
Online Spatial Data Gathering as a Powerful Arm in Urban
Management (Study in Iranian Municipality)
*
Mohammad Ghaderi
Department of Urban Planning, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, Iran
Keywords: Spatial Data, Online Survey, SDI, Municipality.
Abstract: The old version of the spatial data collection method is not so convenient, is expensive and time-consuming
it causing the reluctance of municipalities to conduct space surveys. Online spatial data collection is a solution
to improve urban data surveys and facilitate relationships between databases. The SDI system as a host is
needed to save and collect spatial data, and an application running on a smartphone can locate and send
information tables to SDI. By the way, municipalities can define various audit items and investigate functional
by simplicity at a lower cost and faster than before.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urban management has faced many challenges over
the past few decades (Freire and Stren, 2013), and
Iran's urban management system is now transitioning
from traditional to new urban management based on
intelligence technologies we can see, municipality
cost in software development and system installation
is appropriate evidence of this claim.
As we know, information is an asset, and data
gathering is a concern in urban management systems
(Engin et al, 2020), due to the importance of data,
which is required by each organization an annually
significant amount a great deal of cost allocated to the
data gathering and their maintenance (Batty, 2018).
In the use of data, it's undeniable that must be noted
to the validity of data, data is the base of planning and
decision making in any organization (Bertsimas et al.,
2019). So, data collection and database creation is
great thing in city management. The locality of
information points in the urban's plan, location of the
features, location of urban disasters, an urban survey
in various topics, all are significant topics and
requirements of urban management (Haqi & Dühr,
2022). Although in some cases arriving the electronic
system in Iran urban management system facilitate
the current affair on the other side, the plenty number
of affairs doing by hand like an old manner, this
synthesis condition leads to a lack of close
*
The present study proposed in Hamedan Municipality
as an executive project and approved by sep 2021.
supervision, lack of transparency in management
affairs, slowness of the work process and so on, thus
not be able to create an optimum accomplishment. In
an extensive urban survey like an urban property
survey, old kinds of surveys take long about one year
or longer, hence, municipalities don't interest in this
method. Coupled with the high cost, there is not
enough time and technical personnel to control the
inspection data. But, the most important issue that
occurs during this process is the lack of proper
communication between surveying data and
municipalities electronic system (Cassandras, 2016),
one way is to try to scan the proper dossiers, while the
easier way is an online survey with a direct
connection between surveying data online dossiers in
the database. There are other issues in the handy
manner of surveys such as; in the last year's spatial
data gathering in the municipality survey by GPS and
gathering in local GIS that it doesn't have any
connection by the other subsections. The municipality
consists of several parts, each of them attempts to
survey their data in the way of the owner, there is no
integrity in the data gathering. Finally, a Spatial Data
Infrastructure (SDI) must be installed at the
municipality to create a participating database of
spatial data, known as geodatabase.
SDI provides numerous advantages in urban
management system (Ghaderi & Sadeghi Arj, 2019).
It can create an overall geodatabase in the
municipality as a host, and each subsection can
Ghaderi, M.
Online Spatial Data Gathering as a Powerful Arm in Urban Management (Study in Iranian Municipality).
DOI: 10.5220/0011106500003185
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management (GISTAM 2022), pages 163-165
ISBN: 978-989-758-571-5; ISSN: 2184-500X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
163
upload their data and update it simplicity. SDI is not
only a powerful database; it is also a participating
network that receives and corrects spatial data
transmitted by other devices. It can connect to other
devices like GPS, Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), etc.
Using SDI as a host, the idea of an online survey may
become a reality, as described below.
2 METHODOLOGY
As mentioned earlier, to run an online survey
network, SDI is required as a host, and SDI creates
open access for anyone who wants to use the spatial
data SDI is able to receive spatial data from various
sources such as local GIS, other databases, external
devices, etc. Such as GPS and RTK, or even apps
running in smartphones. It is a powerful, newer
smartphone with the ability to locate via internal GPS
and receive signals via GPRS or Wi-Fi. SDI could
define data's forms, these forms are specific in any
project or survey, an application manipulated in
smartphones could open each form by the name of
each project, this app defines the location of each
urban features and it is able to precise locations by
auxiliary maps which presented in its background.
The mobile APP retrieves data online, quickly sends
data to SDI, or offline, and sends data when the device
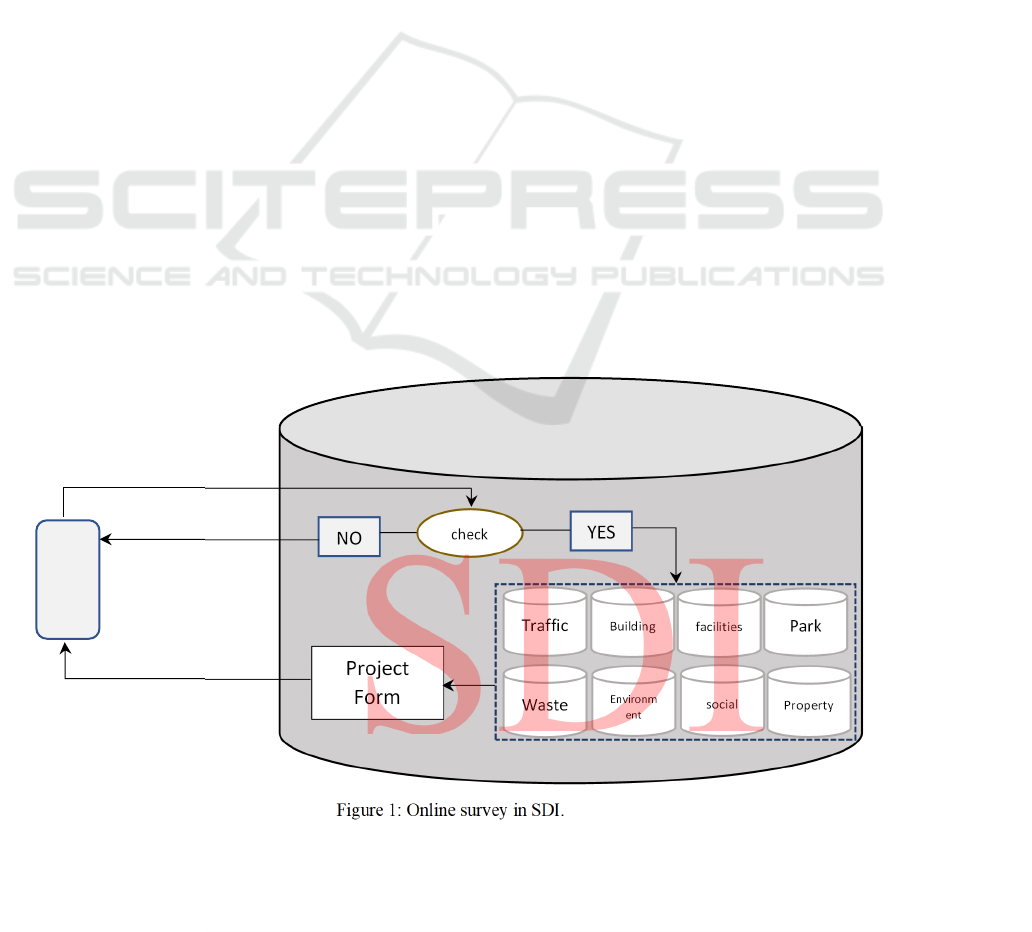
is connected to the Internet. On the SDI side, the audit
data is received in a box, needs to be approved, and
when the operator confirm the data, it is sent to the
GIS layer and called features in the SDI layer. The
operator checks the data received in SDI for
problems, the data may be rejected or returned to the
sender. SDI has several tables in its database, each
table holds specific data for each section or it is a
maintain topic. For example, in a municipality, a table
would hold spatial data for transportation
organization, or a table would hold land property
data. Each form is updated online with their own
survey items, and their specific personnel and
operators can investigate the same data and confirm
its authenticity. Spatial data that receive to SDI not
only could influence in a table, but also could change
the condition of same feature in other layer or tables,
because of the SDI layer or table are related by Main
Key. One of the most famous Key in municipalities is
Dossier ID Property Number. The SDI structure
based on the online survey is shown in the figure
below.
3 CONCLUSION
Online data collecting specifically in the field of
spatial data can improve city management in several
cases. One of the real issues with which cities and its
administration are involved every day is city
violations. The online survey helps municipalities
report city violations, and once that data is turned into
SDI and approved quickly, it can lock down
electronic records and ban online services to the same
home. This limitation cannot be removed until the
issue is resolved.
Figure 1: Online survey in SDI.
Project
Form
mobile
check
NO
YES
Traffic
Waste
Park
Property
Building
Environm
ent
facilities
social
GISTAM 2022 - 8th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
164

Another use of spatial online auditing is in large-
scale projects such as urban surveys, land surveys,
etc. All projects can be implemented in less time and
at lower cost compared to the convenient old way. In
this way, municipal experts can develop their control
over city characteristics and city section, and they can
update every part of the city for which they need
information. The spatial online survey project
completed in the city of Hamadan, Iran as a real
project, and several project defines and spatial data
are being collected, is an exciting conclusion of the
method, which can be seen in the city is enhancing
the level of city services in municipality. It stems
from the case that city services are monitored by the
audit project and any failures services reported
online. Under this approach, the municipal database
is updated daily and corrected for inefficiencies
information doing precisely. All in all spatial online
survey is a powerful arm of urban management as
benefits mentioned.
REFERENCES
Freire M E and Stren R (2001). Challenge of urban
government: Policies and practices. Washington:
World Bank Publications. https://doi.org/10.1596/0-
8213-4738-1.
Haqi F I and Dühr S (2022). The Role of Political
Leadership in Shaping Integrated Urban Policy
Frameworks in the City of Semarang, Indonesia.
Community Empowerment, Sustainable Cities, and
Transformative Economies. Springer, Singapore.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5260-8_30.
Engin Z, Dijk J V, Lan T, Longley P A, Treleaven P, Batty
M and Penn A (2020). Data-driven urban management:
Mapping the landscape. Journal of Urban
Management. 2(9), 140-150. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jum.2019.12.001.
Batty M (2018). Digital twins. Environment and Planning
B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 45 (5), 817-820,
10.1177/2399808318796416.
Bertsimas D, Delarue A, Jaillet P and Martin S. (2019).
Travel time estimation in the age of Big Data.
Operations Research. 67 (2), 498-515, 10.1287/
opre.2018.1784
Cassandras C G (2016). Smart cities as cyber-physical
social systems. Engineering, 2 (2), 156-158, 10.1016/
J.ENG.2016.02.012.
Ghaderi M And Sadeghi Arj M (2019). Define a solution in
urban management integrity by SDI (In Iran Urban
management system). Second international conference
of urban management, Tehran, Iran. [in persian].
https://civilica.com/doc/973668.
Mohammad Ghaderi: Graduated Master of science in
regional planning, IUST, Working IN hamedan
Municipality As the SDI manager and GIS expert Sine
2016.
Online Spatial Data Gathering as a Powerful Arm in Urban Management (Study in Iranian Municipality)
165
