and an overall improvement
towards the control group.
Lai & Hwang, (2016) tried to explore the potential
of the adaptive flipped classroom by initially
assigning study material and quizzes for home study.
Then, they created a self-regulated learning system
that contains four (4) groups: an out-of-class learning
system, a self-regulated monitoring system, a teacher
management system and a database. The
differentiation and the innovation they achieved is
that each student can set his/her learning goals and
evaluate his/her learning performance before and
after the courses. Teachers can track their students'
performance, while the platform provides them with
analysis based on the teacher’s criteria of self-
regulation and the students’ learning logs from the
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
252
out-of-class studying and the self-regulated
monitoring system.
Respectively, in other efforts emphasis was given
to the development of motivation of students such as
in Lamia et al. (2019). The Flipped classroom method
was invoked based on the Context-Aware mobile
learning system (FC-CAMLS) on the English
Linguistics module. The results of the study showed
positive effects on students' learning outcomes, skills
and motivation.
In addition, the study by Gunawan et al., (2020)
created an Intelligent Tutoring System that supports
blended learning to assist secondary science teachers
in creating innovative course plans. Through this
system basic skills are organized into a common
learning theme, students develop higher order
thinking skills and become more active in learning.
Furthermore, it allows the development of higher-
order thinking skills and perceived assessment
patterns fitting in learning.
Finally, an interesting suggestion from Alsowat,
(2016) is to differentiate the platform into two levels
based on Bloom’s taxonomy. The first is related to
lower-order thinking skills and takes place outside of
school, while the second concerns the higher-order
thinking skills taking place inside school. As a result
of their effort, students extended their engagement in
the classroom and their overall satisfaction.
This study indicates that students prefer
autonomous learning that involves technology over
the traditional techniques. Additionally, it expounds
that student activity in the classroom is derived
through the way teaching is carried out.
Objective
The main purpose of the platform is: (a) to create an
innovative theoretical educational model combining
the RBT, adaptive and blended learning theories; and
thus, to provide teachers with a fast and flexible way
of preparing courses and (b) the innovative theoretical
educational model will be supported by a digital
platform that will enable the teacher to create
individual worksheets for each student based on
his/her learning style and cognitive level. At the same
time, the worksheets generated by the platform will
help students to develop 4Cs in a Blended Learning
environment.
Specifically, the objectives of the platform are:
Personalize each student’s worksheets based
on their needs.
Provide the opportunity for each student to
develop new skills.
Allow students to continue learning after
school hours.
Assist the teacher to create personalized
worksheets based on a selected learning
subject.
Monitor the students’ progress by the teacher.
3 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
The system aims for the creation of Adaptive Blended
Learning Worksheets that will encourage learners to
develop low and high order thinking skills. Figure 1
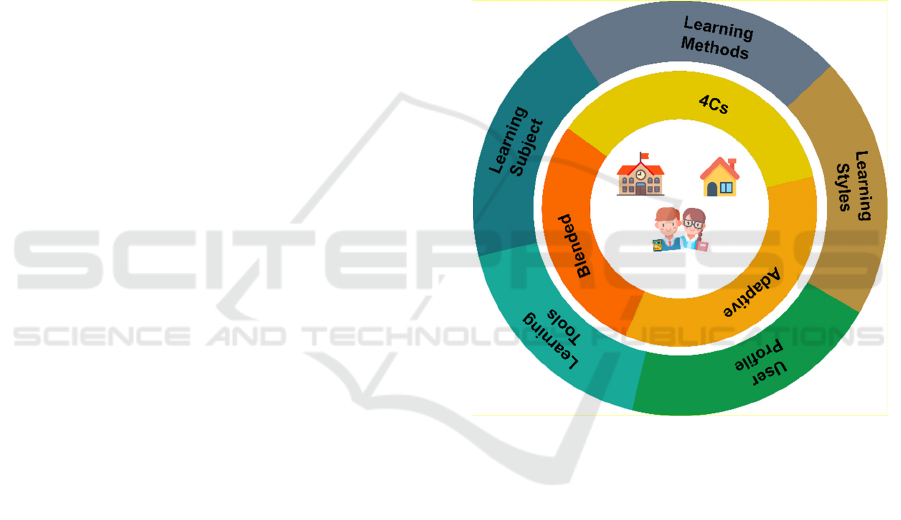
presents the basic concept of the platform. It is a
student-centred approach that attaches importance to
the abilities, inclinations and needs of each
individual.
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework.
The framework allows the learning process to
continue from school to home and vice versa. Finally,
several parameters, methods and tools are used to
produce personalized worksheets, like learning
styles, user profile, learning tools and learning
subjects.
The main features of the innovative theoretical
educational model of the platform are Blended
Learning, Adaptive Learning and 4Cs. Blended
Learning was chosen to provide an agile approach to
the lesson. The second feature is adaptability. A
unique learning path containing a combination of
exercises, activities and assessments reflecting the
needs and preferences of a student can elevate the
learning process. The third feature is the effort to
develop 4Cs through teaching. Students should
develop knowledge and be able to apply it to
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture
253
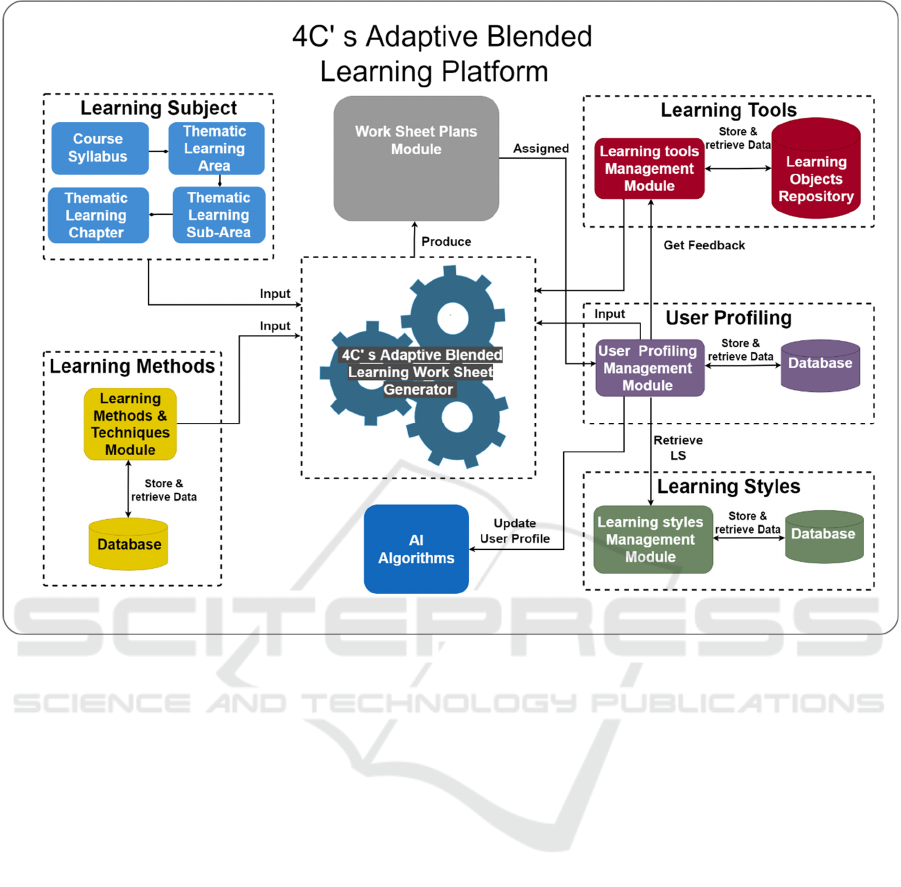
Figure 2: Architecture.
everyday problems. In this framework, 4Cs growth is
achieved through high order thinking skills of RBT.
These principles will be implemented on a digital
platform that students and teachers will use for an
innovative personalized learning experience. The
platform will provide a simple interface for the
teacher to create worksheets and make suggestions
about the learning objects each worksheet should
include. Students will be able to access all their
worksheets from a common interface that will allow
them to complete their homework and collaborate
with each other if necessary.
3.1 Platform Architecture Supporting
the Theoretical Framework
Figure 2 illustrates the architecture of the platform. It
is separated into five components that hold the
information necessary for the creation of a worksheet,
a component responsible for the generation of the
worksheets, and AI algorithms that will be used for
the student’s user profile. In the following paragraphs
we describe each component in detail.
3.1.1 Learning Subject
This component is responsible for the information
required during the creation and selection of a
learning subject. Learning components includes the
information of the learning syllabus, thematic
learning areas, sub-areas and finally the learning
chapter. This information is hierarchically organized
in a manner that each learning syllabus contains the
thematic learning areas, a subset of thematic learning
sub-areas and so on. For instance, if teachers choose
the course syllabus of the sixth grade they will have
the option to select the thematic learning area of
maths that corresponds to that grade; in the thematic
learning sub-area, the decimal sub-area can be found
as it is included on the sixth grade maths curriculum,
and finally the subtraction of decimal numbers can be
selected as the thematic learning chapter.
3.1.2 Learning Methods
Learning Methods comprise the six cognitive levels
of RBT (remembering, understanding, applying,
analysing, evaluating and creating) and the types of
activities each level contains. The purpose of this
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
254

component is to filter the Learning Tools based not
only on the teacher’s choices but also on students’
preferences and abilities.
3.1.3 Learning Tools
Learning tools’ component represents methods, types
and assistance for the creation of learning objects.
They are mainly divided into non-digital and digital.
The former are related to traditional education and are
connected to activities (In classroom) such as
STEAM challenges, while the latter capitalizes on the
advancements of technology (out-of-classroom).
Each learning tool contains tags so that learning style
preferences and cognitive level can be identified by
them. Furthermore, learning objects have tags,
indicating the learning subject, the difficulty level of
the activity and necessary information that is required
by learning objects (title, duration, and more).
Learning tools will be able to collect information
about the student's progress and behaviour so that the
platform can perform data analysis with the intention
to update the user profile of the learner and provide
better personalized content in the future. In case of
non-digital learning objects the information retrieval
will be field in by the teacher.
3.1.4 User Profile
User profile is maybe the most crucial component of
the platform, as it includes the information about the
user’s preferences, performance and behaviour. This
component provides the core features to assemble the
adaptivity in the platform. The user profile will be
updated each time the student completes a worksheet
to ensure that the student will always receive
worksheets that correspond to their current needs. An
important element of the user profile module is to
provide suitable material and feedback, after each
activity, to the learner. The feedback is implemented
in the form of a rating system in an effort to be short
and easy to complete; a small form in which the
learner can provide more information about the
experience of the activities is also available as an
optional step. As designed, the initiation of the user
profile will contain demographic information about
the learner (name, grade, etc.) while the learner is also
invited to answer a questionnaire to set up the starting
learning style preferences.
3.1.5 Learning Styles
In this component the characteristics of Learning
Styles Theories and their respective questionnaires
are defined. It is designed as a separate component
and not embedded in the user profile to support more
Learning Styles in the future if necessary.
3.1.6 Worksheet Generation Engine
The first step of the worksheet generation engine is to
shorten the search range to the learning objects that
are compatible with the teacher’s selection. For this,
we query the learning objects (referred as LOs) and
retrieve a subset 𝑁
⊆𝐿𝑂𝑠 where “m” is the
Learning Method chosen by the teacher and “c” is the
course.
The second step is to filter the retrieved learning
objects ( 𝑁
⊆𝐿𝑂𝑠) to denote the most possible
matches for a user. In detail, we calculate the
similarity of the learning style as well as the distance
(dissimilarity) between 4Cs between each learning
object and the user profile. It is worth noted that we
prefer learning style similarity and 4Cs dissimilarity
to be high as this means that the user is comfortable
with the content of this learning object but needs to
work more on the respected 4Cs.
The third step is to find what the ratings and
scores other users similar to the user have for a
learning object. This is calculated by using
normalized cosine similarity between users.
Furthermore, we calculate with the same method the
ratings and scores the user to similar learning objects.
Each score retrieved from the previous steps is
used to calculate the final score represented the
suitability of the learning object to the user. We
calculate this score with the following equation:
𝑓
𝑐∗𝑤
𝑙∗𝑤
𝑠∗𝑤
𝑢∗𝑤
Where “c” is the 4Cs similarity, “l” is the learning
styles similarity, “s” is the average score of suitability
a learning object has from similar users, “u” is the
average score of suitability obtained by similar
learning objects completed by the user, and with a
corresponding weight “w” each one.
After each learning object has assigned a
suitability score, we group them based on the
Learning Method level. Then we recommend to the
user the learning object with the highest suitability
score from each group.
3.2 Roles
The platform offers a gradation of classification
levels into four roles (Figure 3) besides the
administrator role. This allows the separation of
functionalities into the qualified persons for each
task. Each role and their responsibilities are described
in detail below.
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture
255
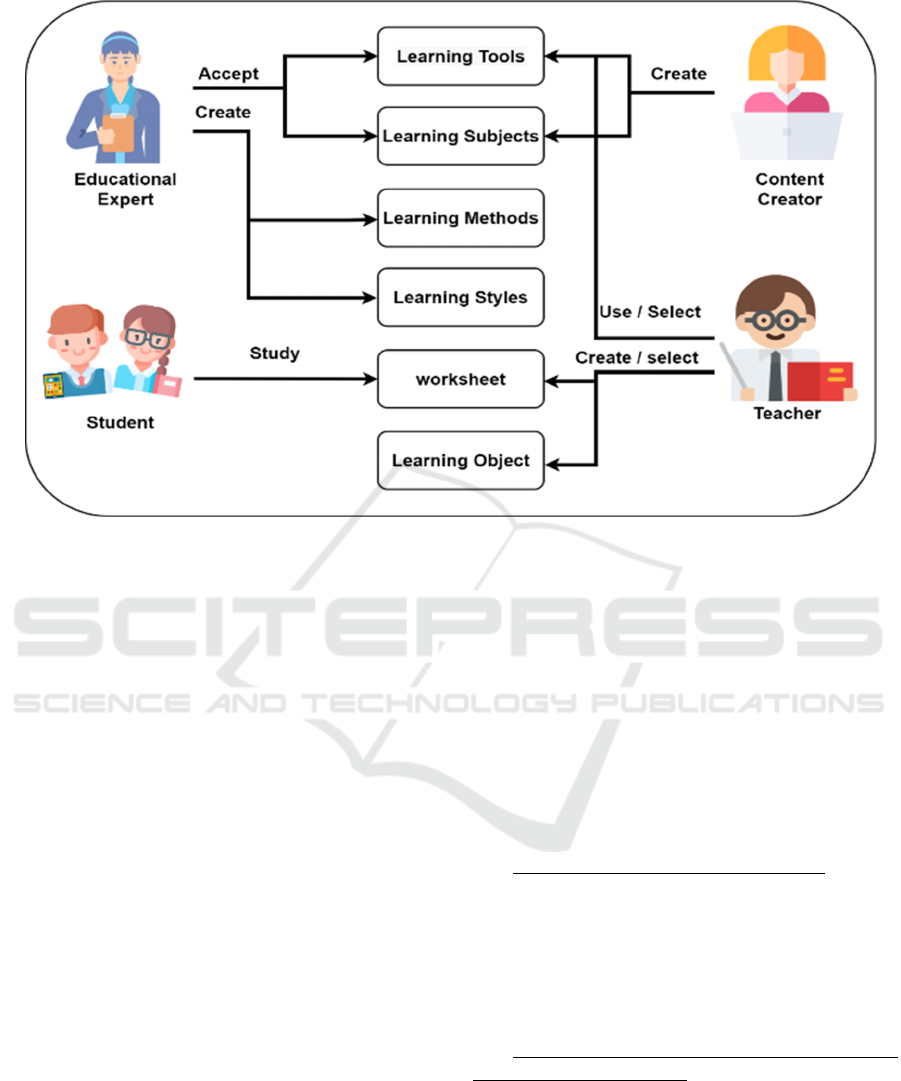
Figure 3: User roles.
Student: The role of a student is to study and
complete worksheets. The student should be able to
use the platform to receive worksheets and read their
content as well as edit specific fields that the student
is invited to fill. When a student completes a
worksheet he/she should be able to provide feedback
on how difficult and enjoyable the worksheet was.
Teacher: The teacher should be able to create
worksheets or select from a list of predefined generic
worksheets. Additionally, for the creation of a
worksheet the teacher have permission to select and
use Learning Subjects and Learning Tools. Through
this process new learning objects can also be created.
Content Creator: The role of content creator is
to create new learning tools and learning subjects for
the platform. This role is filled by persons studying
the literature to extract innovative educational
techniques and to subsequently include them into the
platform as learning tools. Moreover, this role
undertakes the responsibility to check the updates on
the course syllabus and update the learning subjects
or add new ones accordingly.
Educational Expert: Educational experts should
validate the content provided by the content creators
and accept it as valid material for the platform or not.
Another responsibility of educational experts is to
create new learning methods and add new learning
styles in the platform.
3.3 Scenario of Use
This section describes an indicative scenario of use
based on the use case of figure 4 and the architecture
illustrated in figure 2. Our scenario describes two core
usage paths of the platform namely (a) Teacher set up
a virtual classroom and select the constituents for the
creation of individual worksheets for each student
based on his/her learning style and cognitive level and
(b) students logs in the platform to participate in the
virtual classroom and complete the individual
worksheet. In more detail:
Teacher Set Up a Virtual Classroom: When a
teacher logs in the platform, he/she can create virtual
classrooms and assign by invitation students to
participate. Once students are assigned to the virtual
classroom the platform’s procedure that
communicate with the User profile module is initiated
to collect the students’ individual characteristics to be
used for the creation of the individual worksheets.
Teacher Selects the Constituents for the Creation
of Individual Worksheets: The teacher, through a
simple, step by step, predefined process selects the
learning area, sub-area or chapter desired to be taught.
Once this is selected the platform presents all suitable
learning objects for the specific chapter. The teacher
reviews the platform’s learning objects proposal for
assigning to students and make corrections if desired.
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
256
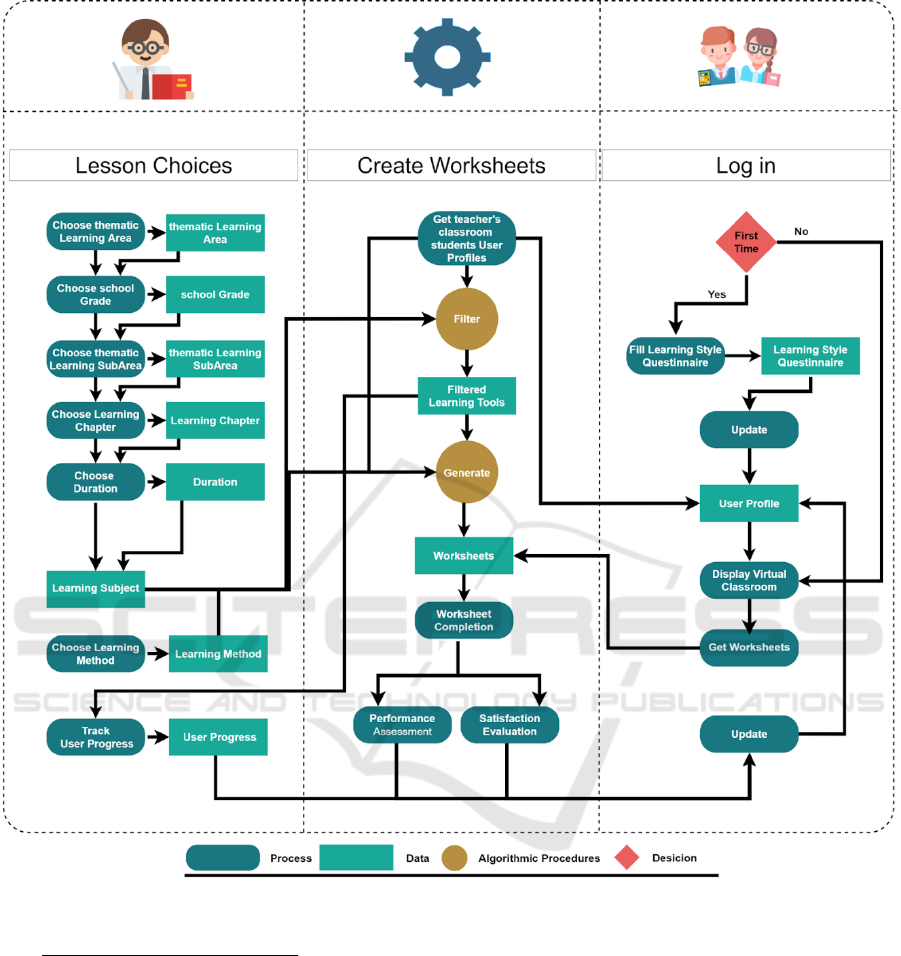
Figure 4: Scenario of use.
Students Logs in the Platform: When students
log in to the platform for the first time the system uses
collaborative student modeling by requesting the
student to fill out an Index of Learning Styles (ILS)
questionnaire in order to identify the student
preferences learning styles, so that their user profile
can be created. Students who have a user profile are
navigated into a screen where their virtual classrooms
are presented and currently active worksheets can be
selected and completed.
Each time students complete a worksheet they
are asked to provide feedback about how satisfied
they are and how difficult they found it. Furthermore,
while students are working on worksheets,
information about their performance is collected and
calculated. This information helps to keep track of the
students’ progress and preferences to update their
user profiles. Students' user profiles combined with
the learning choices of the teacher are used for the
creation of the personalized worksheets. Figure 4
shows the process of the core functionalities of the
platform.
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture
257

4 CONCLUSION - FUTURE
WORK
The Adaptive Blended Learning Platform is an effort
to create a useful tool for the teacher in the attempt to
modernize education. The platform aims to develop
4Cs skills that are considered particularly significant
for 21st-century students. The worksheet creation
process has been designed to be simple for teachers
to follow and review each step of the creation as they
are considered the experts in the educational
processes.
Moreover, we plan to support common
educational learning tools such as GameHub
(Barianos et al., 2021). It is important to have a
plethora of learning tools not only to cover the
preferences of students but also for the data that each
tool can provide. Gamification techniques has been
proven that can increase the quantity and quality of
data (Kalogiannakis et al., 2021).
The platform is currently at its first pilot
development phase and our goal is to be ready for
evaluation within the year. The evaluation of the
platform will be performed in primary and high
schools of the region of Crete, Greece.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Funded by GSRT-Greece matching funds for
European Projects 2019 - Building effective drug
prevention results across Europe, based on prevention
systems analysis and widespread professional
training - ASAP Training.
Icons made by Vectors Market, Flat Icons,
iconixar, Freepik from www.flaticon.com.
REFERENCES
Abdul Latif, G., & Lajiman, J. (2011). A study of student’s
perception of teaching and learning in instructional
design and technology faculty of languages and
communication. International Journal of Humanities
and Social Science, 1(15), 80–86.
Alsowat, H. (2016). An EFL flipped classroom teaching
model: Effects on English language higher-order
thinking skills, student engagement and satisfaction.
Journal of Education and Practice, 7(9), 108–121.
Barianos, A., Papadakis, A., Bartokaymenos, S.,
Sfakiotakis, S., & Vidakis, N. (2021). Adaptable
Edugames Platform, Allowing Educators To Customize
Games. 4957–4965. https://doi.org/10.21125/iceri.20
21.1137
Butler, H. A. (2012). Halpern critical thinking assessment
predicts real-world outcomes of critical thinking.
Applied Cognitive Psychology, 26(5), 721–729.
https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.2851
Gunawan, K. D. H., Liliasari, S., Kaniawati, I., & Setiawan,
W. (2020). Exploring science teachers’ lesson plans by
the implementation of intelligent tutoring systems in
blended learning environments. Universal Journal of
Educational Research, 8(10), 4776–4783.
https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.081049
Horn, M. B., & Staker, H. (2011). Blended learning What
is blended learning ? Performance Improvement, 44(0),
5–64.
Huang, Y. N., & Hong, Z. R. (2016). The effects of a
flipped English classroom intervention on students’
information and communication technology and
English reading comprehension. Educational
Technology Research and Development, 64(2), 175–
193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-015-9412-7
Kakosimos, K. E. (2015). Example of a micro-adaptive
instruction methodology for the improvement of
flipped-classrooms and adaptive-learning based on
advanced blended-learning tools. Education for
Chemical Engineers, 12, 1–11.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ece.2015.06.001
Kalogiannakis, M., Papadakis, S., & Zourmpakis, A. I.
(2021). Gamification in science education. A
systematic review of the literature. Education Sciences,
11(1), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11010022
Katsaris, I., & Vidakis, N. (2021). Adaptive e-learning
systems through learning styles: A review of the
literature. Advances in Mobile Learning Educational
Research, 1(2), 124–145. https://doi.org/10.25082/
amler.2021.02.007
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as
The Source of Learning and Development. Prentice
Hall, Inc., 1984, 20–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-
0-7506-7223-8.50017-4
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A Revision Of Bloom’s
Taxonomy Of Educational Objectives.
Theory into
Practice, 41(4), 302. http://www.citeulike.org/user/
mapto/article/961573%5Cnhttp://www.mendeley.com/
research/a-taxonomy-for-learning-teaching-and-assessi
ng-a-revision-of-blooms-taxonomy-of-educational-obj
ectives-abridged-edition-1/%5Cnhttp://www.amazon.
ca/exec/obidos/redirect?
Lai, C. L., & Hwang, G. J. (2016). A self-regulated flipped
classroom approach to improving students’ learning
performance in a mathematics course. Computers and
Education, 100, 126–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.compedu.2016.05.006
Liu, Q., Peng, W., Zhang, F., Hu, R., Li, Y., & Yan, W.
(2016). The effectiveness of blended learning in health
professions: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Journal of Medical Internet Research, 18(1).
https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4807
Mohamed, H., & Lamia, M. (2018). Implementing flipped
classroom that used an intelligent tutoring system into
learning process. Computers and Education,
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
258

124(December 2017), 62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.compedu.2018.05.011
Morze, N., Varchenko-Trotsenko, L., Terletska, T., &
Smyrnova-Trybulska, E. (2021). Implementation of
adaptive learning at higher education institutions by
means of Moodle LMS. Journal of Physics: Conference
Series, 1840(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-
6596/1840/1/012062
P21 (2015b). Framework for 21st Century Learning. The
Partnership for 21st Century Skills.
http://www.p21.org/about-us/p21-framework
Pheeraphan, N. (2013). Enhancement of the 21 st Century
Skills for Thai Higher Education by Integration of ICT
in Classroom. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 103, 365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.sbspro.2013.10.346
Popescu, E., Bǎdicǎ, C., & Moraret, L. (2009). WELSA: An
intelligent and adaptive web-based educational system.
Studies in Computational Intelligence, 237, 175–185.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03214-1_17
Sharratt, L. & Planche, B. (2016). (2016). Leading
Collaborative Learning : Empowering excellence.
Canadian Journal of Education Administration and
Policy, 186, 2–4.
Vidakis, Nikolaos, Konstantinos, K., & Triantafyllidis, G.
(2017). A multimodal interaction framework for
blended learning. Lecture Notes of the Institute for
Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and
Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST, 196, 205–
211. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55834-9_24
Vidakis, Nikolas, Syntychakis, E., Kalafatis, K.,
Christinaki, E., & Triantafyllidis, G. (2015). Ludic
Educational Game Creation Tool: Teaching Schoolers
Road Safety. 9177. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-
20684-4_55
Yuliati, S. R., & Lestari, I. (2018). Higher-Order Thinking
Skills (Hots) Analysis of Students in Solving Hots
Question in Higher Education. Perspektif Ilmu
Pendidikan, 32(2), 181–188. https://doi.org/10.21009/
pip.322.10
Zaharah Hussin, Saedah Siraj, Ghazali Darusalam, & Nur
Hasbuna Mohd Salleh. (2015). kajian Model Blended
Learning Dalam Jurnal Terpilih: Satu Analisis
Kandungan. Jurnal Kurikulum & Pengajaran Asia
Pasifik, Bil 3(1), 20–31.
Adaptive Blended Learning Platform based on the 4Cs Architecture
259
