
Quality Evaluation of Mobile GIS for Data Collection
Badr El Fhel
1a
, Lamyae Sardi
1b
, and Ali Idri
1,2 c
1
Software Project Management Research Team, ENSIAS, Mohammed V University in Rabat, Rabat, Morocco
2
MSDA, Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, Ben Guerir, Morocco
Keywords:
Mobile GIS for Data Collection, Requirements Engineering, Software Product Quality, ISO/IEC 25010.
Abstract:
High-quality software has to fulfil stakeholders’ requirements identified in a requirement engineering
process.This paper presents an overview of requirements regarding mobile Geographic Information System
for data
collection, which have been extracted based on literature, standards and existing apps in the
market. The
quality model ISO/IEC 25010 was explored using measures stated in the ISO/IEC 25023 standard.
A checklist
that marks the influence of each requirement on the quality characteristics and sub-characteristics
has been
established in order to calculate three degrees of the requirements influence on the external product
quality of
mobile GIS. The result obtained show that requirements related to online data access have the highest
impact
on the external quality characteristics whereas functional suitability and usability are the most
influenced
characteristics by the requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
A Geographic Information System (GIS) allows user
to collect, analyze, and manage data related to space.
During several years, spatial data acquisition has
been considered as a main function of GIS
(Goodchild, 2009). In reality, spatial data collection
(DC) was carried out mainly by surveyors,
cartographers or geographers, which is not obvious
when real-time data is needed. Owing to the advances
made in the technologies of positioning, wireless
communication and GeoWeb 2.0 (Elwood, 2009), the
public user has become an active actor in DC
(Goodchild, 2007). In fact, the proliferation of
smartphones has provided a powerful tool for spatial
DC insofar they are equipped by sensors that allow
geo-location and orientation Mobile GIS has
therefore become an important tool for DC (Song &
Sun, 2009). However, mobile GIS for data collection
(mGIS-DC) is now being also used by public users
(Goodchild, 2007) which renders questionable the
attractiveness of the application. Note that mGIS-DC
is currently being used in various domains. This
makes defining the functionalities and features of a
generic mGIS-DC more complicated. In general,
mGIS-DC allow users to geo-locate themselves using
Global Positioning System and/or Global Navigation
Satellite System (GPS/GNSS) and survey spatial data
in the field. This process seems to be simple but it
requires several features and functionalities to be
performed. For instance, the system has to operate in
both offline and online mode, this is important to
allow surveying in areas without internet access and
to store data remotely. Hence, local storage and
sensors should be supported. Moreover, common
business needs in GIS like geo processing and
geographic data presentation are a must. In addition,
users need to control and validate the quality of data
during the collection in the field. A set of these
functionalities and features has been identified by the
authors in a requirements catalog based on standards
and literature (El Fhel et al., 2021). However, to
ensure the development of an attractive and high-
quality software product, a software quality
evaluation based on the recommendations of the
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
should be conducted on the most relevant mobile GIS
requirements. The aim of this study is to review the
existing requirements of mGIS-DC in order to
identify the requirements that should be included in
a
b
c
h
ttps://orcid.org/0000-0003-0424-5104
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6696-3190
htt
p
s://orcid.or
g
/0000-0002-4586-4158
El Fhel, B., Sardi, L. and Idri, A.
Quality Evaluation of Mobile GIS for Data Collection.
DOI: 10.5220/0011033900003176
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2022), pages 309-316
ISBN: 978-989-758-568-5; ISSN: 2184-4895
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
309

the software product quality (SPQ) evaluation of
mGIS-DC. The paper also proposes a checklist for
these requirements and analyzes their impact on SPQ
characteristics using the ISO/IEC 25010 standard
(ISO/IEC/IEEE-25010, 2011).
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2
summarizes the related work and standards. Section 3
details the process of requirements’ extraction.
Section 4 provides an analysis of the influence of
mGIS-DC requirements on SPQ. The results are then
presented in Section 5 and discussed in section 6.
Finally, Section 7 presents the conclusions and some
suggestions for future research.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
In order to develop the requirements of mGIS-DC and
analyze their influence on the SPQ, this study relies
upon standards, literature and functionalities/features
of existing apps. In fact, the research standardization
project SQuaRE (Systems and software Quality
Requirements and Evaluation) established a series of
international standards, ISO/IEC 250xx. The
ISO/IEC-25030 model (ISO/IEC/IEEE-25030, 2019)
provides a set of recommendations and guidelines for
the specification of software quality requirements.
Another part of the SQuaRE series is the ISO/IEC
25010:2011 System and software quality model. This
model was revised in 2017 and it is typically divided
into two sub-models; a SPQ model which defines
eight characteristics related to static and dynamic
properties of a system or software product and a
quality in use model composed of five characteristics
that mainly reflects how well the software product
conforms to the design and non-functional
requirements (ISO/IEC/IEEE-25010, 2011). In
addition, the ISO/IEC 25023:2016 model
(ISO/IEC/IEEE-25023, 2016) defines quality
measures for quantitatively evaluating system and
SPQ in terms of the characteristics and sub-
characteristics defined in the ISO/IEC 25010 model.
Previous studies have covered the quality of GIS
including mGIS-DC; Clark et al. carried out an
evaluation of 13 mGIS-DC apps regarding their
usability. Song-jae et al. evaluated 10 GIS software
using quality characteristics (QC) defined in standard
ISO/25010 (Jo & Kim, 2011). Another work by Smith
et al. concerns the evaluation of 30 GIS products
using a template of 56 questions based on 13 software
qualities (Smith, 2017). Moreover, several studies
have used the ISO/IEC 25010 standard to evaluate the
quality of mobile applications such as: gamified
blood donation apps (Idri et al., 2018) and pregnancy
monitoring mobile personal health records (Idri et al.,
2016). To the best of our knowledge, there have been
no previous evaluations of the SPQ of mGIS-DC
using the ISO/IEC 25010 standard.
3 mGIS-DC REQUIREMENTS
In this section, the common requirements of mGIS-
DC are outlined. Only requirements which are
unambiguous, complete, consistent, feasible,
comprehensible and testable were extracted as claimed
by the ISO/IEC/IEEE 29148 standard (SO/IEC/IEEE-
29148, 2018). Hence, the extraction was based on the
following sources: 1) the existing requirements
catalog of mGIS-DC (El Fhel et al., 2021), 2) studies
on the development of mGIS-DC apps (Chen & Xiao,
2011; Shadin & Tahar, 2015; Yan et al., 2009; Ye et
al.; Ye et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2009), 3) existing
requirements catalog regarding sustainability and
internationalization (Bachiri et al., 2019; Ouhbi et al.,
2017; Ouhbi et al., 2018). Moreover, mGIS-DC
available in the apps’ repositories were evaluated in
order to extract the main features and functionalities.
A list of these apps is available upon request by email
to the authors. The requirements of mGIS-DC were
extracted and grouped in eight blocks as presented
hereafter.
3.1 App’s Accessibility
The accessibility refers to the availability of the
application, before and after installation. This block of
requirements includes: AA1 Operating system OS
type the OS is a key factor while installing a mobile
app (iOS, Android). AA2 The OS version is further
important insofar it impacts the compatibility of the app
with the user’s device. AA3 Cost, the app’s cost can
create distinction between apps. AA4 Geographical
limitation defines whether the app is available
worldwide or in a specific region. AA5 Internet
Access, this requirement indicates whether internet
access is needed to use the app or not. AA6 Geo-
positioning in the world indicates if the app is able to
provide worldwide geo-location. AA7 Language
indicates if the app can be adapted to the user’s
language. AA8 Units, this indicates whether the app
supports multiple units for area and distance (meter,
feet). AA9 Night mode, indicates if the app is able to
operate in night mode. In addition, requirements
about the ability of the app to support device sensors
such as: AA10 GPS, to allow positioning using the
GPS system AA11 Compass, to
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
310

obtain geographic rotations and orientations. AA12
GNSS, to perform a positioning using the GNSS
system.
3.2 User’s Actions (UA)
This block includes a set of requirements that
indicates whether the user can or cannot perform
these actions: UA1 Drawing on the map, users shall
be able to add new data to the map. UA2 Edit
markers, refers to markers plotted on the map to
determine point of interest. UA3 Measure area and
distance. UA4 Center the map, indicates if the app
provides a button to center the map to user’s position.
UA5 Switch layers, GIS data is classified and
displayed as multiple layers. UA6 Customize
graphical properties, users shall be able to apply
adequate styles to geographical data. UA7 Define
data integrity constraint, users shall be able to
define some validity conditions and apply them to
spatial data such as closing polygons. UA8 Export
data in a common GIS file format (e.g. Shapefile SHP
and Keyhole Markup Language KML). UA9
Parameter the capacity, refers to the capacity of
storage allowed to the application. UA10 share
position and UA11 share route.
3.3 Coordinates System (Cs)
This block refers to functionalities that indicate if the
application supports: CS1 Multiple CS. Coordinates
can be defined through multiple CS. CS2 Find place
using coordinates, users shall be able to find locations
using coordinates.
3.4 Data Acquisition (DA)
Requirements in this block refers to functionalities
that allow user to perform DC. These requirements
are: DA1 Save user position: to collect GIS data, users
shall be able to save their device positions. DA2 Geo-
locate pictures, this allows users to assign geographic
coordinates to photos, DA3 Place note, while
operating in the field, users can assign additional
information to the collected data. DA4 Record videos,
DA5 Record audio and DA6 Record Track which
indicates if users can perform continuous surveilling
along a road or track.
3.5 Geographical Data Visualization
(GDV)
As mGIS-DC is dedicated to manage data,
requirements aboutGDV re: GDV1 Access
attributes, in GIS, attributes can be assigned to
geographical data. GDV2 Labelling feature, users shall
be able to assign labels to geographical data. GDV3
Map display, various useful maps are available via
internet such as Google Maps and Bing Maps. GDV4
User location, this corresponds to the user device
location. GDV5 Map scale, in geography, features
visible on a map with a large scale are not necessarily
shown on a map with a small one. GDV6 Device
coordinates, the app shall display the current coordinate
of the user device.
3.6 Geo-Location (GL)
This block refers to requirements about positioning, it
includes: GL1 Synchronize user position: While
displaying user position on the map, the real position
shall be synchronized with the concerned marker in an
acceptable time. GL2 GPS Satellites’ number, this
information helps GIS users to verify the accuracy of
the given GPS position. GL3 position accuracy, the app
shall provide clear information about positioning
accuracy.
3.7 Online Data Access (ONDA)
ONDA requirements refer to the possibility to access or
store spatial data remotely. These requirements are:
ONDA1 Remote database which indicates if the app
can be connected to a spatial database. ONDA2
Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) web
services, ESRI’s implementation of GIS Web Services
delivers some of the most popular GIS capabilities, such
as address matching and routing. ONDA3 Open
Geospatial Consortium OGC web services, various
OGC web services are widely known in GIS domain,
(e.g Web Feature Service WFS, Web Map Service
WMS and Web Coverage Service WCS). ONDA4
Dropbox, indicates if the app supports the Dropbox
platform.
3.8 Offline Data Access (OFDA)
OFDA requirements regarding the ability of the app to
access data locally, these requirements are: OFDA1
Offline mode support, the app shall operate without
being connected to the internet. OFDA2 Device local
storage, indicates if the app accesses the internal
memory of the device. OFDA3 known GIS File Format,
indicates if the data is directly saved into known GIS
format such as SHP and KML. OFDA4 Memory
check, users shall be able to check the internal memory
space of the device. OFDA5 Clear data cache.
Quality Evaluation of Mobile GIS for Data Collection
311

3.9 Spatial Data Analysis (SDA)
Requirements in this block concern the
implementation of common GIS algorithms such as:
SDA1 Buffer generation, SDA2 Voronoi diagram,
SDA3 data envelopment analysis, SDA4 bounding
box and SDA5 spatial data filter. In addition, SDA6
Coordinates to address, indicates if the app provides
a conversion of the coordinates to postal address.
SDA7 WHAT3WORDS locator: indicates if the app
interprets addresses written as three words. SDA8
Location by name, indicates if the app supports
postal address positioning. SDA9 Nearby search,
refers to the capability of searching places within a
specified area and SDA10 Find route. Moreover,
regarding the data quality: SDA11 Data accuracy,
the app shall inform users about the accuracy of data.
SDA12 Errors about data quality, the app shall
alert user about errors related to the DC.
4 mGIS-DC IMPACT ANALYSIS
In order to calculate the influence of the requirements
of mGIS-DC on SPQ, an analysis process composed
of three steps was followed. Note that the same
process was used in previous studies regarding the
impact analysis of software requirements (Idri et al.,
2018; Ouhbi et al., 2015). These steps are:
Step 1: Analysis of the Product QC
and Sub-characteristics
The quality model ISO/IEC 25010 determines QC
and sub-characteristics QsC that will be taken into
account when evaluating the properties of a software
product. These characteristics were analyzed in
conjunction with the ISO/IEC 25023 which defines
quality measures for quantitatively evaluating system
and SPQ in terms of QC and QsC.
Step 2: Checklist of mGIS-DC Apps’
Requirements and SPQ Model
In order to identify the impact of requirements on the
external characteristics. A checklist containing
requirements and QsC was established. Each
requirement was considered to influence a quality
sub-characteristic if this requirement affects the
variable used in the calculation of the concerned
external metric. The evaluation was performed by the
two first authors and verified by the third one. Note
that there was no disagreement between the authors.
The checklist is available upon request by email to the
authors.
Step 3: Degree of Influence of the
Requirements on SPQ
.
Three degrees are calculated using the checklist:
1. Degree of impact of a block of requirements B on
an external characteristic EC: DI(EC,B) =
∑DI(EC;R)/ N(R), where DI(EC,R) is the degree
of impact of a requirement R on an EC, and N(R)
is the total number of requirements in that block.
This degree was classified into five categories:
Very high if the degree is between 0.90 and 1.00;
High [0.7, 0.89]; Moderate [0.4,
0.69]; Low [0.2, 0.39] ; and Very low [0, 0.19].
2. Degree of impact of R on an EC: DI(EC, R) =
N(EsC, R)/ N(EsC) where N(EsC, R) is the
number of sub-characteristics EsC of EC that are
influenced by that R, N(EsC) is the total number of
sub-characteristics of EC.
3. Degree of impact of a B on an EsC : DI(EsC, B) =
∑DI(EsC;R)/ N(R), where DI(EsC;R) is the
degree of impact of R on an EsC.
5 RESULTS
This section presents the results of the calculated
degrees. A set of nine blocks encompassing 61
requirements was assessed according to eight QC and 31
QsC. The degree of impact of the block of
requirements on the QC is presented in Figure 1. The
block ONDA has the highest degree of impact on
external quality EQ. It has a very high degree on
performance efficiency and a moderate degree on
functional suitability and compatibility characteristics.
Note that this block has a low influence on
portability, security and usability but it does not
influence at all the maintainability and the reliability
of the software product. The CS has a very high impact
on functional suitability and a moderate influence on
compatibility but it has a very low degree on
compatibility and no impact elsewhere. The GDV
block has the lowest influence on software QC,
however, it moderately influences the functional
suitability and the usability characteristics. Figure 2
presents the degree of impact of each requirement on
the QC. Functional Suitability and Usability are the
most influenced characteristics by the requirements.
Each of these two QC is impacted by 92% of the
requirements. The remaining characteristics are
influenced by the requirements as follow:
Performance efficiency 44%, Reliability 39%,
Security 32%, Portability 23%, Compatibility 15%
and Maintainability 8%. Moreover, according to
Figure 2, ONDA4 is the requirement that has the
highest impact on the QC, this requirement is slightly
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
312

higher than ONDA1, ONDA2 and ONDA3 which are
in the same block. Regarding QsC, Figure 3 shows
that Functional appropriateness is the only sub-
characteristic that is influenced by all blocks of
requirements (77%). The Appropriateness
recognizability is also highly impacted by the
requirements (77%). In contrast, the mGIS-DC
requirements have no impact on the following six
sub-characteristics: Learnability, Non-repudiation,
Accountability, Analyzability, Modifiability and
Testability.
6 DISCUSSION
This section discusses the main findings and presents
their implications for mGIS-DC.
6.1 Main Findings
In this study, a set of 61 requirements of mGIS-DC
was identified based on standards, literature and
functionalities/features retrieved from existing apps.
A calculation of three degrees of impact of the
selected requirements on the EQ of the software
product was performed. The results obtained show
that requirements related to online data access
(ONDA) has the most impact on SPQ. In this block,
ONDA4 was identified as the requirement that has the
highest influence on software quality. It differs
slightly from ONDA1, ONDA2 and ONDA3.
Supporting Dropbox in mGIS-DC allows users to
share and find out data. Dropbox is a leading cloud
file hosting service and it counts above 700 million
users in 2020 (Dropbox Usage and Revenue Stats
(2021)). The integration of a cloud service in mobile
GIS is important to alleviate the limitation of the
storage capacity in mobile devices (Wasserman,
2010). In contrast, ONDA1, ONDA2 and ONDA3 are
not dedicated to public users but they have a high
impact on SPQ of mGIS-DC. These three
requirements are more adapted to be used by
professional GIS users and they are subject to
dedicated protocols. The OGC proposes a collection
of open standards to facilitate the exchange of spatial
resources between applications (Consortium). These
standards concern web services and their implication
with spatial data, especially regarding maps and
features through WFS, WMS and WCS. ESRI's
implementation of Web services , provide
commercially hosted spatial data and GIS
functionality via the Internet (ESRI). This solution
provides the advantage of ESRI organization but with
a payment in return. This can affect the attractiveness of
the apps since mGIS-DC are considered as an
alternative of conventional system given their low
cost (Döner & Yomralıoğlu, 2008). Remote spatial
database allows user to access data and execute spatial
queries without consuming the local device resources.
This has an important role in mGIS-DC especially
for professional users who need to execute geo-
processing operations that require online or
distributed geoprocessing. Regarding AA10 and
AA12, GPS and GNSS support affect the quality
insofar they provide the position of the data to collect.
GPS positioning is considered as a key component of
mobile GIS (Abdalla, 2016).In addition to the GPS
support, the given accuracy of positioning (GL3) is
important as well, since the user has to be aware of
errors that might affect the positioning (Wang &
Reinhardt, 2006). The AA11 correspond to the
compass support, this sensor is helpful as it allows
orientation in the field. The contribution of the
remaining 53 requirements can be explained by
analyzing the QC since their impact is not very high
as the aforementioned requirements. However, we
note that UA4, UA5 and UA6 obtain the lowest degree
of impact on the quality and they contribute to the
usability and functional suitability of the apps. The
process of DC in the field involves multiple tasks
regarding positioning, analyzing, storing and
displaying data. Functionalities with regards to this
process are intended to be executed successively to
cover the overall process of DC. This explains the
highest impact of the requirements on the functional
completeness. For the functional appropriateness, we
note that the mGIS-DC is applied in various domain
and it requires basic business knowledge which is not
obvious for public user. Therefore, the app requires
functions that facilitate the accomplishment of the
DC. It has been observed that the limitation of mGIS-
DC regarding the accuracy of positioning (Clark, 2015)
significantly affects the functional correctness sub-
characteristic. It is therefore important to consider
requirements that allow the control of data quality
during DC (Wang & Reinhardt, 2006). According to
the results, the usability characteristic is highly affected
by the requirements. It was identified as an issue for the
improvement of mobile GIS (Shah, 2011) and it is very
important in mGIS-DC; Song-Jae et al. pointed out
that most common defect in GIS software is related to
usability (Jo & Kim, 2011). This indicates that
developers have to put more effort into meeting the
usability requirements. Furthermore, a usability test
conducted by Clark et al. shows that the usability of
mGIS-DC does not exceed the usability of the
conventional system of DC (Clark, 2015).
Quality Evaluation of Mobile GIS for Data Collection
313
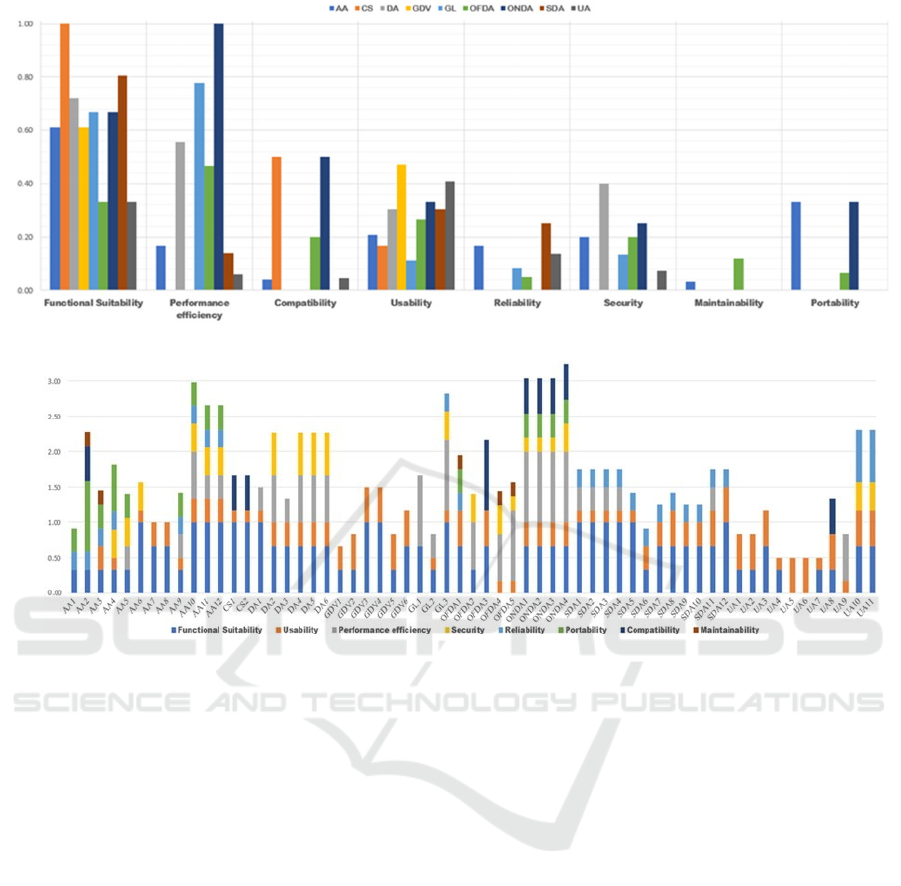
Figure 1: Impact of a block of requirements on an external characteristic.
Figure 2: Degree of influence of a requirement on an external characteristic.
6.2 Implications for mGIS-DC
This study has identified requirements regarding
mGIS-DC. The degree of influence of these
requirements on SPQ was calculated. Stakeholders
and developers can translate them in order to pinpoint
the software quality requirements. Therefore, they
can formulate an assessment of their existing
software. The result can also be used to check
functionalities and features for new mGIS-DC apps
taking in consideration, the influence of the
requirements on the SPQ.
6.3 Limitations
This study may have some limitations such as: 1) The
list of the apps explored for the purpose of the
requirements extraction is not exhaustive insofar new
apps are being released every day. To alleviate this
threat, mGIS-DC concerned by this study were
carefully and recently chosen. 2) Some of the external
characteristics might be influenced by environmental
attributes like the GPS signal and cellular connection.
However, our study covers only measurable
requirements. Nevertheless, we believe that our
findings may be used in future works.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, a set of 61 requirements was identified
according to literature, standards and existing mGIS-
DC. A software quality assessment was performed
using the ISO/IEC 25010 quality model in
conjunction with ISO/IEC 25023 standard. In order to
calculate the impact of the requirements on the SPQ, a
checklist was established according to eight QC and 31
QsC. According to the outcome of this study,
requirements regarding online data access have a high
degree of impact on the external QC. Functional
suitability and usability have been identified as the
most influenced characteristics by the requirements.
As a future work, we intended to improve the
requirements by proposing a prioritization
requirements method. In addition, we plan to study
the quality-in-use of mGIS-DC using the ISO/IEC
25010 quality model.
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
314
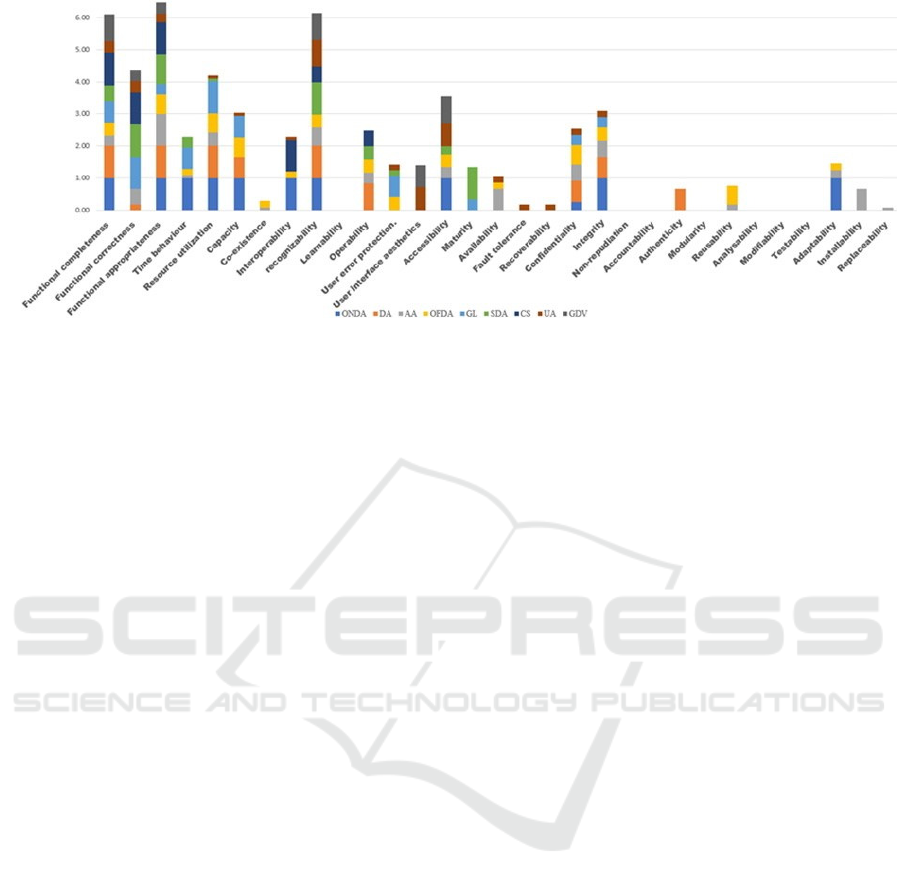
Figure 3: Impact of each block of requirements on the external sub-characteristics.
REFERENCES
Abdalla, R. (2016). Mobile GIS and Location-Based
Services (LBS). In Introduction to Geospatial
Information and Communication Technology (GeoICT)
(pp. 83-103). Springer International Publishing. http://
link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-319-33603-9_5
Bachiri, M., Idri, A., Redman, L. M., Fernandez-Aleman, J.
L., & Toval, A. (2019). A Requirements Catalog of
Mobile Personal Health Records for Prenatal Care. In
S. Misra, O. Gervasi, B. Murgante, E. Stankova, V.
Korkhov, C. Torre, A. M. A. C. Rocha, D. Taniar, B. O.
Apduhan, & E. Tarantino (Eds.), Computational
Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2019 (Vol. 11622,
pp. 483-495). Springer International Publishing.
http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-030-24305-0_36
Chen, H., & Xiao, K. (2011, 24-26 June 2011). The design
and implementation of the geological data acquisition
system based on mobile GIS. 2011 19th International
Conference on Geoinformatics,
Clark, J. (2015). Location Gathering: An Evaluation of
Smartphone-Based Geographic Mobile Field Data
Collection Hardware and Applications [Master of Arts,
San Jose State University]. San Jose, CA, USA.
https://scholarworks.sjsu.edu/etd_theses/4577
Consortium, O. G. OGC Web Services Context Document
(OWS Context). In.
Döner, F., & Yomralıoğlu. (2008). Examination and
comparison of mobile GIS technology for real time Geo-
data acquisition in the field. Survey Review, 40 (309), 221-
234. https://doi.org/10.1179/003962608X291013
Dropbox Usage and Revenue Stats (2021). Retrieved 23
Nov 2021 from https://backlinko.com/dropbox-users
El Fhel, B., Sardi, L., & Idri, A. (2021). A Requirements
Catalog of Mobile Geographic Information System for
Data Collection. In Á. Rocha, H. Adeli, G. Dzemyda, F.
Moreira, & A. M. Ramalho Correia (Eds.), Trends and
Applications in Information Systems and Technologies
(Vol. 1366, pp. 324-336). Springer International
Publishing. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-030-
72651-5_32
Elwood, S. (2009). Geographic information science:
emerging research on the societal implications of the
geospatial web. Progress in Human Geography, 34(3),
349-357. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309132509340711
ESRI. Web Services—A Standards-Based Framework for
Integration. In.
Goodchild, M. F. (2007). Citizens as sensors: the world of
volunteered geography. GeoJournal, 69(4), 211-221.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-007-9111-y
Goodchild, M. F. (2009). Geographic information systems
and science: today and tomorrow. Annals of GIS, 15(1),
3-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475680903250715
Idri, A., Bachiri, M., & Fernández-Alemán, J. L. (2016). A
Framework for Evaluating the Software Product
Quality of Pregnancy Monitoring Mobile Personal
Health Records. Journal of Medical Systems, 40(3), 50.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0415-z
Idri, A., Sardi, L., & Fernández-Alemán, J. L. (2018).
Quality Evaluation of Gamified Blood Donation Apps
using ISO/IEC 25010 Standard. 11th International
Conference on Health Informatics,
ISO/IEC/IEEE-25010, I. S. (2011). ISO/IEC 25010:2011
System and software quality models. In.
ISO/IEC/IEEE-25023, I. S. (2016). ISO/IEC 25023:2016
Measurement of system and software product quality.
In.
ISO/IEC/IEEE-25030, I. S. (2019). ISO/IEC 25030:2019
Quality requirements framework. In.
Jo, S.-J., & Kim, S.-B.(2011). GIS Software Quality
Improvement Expense For a Testing Instance. Journal
of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society,
12(1), 474-485. https://doi.org/10.5762/KAIS.2011.12.
1.474
Ouhbi, S., Fernández-Alemán, J. L., Idri, A., Toval, A.,
Pozo, J. R., & El Bajta, M. (2017, 2017). A Reusable
Requirements Catalog for Internationalized and
Sustainable Blood Donation Apps. 12th International
Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to
Software Engineering,
Quality Evaluation of Mobile GIS for Data Collection
315

Ouhbi, S., Fernández-Alemán, J. L., Toval, A.,
Rivera Pozo, J., & Idri, A. (2018). Sustainability
requirements
for
connected health applications:
Sustainability requirements for connected health
applications. Journal of Software: Evolution and
Process, 30(7), e1922. https://doi.org/10.1002/smr.1922
Ouhbi, S., Idri, A., Fernández-Alemán, J. L., Toval, A.,
& Benjelloun, H. (2015, 2015). Applying ISO/IEC
25010
on Mobile Personal Health Records. International
Conference on Health Informatics,
Shadin, M. S., & Tahar, K. N. (2015, 10-12 Aug. 2015).
The implementation of mobile GIS for fire hydrant
mapping. 2015 International Conference on Space
Science and Communication (IconSpace),
Shah, I. A. S. S. A. (2011). Usability Requirements for GIS
Application : Comparative Study of Google Maps on
PC and Smartphone’
Smith, S. (2017). Software Quality Grades for GIS
Software. In: Mendeley.
SO/IEC/IEEE-29148. (2018). Systems and software
engineering — Life cycle processes — Requirements
engineering. In.
Song, W., & Sun, G. (2009, 26-28 Dec. 2009). Using
Mobile GIS as Volunteered GI Provider. 2009 First
International Conference on Information Science and
Engineering,
Wang, F., & Reinhardt, W. (2006). Spatial data quality
concerns for field data collection in mobile GIS.
Proc.SPIE,
Wasserman, A. I. (2010). Software engineering issues for
mobile application development. the FSE/SDP
workshop,
Yan, Y., Yu, J., Wu, J., & Ma, S. (2009, 31 March-2 April
2009). Design and Implementation of a Mobile GIS for
Field Data Collection. 2009 WRI World Congress on
Computer Science and Information Engineering,
Ye, S., Zhu, D., Yao, X., Zhang, N., Fang, S., & Li, L.
(2014). Development of a Highly Flexible Mobile GIS-
Based System for Collecting Arable Land Quality Data.
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth
Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(11), 4432-4441.
https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320635
Ye, S., Zhu, D., Yao, X., Zhang, X., & Li, L. (2016, 18-20
July 2016). Developing a mobile GIS-based component to
collect field data. 2016 Fifth International Conference on
Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics),
Zhang, S., Ma, S., & Zhang, Y. (2009, 4-6 June 2009).
Research on Collaborative Environment of Data
Collection and Application in Mobile GIS. 2009 Third
International C onference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous
Engineering,
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
316
