
Berberine Can Target the VEGFR2/ERK Pathway to Inhibit
Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Xenografts
Huaze Liu
Northeast Yucai School, Shenyang, Liaoning, 110179, China
Keywords:
Glioblastoma, VEGFR2/ERK Pathway, Berberine.
Abstract: The purpose of this article is to investigate the concrete effect of berberine on angiogenesis of glioblastoma
cells. The glioblastoma is the most malignant cancer with high mortality and it is also difficult to treat with
modern medical methods. The fractionated radiotherapy, interstitial radiotherapy or stereotactic radiosurgery
all have unstable effects on tumor. Previous study has reported that berberine can inhibit the angiogenesis in
glioblastoma xenografts through targeting the VEGFR2/ERK pathway. And this study investigates the
concrete effect of berberine on angiogenesis of glioblastoma cells. In the hypothetical experiment, we will
treat glioblastoma xenograft mice with increasing amounts of injected Berberine (0, 0.1, 0.3, 1 mg/ml, 10
mg/ml) for 0 min, 1 day, 7 days, 2 weeks and then measure tumor weight and size, and perform confocal
microscopy/ immunohistochemistry (IHC) for VEGFR2, or phospho-ERK and unphosphorylate ERK. The
experiment will also measure VEGFR2, phosphorylate ERK, unphosphorylate ERK by western blot. Positive
control is Temozolomide treatment.There are three most possible results: (1) Berberine inhibit the
angiogenesis of glioblastoma cells in both in vitro and in vivo cell lines; (2) berberine can only inhibit the
angiogenesis of glioblastoma cells in in vitro cell cultures; (3) berberine only inhibit the angiogenesis of
glioblastoma cells in determined human and murine glioblastoma. In conclusion, the results of this study will
provide important information for future clinical trials of berberine treatment. Future studies should focus on
improving in vivo delivery methods, finding more inhibitors of the angiogenic pathway in glioblastoma, and
exploring in detail the specific mechanisms of berberine.
1 INTRODUCTION
Malignant tumor is a potential killer of human life and
seriously endangers people's healthy life. According
to the report of World Health Organization, the
incidence and mortality rate of malignant tumors are
gradually increasing all over the world. 10 million
new malignant tumors occur each year, and 6-7
million people die from this disease, accounting for
12% of the total, which becomes the second cause of
human death. The main types of malignant tumors are
lung cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, colorectal
cancer and breast cancer, and their causative factors
include environmental and life factors such as air
pollution, smoking, poor living habits, food additives
and drug abuse. In recent years, with the development
of science and technology, chemotherapy for tumors
has made some progress, and the life expectancy of
tumor patients has been significantly extended, such
as in leukemia, malignant lymphoma, etc., but there
is still no effective approach for most solid tumors.
Scientific researchers have gradually realized that in
order to make a breakthrough, we must start from the
mechanism of tumor development in order to solve
the problem at root. Anti-tumor drugs are gradually
moving from traditional cytotoxic drugs to multi-
targeted drugs and exploring various new drugs. The
development of new natural drugs.
Glioblastoma is one of the most malignant
astrocytomas. The tumor is located in the subcortical
region and most grows over the cerebral hemispheres.
It usually invades several lobes and deep structures of
the brain. It can also spread through the corpus
callosum to the contralateral cerebral hemisphere.
Meanwhile, glioblastoma is the most common
primary brain tumor in adults, with an annual
incidence of 52.6 per 1 million people and
approximately 17,000 new cases diagnosed each
year. The etiology of most cases of glioblastoma and
its prevention have not been clarified. Rare risk
factors include genetic disorders (e.g.,
Liu, H.
Berberine Can Target the VEGFR2/ERK Pathway to Inhibit Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Xenografts.
DOI: 10.5220/0011313500003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 951-956
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
951

neurofibromatosis and Li-Fermini syndrome) and
chemotherapy.
Angiogenesis is a process in which
physiologically new microvessels develop into a
blood supply system. Whereas Vasculogenesis
usually refers to spontaneous blood vessel formation,
Intussusception refers to the more general process of
rapid formation of new blood vessels. This process is
common in human growth and development, and in
wound healing. In addition, angiogenesis is an
important step in tumor progression, and in tumor
growth, it can be the key to the transformation of a
tumor from dormant to malignant, rapidly growing,
and potentially invasive to other tissues.
Neovascularization is an important way for tumors to
obtain nutrients to ensure their own development, and
tumor angiogenesis is the result of the combination of
multiple factors induced by tumors. Tumor
angiogenesis is the result of the combined action of
multiple factors in the tumor-induced body, mainly
promoters and inhibitors, which are in a balanced
state under normal conditions. Among the various
promoting factors, vascular endothelial VEGF is an
important regulator of angiogenesis, and its receptors
(VEGFR) are mainly VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2 and
VEGFR-33. It has been suggested that inhibition of
angiogenesis is a powerful strategy for cancer
treatment, and when one of these factors is affected,
angiogenesis will not occur properly. induced
proliferation, migration, invasion and duct formation
at sub-toxic doses. In addition, HDT significantly
inhibited the in vivo production of villi allantoic
membranes without showing cytotoxicity.
Furthermore, HDT reduced not only VEGFR2
signaling in HUVECs but also hypoxia-inducible
factor (HIF)-1 expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. The currently investigated antitumor
peptide drugs in inhibiting mechanism of
angiogenesis is a hot topic of research for most
scholars. NT4 was shown to have important effects
on endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube
formation, especially when induced by FGF2 and
coagulation. when induced by FGF2 and thrombin. In
addition, NT4 has an important role in the migration
and invasion of aggressive tumor cells. Therefore, the
anti-angiogenic mechanism of anti-tumor peptides
provides clues for their development as tumor-
targeting drugs. The anti-angiogenic mechanism of
antitumor peptides thus provides clues for their
development as tumor-targeting agents.
EGFR is a transmembrane receptor that, when
bound to a ligand, phosphorylates and binds some
intracellular adapter molecules or forms homo- or
heterodimers with other receptors, thereby activating
a series of downstream signaling pathways that lead
to cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and
metastasis. Several solid tumors are known to occur
in association with aberrant activation of EGFR in
tumor tissue. Gefitinib competitively binds to the Mg-
ATP site in the EGFR-TK catalytic region on the cell
surface, blocking intracellular signaling, thereby
inhibiting cell proliferation and metastasis and
producing an anti-tumor effect. This inhibits cell
proliferation and metastasis, resulting in anti-tumor
effects. The drug was launched in February 2005 for
the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-
small cell lung cancer in patients who have received
prior chemotherapy or are unsuitable for
chemotherapy. It has also been shown to inhibit
microangiogenesis, modulate the cell cycle and
increase chemotherapy sensitivity, and in some areas
to potentiate the antitumor effects of cisplatin,
carboplatin, platinum oxalate, adriamycin, topotecan,
ralitrexed, paclitaxel, paclitaxel ester, glucosamine,
and interferon.
Alkaloid is a naturally occurring basic compound
that contains a nitrogen atom. Some compounds that
are chemically synthesized but structurally similar to
alkaloids are sometimes referred to as alkaloids. In
addition to C, H, and N, alkaloids can also contain O,
S, or other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and
phosphorus. Alkaloids are mostly derivatives of
amino acids and taste bitter and astringent. They are
often found as secondary metabolites in plants,
animals, and mushrooms. Most of the alkaloids can
be obtained from their plant extracts by acid-base
extraction. Among the plant derivatives with
biological properties, berberine, an isoquinoline
quaternary alkaloid isolated mainly from Huanglian,
has a wide range of therapeutic effects on a variety of
diseases. In recent years, berberine has been reported
to inhibit cell proliferation and be cytotoxic to cancer
cells. Therefore, many derivatives have been
synthesized to improve the efficiency and selectivity
of berberine.(Ortiz, Lombardi, Tillhon, Scovassi
2014). In this study, we tested the inhibitory activity
of berberine on angiogenesis in cell-based
experiments and in a mouse xenograft model of
human glioblastoma, and clarified the involvement of
the VEGFR2/ERK pathway (Jin, Xie, Huang & Zhao
2018).
2 METHOD AND MATERIALS
I predict that Berberine inhibits angiogenesis in
glioblastoma xenografts by targeting the
VEGFR2/ERK pathway. I will treat glioblastoma
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
952

xenograft mice will increasing amounts of injected
Berberine (0, 0.1, 0.3, 1 mg/ml, 10 mg/ml) for 0 min,
1 day, 7 days, 2 weeks and then measure tumor weight
and size, and perform confocal microscopy/
immunohistochemistry (IHC) for VEGFR2, or
phospho-ERK and unphosphorylate ERK. Also
measure VEGFR2, phosphorylate ERK,
unphosphorylate ERK by western blot. Positive
control is Temozolomide treatment.
① Reagents
Berberine: Berberine powder was dissolved in
phosphate buffered saline (PBS), then sterilized using
a 0.22 μm pore filter and stored at 4 °C until use.
Temozolomide: Compounds were resuspended in
DMSO and stored at room temperature (O6BG) or -
20℃ (all others).
② Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry of VEGFR2, or phospho-
ERK and unphospho-ERK were performed as
described previously.
3 POSSIBLE RESULT
Possible Result 1: Berberine was applied to inhibit
the VGEFR2/ERK pathway in defined human and
murine glioblastoma cell lines, cell lines from
clinical samples and cell lines from in vivo animal
models. (Luan, 2020)
Berberine inhibits glioblastoma in all of the in
vitro and in vivo cell samples, decreasing VEGF-C or
VEGF-D binding to VEGFR2, and decreasing
activity of ERK outside the cells, as shown in table 1.
The proliferations of cell samples are inhibited
significantly. The animal experiments display that
berberine has therapeutic effect on angiogenesis of
glioblastoma cells, as shown in table 2. In the
simulation experiment, to investigate the possible
molecular mechanism of berberine-induced
inhibition of angiogenesis, this experiment will
analyze the protein expression of VEGFR2 and
MAPK pathways by Western blots. The total
expression of VEGFR2 will not change after
berberine treatment, while the phosphorylation of
VEGFR2 will be significantly reduced (p ˂ 0.001,
Figure 1). Likewise, phosphorylation of ERK and p38
will also reduce after berberine treatment (p ˂ 0.001
and p ˂ 0.01, respectively, Figure 1). (Jin, Xie, Huang
& Zhao 2018)
Figure 1: Molecular mechanisms involved in
antiangiogenic effect of berberine. Tumor tissue from
ectopic xenograft model was isolated and homogenized for
Western blot analysis. ***p< 0.001 vs. vehicle group, **p<
0.01 vs. vehicle group. N = 6 for each group (Jin, Xie,
Huang & Zhao 2018) .
Possible Result 2: Berberine was applied to
inhibit the VGEFR2/ERK pathway in defined
human and murine glioblastoma cell lines, cell
lines from clinical samples, but not in cell lines
from in vivo animal models. (Wang, Zhou, Xu,
Song, Qian, Lv, Luan 2019)
Berberine inhibits glioblastoma in all of the in
vitro cell samples, decreasing VEGF-C or VEGF-D
binding to VEGFR2, and decreasing activity of ERK
outside the cells, as shown in table 1. The
proliferations of in vitro cell samples are inhibited
significantly. However, the berberine does not
successfully decrease in vivo VEGF-C or VEGF-D
binding to VEGFR2 or decreasing activity of ERK
outside the cells, or the animal experiments do not
display a significant therapeutic effect of berberine
inhibits VEGFR2/ERK pathway of angiogenesis, as
shown in table 2.
Possible Result 3: Berberine was applied to
inhibit the VGEFR2/ERK pathway in identified
human and murine glioblastoma cell lines, but not
cell lines derived from clinical samples.
Berberine inhibits glioblastoma in CUTLL1,
HPBALL, NS2, and W44, as shown in table 1. The
proliferations of these in vitro cell samples are
inhibited significantly. However, the berberine does
not successfully decrease VEGF-C or VEGF-D
binding to VEGFR2, or decrease activity of ERK
outside the cells in the clinical samples. The animal
experiment involving the NOD-CID model will fail
as described in Possible Result 2 since this model has
glioblastoma cells from clinical samples, as shown in
table 2.
Possible Result 4: Application of berberine
inhibited the VGEFR2/ERK pathway in defined
human cell lines and clinical samples, but had no
effect on murine cell lines.
Berberine inhibits glioblastoma in CUTLL1,
HPBALL, and the majority of the clinical samples
Berberine Can Target the VEGFR2/ERK Pathway to Inhibit Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Xenografts
953
and reduces VEGF-C or VEGF-D binding to
VEGFR2 and decrease activity of ERK outside the
cells, as shown in table 1. The proliferations of these
in vitro cell samples are inhibited significantly.
However, applying berberine to NS2, and W44 does
not successfully decrease the reduces VEGF-C or
VEGF-D binding to VEGFR2 and decrease activity
of ERK outside the cells. Since the animal model is
constructed using human cell lines, there are still
possibility that berberine will decrease in vivo VEGF-
C or VEGF-D binding to VEGFR2 and decrease
activity of ERK outside the cells in animal
experiments, as shown in table 2.
Possible Result 5: Application of berberine did
not inhibit the VGEFR2/ERK pathway in any cell
line.
The berberine does not significantly reduce
VEGF-C or VEGF-D binding to VEGFR2 and
decrease activity of ERK outside the cells in any cell
lines, as shown in table 1. The animal experiment will
not be successfully conducted in this scenario, as
shown in table 2. Additional Possible Results on
VEGFR2/ERK Pathway Different from Previous
Researches
Possible Results 6: Berberine inhibits the
VGEFR2/ERK pathway, but does not have effects
on angiogenesis levels. (Luan 2020)
The level of angiogenesis of glioblastoma
determined by VGEFR2/ERK pathway is low. The
cell proliferation decreases. However, the level of
angiogenesis of tumors does not change significantly,
as shown in table 1 and table 2.
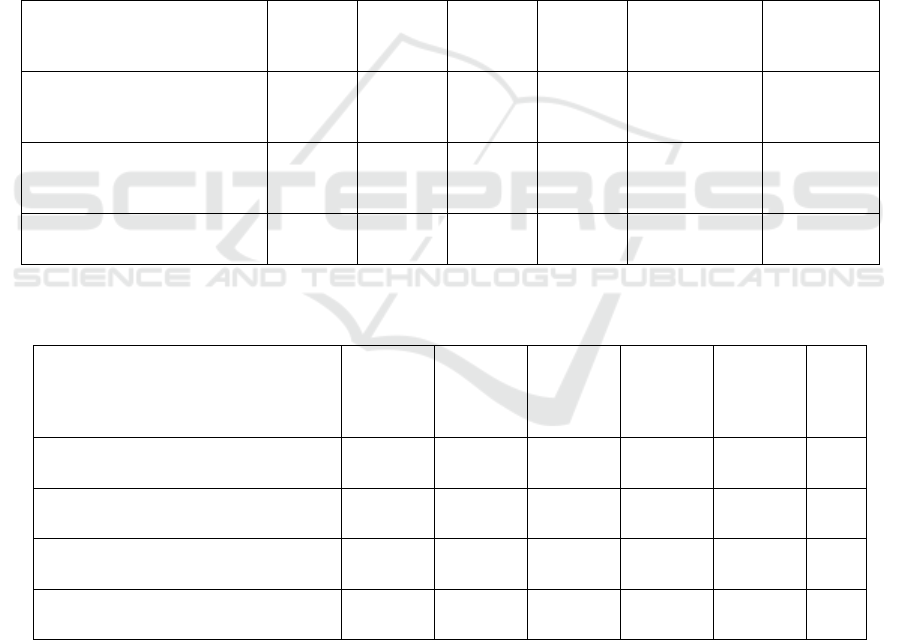
Table 1: Possible Results.
Cell Line
Result Ⅰ
Result
Ⅱ
Result
Ⅲ
Result
Ⅳ
Result Ⅴ Result Ⅵ
Tumor size decreases with
Increasing
b
erberine
+ - - -
No
inhibition(+)
Negative
inhibition(-)
VEGFR WB level
+ - + -
No
reduction(-)
No
reduction(-)
Phospho
r
-AKT decrease + +
/
-+
/
- - Partly agree -
Note. “+” represents a significant decrease in cell proliferations. “-” represent not significantly different from negative control.
Table 2: Possible Results on Cell Proliferation.
Cell Line
Result Ⅰ Result Ⅱ
Result
Ⅲ
Result
Ⅳ
Result Ⅴ
Res
ult
Ⅵ
VEFG/HIF-1 ex
p
ression + + + + + +
An
g
io
g
enesis of HUVECs + + + + - -
Tumo
r
growth in vivo + + - - - -
PI3
K
p
athwa
y
YNYNY N
Note. “+” represents a significant decrease in cell proliferations. “-” represent not significantly different from negative control.
4 CONCLUSION
The Possible Results 1 are consistent with previous
studies on the effect of berberine on glioblastoma
angiogenesis. To gain insight into the structure and
function of berberine, the specific gene regulatory
mechanisms of berberine should be further
investigated. The relationship between berberine and
RNA interference with VGEFR should also be
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
954

studied to investigate more specific pathways that can
be used to treat glioblastoma angiogenesis.
Preclinical testing on more complex and
representative animal models should also be
conducted before transitioning to clinical testing of
berberine treatment. Better delivery platforms, such
as nanodrugs or mechanisms involving endocytosis,
should also be applied in order to improve this
therapeutic approach.
What makes the failure of the experiments in vivo
in Possible Result 2 is most likely due to unsuccessful
delivery of berberine: either the cells in the animal did
not take up berberine or berberine was not maintained
in vivo long enough to perform its function. The final
result would indicate a high expression level of
berberine and a low expression level of berberine. In
order to improve this experiment, an efficient and
reliable delivery method should be developed. The
experiment can be repeated again with the traditional
retroviral infection method as it has proven successful
in previous experiments. The safety level of retroviral
gene therapy should be improved prior to clinical
trials. In addition, pharmacological angiogenic
inhibitors of glioblastoma could be developed for
berberine.
Only if the berberine reduces the activity of
angiogenesis in the tumor, the berberine treatment
targeting the VGEFR2/BRK pathway will potentially
have therapeutic effects and should be carried on to
clinical trial. Possible Result 3 suggests that berberine
does not qualify as a universal treatment for
glioblastoma because a subset of clinical samples do
not have abnormal gap expression or because they
have different types of gaps and angiogenic
mechanisms. This requires future studies to reassess
the relationship between berberine, the
VGEFR2/ERK pathway, and the general type of
glioblastoma.
The unlike Possible Results 4 and 5 indicate
potential systematic errors in the experimental
designs. Possible Result 4 indicate the berberine used
in this experiment cannot be applied on mice. The
redesign of potential drug will be required for future
studies on animal cell lines. Possible Results 5 is
likely to be caused by the offtarget of the berberine
used in this experiment.
The Possible Results 6 contradicts with the
current understanding of berberine’s effects on
VGEFR/ERK pathway. Result 6 indicates that an
alternative pathway that is crucial for the
angiogenesis of glioblastoma maintenance. Future
studies should use experiments like dual-luciferase
reporter assay to verify the relationship between
berberine and other potential glioblastoma
oncogenes.
In conclusion, white tyrosine kinases occupy a
very important position in the cell signaling pathway,
regulating a series of physiological and biochemical
processes such as cell growth, differentiation and
death. More than 50% of proto-oncogenes and
oncogenes are tyrosine kinases, and their abnormal
expression usually leads to disruption of cell
proliferation regulation, resulting in tumorigenesis.
More than 20 different families of receptor and non-
receptor tyrosine kinases have been used as targets for
antitumor drug screening, including epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR), vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived
growth factor receptor (PDGFR), fibroblast growth
factor receptor (FGFR), insulin receptor (InsR), Src ,
Abl, etc. (representative drugs: Imatinib, Gefitinib,
Erlotinib, Exatinib, Sorafenib, Sunitinib, Crizotinib).
Recently, another challenging concept has been
proposed for molecularly targeted antitumor drug
therapy: the strategy of mul-tipletargeted tyrosine
kinase inhibition. Based on the complexity of tumor
development, the vast majority of tumors do not rely
on a single signaling pathway to maintain their
growth and survival; there are crossovers and
compensations between signaling pathways. Multi-
targeted drugs can achieve the dual function of
synergistic treatment and overcoming drug resistance
by inhibiting multiple signaling pathways or multiple
molecules upstream and downstream in one pathway
(representative drugs: lapatinib, afatinib, daclatinib,
axitinib, ceritinib, etc.).
Mechanism of tumor neovascularization
inhibition: Targeting VEGFR, FGFR, EGFR and
other receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors with tumor
neovascularization-promoting effects represents
another important direction in antitumor targeted
drug research - inhibition of tumor
neovascularization. Blocking tumor
neovascularization to varying degrees can slow down
the growth of solid tumor tissue (representative drugs:
bevacizumab, sorafenib, sunitinib).
Stimulated by cancer cell growth, VEGF binds to
specific endothelial cell receptors, leading to
angiogenesis and the production of new blood vessels
to feed tumor tissue. VEGF inhibitors destroy tumor
tissue by blocking this process. Everolimus and
pazopanib are used clinically in the treatment of renal
cell carcinoma, and bevacizumab, which has the
structure of a human-derived antibody structural
region and the complementary decision region of a
murine-derived monoclonal antibody that binds
VEGF, is used in the treatment of non-small cell lung
Berberine Can Target the VEGFR2/ERK Pathway to Inhibit Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Xenografts
955

cancer. Due to the tolerability of this class of drugs,
tumor recurrence and metastasis can occur after
discontinuation of the drug, rendering the treatment
ineffective. Adverse effects include increased blood
pressure, delayed wound healing, bleeding,
thrombosis, intestinal perforation, heart failure, and
heart disease. Some of these drugs currently interfere
with the regulation of the activity of other cellular
pathways. The mechanism of action is not well
understood.
In addition, HER-2 has a transmembrane tyrosine
kinase receptor, and its positive expression is closely
related to tumor cell development, progression and
prognosis, of which only the intracellular ligand-
binding region has tyrosine kinase activity. Her-2
oncogene amplification causes receptor
overexpression, activates the intracellular region and
phosphorylates at the tyrosine kinase site, activates
the downstream PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways, and
regulates tumor cell proliferation, differentiation,
migration and apoptosis. Trastuzumab is a humanized
monoclonal antibody that binds to the Her-2
oncogene expression product P185 protein on tumor
cell membranes to produce anti-cancer effects.
Currently, it is mainly used for the treatment of lung
cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer
and kidney cancer, etc. It has a wide spectrum of anti-
tumor, high efficiency and low toxicity. Due to the
emergence of tumor cell drug resistance
phenomenon, with the investigation of its anti-tumor
and tumor drug resistance reversal mechanism, the
screening of drug-resistant target markers will help to
develop combination drug regimens and provide a
new way out for Her-2-positive tumor patients.
REFERENCES
Jin F, Xie T, Huang X & Zhao X (2018) Berberine
inhibits angiogenesis in glioblastoma xenografts by
targeting the VEGFR2/ERK pathway, Pharmaceutical
Biology, Volume 56 Issue 1
Liu Q, Xu X, Zhao M, Wei Z, Li X, Zhang X, Liu Z, Gong
Y and Shao C (2015) Berberine Induces Senescence of
Human Glioblastoma Cells by Downregulating the
EGFR–MEK–ERK Signaling Pathway, ACCR,
Volume 14 Issue 2
Mairin K. Buchanan, Chase N. Needham, Nina E. Neill,
Maria C. White et al. "Glycoconjugated Site-Selective
DNA-Methylating Agent Targeting Glucose
Transporters on Glioma Cells", Biochemistry, 2017.
Ortiz L.M.G., Lombardi P , Tillhon M , Scovassi A.I.
(2014) Molecules, Volume 19, Issue 8, 120 articles,
Pages 10670-12897
Qitong Luan (2020) Downregulating Lunar1 to “Notch-
Down” the Progression of Human t-All, The Frontiers
of Society, Science and Technology.
Qitong Luan Downregulating Lunar1 to “Notch-Down” the
Progression of Human t-All, 2020. https://francis-
press.com/uploads/papers/b2n1sbaCFR0xrZdwnslVq
NkAQJdmGP9HwhsW9mIP.pdf
Sheng Wang, Dexi Zhou, Zhenyu Xu, Jing Song, Xueyi
Qian, Xiongwen Lv, Jiajie Luan. "Antitumor Drug
Targets Analysis: Current Insight and Future Prospect",
Current Drug Targets, 2019.
Viallard C & Larrivée B (2017) Tumor angiogenesis and
vascular normalization: alternative therapeutic targets
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10456-
017-9562-9.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
956
