
A Literature Review on Methods for Learning to Rank
Junior Zilles
a
, Giancarlo Lucca
b
and Eduardo Nunes Borges
c
Centro de Ci
ˆ
encias Computacionais, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande – FURG,
Av. It
´
alia, km 8, Rio Grande, RS, 96203-900, Brazil
Keywords:
Information Retrieval, Learning to Rank, Algorithms.
Abstract:
The increasing number of indexed documents makes manual retrieval almost impossible when they are re-
trieved or stored automatically. The solution to this problem consists of using information retrieval systems,
which seek to present the most relevant data items to the user in order of relevance. Therefore, this work aims
to conduct a theoretical survey of the most used algorithms in the Information Retrieval field using Learning
to Rank methods. We also provide an analysis regarding the datasets used as benchmarks in the literature. We
observed that RankSVM and LETOR collection are the most frequent method and datasets employed in the
analyzed works.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increasing number of indexed documents makes
the retrieval process unmanageable for a user to find
any relevant information without the help of an in-
formation retrieval system (Kowalski and Maybury,
2002). In this kind of system, an important point is re-
lated to the necessity that the most relevant documents
appear at the top of the query results. The problem of
ordering a list of documents that satisfy user needs is
pointed out as central in Information Retrieval (IR)
research (Baeza-Yates and Ribeiro-Neto, 1999). IR is
also concerned with the structure, analysis, organiza-
tion, storage, research, and dissemination of informa-
tion (Salton and Harman, 2003).
An IR system is designed to make a particular
collection of information available to a population of
users. Thus, it is expected that, given a search term,
the order of the returned documents follows a logical
sequence of importance or probability of relevance.
Most relevant are at the top and the least at the fi-
nal positions of the query result. Approaches such as
Boolean model, Vector Space Model, Okapi BM25,
and others are usually used to perform the document
ordering task (Phophalia, 2011).
The classic approach of ranking consists of ana-
lyzing the terms found in the documents, with no re-
lation to the context applied to the search performed
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5748-4788
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3776-0260
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1595-7676
by the user. One of the existing alternatives is the ap-
plication of Machine Learning (ML) (Carbonell et al.,
1983), which allows the ranking of documents con-
sidering the context in which they are inserted. This
alternative seeks to solve the ranking problem, mak-
ing the retrieval system more optimized to satisfy the
queries performed by users.
The ranking of documents takes into account three
main characteristics (He et al., 2008; Harrag and
Khamliche, 2020):
• Relevance: produces a score for each document
that indicates its relevance to user input. The
task of ranking by relevance consists of ordering
a set of objects with respect to a given criterion
(Rigutini et al., 2011).
• Importance: considers the degree of importance
of the document in relation to the input. There-
fore, if two documents have the same relevance
score but address different content, the one that
should be at the top is the document with the high-
est degree of importance or which addresses con-
tent more related to the entry term.
• Preference: evaluates the behavior of the user
who searches for documents. Therefore, an effec-
tive model must store the user’s real-time behavior
to adapt searches to their profile.
The following is an example of the ranking prob-
lem and how IR addresses this issue. Furthermore, the
difference among Preference, Importance, and Rele-
vance is addressed, as they are essential for IR. To do
Zilles, J., Lucca, G. and Borges, E.
A Literature Review on Methods for Learning to Rank.
DOI: 10.5220/0011065600003179
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2022) - Volume 1, pages 545-552
ISBN: 978-989-758-569-2; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
545

Figure 1: Example of ranking problem with difference be-
tween Relevance, Importance and Preference.
so, consider a query made by a user, where he wants
to find images of mice using the term (mouse). The
result of this query is shown in Figure 1, where the
first three results returned can be considered relevant,
as they are mice. It should be noted here that this is
precisely the idea behind the ranking problem.
Also, regarding the example presented, it is possi-
ble to observe that an IR system must consider that the
user’s objective is rats of the animal kind. So, due to
the importance of the result, only the first and second
are selected. Finally, suppose the user interacts only
with the second element. In that case, his or her pref-
erence consists only of the second document in the
list. This preference is significant information about
the problem.
It is noteworthy that knowing the user’s prefer-
ence, it is possible to use ML techniques to help solve
the ranking problem. It is precisely this preference
that is used to improve the model. The use of ML to
solve the ranking problem is defined as Learning to
Rank (LR) (Li, 2011), being a field of research in the
IR area.
This paper aims to provide a systematic review of
the literature that addresses Learning to Rank. Our
review would help future information systems re-
searchers to better define their scope by piking the
methodologies pointed out. Moreover, to provide a
complete study, we show an analysis considering the
datasets used to train the models.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 de-
fines LR. Section 3 provides insight into how the re-
search was done. Section 4 shows the gotten results.
Finally, the conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2 LEARNING TO RANK
Learning to Rank concerns all methods that use ma-
chine learning to solve the ranking problem (Li, 2011;
Liu, 2011). Some examples of fields where the rank-
ing problem is applied are document retrieval, entity
resolution, question answering (QA), meta-search,
custom search, online advertising, collaborative fil-
tering, summarization of documents, and automatic
translation (Li, 2011).
The main task of LR is to learn a function, which,
given a context (queries), arranges a set of items (doc-
uments) in ordered lists to maximize a given metric.
LR methods usually approach the ranking problem as
a “score and order” problem, so the goal is to learn
a “score” function to estimate the relevance of docu-
ments to a query (Bruch, 2019).
The LR algorithms mostly differ in two factors,
the first one regarding the parameterization of scor-
ing functions (Scoring Function), for example linear
functions, boosted weak learners, gradient boosted
trees, SVM and neural networks (Ai et al., 2019).
The second factor is related to three different ap-
proaches, namely:
• Pointwise – each document is evaluated only with
the relation to the query, and the value gives the
ordering that each document receives in relation
to the query;
• Pairwise – pairs of documents are selected, and
each par is compared with the others to come up
with the more relevant, in this way, the ordering
occurs concerning the relevance of the pair;
• Listwise – which evaluates the entire list of docu-
ments in the query and proposes to optimize their
order based on their permutations.
3 SYSTEMATIC
METHODOLOGY TO SELECT
THE STUDIES
This section presents how we conduct the literature
review on LR. The collected papers match in one of
the following topics: (i) developing a new algorithm
or model, (ii) introducing a new strategy, or (iii) com-
parative research on the topic.
The bibliographic source chosen was Mendeley
1
,
which has a catalog with more than 300 million doc-
uments. It is built from the users’ contribution when
they add references of documents to their libraries. In
this way, the system groups the references of different
1
https://www.mendeley.com/search/
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
546
users imported from other bibliographic sources like
SCOPUS or Web of Science and generates a canoni-
cal reference for each document.
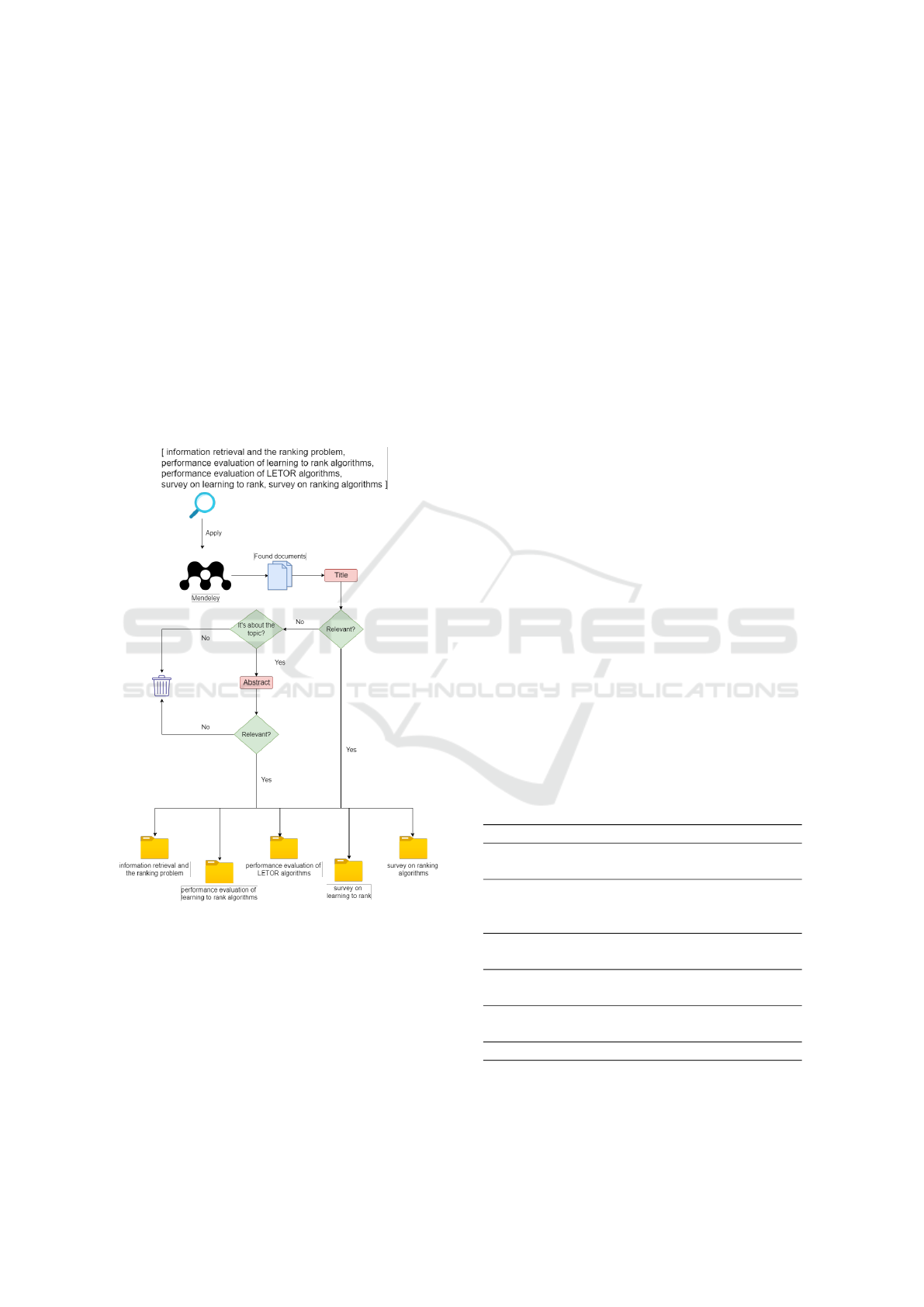
Figure 2 present our systematic methodology,
where there are four distinct queries, which were per-
formed in the Mendeley search tool. Each query re-
turns a different number of articles and papers. Two
researchers screened the studies using the title and
stored them in a folder corresponding to the query.
The article was screened using the abstract if the title
was irrelevant to the review, but it addressed the LR
theme. Otherwise, the document was ignored. Lit-
erature returned by different search queries was con-
sidered only the first time. In addition to organizing,
each query became a folder containing all the selected
works.
Figure 2: Flowchart of the methodology for the theoretical
survey.
4 THE SELECTED STUDIES
In this section, the results of this survey are presented.
In order to make a robust analysis, we have divided it
into three different parts. The first one is related to the
studies on LR. The second summarizes the datasets
used by the selected studies, and the last one shows
a general analysis by classifying them into different
categories.
The queries formulated for the survey consists of
the following terms:
1. information retrieval and the ranking problem
2. performance evaluation of learning to rank algo-
rithms
3. performance evaluation of LETOR algorithms
4. survey on learning to rank
5. survey on ranking algorithms
The considered research queries returned 5.977
bibliographic references, of which 54 were selected.
The complete analysis is provided in Table 1, where
the rows are related with the different queries and the
columns are the amount of returned and selected stud-
ies.
The fourth query has returned 2,156 references
(the more significant amount), but only nine were se-
lected. This difference can be explained by the fact
that most of the returned studies address topics related
to education, like student performance and learning
environments. Our review focused on discovering the
most used methods in the field of LR, i.e., on build-
ing a roadmap to people that are starting on the field.
Also, the first query was the second that returned
more references, where 21 were selected.
Additionally, the query “performance evaluation
of LETOR algorithms” did not return a lot of docu-
ments that can be explained by the fact of misunder-
standing of the LETOR (Qin et al., 2010; Qin and
Liu, 2013) term, which means a collection of datasets
and not another way of referring to Learning to Rank
also referenced on some papers as L2R. This query
obtained the highest ratio (1/3) of relevant retrieved
despite not returning many references.
Table 1: Search results.
Used Terms Returned Selected
Information retrieval and
the ranking problem
1,558 21
Performance evaluation
of learning to rank algo-
rithms
984 10
Performance evaluation
of LETOR algorithms
11 4
Survey on learning to
rank
2,156 8
Survey on ranking algo-
rithms
1,268 11
Total 5,977 54
In order to ease the understanding of the obtained
results, we show in Figure 3 the relation of the tech-
niques used in research from 2005 to 2021. The
A Literature Review on Methods for Learning to Rank
547
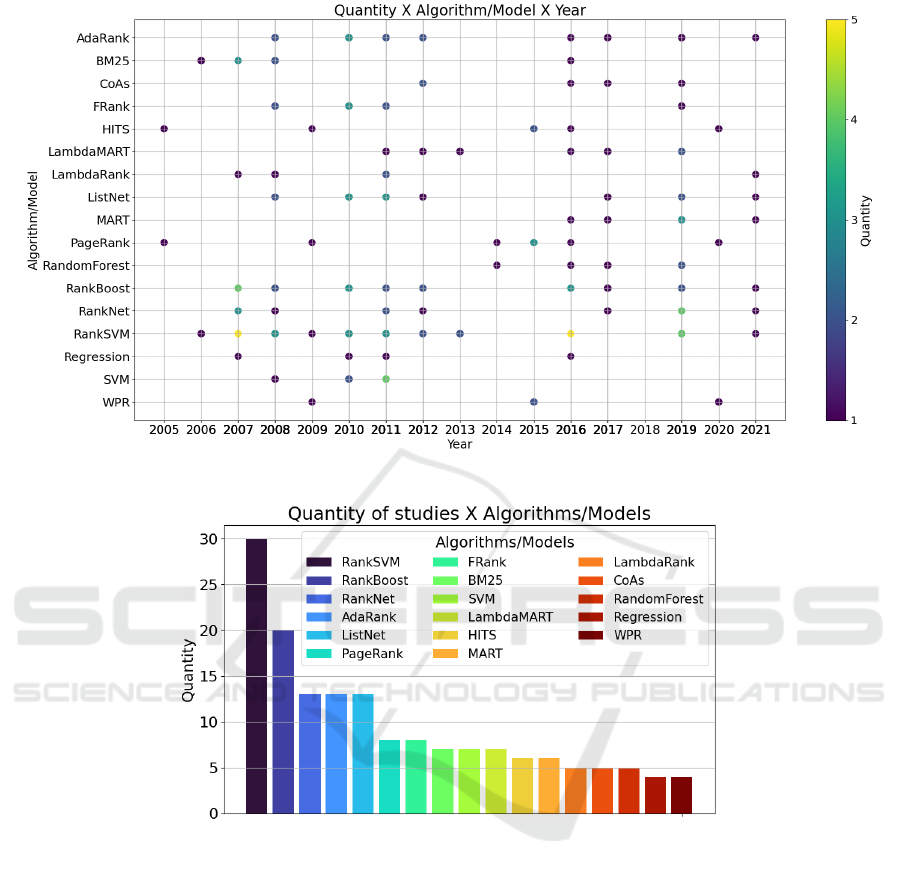
Figure 3: Number of algorithms/models per year.
Figure 4: Number of papers that used the algorithm/model.
circles represent the frequency of studies employing
each algorithm or model. In otter words, for a se-
lected algorithm, if the circle is smooth (tending to
yellow), more studies have cited or conducted experi-
ments using that approach.
From Figure 3, it is possible to observe that
RankSVM is the most used model in the studies sur-
veyed. Precisely, this approach appears in 2007 and
2016 (5 studies each year), in 2019 (4), in 2008, 2010
and 2011 (3), in 2012 and 2013 (2) and, in 2006 and
2021 (1 study each year). Another highlighted ap-
proach is RankBoost, which got in 2007 (4 studies),
in 2010 and 2016 (3), in 2008, 2011, 2012 and 2019
(2) and, in 2017 and 2021 (1 mention).
Considering the relation of the algorithms/models
and the total number of studies that consider them,
we provided another analysis in Figure 4. RankSVM
ranks first with 29 studies, RankBoost in the sec-
ond position with 20 different studies, and RankNet,
AdaRank, and ListNet algorithms with 13 appear-
ances in different studies in third, fourth, and fifth po-
sitions. Therefore, from the observed Figures 3 and 4,
RankSVM and RankBoost are the most mentioned in
the literature in the period observed.
Furthermore, it can be observed that algorithms
widely used from 2006 to 2012, such as AdaRank,
BM25, FRank, LambdaRank, and SVM, had a de-
cline in their use in the following years. Models based
on DING, Eigen Rumor, Popularity and Similarity-
Based Page Rank (PSPR), SortNet, TagRank, and
Time Rank are not commonly used compared with
other algorithms.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
548
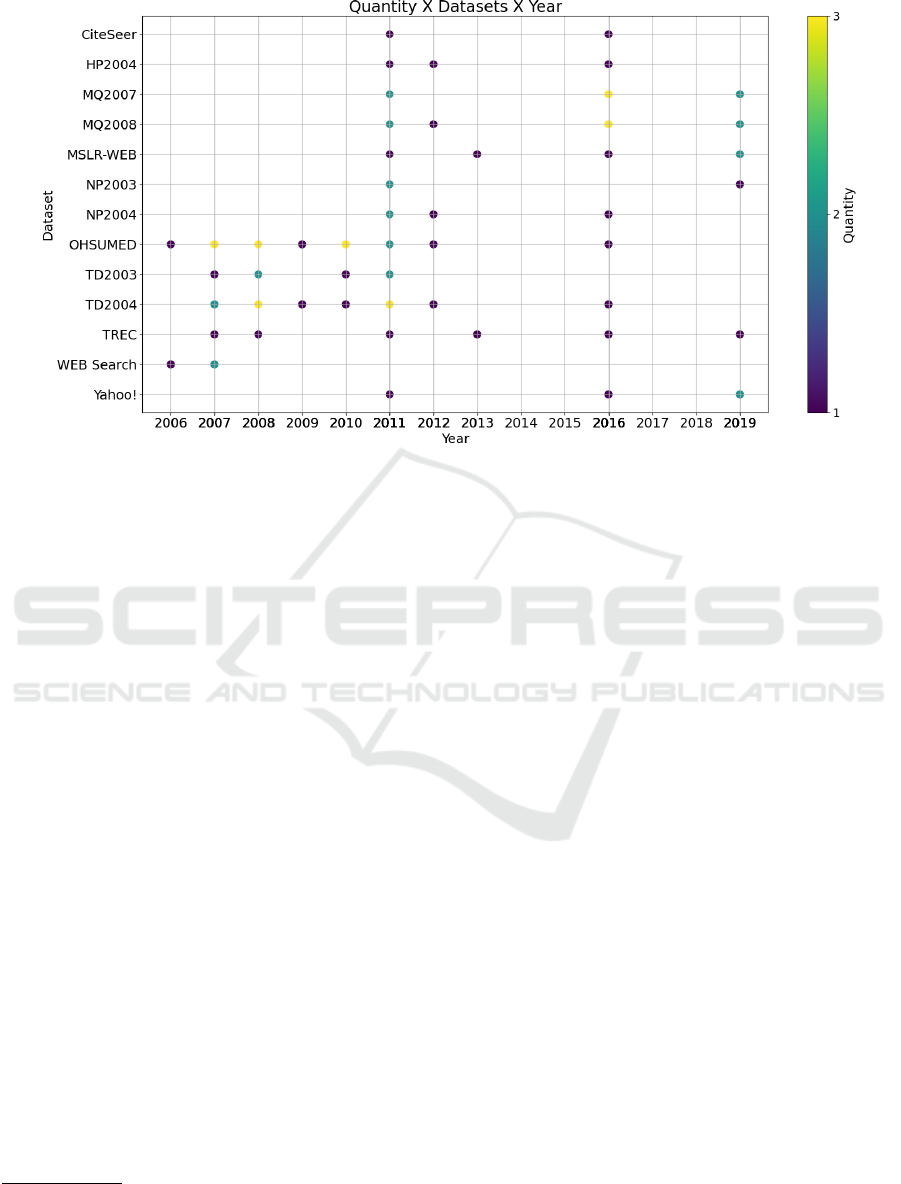
Figure 5: Number of papers that used each dataset.
4.1 An Analysis of the Datasets Used for
Training the Models
Another key point related to the topic tackled in this
investigation is the datasets used for training the ma-
chine learning models. Considering the selected stud-
ies, we have 13 data sources considerable used from
2006 to 2019. Most of them are part of the collec-
tion of datasets LETOR
2
from versions 3.0 (TD2003,
TD2004, OHSUMED, HP2004, NP2003, NP2004)
and 4.0 (MQ2007, MQ2008, MSLR-WEB), which
makes sense since the LETOR collection emerged to
become a basis to allow researchers to compare the
results obtained with existing algorithms with those
developed.
As a result, the OHSUMED dataset was the most
used in the studies, followed by the TD2004. Note
that in 2011 almost all datasets had at least one
appearance in some study, except the Web Search
dataset. Similarly, in 2016 we have almost all except
for TD2003, NP2003, and Web Search. We can as-
sume that LR was more on the rise, as the best-known
datasets were used for performance comparison. This
fact is related in Figure 5, which follows the same
structure as Figure 3.
2
https://www.microsoft.com/en-
us/research/project/letor-learning-rank-information-
retrieval/
4.2 General Analysis of Related Work
To help the general understanding of the surveyed
works, we have distinguished the collected articles
and papers into two categories. The first contains re-
ports that focus on the presentation of related content
in the field of LR. The second category includes pro-
posals of new algorithms, methods, approaches, mod-
els, strategies, or evaluation measures. Each study
was classified on Table 2.
From this table, it is observable that all 54 sur-
veyed studies were presented. Also, concerning the
year of these studies, we can see that they range from
2005 to 2021. The most significant number of studies
are from 2019. Considering the categories, we have
that 24 studies fit in the first category and 30 in the
second. However, the studies are generally related to
the beginning of the decade.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The number of studies about Learning to Rank cor-
roborates the importance of its use, considering that
there has been an evolution since the beginnings of
information retrieval with classical algorithms. The
use of LR allows reaching fields where they were not
reached before, considering only the relevance of the
search terms. Therefore, the best retrieval system will
be the one that manages to use relevance, importance,
and preference to return the best result requested by
the user.
A Literature Review on Methods for Learning to Rank
549

Table 2: Categories References.
Category 2005-2010 2011-2015 2016 - 2021
Focus on
introduce
some related
content in the
field of LR
(Signorini, 2005), (Tieyan
et al., 2007), (Wang et al.,
2008), (He et al., 2008),
(Duhan et al., 2009), (Qin
et al., 2010), (LI, 2011),
(Liu, 2011)
(Phophalia, 2011), (Li,
2011), (Busa-Fekete et al.,
2012), (Roa-Valverde and
Sicilia, 2014), (Gupta et al.,
2014), (Lal and Qamar,
2015), (Bama et al., 2015),
(Garg and Jain, 2015)
(Saravaiya Viralkumar et al.,
2016), (Shi et al., 2018),
(Serrano, 2019), (Rahang-
dale and Raut, 2019), (Har-
rag and Khamliche, 2020),
(Sharma et al., 2020), (Guo
et al., 2020), (Chavhan et al.,
2021)
Propose new
methods on
LR
(Cao et al., 2006), (Tsai
et al., 2007), (Xu and Li,
2007), (Geng et al., 2007),
(Qin et al., 2008b), (Li et al.,
2007), (Qin et al., 2008a),
(Veloso et al., 2008), (Xu
et al., 2008), (Moon et al.,
2010), (McFee and Lanck-
riet, 2010), (Chapelle and
Keerthi, 2010), (Alejo et al.,
2010), (Santos et al., 2011)
(Hong et al., 2012), (Yang
and Gopal, 2012), (Shaw
et al., 2013), (Lai et al.,
2013), (Cheng et al., 2013),
(Suhara et al., 2013), (Yang
et al., 2015)
(Ma et al., 2016), (Xu
et al., 2016), (Li et al.,
2016), (Ibrahim and Car-
man, 2016), (Keyhanipour
et al., 2016a), (Keyhanipour
et al., 2016b), (Zhao et al.,
2019), (Wang et al., 2019),
(Ai et al., 2019)
The survey of the related works that approach the
theme of Learning to Rank allowed us to observe how
new LR algorithms are evaluated and compared to the
state-of-the-art. We can say that RankSVM usually
corresponds to the most used algorithm when com-
paring different algorithms. In recent years, datasets
from the LETOR collection have been used as a
benchmark.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by CNPq (305805/2021-5)
and PNPD/CAPES (464880/2019-00).
REFERENCES
Ai, Q., Wang, X., Bruch, S., Golbandi, N., Bendersky, M.,
and Najork, M. (2019). Learning groupwise multivari-
ate scoring functions using deep neural networks. In
Fang, Y., Zhang, Y., Allan, J., Balog, K., Carterette,
B., and Guo, J., editors, Proceedings of the 2019 ACM
SIGIR International Conference on Theory of Infor-
mation Retrieval, ICTIR 2019, Santa Clara, CA, USA,
October 2-5, 2019, pages 85–92. ACM.
Alejo, O., Fern
´
andez-Luna, J. M., Huete, J. F., and Perez-
V
´
azquez, R. (2010). Direct optimization of evaluation
measures in learning to rank using particle swarm. In
2010 Workshops on Database and Expert Systems Ap-
plications, pages 42–46.
Baeza-Yates, R. A. and Ribeiro-Neto, B. (1999). Mod-
ern Information Retrieval. Addison-Wesley Longman
Publishing Co., Inc., USA.
Bama, S. S., Ahmed, M., and Saravanan, A. (2015). A sur-
vey on performance evaluation measures for informa-
tion retrieval system. International Research Journal
of Engineering and Technology, 2(2):1015–1020.
Bruch, S. (2019). An alternative cross entropy loss for
learning-to-rank. CoRR, abs/1911.09798.
Busa-Fekete, R., Szarvas, G.,
´
Elteto, T., and K
´
egl, B.
(2012). An apple-to-apple comparison of Learning-
to-rank algorithms in terms of Normalized Discounted
Cumulative Gain. In Raedt, D., L., Bessiere, C.,
Dubois, D., Doherty, P., Frasconi, P., Heintz, F., Lu-
cas, and P., editors, ECAI 2012 - 20th European Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence : Preference Learn-
ing: Problems and Applications in AI Workshop, vol-
ume 242, Montpellier, France. Ios Press.
Cao, Y., Xu, J., Liu, T.-Y., Li, H., Huang, Y., and Hon,
H.-W. (2006). Adapting ranking svm to document re-
trieval. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Interna-
tional ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and De-
velopment in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’06, page
186–193, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Carbonell, J. G., Michalski, R. S., and Mitchell, T. M.
(1983). 1 - an overview of machine learning. In
Michalski, R. S., Carbonell, J. G., and Mitchell,
T. M., editors, Machine Learning, pages 3–23. Mor-
gan Kaufmann, San Francisco (CA).
Chapelle, O. and Keerthi, S. S. (2010). Efficient algorithms
for ranking with svms. Inf. Retr., 13(3):201–215.
Chavhan, S., Raghuwanshi, M. M., and Dharmik, R. C.
(2021). Information retrieval using machine learning
for ranking: A review. Journal of Physics: Conference
Series, 1913(1):012150.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
550

Cheng, F., Zhang, X., He, B., Luo, T., and Wang, W.
(2013). A survey of learning to rank for real-time
twitter search. In Zu, Q., Hu, B., and Elc¸i, A., editors,
Pervasive Computing and the Networked World, pages
150–164, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
Duhan, N., Sharma, A. K., and Bhatia, K. K. (2009). Page
ranking algorithms: A survey. In 2009 IEEE Interna-
tional Advance Computing Conference, pages 1530–
1537.
Garg, Y. and Jain, M. (2015). A brief survey of various rank-
ing algorithms for web page retrieval in web structure
mining. International Journal of Engineering Trends
and Technology, 21(3):168–172.
Geng, X., Liu, T.-Y., Qin, T., and Li, H. (2007). Fea-
ture selection for ranking. In Proceedings of the 30th
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Re-
search and Development in Information Retrieval, SI-
GIR ’07, page 407–414, New York, NY, USA. Asso-
ciation for Computing Machinery.
Guo, J., Fan, Y., Pang, L., Yang, L., Ai, Q., Zamani, H.,
Wu, C., Croft, W. B., and Cheng, X. (2020). A
deep look into neural ranking models for informa-
tion retrieval. Information Processing & Management,
57(6):102067.
Gupta, S., Duhan, N., Bansal, P., and Sidhu, J. (2014). Page
ranking algorithms in online digital libraries: A sur-
vey. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference
on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimiza-
tion, pages 1–6.
Harrag, F. and Khamliche, M. (2020). Mining stack over-
flow: a recommender systems-based model.
He, C., Wang, C., Zhong, Y.-X., and Li, R.-F. (2008). A sur-
vey on learning to rank. In 2008 International Con-
ference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, vol-
ume 3, pages 1734–1739.
Hong, L., Bekkerman, R., Adler, J., and Davison, B. D.
(2012). Learning to rank social update streams. In
Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR
Conference on Research and Development in Informa-
tion Retrieval, SIGIR ’12, page 651–660, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Ibrahim, M. and Carman, M. (2016). Comparing pointwise
and listwise objective functions for random-forest-
based learning-to-rank. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst., 34(4).
Keyhanipour, A. H., Moshiri, B., Piroozmand, M., Oroum-
chian, F., and Moeini, A. (2016a). Learning to rank
with click-through features in a reinforcement learn-
ing framework. International Journal of Web Infor-
mation Systems.
Keyhanipour, A. H., Moshiri, B., Piroozmand, M., Oroum-
chian, F., and Moeini, A. (2016b). Learning to rank
with click-through features in a reinforcement learn-
ing framework. Int. J. Web Inf. Syst., 12(4):448–476.
Kowalski, G. J. and Maybury, M. T. (2002). Introduction
to information retrieval systems. Information Storage
and Retrieval Systems: Theory and Implementation,
pages 1–25.
Lai, H., Pan, Y., Liu, C., Lin, L., and Wu, J. (2013). Sparse
learning-to-rank via an efficient primal-dual algo-
rithm. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 62(6):1221–
1233.
Lal, N. and Qamar, S. (2015). Comparison of ranking algo-
rithms with dataspace. In 2015 International Confer-
ence on Advances in Computer Engineering and Ap-
plications, pages 565–572.
Li, B., Chaudhuri, S., and Tewari, A. (2016). Handling class
imbalance in link prediction using learning to rank
techniques. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, 30(1).
Li, H. (2011). Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval
and Natural Language Processing. Synthesis Lec-
tures on Human Language Technologies. Morgan &
Claypool Publishers.
LI, H. (2011). A short introduction to learning to rank.
IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems,
E94.D(10):1854–1862.
Li, P., Burges, C. J. C., and Wu, Q. (2007). Mcrank: Learn-
ing to rank using multiple classification and gradient
boosting. In Proceedings of the 20th International
Conference on Neural Information Processing Sys-
tems, NIPS’07, page 897–904, Red Hook, NY, USA.
Curran Associates Inc.
Liu, T. (2011). Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval.
Springer.
Ma, Q., He, B., and Xu, J. (2016). Direct measurement of
training query quality for learning to rank. In Proceed-
ings of the 31st Annual ACM Symposium on Applied
Computing, SAC ’16, page 1035–1040, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
McFee, B. and Lanckriet, G. (2010). Metric learning to
rank. In Proceedings of the 27th International Confer-
ence on International Conference on Machine Learn-
ing, ICML’10, page 775–782, Madison, WI, USA.
Omnipress.
Moon, T., Smola, A., Chang, Y., and Zheng, Z. (2010). In-
tervalrank: Isotonic regression with listwise and pair-
wise constraints. In Proceedings of the Third ACM In-
ternational Conference on Web Search and Data Min-
ing, WSDM ’10, page 151–160, New York, NY, USA.
Association for Computing Machinery.
Phophalia, A. (2011). A survey on learning to rank (letor)
approaches in information retrieval. In 2011 Nirma
University International Conference on Engineering,
pages 1–6.
Qin, T. and Liu, T. (2013). Introducing LETOR 4.0 datasets.
CoRR, abs/1306.2597.
Qin, T., Liu, T.-Y., Xu, J., and Li, H. (2010). Letor: A
benchmark collection for research on learning to rank
for information retrieval. Inf. Retr., 13(4):346–374.
Qin, T., Liu, T.-Y., Zhang, X.-D., Wang, D.-S., and Li, H.
(2008a). Global ranking using continuous conditional
random fields. In Proceedings of the 21st Interna-
tional Conference on Neural Information Processing
Systems, NIPS’08, page 1281–1288, Red Hook, NY,
USA. Curran Associates Inc.
Qin, T., Zhang, X.-D., Tsai, M.-F., Wang, D.-S., Liu, T.-
Y., and Li, H. (2008b). Query-level loss functions
for information retrieval. Information Processing &
Management, 44(2):838–855. Evaluating Exploratory
A Literature Review on Methods for Learning to Rank
551

Search Systems Digital Libraries in the Context of
Users’ Broader Activities.
Rahangdale, A. and Raut, S. (2019). Machine learn-
ing methods for ranking. International Journal of
Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering,
29(06):729–761.
Rigutini, L., Papini, T., Maggini, M., and Scarselli, F.
(2011). Sortnet: Learning to rank by a neural pref-
erence function. IEEE Transactions on Neural Net-
works, 22(9):1368–1380.
Roa-Valverde, A. J. and Sicilia, M.-A. (2014). A survey of
approaches for ranking on the web of data. Informa-
tion Retrieval, 17(4):295–325.
Salton, G. and Harman, D. (2003). Information Retrieval.
John Wiley and Sons Ltd., GBR.
Santos, R. L., Macdonald, C., and Ounis, I. (2011). Intent-
aware search result diversification. In Proceedings of
the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Re-
search and Development in Information Retrieval, SI-
GIR ’11, page 595–604, New York, NY, USA. Asso-
ciation for Computing Machinery.
Saravaiya Viralkumar, M., Patel, R. J., and Singh, N. K.
(2016). Web mining: A survey on various web page
ranking algorithms. International Research Journal of
Engineering and Technology (IRJET), e-ISSN, pages
2395–0056.
Serrano, W. (2019). Neural networks in big data and web
search. Data, 4(1).
Sharma, P. S., Yadav, D., and Garg, P. (2020). A system-
atic review on page ranking algorithms. International
Journal of Information Technology, 12:329–337.
Shaw, B., Shea, J., Sinha, S., and Hogue, A. (2013). Learn-
ing to rank for spatiotemporal search. In Proceedings
of the Sixth ACM International Conference on Web
Search and Data Mining, WSDM ’13, page 717–726,
New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Ma-
chinery.
Shi, Z., Keung, J., Bennin, K. E., and Zhang, X. (2018).
Comparing learning to rank techniques in hybrid bug
localization. Applied Soft Computing, 62:636–648.
Signorini, A. (2005). A survey of ranking al-
gorithms. Department of Computer Sci-
ence, University of Iowa. Available at:
http://www.algorithmcapital.com/survey-of-ranking-
search-algorithms-possible-link.pdf. Accessed: Dec.
2021.
Suhara, Y., Suzuki, J., and Kataoka, R. (2013). Robust on-
line learning to rank via selective pairwise approach
based on evaluation measures. Information and Me-
dia Technologies, 8(1):118–129.
Tieyan, L., Tao, Q., Jun, X., et al. (2007). Letor: Bench-
mark dataset for research on learning to rank for in-
formation retrieval. In Proceedings of the Workshop
on Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval, pages
137–145.
Tsai, M.-F., Liu, T.-Y., Qin, T., Chen, H.-H., and Ma, W.-Y.
(2007). Frank: A ranking method with fidelity loss. In
Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SI-
GIR Conference on Research and Development in In-
formation Retrieval, SIGIR ’07, page 383–390, New
York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
Veloso, A. A., Almeida, H. M., Gonc¸alves, M. A., and
Meira Jr., W. (2008). Learning to rank at query-time
using association rules. In Proceedings of the 31st
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Re-
search and Development in Information Retrieval, SI-
GIR ’08, page 267–274, New York, NY, USA. Asso-
ciation for Computing Machinery.
Wang, H., Kim, S., McCord-Snook, E., Wu, Q., and Wang,
H. (2019). Variance reduction in gradient exploration
for online learning to rank. In Piwowarski, B., Cheva-
lier, M., Gaussier,
´
E., Maarek, Y., Nie, J., and Scholer,
F., editors, Proceedings of the 42nd International
ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Develop-
ment in Information Retrieval, SIGIR 2019, Paris,
France, July 21-25, 2019, pages 835–844. ACM.
Wang, J., Robertson, S., de Vries, A. P., and Reinders, M.
J. T. (2008). Probabilistic relevance ranking for col-
laborative filtering. Inf. Retr., 11(6):477–497.
Xu, B., Lin, H., and Lin, Y. (2016). Assessment of learning
to rank methods for query expansion. Journal of the
Association for Information Science and Technology,
67(6):1345–1357.
Xu, J. and Li, H. (2007). Adarank: A boosting algorithm
for information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 30th
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Re-
search and Development in Information Retrieval, SI-
GIR ’07, page 391–398, New York, NY, USA. Asso-
ciation for Computing Machinery.
Xu, J., Liu, T.-Y., Lu, M., Li, H., and Ma, W.-Y. (2008).
Directly optimizing evaluation measures in learning
to rank. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Interna-
tional ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and De-
velopment in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’08, page
107–114, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Yang, X., Tang, K., and Yao, X. (2015). A learning-to-rank
approach to software defect prediction. IEEE Trans-
actions on Reliability, 64(1):234–246.
Yang, Y. and Gopal, S. (2012). Multilabel classification
with meta-level features in a learning-to-rank frame-
work. Mach. Learn., 88(1–2):47–68.
Zhao, G., da Costa, D. A., and Zou, Y. (2019). Improv-
ing the pull requests review process using learning-
to-rank algorithms. Empir. Softw. Eng., 24(4):2140–
2170.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
552
