
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for
Parkinson's Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
Huimin Wang
a
and Tianyang Zhu
*b
Department of Art and Design Beijing University of Chemical Technology Beijing, China
Keywords: Parkinson's, Rehabilitation Assistive Devices, Hierarchical Analysis, Optimal Design.
Abstract: Objective: The Parkinson's disease has gradually increased in the elderly population in China, and the
research of rehabilitation assistive devices for patients with Parkinson's has become more and more
important. This study analyzes the existing Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive devices in the market, and
proposes an optimization strategy for the design of rehabilitation assistive devices for Parkinson's patients
according to the actual needs of patients. Methods: The existing research results of Parkinson's
rehabilitation assistive devices were sorted out by inductive method, and the tendency of patients' needs
between each level of rehabilitation products of assistive devices was extracted from functional level,
service level and emotional level based on hierarchical analysis. Conclusion: At this stage, domestic
research on the design of medical assistive devices for Parkinson's disease remains relatively scarce. The
functions of the products are mostly limited to self-care or mobility assistance under the action of external
forces; these products have problems such as insufficient targeting of functional positioning, lack of
systemic and sustainability in the use process, and lack of emotionality. The optimized solutions and design
strategies of inclusiveness and autonomy, systemic and sustainability, and emotional design are proposed to
provide reference for future product design and application of training assistive devices for Parkinson's
patients.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Parkinson's syndrome (PD) is a neurodegenerative
disease common in middle and old age (Liu 2016),
and the number of Parkinson's patients in the world
is about 6 million (Zhuang 2017). The increase in
the number of Parkinson's patients and the
weakening capacity of home-based patient care
services have exacerbated the burden on family
finances and social health care services. With the
current scientific treatments, Parkinson's disease
cannot be cured and can only be assisted by
medication and physical rehabilitation training. It is
an urgent problem to address in rehabilitation
research on how to make patients less distressed and
restore their ability to take care of themselves (Liu
2021). In the early stage of Parkinson's symptoms,
the use of reasonable and scientific rehabilitation
assistive devices is one of the effective methods to
slow down the physical function lesions and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4398-8584
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5118-8216
improve the quality of life of patients. With the
progression of Parkinson's disease, the tremor of
movement and delayed gait impairment, as well as
the psychological negativity lead to the gradual
narrowing of the patient's range of activities, and the
home becomes the patient's main place of activity.
As patients spend more time at home, the need for
physical exercise increases, which requires the
optimal design of assistive devices in terms of
autonomous exercise and emotional companionship
to provide a more effective and comfortable
home-based rehabilitation environment for
Parkinson's patients, so as to realize the need for
patients to complete autonomous exercise through
assistive devices, which enhances the sense of
self-efficacy and improves the sense of well-being.
Wang, H. and Zhu, T.
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011206600003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 25-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
25

2 OVERVIEW OF
REHABILITATION ASSISTIVE
DEVICES FOR PD
Parkinson's assistive devices are assistive devices
that help patients overcome the obstacles of the
disease, alleviate the adverse effects of symptoms
such as tremor, bradykinesia and dyskinesia, and
improve the ability to care for themselves in daily
life. Through the use of medical assistive devices,
Parkinson's patients can improve the completion of
basic behavioral movements and effectively improve
their quality of life while enhancing their ability to
adapt to their environment. The improvement of
self-care ability can promote the self-efficacy of
Parkinson's patients, regulate negative psychological
emotions, and alleviate the burden and stress of
health care workers and family members.
2.1 Classification of Existing
Parkinson's Rehabilitation Assistive
Devices
In order to allow Parkinson's patients to spend their
old age peacefully, elderly care with technology and
assistive devices has gradually become the
mainstream of social development (Li 2018)
Research and analysis of existing Parkinson's
assistive devices in the market can be categorized
into whole-body assistive devices, upper limb
assistive devices, and lower limb assistive devices
based on their target limb parts, as shown in Table 1.
Whole-body assistive devices tend to act on the
whole limb of the patient for rehabilitation treatment
or data monitoring, and the main existing
whole-body assistive devices are hyperbaric oxygen
chamber, Parkinson's therapy device and physical
data monitor, etc. (Mao 2020). The effect of
cognitive training on exercise training in Parkinson's
rehabilitation was investigated by Davide Ferrazzoli
et al. It was found that cognitive training has a
crucial role in motor training and sustained
concentration is effective in accomplishing the target
movement behaviors, and that hyperbaric chamber
plays a role in improving cognitive impairment for
Parkinson's patients (Davide 2018). Parkinson's
therapeutic device is an innovative technology based
on brain pacemakers and brain rehabilitation
therapies that act on the patient's head, ears and feet
to compensate for the lack of pharmacological and
surgical treatment and improve tremor, rigidity and
bradykinesia. The data monitor is applied to the
patient's rehabilitation process to provide real-time
data detection and feedback based on the patient's
behavioral response, helping healthcare
professionals to effectively monitor the patient's
pathology and treatment effects.
Upper limb assistive devices are mainly applied
to the patient's hand, and are used for patients with
resting hand tremor to carry out rehabilitation
training or assisted movement, and to improve the
dexterity and completion of fetching movements,
including finger training inserts, finger extension
trainers, convenient fetchers and training gloves. The
finger training board is equipped with wooden sticks
of different diameters to guide patients to insert the
sticks into the holes precisely, train the flexibility of
finger joints and hand strength control ability, and
improve hand and eye coordination function. The
finger extension trainer includes grip strength ball,
elastic finger sleeve and finger presser to help
patients strengthen grip strength training and finger
flexion and extension rehabilitation in the process of
using the assistive device. The ergonomically
designed gun-shaped convenient fetcher can help
patients reduce tremor interference and provide
convenience for patients to grasp various objects of
different shapes and sizes, soft and hard.
The lower extremity aids mainly focus on the
patient's legs, alleviating gait disorders caused by
slow and rigid movement through intensive pace
training, including laser crutches, walkers, exercise
scooters, lower extremity gait exoskeletons and gait
trainers. For plantar pressure correction, Liu Yan et
al. started a ten-week training with the Lokomat
lower limb robotic gait exercise system in forty
Parkinson's patients, and the treatment confirmed
that rehabilitation training with the lower limb robot
had more significant effects than conventional
rehabilitation training (Liu 2017). The BioMot, a
lower extremity gait exoskeleton, can provide
assistance to patients with gait rehabilitation and
musculoskeletal injuries, and also allows for
seamless interaction and safe movement to
accommodate the user's intent and ability (Bacek
2017). The gait trainer can improve gait movements,
limb coordination and muscle flexibility by training
the patient's lower extremity muscles and nerve
responses to achieve a balanced gait.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
26
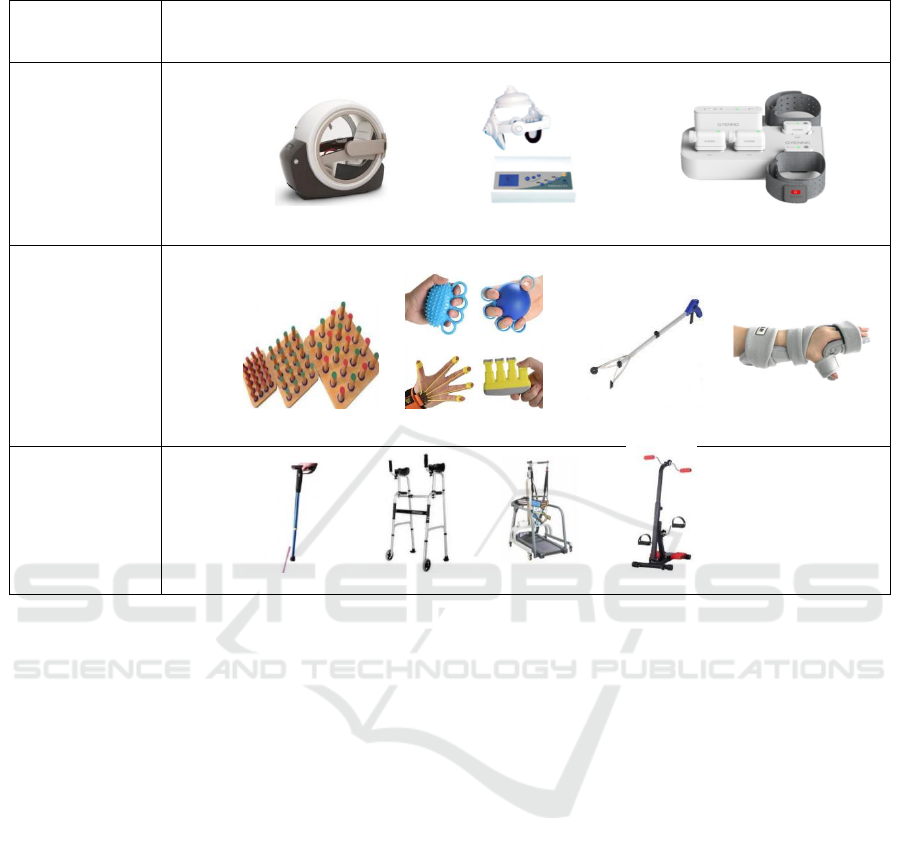
Table 1: Classification of Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive devices.
Targeted parts Available products for assistive devices
Whole body
Hyperbaric oxygen chamber Parkinson's therapy device Physical data monitor
Upper Extremity
Finger training board Finger extension trainer Handy picker Training gloves
Lower Extremity
Laser crutch Mobility aid Gait trainer Exercise scoote
r
2.2 Analysis of the Advantages and
Disadvantages of Existing
Parkinson's Assistive Devices
The current assistive devices for Parkinson's disease
and their peripheral services are designed to have
significant effects on patients' life assistance,
medical care and functional exercise. In terms of life
assistance, it is close to the patients' daily life, which
can alleviate their impairment of clothing, food,
housing, and transportation, improve their self-care
ability, and improve the quality of life of Parkinson's
patients. In terms of medical care, the product can
effectively monitor the patient's health index and
slow down the spread of the disease through medical
means. In terms of functional training, patients are
guided to use assistive device products for simple
game interaction, physical exercise of local lesion
areas, and enhancement of limb function. However,
the existing design of Parkinson's assistive device in
China remains in the exploration stage, and there are
deficiencies in the detailed aspects.
The prevalence of Parkinson's disease in China is
about 17%, with nearly more than 2 million
Parkinson's patients (Mina 2019). The huge group
base combined with the obvious differences in the
degree of disease staging, onset site, significant
symptoms, and changes in disease among patients,
these problems lead to the difficulty of more refined
functional positioning of Parkinson's assistive device
products for different patients. According to the
above analysis and comparison of existing assistive
device products, it can be found that although the
current assistive device has achieved a simple
division for different parts of the patient's limbs.
However, the assistive device for the whole body is
only limited to the medical aspect and lacks the
function training of the limbs. The assistive devices
for upper and lower extremities only work on the
common areas of the patient's body, such as the
hands and legs, and lack attention to small areas of
the body, such as the shoulders, small arms, knees,
or feet.
Parkinson's disease is comprehensive, complex
and long-term in nature. Existing assistive device
products often only provide superficial and simple
training for conditions such as hand tremor and short
gait. If the patient's tremor amplitude deepens or
decreases during use, or if other parts of the body
other than the hands and legs are added, the single
function cannot meet the complex disease situation
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
27
in real time, and it is difficult to achieve in-depth
and lasting support for the patient's condition and
variations. The existing Parkinson's assistive devices
have certain defects in terms of volume structure and
emotional care, in addition to basic functions. Most
medical care assistive devices such as hyperbaric
chamber, Parkinson's therapy device, gait trainer,
etc. are large and expensive, and their use is limited
to exclusive places such as hospitals and nursing
homes. Considering the individual differences in
patients' different status backgrounds, home living
environments and economic bases, many high-end
assistive device products are difficult to access. The
limitations of the existing Parkinson's assistive
devices in terms of targeted features, use sites,
system services and emotional care are all pressing
issues that need to be addressed in future designs.
3 NEEDS ANALYSIS OF
PARKINSON'S PATIENTS
3.1 Motion Extraction for Parkinson's
Patients
Standardized management of Parkinson's disease
includes standardized clinical diagnosis, disease
severity scores, and treatment decisions. Some
standardized assessment systems such as the Unified
Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) score
and Hoehn and Yahr (HY) staging provide good
support for the docking of the Parkinson's
rehabilitation assistive devices (Tan 2019).
Parkinson's disease is currently classified by the
Hoehn and Yahr (HY) staging, which is medically
accepted. HY staging is divided into five stages,
where staging <3 is defined as early Parkinson's
disease, staging at 3-4 is defined as mid- to
late-stage Parkinson's disease, and staging at 5 is
defined as late-stage Parkinson's disease (Wang
2017). In the early and middle stages of Parkinson's,
the use of assistive devices can be effective in
improving patients' self-care ability and quality of
life, and the design of interventions should be
considered for the disease and actual needs of
patients at this stage. Based on the Unified
Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS version
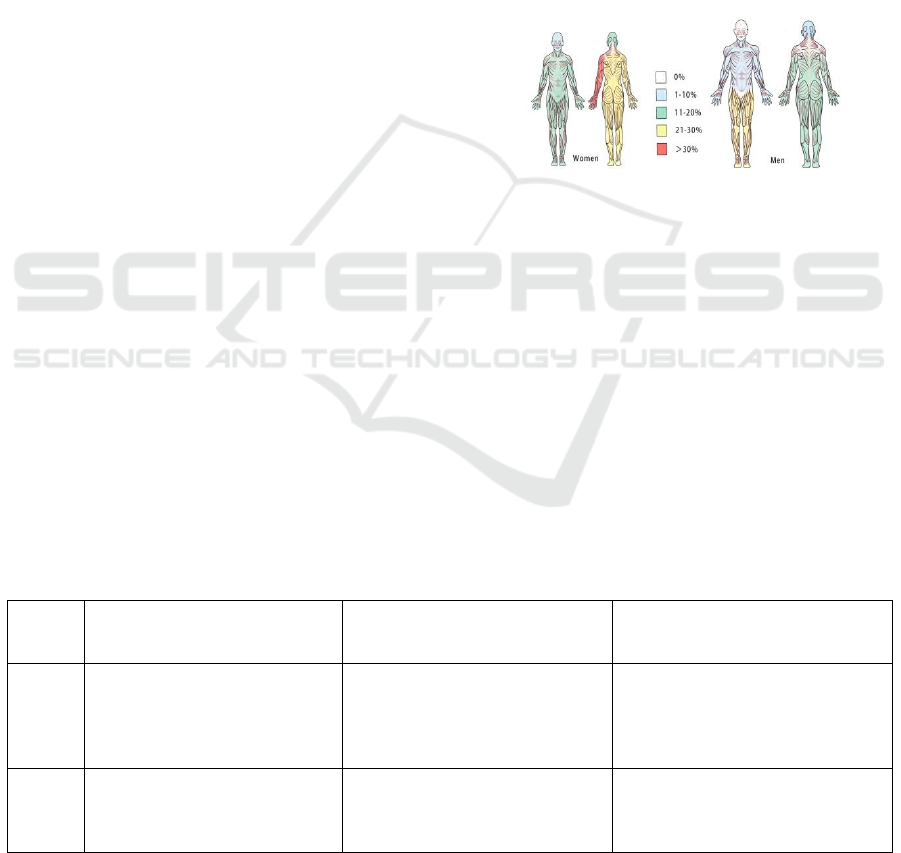
3.0), the distribution of muscle pain in Parkinson's
patients in Figure 1 shows that the main lesions are
in the back, arms and hands of the upper extremities,
and the leg muscles of the lower extremities, where
the assistive device can be used for targeted
rehabilitation.
Figure 1: Distribution of muscle pain sites with
Parkinson's patients.
The assessment of the activities of daily living
and mobility check of the scale takes into account
the impact of changes in the onset and degree of
resting tremor and muscle tonus on patients' daily
behavioral movements. Combined with the analysis
of the symptom performance of patients in the early
and middle stages of PD, the key behavioral actions
of patients were extracted to set the reference of
assistive device actions and to make design guidance
for the corresponding functional services of the
Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive device, as shown
in Table 2.
Table 2: Correlation analysis based on stage symptoms of Parkinson's disease and the needs of the patients.
Staging Symptoms Mobility Summary Demands for assistive devices
Stage 1
Tremor with unilateral limb,
myotonia or bradykinesia
without significant functional
impairment or with mild
im
p
airment.
Basic fluency in daily activities.
There is no need for assistive
device intervention.
Stage 2
Resting tremor, myotonia or
bradykinesia extending to both
limbs.
Patients can still maintain normal
posture with mild impact on daily
life.
Assistive device needs exist for
basic actions in daily life, and the
efficiency of actions is improved to
some extent b
y
assistive device.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
28
Stage 3
Presence of some degree of
limitation of mobility with mild
or moderate functional
impairment.
There is some impairment in
activities such as getting up,
dressing, walking, tying
shoelaces, and writing. However,
the patient can live independently
without rel
y
in
g
on others.
The need for assistive device is
high for daily life, and the
improvement effect is more
obvious by using assistive devices.
Stage 4
People with more severe tremor,
myotonia, bradykinesia, and
dyskinesia have difficulty taking
care of themselves and require
caregiver assistance for some
b
ehaviors
The impairment in activities such
as getting up, dressing, walking,
tying shoelaces, writing, etc. is
relatively severe, and the patient
can still manage to stand or walk
without support.
The need for assistive devices is
high, and the functions and services
need to be enhanced for mobility
assistance, medical care, and
emotional care for co-occurring
p
sychological problems.
Stage 5
The symptoms of the disease are
so severe that they cannot take
care of themselves and require a
caregiver to accompany them
throu
g
hout their lives.
Unable to stand and confined to
bed or wheelchair without
assistance.
Patients have difficulty operating
the assistive device on their own
and have limited needs.
3.2 User Role Establishment and Its
Requirements
In the context of social medical technology
development and family economic conditions
improvement, more families with Parkinson's
disease are beginning to value the use of assistive
medical products, and can afford more to improve
self-efficacy and quality of life for their patients and
enhance their sense of well-being. Most Parkinson's
patients tend to be senior citizens, with an average
age of onset of about 60 years old. The material and
spiritual life needs of elderly Parkinson's patients are
characterized by their age, diversity, differences,
emotions and stages (Huang 2020). Therefore, the
above characteristics put forward new requirements
for the design of paramedical products, and the
functional focus of the study was extended from a
single improvement in quality of life to helping
patients to exercise themselves to alleviate the
progression of the disease, with a more advanced
goal of achieving patient self-efficacy. In this study,
we selected elderly Parkinson's patients aged 60-75
years old as the target users, collected the impact of
patients' different symptoms on their daily actions
through Kano questionnaire, and summarized the
functional requirements of Parkinson's assistive
devices in order to optimize the experience of using
them, enhance their physical functions and improve
their quality of life. The purpose of the study is to
optimize the experience of using the assistive
device, enhance the physical function of patients and
improve the quality of life. Through the basic
research of Parkinson's patients, the user
representatives were selected to make a typical
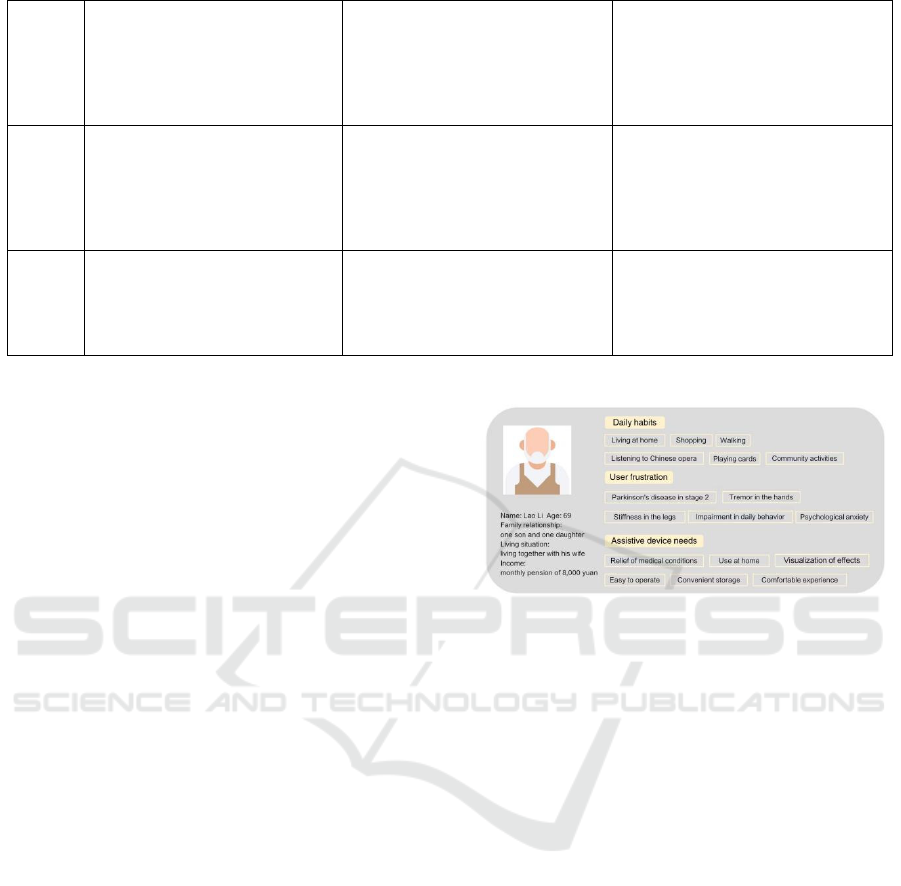
target user portrait, see Figure 2.
Figure 2: Typical target user profile
A list of 18 basic functional needs of Parkinson's
patients for assistive devices based on their motor
behaviors such as tremor, bradykinesia or
dyskinesia, and psychological behavioral
characteristics such as depression, anxiety and
dependence, combined with action extraction of
symptom performance and typical target user
portrait analysis. Among them, the material life
perspective includes the basic ability needs of
patients in daily life; the rehabilitation medical
perspective includes the needs of patients' physical
function status and mental health; the
mental-emotional perspective includes patients' own
emotional development and the overall
communication with family and society. Through the
information feedback from the Kano questionnaire,
the scatter diagram of basic functional needs of
Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive devices was
drawn according to the priority level of the 18
functional needs of the patients under investigation,
which were classified as charismatic needs,
expectation needs, undifferentiated needs and
essential needs, as shown in Figure 3
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
29
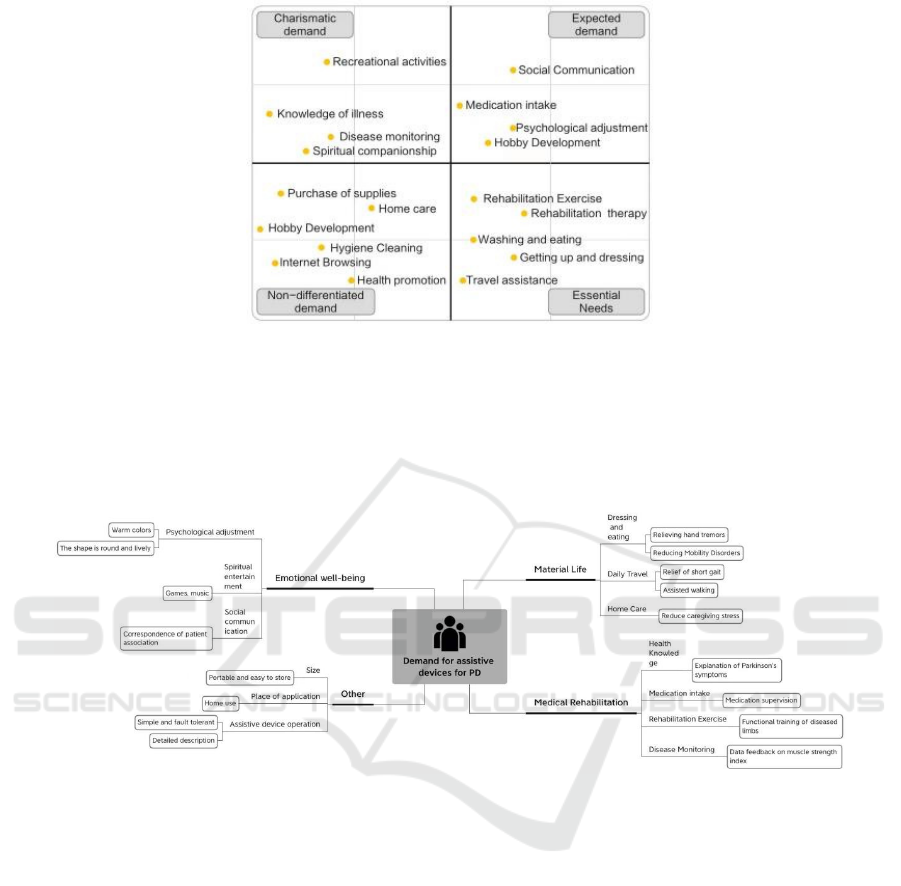
Figure 3: Scatter diagram of basic functional needs for Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive devices.
Through the user feedback of Parkinson's
assistive device on the Internet, 18 basic functional
requirements were sorted and summarized based on
three levels: physical life, medical rehabilitation, and
spiritual and emotional life, as shown in Figure 4.
Combined with the data from the research
questionnaire, the functional demand points of
Parkinson's assistive devices that appear more
frequently in the user experience and expectation
feedback were summarized.
Figure 4: Summary of functional requirement points for Parkinson's assistive devices
4 HIERARCHICAL ANALYSIS
OF FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS
OF PARKINSON 'S ASSISTIVE
DEVICES
4.1 Functional Element Hierarchy
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) refers to the
hierarchy of complex decision-making systems,
transforming multi-element decisions into
multi-level single-element problems, and helping to
analyze the weights or priorities among the elements
at different levels (Wang 2021). To address the issue
of the basic functions of rehabilitation assistive
devices for Parkinson's patients, it is necessary to
analyze the structural appearance, operational
processes, functional services, emotional care and
other design elements of rehabilitation assistive
devices, taking into account the different identity
backgrounds, generational relationships, life
socialization, goal preferences, behavioral habits and
health status of patients and other relevant factors.
The demand for rehabilitation assistive device use
by Parkinson's patients is diversified and
differentiated, and there is no obvious demand
hierarchy and structural division of demand
direction yet, so it is suitable to use hierarchical
analysis to summarize and analyze the
interrelationship and importance degree among
different elements.
According to the complex basic need points of
Parkinson's patients, it can be seen that the patients
have high needs for basic life at home in terms of
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
30

clothing, food, transportation, medical rehabilitation
effects of the disease and emotional spiritual
companionship. To meet these needs, the functional
design of assistive devices should focus on whether
the structure of the product is lightweight,
convenient, easy to operate, and suitable for patients
with mobility impairments to use at home. The
design of assistive devices should also consider
whether the services can meet the needs of patients
to establish contact with their families and
healthcare professionals, whether the efficacy of the
devices can meet the needs of patients to improve
their self-care ability and medical rehabilitation, and
whether they can provide emotional care to patients'
psychological, emotional and attitudinal preferences.
Following a generalization of the above needs
analysis, five basic requirements for Parkinson's
assistive devices to meet the needs were derived:
appearance structure, operation process, service
level, functional effectiveness, and emotional care,
which constitutes the hierarchical analysis model
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Analysis of functional elements of Parkinson's
rehabilitation assistive devices.
The functional aspects include the basic
functions that an assistive device should have for
Parkinson's rehabilitation. According to user analysis
and research, for patients suffering from resting
tremor, myotonia and dyskinesia or bradykinesia,
their basic needs for assistive devices should include
the ability to improve their mobility skills in daily
life, such as dressing, dining, cleaning, walking, etc.,
and to improve their self-care ability. The assistive
device can be used for simple movement training
and scientific medical interventions to improve
physical functions, monitor the feedback of the
disease and alleviate the extent of the disease to a
certain extent. The design of Parkinson's assistive
devices should include diverse functional designs for
patients with different differences, combining
elements such as the user's background, physical
health condition and the environment in which the
product is used, to meet the patient's needs for
self-care and medical rehabilitation in daily life.
The service dimension mainly refers to the
service design of the Parkinson's rehabilitation
assistive devices. The service of the rehabilitation
assistive devices not only includes the service for the
patients themselves, but also needs to consider the
connection between the patients' families,
communities and medical care, and build a
multi-point and related service system. For the
patients themselves, the services of rehabilitation
assistive device products cannot be limited to a
certain stage and a certain problem. The long onset
cycle of Parkinson's disease requires that assistive
device products should extend the time span of
services, deepen the patients' memory of using them,
and strengthen the service effect and user
experience. For the patient's peripheral relationships,
it is necessary to strengthen the connectivity
between each relationship for integrated services.
The Parkinson's rehabilitation assistive device
should be a more "people-oriented" product, and the
product design should incorporate emotional care for
patients. Parkinson's disease is a common
degenerative disease of the nervous system, caused
by lesions in certain functional areas of the brain. If
the lesions in these areas involve functional areas
that control mood and emotion, it will affect the
patient's psychological mood, and its nonmotor
symptoms are mainly manifested in psychological
behavior as depression, anxiety and dependence.
Patients with PD suffer from the disease and are
often in a closed environment due to limited
mobility and lack of communication with the outside
world, and are prone to persistent depression,
difficulty concentrating, lack of interest in life and
work, and other depressive moods. The confusion
and uncertainty about the future and the dependence
on medical staff and family members due to the
inability to take care of themselves are emotional
factors that need to be considered and taken care of
in the design of the Parkinson's rehabilitation
assistive device. The design of rehabilitation
assistive devices can enhance the emotional care of
patients in terms of needs such as fun games, music
videos, emotional de-escalation and color healing.
4.2 Integration of Functional Elements
From the summary of the demand points of
Parkinson's patients, it can be concluded that the
main expectation of users for assistive devices is to
effectively alleviate the degree of their own lesions,
reduce the impact of symptoms such as limb tremors
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
31

and muscle stiffness on behavioral movements,
improve movement flexibility, and restore normal
body posture. Therefore, functional rehabilitation
training is the primary function, and the peripheral
design can be enriched on this basis. In addition, the
target users of assistive devices should target the
elderly Parkinson's group and its surrounding
relationship network, and systematic services
between patients and their families, communities
and medical care should be established. Considering
that the place of use of the product is suitable for
home use, the product can be designed to be more
convenient for carrying and storage. In recent years,
wearable devices are widely used in the medical
field and have an important role in health
monitoring, efficacy measurement, and disease
discovery, etc. Applying them to the medical field
has become a hot topic for medical device
innovation, and the products are gradually applied to
clinical practice (Hu 2018).
At present, there are few independently
developed wearable device products in China, and
they are generally bulky and heavy and not easy to
wear (Chen 2017). However, this could contribute to
the design of assistive devices for Parkinson's
rehabilitation, and the design of assistive devices as
wearable is considered from the perspective of
usage, and the structure of more lightweight and
handy wearable assistive devices is studied. In view
of the psychological and emotional characteristics of
patients, the functions and services should also be
integrated into the corresponding emotional care.
The basic needs of Parkinson's patients for the
rehabilitation assistive devices and the functional
elements that the assistive devices should have are
clarified through the preliminary research, based on
which the logical relationship between the two is
further combined, the integration of functional
elements shown in Figure 6 is carried out to find the
inner connection between patients' needs and the
functional embodiment of the assistive devices, so as
to guide the optimal design of the product.
Figure 6: Integration of functional elements of Parkinson's
assistive devices.
5 OPTIMIZATION STRATEGY
FOR ASSISTIVE DEVICE
DESIGN FOR PARKINSON 'S
REHABILITATION
The design of assistive devices for Parkinson's
rehabilitation requires comprehensive consideration
of the product's structural appearance, functional
services, and user experience. Combining the above
research and analysis results, the design of assistive
devices for Parkinson's rehabilitation can be
optimized at three levels: functional, service, and
emotional. At the functional level, assistive devices
for Parkinson's rehabilitation should be designed to
meet the basic needs of users for self-care, taking
into account the differences in the specific parts of
the patient's body and the degree of the disease. At
the service level, assistive devices for PD should pay
more attention to the systematic connection between
patients and their families, medical and nursing staff
and social relationships, and meet the actual
changing needs of patients with a comprehensive
developmental perspective, and be able to provide
sustainable assistance as the patients' own conditions
change. At the emotional aspect, assistive device
products should include emotional design to give
users respect and care, so that they can feel warmth
and companionship during their use experience.
5.1 Implanting Diverse Linkage Design
The functional dimension of assistive devices for
Parkinson's rehabilitation considers the concept of
inclusion in functional design. Inclusive design
means that designers, product manufacturers, and
suppliers ensure that their products and services
meet the needs of the widest possible audience,
regardless of age, their own abilities, or special
circumstances, so that more people have equal
access to the products. Based on the concept of
inclusive design, the design of training assistive
devices for Parkinson's patients should take more
into account the diverse needs of different patients,
fully consider the individual differences of the
audience, and make targeted designs for the
functions, services and use environment of the
products. The rehabilitation pressure and
psychological conditions of Parkinson's patients
require that the design of assistive devices should
avoid labels such as "sick", "disabled" and "disable".
It is important to put aside narrow assumptions
about patients, to maintain and respect the
self-esteem of the audience as much as possible, to
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
32

enable patients with different degrees of illness to
feel the corresponding reasonable care, and to meet
the specific needs of patients rather than deepen the
psychological burden of rehabilitation. Patients with
PD have different needs based on their background,
family environment, health care services and
economic level. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct
a comprehensive research on the users, to make a
reasonable and accurate positioning of the product
according to the actual needs, and to meet the
personalized training assistive device needs of the
patients. The focus of the design of assistive devices
for Parkinson's patients can be shifted from large
and expensive specialized medical assistive devices
to compact and universal home portable training
assistive devices with more diverse functions to
strengthen the wide applicability of the products.
Parkinson's patients have reduced independent
living ability due to resting tremor, bradykinesia and
dyskinesia, and many of them need personal
accompaniment to dress and eat, wash and clean,
and even travel. The design of assistive devices for
these patients should take into account the patients'
behavioral needs, be in line with ergonomics, and be
more suitable for the patients' diseased limbs in
terms of structure and function. The wearable
rehabilitative assistive devices are lightweight and
portable, and more flexible in terms of place and
mode of use. This paper proposes a conceptual
drawing and design reference of the product, which
can be used for targeted rehabilitation training from
the past single non-linkage product to multi-point
linkage design for different lesion sites and degrees
of lesions of patients.
Figure 7: Concept diagram of wearable rehabilitation
assistive device for PD.
As shown in Figure 7, the design of wearable
elastic back belt is adopted for the patient's low
back, which is combined with the exoskeleton to
strengthen the support effect and correct the patient's
flexion posture. For the upper limb area, a spring
glove design is adopted to strengthen the resistance
of the small arm and hand muscles. For the lower
limbs, the acupuncture point electrotherapy knee
brace and pace standardizer are designed to
stimulate the muscle strength of the lower limbs and
give the patient standardized pace parameters to
relieve short gait through stride training. Compared
with high-end medical devices, the operation process
setting of assistive devices should be more
simplified to improve the fault tolerance and meet
the needs that patients can achieve independent
training as users. Through scientific and effective
training, the patient can improve the completion of
basic movements required for life, strengthen his or
her self-care ability, and thus obtain a higher sense
of self-efficacy, while reducing the burden of care on
the family and health care personnel.
5.2 Establishing a Systematic Service
Network
The service aspect for designing assistive devices for
Parkinson's rehabilitation should place more
emphasis on systemic and sustainability to improve
the service quality of the product. Systematic design
requires that the users of the product are not only the
users themselves, but also the surrounding
relationships of the users, and establishes a
systematic connection for the user groups involved
in the use and service process of the whole product.
The service design of assistive devices for
Parkinson's training can integrate the functional
characteristics of smart home and the background of
the era of smart IOT to build a service system for
patients and families, communities and hospitals to
care for the rehabilitation process of Parkinson's
patients to provide systematic services and improve
the overall environment for the use of assistive
devices. A cell phone APP can be designed for the
training assistive devices, see Figure 8.
The app can provide sub-functions such as
assistive device operation, data feedback, interactive
training and communication community. Users can
use the rehabilitation assistive device app to learn
how to use the device, learn how to wear it, and
learn how to use it. The user's account is linked to
family members, doctors and caregivers, and the
patient's use of the assistive device is uploaded to the
network in real time. The feedback on the changes in
physical data generated by the use of the assistive
device helps medical and family members to better
grasp the actual situation of the patient and take
corresponding medical and caregiving measures.
The interactive training in the app can improve
patients' training enthusiasm and participation
through a game-like approach, and help patients
improve their physical functions in the training
process. The communication community can set up
patient
associations and physician consultation to
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
33

Figure 8: User-side interface design of assistive device APP for Parkinson's rehabilitation.
strengthen the systematic connection between users
and build a diversified service chain.
The concept of sustainability is applied to the
design of assisttive devices for Parkinson's training,
which is reflected in the product's functional service
focusing on the overall long-term process of the
patient's condition. The Parkinson's syndrome is an
irreversible degenerative disease that cannot be
cured by the current level of medical research. The
assistive devices can be designed to intervene in the
degenerative process of the patient's physical
function, and the products cover different degrees of
degenerative corresponding training functions to
meet the user's continuous auxiliary training needs.
For patients with early stage PD, training assistive
devices can provide simple limb exercises for
unilateral limbs with mild symptoms, improve
muscle flexibility, reduce resting tremor, and delay
muscle stiffness and tonicity. For patients with
middle and advanced Parkinson's disease, we can
provide comprehensive functional training and
assisted living services to improve patients' ability to
take care of themselves and their quality of life on
the basis of continuous muscle exercise. The service
process will be sustainable and the service life of the
assistive device will be extended.
5.3 Deepen the Emotional User
Experience
The special psychological attitude of Parkinson's
patients determines that the design of the relevant
training assistive devices should pay attention to the
user's reflective emotions during the usage, taking
into account the patient's expectation of respect, the
desire for disease relief, the need for companionship
and emotional relief and other instinctive needs. This
instinctive layer of emotion transcends the logical
judgment of thinking and it is reflected in the
appearance of the assistive device product, which
can attract the patient's attention from the shape and
color matching in the first place, thus creating the
impulse to understand and use. Excellent design on
instinctive level emotion can reasonably avoid the
rejection of assistive device products by some
patients with low self-esteem and bigotry.
Training assistive device products for PD need to
consider avoiding the label of "aging", reducing the
use of cold metal and minimalist industrial style in
the design, and adopting more rounded and youthful
design to reduce the emotional stimulation and
psychological pressure of patients for rehabilitation
training and improve the acceptance of the product.
In order to alleviate patients' negative psychology
such as depressed mood and anxiety and depression,
the choice of color of assistive devices can be
combined with the medical concept of color healing
therapy. Scientific studies have shown that warm
colors, such as yellow and orange, can alleviate
depression and pessimism, while cool colors, such as
blue and green, can soothe boredom and anxiety.
Exposing Parkinson's patients to a scientific color
palette in the color selection of assistive devices can
effectively alleviate the psycho-emotional symptoms
of non-motor disorders in Parkinson's patients.
The color matching design of the Parkinson's
rehabilitation assistive device was based on the color
healing method. As shown in Figure 9, for patients
whose psycho-emotional expression of non-motor
symptoms is low and pessimistic, warm colors are
considered as the main color scheme, retaining 20%
of the gray degree joint connection as well as 20%
of the cold color decoration reflecting the
technological sense of the product and enhancing the
conviction of the medical product. For patients
whose psychological mood manifests as boredom
and anxiety, color matching makes cold and warm
contrasts, and on the basis of soothing boredom
through cold colors, warm color decorations are
used to alleviate the excessive mechanization caused
by cold tones bringing psychological pressure to
patients.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
34

Figure 9: Color matching scheme of assistive devices for
Parkinson's rehabilitation.
Further behaviors are guided by instinctive
emotions. The behavioral level of training of the
assistive device is designed to correlate with the
patient's experience of using the assistive device.
The level of behavior that governs daily behavior
and brain activity is reflected by the experience of
using the assistive device. The design for the
patient's behavioral level should take into account
the efficiency and enjoyment of using the training
assistive device product. Due to the aging of the
patient group with Parkinson's disease and the
special characteristics of action behavior and mental
behavior, the functional design requires the
operation process of assistive device to be simple
and easy to understand, with a simple and clear
command interface and a certain degree of fault
tolerance, so that patients can quickly accumulate
operating experience and enhance the efficiency of
using the product. Games are not only an aid to
conventional rehabilitation, but also an alternative
therapy(Meijer 2017). In the overall use process of
the product, human-computer interaction can be
enhanced through simple games, such as setting
levels and sending simple instructions to guide
patients to complete the corresponding training, and
matching encouraging points and reward exchange
mechanisms. Game-like behavioral design facilitates
the user to have fun and regulate their emotions
while increasing their motivation to use the device.
Through the optimal design of instinctive and
behavioral aspects, we can enhance the meaningful
value of the product and realize the emotionality of
the reflective aspect. Training assistive devices for
Parkinson's patients should fully understand the
users' own psychological aspirations and meet their
diverse emotional needs. Adhering to the
people-oriented principle and creating a design that
truly impresses people can increase patients'
satisfaction with the use, establish a two-way
connection and emotional bond between the user and
the product, establish the centrality of this training
assistive device product, and deepen patients'
awareness and loyalty to the training assistive device
product.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The increasing prevalence of Parkinson's disease and
the diverse treatment needs of a large group of
patients have raised higher requirements for the
corresponding training assistive devices. The
optimal design of training assistive devices for
Parkinson's patients should be based on a thorough
research of the patient population and a
comprehensive understanding of the patient's
background, degree of disease, behavior, family
environment, social relationships, and the medical
treatment received. It should meet the actual needs
of the users and establish a multifaceted connection
of "patient-family-community-medical care" to form
an integrated product service system. It should
analyze the strengths and weaknesses of various
assistive device products in the market, such as life
support, medical care, and functional exercise, and
propose corresponding optimization solutions. The
future design of Parkinson's training assistive
devices should pay more attention to the
inclusiveness and autonomy of the products, so that
each patient can use the training assistive device
equally and with dignity, and enhance the user's
self-care ability. The process of using the product
should place more emphasis on the systemic nature
of the service and the sustainability of the use of
long-term effects. The systemic service should
strengthen multiple connections and enhance the
patient's self-efficacy through long-term
accompanying treatment. The design also needs to
integrate the emotional care for patients, adhere to
the "people-oriented" emotional design. The social
background of PD determines that the training
assistive devices for the patient group have a broad
market development prospect, and we should
actively promote the innovative design of training
assistive devices for PD to provide better services
for more people with the disease, increase the sense
of well-being, and relieve the pressure and burden of
the patient's family and social health care.
REFERENCES
Bacek T,Moltedo M,Langlois K,et al. (2017). BioMot
exoskeleton-Towards a smart wearable robot for
symbiotic human-robot interaction. C. //International
Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics.IEEE Int Conf
Rehabil Robot. 1666.
Chen X.B.,Liu L.R.,An Zheng,et al. (2017). Analysis of
the current situation of clinical application of wearable
Optimization Strategies for the Design of Rehabilitation Aids for Parkinson’s Patients based on Hierarchical Analysis
35

exoskeleton rehabilitation assistive device .J. Science
and Technology Herald. 35(2), 50-54.
Davide Ferrazzoli,Paola Ortelli,Graziella Madeo,Nir
Giladi,Giselle M. Petzinger,Giuseppe Frazzitta.
(2018). Basal ganglia and beyond: The interplay
between motor and cognitive aspects in Parkinson's
disease rehabilitation. J. Neuroscience and
Biobehavioral Reviews.90.
Hu Kehui,Chen Zhenyun,Zhang Shuxin,Feng Li,Song
Yang Yang,Huang Wanru,Pei Zhigang. (2018).
Research and application of wearable devices in
rehabilitation medicine in developed countries. J.
China Digital Medicine.13(08),56-59+15.
Huang Qun,Huang Juan. (2020). Study on the optimal
design of assistive device for senior citizens in home
care model. J. Design Art Research. 10(03), 71-75.
Li F, Liu Q, Li J. (2018). Design of assistive device for
geriatric rehabilitation based on morphological
experience. J. Packaging Engineering. 39(20),
152-158.
Liu QH,He J,Wang M. (2021). Effect of rehabilitation
exercise training on limb function and self-care ability
of Parkinson's disease patients. J. Qilu Nursing
Journal. 27(11), 150-152.
Liu S.Y., Chen B. (2016). Current status of Parkinson's
disease prevalence. J. Chinese Journal of Modern
Neurological Diseases. 16 (02), 98-101.
Liu YP,Chen MY. (2017). Study on the efficacy of
Lokomat lower limb rehabilitation robot on improving
walking ability of patients with Parkinson's disease. J.
China Rehabilitation. 32(1), 30-32.
Mao B,Li Y,Yang Yang. (2020). A review of Parkinson's
rehabilitation assistive device design. J. Packaging
Engineering. 41(08), 23-29.
Meijer HA,Graafland M,Goslings JC,et al. (2017).
Systematic review on the effect of serious games and
wearable technology used in rehabilitation of patients
with traumatic bone and soft tissue injuries. J. Arch
Phys Med Rehabil.
Mina Chen. (2019). The design and application of
Parkinson's "mask face" passive massage
rehabilitation exercise. D. Hangzhou Normal
University.
Tan Y, Hao HL, Li YF. (2019). Current development of
wearable devices in the chronic disease management
of Parkinson's disease. J. Chinese Journal of
Neuroimmunology and Neurology. 26(01), 52-55.
Wang Luyao,Zhou Yuhui,Li Yongchun. (2021).Research
on museum cultural and creative design based on
hierarchical analysis. J/OL. Packaging
Engineering.1-10.
Wang Y, Pan H, Jian F, Chen N, Zhang L, Yang SH.
(2017). Analysis of tremor characteristics in patients
with different clinical stages of Parkinson's disease. J.
Chinese Journal of Neuroimmunology and Neurology.
24(01),25-28.
Zhuang Yuan. (2017). Design study of assistive device for
Parkinson's patients' self-care class under universal
design vision. D. Wuhan University of Technology.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
36
