
Assessment of Factors Shaping Sustainable Development of Kursk
Region
S. А. Markina
a
, L. V. Afanasyeva
b
and I. N. Rodionova
c
Southwest State University, Kursk, Russia
Keywords: Sustainable Development, Gross Regional Product, per Capita Income, Inflation, Economic Security, Social
Security, Environmental Security, Integrated Sustainable Development Indicator of the Region.
Abstract: One of the state policy priorities in ensuring economic security is the sustainable development of regions. The
article deals with the problems of sustainable development of the region in modern challenges and threats.
The problems of theoretical and methodological substantiation of the main directions, mechanisms, and
factors of the region's transition to sustainable economic development were investigated. The main approaches
to determining the level of influence of factors on the stability of the regional economic development are
substantiated. The methodology for assessing the region's sustainable development based on the calculation
of private indicators of sustainable development, such as economic, social, and environmental security, is
proposed. The factors that have a dominant influence on the level of sustainable development of Kursk region
were identified. On their basis, the necessary conditions for the development of the economy of Kursk region
were determined.
1 INTRODUCTION
Globalization poses completely new challenges to
society in shaping the concept of international
security, including economic security of the global
space. Decree of the President of the Russian
Federation, dated May 13 2017, approved the strategy
No. 208 "On the strategy of economic security of the
Russian Federation for the period up to 2030". This
document reflects challenges and threats to the
economic security of the Russian Federation, as well
as the goals, main directions, and objectives of state
policy in the sphere of economic security. One of the
state policy priorities in ensuring economic security
is the sustainable development of regions.
Sustainable development characterizes the
strength and reliability of all elements, horizontal,
vertical, and other links within the system. One sign
of sustainability is the long-term stability of
development without sharp fluctuations in economic,
social, and environmental indicators and the gradual
but steady elimination of existing imbalances
(Tsiklauri et al, 2019). The main property that
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5727-8765
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2880-8872
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2741-580Х
determines the system's safety is the balance of
internal and external conditions of its existence,
allowing the system to realize the interests of both its
present and future development.
Russia's security is made up of each territory's
capabilities, so the state of sustainability of socio-
economic development of a single subject of the
Russian Federation is important (Tsiklauri et al,
2017).
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This article will investigate theoretical and
methodological justification of the main directions,
mechanisms, and factors for the region's transition to
sustainable economic development.
K.V. Kopteva notes in her work that sustainable
development combines global, regional, and local
aspects of security into a single systemic whole based
on planetary imperatives. Its synergetic nature is also
manifested in the fact that it integrates at least three
spheres of human activity - economic, social, and
172
Markina, S., Afanasyeva, L. and Rodionova, I.
Assessment of Factors Shaping Sustainable Development of Kursk Region.
DOI: 10.5220/0010665600003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 172-177
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

environmental - into a coherent system, creating a
systemic effect of sustainable development that did
not exist before because it focuses on at least three
compatible goals - ensuring economic efficiency,
social justice and environmental imperatives
(Kopteva, 2008).
The problems of sustainability and economic
security of the region should be studied in the same
context due to their proximity and ideological
orientation to ensure normal, effective development
of the region. Sustainable development and security
are essential characteristics of the economy as a
single system (Galbreath et al, 2020).
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
One of the most important indicators of the region's
economic development is the gross regional product,
which characterizes the process of production of
goods and services for final consumption. This
indicator should be considered in the dynamics over
several years in the region as a whole, per capita and
square kilometer.
The dynamics of the gross regional product
indicator in current prices, in the region as a whole,
per capita, and per square kilometer in the Kursk
region for 2015-2020 are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Analysis of gross regional product indicator of Kursk region for 2015-2020, at the beginning of the year
Interpretation of the indicator 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
In the re
g
ion as a whole, bln. rub. 298.3 336.9 362.4 387.3 428.4 496.7
Per ca
p
ita, thsd rub 266.8 301.2 323.1 346.1 385.6 449.3
Per square kilometer, mln rub 9.94 11.23 12.08 12.91 14.28 15.08
Index of physical volume of gross regional
product (in constant prices), in % to the
p
revious year
104.5 102.9 103.9 102.5 102.6 102.7
From 2015 to 2020, the absolute value of the gross
regional product in the region increased by 198.4
billion rubles (+66.5%), which is a positive trend.
As of 2020, there are four key sectors:
"Agriculture, Forestry, Hunting, Fishing and Fish
farming", "Manufacturing industries", "Mining",
"Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles
and motorcycles" in the structure of gross value added
in Kursk region.
The development of the socio-economic forecast
for Kursk region this year was in a state of uncertainty
due to the spread of coronavirus. At the end of 2020,
there was a decline in the number of economic
indicators. The economy is not expected to recover
until 2021. Moreover, this forecast is moderately
optimistic.
So, the results of 2020 in the Kursk region show a
decrease in GDP by about 3.4%. The Governor has
stated that agriculture in the region is the only
industry that has shown a profit in the current
coronavirus year.
Also, one of the key indicators characterizing the
level of economic security of the region is
"Investment in fixed capital". It is advisable to
analyze this indicator not only in terms of dynamics
over a certain time period, but also to determine its
share in the total volume of gross regional product in
the relevant year.
Table 2 presents the analysis of the indicator
"Investment in fixed capital" (in current prices) for
Kursk region for 2015-2020.
In total, from 2015 to 2020, the volume of
investment in fixed capital in the economy of Kursk
region increased twofold, which in absolute terms
amounts to +79.5 billion rubles. At the same time, at
the end of the analyzed period in the structure of
investments in fixed capital by types of economic
activity, the priority sectors are "Agriculture, forestry,
hunting, fishing and fish farming", "Manufacturing",
"Provision with electric energy, gas, and steam; air
conditioning".
Table 2: Vertical and horizontal analysis of investment in fixed capital (in current prices) in Kursk region for 2015-2020.
Interpretation of the indicator 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Volume of investment in fixed capital, bln.
rub.
73.7 93.7 100.9 120.7 142.7 153.2
Growth rate of investment in fixed assets
com
p
ared to the
p
revious
y
ear %
100.07 127.00 107.73 119.66 118.23 107.36
Volume of investment in fixed capital to
gross regional product, %
21.88 25.84 26.05 28.18 28.73 29.57
Assessment of Factors Shaping Sustainable Development of Kursk Region
173
One of the necessary conditions for ensuring
sustainable development and economic security of
the region is the socio-economic well-being of
citizens. The analysis of the values and dynamics of
these indicators reflecting the socio-economic
situation of the population of Kursk region in 2015-
2020 is presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Analysis of indicators reflecting the socio-economic situation of the population of Kursk region in 2015-2020.
Name of indicato
r
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Average per capita cash income of the population
p
er month, rub.
25330.2 25354.9 26211.8 27275.4 29246.6 29706.4
Average monthly nominal accrued salary of
employees of organizations, rub.
23921.4 25326.6 27274.1 29937.1 32709.4 35952.0
Number of population with monetary income
below the subsistence minimum from the total
population of the region, %
10.4 10.5 10.3 9.9 9.9 11.0
Officially registered unemployment rate, % 1.2 0.97 0.76 0.69 0.61 2.62
Despite positive growth dynamics of average cash
income per capita (+11.72% in 2015-2020), average
nominal monthly accrued wage (+50.29% in 2015-
2020), the number of people with cash income below
the minimum subsistence level remains at a rather
high level - 11% of the total population in the region
as of 2020. There has also been an increase in
officially registered unemployment (by 2.2 times in
2020 compared to 2015 and by 4.3 times compared to
2019).
Special attention should be paid to the crime rate
in the region. Ensuring a high level of economic
security and development of the region should be
achieved through economic, social as well as law
enforcement measures. Thus, according to the
materials of information and analytical notes on the
results of operational and service activities of the
Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia in the Kursk
region for 2015-2020, we can determine the dynamics
of the total number of registered crimes in the region
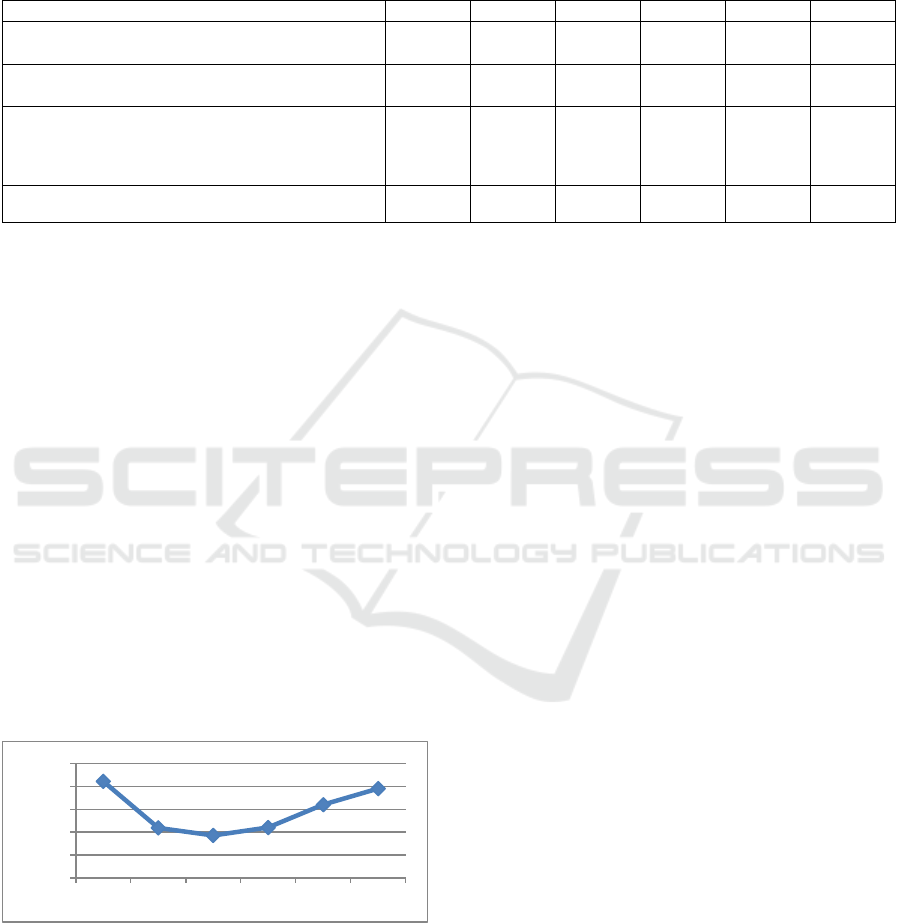
(figure 1).
Figure 1: Dynamics of the value of the indicator "number
of crimes registered in the territory of Kursk region".
Over the analyzed time interval crime in Kursk
region decreased until 2017, then there is a steady
trend, so in 2020 the indicator is higher than the level
of 2019 by 5.3%, which is a negative trend and a
negative factor in economic security of the region as
a whole.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
The basis for the diagnostics of the region's
sustainable development are the methods of
indicative analysis, according to which the diagnosis
is carried out by a set of indicators of economic, social
and environmental security (Kirilchuk et al, 2018).
On this basis, the methodology for assessing the
sustainable development of the region is presented in
Figure 2.
14224
12190
11864
12210
13203
13903
10000
11000
12000
13000
14000
15000
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
174
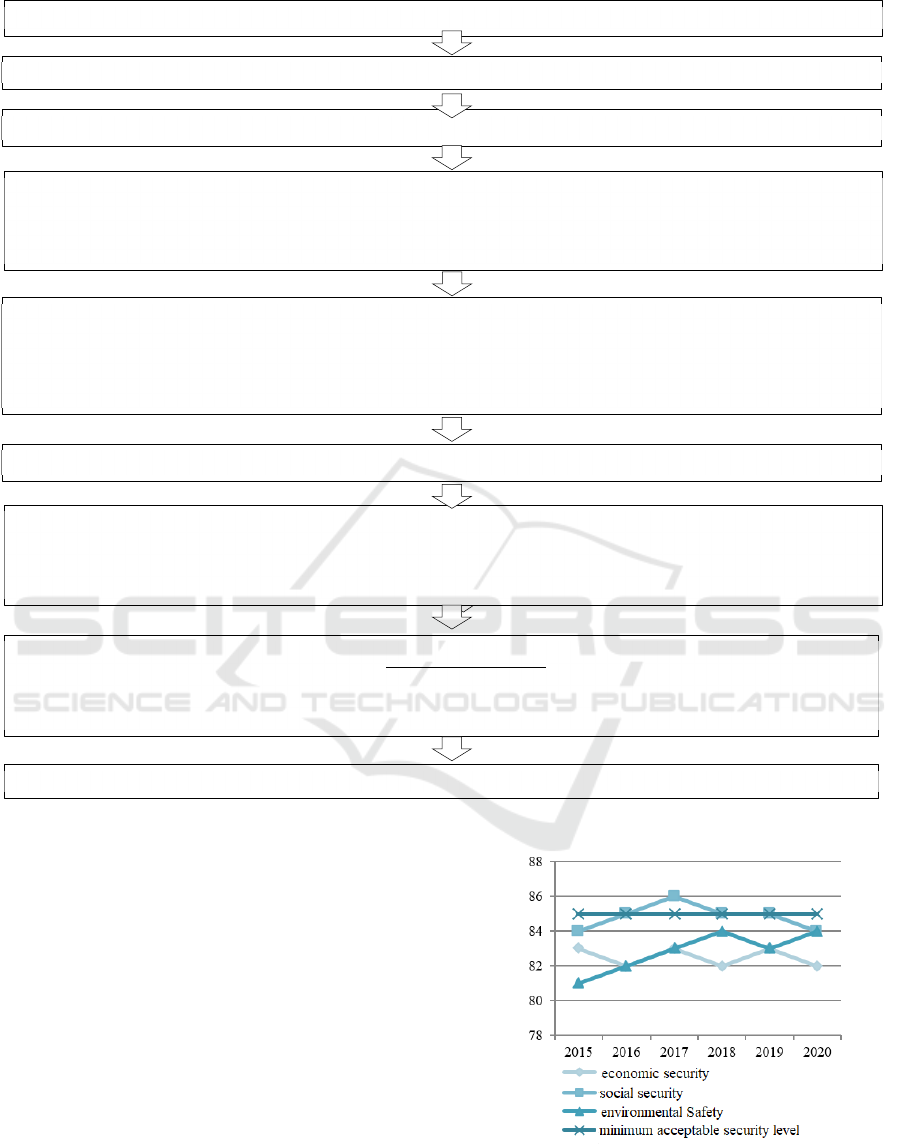
Figure 2: Methodology for assessing the sustainable development of the region.
On the basis of the proposed methodology, the
calculation and assessment of particular indicators of
sustainable development of Kursk region was carried
out, the results of the calculations are shown in Figure
3.
Figure 3: Dynamics of particular indicators of sustainable
development of Kursk region.
Figure 3 clearly shows that in Kursk region, the
majority of private indicators of sustainable
Determination of the most si
g
nificant factors
,
influencin
g
the sustainable develo
p
ment of the re
g
ion
Formation of a s
y
stem of indicators of the level of sustainable develo
p
ment of the re
g
ion
Determinin
g
Thresholds for Selected Indicators
Analysis and assessment of criteria for the level of sustainable development of the region
The ratio of the actual values of indicators of sustainable development of the region with their threshold values:
Кi = Ф / П, Бi → max Кi = П / Ф, Бi → min
Кi - estimated indicator, Ф – actual value of the indicator,
П – threshold, Бi – safety factor
Ranking of the calculated values of safety factors on a 100-point rating scale
Assessment of the calculated values of the safety factors on the scale:
Кi > 1,5 – safe state
1 > Кi > 1,5 – pre-crisis state
0,5 > Кi > 1 – crisis state
0
,
5 < Кi
–
critical level
Calculation of particular indicators of the stability of the region:
- indicators of economic security
- indicators of social security
- indicators of environmental safety
Calculation of a comprehensive indicator of sustainable development of the region:
У
Б
Экон
Б
Соц
Б
Экол
У – complex indicator of sustainable development of the region; Б
Экон
– private indicator of economic security;
Б
Со
ц
–
p
rivate indicator of social securit
y;
Б
Экол
–
p
rivate indicator of environmental safet
y
Assessment of Factors Shaping Sustainable Development of Kursk Region
175
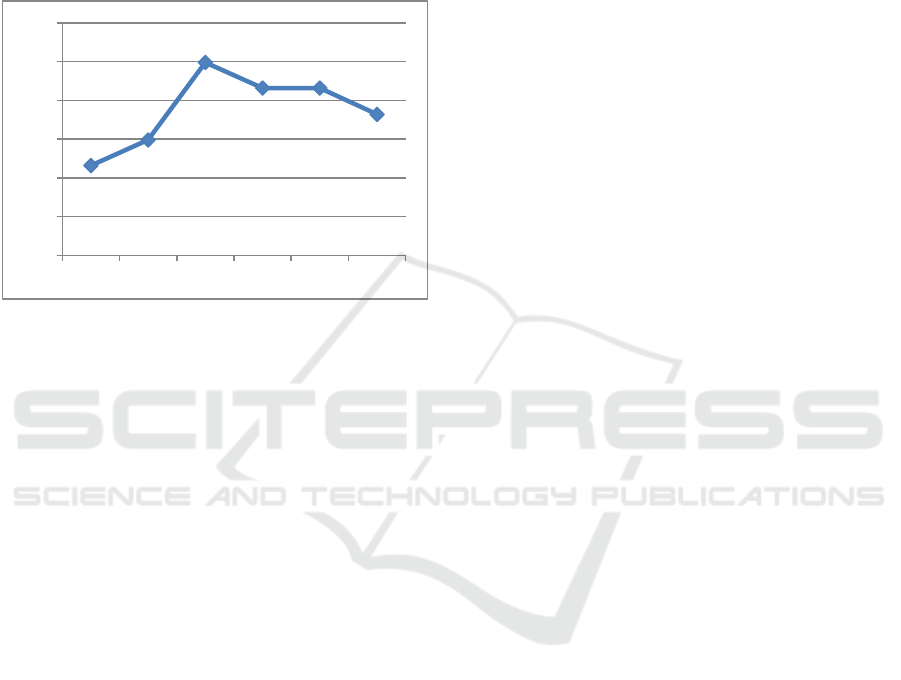
development during the study period were below the
minimum acceptable level, and in 2020 the indicators
showed negative dynamics and did not reach the safe
level.
The calculated composite indicator of the region's
sustainable development (Fig. 4) allows us to
determine the dependence of Kursk region
development on destabilizing external and internal
influences.
Figure 4: Dynamics of the complex indicator of sustainable
development of Kursk region.
Based on the data of Figure 3, we can conclude
that the Kursk region is characterized by cyclical
changes in the presented indicator, which largely
depends on the economic situation in the Russian
Federation. There is low resilience to external factors
in terms of sustainability.
The use of factor analysis, made it possible to
establish the factors that have a dominant influence
on the level of sustainable development of Kursk
region out of the totality of the analyzed indicators.
Such factors include: GRP; investment in fixed
capital; average per capita income of the population;
population density; generation and use of toxic waste.
The listed main factors will allow us to determine
the ways to improve the effectiveness and
sustainability of individual economic entities, as an
integral part of the unified socio-economic system of
Kursk region in the future.
5 CONCLUSION
Summarizing the above, we can conclude that the
state of economic security of Kursk region is
characterized by the growth trend of gross regional
product, which is achieved mainly through the
effective functioning and development of agriculture,
metallurgy and industrial production, which products
are successfully exported to neighboring and distant
foreign countries.
Another positive factor is the growth of
investment in fixed assets in the economy of Kursk
region, which allows to increase the volume and
quality of products.
However, the pressing economic and social
problems in Kursk region include a high number of
people with incomes below the subsistence level -
almost every 11th inhabitant of Kursk region belongs
to this group.
The level of economic security in Kursk region is
below threshold only by one of 6 indicators - it is the
unemployment rate, which is 0.3% higher than the
permissible norm. In general, the state of economic
security of the region can be considered stable.
Thus, the Kursk region was among the regions
that ensured sustainable development of industry.
Despite the coronavirus pandemic and related
restrictions, the industrial production index for 2020
was 101.7%, above the national average.
The necessary conditions for the development of
the economy of Kursk region are: increasing the gross
regional product; providing the necessary level of the
social and economic well-being of the inhabitants;
ensuring a low level of crime; stability of the
economy of the region as a whole.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Performed as part of the Southwestern State
University state assignment, project code 0851-2020-
0034.
REFERENCES
Galbreath, J., Lucianetti, L., Tisch, D., & Thomas, B.
(2020). Firm strategy and CSR: The moderating role of
performance management systems. Journal of
Management & Organization, 1-19.
DOI:10.1017/jmo.2020.27
Kirilchuk I., Rykunova V., Panskov V. (2018). Features of
calculation and analysis of ekology- ekonomic index of
the region on the example of Kursk region.18th
International Multidisciplinary Scientific
GeoConferences SGEM 2018. Conference
proceedings, 375-382.
Kirilchuk I., Rykunova V., Panskov V. (2018). Indicators
of sustainable development as indicators of ecological-
economic safety. 18th International Multidisciplinary
Scientific GeoConferences SGEM 2018. Conference
proceedings, 491-498.
82,66
82,99
83,99
83,66
83,66
83,32
81,5
82
82,5
83
83,5
84
84,5
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
176

Klimenko, P., Markina, S., Mashkina, N. (2017). The
influence of processes of financial globalization and
transformation on the word financial and credit system.
SGEM International Multidisciplinary Scientific
Conference on Social sciences and Arts: 847.
Kopteva, K.V. (2008). Otsenka ustoychivosti sotsial'no-
ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Kurskoy oblasti. Strategiya
razvitiya regiona, 4 (61):19-21.
Muurlink, O., Macht, S. (2020). Managing (out) corruption
in NGOs: A case study from the Bangladesh
delta. Journal of Management & Organization, 1-16.
DOI:10.1017/jmo.2020.17
Ofitsial'nyy sayt territorial'nogo organa Federal'noy
sluzhby statistiki po Kurskoy oblasti. URL:
kurskstat.gks.ru
Rykunova, V., Goncharenko, L., Belousova, S. (2017).
Enhancement of the incentive function of economic
mechanism for rational natural resources management.
17th international multidisciplinary scientific
geoconference SGEM 2017, 285-292.
Tsiklauri, V., Sevryukova, L., Devyatilova, A., Belousova,
S. (2019). Bankruptcy of enterprises as an indicator of
disturbance of sustainable economic development.
Proceedings of the 33rd International Business
Information Management Association Conference,
IBIMA 2019: Education Excellence and Innovation
Management through Vision 2020. Education
Excellence and Innovation Management through Vision
2020, 33: 2395-2403.
Tsiklauri, V.Yu., Devyatilova, A.I., Artemov, R.V.,
Markina, S.A. (2017). Shadow globalization as a threat
to world economic growth. Education Excellence and
Innovation Management through Vision 2020 From
Regional Development Sustainability to Global
Economic Growth: Proceedings of the 29th
International Business Information Management
Association Conference, 2478-2489.
Assessment of Factors Shaping Sustainable Development of Kursk Region
177
