
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the
Knowledge of a Legal Document
Thinh H. Nguyen
1,2
, Hien D. Nguyen
1,2 a,*
, Vuong T. Pham
3
, Dung A. Tran
4
and Ali Selamat
5,6 b
1
Faculty of Computer Science, University of Information Technology, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
2
Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
3
Faculty of Information Technology, Sai Gon University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
4
Faculty of Software Engineering, University of Information Technology, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
5
Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology (MJIIT), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
6
Center for Basic and Applied Research, Faculty of Informatics and Management, University of Hradec Kralove,
Rokitanskeho 62, Hradec Kralove 50003, Czech Republic
Keywords: Ontology, Law Document, Knowledge Representation, Semantic, Intelligent System, Information Retrieval.
Abstract: In the legal knowledge domain, legal norm documents are general rules which are mandatory for people in a
certain field. Many regulations are affecting to activities in a field. Ontology is an effective approach for
representing practical knowledge domains. In this paper, an integration ontology for representing the
knowledge of a law document is proposed. This model is integrated of ontology about relational knowledge
and the graph of keyphrases as a conceptual graph. It can represent semantic of contents in the law document.
Based on this integrated model, the improvement method of self-attention network by language-oriented
semantic analyzing is studied for intellectual retrieval on the law document. Moreover, the proposed method
is applied to construct an intelligent support system for knowledge querying on Vietnam Land Law. It can
help users to query some meaning of terminology in land law and some land-related administrative procedures.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the legal knowledge, legal norm documents which
issued by the government contain general rules that
are mandatory for people in a certain field (Casellas,
2011, Sartor et al., 2011). For each field, many
regulations affect to activities in that field. Those
regulations have a complicated relationship with
other regulations: the regulations which are issued by
the administrative unit depend on the regulations of
the superior unit, and also are affected by the
regulations of other related units in that field.
In Vietnam, the system of legal documents has
many levels: 1/ The highest validity is Constitution;
2/ Codes/Laws and resolutions of National Assembly;
3/ Sub-law documents for instructing the detail of the
law established by Vietnam National Assembly.
Thus, a support system for intellectual retrieval on
law knowledge is very necessary for people.
* Corresponding author.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8527-0602
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9746-8459
Nowadays, there are many systems organize the
database of law documents (Leone et al., 2018, Fawei
et al., 2019). Szostek and Zatucki (2022) introduced
some information tools in the administration of
justice. The CEN Workshop on an Open XML
Interchange Format for Legal and Legislative
Resources (Metalex) developed the standards for
representing sources of law and references to sources
of law in XML (Sartor et al., 2011). It can answer to
the urgent request to normalize the abundance of local
legal XML dialects. Nonetheless, those systems still
have some limitations to represent the semantic of
those documents. This led to current searching
systems on law domain only can retrieve some
articles in law document and have not yet retrieve
deeper in content, such as administrative procedures
about a determined service.
426
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, H., Pham, V., Tran, D. and Selamat, A.
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the Knowledge of a Legal Document.
DOI: 10.5220/0011066300003176
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineer ing (ENASE 2022), pages 426-434
ISBN: 978-989-758-568-5; ISSN: 2184-4895
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In this paper, an ontology for representing the
knowledge of a law document is proposed. This
model is the integration of ontology Rela-model,
which is useful to represent relational knowledge
domains (Do et al., 2018), and the graph of key
phrases as a conceptual graph (Shi et al., 2018). The
integration model, called Legal Rela-model, has the
foundation including concepts in law domain,
relations between concepts, inference rules of this
domain and relations between key phrases, concepts
in law document and database storing law contents.
This model can represent complex relations between
concepts in a law document to retrieve some required
knowledge to people. Besides, the method for
intellectual retrieval on the law document is
proposed. The improvement of self-attention network
(Vaswani et al., 2017) is presented by language-
oriented semantic analyzing in Vietnamese (Nguyen
et al., 2020a). This technique is used to extract key
phrases of a law document.
Moreover, the proposed method is applied to
construct an intelligent support system for querying
on Vietnamese land law (Nguyen et al., 2020c) with
its knowledge base is organized by ontology Legal
Rela-model. This system can help users to query
some meaning of terminology in land law and some
land-related administrative procedures. It also tested
by major lawyers and got positive feedback from
users.
The next section presents some related work
about methods for organizing the document
repository, especially for law documents. Section 3
proposes a knowledge model for representing the
content of a law document, called Legal Rela-model,
based on the integration of ontology Rela-model and
the conceptual graph of key phrases. Section 4
designs the method for solving problems about
querying knowledge content of the law document by
Vietnamese. Section 5 shows the architecture of a
support system in land resource for querying on
Vietnamese Land Law and its testing results. The last
section concludes and presents some future work.
2 RELATED WORK
The law document is a general rule of conduct,
commonly binding on agencies, organizations and
individuals nationwide or within a certain
administrative unit (Vietnam Ministry of Justice,
2011, Nguyen et al., 2022). With a determined
domain, there are many documents related together
impacting to that domain. Ontology is an effective
approach to organize semantic document repository
(Huynh et al., 2019, Doan et al, 2003). However,
those methods are not suitable to organize law
documents.
LIDO is an ontology for Legal Informatics
Document (Sartor, 2019). This ontology can be
represented the legal actions affecting the document,
the legal temporal events, the structure of the legal
resource, and the semantic structure of the legal
document organization.
Huynh et al. (2019) constructed the integrating
method of an ontology describing domain knowledge,
and a database of document repository. This method
includes a model of domain knowledge for various
information retrieval tasks, called The Classed
Keyphrase based Ontology (CK-ONTO).
Nonetheless, this graph-based measure has not been
used to evaluate the semantic relevance in documents.
Ngo et al. (2021) designed a system for
Vietnamese legal text processing by leveraging the
strength of traditional information retrieval methods
(BM25), pre-trained masked language models
(BERT), and legal domain knowledge. They also
proposed a novel data augmentation method which is
based on legal domain knowledge in the legal textual
entailment. However, the proposed method does not
represent the semantic of the legal document.
The chatbot in (Nguyen et al., 2020c) was
designed to tutor some administrative procedures,
such as how to get a printing license. However, this
system cannot support to query the content in a law
document related to the working domain.
Statistical relational learning (SRL) and graph
neural networks (GNNs) are two powerful
approaches for learning and inference over graphs.
Typically, they are evaluated in terms of simple
metrics such as accuracy over individual node labels.
The study in (Embar and Srinivasan, 2021) proposed
a sampling framework to tractably compute the
values of aggregate graph queries (AGQ). That
method only works on information of social network
and cannot be used for organizing the meaning of a
legal document.
Ontology is a useful method for representing the
knowledge domain and searching on it (Do et al.,
2020). This study presents a method for organizing
the content of a law document and its meaning in each
article by integrated ontology. It is the foundation to
design techniques for querying some meaning of law
terminology and some administrative procedures in
Vietnamese.
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the Knowledge of a Legal Document
427

3 KNOWLEDGE MODEL OF
RELATIONS FOR LAW
DOMAIN
The system of Vietnamese legal documents includes:
• The Constitution: the highest legal-valued
document for constructing other documents.
• Codes/Laws and resolutions of National
Assembly: In a determined domain, this document is
a general rule of conduct, commonly binding on and
applied repeatedly to agencies, organizations and
individuals nationwide or within a certain
administrative unit in this domain.
• Sub-law documents: Those are documents
instructing the detail of the law established by
National Assembly. Some of sub-law documents are:
Decrees of the Government, Decisions of Prime
Minister, Circulars or Joint circulars of ministers who
are related to the scope of the law, Decisions of
provincial-level People’s Committees, etc.
This section presents a model to represent a law
document by its content and its meaning. This model
is improved based on Rela-model, called Legal Rela-
model. This ontology is an integration between
ontology Rela-model representing the knowledge of
law and a conceptual graph representing relations
between legal key phrases. Moreover, the ontology
Legal Rela-model is connected to the structure of
Vietnamese legal document.
At the article 11 of the circular of Vietnam
Ministry of Justice (2011), the structure of a law
document is one of the followed kinds:
a) Part, Chapter, Section, Article, Clause,
Point; or
b) Chapter, Section, Article, Clause, Point; or
c) Section, Article, Clause, Point; or
d) Clause, Point.
Based on those structures, the database for
contents of a law document can be organized.
Through that database, the knowledge of the law
document can represent by ontology Legal Rela-
model.
Definition 3.1: The ontology for representing a
legal document, called Legal Rela-model, consists of
components as follows:
K = (C, R, RULES) + (Key, Rel, weight)
In which:
(C, R, RULES) is a structure of Rela-model
(Do et al., 2018, Nguyen et al., 2020b), where C is a
set of concepts, but each concept in C has been
improved its internal structure to organize its law
information; R is a set of relations, those relations are
between concepts, key phrases and database storing
the content of the law document; and RULES is a set
of inference rules of the knowledge domain.
(Key, Rel, weight) is a conceptual graph
representing the relations between key phrases of
legal documents. In which, Key is a set of key phrases
of the law document, Rel is the set of arcs, and weight
is a map from Key to binary similarly vector.
3.1 C – The Set of Concepts
The law includes general rules constituted based on
concepts which are taken for granted. In the real-
world, a concept in a legal document is defined based
on its structure and relations in articles of the law
document. The followed definition is about the
structure of a concept in each law document d.
Definition 3.2: The structure of a concept
Each concept in C consists of five elements:
(Name, Content, InnerRel, Phrases, Attributes)
where: Name: The name of the concept in the law.
Content: Content or meaning of the concepts.
InnerRel: List of articles in the document d
related to the corresponding concept.
Phrases: The list of key phrases related to
concepts in each article of the document d.
Attributes: List of components (or other
concepts) which are the foundation to build
the corresponding concept (if necessary) in
the document d.
Example 3.1: With the Vietnam Land Law 2013
in (Vietnam National Assembly, 2013), the
components of the concept “Certificate of land use
rights” are:
Component Content
Name Certificate of land use rights
Content
Certificate of land use rights is a legal
certificate in which the State certifies the
lawful land use rights and ownership of houses
and land-attached assets of the person who has
land use rights and ownership of houses and
lan
d
-attached assets.
InnerRel
Article 3, Point 16.
Article 11, Point 1.
Article 75, Point 1.
Article 97, Point 1,2.
Article 100, Point 1,2,3,4,5.
Phrases
land use rights, ownership of houses, land-
attached assets, lan
d
-attached houses
Attributes
Land use rights,
Inheritance land-attached assets,
Donation land-attached assets,
Hand-over of land-attached gratitude house,
Transfer of land use rights,
Purchase of residential land-attached houses,
Liquidation of residential land-attached
houses.
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
428

3.2 R – The Set of Relations
Set R is classified to three kinds of relations:
R = R
concept
R
keyphrases
R
database
R
concept
is a set of relations between concepts in
C. Those relations are “is-a”, “has-a”, “a-part-of”,
and other relations between concepts.
R
concept
C C
Some properties of each relation r
R
concept
are considered: symmetric, transitive.
R
keyphrases
is a set of relations between key
phrases in the law document. It also includes some
relations between key phrases and a concept which
are characteristic to determine the concept’s meaning.
R
keyphrases
Key Key
and R
keyphrases
Key C.Phrases
R
database
is a set of relations between concepts
and keyphrases which are connected to database of
the law document.
3.3 RULES – The Set of Rules
The rules in the RULES-set represent the constraint
and inferring relation between keyphrases, and
concepts. Using deductive rules helps to reduce
workload of a knowledge engineer when building
ontology data. The RULES-set deduces the direct or
indirect relationships between key phrases or
concepts which are used to determine the semantic
similarity among key phrases and concepts.
A rule r RULES is a deductive rule on facts
related to key phrases and concepts. It can be
described as follows:
r: {f
1
, f
2
,…, f
n
} {g
1
, g
2
,…, g
m
}
with {f
1
, f
2
,…, f
n
}
are hypothesis facts and {g
1
,
g
2
,…, g
m
}
are goal facts of the rule. There are three
kinds of facts:
Table 1: Kinds of Facts.
Kind Meanin
g
S
p
ecification
1
Show a property of
a relation
[<rel> is < property >]
rel R is a relation.
2
Relations between
concepts.
[<c
1
><rel><c2>]
c
1
, c
2
C
3
Relations between
key phrases.
[<k
1
><rel><k
2
>]
k
1
,
k
2
K
ey
4
Relations between
key phrases and a
conce
p
t.
[<k><rel><c.Phrases>]
k
Key, c C
Example 3.2: Some rules in the domain:
r
1
: if [ is symmetric] and [k
1
k
2
] then [k
2
k
1
]
r
2
: if [ is transitive] and [k
1
k
2
] and [k
2
k
3
] then
[k
1
k
3
]
3.4 (Key, Rel, weight) – The
Conceptual Graph
The structure of Rela-model (C, R, RULES)
organizes the knowledge of a law document.
However, in the practice, when retrieval a content of
law, there are some main key phrases in the query
sentence has been connected to the knowledge
through their semantic. In this study, the semantic of
key phrases are organized by a conceptual graph.
Definition 3.3: Given a document law d. The
structure of the graph representing relations between
key phrases in the document d is a tube:
(Key, Rel, weight)
where: Key = {k | k is a key phrase of the legal
document}.
Rel = {e = (k
1
, k
2
) Key Key | k
1
are k
2
are key phrases appearing in the same article of the
law document}
weight: Key R R is a map to compute
the similarly binary vector for each key phrases in
Key. (R is the set of real number).
The measure for similarly key phrases is computed
by the tube (tf(v, d), idf(v, d)), where tf(v, d) is the
term frequency representing the frequency of a key
phrase v in a document d, and idf(v, d) is the inverse
articles frequency representing the specificity of the
key phrase v in the document d. The formulas of (tf(v,
d), idf(v, d)) are established as follows (Le et al.,
2019):
,
',
( , ) : (1 ) (1)
max{ | ' }
vd
vd
n
tf v o c c
nvKey
where, n
v,o
is the number of occurrences of the key
phrase v in the document d,
c [0, 1] is a parameter which is the minimum
value for every key phrases.
()
card ( )
(, ): log
1card{ ()| ( )}
ar Article d
keyphrases ar
idf v d
ar Article d v keyphrase ar
(2)
where, Article(d) is the set of articles of the law
document d.
keyphrase(ar) is the set of key phrases of the
article ar in the document d.
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the Knowledge of a Legal Document
429
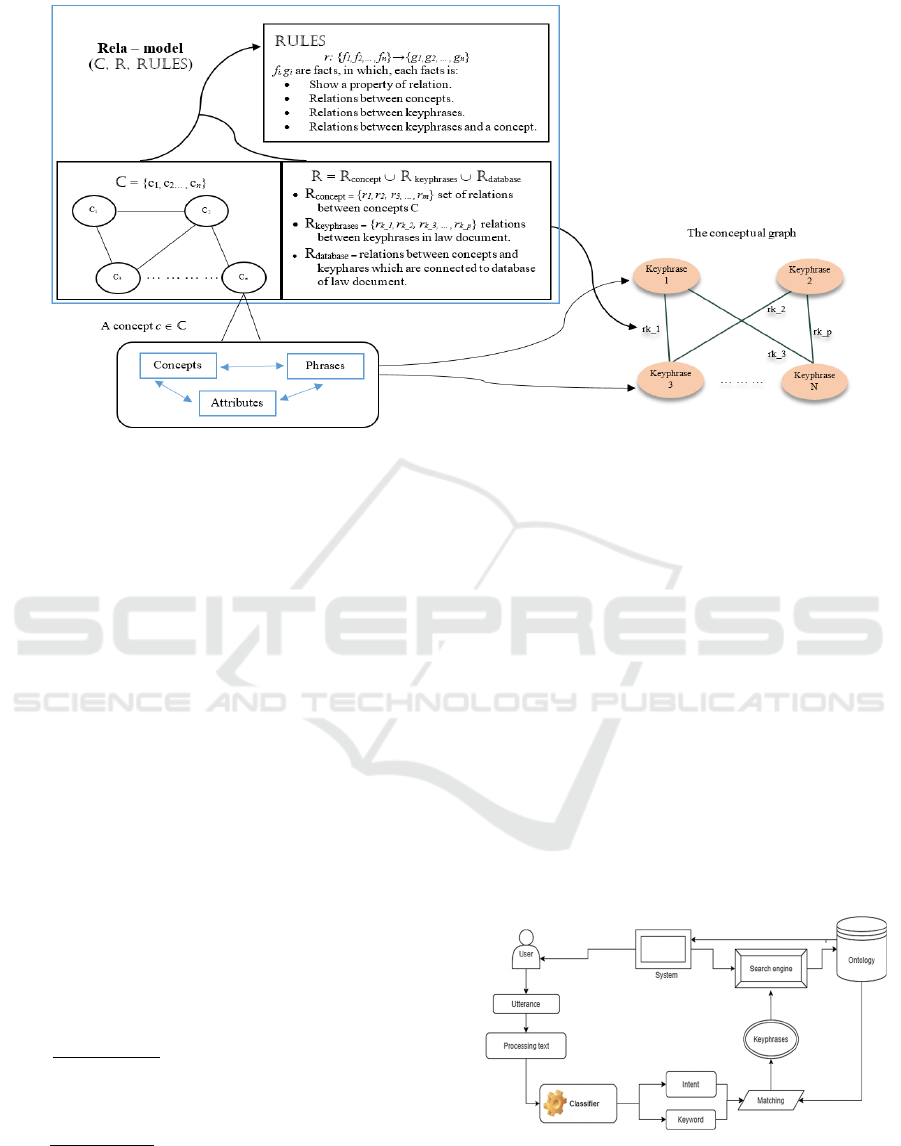
Figure 1: The structure of Legal Rela-model.
Figure 1 represents the structure of the ontology
Legal Rela-model. In this structure, the Rela-model is
combined with the graph of key phrases via key
phrases and their relations. When key phrases are
objects in the land law, those relations between them
are behaviours of them which were determined in
law.
4 KNOWLEDGE QUERYING ON
A LEGAL DOCUMENT
Let K be a knowledge domain of the law document d
as ontology Legal Rela-model, and the database of the
document d. When a query is inputted to retrieve the
knowledge from K , the searching system will process
to extract some main key phrases and compare with
the structure of the knowledge model’s components
through relations between key phrases leading to
corresponding concepts. In the matching process,
inference rules of the knowledge base help to deduce
more relations related to the content of the query and
retrieve results for the inputted query. Some of main
problems are as follows:
(1) Problem 4.1: Classifying the inputted query.
From the query inputted as Vietnamese text, this
problem extracts the main key phrases of the query to
determine the meaning of the query and classify it.
(2) Problem 4.2: Retrieving suitable articles in the
document and searching the content of concepts
based on matching the key phrases. Based on
extracted key phrases, a method to compare the
similarity between the meaning of the key phrases
and the content in the knowledge base is proposed.
For the problem 4.1, in Vietnamese, the structure
of a sentence includes subject and predicate. In this
study, we only mention to the declarative sentence
type. Besides, the query sentence is also classified
into five kinds: queries about concepts/definitions in
the Land Law, queries about procedures of this law,
and queries about some knowledge related to current
results. The solution for this problem is designed
similarly to (Nguyen et al., 2021). Hence, this section
presents the method to retrieve suitable articles in the
document and searching the content of concepts
based on matching the key phrases in the problem 4.2.
After extracting the key phrases and intents of the
utterance, the system will match those key phrases
with the content of the knowledge for defining and
comparing texts based on ontology Legal Rela-
model. The matching technique for the search engine
can be designed based on the solution in (Nguyen et
al., 2021), but it has some improvements as Figure 2.
Figure 2: The matching technique for search engine.
After classifying of the inputted query, this
process also extracts main key phrases of the query.
Those key phrases are used to retrieve the suitable
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
430
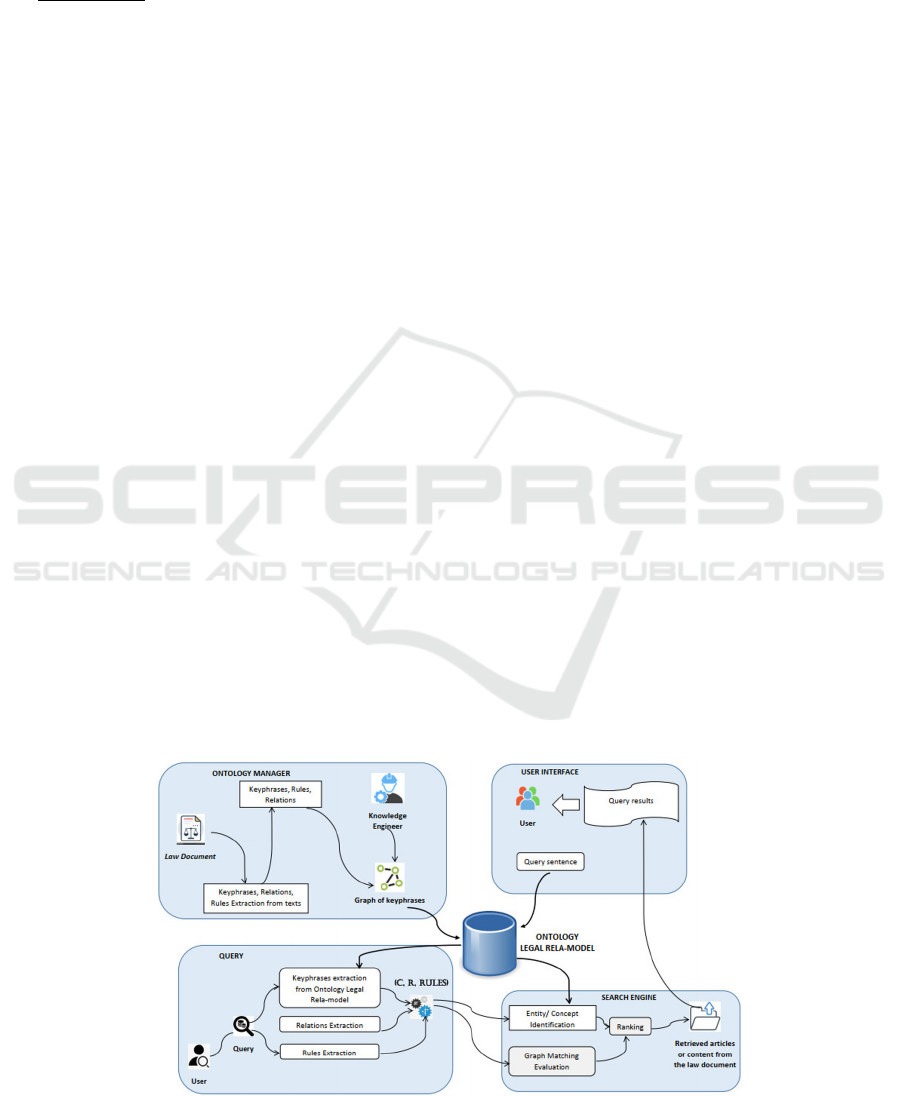
content from the knowledge base in Problem 4.2. The
key phrases dictionary is established from the
knowledge base of the search system and from the
experts in the law domain, such as lawyers, senior law
employees, senior lecturers in the law domain.
Example 4.1: Some key phrases in the dictionary
of the Vietnamese Land Law 2013 in (Vietnam
National Assembly, 2013):
Some individuals in the dictionary: Cadastral
map, Transfer of land use rights, Certificate of land
use rights, kinds of agricultural land (Land for
cultivation of annual crops, Land for cultivation of
perennial trees, Production Forest land, Aquaculture
land, etc.), non-agricultural land (Residential land,
Land for construction of offices, Land used for
public purposes, etc.).
The synonyms of a key phrases in the
dictionary: “What is” is equivalent to “Define”,
“How to use” is equivalent to “Usage”.
The extracted key phrases of the utterance are
compared with the dictionary to create a set of key
phrases. The search engine uses those key phrases to
retrieve the knowledge of law from the knowledge
base. The system also recommends some related
knowledge through relations of obtained results and
inference rules of the knowledge base.
Algorithm 4.1: Given the law document d which
represented by the ontology Legal Rela-model.
Input: a query q.
Output: The set of knowledge content in the
document d which matches the meaning of query q.
Step 1:
Extract keyphrases from the query sentence
and establish set of key phrases of q.
W := keyphrases(q)
Expand the set of key phrases W based on
relations in R
keyphrases
.
Update the set W.
Mapping keyphrases in W to the sub-graph G
of the conceptual graph (Key, Rel, weight)
with a weight vector for each key phrases.
S t e p 2 : Knowledge := {} // set of results.
Concept :={};
For each phrase G do
Use relations in R
keyphrases
and inference
rules in RULES for linking phrase
with a corresponding concept c C.
Update c into Concept.
Expand the set of concepts in Concept:
Based on relations in R
keyphrases
.
Update the set W.
Retrieve knowledge from components of
each concept c Concept
Update Knowledge.
S t e p 3 :
Unification of facts in the knowledge model
and compare the meaning using Problem
1.
Update Knowledge.
Step 4: Return results in Knowledge
The searching for the knowledge content returns
a set of knowledge based on the meaning of an
inputted query. The system determines the meaning
of this query from its extracted keywords and
comparing by using stored knowledge.
5 THE QUERYING SYSTEM FOR
VIETNAM LAND LAW
Land resource is one of important resource in
Vietnamese economic. It is attracted by investors
because of its stability and increasing of value during
the time (Tran, 2013). Legality is one of key factors
determining the value of a land.
Figure 3: The architecture of the querying system on land law.
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the Knowledge of a Legal Document
431
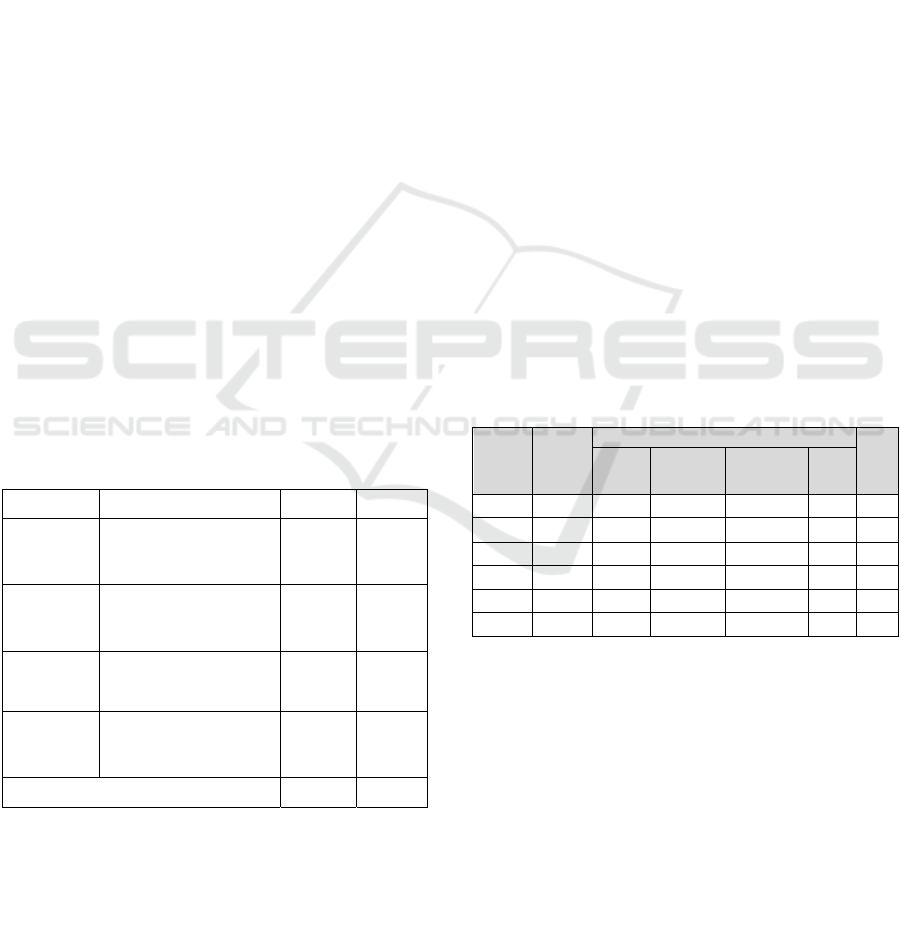
The land law is a document promulgated by a
state agency, and contains general rules for
conducting, commonly binding on agencies,
organizations in the domain of land (Vietnam
National Assembly, 2013, Tran, 2013). It will have
some sub-law documents to detail instruct the process
of this law. In this section, a querying system for the
land law in Vietnam is designed. Its knowledge base
is constructed based on the Vietnamese Land
(Vietnam National Assembly, 2013) by using
ontology Legal Rela-model. This system can help
users to query some meaning of terminology in land
law and some land-related administrative procedures.
The structure of this system is presented in Figure 3.
5.1 Dataset and Organizing the
Knowledge Base of Land Law
Document
The Vietnamese Land Law 2013 includes 14 chapters
with 212 articles (Vietnam National Assembly,
2013). It is a general rule for all working in the land
domain. The content of this law is organized by a
database as the structure of Chapter – Section –
Articles – Paragraph - Point. Ontology Legal Rela-
model is used to represent it’s content and meaning.
There were 625 collected queries to training for
classifying by Problem 4.1. It includes 521 in-scope
queries covering three intent classes and 104 out-of-
scope queries. Table 2 classifies the training queries
and the results for training them in collected dataset.
Table 2: Classification of queries.
Class Meaning Training Tested
Concept
Require to determine
definition or attributes of
a concept
211 54
Procedure
Require to determine list
of documents for a
procedure in land law.
93 24
Related
knowledge
Require knowledge
related to obtained results
107 32
Out of scope
Queries related to real-
estate but they do not use
land law.
83 21
Total 494 131
In-scope data were collected from the frequently
asked questions (FAQs) in land law by the consulting
of major lawyers (FAQs, 2022). The intents were
grouped on the basis of the scope of the system in this
study. Out-of-scope data were collected from FAQs
related to real-estate but they do not use the
knowledge of land law.
5.2 Search Engine
When a query sentence is inputted, its key phrases are
extracted. Using the knowledge as ontology Legal
Rela-model, some rules and relations will be applied
to get more some related key phrases and their
relations. By the problem 4.2, the set of knowledge
content in the document d which matches the
meaning of those key phrases is retrieved. The results
are articles or content from the Land Law.
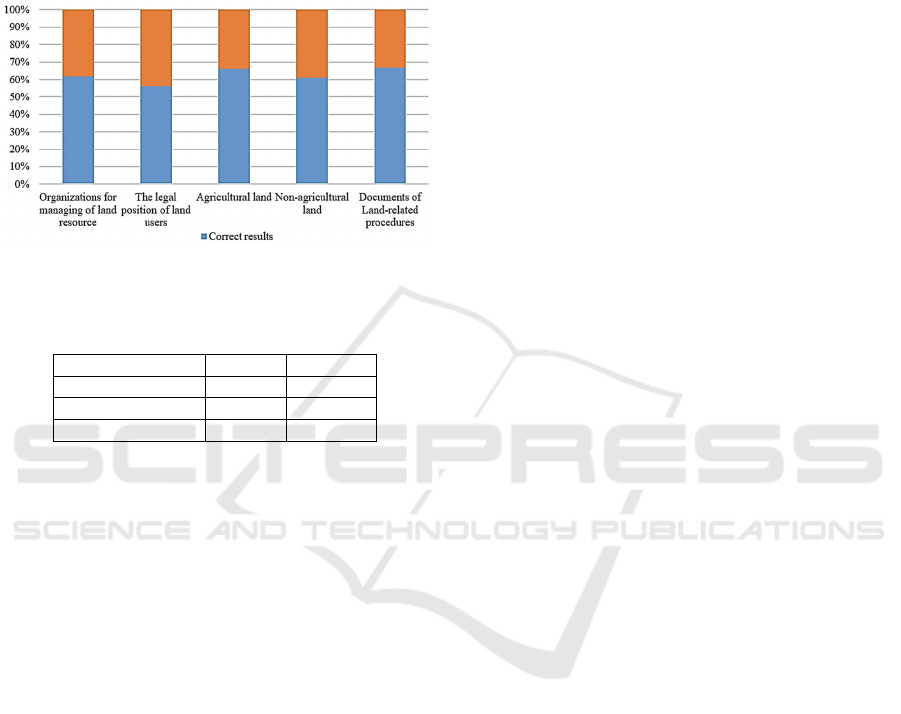
5.3 Experimental Results
This study implements the experiments about
querying on some meaning of terminology in land
law and some land-related administrative procedures.
Its knowledge content is splitted into 05 kinds:
Kind 1: Organize to manage land resource.
Kind 2: The legal position of land users.
Kind 3: Agricultural land.
Kind 4: Non-agricultural land.
Kind 5: Documents of Land-related procedures
When users inputt their queries, the system
classifies those queries into concepts, procedures or
related knowledge; then it retrieves results for users.
The process of theis system was checked by a lawyer
and a law lecturer in land resource. Table 3 and Figure
5 show the testing results for each topic.
Table 3: Results of Querying on Vietnam Land Law.
Content Queries
Number of correct results
Prop.
(%)
Concept Procedure
Related
Knowledge
Total
1 42 11 9 6 26 62%
2 48 10 10 7 27 56%
3 59 19 15 5 39 66%
4 36 9 8 5 22 61%
5 24 5 7 4 16 67%
Total 209 54 49 27 130 62%
Table 4 compares our system with some good
systems, Aleph and AimeLaw, in ALQAC-2021
(Automated Question Answering Competition) at the
task 1 - Legal Document Retrieval, and the task 2 -
Legal Text Entailment (ALQAC-2021, 2021).
Task 1 - Legal Document Retrieval: The
requirement of this task is the retrieval of all the
articles that are relevant to a statement.
Task 2 - Legal Text Entailment: This task is
built for yes/no question answering systems for legal
queries. The system will answer whether the
statement is true or false.
Tieu et al. (2021) built Aleph as an article ranking
model by finetuning their own pre-trained model
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
432
VNLawBERT with a binary classification problem
(Chau et al., 2020). It makes negative samples by
choosing the closest candidate with the gold samples.
AimeLaw in (Ngo et al., 2021) is an approach of
combining scores of BM25 with Domaint Invariant
Supporting Model and Deep CNN Supporting Model
using weighted sum function.
Figure 5: The precision of the querying system on each
content of Vietnamese Land Law.
Table 4: Compare systems in tasks.
S
y
stem Task 1 Task 2
Aleph 88.07% 69.89%
AimeLaw 80.61% 69.89%
Our s
y
stem 62% 62%
Although the precision of our querying system
gets more than 60%, it can retrieve the concepts in the
document with related articles. Besides, some kinds
of content in the Land Law have the precision more
than 65%, such as Agricultural Land and Documents
of Land-related procedures.
Moreover, the strengthen point of the built system
is the organizing of the knowledge domain about the
law document. It can represent the complex relations
between legal entities in the document. It has more
rooms to develop a querying system for supporting of
a certain law field with many related legal documents.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study proposed an integrating ontology for
representing the knowledge of a law document, called
Legal Rela-model. This model is integrated of
ontology Rela-model and the graph of key phrases as
a conceptual graph (Shi et al., 2017). The Legal Rela-
model includes concepts in the law domain, relations
between concepts, inference rules of this domain and
relations between key phrases, concepts in the law
document which connects to database storing law
contents. The method for intellectual retrieval on this
document is also studied by extracting key phrases
and matching the content of articles in the law
document.
In addition, an intelligent support system for
querying on Land Law of Vietnam National
Assembly (2013) is constructed. Its knowledge base
is organized by ontology Legal Rela-model. The
designed system can help users to query some
meaning of land law terminology land-related
administrative procedures. The testing results show
that the precision of the current method is more than
60%.
Moreover, the law domain of a field includes
many related documents. The advantage of Rela-
model is the ability to integrate multiple knowledge
domains. Thus, using ontology Legal Rela-model, the
connection between legal documents can be
represented in which each document is organized by
this ontology. This will make a completely legal
document system for a certain field.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by The VNUHCM-
University of Information Technology's Scientific
Research Support Fund.
REFERENCES
ALQAC-2021, 2021: https://tinyurl.com/ALQAC2021
Casellas, N. 2011. Legal ontology engineering:
Methodologies, modelling trends, and the ontology of
professional judicial knowledge. Springer Science &
Business Media, vol. 3.
Chau, C., Nguyen, T.S., Nguyen, M. 2020. VNLawBERT:
A Vietnamese Legal Answer Selection Approach Using
BERT Language Model. In NICS 2020, 7
th
NAFOSTED
Conference on Information and Computer Science,
Nov. 2020. IEEE, 298 – 301.
Do, N., Nguyen, H., Selamat, A. 2018. Knowledge-Based
model of Expert Systems using Rela-model.
International Journal of Software Engineering and
Knowledge Engineering 28(8), 1047 - 1090.
Do, N., Nguyen, H., Hoang, L. 2020. Some Techniques for
Intelligent Searching on Ontology-based Knowledge
Domain in e-Learning. In IC3K 2020, 12th
International Joint Conference on Knowledge
Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge
Management, Vol. 2: KEOD, Nov. 2020.
SCITEPRESS. 313-320.
Doan, A., Madhavan, J., Dhamankar, R., et al. 2003.
Learning to match ontologies on the Semantic Web.
VLDB 12, 303–319, 2003.
Embar, V., Srinivasan, S., Getoor, L. 2021. A comparison
of statistical relational learning and graph neural
Legal-Onto: An Ontology-based Model for Representing the Knowledge of a Legal Document
433

networks for aggregate graph queries. Machine
Learning 110, 1847–1866.
FAQs in the land law, 2022: https://dichvucong.
longan.gov.vn/trangchu/cauhoithuonggap
Fawei, B., Pan, J.Z, el al. 2019. A Semi-Automated
Ontology Construction for Legal Question Answering.
New Generation Computing 37(4), 453-478, 2019.
Huynh, T., Nguyen, A., Do, N. 2019. A Method for
Designing Domain-Specific Document Retrieval
Systems using Semantic Indexing. International
Journal of Advanced Computer Science and
Applications 10(10), 461 – 481.
Le, T., et al. 2019. Knowledge representation method for
designing an Intelligent Tutoring System in Learning of
courses about Algorithms. In APCC 2019, 25th Asia-
Pacific Conference on Communications, Nov. 2019.
IEEE, 310-315.
Leone, V., Caro, L., Villata, S. 2018. Legal Ontologies and
How to Choose Them: the InvestigatiOnt Tool? In
ISWC 2018, Posters & Demonstrations, Industry and
Blue Sky Ideas Tracks co-located with 17th
International Semantic Web Conference, Oct. 2018.
Ngo, H., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, D., Pham, M. 2021.
AimeLaw at ALQAC 2021: Enriching Neural Network
Models with Legal-Domain Knowledge. In KSE 2021,
13th International Conference on Knowledge and
Systems Engineering, Nov. 2021. IEEE.
Nguyen, H., Huynh, T., et al. 2020a. Language-oriented
Sentiment Analysis based on the grammar structure and
improved Self-attention network. In ENASE 2020, 15
th
International Conference on Evaluation of Novel
Approaches to Software Engineering, May 2020.
SCITEPRESS. 339-346.
Nguyen, H.D., Do, N.V., Pham, V., et al. 2020b. A method
for knowledge representation to design Intelligent
Problems Solver in mathematics based on Rela-Ops
model. IEEE Access 8, 76991–77012.
Nguyen, H., Tran, D., Pham, H., Pham, V. 2020c. Design
an intelligent system to automatically tutor the method
for solving problems. International Journal of
Integrated Engineering 12(7), 211 – 223.
Nguyen, H., Tran, V., Pham, T., et al. 2021. Ontology-
based Integration of Knowledge Base for Building an
Intelligent Searching Chatbot. Sensors and Materials
33(9), 3101 – 3121.
Nguyen, H.D, e 2022. Chapter 10 - A methodology for
designing knowledge-based systems and applications.
In Application of Computational Intelligence in Multi-
disciplinary Research, A. Elgnar, et al. (Eds), Elsevier.
Sartor, G., et al. 2011. Approaches to Legal Ontologies.
Springer Dordrecht Heidelberg, London, New York.
Shi, W., et al. 2017. Keyphrase Extraction Using
Knowledge Graphs. Data Sci Eng 2, 275–288.
Szostek, D., Zatucki, M. 2022. Legal Tech. Nomos
Verlagsgesellschaft, Waldseestraße, Germany.
Tieu, T., Chau, C., Bui, N., et al. 2021. Apply Bert-based
models and Domain knowledge for Automated Legal
Question Answering tasks at ALQAC 2021. In KSE
2021, 13
th
International Conference on Knowledge and
Systems Engineering, Nov. 2021. IEEE.
Tran, H. 2013. Land Law (Texbook). Hanoi Law
University, 2013. (Vietnamese).
Vaswani, A., et al. 2017. Attention is all you need. In NIPS
2017, 31
st
Conference on Neural Information
Processing Systems, Dec. 2017.
Vietnam Ministry of Justice. 2011. Circular of the Minister
about the formats, and techniques for legal documents
– No. 25/2011/TT-BTP, Dec. 2011.
Vietnam National Assembly. 2013. Vietnamese Land Law
2013 - No. 45/2013/QH13, Nov. 2013.
ENASE 2022 - 17th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
434
