
Parasporal Cry Protein Parasporin-2 Produced by Bacillus
thuringiensis Has in Vitro Toxicity on Human Cancer Cells (HepG2)
under the Action of Proteinase K
Xuan Zhou
School of Biochemistry and molecular biology, University of Western Australia, Perth, WA6009, Australia
Keywords: Parasporal Cry Protein, Bacillus thuringiensis, Cancer Cells, Proteinase K.
Abstract: Liver cancer is one of the malignant tumors with the fastest increasing morbidity and mortality and the greatest
threat to people's health and life. This article investigates whether parasporin-2 produced by the hydrolytic
non-hemolytic Bacillus thuriensis can recognize liver cancer cells and have cytotoxicity to them. In this paper,
Bacillus thurinensis parasporal Cry protein—parasporin genotypes were determined in this strain using the
PCR amplification. Then, parasporin-2 was separated by SDS-PAGE and purified. The same concentration of
cultured HepG2 (human liver cancer cells) and L-O2 (normal human liver fibroblasts) was added to the plate
and divided into two groups. Then, 3 solutions contain parasporin-2 and protease K was added to the plate.
The damage to the cells was observed under a microscope and graded the degree of cell damage (CPE), and
MTT then determined cytotoxicity (CT). Analysis the SDS-page and following conclusions may be drawn by
comparing CPE and CT in each group. First, through horizontal comparison, the data of HepG2 and L-O2
cells in each group were compared, to determine whether parasporin-2 is toxic to liver cancer cells but not to
ordinary liver fibroblasts. Besides, longitudinal comparison is the situation of CPE and CT in different groups,
whether Parasporin-2 plus Protease K can produce toxicity on HepG2 of liver cancer cells. Bacillus
thuringiensis can produce parasporin-2, and after the decomposition of protease K protein, parasporin-2 can
produce recognition and cytotoxicity to liver cancer cells. analysis the degree of cell destruction and toxicity,
after dealing with the proteinase k, cut parasporin – 2 toxicity is activated. Conclude that parasporin - 2 which
hydrolyzed by protease k has a recognition on the liver cancer cells and it's toxic to cancer cells but will not
produce toxicity to normal liver cells.
1 INTRODUCTION
Shigetane Ishiwata, a Japanese, first discovered
Bacillus thuringiensis in Japan in 1901 and described
the dying state of the larvae in Bacillus thuringiensis
(E. Hough, 1989). In 1905, from his experiments, he
realized that the poisoning appeared to be caused by a
sort of poison and occurred before the multiplication
of bacillus. His incomplete identification led to the
German Ernst Berliner's first morphologically valid
description and the successful isolation and naming of
Bacillus thuringiensis from Anagasta Kuehniella in
the Mediterranean (Sansinenea, 2012).
Bacillus thuringiensis is an aerobic, gram-positive,
spore-forming facultative bacterial pathogen. Under
conditions of adequate nutrition and environment,
spores germinate and then produce vegetative cells,
which grow and reproduce by fission and produce a
variety of nutrients. Bacterial spores consist mainly of
one or more insecticidal proteins in the form of
crystalline inclusions, known as insecticidal crystal
proteins (ICP) or 𝛿 -endotoxin (Kim, 2000). The
insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis
mainly consist of CRY crystal protein and CYT
cytolytic protein.
Bacillus thuringiensis, as a soil bacterium, is
known to be used as a biological insecticide and
mosquito control in agriculture and forestry. Today,
the use of biological insecticides is one of the most
important components of integrated pest management
and has been recognized by countries around the
world. However, bacillus thuringiensis was shown in
1999 to have a new cytotoxic effect on human cancer
cells (Akao, Mizuki, Yamashita, Saitoh, and Ohba,
1999).
Parasporin-2 is a new Cry crystal protein that can
be isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis. Through
research, the n-terminal region of Parasporin-2 can be
Zhou, X.
Parasporal Cry Protein Parasporin-2 Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis Has in Vitro Toxicity on Human Cancer Cells (HepG2) under the Action of Proteinase K.
DOI: 10.5220/0011264400003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 723-728
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
723

cleared to effectively activate the toxin activity, while
C-terminal digestion can also lead to cell damage
(Akiba, 2009); (Kitada, 2006). This paper investigates
whether the human liver cells HepG2 can be killed by
Parasporin-2— a kind of crystal protein of Bacillus
thurinensis in vitro. This study predict that parasporin-
2 can induce toxicity on liver cancer cells (HepG2)
under the action of protease K.
2 METHODS AND MATERIALS
Bacteria cultivation- The soil isolates of Bacillus
subtilis HepG2 were grown on AGAR at 28 ° C for 8
days, and an appropriate amount of beef powder and
polypeptide were added, along with a small amount of
NaCl, and the PH was maintained at 7.6.
Human cells cultivation- In this study, we used
HepG2 (human liver cancer cells) and L-O2 (human
normal liver fibroblasts) cell lines and purchased
normal T cells in the blood center to separate from
lymphocytes. Cells were maintained in RPMI 1640
and 10% fetal BSA and 30uL kanamycin were added
at 37℃, and prepare normal human red blood cells
(Mizuki, Ohba, Akao, Yamashita, Saitoh, and Park,
1999).
DNA isolation and PCR amplification- PCR was
used to test the gene of parasporin-2. Total genomic
DNA was used as PCR template by parasporin pure
bacterial DNA purification equipment isolated from
parasporal protein. Heat circulator was used to prepare
a reaction mixture containing 50-100 ng total genome
DNA of Bacillus thuringiensis with 19× L PCR buffer
(10 mM TRis-HCl). PH value 9.0, 50mm KCl, 1.5mm
MgCl
2
), dNTPs 75×M each, primers 0.2×M each
(Table 1), Taq DNA polymerase 1.5U. Template DNA
preheated at 94℃ for 2 minutes. Denaturation at 94℃
for 1 min, primer annealing for 45 s, PCR
amplification at 72℃ for 1 min. PCR detection was
performed for 30 cycles. PCR was analyzed under
1.2% agarose gel, and then stained with UV irradiation
(Sansinenea, 2012).
DNA sequencing- PCR products were purified
using PCR purification kit (Bolotin, 2016).
Isolation Parasporin from parasporal crystals-
Separation spores of Bacillus thuringiensis strains
cells with distilled water three times, and broken in
distilled water, using two-way separation purification
spores by parasposal crystal, the parasposal Cry
protein in the 50 mM, ph10 NaCO
3
dissolve 1 h, then
add 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and EDTA
to stop. The protein solution of PH10.0 was treated
with protease K and incubated at 37°C for 90min, and
PMSF is used to stop protease digestion. Combining
on ion exchange column, with 50 mm NaCl elution
toxin protein parasporin 20 mM Tris HCl buffer, in pH
8.0. The active component is then treated and gel
filtration (Ito, 2004).
SDS-PAGE AND WESTERN BLOTTING-
Membrane-enriched or cytosolic fractions were
suspended in SDS sample buffer for SDS-PAGE. The
separated proteins were transferred
electrophoretically to nitrocellulose membranes, and
immunodetection was carried out using antibodies
against parasporin-2. Binding of the primary antibody
was visualized using a horseradish peroxidase-labeled
anti-rabbit parasporin-2 secondary antibody and
Lumilight plus. Chemiluminescence need to use
FluorS-MultImager.
Cytotoxicity assay and Hemolytic assay- prepare
some microplates each containing the same amount
and concentration of HEPG2 and L-O2 cell solutions
in each well. The measured solution was divided into
six groups as below (Table 2), group 1&2 were the
negative control group, and the solution was 100%
absorbent cell suspension. Group 3&4 was
parasporin-2 solution actioned with protease K. Group
4&5 are parasporin-2 solution after separation and
purification. At the same time, Drop three solutions,
each solution into an HEPG2 plate and an L-O2 plate.
Then mark microplates. Measure their absorbance and
repeat the experiment more than three times. The
degree of CPE was graded based on the proportion of
damaged cells (Table 3).
Table 1: Solution and cell composition tables for each group of microplates. Contain (✓).
Buffer Parasporin-2 Protease
K
HepG2 L-O2
Group 1 ✓ ✓ ✓
Group 2 ✓ ✓ ✓
Group 3
✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Group 4
✓ ✓ ✓
✓
Group 5 ✓ ✓ ✓
Group 6
✓ ✓
✓
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
724
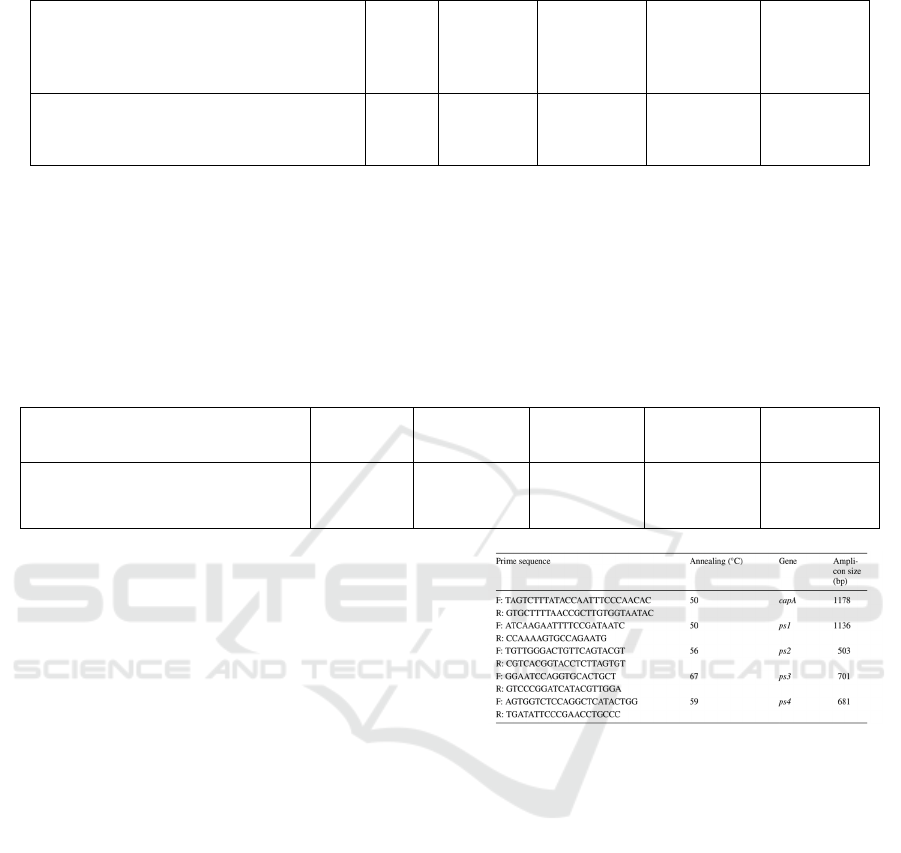
Table 2: The expression of percentage of cells destroyed.
𝟓%
5%-10% 10%-30% 30% -60% 60%-90%
The proportion of damaged cells (CPE) - + ++ +++ ++++
The experiment was repeated for more than three
times. Cytotoxicity was determined by MTT [3-(4, 5-
Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2h Tetrazolium
Bromide] (Mizuki, 2000). Each of the microplates
contained 90 microliters of cell suspension, each
containing a certain number of cells. Measurements
were made using a nonradioactive cell test system.
The number of cell proliferations was measured after
incubation for 16 hours at 37 ° c and 24h after
administration. Calculate survival rate. The average
absorption properties of the sample had 100% cell
survival as a negative control. The degree of
cytotoxicity (CT) was graded on the basis of the
relative value of absorbance. (Table 4)
Table 3: The expression of the degree of cytotoxicity.
0.70
0.60-0.90 0.30-0.60 0.10-0.30
0.10
The degree of cytotoxicity (CT) - + ++ +++ ++++
Statistical analysis- All of the numerical data
were analyzed through one-way ANOVA method All
of the mean multiple comparisons were conducted
using Tukey’s Post Hoc test. P≤0.05 was considered
a significant difference. Graphs were prepared using
Microsoft Office Excel.
3
RESULTS
3.1 Analyze the PCR Results
PCR is a rapid and highly sensitive method for
detecting and identifying Bt genes (Carozzi, Kramer,
Warren, Evola, and Koziel, 1991). The efficacy of
PCR for cry genes and ps genes identification relies
on the alternation of conserved and variable
nucleotide regions. Through comparison and inquiry,
the existence of parasporin-2 genes in the parasporal
protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis strain was
confirmed (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Prime sequences of gene capA, ps1, ps2, ps3, ps4
(Moazamian, Bahador, Azarpira, and Rasouli, 2018).
3.2 SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
Analysis
Protein gel electrophoresis provides an obvious
display of complex protein collections from a
biological sample. The gels can be compared with
each other to evaluate the similarities and differences
between samples. The two-dimensional gel provides
separation and information on two important physical
properties of protein components in the sample,
namely, apparent molecular mass. Western blot was
used to isolate and purify parasporin-2 in
combination with anti-Parasporin-2 (which can be
obtained by injecting antibodies into rabbits).
Through SDS analysis, the paracrystal protein
produced by Bacillus thuringiensis HepG2 was
hydrolyzed after being hydrolyzed by protease K, and
the reference strains of SDS-PAGE swimming lane 3-
Parasporal Cry Protein Parasporin-2 Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis Has in Vitro Toxicity on Human Cancer Cells (HepG2) under the
Action of Proteinase K
725
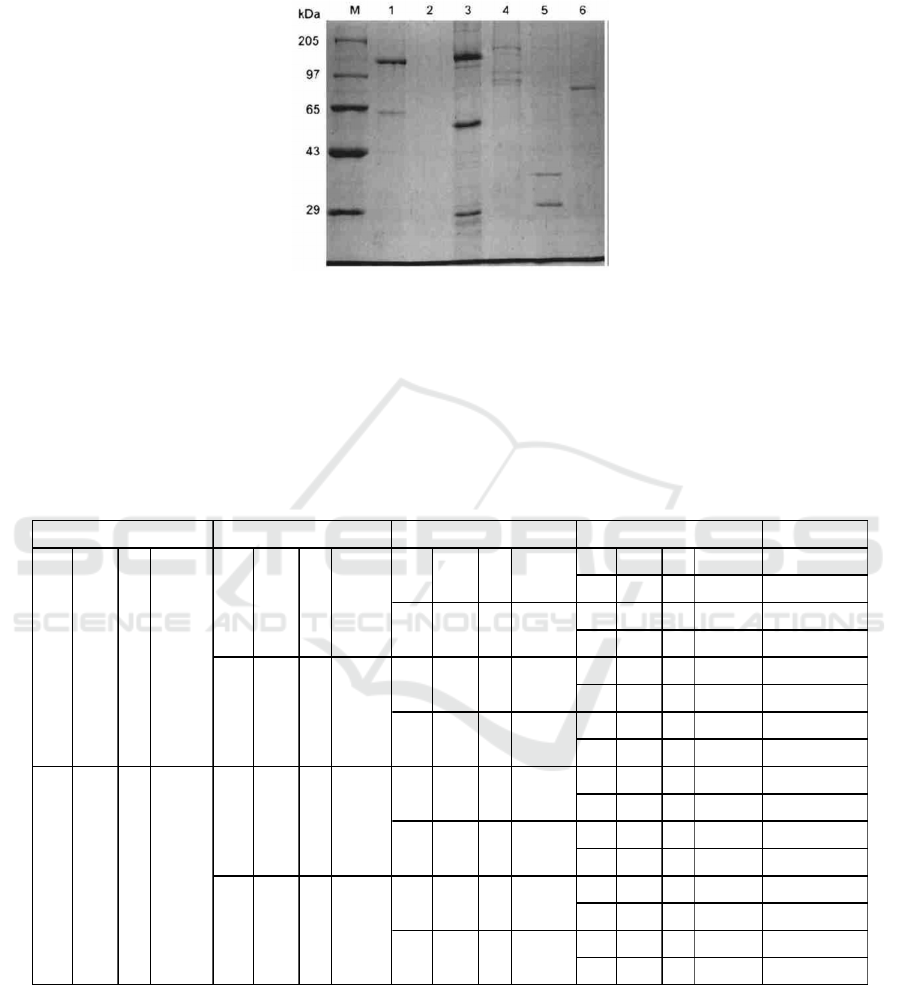
6 were parasporin-1,2,3,4. (Figure 2) Primary and
secondary of parasporin-2 antibodies were detected
and imaged by Western Blot using
immunofluorescence (Lenina, Naveenkumar,
Sozhavendan, Balakrishnan, Balasubramani, and
Udayasuriyan, 2014).
Figure 2. Lanes 3–6 reference strains of parasporin (PS4, PS3, PS2 and PS1) (Lenina, Naveenkumar, Sozhavendan,
Balakrishnan, Balasubramani, and Udayasuriyan, 2014).
3.3 Cytotoxicity Analysis
Detect the proportion of HegG2 and L-O2 cells
distraction and the degree of cytotoxicity. Each group
for possible results corresponds to the groups in Table
2.
Table 5 shows all the possible outcomes, but since
many of the outcomes were not possible, by making
a separate table of the following possible outcomes.
Table 4: All outcomes of cytotoxicity assay and Hemolytic assay.
The possible results are as follows:(1) As the
Table 6 shows, it means group 3&4 have high
proportion on cell damage and high degree of
cytotoxicity. Group 1,2,5&6 have low proportion on
cell damage and low degree of cytotoxicity. (2) As the
Table 7 shows, it means all groups have low
proportion on cell damage and low degree of
cytotoxicity. (3) As the Table 8 shows, it means group
1&2 have high proportion on cell damage and high
degree of cytotoxicity. Group 3,4,5&6 have low
proportion on cell damage and low degree of
cytotoxicity, etc.
OUT COM ES
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 1
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 2
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 3
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 4
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 5
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 6
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 7
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 8
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 9
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 10
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 11
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 12
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 13
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 14
CPE - CT ++++ OUTCOME 15
CPE ++++ CT - OUTCOME 16
++++
-
-
++++
-
THE CPR
/
CT OF GROUP 3
CPE CT
CPE CT
-
++++
CPE
CPE
CT
CT
CT
CT
-
++++
-
++++
++++
++++
-
++++
-
++++
-
++++
-
CT
CT
CT
-
++++
-
++++
-
++++
-
CPE
CPE
CPE
CPE
CPE
CT
CT
CT
CT
CT
THE CPR
/
CT OF GROUP
6
THE CPR
/
CT OF GROUP
5
CPE
CPE
CPE
THE CPR
/
CT OF GROUP
4
CPE
CPE
++++
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
726
Table 5-12. The possible results 5-12. The above table
reflects the results of Cytotoxicity assay and Hemolytic
assay. An increase in the number of + indicates an increase
in the value. For example, ++++ indicates that the value is
too large, and + indicates that the value is small. And-means
that the value is close to 0. CEP stands for proportion of
damaged cells, and CT stands for the relative value of
absorbance. The step of Cytotoxicity assay and Hemolytic
assay should be repeated at least 3 times.
4 CONCLUSION
The morphology of Bacillus thuringiensis spores
(cubic, spherical, rhomboid and irregular) was
observed by isolation. It indicates the parasporal
crystal protein. Through SDS-PAGE analysis and
Western Blot, which can determine the existence of
parasporin-2. Through the observation of brightfield
confocal microscopy and MTT results, the
absorbance of solution (which contain parasporin and
protease K) were analyzed.
The cells observed under the microscope were
compared with Figure 3 and 4, and the damage
degree of the cells was calculated. The higher the
degree of cell destruction, the higher the
transmittance measured by MTT, indicating the
stronger the cytotoxicity of the solution. The next step
is to analyze possible results (Table 5-12). For
possible result 1, it means parasporin-2 after action
with protease K is toxic, and it don’t have specific
identification of cancer cells. Possible result 2 reflects
neither parasporin-2 with protease K nor solutions
containing only parasporin-2 are not toxic to cancer
cells. In possible result 3, it means parasporin-2 is
toxic to liver cells. As to possible result 4, which is
closest to my prediction, reflects only after reaction
with protease K, parasporin-2 can identify the cancer
cells and kill them, but it is no toxic to normal liver
cells. Besides, the solution contains only parasporin-
2 are not toxic to HepG2 and L-O2. In possible result
5, contrarily with the possible result 4, the group with
the solution contains only parasporin-2 has high
damaged cells and high cytotoxicity, which means
parasporin-2 is toxic and has identification of cancer
cells. Possible result 6 reflects that parasporin-2 is
toxic to cancer liver cells, whether it reacts with
protease K. In possible result 7, which is contrary to
the possible result 6. It means parasporin-2 is toxic to
normal liver cells, whether it reacts with protease K.
As for the possible result 8, parasporin-2 reacts with
protease K isn’t toxic to HepG2 but is toxic to L-O2,
and parasporin-2 is toxic to not only live cancer cells
and normal liver cells.
Protease K acts on the C terminal and activates
parasporin-2 to identify and produce cytotoxicity on
liver cancer cells. Parasporin-2 can specifically
bound to the plasma membrane of liver cancer cells.
It rapidly increases the membrane permeability, and
that it dramatically alters the cytoskeleton and
organelle morphologies. Thus, parasporin-2 is a cell
discriminating, membrane-targeting, and pore-
inducing toxin that subsequently causes irreversible
intracellular decay in liver cancer cells. It can be
found from other studies that the insecticidal spectra
of many strains of Bacillus thuringiensis currently
studied are very narrow. For example, cry crystals
produced by a hemolytic bacillus thuringiensis
studied in Japan produce toxins in only a few genera
of the beetle family (Kaur, 2006). Therefore, Bacillus
thuringiensis may have tremendous potential for non-
insecticidal applications, such as the treatment of
human cancers.
Tabl e 5 Tabl e 6
CPE CT CEP CT
Group 1 - ++++ Gr oup 1 - ++++
Group 2 - ++++ Gr oup 2 - ++++
Group 3 ++++ - Gr oup 3 - ++++
Group 4 ++++ - Gr oup 4 - ++++
Group 5 - ++++ Gr oup 5 - ++++
Grouo 6 - ++++ Gr ouo 6 - ++++
Tabl e 7 Tabl e 8
CEP CT CEP CT
Group 1 - ++++ Gr oup 1 - ++++
Group 2 - ++++ Gr oup 2 - ++++
Group 3 ++++ - Gr oup 3 ++++ -
Group 4 ++++ - Gr oup 4 - ++++
Group 5 ++++ - Gr oup 5 - ++++
Grouo 6 ++++ - Gr ouo 6 - ++++
Tabl e 9 Tabl e 10
CEP CT CEP CT
Group 1 - ++++ Gr oup 1 - ++++
Group 2 - ++++ Gr oup 2 - ++++
Group 3 - ++++ Gr oup 3 ++++ -
Group 4 - ++++ Gr oup 4 - ++++
Group 5 ++++ - Group 5 ++++ -
Grouo 6 - ++++ Gr ouo 6 - ++++
Tabl e 11 Tabl e 12
CEP CT CEP CT
Group 1 - ++++ Gr oup 1 - ++++
Group 2 - ++++ Gr oup 2 - ++++
Group 3 - ++++ Gr oup 3 - ++++
Group 4 ++++ - Group 4 ++++ -
Group 5 - ++++ Gr oup 5 ++++ -
Grouo 6 ++++ - Grouo 6 ++++ -
Parasporal Cry Protein Parasporin-2 Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis Has in Vitro Toxicity on Human Cancer Cells (HepG2) under the
Action of Proteinase K
727
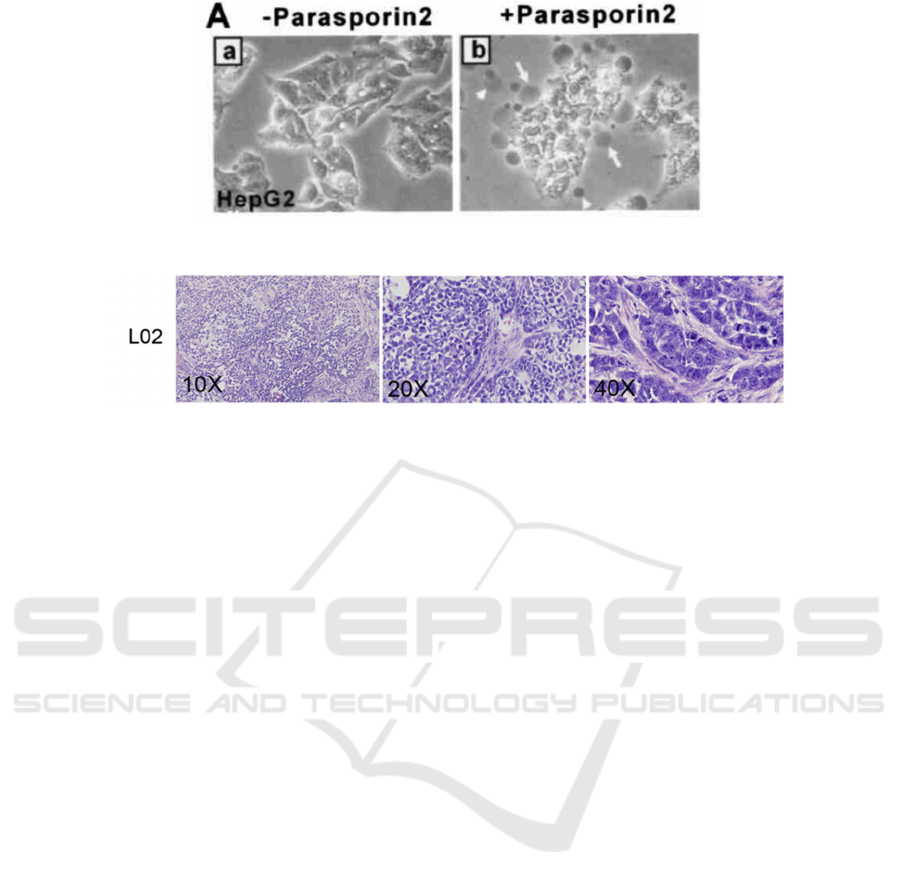
Figure 3: HepG2 cells with parasporin-2 under the brightfield confocal microscopy (S. Kitadam 2006).
Figure 4: L-O2 cells under the brightfield confocal microscopy (X. Liang, G. Xu, Q. Gao, and X. Tao, 2016).
REFERENCES
A. Bolotin et al., "Comparative genomics of
extrachromosomal elements in Bacillus thuringiensis
subsp. israelensis," Research in Microbiology, vol. 168,
no. 4, pp. 331-344, 2017/05/01/ 2017, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2016.10.008.
A. Ito et al., "A Bacillus thuringiensis Crystal Protein with
Selective Cytocidal Action to Human Cells," The
Journal of biological chemistry, vol. 279, no. 20, pp.
21282-21286, 2004, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401881200.
E. Hough et al., "High-resolution (1.5 Å) crystal structure
of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus," Nature
(London), vol. 338, no. 6213, pp. 357-360, 1989, doi:
10.1038/338357a0.
E. Sansinenea, Bacillus thuringiensis Biotechnology, 1st ed.
2012. ed. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2012.
E. Mizuki, M. Ohba, T. Akao, S. Yamashita, H. Saitoh, and
Y. S. Park, "Unique activity associated with non‐
insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal inclusions:
in vitro cell‐killing action on human cancer cells,"
Journal of applied microbiology, vol. 86, no. 3, pp. 477-
486, 1999, doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00692.x.
E. Mizuki et al., "Parasporin, a Human Leukemic Cell-
Recognizing Parasporal Protein of Bacillus
thuringiensis," Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory
Immunology, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 625-634, 2000, doi:
10.1128/CDLI.7.4.625-634.2000.
E. Moazamian, N. Bahador, N. Azarpira, and M. Rasouli,
"Anti-cancer Parasporin Toxins of New Bacillus
thuringiensis Against Human Colon (HCT-116) and
Blood (CCRF-CEM) Cancer Cell Lines," Current
microbiology, vol. 75, no. 8, pp. 1090-1098, 2018, doi:
10.1007/s00284-018-1479-z.
H. S. Kim et al., "In vitro cytotoxicity of non‐Cyt inclusion
proteins of a Bacillus thuringiensis isolate against
human cells, including cancer cells," Journal of applied
microbiology, vol. 89, no. 1, pp. 16-23, 2000, doi:
10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01087.x.
N. B. Carozzi, V. C. Kramer, G. W. Warren, S. Evola, and
M. G. Koziel, "Prediction of insecticidal activity of
Bacillus thuringiensis strains by polymerase chain
reaction product profiles," Applied and environmental
microbiology, vol. 57, no. 11, pp. 3057-3061, 1991, doi:
10.1128/aem.57.11.3057-3061.1991.
N. K. Lenina, A. Naveenkumar, A. E. Sozhavendan, N.
Balakrishnan, V. Balasubramani, and V. Udayasuriyan,
"Characterization of parasporin gene harboring Indian
isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis," 3 Biotech, vol. 4, no.
5, pp. 545-551, 2014, doi: 10.1007/s13205-013-0190-9.
S. Kitada et al., "Cytocidal Actions of Parasporin-2, an
Anti-tumor Crystal Toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis,"
The Journal of biological chemistry, vol. 281, no. 36,
pp. 26350-26360, 2006, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602589200.
S. Kaur, "Molecular approaches for identification and
construction of novel insecticidal genes for crop
protection," World journal of microbiology &
biotechnology, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 233-253, 2006, doi:
10.1007/s11274-005-9027-y.
T. Akao, E. Mizuki, S. Yamashita, H. Saitoh, and M. Ohba,
"Lectin activity of Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal
inclusion proteins," FEMS microbiology letters, vol.
179, no. 2, pp. 415-421, 1999, doi: 10.1016/S0378-
1097(99)00444-9.
T. Akiba et al., "Crystal Structure of the Parasporin-2
Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin That Recognizes Cancer
Cells," Journal of Molecular Biology, vol. 386, no. 1,
pp. 121-133, 2009/02/13/ 2009, doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.002.
X. Liang, G. Xu, Q. Gao, and X. Tao, "LKB1 expression
reverses the tumorigenicity of L02 cells," Oncology
reports, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 1055-1061, 2016, doi:
10.3892/or.2016.4900.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
728
