
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis
Mengqi Gu
Qibaodwight High School, Minhang, Shanghai, 201101, China
Keywords:
Tuberculosis, Drug Mechanism, Drug Resistance, Modes of Delivery, Drug Economics.
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB), the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, remains as a severe issue around the globe,
killing 1.4 million people in 2019. In this review, rifampicin, a major component of multidrug regimen, and
bedaquiline, a novel drug specifically treats multidrug-resistant TB, are discussed and compared. Rifampicin
(Rif) inhibits RNA polymerase by binding to the β subunit and blocks the elongation of transcription, while
bedaquiline inhibits the F-ATP synthase by preventing c-ring rotation when it binds to the c subunit. However,
multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) has become severe. Mutations can result in key amino acid substitutions
in conformational changes of RNA polymerase, disabling rifampicin to bind. New techniques and possibilities
in the mode of delivery are also explored, as oral rifampicin can be improved by solid self-nanoemulsifying
drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) and bedaquiline can be improved by inhalation and long-acting injection.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview of Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can be spread from
person to person via air. TB usually occurs on the
lungs, but it can take place in kidneys, spine, or brain
as well.
There are two types of TB, latent and active.
People infected by latent TB would not have any
symptoms and would not spread the disease. Latent
TB can only be detected by tuberculin or TB blood
test. While some people can develop active TB from
latent TB the bacteria overcome the immune system
and begin to reproduce. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
can multiply and damage human body issues. Active
TB patients are possibly spread the bacteria. People
with deficient immune system, such as HIV carriers,
are likely to get active TB.
1.2 Mortailities
Up to 2019, the estimated number of people with
latent tuberculosis infection (LTIB) is one-quarter of
the world’s population, who are potentially infectors
of reactivated TB (Cohen, Adam, 2019). In 2019,
According to WHO, 1.2 million children caught TB
due to the difficulty of diagnosing, and 1.4 million
people died in 2019 due to TB. A person has 5-10%
lifetime risk to get active TB when he or she is
infected with bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
and 45% of active TB infectors (without HIV) would
die.
1.3 Typical Symptoms
Active TB can lead to coughing with or without
blood and mucus, chest pain, loss of weight, fever,
fatigue, night sweats, loss of appetite, etc. (Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention, 2016). Recently,
depression and anxiety were found to be common
among pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) infectors
(Wang, 2018). Usually, the symptoms are mild for
several months, which result in transmissions to
other people.
1.4 Significance in China and the
World
In China, the incidence of TB has reduced 24% from
2010 to 2019, but China still remains as a high-
burden TB country with 833,000 TB patients in 2019
(WHO China TB treatment).
In 2019, most new TB cases took place in South-
East Asian region (44%), African region (25%), and
Western Pacific (18%) (World Health Organization,
2020).
Gu, M.
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011382200003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 1179-1187
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1179
1.5 Drugs for Tuberculosis and Their
History
Isoniazid, developed in 1952, is considered as a
highly critical for human medicine by WHO (World
Health Organization, 2015). It was first synthesized
by Meyer and Malley in 2019, while its anti-
tuberculosis activity was discovered in 1945, being
part of the combined drug regimen to solve
streptomycin resistance (Fernandes, 2017). Also in
1952, pyrazinamide was found out to be effective at
tuberculosis (Zhang, 2014). Then, ethambutol was
introduced in 1961. In 1966, Rifampicin was
developed by the Lepetit group as a semisynthetic
drug from Amycolatopsis rifamycinica (Sensi, 1983).
These four drugs consist the combination therapy.
As multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
appears, second-line drugs such as cycloserine,
ethionamide, and bedaquiline are applied.
Rifampicin, a widely used first-line drug for TB,
and bedaquiline, the latest drug developed in 2012
for treating MDR-TB, are evaluated in this literature
review to discuss the futural development of anti-TB
drugs.
2 DRUG PHARMOCOLOGY
2.1 Introduction of Rifampicin and
Bedaquiline
Rifampicin is one of the frequently prescribed first-
line drugs for treating TB, while bedaquiline is a
relatively novel drug to treat multidrug-resistant
Tuberculosis (TB), especially patients who are
resistance to rifampicin (Centers for Disease Control
and Prevention, 2016); (PubChem).
This literature review covers from rifampicin and
bedaquiline chemical structure, drug mechanisms,
new insights into the modes of delivery, and drug
economics. This include details of how rifampicin
inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase by blocking
transcription elongation and how bedaquiline
inhibits F-ATP synthase by halting c-ring rotation
are included. This review also discusses how oral
rifampicin is improved by self-nanoemulsifying drug
delivery system (SNEDDS) and how bedaquiline can
be possibly delivered by inhalation and injection.
This review aims to compare rifampicin, a
conventional anti-TB drug, and bedaquiline, a novel
drug, evaluating the futural uses in TB treatment.
2.2 Chemical Structure
Rifampicin is a semi-synthetic drug derived from
rifamycin B (a macrolactam antibiotic), belonging to
ansamycins, as it contains an aliphatic ansa chain
(PubChem). Rifampicin is also a polyketide with
alternating carbonyl groups and methylene groups.
To synthesize rifampicin, aqueous solution of
rifampicin is oxided to rifampicin S. Then, the
rifampicin S quinone structure is reduced with
hydrogen, giving off rifampicin SV. The rifampicin
SV undergoes aminomethylation and turns into 3-
pyrrolidi nomethylrifampicin SV. The product is
oxidized to an enamine and is then hydrolyzed to 3-
formylrifamicin SV, which reacts with 1-amino-4-
methylpiperazine to give off rifampicin.
Bedaquiline, or 1-(6-bromo-2-methoxy-quinolin-
3-yl)-4-dimethylamino-2-naphthalen-1-yl-1-phenyl-
butan-2-ol, is a compound in the diarylquinoline
group (Andries, 2005). Bedaquiline contains a
quinolinic central heterocyclic nucleus with alcohol
and amine side chains, which are responsible for the
antimycobacterial property (Pontali, Emanuele,
2016).
2.3 Mechanism
2.3.1
Rifampicin (Rif) Is A N-Amino-Nʹ-
Methylpiperazine Derivative from
Rifamycin
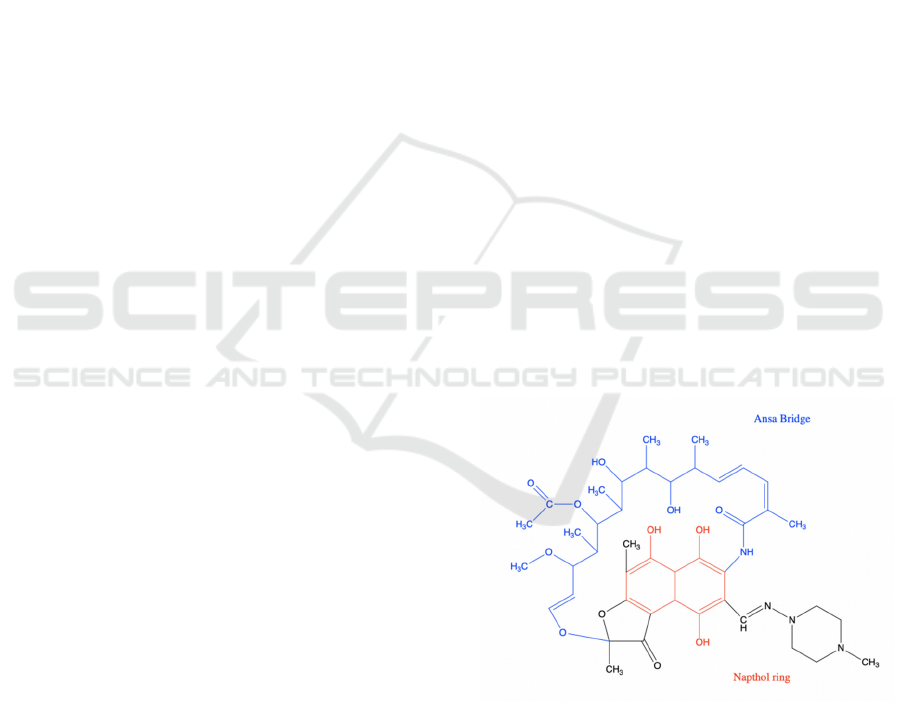
Figure 1: The chemical structure of rifampicin.
As shown in Figure 1, the blue part indicates the
Ansa bridge and the red part indicates the Napthol
ring. The graph depicts a 2-D chemical structure of
the drug.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1180
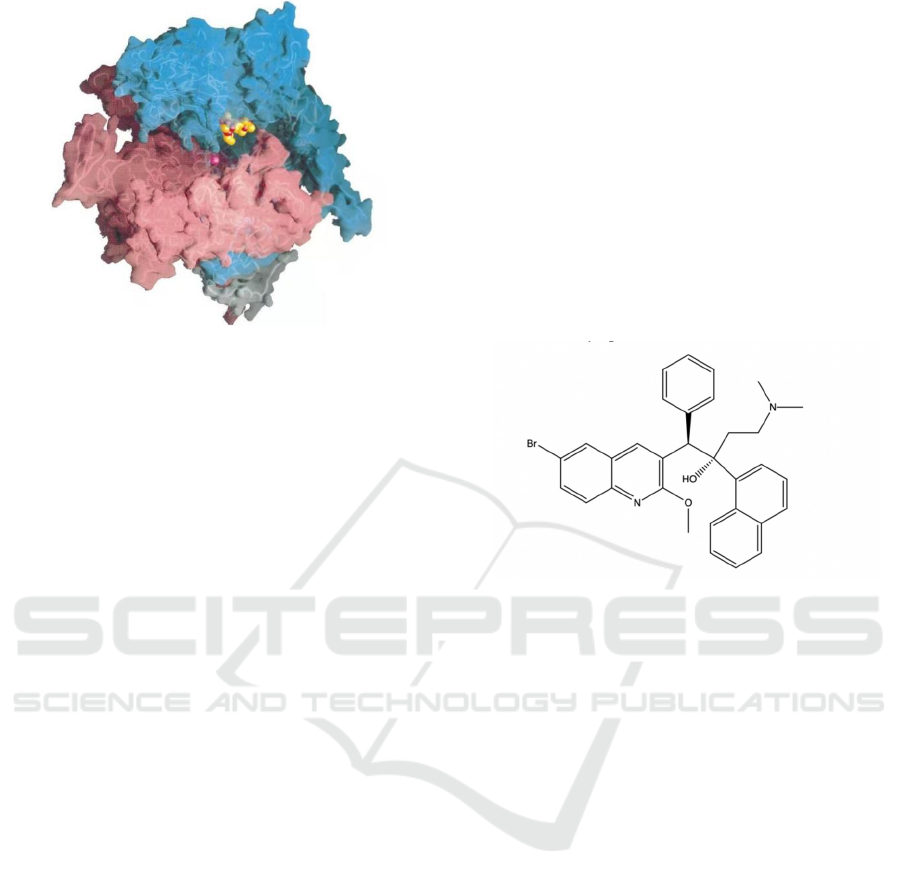
Figure 2: Rif-RNAP cocrystal structure (Campbell,
Elizabeth A, 2001).
As shown in Figure 2, RNAP backbone is
presented by tubes, with transparent molecular
surface. Cyan: β; Pink: β’; white: 𝜔. Rifampicin
shown as CPK atoms, in which carbon is orange,
oxygen is red, nitrogen is blue. The magenta sphere
stands for Mg
2+
ion at the active site.
Rifampicin can inhibit the bacterial RNA
polymerase (RNAP). RNAP, an enzyme catalyzes
the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template, can
no longer produce mRNA and thus the bacteria
would be unable to produce essential proteins. This
inhibition makes rifampicin a bactericidal drug. The
inhibitor binds to the pocket of RNAP β sub-unit in
the DNA channel or RNA channel (Campbell,
Elizabeth A, 2001)
Rifampicin contains two polar groups on napthol
ring and three polar groups on the ansa bridge (Figure
1), which five form hydrogen bonding with the
binding pocket, and van der Waals association is
formed by hydrophobic side chains around the
napthol ring of rifampicin. Rifampicin thus blocks
the path of RNA elongation when the transcript is 2
or 3 nucleotides long, depending on the phosphate
group of the initiating nucleotide.
Rifampicin approximately doubles the apparent
Michaelis constant of initiating substrate at the
RNAP’s i-site, while not affecting the second
nucleotide binding to i+1 site (McClure, 1978). The
formation of the first phosphodiester bond between
these two nucleotides is catalyzed by RNAP. RNAP
would translocate the 2nt transcript upstream,
causing i+1 site replaces i-site (-1 position), and i-site
nucleotide shifts to -2 position, if the initiating
nucleotide contained a 5’ triphosphate (Campbell,
Elizabeth A, 2001). When the nucleotide is shifted to
-2 position, it would clash sterically with rifampicin.
Therefore, the RNAP is stuck at the position, and
repeatedly produce 2nt transcript every time.
However, if the initiating nucleotide carries a 5’
diphosphate or monophosphate, then the formation
of the first phosphodiester bond would be normal, but
the second phosphodiester bond would fail due to the
steric clash with rifampicin, resulting in 3nt
transcript being repeatedly produced.
To sum up, rifampicin is bactericidal because it
sterically blocks the elongation process of the
transcription, as it binds to the β sub-unit in DNA
or RNA channel of the RNAP.
2.3.2
Bedaquiline (BDQ)
BDQ is a diarylquinoline that treats MDR-TB.
Figure 3: The chemical structure of Bedaquiline.
As shown in Figure 3, bedaquiline is displayed by
a 2-D structure. Each solid line represents
intramolecular bonding, with ends representing
Carbon. Other elements are shown by letters.
Generally, Bedaquiline inhibits the F-ATP
synthase of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis to stop
ATP production. This is done by three mechanisms
of the BDQ.
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis
1181
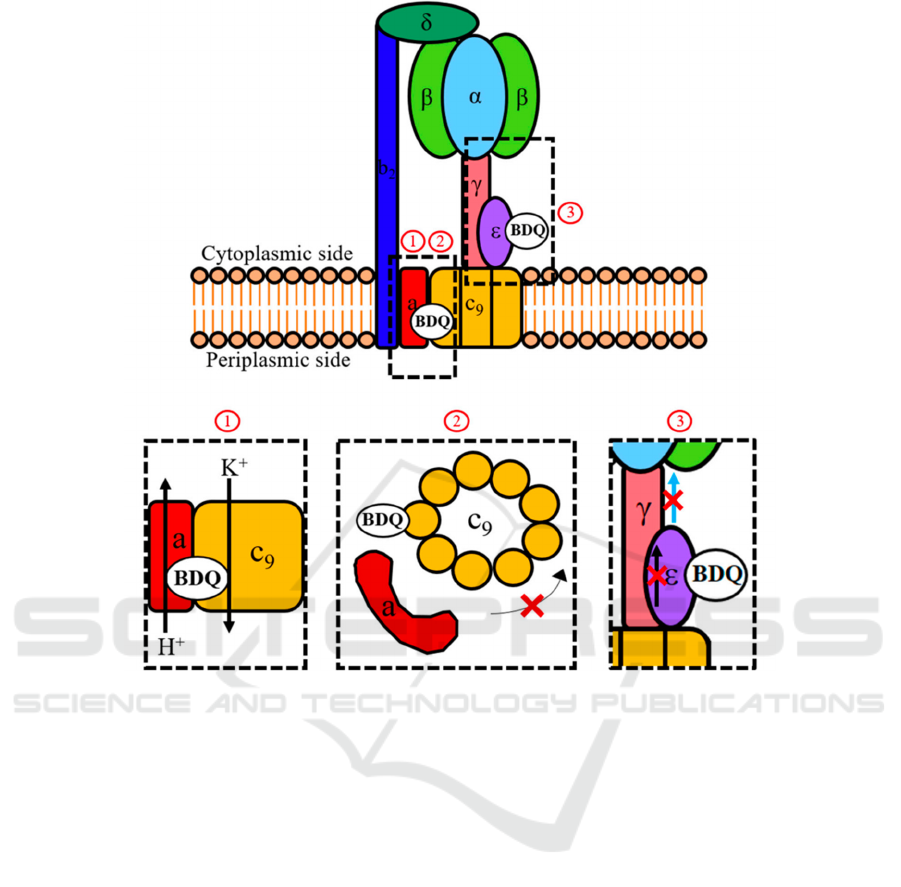
Figure 4: General mechanism of bedaquiline (Sarathy, 2019).
As shown in Figure 4, BDQ functions at the cell
membrane and inhibits ATP synthase. No. 1
visualizes BDQ blocking the flow of proton, no. 2
visualizes BDQ stopping c-ring rotation by binding
to ε-subunit, and no. 3 shows BDQ uncoupling
electron transportation.
First, BDQ can halt c-ring rotation by binding to
the c-ring on mycobacterial F-ATP synthase (Preiss,
2015). The c-ring has two c-submits, which have a
cleft between them. The cleft is the binding site of
BDQ, consisting of M. phlei counterparts of D28,
E61, A63, I66 amino acid residues (Preiss, 2015).
The c-ring can be bound by several BDQ molecules
at the same time, and the binding affinity of a single
BDQ molecule would increase if another BDQ
molecule is joined to form complementary binding
(Salifu, 2019). The binding to the c-ring would be
sterically blocked and unable to pass between the
interface of the F-ATP synthase’s a-subunit and c-
ring. The interaction between BDQ and E61 amino
acid residue would prevent the ion exchange, an
essential process for the flow of proton down the
transmembrane pH gradient. Therefore, F-ATP
synthase activity is halted and ATP synthesis is
prevented.
The second target of BDQ is the ε-subunit, is also
related with the c-ring rotation, on the F-ATP
synthase (Biuković, 2012). Mtb ε-subunit connects
c-ring rotation to the ATP formation at the α
3
β
3
-
headpiece, and it has an interdomain amino acid
interaction network that can deliver information on
c-ring rotation to its C-terminus (Sarathy, 2019). The
C-terminus leads to conformation to contact with
α
3
β
3
-headpiece and transmits the information.
However, BDQ binds to the Mtb ε-subunit at A10-
W16 amino acid region (Biuković, 2012) and leads
to intra-protein structural changes, damaging the
intra-subunit communication network and thus
inhibiting the Mtb ε-subunit function of connecting
c-ring rotation to the ATP synthesis. The target’s
effect is currently considered as secondary, because,
first, BDQ only has moderate binding to the ε-
subunit (Biuković, 2012), and second, the BDQ
resistance mutations in Mtb only occurs to the c-
subunit (Segala, 2012).
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1182
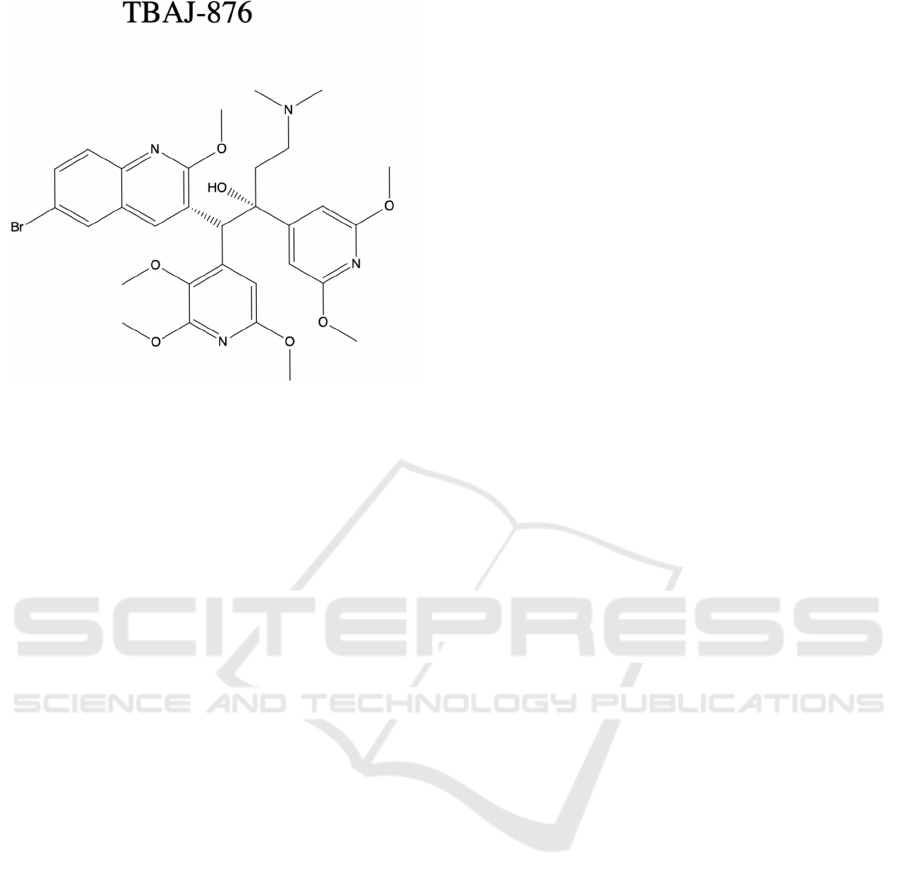
Figure 5: Chemical structure of analogue of bedaquiline,
TBAJ-876.
As shown in Figure 5, structure is analyzed by 2-
D chemical structure, which can be compared with
bedaquiline structure in Figure 4.
The third mechanism, uncoupling electron
transport from ATP synthesis, is still left
controversial. TBAJ-876, a new BDQ analogue
included in Sarathy et al. research, achieves a similar
antibacterial property of BDQ. The TBAJ-876 has
the same two mechanisms covered previously, but it
doesn’t have BDQ’s uncoupler activity (Sarathy,
2019). This indicates that uncoupler activity is not an
essential part of anti-mycobacterial activity.
3 DRUG-RESISTANT
TUBERCULOSIS
3.1 Significance
The challenge of controlling tuberculosis is now even
furthered due to multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB)
and extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB)
(Dheda, 2017). Drug-resistant TB is responsible for
approximately 25% of global TB mortality and is
trickly to cure (World Health Organization, 2020).
Furthermore, the cost of treating MDR-TB is
significant, as 54% of the fund ($2.26 billion out of
$4.2 billion) was spent on the treatment and
diagnosis of MDR-TB in 2020 (World Health
Organization, 2020).
3.2 Rifampicin Resistance
Rifampicin, a major component of multidrug
regimens to treat TB, is found to be ineffective at
MDR-TB. The rifampicin resistance is caused by the
conformational changes of RNA polymerase, as
substitution of the key amino acids can alter the
structure of RNA polymerase. These changes of
amino acids in β subunit of RNAP would prevent
the binding of rifampicin to the enzyme and thus
develop rifampicin resistance (Telenti, 1993).
3.3 Bedaquiline Resistance
Even bedaquiline, the novel drug specific for treating
MDR-TB and XDR-TB, has been reported with
resistance. Due to incomplete treatment, mutations in
the atpE gene can stop BDQ from binding to the c-
subunit of the F-ATP synthase (Koul, 2007). In this
way, BDQ cannot inhibit ATP production and its
bactericidal effect diminishes.
Overall, drug-resistant TB circumstances should
be strictly supervised. Not only conventional
regimen should be improved by optimization, but
also novel drug such as bedaquiline should be further
studied to prevent the rapid loss of this new drug.
4 MODE OF DELIVERY
4.1 Rifampicin (RIF) Delivery
4.1.1
S-SNEDDS
RIF has a poor solubility and bioavailability, while
also causing skin microbiome modification and
hepatotoxicity (Hakkimane, 2018). In the acidic
system, RIF is hydrolyzed to 3-formylrifamycin SV
and 1-amino-4-methylpiperazine and in alkaline
environment, it is autoxidized into oxidized species
like inactive rifampicin quione (Mishra, 2019). To
solve this problem, the self-nanoemulsifying drug
delivery system (SNEDDS), a lipid-based
nanocarrier, is suggested, since it can improve
rifampicin’s solubility, bioavailblity, and stability
(Verma, 2015). SNEDDS can possibly increase the
penetration of nanocarrier-based drug through the
intestinal mucosa (Hussain, 2019).
Recently, solidified SNEDDS (S-SNEDDS) was
developed from the liquid SNEDDS to improve oral
bioavailability. It is also an effective dispersible
nanoemulsion when contacting with gastric fluid
(Hussain, 2019). In the experiment, placebo
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis
1183

SNEDDS performed a stable nano-emulsification
after reconstituting with distilled water and an
improved permeation across rat intestinal membrane
(Hussain, 2019). The dissolution rate was also
promoted, as the solid adsorbent increased the
specific surface area.
Generally speaking, rifampicin’s solubility,
bioavailability, and the oral penetration through
intestinal mucosal membrane are likely to be
improved by SNEDDS, while the S-SNEDDS
furthers the benefits of this delivery system.
4.2 Bedaquiline (BDQ) Delivery
4.2.1 Oral Tablets
Currently, BDQ is delivered by oral as tablets, but
since it is a novel drug, the mode of delivery is still
left for exploration. Two possible routes, inhalation
and injection, are discussed below.
4.2.2 Inhalation Delivery
Since TB is a disease in lungs, inhalation might be a
target-specific method, with short duration treatment
and minimize the side effects caused by oral delivery
(Rawal, 2018). The delivery is carried out by
nanoparticles (NPs), which are small enough to be
easily uptaken by alveolar macrophages (Paranjpe,
2014).
BDQ NPs in the study shows positively charged
behavior, facilitating high uptake by the negatively
charged sialic acid on alveolar macrophages (Rawal,
2018). No toxicity on cells or organs was shown by
the NP formulation, and NP formulation is likely to
reduce BDQ dosing frequency comparing to dry
powder inhalation (DPI) and oral delivery (Rawal,
2018).
4.2.3 Injectable Delivery by Long-Acting
Injectable (LAI) Formulations
LAI formulations are considered to enhance the
latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) completion rates
(Swindells, 2018). LAI formulations could also be
more convenient for children than oral daily
formulations.
To be suitable for LAI, the antibiotic typically has
a low aqueous solubilty, which prevents immediate
dissolution and release of the drug, and a relatively
long pharmacokinetic (PK) elimination half-life
(Park, 2013). BDQ, which has a low minimum
inhibitory concentration and a long half-life, would
probably fits the standards (Kaushik, 2019).
LAI formulations for BDQ can help to overcome
poor oral bioavailability, ease the toxicity of BDQ,
and reduce drug to drug interactions (Kaushik, 2019).
In the study of Kaushik et al., a single dose of long-
acting BDQ resulted in apparent duration of
bactericidal property, which could last more than 12
weeks, meaning that the plasma BDQ levels were
above the MIC for at least 12 weeks after
administration. The bactericidal activity of a single
injection during those 12 weeks was also
significantly more active than the daily oral regimen
of same total dose (Kaushik, 2019). This would make
possible that two injections of long-acting BDQ,
which are administrated 4 weeks apart, can result in
the same effect as the WHO-recommended LTBI
treatment regimens.
5 DRUG ECONOMICS
5.1 Rifampicin
Before figuring out the medical cost, we have to
know the optimum dosage of the drug. Usually,
rifampicin is given 10mg/kg (or 600mg) once a day
due to a consideration of economics and toxicity
(Van Ingen, 2011). However, this dosage might be
suboptimal and result in a lower end on the dose-
response curve (Boeree, 2015), which is partially
responsible for the MDR-TB (Hu, 2015). A new
research suggested that 32mg/kg of daily rifampicin
is safe and effective at severely-ill patients (Seijger,
2019).
According to Global Drug facility, the price of
600mg daily rifampicin for 25 days is ranged from
$5.44 to $14.85. If we apply the new dosage,
32mg/kg daily dosage, the price would be higher, and
even tripled.
To treat active TB, rifampicin is taken with
ethambutol daily for 2 months and then a
combination of rifampicin and isoniazid is
implemented for 7 months (Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention, 2020). This means that
rifampicin alone would be taken each day for 9
months in total, which is already expensive. For
latent TB infection, rifampicin is used daily for 7
months in total.
5.2 Bedaquiline
The price of BDQ for a month, comparing to
rifampicin, is even higher. The cost of BDQ for 6
months is around $900, $3,000, and $30,000 in low-
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1184

income, middle-income, and high-income countries
respectively (World Health Organization, 2016).
6 CONCLUSION
6.1 Summary
To sum up, rifampicin and bedaquiline are both
bactericidal, while rifampicin inhibits transcription
and bedaquiline inhibits the ATP synthesis. As
rifampicin is a major component in the most common
multidrug regimen, the rifampicin resistance has
been severe (Dorman, 2018). In 2015, 125,000
rifampicin-resistant were identified while the
estimated number was 580,000 (World Health
Organization, 2016). To mitigate the resistance, a
maximum rifampicin dosage was found to be
32mg/kg daily (Seijger, 2019), but an optimum
dosage should be further investigated. The increased
dosage might lead to an even higher medical cost of
rifampicin. In contrast, since bedaquiline is novel and
has a special mechanism of inhibiting ATP synthesis,
less resistance to the drug has appeared (Preiss,
2015). Bedaquiline resistance should be studied and
regulated strictly because it is one of the few
treatments for XDR-TB (Karmakar, 2019). A
limitation of BDQ is that it can only be used for
MDR-TB, and it is also expensive ($900 for 6
months treatment in low-income areas) for
underdeveloped countries to afford (World Health
Organization, 2019). Bedaquiline is a novel drug
with significant potential, as it has the opportunity to
be administrated by inhalation or long-acting
injection. BDQ can directly reach lungs, the site of
TB injection, by inhalation method (Rawal, 2018),
while long-acting injection enables BDQ to be
administrated once a week, improving the
completion rate (Kaushik, 2019).
6.2 Evaluation and Future Work
Although oral rifampicin is already mature, it can be
improved by new delivery systems such as
SNEDDS, so further investigation is still in need.
Generally speaking, rifampicin is currently
irreplaceable, but it requires solutions to the drug
resistance and new strategies to improve its quality,
while bedaquiline is a highly critical for treating
MDR-TB and XDR-TB, and its delivery methods are
still left for explorations.
REFERENCES
Andries, Koen, et al. “A Diarylquinoline Drug Active on
the Atp Synthase of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis.”
Science, American Association for the Advancement
of Science, 14 Jan. 2005,
science.sciencemag.org/content/307/5707/223?ijkey=
2e77a4a31e286cfe8f600fce88d191a6123d3e35&keyt
ype2=tf_ipsecsha.
Biuković, Goran, et al. “Variations of Subunit ε of the
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis F1FoATP Synthase and
a Novel Model for Mechanism of Action of the
Tuberculosis Drug TMC207.” Antimicrobial Agents
and Chemotherapy, vol. 57, no. 1, 2012, pp. 168–176.,
doi:10.1128/aac.01039-12.
Boeree, Martin J., et al. “A Dose-Ranging Trial to
Optimize the Dose of Rifampin in the Treatment of
Tuberculosis.” American Journal of Respiratory and
Critical Care Medicine, vol. 191, no. 9, 2015, pp.
1058–1065., doi:10.1164/rccm.201407-1264oc.
Cohen, Adam, et al. “The Global Prevalence of Latent
Tuberculosis: a Systematic Review and Meta-
Analysis.” European Respiratory Society, European
Respiratory Society, 1 Sept. 2019,
erj.ersjournals.com/content/54/3/1900655.short.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Basic TB
Facts.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 17 Mar.
2016,
www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/signsandsymptoms.htm.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Treatment of
Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Bedaquiline.”
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention, 4 May 2016,
www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/factsheets/treatment/bed
aquiline.htm.
Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. “Treatment for
Tb Disease.” Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention, 5 Apr. 2016,
www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/tbdisease.htm.
Campbell, Elizabeth A., et al. “Structural Mechanism for
Rifampicin Inhibition of Bacterial RNA Polymerase.”
Cell, vol. 104, no. 6, 2001, pp. 901–912.,
doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00286-0.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Treatment
for Tb Disease & Pregnancy.” Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control
and Prevention, 13 Aug. 2020,
www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/pregnancy.htm.
Dheda, Keertan, et al. “The Epidemiology, Pathogenesis,
Transmission, Diagnosis, and Management of
Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant, and
Incurable Tuberculosis.” The Lancet Respiratory
Medicine, vol. 5, no. 4, 23 Mar. 2017, pp. 291–360.,
doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(17)30079-6.
Dorman, Susan E, et al. “Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for
Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and
RIFAMPICIN Resistance: A Prospective
MULTICENTRE Diagnostic Accuracy Study.” The
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis
1185

Lancet Infectious Diseases, vol. 18, no. 1, 2018, pp.
76–84., doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(17)30691-6.
Fernandes, Guilherme Felipe, et al. “Isoniazid: A Review
of Characteristics, Properties and Analytical
Methods.” Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry,
vol. 47, no. 4, 2017, pp. 298–308.,
doi:10.1080/10408347.2017.1281098.
Hussain, Afzal, et al. “Solidified Snedds for the Oral
Delivery of Rifampicin: Evaluation, Proof of Concept,
in Vivo Kinetics, and in Silico Gastroplustm
Simulation.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics,
vol. 566, 2019, pp. 203–217.,
doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.061.
Hakkimane, Sushruta, et al. “Antimycobacterial
Susceptibility Evaluation of Rifampicin and Isoniazid
Benz-Hydrazone in Biodegradable Polymeric
Nanoparticles against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
H37Rv Strain.” International Journal of
Nanomedicine, Volume 13, 2018, pp. 4303–4318.,
doi:10.2147/ijn.s163925.
Hu, Yanmin, et al. “High-Dose Rifampicin Kills Persisters,
Shortens Treatment Duration, and Reduces Relapse
Rate in Vitro and in Vivo.” Frontiers in Microbiology,
vol. 6, 2015, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00641.
Koul, Anil, et al. “Diarylquinolines Target Subunit C Of
Mycobacterial ATP Synthase.” Nature Chemical
Biology, vol. 3, no. 6, 2007, pp. 323–324.,
doi:10.1038/nchembio884.
Kaushik, Amit, et al. “Activity of a Long-Acting Injectable
Bedaquiline Formulation in a Paucibacillary Mouse
Model of Latent Tuberculosis Infection.”
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, vol. 63, no.
4, 2019, doi:10.1128/aac.00007-19.
Karmakar, Malancha, et al. “Empirical Ways to Identify
NOVEL Bedaquiline Resistance Mutations in Atpe.”
PLOS ONE, vol. 14, no. 5, 2019,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0217169.
McClure, W.R., and C.L. Cech. “On the Mechanism of
Rifampicin Inhibition of RNA Synthesis.” Journal of
Biological Chemistry, vol. 253, no. 24, 1978, pp.
8949–8956., doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)34269-2.
Mishra, Pooja, et al. “Stability Studies of Rifampicin in
Plasma and Urine of Tuberculosis Patients According
to the European Medicines Agency Guidelines.”
Bioanalysis, vol. 11, no. 8, 2019, pp. 713–726.,
doi:10.4155/bio-2018-0174.
PubChem. “Rifampicin.” National Center for
Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound
Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine,
pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Rifampicin#sec
tion=2D-Structure.
Pontali, Emanuele, et al. “Bedaquiline and Multidrug-
Resistant TUBERCULOSIS: A Systematic and
Critical Analysis of the Evidence.” European
Respiratory Society, European Respiratory Society, 1
Feb. 2016, erj.ersjournals.com/content/47/2/394.
Preiss, L., et al. “Crystal Structure of a Mycobacterial ATP
Synthase Rotor Ring in Complex with Bedaquiline.”
Europe PMC, 2015, doi:10.2210/pdb4v1f/pdb.
Paranjpe, Mukta, and Christel Müller-Goymann.
“Nanoparticle-Mediated Pulmonary Drug Delivery: A
Review.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences,
vol. 15, no. 4, 2014, pp. 5852–5873.,
doi:10.3390/ijms15045852.
Park, Eun Ji, et al. “Long-Acting Injectable Formulations
of Antipsychotic Drugs for the Treatment of
Schizophrenia.” Archives of Pharmacal Research, vol.
36, no. 6, 2013, pp. 651–659., doi:10.1007/s12272-
013-0105-7.
Rawal, Tejal, et al. “Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Promising
Approach for Pulmonary Delivery of Bedaquiline.”
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol.
124, 2018, pp. 273–287.,
doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2018.08.038.
Sensi, P. “History of the Development of Rifampin.”
Clinical Infectious Diseases, vol. 5, no. Supplement_3,
1983, doi:10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_3.s402.
Sarathy, Jickky Palmae, et al. “Re-Understanding the
Mechanisms of Action of the Anti-Mycobacterial Drug
Bedaquiline.” Antibiotics, vol. 8, no. 4, 2019, p. 261.,
doi:10.3390/antibiotics8040261.
Salifu, Elliasu Y., et al. “Halting Ionic Shuttle to Disrupt
the Synthetic Machinery—Structural and Molecular
Insights into the Inhibitory Roles of Bedaquiline
towards Mycobacterium Tuberculosis ATP Synthase
in the Treatment of Tuberculosis.” Journal of Cellular
Biochemistry, vol. 120, no. 9, 2019, pp. 16108–16119.,
doi:10.1002/jcb.28891.
Segala, Elena, et al. “New Mutations in the Mycobacterial
ATP Synthase: New Insights into the Binding of the
Diarylquinoline TMC207 to the ATP Synthase C-Ring
Structure.” Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy,
vol. 56, no. 5, 2012, pp. 2326–2334.,
doi:10.1128/aac.06154-11.
Swindells, S., et al. “Long-Acting Formulations for the
Treatment of Latent Tuberculous Infection:
Opportunities and Challenges.” The International
Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, vol. 22, no.
2, 2018, pp. 125–132., doi:10.5588/ijtld.17.0486.
Seijger, Charlotte, et al. “High-Dose Rifampicin in
TUBERCULOSIS: Experiences from a Dutch
Tuberculosis Centre.” PLOS ONE, vol. 14, no. 3, 2019,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0213718.
Telenti, A, et al. “Detection of Rifampicin-Resistance
Mutations in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis.” The
Lancet, vol. 341, no. 8846, 1993, pp. 647–651.,
doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)90417-f.
Verma, Samridhi, et al. “Fabrication of Lipidic
Nanocarriers of Loratadine for Facilitated Intestinal
Permeation Using Multivariate Design Approach.”
Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, vol. 42,
no. 2, 2015, pp. 288–306.,
doi:10.3109/03639045.2015.1052078.
Van Ingen, J., et al. “Why Do We Use 600 Mg Of
RIFAMPICIN In Tuberculosis Treatment?” Clinical
Infectious Diseases, vol. 52, no. 9, 2011,
doi:10.1093/cid/cir184.
Wang, Xiao-bo, et al. “A Survey of Anxiety and
Depressive Symptoms in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Patients With and Without Tracheobronchial
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1186

Tuberculosis.” Frontiers, Frontiers, 1 Jan. 1AD,
www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.0030
8/full.
WHO China TB treatment. “Tuberculosis China.” World
Health Organization, World Health Organization,
www.who.int/china/health-topics/tuberculosis.
World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report
2020. World Health Organization, 2020.
World Health Organization. The Selection and Use of
Essential MEDICINES Report of the WHO Expert
Committee, 2015 (Including the 19th Who Model List
of Essential Medicines and the 5th Who Model List of
Essential Medicines for Children). World Health
Organization, 2015.
World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis REPORT
2016. World Health Organization, 2016.
World Health Organization. “Critically Important
Antimicrobials for Human Medicine: 6th Revision.”
World Health Organization, World Health
Organization, 2019, www.who.int/publications-detail-
redirect/9789241515528.
Zhang, Ying, et al. “Mechanisms of Pyrazinamide Action
and Resistance.” Microbiology Spectrum, vol. 2, no. 4,
2014, doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.mgm2-0023-2013.
Rifampicin and Bedaquiline: New Insights into Treating Tuberculosis
1187
