
Prediction of Drug Penetration Coefficients for Transdermal Drug
Delivery using Artificial Neural Networks
Yilun Han
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Jalan Sunsuria, Bandar Sunsuria, 43900,
Sepang, Selangor, Malaysia
Keywords: Transdermal Administration, Permeability Coefficient, Artificial Neural Networks, BP Neural Network.
Abstract: The penetration of drug molecules into the skin is a crucial stage in the transdermal drug delivery process.
Traditional direct measuring techniques have a number of flaws. The creation of a transdermal penetration
model that predicts a drug's penetration coefficient might be a viable answer to these issues. Combined with
the analysis of the quantitative structure-activity relationship, a new statistical method, artificial neural
network, is introduced. Establish a BP neural network, take the molecular weight of the drug molecule, the n-
octanol/water partition coefficient, the number of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors as the input values of
the artificial neural network, and the drug transdermal permeability coefficient as the output of the neural
network value. Train and optimize the built network model and predict the transdermal permeability
coefficients of 10 drugs. The correlation coefficient between the predicted value and the measured value is
R2=0.9953, and there is no significant difference within the 99% confidence interval. It shows that the model
has a high prediction accuracy and a wide prediction range, which can provide reliable data reference help for
the actual drug design stage.
1 INTRODUCTION
Oral administration is currently the most common
route of administration, and most small molecule
medications are given this way (Yu, Yang, Wu, Fan,
2021). Portability, consistent dose, and patient self-
administration are all advantages of the oral route
(Brambilla, Luciani, Leroux, 2014;
Ita, 2014).
However, due to variables such as quick breakdown
and restricted transport in the stomach and small
intestine, most protein-based medicines are not
supplied by the oral route (McCrudden, Singh,
Migalska, Donnelly, 2013). As a result, injection is
the most common method of administering big
molecule medications. Injectable medication delivery
still has significant drawbacks because it causes
tissue damage, discomfort, and the risk of infection
(Schoellhammer, Blankschtein, Langer, 2014).
Transdermal drug delivery is a painless way of
systemically distributing medications by putting the
drug formulation to healthy skin that is intact (Han,
Das, 2015). Transdermal drug delivery has several
advantages over other traditional modes of
administration, including a more consistent
pharmacokinetic profile with fewer peaks, which
reduces the likelihood of harmful side effects. Pre-
systemic metabolism is avoided with transdermal
medication administration, which improves
bioavailability (Arora, Prausnitz, Mitragotri, 2008).
The mobility of the drug through the skin barrier is
crucial to the effectiveness of transdermal drug
delivery.
Although the skin serves as the primary vehicle
for transdermal medication delivery, the stratum
corneum acts as a significant barrier to drug
penetration (Dhote, 2012;
Grice et al., 2017), limiting
both local and transdermal bioavailability
(Subramony, 2013). The medication's penetration is
thus crucial in transdermal drug development.
To facilitate later operations in the research and
development of transdermal medications, it is vital to
understand the features of the relevant drug
percutaneous penetration in advance. The old method
of directly measuring the drug's permeability
coefficient in vitro or on the skin has several flaws.
The experimental conditions, for example, are
demanding, requiring a particular level of skin
activity and medication concentration to be
maintained. Individual differences influence
measurement results, so they are not universally
applicable. It leads to drug misuse and waste, and the
Han, Y.
Prediction of Drug Penetration Coefficients for Transdermal Drug Delivery using Artificial Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0011375400003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 999-1006
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
999
squandering of some expensive pharmaceuticals
raises development expenses. The experiment will
take some time to complete (Terzić et al., 2017). It is
necessary to establish a drug transdermal penetration
model to predict drug penetration characteristics in
the process of drug development, which can
effectively avoid the above-mentioned problems.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1
Drug Penetration Influencing
Factors
2.1.1 Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is an important type of interaction
because it plays a key role in structural stability,
enzyme catalysis and drug distribution and
permeability
(Coimbra, Feghali, Ribeiro, Ramos,
Fernandes, 2021). The presence of functional groups
capable of establishing hydrogen bonds in the
structure of a drug molecule boosts its solubility and
capacity to make critical interactions with its
biomolecular targets, resulting in successful binding
and selectivity. Excess hydrogen bonding
donors/acceptors can have a negative impact on the
drug's membrane partitioning and permeability
(Coimbra, Feghali, Ribeiro, Ramos, Fernandes,
2021). These polar groups reduce the affinity for
hydrophobic membrane regions and increase water
desolvation losses during drug permeation.
2.1.2 Oil-Water Partition Coefficients
Because medications must have good
pharmacokinetics as well as the required biological
activity, a good balance of lipophilicity and
hydrophilicity is critical. The partition coefficient can
be assessed in terms of a chemical substance's
hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity (Ding, 1998), and it
can also be used to estimate drug distribution in vivo.
Hydrophobic medicines with high octanol-water
partition coefficients are primarily found in
hydrophobic cell areas like the lipid bilayer.
Hydrophilic medicines with low octanol/water
partition coefficients, on the other hand, are usually
found in watery environments. Transdermally given
medicines must be hydrophobic enough to partition
into the phospholipid bilayer to be delivered
successfully.
2.2
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANN) are the product of
simulating human brain intelligence (Saxén,
Pettersson, 2005). It is a parallel distributed processor
with powerful connections. It acquires knowledge
and the ability to solve problems through continuous
learning. The distribution of knowledge is stored in
the weight of the connection. According to the system
point of view, an artificial neural network is an
adaptive nonlinear dynamic system composed of
many neurons through rich and perfect connections
(Lv et al., 2018).
Among many types, Rinehart and McClelland et
al. proposed the Back Propagation (BP)-learning
algorithm of multi-layer feed forward network in
1986
(Ma, Hu, Xu, 2017). BP network uses nonlinear
differentiable functions to train the network. The
learning algorithm has strong plasticity and a simple
structure, so it has been widely used in many fields.
BP learning algorithm, also known as BP network, is
a supervised learning algorithm. The principle is to
select suitable samples from each sample as the input
of the network and test them. This is to make a
judgment basis for the modification of network
weights and thresholds (Moraga, 2007). Through
network learning, the total error between the actual
output and the expected output of the sample is
continuously reduced, to fit the correspondence
between the input and output data.
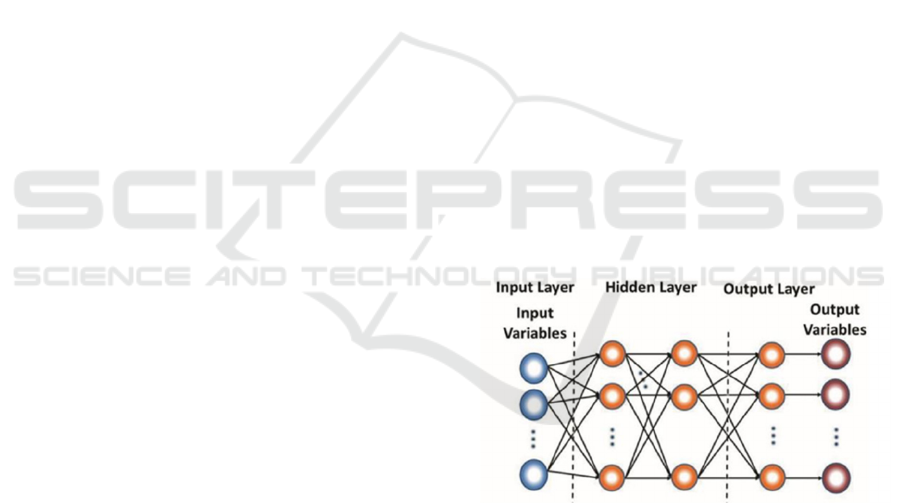
Figure 1: Structure of BP neural network.
The structure of the BP neural network is shown
in Figure 1. BP neural network is a kind of multi-layer
feed forward neural network, the signal is transmitted
forward, and the error is propagated backward, there
is no signal feedback process. A typical BP neural
network consists of three parts: input layer, hidden
layer, and output layer. The number of neurons
contained in each layer is arbitrary, and it may also
contain a hidden layer structure of 0 to n layers. And
there is no interconnection between neurons in the
same layer, but the upper and lower layers are fully
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1000
connected, and the output of each node is used as the
input of the next neural node, and the signal is
forwarded in this way.
The entire network is constructed through the
forward propagation of the signal and the backward
propagation of the error.
3 METHODOLOGY
The quantitative structure-activity connection is a
mathematical and statistical tool for analyzing the
physicochemical attributes and biological activities
of diverse substances using molecular structural data.
Other physical and chemical features of substances,
biological activity, toxicity, and various metabolic
parameters of medications are among the research
objects. Drug design, analytical chemistry,
environmental chemistry, food science, and material
science are among the research fields.
The qualities of drug penetration through the skin
are inextricably linked to certain structural factors of
drug molecules, such as molecular weight and
volume
(Matsson, Kihlberg, 2017), molecular
polarity
(Coimbra, Feghali, Ribeiro, Ramos,
Fernandes, 2021), and molecular acidity and
alkalinity
(Bartlett, van der Voort Maarschalk, 2012).
However, because there are complex nonlinearities
between the parameters, the created model must have
good nonlinear relationship processing capabilities.
3.1
Data Selection
The artificial neural network model is mainly used to
predict the permeability coefficient of chemical
substances. According to the experimental data
obtained from the literature review, the data shows
the structure parameters and permeability
coefficients of 50 chemical substances. Use this data
to construct a neural network to predict the
permeability coefficient of chemical substances.
Structural parameters, hydrogen bonds and oil-water
balance coefficients will all affect the permeability.
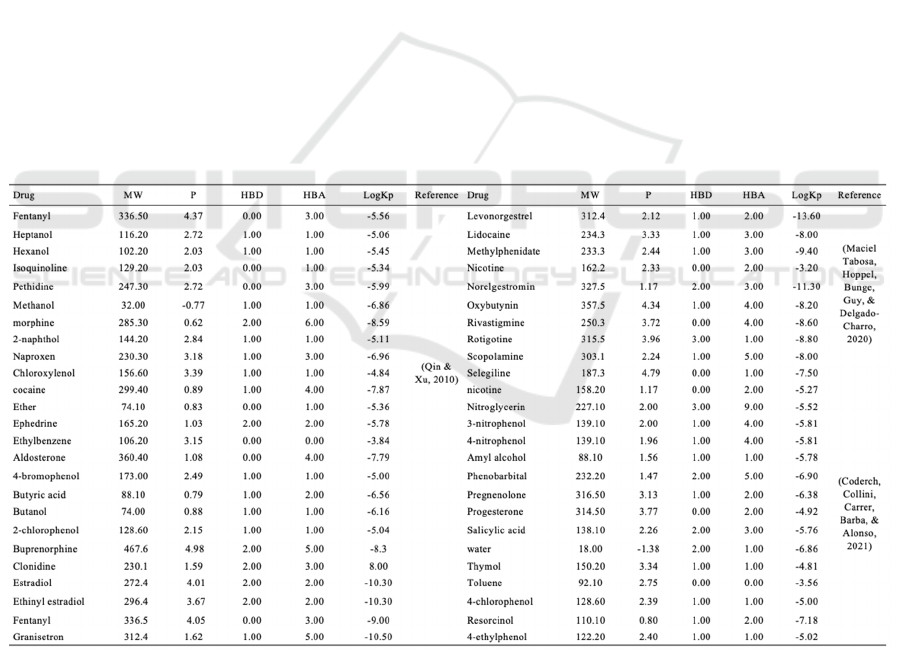
Table 1 shows the experimental data needed to build
the neural network. Table 2 shows another set of
experimental data, which will be used to verify the
neural network.
Table 1: Model training dataset
MW is molecular weight, P is the octanol-water
partition coefficient, HBD is the number of hydrogen
bond donors and HBA is the number of hydrogen
bond acceptors.
Prediction of Drug Penetration Coefficients for Transdermal Drug Delivery using Artificial Neural Networks
1001
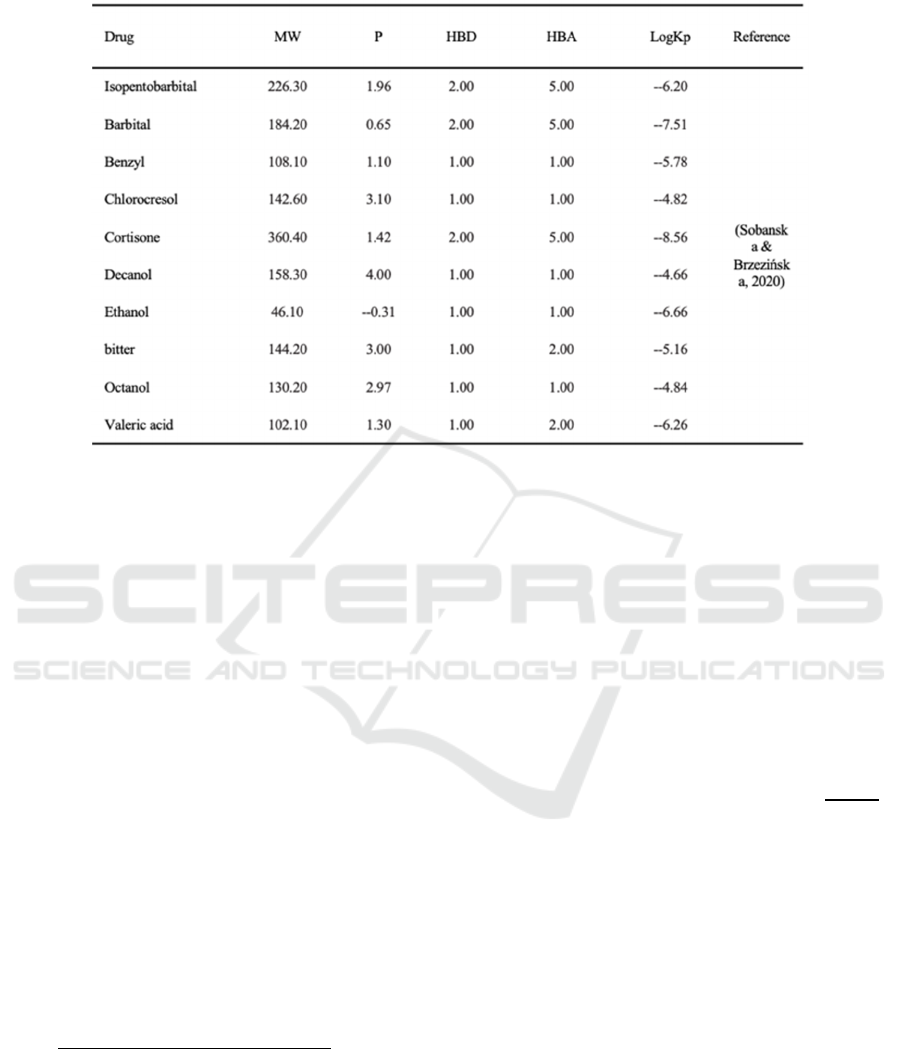
Table 2: Model validation dataset.
3.2 The Training Process of BP Neural
Network
The working process of the artificial neural network
model is mainly divided into 4 parts. First, the data is
preprocessed, and then the data is divided into a
training group, a verification group and a test group.
Then the artificial neural network is constructed, and
the artificial neural network is trained using the
training data. Use the trained artificial neural network
to predict the result (Saxén, Pettersson, 2006).
Artificial neural networks need to select
appropriate data from the database as input and
output values. The permeability coefficient of the
drug is selected as the output value of the neural
network. The choice of input value has a significant
impact on the construction and prediction ability of
the artificial neural network model and will affect the
accuracy of the prediction result to a large extent. The
relative molecular weight, the number of hydrogen
bond donors and acceptors, and the oil-water balance
coefficient are used as input values. Use Equation 3.1
to normalize the input data.
S
X
minX
,…,…
maxX
,,……,
minX
,,……,
Eq. 3.1
Among them, Sik represents the parameter after
normalization, Xik represents the parameter before
normalization, i is the number of types of input
parameters, and k is the number of groups of data (Lv
et al., 2018). After the input value and output value
are selected, the data is divided into a training group,
verification group and test group. The more and more
extensive the data used for training, the better the
learning effect of the neural network. Data were
randomly split into 70%: 15%: 15% to construct an
artificial neural network.
3.3
Optimization of Neural Networks
It was shown that an artificial neural network with a
single hidden layer could be sufficient for the
accurate prediction of drug permeability, so a three-
layer artificial neural network was created. The range
of the number of hidden neurons is determined by the
following empirical formula (Lv et al., 2018).
1. n
√
NM
1~10
, N is input neurons, M is output neurons
2.nlog
N
3.
∑
C
R, R is number of sample
After completing the training, the number of
hidden neurons with the lowest error is selected as the
final choice to complete the construction of the
artificial neural network.
By inputting the verification data into the
optimized artificial neural network model, the
permeability coefficient is predicted through the
model. Compare the predicted permeability
coefficient with the experimental value to judge the
applicability of the artificial neural network.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1002
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1
Optimization Results of the Neural
Network
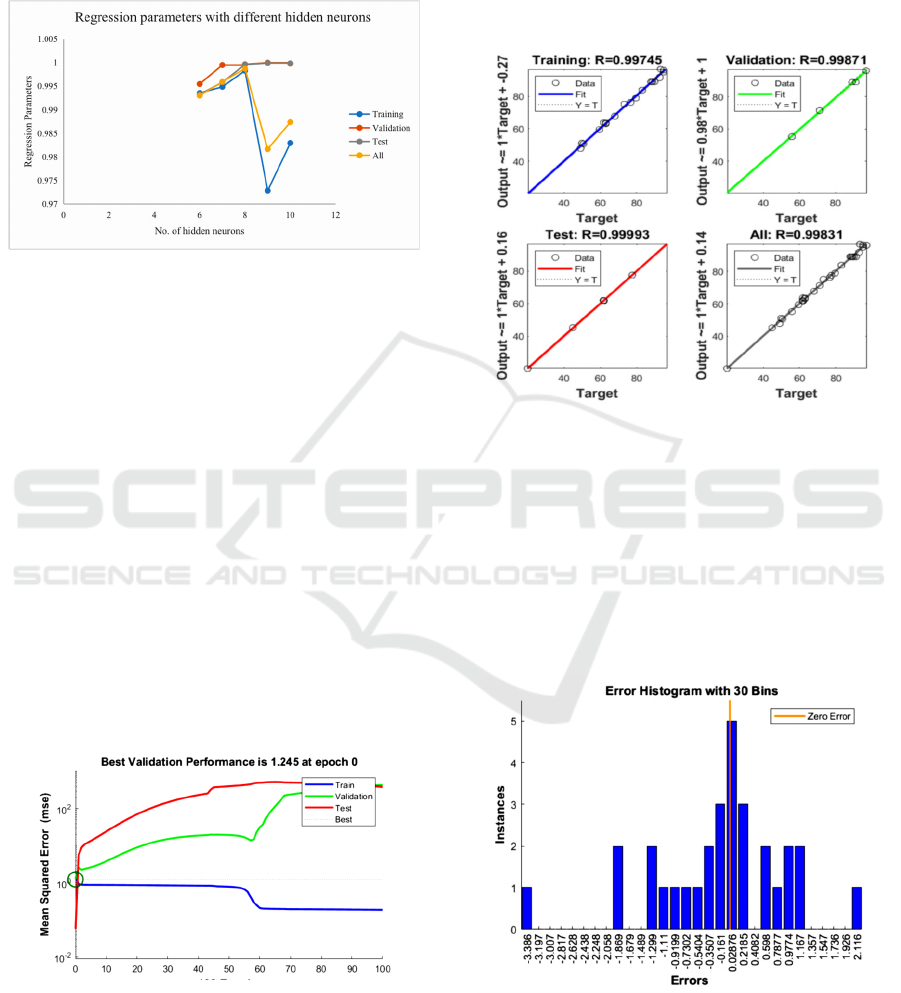
Figure 2: The relationship between regression parameters
and the number of hidden neurons.
The optimized training of the network needs to set the
corresponding training parameters, where the
maximum number of training times is 500, and the
number of displayed training iterations is 50. It can
be seen from Figure 2 that under the same accuracy
requirements, the number of neurons in the hidden
layer is in the range of 6-10, and the regression
parameters have significant changes. In the case of 8
hidden neurons, the regression parameter is closest to
1. According to the "razor" principle: If a smaller
neural network can meet the requirements, then a
larger network is not used. Because the more hidden
nodes and the more hidden layers, the phenomenon
of "over-fitting" tends to occur, which in turn leads to
a decrease in the generalization ability of the neural
network. At the same time, in order to ensure the
computational efficiency of the artificial neural
network, a smaller number of neurons is selected.
Figure 3: Performance of forwarding model for
permeability coefficient.
The calculation result of the neural network is
shown in Figure 3. The best performance is obtained
after 75 trainings at epoch 0, and the minimum
verification is 1.245. The artificial neural network
requires that the error between the predicted value
and the experimental value is small. The smaller the
mean square error, the more accurate the prediction
result. As shown in the figure, because the test curve
does not increase significantly before the verification
curve increases, there is no over-fitting phenomenon.
Figure 4: Regression parameters of the forward model for
permeability coefficient.
Figure 4 shows that the regression parameters for
training, validation, testing, and overall are 0.99745,
0.99871, 0.99993, and 0.99831, respectively. The
values of the four regression parameters are all close
to 1. Data analysis based on the mean square error and
regression parameters show that the artificial neural
network can accurately predict the output parameter,
that is, the permeability coefficient of the compound.
Figure 5: Error histogram of forwarding model for
permeability coefficient.
The error histogram can also be used to verify and
evaluate the performance of artificial neural networks.
Prediction of Drug Penetration Coefficients for Transdermal Drug Delivery using Artificial Neural Networks
1003
As shown in Figure 5, the error range is divided into
30 bins. Most errors are in the range of -1.299 to
1.167. There are some errors, such as -3.386, -1.869,
and 2.116. The error value of abnormal data is also
very small. In general, the error between the
experimental value and the output value is small, and
the obtained artificial neural network can give more
accurate predictions.
According to the analysis of the prediction results
of the above artificial neural network, the successful
construction of the model is indicated, which can be
used for further verification and analysis.
4.2
Verification of the Artificial Neural
Network Model
Input the experimental data set used to verify the
accuracy of the model into the optimized artificial
neural network model. After model prediction and
calculation, the final prediction results of penetration
parameters are obtained. By comparing the predicted
value with the experimental value, according to the
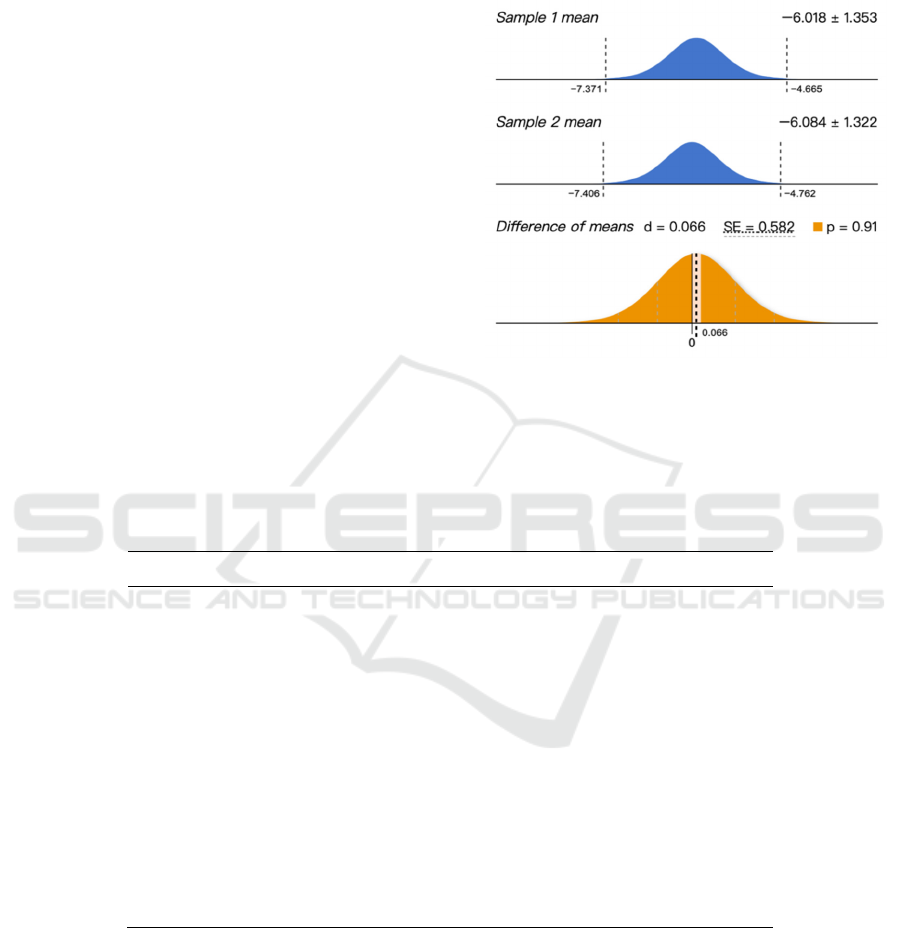
results of t-test, it is found that based on the 99%
credit rating, it is found that the predicted value of the
artificial neural network constructed using the
experimental data is similar to the actual
experimental data, and there is no significant
difference. It shows that the network model can
effectively and reasonably predict the permeability
coefficient.
Figure 6: The result of t-test.
According to the regression linear equation of the
predicted value and the experimental value, the
regression parameter of the equation is 0.9953, which
is very close to 1.
Table 3: Predicted values and errors.
LogKp Predict value Deviation
-6.20 -6.25 -0.05
-7.51 -7.63 -0.12
-5.78 -5.83 -0.05
-4.82 -4.92 -0.1
-8.56 -8.53 0.03
-4.66 -4.63 0.03
-6.66 -6.87 -0.21
-5.16 -5.15 0.01
-4.84 -4.79 0.05
-6.26 -6.18 0.08
Table 3 shows the errors between the
experimental values and the predicted values derived
from the artificial neural network model. Therefore,
the experimental value and the predicted value
conform to a linear relationship, and the error
between the two is very small. The artificial neural
network has a good predictive ability for infiltration
parameters.
Since the data used to build the artificial neural
network model and verify the model contains a
variety of chemical substances, the results of the
model prediction show that the model has a good
ability to predict penetration parameters. Therefore,
the model is universal in prediction and can be widely
used to predict the permeability coefficient of various
drugs.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1004
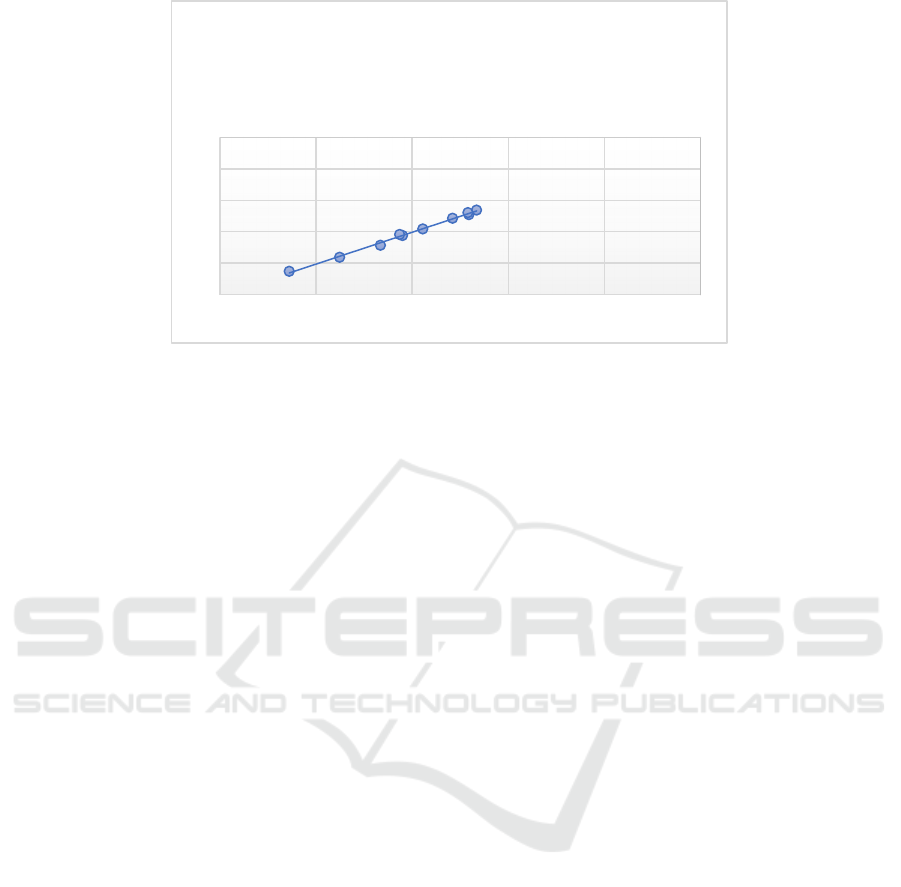
Figure 7: Linear equation of experimental value and predicted value.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on quantitative constitutive relationships, new
statistical methods, such as artificial neural networks,
were introduced to extend the range of data structures
that can be modeled by two-dimensional quantitative
constitutive relationships. A three-layer BP neural
network was constructed using the molecular weight
of the drug, the oil-water partition coefficient and the
number of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors as the
input values for the artificial neural network, which
was trained and optimized. The results of comparing
the predicted values of the network with the
experimental values show that the prediction
accuracy and confidence of the model are high.
Moreover, the network model has predictive
generality and can be used for the prediction of
permeation coefficients for a wide range of drugs. It
can provide a more accurate data reference in the drug
development phase of transdermal drug delivery,
avoiding unnecessary time and financial
consumption. The model has only been shown to
predict the permeation rate of a single drug but has
not been shown to predict the state of a mixture of
multiple drugs. Therefore, more sophisticated models
could be developed to achieve permeation prediction
for mixed drugs. Interactions between drugs could be
included in the range of variables, while more
accurate genetic algorithms could be introduced to
improve the accuracy of the artificial neural network
model.
REFERENCES
Arora, A., Prausnitz, M. R., & Mitragotri, S. (2008). Micro-
scale devices for transdermal drug delivery.
International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 364(2), 227–
236.
Bartlett, J. A., & van der Voort Maarschalk, K. (2012).
Understanding the oral mucosal absorption and
resulting clinical pharmacokinetics of asenapine.
AAPS PharmSciTech, 13(4), 1110–1115.
Brambilla, D., Luciani, P., & Leroux, J.-C. (2014).
Breakthrough discoveries in drug delivery
technologies: The next 30 years. Journal of Controlled
Release, 190, 9–14.
Coderch, L., Collini, I., Carrer, V., Barba, C., & Alonso, C.
(2021). Assessment of finite and infinite dose in vitro
experiments in transdermal drug delivery.
Pharmaceutics, 13(3), 364.
Coimbra, J. T. S., Feghali, R., Ribeiro, R. P., Ramos, M. J.,
& Fernandes, P. A. (2021). The importance of
intramolecular hydrogen bonds on the translocation of
the small drug piracetam through a lipid bilayer. RSC
Advances, 11(2), 899–908.
Dhote, V. (2012). Iontophoresis: A potential emergence of
a transdermal drug delivery system. Scientia
Pharmaceutica, 80(1), 1–28.
Ding, P. (1998). Prediciting permeability of drugs with
oil/water partition coefficient. Chinese Journal of
Pharmaceuticals, 04.
Grice, J. E., Moghimi, H. R., Ryan, E., Zhang, Q., Haridass,
I., Mohammed, Y., & Roberts, M. S. (2017). Non-
formulation parameters that affect penetrant-skin-
vehicle interactions and percutaneous absorption. In
Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Drug Penetration
Into/Through the Skin (pp. 45–75). Berlin, Heidelberg:
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Han, T., & Das, D. B. (2015). Potential of combined
ultrasound and microneedles for enhanced transdermal
y = 1,0133x + 0,0475
R² = 0,9953
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
-10-8-6-4-2 0
Predictive value
Experimental value
Regression linear equation of
predicted value and experimental
value
Prediction of Drug Penetration Coefficients for Transdermal Drug Delivery using Artificial Neural Networks
1005

drug permeation: A review. European Journal of
Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 89, 312–328.
Ita, K. B. (2014). Transdermal drug delivery: Progress and
challenges. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and
Technology, 24(3), 245–250.
Lv, C., Xing, Y., Zhang, J., Na, X., Li, Y., Liu, T., … Wang,
F.-Y. (2018). Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation
training of multilayer neural networks for state
estimation of a safety-critical cyber-physical system.
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 14(8),
3436–3446.
Ma, H., Hu, H., & Xu, Z. (2017). Exploration of Bionic
Self-Growing Self-Organizing Neural Network.
Computer Engineering and Design, 38(4), 1014–1018.
Maciel Tabosa, M. A., Hoppel, M., Bunge, A. L., Guy, R.
H., & Delgado-Charro, M. B. (2020). Predicting topical
drug clearance from the skin. Drug Delivery and
Translational Research, 11(2), 729–740.
Matsson, P., & Kihlberg, J. (2017). How big is too big for
cell permeability? Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,
60(5), 1662–1664.
McCrudden, M. T., Singh, T. R. R., Migalska, K., &
Donnelly, R. F. (2013). Strategies for enhanced peptide
and protein delivery. Therapeutic Delivery, 4(5), 593–
614.
Moraga, C. (2007). Multilayer Feedforward Neural
Network Based on Multi-Valued Neurons. IGOR
AIZENBERG, 169–183.
Qin, H., & Xu, C. (2010). BP-NN for predicting drug
permeation via the skin. Science & Technology
Information, (5), 457–458.
Saxén, H., & Pettersson, F. (2005). A simple method for
selection of inputs and structure of feedforward neural
networks. In Adaptive and Natural Computing
Algorithms (pp. 9–12). Vienna: Springer-Verlag.
Saxén, H., & Pettersson, F. (2006). Method for the selection
of inputs and structure of feedforward neural networks.
Computers & Chemical Engineering, 30(6–7), 1038–
1045.
Schoellhammer, C. M., Blankschtein, D., & Langer, R.
(2014). Skin permeabilization for transdermal drug
delivery: Recent advances and future prospects. Expert
Opinion on Drug Delivery, 11(3), 393–407.
Sobanska, A., & Brzezińska, E. (2020). Application of RP-
18 TLC retention data to prediction of transdermal
absorption of drugs. Proceedings of 6th International
Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry. Basel,
Switzerland: MDPI.
Subramony, J. A. (2013). Needle free parenteral drug
delivery: Leveraging active transdermal technologies
for pediatric use. International Journal of
Pharmaceutics, 455(1–2), 14–18.
Terzić, V., Tarakčija, A., Vardo, A., Hadžajlić, A., Šakić,
V., Smajlović, S., … Dedić, M. (2017). Passive
absorption prediction of transdermal drug application
with Artificial Neural Network. In IFMBE Proceedings
(pp. 756–761). Singapore: Springer Singapore.
Yu, Y., Yang, X., Wu, X., & Fan, Y. (2021). Enhancing
permeation of drug molecules across the skin via
delivery in nanocarriers: Novel strategies for effective
transdermal applications. Frontiers in Bioengineering
and Biotechnology, 9.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1006
