
Research on Active Constituents from Chinese Medicine against
Leukemia Targeting ENL based on Molecular Docking
Hao Sun
a
and Jian Tang
b
School of Chinese Medicine, Bozhou University, Bozhou, Anhui, China
Keywords: Leukaemia ENL Protein, Traditional Chinese Medicine Active Ingredients, Molecular Docking.
Abstract: Leukemia is a class of malignant clonal disease of hematopoietic stem cells. It poses a huge threat to human
health. Over the years, progress has been made in using traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in China to
treat and relieve various leukemia symptoms. Erb and he Wan et al noted that ENL protein is a key factor
affecting the viability of MLL-r cells in leukemia. Molecular adding or removing molecular group
modification on the histone can regulate gene expression A prominent structural feature of the ENL protein
is a YEATS domain that identifies a specific acetyl (Ac) on the histone H3. Computer-aided Drug Design
(CADD) method has gradually mature and plays an increasingly important role in drug development.
Molecular docking is the most widely used and successful method in structure-based drug design. Molecular
docking generally refers to the process in which two or more molecules identify each other through
geometric and energy matching. Two major topics of molecular docking methods are spatial identification
and energy identification between molecules.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Leukemia is a class of malignant clonal disease of
hematopoietic stem cells. It poses a huge threat to
human health. Scientists have found that the
regulatory protein ENL promotes leukemogenesis.
Over the years, progress has been made in using
traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in China to
treat and relieve various leukemia symptoms.
Mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) is named for the
chromosome translocation of the MLL fusion
protein at 11q23.This type of leukemia has attracted
wide attention for its unique clinical and biological
characteristics.
The cause of leukemia is usually chromosomal
translocation, producing fusion proteins formed by
fragment junctions of two proteins that ultimately
cause disease. Fusion proteins in MLL are typical so
commonly present in aggressive childhood leukemia
and are associated with poor prognosis. Therefore, it
is very necessary to develop leukemia treatment
strategies based on MLL rearrangement (MLL-
rearranged, MLL-r) fusion proteins. Erb and he Wan
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5748-7516
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3289-3352
et al noted that ENL protein is a key factor affecting
the viability of MLL-r cells in leukemia (Wan 2017).
The histones containing DNA in the cells are
structural and signaling factors. Molecular adding or
removing molecular group modification on the
histone can regulate gene expression A prominent
structural feature of the ENL protein is a YEATS
domain that identifies a specific acetyl (Ac) on the
histone H3. This suggests that this "read" ability of
ENL to acetylated histone is essential for the
induction of MLL-r leukemia.
Another complementary mechanism for SEC and
DotCom stability was identified by Erb and he Wan
et al. They found that inactivation of ENL impaired
the SEC and DotCom function in MLL-r cells. The
ability of ENL to bind to SEC, DotCom drops a hint
that a model-ENL, through the YEATS domain,
recognizes that acetylated H3, enhances the stability
of binding of SEC and DotCom complexes to DNA
and regulates the activity of aberrant regions of the
genome.
Protein ENL is essential for MLL-r leukemia.
Some leukemias exist resulting from a mixture of
some MLL protein and part of another. The second
protein is typically part of the SEC (super elongation
complex) protein complex or the DotCom (DOT1L-
containing complex). Both protein complexes
Sun, H. and Tang, J.
Research on Active Constituents from Chinese Medicine against Leukemia Targeting ENL based on Molecular Docking.
DOI: 10.5220/0011211800003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 391-396
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
391

regulate gene transcriptional programs in MLL-r
leukemia (the intact and partially fused SEC/
DotCom complex is highlighted in red in Fig). The
ENL protein binds to both complexes while the
complex is fused to MLL in cells, and ENL interacts
both with unfused SEC/ DotCom and with fused
SEC/ DotCom. ENL contains a YEATS domain that
can recognize a specific acetyl group (Ac) on the
histone H3. Erb and Wan et al confirmed that the
YEATS domain of ENL protein helps stabilize the
binding of SEC and DotCom to DNA, promoting
gene expression in the driving leukemic manner.
This pathway of action presents a way: using a
small molecule inhibitor targeting the ENL protein
YEATS domain as a drug molecule can selectively
kill leukemia MLL-r cells and then treat leukemia.
Other cell types seem to largely tolerate ENL loss,
but both SEC, DotCom and ENL are expressed in
multiple cells, so it is important that when
developing such drugs is to understand this
difference in tolerance.
In MLL-r leukemia, the importance of ENL is
consistent with multiple studies. These studies show
that poor regulation of DOT1L viability is required
for the survival and proliferation of MLL-r cells.
H3K79 methylation has long been associated with
gene transcriptional viability and is a regulatory
mechanism controlling DOT1L activity. A key
unanswered question is how these histone
modifications can directly affect transcription.
Methyl-lysine signaling is often coupled to
downstream processes by a similar mechanism to the
methylation modification of the YEATS domain
read. All the reader domains of the major histone
methylation sites have been identified except for
H3K79. Furthermore, methylated lysine can be
dynamically regulated by demethylases, but
demethylases that remove methyl groups at H3K79
remain to be characterized. The study by Erb and he
Wan et al further encouraged researchers to identify
and identify "readers" and demethylases for H3K79
methylation because these enzymes cross with ENL-
mediated signaling pathways and may also become
therapeutic targets for MLL-r leukemia.
There is currently a new theory that epigenetic
regulators can play an important role in disease.
Driven by this awareness, a growing number of
academics and businesses are working to develop
inhibitors of these mechanisms to treat cancer.
Clinical trials of MLL-r leukemia have evaluated
DOT1L inhibitors, and Erb et al. found that in
cellular models, using DOT1L inhibitors, plus
knockin of ENL mutant genes that do not recognize
acetylated lysine, was more effective than inhibiting
gene expression programs that drive leukemenesis in
both methods alone. This suggests that there is a
synergy between the two therapies.
Wan et al. also investigated the potential of
combinatorial therapies for MLL-r leukemia by
targeting the ENL YEATS domain with the bromine
domain of another reader of lysine acetylation, BET
family proteins. BET proteins typically interact with
SEC. And also promotes transcriptional elongation.
BET inhibitors disrupt the binding of the BET
protein to the acetyl-lysine fraction, and there are
about 20 clinical trials testing the efficacy of these
drugs in cancer treatment. Moreover, the
combination of the YEATS domain inhibitor of ENL
with the BET inhibitor JQ1 is highly toxic to MLL-r
leukemia cells.
The effects of these combinatorial therapies
suggest that multiple histone modification signals
act together to form a characteristic epigenetic state
of MLL-r leukemia. Therefore, multiple targeted
therapies are more effective and can reduce the
emergence of-with resistance, which is one of the
risks of monotherapy.
Drug developers have long focused mainly on
targeting enzymatic activity, rather than protein –
protein interactions. However, the development of
"reader" therapies targeting multiple apparent
modification groups has become increasingly
popular, thanks in part to the success of BET
inhibitors. The binding site of the YEATS domain is
also a very attractive target for drug development.
TCM treatment has made progress in the
treatment of leukemia for many years, and has
developed continuously, while the treatment of
leukemia is not limited to western medicine
technology. At present, the application of TCM has
become an important treatment means of leukemia.
According to researchers, there are six TCM that
have a good anti-leukemia effect, and specifically
list the relevant active ingredients.
Computer-aided Drug Design (CADD), is a
computer chemistry based approach to predicting
testing and computing the relationship between
ligand and receptor biological macromolecules
through computer simulations, enabling optimization
and design of lead compounds (Xie 2019). At
present, CADD method has gradually mature and
plays an increasingly important role in drug
development, which can greatly shorten the
development cycle of new drugs and reduce
development costs.
Molecular docking is the most widely used and
successful method in structure-based drug design.
Molecular docking generally refers to the process in
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
392

which two or more molecules identify each other
through geometric and energy matching. Two major
topics of molecular docking methods are spatial
identification and energy identification between
molecules. Spatial matching is the basis of
intermolecular interactions, and energy matching is
the basis for maintaining a stable binding between
molecules. For geometric matching calculation,
lattice calculation, fragment growth are usually used,
while energy calculation uses simulated annealing
and genetic algorithm.
When the binding site of the ligand to the
receptor protein is unknown, its site can be predicted
by CADD methods and can guide mutation
experiments and drug design. It is therefore
important to identify the sites where the receptor
protein surface interacts with the ligands for drug
design.
The molecular docking technology has been used
to virtually screen the bioactive constituents from
TCM and determine the targets in recent years. Xu
Cao and Singh have made outstanding contributions
in the drug field using molecular docking (Cao 2021,
Singh 2012). Which is efficient in ‘narrowing’ the
chemical database before pharmacological assays in
vivo or in vitro.
2 METHODS AND MATERIALS
2.1 Software
ChemOffice Professional (PerkinElmer Inc., USA),
AutoDock Tools1.5.6 and AutoDock Vina (The
Scripps Research Institute, USA), PyMOL (TM)
1.7.4.5 Edu (Schrodinger, LLC Inc., USA) and
Discovery Studio 2016 client (BIOVIA Co., USA).
2.2 Establish A Ligand Database
The Chinese medicinal materials with the effect of
treating leukemia contain multiple active
ingredients, and the ligand database required for this
test can be summarized.
Seven Chinese medicine materials, including
Paridis Rhizoma (Guan 2007), Sophorae
Flavescentis Radix (Yan 2014), Scutellariae
Barbatae Herba (Niu 2021), Herba Hedyotidis (Qin
2008), Paeoniae Radix Rubra (Lu 2015), Salviae
Miltiorrhiza Radix et Rhizoma (Xu 2021),
Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Huang 2017), were
chosen for the remarkable effects in the treatment of
leukemia. The total 50 main constituents from these
herbs were collected via reviewing the related
articles. The structural files of these materials were
all downloaded from the PUBCHEM (PubChem
(nih.gov) and processed with MM2 in Chem3D,
stand as mol2 documents. Followed by Autodock,
all the mol2 documents saved as pdbqt documents.
2.3 Locking the ENL Protein Active
Site
We used Autodock tools to process ENL with
dehydration molecules, deligand, etc, and exported
them as pdbqt files. The ENL protein has a YEATS
domain (gully) that recognizes the acetylation
modification. It can serve as an active site for
molecular docking. By operating on the software,
the active site of the ENL was determined as
center_x =0.954 nm, center_y = -0.12 nm, center_z
= 10.368 nm.
2.4 Molecular Docking of ENL with
Small Moleculares
The PDBQT format file of the ENL protein as the
ligand of the ligand and the ligand library was
imported into the Autodock. vina software, and the
computer then scored each group. The acceptable
ligand GKN displayed by the ENL protein in the
RCSB PDB database was exported from GKT to the
PDBQT format and used as a ligand as a positive
control. The two groups of scores were finally
compared, and ligand scores near or beyond the
GKT, score were selected as the final screening
results, and could be used as a valuable reference for
the development of ENL inhibitor drugs for
leukemia.
3 RESULTS
The original ligand-GKT in the ENL complex (PDB
ID: 6HPW) showed an affinity of -7.2 kcal/mol.
Among the 50 constituents, 26 compounds had
higher binding affinity than GKT, respectively listed
in the table 1 below.
Research on Active Constituents from Chinese Medicine against Leukemia Targeting ENL based on Molecular Docking
393
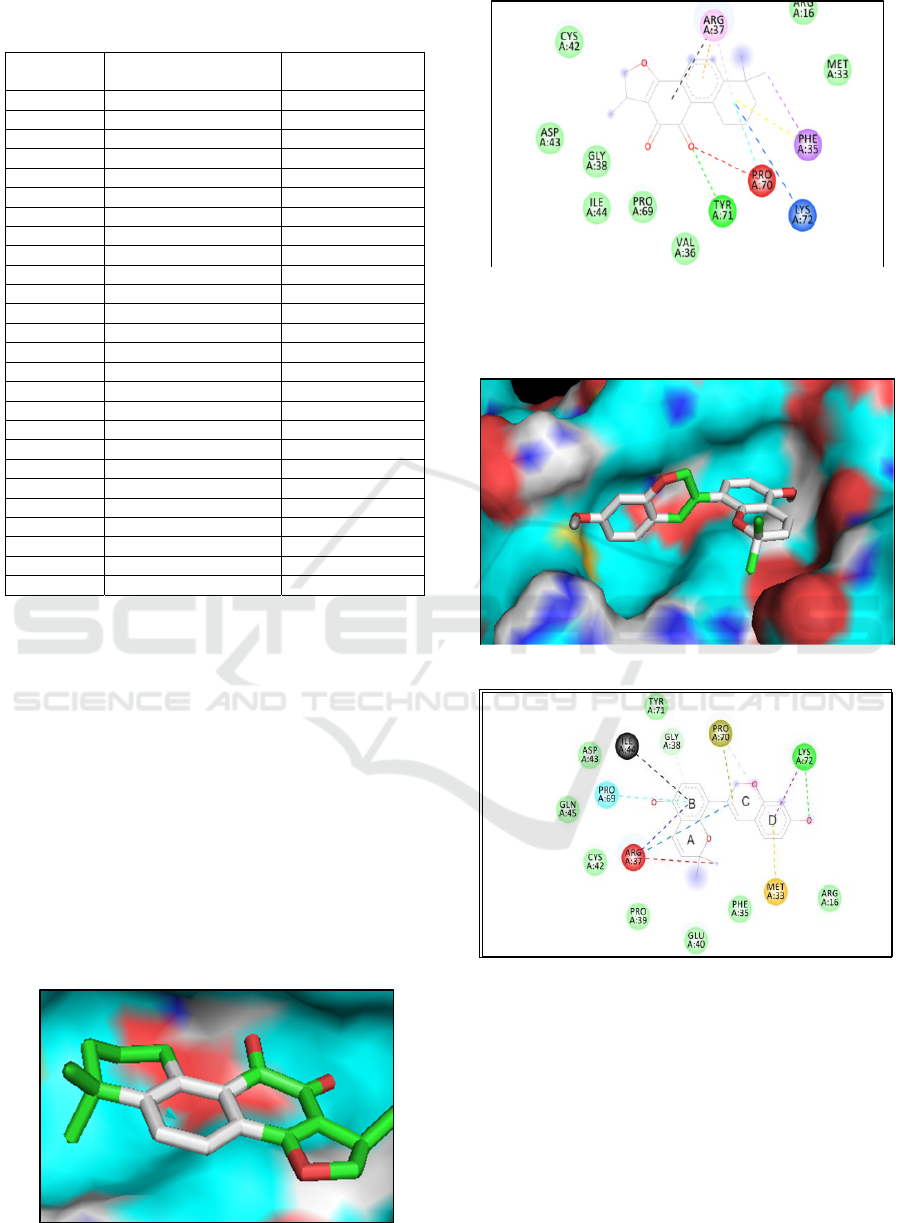
Table 1: Affinity scores of molecular docking of ENL
with 26 compounds.
NO.
Compounds
Binding Affinity
(kcal/mol)
1 Cryptotanshinone -8.5
2 Glabrene -8.4
3 Tanshinone IIA -8.3
4 Trifolirhizin -8.2
5 Paeoniflorigenone -8.2
6 Polyphyllin I -8.1
7 Oleanolic acid -8.1
8 Norkurarinone -7.9
9 Baicalin -7.9
10 Ursolic acid -7.9
11 Benzoylpaeoniflorin -7.8
12 Pseudoproto-Pb -7.7
13 Enoxolone -7.7
14 Glabridin -7.7
15 Paeoniflorin -7.6
16 Polyphyllin II -7.4
17 Quercetin -7.4
18 Albiflorin -7.4
19 Benzoyloxypaeoniflorin -7.4
20 Stigmasterol -7.4
21 Baicalein -7.3
22 Naringenin -7.3
23 Oroxylin A -7.3
24 Wogonin -7.3
25
K
uraridin -7.2
26 Oxypaeoniflorin -7.2
Cryptotanshinone has a strong binding affinity -
8.5 (kcal/mol) with 6HPW, Above the threshold
value, The molecular docking plan (Figure 1b)
shows the Van Der Waals ineraction between it and
the amino acids such as CYS42 in the 6HPW
protein; The quinone ring has a Pi-Alkyl interaction
between cryptotanshinone and ARG37; The benzene
ring between cryptotanshinone has a Pi-Alkyl
interaction and ARG37; Alkyl functions between the
fat loop of cryptotanshinone and ARG37, PRO70,
LYS72, Pi-Alkyl interaction between it and PHE35;
Conventional Hydrogen Bond interaction between 2
of cryptotanshinone-O and TYR71, a week
hydrogen Bond interaction between it and PRO70;
Pi-Sigma interaction between 11-C of
cryptotanshinone and PHE35.
Figure 1a: 3D model.
Figure 1b: 2D modle
Figure 1: Molecular docking model for Cryptotanshinone
and ENL.
Figure 2a: 3D model
Figure 2b: 2D modle
Figure 2: Molecular docking model for Glabrene and
ENL.
Glabrene has a strong binding affinity energy
with 6HPW, Above the threshold value, Molecular
docking plan (Figure 2b) shows a van der Waals
interaction between it and TYR71 et al. in the
6HPW protein; The B loop of Glabrene and GLY38
have a Pi-Donor hydrogen Bond interaction, Pi-
Sigma interaction between both and ILE44, PRO69,
ARG37; The carbon-carbon double bond on the C
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
394
loop of Glabrene and PRO70, ARG37 both have
Alkyl interactions; Alkyl interaction between the D
loop of ligand and PRO70, Pi-Sigma interaction
between it and LYS72, Pi-Sulfur interaction with
MET33zhijian; The carbon on the A loop CH3 of
Glabrene and ARG37 have Alkyl interaction; The
Conventional Hydrogen Bond interaction occurs
between O on the D loop of Glabrene and LYS72.
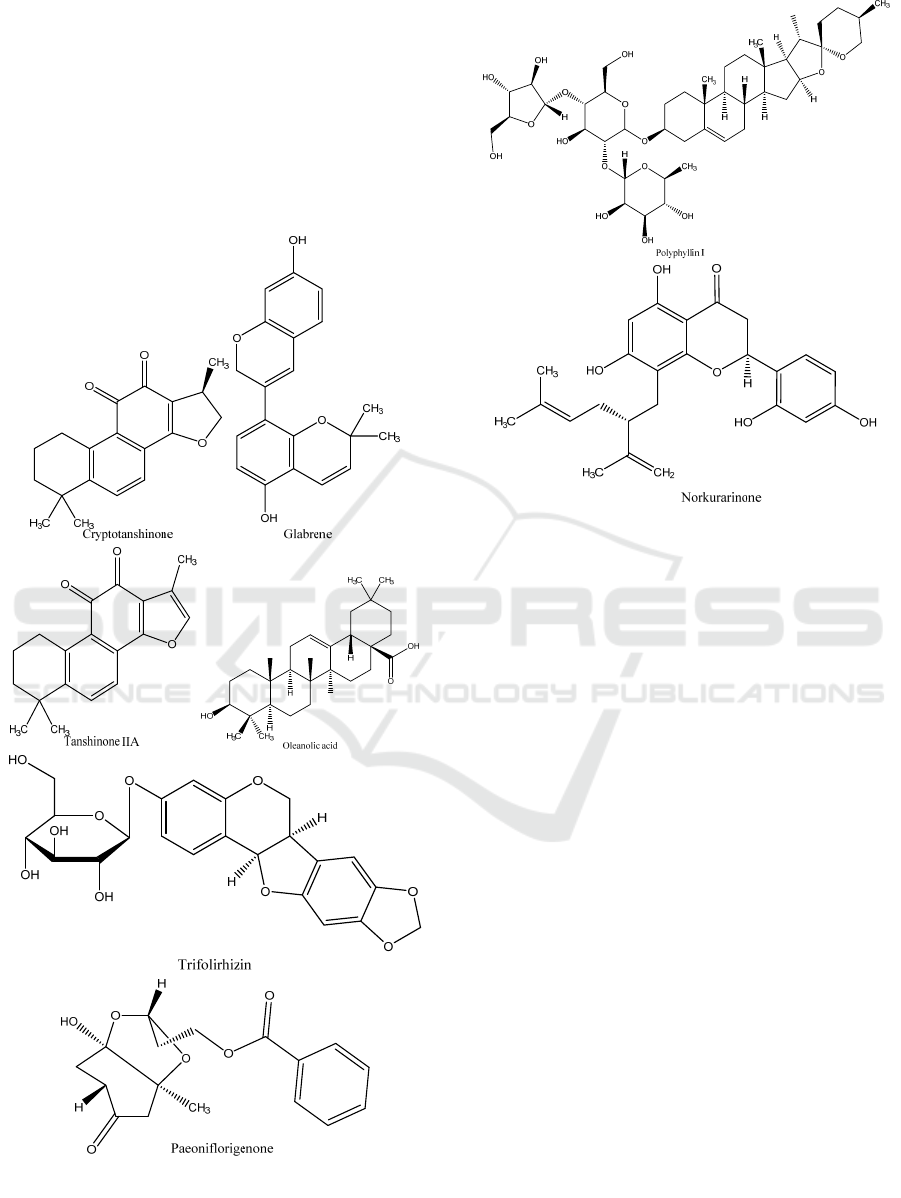
The structures of compounds in the top 8 affinity
scores of molecular docking are listed in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Chemical structures of compounds with top 8
affinity scores.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results showed that the active TCM components
represented by Cryptotanshinone, Glabrene were
well and stably bound with the ENL associated with
leukemia. The results show that the TCM active
Chinese ingredients represented by
cryptodenshinone and photoglycyrrhizin bind well
and stably to the ENL associated with blood
carcinogenesis.This series of molecules represented
by cryptodanshinone and photoglycyrrhizin can
efficiently bind to ENL proteins and potentially
affect the function of ENL proteins. In addition the
effect of Cryptotanshinone and Glabrene on cancer
have been confirmed to some extent by Yuqing Ge
and Yuting Huang (Ge 2015, Huang 2017).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Wentao Zhang for software analysis, and
Yutong Han for the supply and literature database.
This work was supported by Key Laboratory of
Chinese Medicine Materials Research of Anhui
Higher Education Institutes (Bozhou University,
KLAHEI18032) and Bozhou University Research
Grant (BZQD201901). Hopefully, one day, my
Research on Active Constituents from Chinese Medicine against Leukemia Targeting ENL based on Molecular Docking
395

experimental data can be based on more help, which
is also a good thing for me.
REFERENCES
Cao, X., Zao, X., Xue, B. et al. (2021). The mechanism of
TiaoGanYiPi formula for treating chronic hepatitis B
by network pharmacology and molecular docking
verification. Sci Rep 11, 8402.
Ge Yuqing, Rubinb Cheng, Bo Yang et al. (2015). Effect
of cryptodenshinone on imatinib sensitivity and P-
glycoprotein expression in leukemic cells [J].Chinese
Chinese Chinese Medicine Journal, 40 (12): 2389–
2395.
Guan Luhan. (2007). Study on the Chemical Composition
and Activity of Traditional Chinese Medicine Paridis
Rhizoma [D]. Chongqing University.
Huang Yuting, Chi Zongliang, Wang Shumei et al. (2017).
Progress in flavonoids composition in Glycyrrhizae
Radix et Rhizomaand its antitumor activity [J].
Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 26 (13): 1532–1537.
Huang Yuting , Chi Zongliang, Wang Shumei et al.
(2017). Progress in flavonoids composition in licorice
and its antitumor activity [J]. Chinese Journal of New
Drugs,26 (13): 1532–1537.
Lu Xiaohua, Ma Xiao, Wang Jian et al. (2015). Advances
in the chemical composition and pharmacological
effects of Paeoniae Radix Rubra [J]. Chinese Herbal
Medicine, 46 (04): 595–602.
Niu Shurui, Shi Yun, Yang Xin et al. (2021). Progress in
antitumor effects of Scutellariae Barbatae Herba [J].
Chinese Pharmacy, 32 (15): 1915–1920.
Qin Lilan, Deng jiagang. (2008). Progress in antitumor
effects of Herba Hedyotidis [J]. Inner Mongolia
Traditional Chinese Medicine, (07): 42–45.
Singh, P., Shukla, P. (2012). A prelude report on
molecular docking of HER2 protein towards
comprehending anti-cancer properties of saponins
from Solanum tuberosum.
Wan, L., Wen, H., Li, Y. et al. (2017). ENL links histone
acetylation to oncogenic gene expression in acute
myeloid leukaemia. Nature, 543, 265–269.
Xie Zhishen, Song barracks, Zhang Zhenqiang et al.
(2019). Computer-aided Drug Design Methods and Its
Application in New Drug Research and Development
[J]. Journal of Henan University (Medical edition), 38
(02): 148–152.
Xu Yi, Chen Tu, Chen Ming. (2021). Progress in the
chemical composition of Salviae Miltiorrhiza Radix et
Rhizoma and its pharmacological effects [J]. Straits
Pharmacy, 33 (05): 45–48.
Yan Deji, Yan Yingnan, Alimu Maimaiti et al. (2014).
Progress in the anti-tumor mechanism of active
components of Sophorae Flavescentis Radix [J].
Modern Biomedical Progress, 14 (24): 4776–4779.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
396
