
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19
Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima
Sara Haro-Hoyo, Edgard Inga-Quillas and Willy Ugarte
a
Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Peru
Keywords:
CoViD19, Technological Solution, IoT, Monitoring, Patients.
Abstract:
The aim of the article is to present the implementation of a technological solution based on the use of wearable
that allows optimizing the monitoring process of elderly patients with CoViD19. This is a current big problem
since the pandemic has make a lot of issues emerge for elderly patients. For instance, since elder people are
more vulnerable for CoViD19, they require to avoid social contact or follow more strict rules for lockdowns.
This work addresses and applies aspects from the use of IoT for the monitoring of elderly patients, application
of technological models in real time, and the supervision of symptoms of CoViD19. Our results show the
feasibility of our approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization
(WHO) reported the existence of a total of 7,818 peo-
ple infected with CoViD19 worldwide, most of them
from China.
According to the Pan American Health Organiza-
tion (PAHO), the WHO declared China as very high
risk and the other countries as high.
Likewise, the WHO published the Strategic Pre-
paredness and Response Plan of the international
community, to help states with poor health systems
to protect themselves from the new virus.
More than 2.9 million people worldwide have died
from the new SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus and about
134.1 million infected.
It is worth mentioning that the country most af-
fected by 2021 is the United States with more than 31
million infections and 560,000 deaths; Brazil follows,
with over 13.2 million diagnosed and with 345,000
deaths; and India exceeds 13 million infected and
167,000 deaths.
According to the latest report from the Ministry
of Health of Peru (MINSA), as of September 2021,
199,727 deaths were registered in our country, where
the most affected province was Metropolitan Lima
with 81,389 deaths, with a 9.23% fatality rate of the
virus.
With these indicators, many countries are in a state
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7510-618X
of health emergency due to this pandemic, hence the
need to find technological solutions based on innova-
tion within the field of medicine.
Hence, this article aims to contribute with a pro-
posal for improvement in the process of monitoring
patients with symptoms of this disease, as well as in
the recovery process of the patient infected with this
virus.
A precedent is the study of Remote health mon-
itoring of elderly through wearable sensors (Al-
Khafajiy et al., 2019), which focused on the design
and implementation of an intelligent health monitor-
ing system that can observe the elderly remotely.
The objective of this article is to present a techno-
logical solution based on 2 mobile applications:
• “CoViDSalud Paciente” and
• “CoViDSalud Atenci
´
on”
Seeking to optimally monitor the symptoms of
CoViD-19 in elderly patients in Metropolitan Lima.
Therefore, the main matrix of the technological
solution is to have a mobile application that can be
linked to a “wearable” device; to obtain constant con-
trol and monitoring of the patient.
This application presents a friendly interface; in
other words, it is easy to use for the target audience,
who are older people, who present specific and dis-
tinctive needs, as well as significant demands regard-
ing the use of ICTs.
The development of this APP contributes as a data
control and monitoring tool that can refer to a possi-
Haro-Hoyo, S., Inga-Quillas, E. and Ugarte, W.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19 Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima.
DOI: 10.5220/0011034400003188
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2022), pages 17-25
ISBN: 978-989-758-566-1; ISSN: 2184-4984
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
17

ble CoViD19 alert; o provide support in the process
of a patient who has already been diagnosed and that
these can serve as an accurate reference for the doc-
tor and thus also contribute to the recovery process of
the patient throughout their process from beginning to
end of the disease.
• We analyze the main technological tools that
allow the development of the solution to opti-
mize the process of monitoring the symptoms of
CoViD19 in elderly patients.
• We validate the solution of the technological
model proposed in elderly patients through the use
of wearable.
• We propose a business continuity plan for the
implementation of the technological solution for
monitoring the symptoms of CoViD19 in elderly
patients.
This paper is organized as follows. In section 2, we
will describe the differences and comparisons with
other works about the evaluation of the level of de-
pression; in section 3 we will address the key con-
cept for the core of our approach in the evaluation
of depression level with facial and voice analysis and
the aggregated value of the our work according to the
evaluation of the level of depression. Subsequently, in
section 4 we will present the validation of the techno-
logical model functionalities in a simulated scenario.
Finally, in section 5 we will specify our main con-
clusions and results of the finished application.
2 RELATED
WORKS/DISCUSSION
For the development of the proposed technological
solution, 2 mobile applications were implemented
that are linked to a “wearable” device to obtain
constant control and monitoring of the patient with
CoViD19.
For this, an analysis of the state of the art was car-
ried out, selecting its most relevant scientific articles:
In the paper (Mohammadzadeh et al., 2020), the
author achieved the optimization in the informa-
tion reporting processes of the main symptoms of
CoViD19, so that it serves as part of the process of
studies considered in possible diagnoses.
What differs from our paper is that we will con-
sider four measurement indicators, temperature, heart
rate, sleep status and blood saturation.
In the same way, in the paper (de Morais Bar-
roca Filho et al., 2021), the authors manage to demon-
strate the need for an intelligent diagnosis and mon-
itoring of infected patients to reduce hospital care,
since they are the most vulnerable people, and this
could have great consequences.
The objective of this research is to present a plat-
form designed for constant monitoring of patients in
critical condition, using portable sensors to monitor
patients infected with coronavirus.
What sets us apart from this paper is that we not
only rely on monitoring, but we also provide virtual
medical assistance to those who use our application.
Another study that follows the same line of re-
search is the paper (Rathee et al., 2021), which delves
into the 2 studies already mentioned, since it explains
the importance of the use of AI in the health sector,
mainly, in medical systems, which can be very use-
ful to automate and remotely quantify CoViD19 pa-
tients and improve recognition of infected patients in
the early stages of contagion.
What differentiates us from this paper is that they
are based on the first stages of contagion, however, we
already work with patients infected with CoViD-19,
providing them with continuous monitoring, medical
and laboratory assistance from day one.
Hence, when we are faced with the inexplicable
situation of a pandemic that has not yet been over-
come, the motivation of the researchers of the pa-
per (He et al., 2021) is observed, to propose exten-
sive analyzes and evaluations on the technological so-
lutions that can help in the fight against the expan-
sion of CoViD-19, and thus continue to inspire other
researchers to continue making their contributions to
mitigate the damages of the pandemic.
What differentiates us from this paper is that we
already apply a solution to CoViD-19 patients mon-
itoring the main symptoms and there will also be a
caregiver who will also follow the steps of a respec-
tive patient.
However, one of the most vulnerable groups and
that suffered high mortality rates were the elderly,
therefore, in paper (Gordon et al., 2020), it refers to
the importance of constant monitoring with the el-
derly, since they are more vulnerable due to the pos-
sible congenital diseases, or those already developed
by age.
Therefore, and according to the positions, it is vi-
tally important to interconnect with the integrated sys-
tems developed to combat CoViD19.
Compared to this paper, our solution implements
an alert system to our elderly patients that is sent both
to the patient, caregiver, and GP.
ICT4AWE 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
18
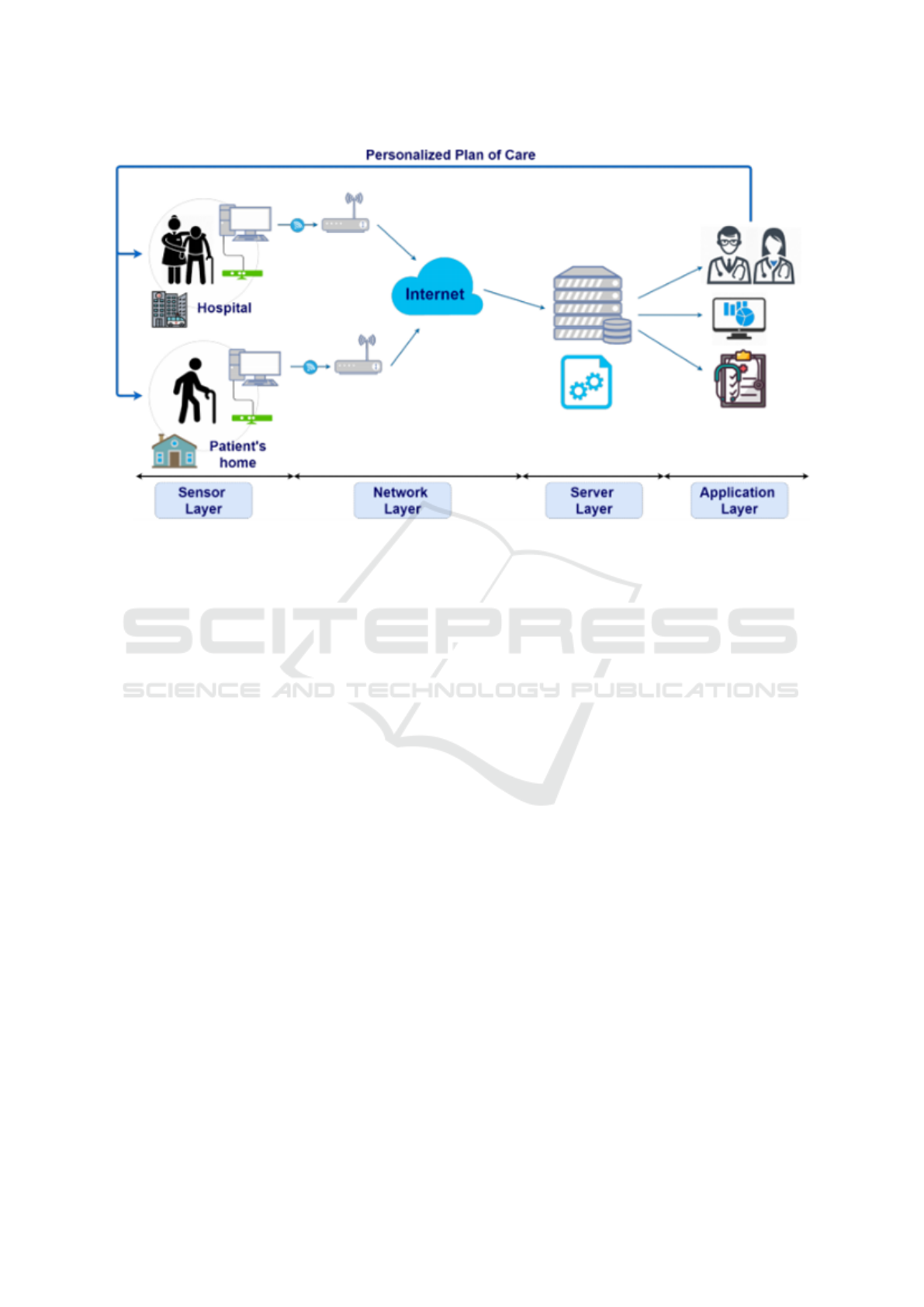
Figure 1: Remote Monitoring Validation Engineering System (ReMoVES) Architecture (Trombini et al., 2021).
3 TECHNOLOGICAL SOLUTION
3.1 Preliminary Concepts
In this section, the main concepts involved in our re-
search will be developed.
We propose that, for each concept, there is a def-
inition and a respective example based on a review
of the literature on depressive disorder and facial and
voice recognition.
Definition 1 (Use of IoT technologies (Blas et al.,
2021; Trombini et al., 2021; de Morais Barroca Filho
et al., 2021; Rathee et al., 2021; Vedaei et al., 2020)).
The concept of IoT refers to a digital interconnection
of everyday objects with the internet. It is the internet
connection more with objects than with people.
According to Forbes, with the appearance of
CoViD19, at the beginning of 2020, thermometers be-
gan to be used, which were connected by a 5G net-
work, such as smart rings and / or bracelets that had
the function of collecting data from patients such as
the blood oxygen level and heart rate (Milenkovic,
2020).
Example 1. In (Trombini et al., 2021), the research,
presents a system based on IoT that provides us with
a program where the patient can perform his totally
personalized rehabilitation and is reviewed by a pro-
fessional to monitor the performance and efficiency
of workouts from any device. This work used a Re-
MoVES architecture which has 4 layers as shown in
Fig. 1:
3.1.1 Wearable Sensors
Advanced technology to ”carry”, mobility is its main
characteristic and the IoT the basis of its approach,
since sensors allow data to be constantly collected and
transmitted to different devices, accessories, and gar-
ments.
While it might seem like most wearables are worn
on the wrist, there are devices designed to be worn
almost anywhere on the body.
For this reason, in addition to bracelets, wearables
can be found in rings, necklaces, headbands and even
shoe inserts with advanced functions (Motti, 2020).
According to Filho (de Morais Barroca Filho
et al., 2021), an analysis of the various previous stud-
ies for the spread of CoViD19 based on IoT technolo-
gies, cloud computing and mobile applications can be
carried out.
Which are already being used to process patient
data regarding health monitoring and obtain an im-
mediate response as soon as the patient needs it. See
Fig. 2.
According to the Pan American Health Organi-
zation (2021), the epidemiological update caused by
SARS-CoV 2 has had different variants that affect
public health.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19 Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima
19
Figure 2: Methodology to develop PAR (de Morais Bar-
roca Filho et al., 2021).
In October 2020, a new variant was detected in
India called B.1.617, which is under investigation.
Also, other variants of great interest for public health
have emerged, such as variant P.1, lineage B.1.1.28
on January 9, 2021, in Japan, which was detected in
travelers coming from Brazil.
According to the virologist Kamil, one of the mu-
tations of this new variant is like those identified in
the countries of Brazil and South Africa and he con-
siders it to be less infectious compared to the variant
in the United Kingdom
1
According to (Rathee et al., 2021), the authors
propose the use of monitoring of 15 symptoms of in-
fected patients in an-ANN-based system to manage
patient data, to improve the classification of CoViD19
infected patients.
The model used in this research is the multilayer
perceptron network (MLP) which is considered a type
of ANN those researchers often use frequently, see
Fig. 3.
Figure 3: Multilayer perceptron architecture net-
work (Rathee et al., 2021).
3.2 Method
Prior to the development and proposal, a benchmark-
ing analysis was carried out as the methodology to ex-
1
Epidemiological Update - PAHO
tract the data, using Gartner
2
, which has a wide field
regarding the evaluation of tools from different areas.
On this occasion, this methodology was adapted
to generate a quantitative report that serves to qualify
the tools in question.
3.2.1 Phases
The project development approach was based on five
phases, which are detailed below:
• In the first phase, the scope of the project was de-
fined together with the Product Owner. Likewise,
an in-depth investigation was generated regard-
ing the initially agreed requirements. With these
premises, the Project Charter documentation be-
gins.
• For the second phase, an analysis was carried out
regarding the technologies that would be involved
for the proposed solution.
• In the third phase, the technological model was
designed, validated by the Product Owner.
• During the fourth phase, the development of the
proposed solution (product) that was delivered to
the Product Owner was carried out. Addition-
ally, the corresponding validations were generated
based on the initial requirements.
• Finally, in the fifth phase, the results of the project
(final product) were presented.
3.2.2 Execution
Two mobile applications will be developed for the
Android operating system as part of the technologi-
cal solution, which will bear the name of ”CoViD-
Salud Paciente” whose main purpose will be to op-
timize the monitoring of main symptoms of elderly
patients to rule out or accompany the CoViD19, using
a wearable device via Bluetooth connection.
And it will work together with another application
called ”CoViDSalud Atenci
´
on”, whose main purpose
will be to contribute to the management of doctors,
caregivers and laboratories, to be able to provide med-
ical assistance to patients, by appointment in an effi-
cient manner.
This technological solution will contribute with
the monitoring of the main symptoms to prevent the
patient from getting worse his state of health, as well
as keep a record in the reports of symptoms that keep
the patient stable and collaborate with the tranquility
of this (see Fig. 4).
This research is aimed at elderly patients, that is,
60 years and older, since according to WHO research
2
Benchmark Analytics
ICT4AWE 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
20
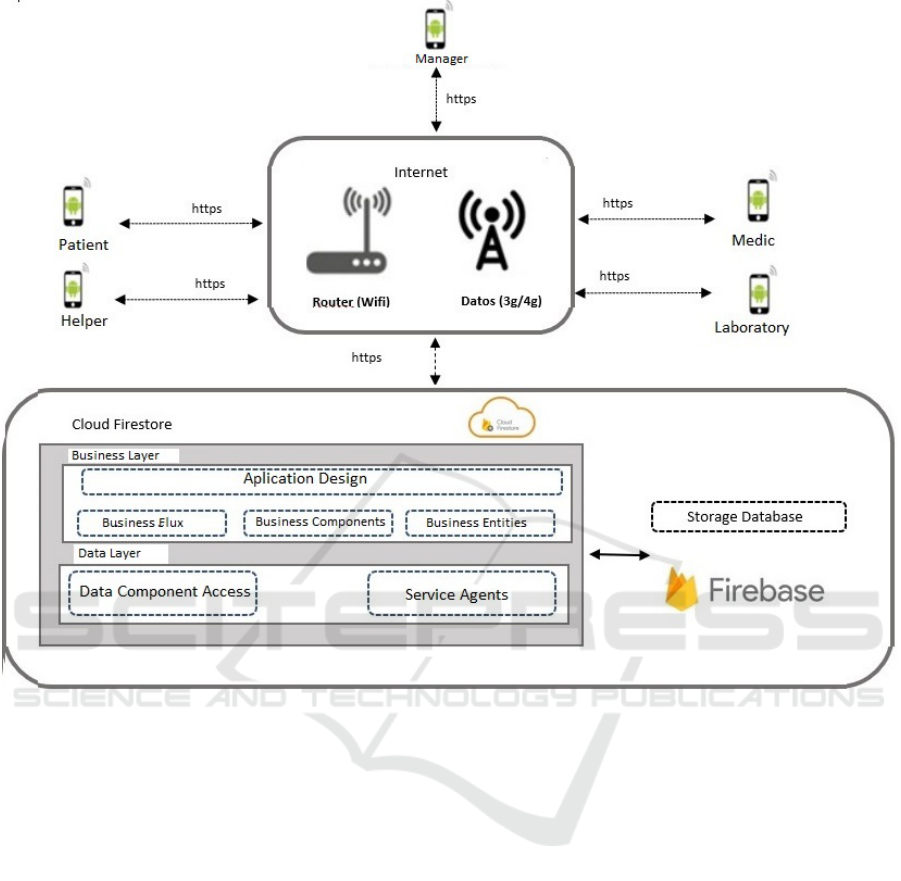
Figure 4: Physical Architecture Diagram.
statistics (2020), they are the society with the greatest
vulnerability and/or risk against CoViD19.
This part of the population has a weaker immune
system and, in most cases, they have one or more
chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, car-
diovascular and pulmonary conditions (COPD), so
their ability to respond to infections is less.
The objective of this architecture, see Fig. 5, is
to be able to identify the requirements that have an
impact on the software structure and reduce the risks
associated with its construction.
The architecture must support future changes in
software, hardware and functionality demanded by
customers (which occur very often).
Similarly, it is the responsibility of the software
architect to analyze the impact of his design deci-
sions and establish a compromise between the differ-
ent quality requirements, as well as between the com-
promises necessary to satisfy the users, the software,
and the business objectives, and which are functional
and quality requirements, hence it is vital to determine
the type of software to be developed.
Presentation Layer. It is the part of the system
with which the user interacts. Your screens, forms are
all user interfaces (UI) that are part of the presentation
layer User interfaces can make use of components or
user process controllers (UIC) to communicate with
the back end and navigate or process the user inter-
face.
Service Layer. The services layer in the archi-
tecture allows the functionality of the system to be
exposed to client and external applications. It is also
the key to achieving cross-platform and interopera-
ble solutions. Service components expose the func-
tionality of the components through contracts, which
are the interfaces where service providers and service
consumers agree and must be immutable.
Business Logic Layer. It contains all the pro-
cessing logic to make the application possible. The
Component is where you put this processing logic
where each one can be coded in independent meth-
ods.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19 Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima
21
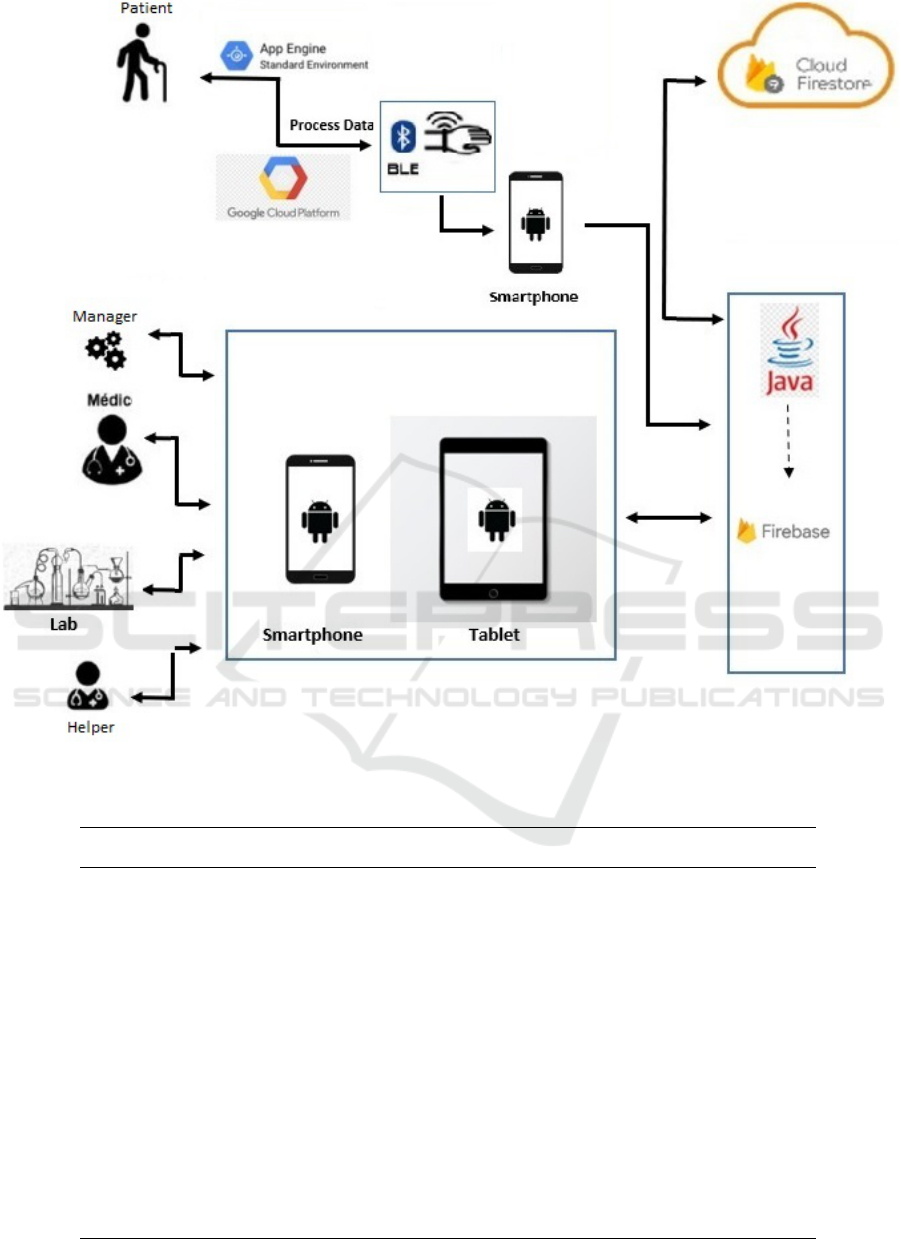
Figure 5: Integrated Architecture Diagram.
Table 1: Modules and responsibilities.
Module Responsibility
User interface (UI) Forms are all user interfaces (UI) that are part of the pre-
sentation layer.
Presentation logic components Process a request, generating response content, and for-
matting the page for the client
Contracts (Service interfaces) Allows data transfer, it applies specific actions (POST,
GET, PUT and DELETE) on resources.
Services Provide additional services that the application requires.
App Expose the business logic.
Workflows Organize the flow that carries out the execution of the
business process
Components (edit) Component that performs business tasks
Entities Component that represents custom business classes.
Data access components to Data Components that deal with the database tables
ICT4AWE 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
22

Table 2: Scenarios.
Patient 1 2 3 4 5
Preexisting
Morbidity
Alzheimer’s
Irritable colon,
Gastritis
Type 2
diabetes
Low back
pain
Migraine
Age 89 89 67 65 61
Heartrate (bpm)
CONTEC-CMS50D 91 90 90 88 89
AFK-YK009 89 88 89 86 87
HUAWEI BAND 6 92 91 92 90 90
SpO2 (%)
CONTEC-CMS50D 97 98 97 99 98
AFK-YK009 95 96 95 97 96
HUAWEI BAND 6 98 99 98 99 99
Temperature(
◦
C)
Thermometer Mercury 36.3 36.5 36.5 36.5 36.8
Thermometer Digital 36.2 36.4 36.4 36.5 36.7
DreamState
Galaxy Wacth (h/d) 7:15 6:15 7:46 8:20 7:00
HUAWEI BAND 6 8:15 7:15 8:10 8:40 8:15
Data Layer. The data layer is where we save our
components as CRUD operations, which handle the
insertion (Create), the selection (Read), the modifi-
cation (Update) and the elimination (Delete) of data,
see Table 1. In this presentation we show the different
modules with their respective responsibilities.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section we are going to treat an experimental
study to show the feasibility of our project, in each of
the following paragraphs the experimental protocol,
the results measuring the efficiency of the proposal
and a short discussion will be detailed.
4.1 Experimental Protocol
For the development of our solution, an IDE called
Android Studio 3.6 was used, where the Java and
Kotlin language were used for the entire Front-end
part.
Firebase cloud-based platform for the back end,
HMS Core (Huawei Mobile Services) for wearable
and mobile device connectivity.
However, for those users who do not have mobiles
with an Android operating system, an emulator called
Blue Stacks 5 with an instance in Android 9.0 was
used to run the tests of our application.
In the same way, to run the programs used, a com-
puter with 10th generation Core i7, 16GB of RAM
and a 10GB reserved storage for the application was
used.
Likewise, to carry out the respective tests, a Sam-
sung Galaxy Note 20 Ultra cell phone with Android
11.0 operating system was used, accompanied by a
Huawei Band 6 Smart Band with Bluetooth connec-
tion.
Then install the Huawei Health Kit and create an
account that will be associated with the wearable.
When opening the app, it will ask to connect with
Huawei services, for this Huawei HMS Core will be
downloaded.
Immediately after downloading it, you will enter
the application and you will be prompted to enter your
Huawei account email and password.
Finally, it will ask for the permissions to read your
data, it should be noted that all the data it reads is
saved in Firebase.
Our code and our data are publicly available at the
following links:
For the main apk: https://github.com/retto710/
CoViDSaludAppAndroid and for the patient apk:
https://github.com/retto710/CoViDSaludPaciente.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19 Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima
23
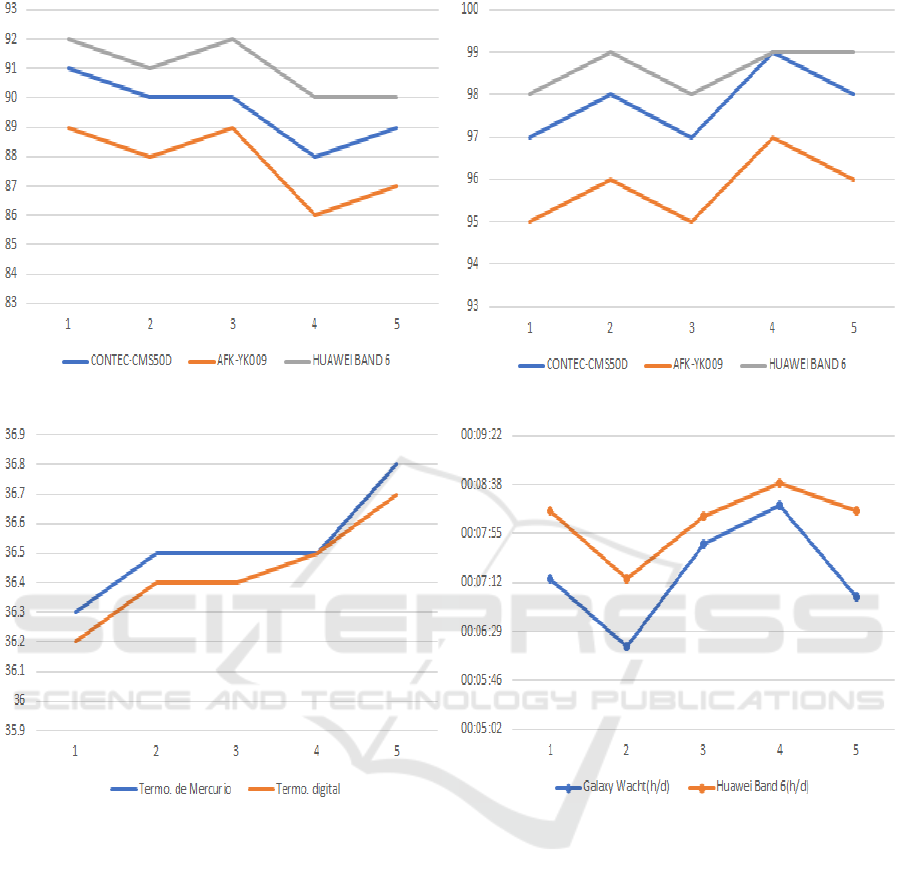
(a) Morbidity vs Heart Rate. (b) Morbidity vs SpO2.
(c) Preexisting Morbidity vs Temperature. (d) Preexisting Morbidity vs Sleep State.
Figure 6: Comparison of results.
4.2 Results
This section will show the solution developed from
the proposed architecture.
In addition, to validate the developed solution, the
test to which it was subjected, and the results obtained
from it in different elderly patients with different mor-
bidities are shown.
Our final IoT-enabled prototype is designed with a
Huawei Band 6 wearable and a mobile device where
the measurements of the main symptoms will be dis-
played.
The accuracy of heart rate and oxygen saturation
measurement are compared using two handheld de-
vices: CONTEC-CMS50D and AFK-YK009.
As shown in scenario 1, see Table 2, measure-
ments with the Band 6 device are more effective, see
also Fig. 6 for variations.
On the other hand, the temperature measured by
the device is compared with the Thermometer mer-
cury thermometer.
It can be seen in Table 2 that the results shown for
5 patients with different ages by the proposed IOT-
enabled wearable device are almost close to the values
obtained by the smart band and the thermometer.
Finally, for the sleep state, a comparison was made
between two wearable devices: Galaxy Watch and
Huawei Band 6, in which the following results are
shown.
ICT4AWE 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
24

4.3 Discussion
We describe the implementation and impact of a
CoViD-19 senior monitoring solution, in which we
found that the RPM program was associated with sig-
nificantly lower risk from our endpoint and the per-
centage of hospitalized or readmission patients hos-
pitable has decreased.
In addition, among patients who have used our
app, 67% did not produce alerts for symptoms that re-
quire manual monitoring, suggesting that PROM for
CoViD-19 patients can provide extensive monitoring
without the need to directly contact a physician. for
your review.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
PERSPECTIVES
The main objective of this research was to analyze the
main technological tools regarding the different types
of follow-ups to patients with CoViD-19, during the
first stage of contagion.
The paper determines the management of scien-
tific information, as well as the capture of data in
terms of health monitoring and analysis of results
with the laboratory approach.
As a second conclusion, the solution of the pro-
posed technological model was validated, since IOT
technology was used using a wearable to capture data
on oxygenation in the blood, heart rate and sleep
status, and thus see the progress and monitoring of
the main symptoms of CoViD-19 patients in a timely
manner.
The experimental results of the proposed solution
show higher precision and shorter response time in
various functions of our application using Huawei’s
smart band 6 device.
Therefore, this project represents a preliminary
study, a precedent to continue developing improve-
ments in the Peruvian health system with the use of
technologies and encourage the involvement of pri-
vate companies for the creation of I+D+I, Research,
development, and innovation.
Evenmore, using Genetic information to seek for
historical data about a patients (Arroyo-Mari
˜
nos et al.,
2021) or monitoring symptoms with a similar tech-
nological solution for other diseases (Jorge-L
´
evano
et al., 2021).
REFERENCES
Al-Khafajiy, M., Baker, T., Chalmers, C., Asim, M., Ko-
livand, H., Fahim, M., and Waraich, A. (2019). Re-
mote health monitoring of elderly through wearable
sensors. Multim. Tools Appl., 78(17):24681–24706.
Arroyo-Mari
˜
nos, J. C., Mejia-Valle, K. M., and Ugarte, W.
(2021). Technological model for the protection of ge-
netic information using blockchain technology in the
private health sector. In ICT4AWE.
Blas, H. S. S., Mendes, A. S., Encinas, F. G., Silva, L. A.,
and Gonz
´
alez, G. V. (2021). A multi-agent system for
data fusion techniques applied to the internet of things
enabling physical rehabilitation monitoring. Applied
Sciences, 11(1).
de Morais Barroca Filho, I., Aquino, G., Malaquias, R. S.,
Gir
˜
ao, G., and Melo, S. R. M. (2021). An iot-based
healthcare platform for patients in ICU beds during
the COVID-19 outbreak. IEEE Access, 9:27262–
27277.
Gordon, W. J., Henderson, D., Desharone, A., Fisher, H. N.,
Judge, J., Levine, D. M., Maclean, L., Sousa, D., Su,
M. Y., and Boxer, R. (2020). Remote patient moni-
toring program for hospital discharged COVID-19 pa-
tients. Appl. Clin. Inform., 11(05):792–801.
He, W., Zhang, Z. J., and Li, W. (2021). Information
technology solutions, challenges, and suggestions for
tackling the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Inf. Manag.,
57:102287.
Jorge-L
´
evano, K., Cuya-Chumbile, V., and Ugarte, W.
(2021). Technological solution to optimize the
alzheimer’s disease monitoring process, in metropoli-
tan lima, using the internet of things. In ICT4AWE.
Milenkovic, M. (2020). Internet of Things: Concepts and
System Design. Springer.
Mohammadzadeh, N., Gholamzadeh, M., Saeedi, S., and
Rezayi, S. (2020). The application of wearable smart
sensors for monitoring the vital signs of patients in
epidemics: a systematic literature review. Journal
of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing,
page 3.
Motti, V. G. (2020). Wearable Interaction. Human-
Computer Interaction Series. Springer.
Rathee, G., Garg, S., Kaddoum, G., Wu, Y., Jayakody, D.
N. K., and Alamri, A. (2021). ANN assisted-iot en-
abled COVID-19 patient monitoring. IEEE Access,
9:42483–42492.
Trombini, M., Ferraro, F., Morando, M., Regesta, G., and
Dellepiane, S. G. (2021). A solution for the remote
care of frail elderly individuals via exergames. Sen-
sors, 21(8):2719.
Vedaei, S. S., Fotovvat, A., Mohebbian, M., Rahman, G.
M. E., Wahid, K. A., Babyn, P. S., Marateb, H. R.,
Mansourian, M., and Sami, R. (2020). COVID-SAFE:
an iot-based system for automated health monitoring
and surveillance in post-pandemic life. IEEE Access,
8:188538–188551.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Monitoring of CoViD-19 Symptoms in Seniors Patients in Lima
25
