
Zelda's Effect on Gene Expression in the Early Development of
Drosophila Embryo
Jing Wang
School of Arts, Fordham University, New York, NY, 10023, U.S.A.
Keywords: Zelda, Drosophila Embryos, Transcription Factors, Pair-Rule Genes, Gap Genes.
Abstract: Zinc-finger protein Zelda (Zld) is thought to play an essential role in the development of early-stage
Drosophila embryos, and this paper takes a step further by confirming the Zld’s effect on Class I & II gene
expression, and exploring the synergistic effects of Zld and other transcription factors in gene expression. The
primary methods used in this paper are Zelda-binding pattern and JASPAR analysis results. It was found that
Zld played a direct and indirect, decisive and non-decisive role in Class I and II gene, respectively. Besides
Zld, this paper spotted that the gap proteins derived from gap genes were an key transcription factor in the
expression of the pair-rule genes, a subdivision of the Class II genes. There is also evidence shows that sloppy
paired 1 might be the enhancer of sloppy paired 2. On the basis of previous studies, this work studied the
effects of Zld and other transcription factors on the expression of different types of genes in more detail.
Directions for future research were discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, several studies have explored the
critical role of the zinc-finger protein Zelda (Zld) in
early embryonic drosophila. (Liang, Nien, Liu,
Metzstein, Kirov, Rushlow 2008) confirmed Zld as a
key activator in the early zygotic genome; (Nien,
Liang, Butcher, Sun, Fu, Gocha, Kirov, Manak,
Rushlow 2011) investigated how Zld affects the
timing mechanism of the development of early genes
(Fu, Nien, Liang, Rushlow 2014); demonstrated that
Zld is a predictor of enhancer activity and the co-
coordinate to regulate gene expression. However, the
synergistic effects of Zld and other transcription
factors in the regulation of gene expression in the
preliminary stage still need to be further explored.
For narrowing such a gap, this paper will use
Zelda-binding patterns and JASPAR analysis results
to summarize the effects of Zld on Class I & II genes
and explore whether Zld coordinates with other
transcription factors to influence the gene expression.
In this paper, we defined the Class I gene as the
ubiquitous gene expressed throughout the embryo at
an earlier stage of development. Class II gene, also
known as patterning gene, is expressed in some
regions of embryos in the later stage of development
according to a specific pattern.
We utilized Kuk (CG575) and pairing-rule genes
Slp 1&2 (CG6738 & CG2939) as Class I and II gene
representatives, respectively. Our research showed
that in Class I genes, Zld directly binds to the
promoter to activate its expression, while in Class II
gene, Zld binds to the enhancer to affect certain
expression levels. We also spotted other transcription
factors, gap proteins, that control Class II genes'
expression patterns.
2 METHODS
2.1 Integrated Genome Browser (IGB)
We used Integrated Genome Browser (IGB) to put
several experimental data in order based on
Drosophila melanogaster genes. Wildtype RNA
polymerase expression in Cycle 12 was used as the
baseline reference; wildtype RNA polymerase
expression in Cycle 13 and RNA polymerase
expression in Cycle 13 when Zld knocked out were
used to compare the effect of Zld on gene expression;
wildtype ChIP-seq of Zld and TAGteam
(CAGGTAG) site were used to confirm the Zld
binding pattern. This step enables us to obtain a
620
Wang, J.
Zelda’s Effect on Gene Expression in the Early Development of Drosophila Embryo.
DOI: 10.5220/0011249800003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 620-625
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
preliminary inference about Zld binding patterns
toward the selected genes for conducting further steps.
2.2 JASPAR
JASPAR was used to further affirm Zld’s effect on
gene expression and predict whether other
transcription factors were involved in gene
expression (JASPAR 2020). We first got the Zld
binding peak coordinate from the IGB and used
intercept ± 200bp of it as the region to obtain the
FASTA-formatted targeted gene sequence in
Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (National Center
for Biotechnology Information) database. Based on
the criteria with a relative profile score threshold of
80%, JASPAR scanned all transcription factors that
have the possibility to bind to the given gene
sequence and arranges them by correlation.
2.3 FlyBase & Berkeley Drosophila
Genome Project (BDGP)
FlyBase and Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project
(BDGP) (BDGP 2021) are both information libraries
that can provide data to consolidate our hypothesis.
FlyBase database contains information about genes
and transcription factors, while BDGP contains gene
expression images at different stages.
3 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
3.1 Class I Genes (Ubiquitous Genes)
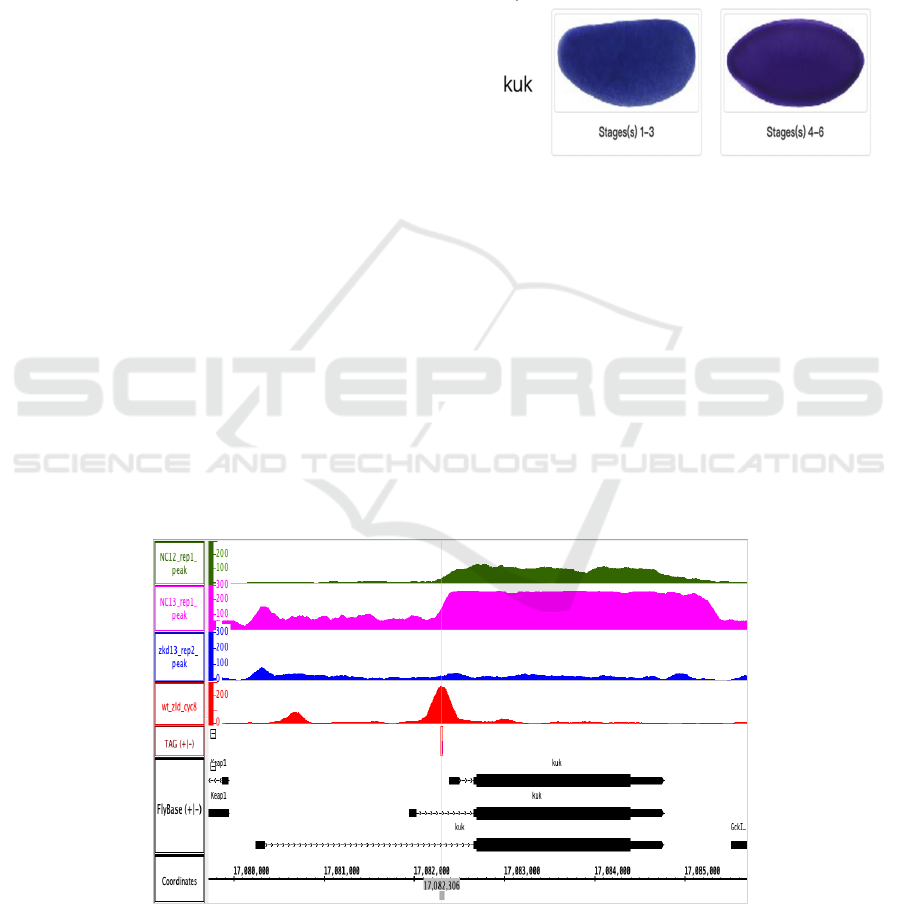
Kugelkern (kuk, CG5175). “[kuk] encodes a nuclear
envelope protein required for nuclear elongation
during cellularization.” (FlyBase Homepage) And it
can be drawn from Figure 1 that kuk is a typical class
I gene as it is expressed throughout the whole
embryo.
Figure 1: Expression Pattern Image for kuk from BDGP.
As shown in Figure 2, the highest Zld binding
peak in the 4th track corresponds to the TAGteam site
(CAGGTAG) in the 5th track. We further used
JASPAR to scan ±200bp near this site, as shown in
table 1, confirming that there was indeed a strong Zld
binding site with a high score of 13.82. Then, by
comparing the kuk expression with or without Zld,
we see that a considerable amount of RNA expression
is demonstrated in wildtype case (the second track),
while the expression level witnesses a huge decrease
when Zld was knocked out (the third track). Such a
phenomenon suggests that Zelda is a key
determinator for the expression of kuk.
Note. RNA polymerase expression in Cycle 12 (the first green track); wildtype RNA polymerase expression in Cycle 13 (the
second pink track); RNA polymerase expression in Cycle 13 when Zld knocked out (the third blue track); wildtype ChIP-seq
of Zld (4th red track) and TAGteam site (5th brown track). The previous four tracks are on the same scale from 0 to 300.
Figure 2: Snapshot of Gene Kuk From IGB.
Zelda’s Effect on Gene Expression in the Early Development of Drosophila Embryo
621
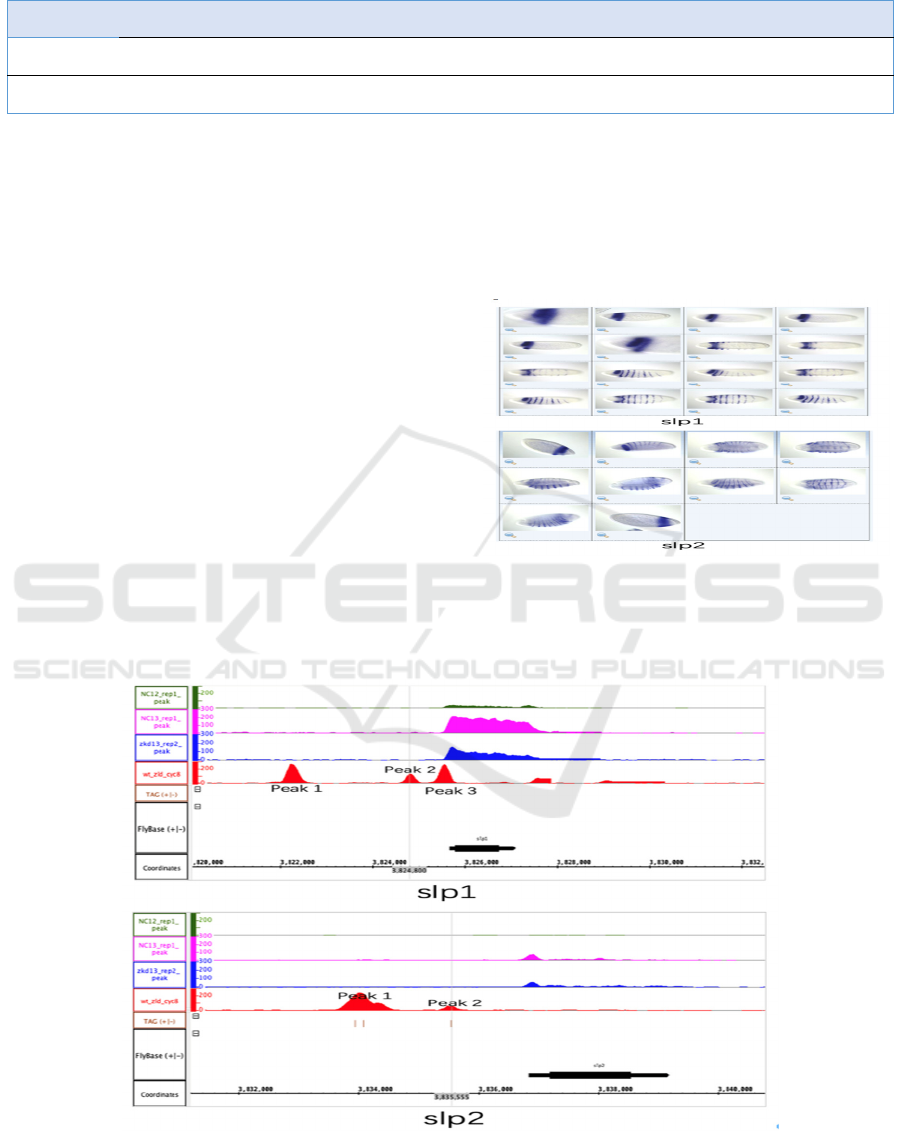
Table 1 JASPAR –kuk–vfl–Analysis Result
Matrix ID Name Score Relative score Sequence ID Start
En
d
Stran
d
Predicted
sequence
MA1462.1 vfl
13.8206
0.993095999606
NT_033777.3:17082105-
17082505
197 208 +
CGGCAGGTAG
AT
MA1462.1 vfl
12.0672
0.958080363668
NT_033777.3:17082105-
17082505
221 232 -
TTGCAGGTAC
GT
Note. Vfl, as known as Zld; The higher the score, the higher the affinity that the transcription factors bind to the gene sequence.
3.2 Class 2 Genes (Patterning Genes)
This research selected sloppy paired 1 (slp1) &
sloppy paired 2 (slp2) / CG16738 & CG2939 as the
Class 2 gene for analysis because they accord with
the Class 2 gene’s criterion of being expressed in a
certain area of the embryo at a later stage of
development (demonstrated in Figure 3). Figure 3
also reveals the similar expression pattern that slp1
and slp2 share, that is, start from the head and
gradually extend to the whole embryo in strips with
intervals. It shows the slp1 and slp2’s role in the
process of establishing body segments as pair-rule
genes.
By comparing the second and third tracks of
Figure 4, we found that after Zld was knocked out,
the gene expression of slp1 experienced a moderate
decline, while the gene expression of slp2 did not
change significantly. In the fourth column, several
Zld binding peaks in this gene segment were
displayed, and JASPAR analysis confirmed that Zld
indeed has high scores in these peaks both in slp1 &
slp2 (Table 2). Therefore, we speculated that Zld
could play an influential but not decisive role in the
expression of Class 2 genes, and other transcription
factors are of more significant impact on their
expression.
Note. Drosophila embryos are in the developmental stage
4-6.
Figure 3: Expression Pattern Image for slp1 & slp2 from
BDGP.
Note. Track contents are the same as Figure 2.
Figure 4: Snapshot of gene slp1 & slp 2 from IGB.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
622

Table 2: JASPAR -slp1 & slp 2 -vfl- Analysis Results Note. The number in the Peak column stands for Zld binding peak in
the 4
th
track of Figure 3.
Gene Matrix ID
Na
me
Score Relative score Sequence ID Start End Strand Predicted sequence Peak
Slp2 MA1462.1 vfl 13.2734
0.982167314
844
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
176 187 + CGGCAGGTAGCG 1
Slp1 MA1462.1 vfl 12.2371
0.961472452
634
NT_033779.5:3825455-
3825655
79 90 - CATCAGGTAGTT 3
Slp1 MA1462.1 vfl 12.0538
0.957812957
086
NT_033779.5:3822050-
3822450
175 186 - CTTCAGGTAGTG 1
Slp1 MA1462.1 vfl 11.035
0.937467450
787
NT_033779.5:3822050-
3822450
144 155 - ATCCAGGTAAGA 1
Slp2 MA1462.1 vfl 10.8576
0.933924242
155
NT_033779.5:3835455-
3835655
83 94 + GCTCAGGTAAAA 2
Slp1 MA1462.1 vfl 10.4841
0.926465843
882
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
185 196 - ACTCAGGTAATC 2
Slp2 MA1462.1 vfl 10.0659
0.918115258
717
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
40 51 + GCGTAGGTAGGA 1
Table 3: JASPAR -slp1 & slp 2 -gap genes- Analysis Results.
Gene Matrix ID
Na
me
Score Relative score Sequence ID Start End Strand Predicted sequence Peak
Slp2
MA0452.
2
Kr 14.616 0.937574067021
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
149 162 + CTTAACCCCTTCAG 1
Slp1
MA0452.
2
Kr 14.5752 0.93695773075
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
172 185 + TTTAACCCCTTCGG 2
Slp1
MA0452.
1
Kr 13.7451 0.966483513258
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
174 184 - CGAAGGGGTTA 2
Slp2
MA0452.
2
Kr 13.5852 0.922015290106
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
1 14 + CTTAACTCTTTCGA 1
Slp1
MA0049.
1
hb 12.8235 1.0000000052
NT_033779.5:3822050-
3822450
388 397 + GCATAAAAAA 1
Slp2
MA0452.
1
Kr 12.4301 0.933338080611
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
151 161 - TGAAGGGGTTA 1
Slp2
MA0452.
1
Kr 11.79 0.917205123065
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
3 13 - CGAAAGAGTTA 1
Slp1
MA0459.
1
tll 11.6933 0.887199901339
NT_033779.5:3822050-
3822450
205 214 + AAAAGTGAAA 1
Slp2
MA0049.
1
hb 11.2386 0.951168571865
NT_033779.5:3835455-
3835655
68 77 - TCATAAAAAA 2
Slp1
MA0452.
2
Kr 10.833 0.880472403084
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
71 84 - GGCAATCCTTTTGG 2
In addition, it was also found from JASPAR
analysis (Table 3) that both slp1 and slp2’s peaks
have high scores of gap protein, e.g., Kruppel (Kr),
Hunchback (hb), and Tailless (tll). According to
Griffiths et al., Kr and hb both are regulators, but
repressor and activator, respectively, jointly control
the expression of the pair-rule gene. Their differences
in concentration at the embryo’s position control each
pair-rule stripe formation (Griffiths, Doebley,
Peichel, Wassarman 2020). Our data reaffirm the
above findings and identify one more gap protein, tll,
as the regulator for forming embryonic stripe
formation.
Other than gap genes, another high score gene
repeated shows up in the peak of slp1 from JASPAR
analysis results (Table 4), namely defective
proventriculus (dve), which is considered as a
transcriptional repressor that involves in
Zelda’s Effect on Gene Expression in the Early Development of Drosophila Embryo
623
developmental patterning (FlyBase Homepage). We
speculate that dve has the same function as the Kr to
control the slp1 gene expression. The data presented
in this paper support such a view, but specifically,
how dve influences the embryonic stripe formation
remains to be determined by further studies.
We also deduced the relationship between slp1
and slp2 through IGB graphic and JASPAR analysis.
Firstly, from the zoom-out snapshot of the two genes
(Figure 4), we found that slp1 and slp2 appeared in
pairs, and slp1 appeared earlier than slp2. Second,
slp1 protein shows high scores in both peaks of slp2
(Table 5). Both phenomena are suggesting that slp1
is an enhancer of slp2. However, this is only
speculation based on the data. A control experiment
should be carried out to compare the expression of
slp2 with or knocking out slp1 to determine the role
of slp1 in slp2’s expression.
Table 4 JASPAR - slp 1 - dve- Analysis Results
Matrix ID
Na
me
Score Relative score Sequence ID Start End
Strand
Predicted sequence Peak
MA0915.1 dve 12.1441 0.985360610986
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
313 320 - CTAATCCC 2
MA0915.1 dve 11.6975 0.975487844496
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
270 277 + ATAATCCC 2
MA0915.1 dve 11.3993 0.968895149107
NT_033779.5:3824600-
3825000
183 190 - GTAATCCG 2
Table 5 JASPAR - slp 2 - slp1- Analysis Results
Matrix ID Name Score Relative score Sequence ID Start End Strand Predicted sequence Peak
MA0458.1 slp1 10.4209 0.904717113268
NT_033779.5:3833900-
3834100
84 94 - CTGTTTACATG 1
MA0458.1 slp1 11.992 0.943959392058
NT_033779.5:3835455-
3835655
181 191 - TTGTTTTCACA 2
4 CONCLUSION
In this study, kuk, slp1 and slp2 were used as
representatives of class 1 and class 2 genes to
investigate the role of Zld in regulating the expression
of different types of genes. Specifically, Zld plays a
decisive role in the expression of class 1 gene, as
when Zld being knocked out, the expression of kuk
will be greatly reduced; The effect of Zld on class 2
gene is not direct and definite because the expression
of slp1 and slp2 don’t witness such significant
decrease after same procedure. These findings further
confirm that zin-finger protein Zld plays an important
role in drosophila embryonic development.
At the same time, this study comes across two
tentative conclusions for further researches to
confirm. First, several transcription factors (i.e. Dve,
Kr, Hb, etc.) were identified that might collaborate
with Zld to control the expression of pair-rule gene.
Secondly, slp 1 is a potential enhancer of slp2. The
data in this paper support these hypothesis, but
uniquely designed experiments are needed to
validate.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Doctor Christine Rushlow for the guidance
and her lab for providing the research data used in this
paper.
REFERENCES
BDGP. (2021). Patterns of gene expression in Drosophila
embryogenesis. Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project.
https://insitu.fruitfly.org/cgi-bin/ex/insitu.pl.
FlyBase. (n.d.). FlyBase homepage. FlyBase Homepage.
https://flybase.org/.
Fu, S., Nien, C.-Y., Liang, H.-L., Rushlow, C. (2014). Co-
activation of microRNAs by Zelda is essential for
EARLY drosophila development. Development,
141(10), 2108–2118.
Griffiths, A., Doebley, J., Peichel, C., Wassarman, D.
(2020). Introduction to genetic analysis. W.H. Freeman
and Company Macmillan Learning, New York.
JASPAR 2020. http://jaspar.genereg.net/.
Liang, H.-L., Nien, C.-Y., Liu, H.-Y., Metzstein, M. M.,
Kirov, N., Rushlow, C. (2008). The zinc-finger protein
Zelda is a key activator of the early zygotic genome in
Drosophila. Nature, 456(7220), 400–403.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
624

Nien, C.-Y., Liang, H.-L., Butcher, S., Sun, Y., Fu, S.,
Gocha, T., Kirov, N., Manak, J. R., Rushlow, C. (2011).
Temporal coordination of gene networks by Zelda in
the EARLY Drosophila Embryo. PLoS Genetics, 7(10).
U.S. National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). National center
for Biotechnology Information. National Center for
Biotechnology Information.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.229.
Zelda’s Effect on Gene Expression in the Early Development of Drosophila Embryo
625
