
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection
Zainab H. Alwan
1
, Gopal Reddy
2
and Balasubramanyam Karanam
3
1
Department of Community Health, Institute of Medical Technology, Middle Technical University Baghdad, Iraq
2
College of Veterinary Medicine, Tuskegee University, Tuskegee AL36088, U.S.A.
3
Department of Biology and Center for Cancer Research, Tuskegee University, Tuskegee, AL36088, U.S.A.
Keywords: Kaiso, HIV-1, Transcriptional Factor, Zinc Finger, CD4, Viral Load.
Abstract: The role of Kaiso, a POZ-ZF transcriptional factor in HIV infection, which has been disparagingly affecting
African Natives as well as African Americans, has not been well studied. For these reasons, this research
aimed to investigate the level of expression and the role of Kaiso in HIV-1 infected African Natives compared
with patients in the United States. In silico data of 185 whole blood samples were analyzed to study gene
expression by array in GEO (Gene expression Omnibus) dataset from the National Center for Biotechnology
Information (NCBI). Different bioinformatics approaches were used to analyze the data. Two or more groups
of samples were compared using GEO2R to identify differentially expressed genes across experimental
conditions. Pathways that were significantly associated with specific gene sets were determined by Gene Set
Enrichment analysis (GSEA). Results showed higher level of Kaiso expression in HIV-1 patients compared
to healthy control (p = 3.89e-10), and it was significantly higher in African Natives compared to United States
patients (p = 0.002). Importantly, this study revealed a negative correlation between Kaiso expression and
CD4+ T cell count in HIV-1 infected African Native patients (p = 0.003). This negative correlation between
Kaiso and CD4+ T cell count was accompanied by increased viral load in African Natives with a higher viral
set point compared to US HIV-1 patients. These data may at least partly explain the reasons for faster
progression to AIDS in African Natives than seen in US patients. Kaiso associated enrichment pathways
showed that Kaiso upregulation may contribute to CD4 depletion in HIV-1 infection, and may upregulate
HIV associated neurological impairment marker genes. The results also showed that Kaiso expression may
also be associated with increased Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by downregulating GSK3β, MAPK1 and
MAPK3 through different downregulated pathways in African Native patients. This study suggests that Kaiso
may play a role in the crosstalk between different pathways in HIV-1 infection. In conclusion, the present
study suggests, for the first time, that Kaiso expression levels may possibly play a role in the faster
acceleration of HIV-1 infection towards AIDS in African ancestry patients and this may be through the
involvement of Wnt/βcatenin signaling pathway. Data of this study also suggests that Kaiso expression level
may contribute to increased crosstalk between different pathways in HIV-1 pathogenesis. Further studies are
needed to fully delineate the role of Kaiso in different HIV1 infected ethnic groups through the involvement
of different intermediary pathways.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the first reports of AIDS cases in early 1980s,
\HIV virus around the world and approximately 32
million people have died. The African region remains
most severely affected, with nearly one in every 25
adults (4.1%) living with HIV and accounting for
nearly two-third of the people living with HIV
worldwide (WHO, https://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en/).
More than half (54%) of the people living with HIV
infections around the world are from East and South
Africa (UNAIDS’AIDSinfo’, 2019).
However, different studies reveal that infection
with HIV occur more in African born black
immigrants rather than U.S. born blacks (Johnson et
al., 2010; Kent, 2005; Kerani et al., 2008; Ashton et
al., 2012) and HIV prevalence was higher in African
born compared to US born blacks and US white
(Ashton et al., 2012). Racial disparities have been
indicated in both HIV-1 (CDC, 2017; Hall et al.,
2007; Klein et al., 2014) and in different human
cancers (Abisoye-Ogunniyan et al., 2018; Bassey-
Archibong et al., 2017; Jones et al., 2014; Jones et al.,
2012; Jones et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2016).
Alwan, Z., Reddy, G. and Karanam, B.
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection.
DOI: 10.5220/0010781100003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 89-98
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
89

Kaiso is Caribbean slang for calypso music, which
accompanied the late-night cloning of this gene.
Kaiso is a 672 amino acid protein belonging to the
BTB/POZ (broad complex, tram track, bric à
brac/pox virus and zinc finger) family of zinc finger
transcription factors (Albagli et al., 1995; Bardwell
and Treisman, 1994). In contrast to many
transcription factors, Kaiso as a transcriptional
regulator with bimodal DNA-binding specificity,
which binds to methylated CGCG and to the non-
methylated consensus KAISO-binding site (KBS)
TCCTGCNA. A few reports have been published
illustrating the role of Kaiso in different types of
cancers (Pierre et al., 2019). In addition, Kaiso
expression is correlated to racial disparities in
different types of cancer; some of these studies
correlate the nuclear expression of Kaiso with
aggressiveness of tumors and metastases in African
Americans (US African) compared to white patients
(Jones et al., 2014; Jones et al., 2012; Bassey-
Archibong et al., 2017).
To our knowledge, no studies have been reported
so far on the expression levels of Kaiso in HIV-
infected people of different ethnic backgrounds/ races
and the role Kaiso may play in infection and
replication of HIV. For these reasons, the objective of
this study were to investigate the role of Kaiso
expression by analyzing in vivo HIV-1 infected
patients dataset (NCBI) in different races and ethnic
groups. Bioinformatics and statistical analysis tools
are used to analyze data.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
To achieve our aim to determine the expression levels
of Kaiso in HIV-infected and uninfected people of
different ethnic/racial backgrounds, in silico data of
185 whole blood samples (from United States, and
Africa) with or without HIV-1 infection was analyzed
by gene array to study gene expression. Geo dataset
from the NCBI’s (National Center for Biotechnology
Information) Gene expression Omnibus (GEO)
accessible through GEO Series accession numbers
GSE29429 were used GSE# (http://www.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gov/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE#).
The gene symbol names associated with each data
set were pulled from each GPL file and merged with
its GSE read using the R merge function. Gene
expression data were analyzed to determine the role
of Kaiso in HIV-1 infection.
2.1 Geo Dataset Analysis
To determine if Kaiso has a role in HIV-1 infection,
expressed genes were subjected to data analysis
using:
1. GEO2R, NCBI (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r/).
GEO2R was used to compare two or more groups
of samples in order to identify genes that are
differentially expressed across experimental
conditions, based on the R programming language
that provides tools for the analysis of high-
throughput genomic data. Results are presented as
a table of genes ordered by significance. 2. GSEA
(Gene Set Enrichment Analysis)
http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp.
(http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp)
. GSEA is a computational method that
determines whether a priorily defined set of genes
shows statistically significant, concordant
differences between two biological states (e.g.,
phenotypes). 3. RStudio (http://Rstudio.org) used
for statistical computing and graphics. 4. Excel
and XLSTAT for further analysis and graphics. 5.
GraphPad prism for data analysis and graphics.
2.2 Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as means ± standard deviation
(SD). The significance of differences between healthy
control and HIV-1 infected groups was evaluated
using One Way ANOVA, Two Way ANOVA, and t-
test analysis. Differences were considered significant
when P < 0.05.
3 RESULTS
3.1 HIV-1 Demographic Data Analysis
Microarray gene expression profiles for 185 patients
from Gene expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset were
downloaded from the National Center for
Biotechnology Information (NCBI). One hundred
forty-seven samples were from HIV1 –infected
patients and thirty-eight samples were from healthy
control people (Table 1). Among the HIV-1 positive
patients, 130 were male and 17 were females. Among
the control healthy people, 22 were male and 16 were
females (Table 1).
In this study, age range was 20-66 years old of
whites and African American HIV-1 patients with the
peak rate at the age of 38 and 28 respectively. While,
age range was 18-38 for African Natives with peak
rate at the age of 18 with infected patients.
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
90
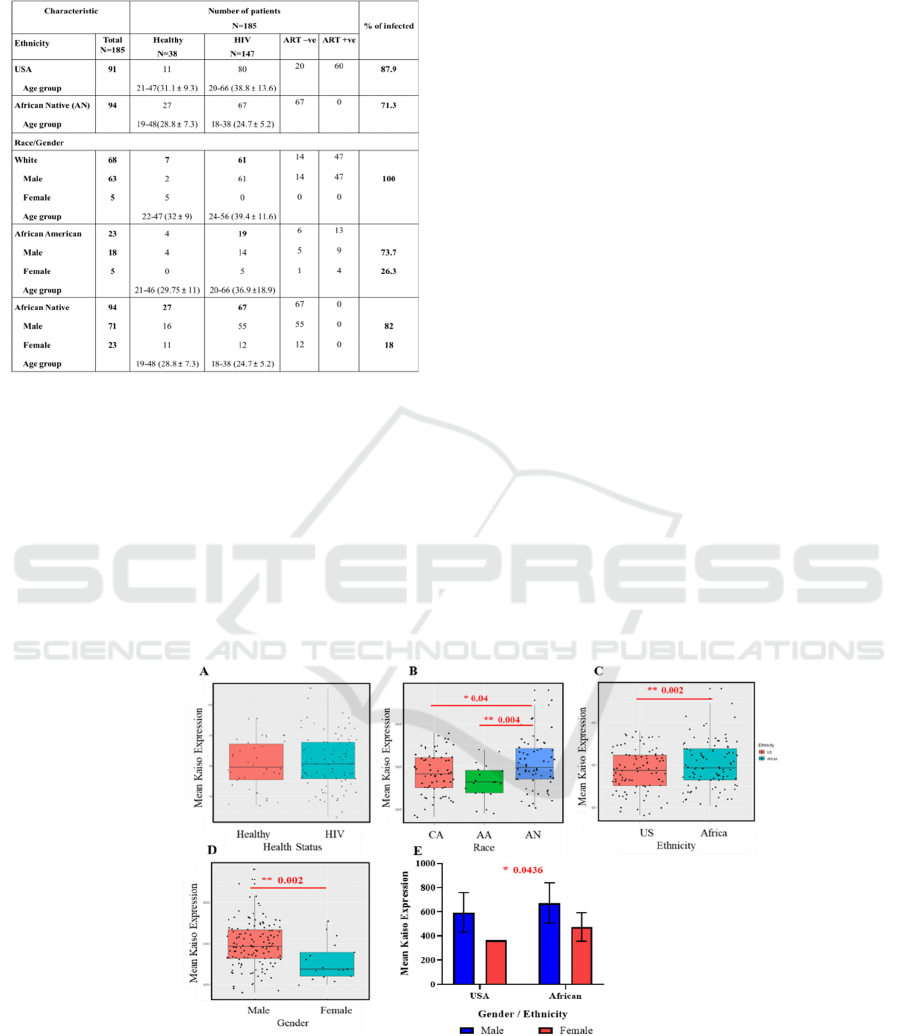
Table 1: Clinical and pathological characteristics of HIV-1
patients-Whole Blood GSE29429.
3.2 Kaiso Expression in HIV-1
Infection Is Significantly Associated
with Gender, Race, and Ethnicity
Dataset were examined using R program for Kaiso
expression, which was found to be upregulated in
HIV-1 infected patients compared to healthy controls
samples (Figure 1-A).
Of the 185 whole blood samples collected from
acute HIV-1 patients (GSE29429), 94 samples were
from African Natives and 91 samples were from the
United States. Their clinical and pathological
characteristics are shown in Table 1. Importantly,
significant differences in Kaiso expression were
observed among different race groups. Kaiso
expression was significantly higher in African
Natives as compared to both African Americans (US
African) and White Caucasians (p = 0.004 and 0.04,
respectively) (Figure 1-B). All the results after this
step were analyzed by comparing African Natives to
United States (U.S) patients since Kaiso were
significantly higher in African Natives compared to
U.S patients (p value 0.002) (Figure 1-C).
Results of RStudio analysis of Kaiso expression
in HIV-1 infected and healthy control samples
demonstrated higher Kaiso expression in HIV-1
patients compared to healthy controls. However,
differences in the expression levels were not
statistically significant (Figure 1-A). while, a highly
significant difference was observed in males
compared to females in acute HIV infected patients (p
=0.002) (Figure 1-D).
Kaiso expression was significantly higher in both
male and female African Natives compared to U.S
acute HIV patients (p = 0.04) (Figure 1-E). Kaiso
expression was also significantly higher in younger
age African patients (mean age 24.7 ± 5.2) in
comparison to U.S patients (mean age 38.8 ± 13.6) (p
< 0.0001).
Figure 1: In HIV-1 infection, Ethnicity, Gender are significantly associated with High expression of Kaiso. R program used
for the analysis and graphics A. Higher Kaiso expression in overall HIV patients (n=87) compared to healthy (n=38). B. Kaiso
is significantly higher in African Native compared to African American (US African) and white Caucasian groups with p
value 0.004 and 0.04 respectively. C. Kaiso is significantly higher in African ethnic group (n=67) in comparison to US patients
(n=20) (p = 0.002). D. Significant gender differences (p = 0.002) in overall HIV males with high Kaiso expression compared
to females, graphpad prism was used for significance analysis and the graphics that show a significant higher Kaiso expression
in African ethnic HIV males and females compared to US males and females with p = 0.0436 (ANOVA test) as shown in (E).
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection
91
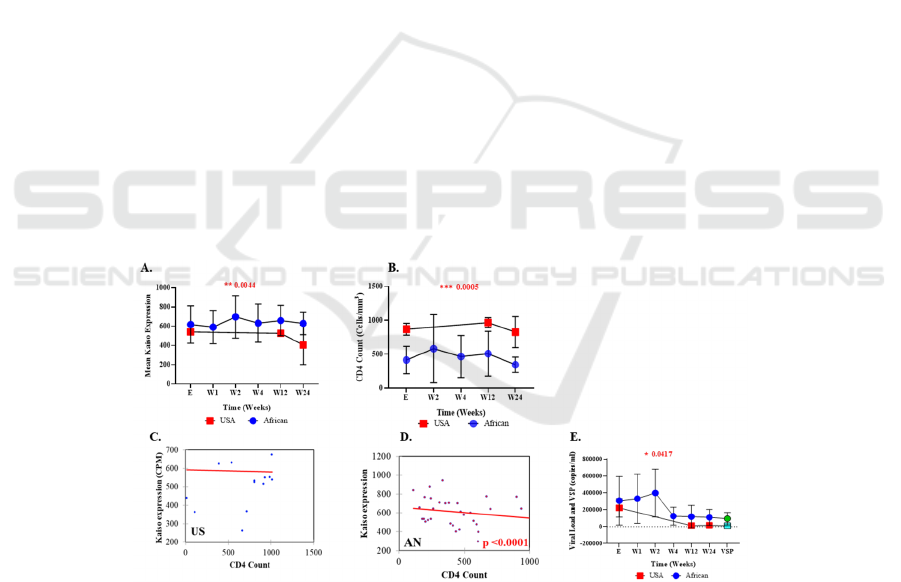
3.3 Trends in Kaiso Expression during
HIV Disease Course
Kaiso expression measured by weeks through HIV
progression (from enrollment to week 24) in US and
African patients, the results showed a significant
higher rate of Kaiso expression in African patients
compared to US HIV patients (p = 0.0044) (Figure 2-
A).
However, a highly significant difference (p =
0.0005) in CD4+ T cells count was observed which
was higher in U.S HIV patients through HIV
progression measured by weeks compared to that of
African Natives (Figure 2-B). Negative correlation
was found between CD4 count and Kaiso expression
in both U.S and African Natives patients Figures (2C
and 2-D) respectively, with significant difference (p
<0.0001). in African Natives Patients.
HIV viral load measures the number of HIV
particles or copies in a milliliter (ml) of blood cells.
Viral load decreased overtime (Figure 2-E) in both
African Natives and US patients. However, the viral
load remained significantly higher (p = 0.0417) in
African Natives (Figure 2-E).
3.4 Pathway Enrichment Analysis of
Kaiso Associated Differential
Expressed Genes
GEO2R from NCBI were used for each dataset to
compare two or more groups of samples in order to
identify genes that are differentially expressed
through experimental conditions. The results
presented as a table of genes ordered by significance.
Significant genes (p value ≤ 0.05) were further
analyzed using GSEA (gene set enrichment analysis),
Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of
Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis were
achieved for the differentially expressed genes.
In GEO2R, a comparison of HIV-1 infection to
healthy control patients in both United States and
African Native patients, heat maps used in order to
identify genes expressed through high and low
expression of Kaiso in both infected groups (Figure
3). Based on the analysis, a total of 530 differentially
expressed genes were identified in US HIV-1 patients
compared to healthy individuals, including 359
upregulated genes and 171 downregulated genes with
p <0.05 and fold change (FC) ≥1.5 set as the threshold
criteria. However, 349 differentially expressed genes
in HIV-1 infected African Native compared to
healthy control individuals with 289 upregulated
genes and 60 downregulated genes with p < 0.05 and
FC ≥1.5.
Figure 2: Negative significant correlation between Kaiso expression and CD4+ T cell count. A. Kaiso expression is
significantly higher in African Natives patients during the progression of HIV-1 infection measured by weeks with a p value
0.004 compared to US patients. B. CD4+ T cells count increase in the first weeks of infection, but decline at week 24 in both
study groups, however, CD4 count is lower in African Natives with highly significant difference (p = 0.0005) to US patients.
C. & D. Negative correlation between Kaiso expression and CD4+ T cells count in both study groups but with a significant
difference in African Natives (AN) (p < 0.0001). E. Viral load (VL) increase significantly and sharply at the first weeks of
infection in African Natives patients compared to US patients (p = 0.041), VL drops rapidly to steady state of viral set point
(VSP) the indicator of AIDS disease progression which is higher in African, this may indicate their progression to AIDS
faster than US patients.
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
92
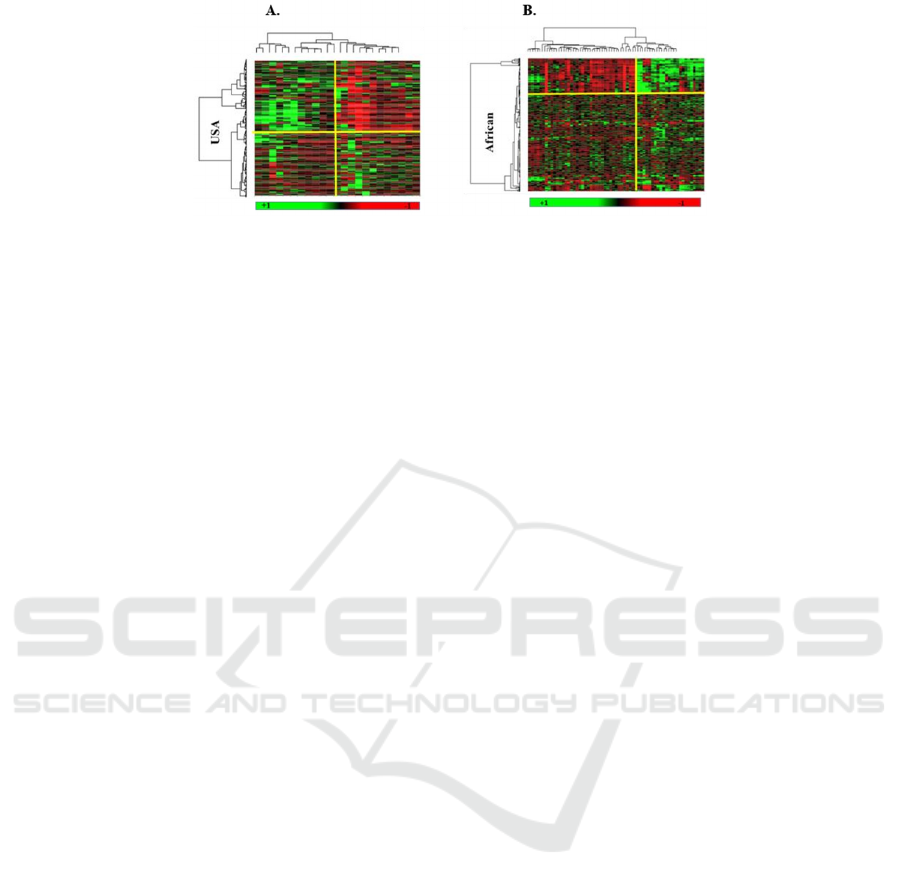
Figure 3: Gene expression analysis. Heat maps illustrating genes associates with Kaiso expression associated genes in: A. US
HIV1 patients with 530 differentially expressed genes identified, including 359 upregulated genes and 171 downregulated
genes with p <0.05 and fold change (FC) ≥1.5 set as the threshold criteria. B. African HIV-1 patients with 349 significant
expressed genes, 289 upregulated genes and 60 downregulated genes with p < 0.05 and FC ≥1.5. Green color indicates
upregulated genes in correlation to high Kaiso expression while red color indicates downregulated genes in correlation to
high Kaiso expression. Columns indicated patients while rows indicated genes.
Finally, the differentially expressed genes were
further analyzed by GSEA analysis for enriched
KEGG pathways. The results showed two pathways
correlated to Kaiso associated upregulated genes in
US patients (Figure 4-A), including “olfactory
transduction” and “Parkinson disease”, while the
Kaiso associated downregulated differentially
expressed genes were enriched in eight pathways,
“lysosome”, “ribosome”, “olfactory transduction”,
“cytokinecytokine receptor interaction”, “JAK STAT
signaling”, “hematopoietic cell lineage”, “dilated
cardiomyopathy”, “neuroactive ligand receptor
interaction” (Figure 4-B). However, ten different
pathways found in African high Kaiso differentiated
associated upregulated genes which are, “cell cycle”,
“cytokine cytokine receptor interaction”, “cell
adhesion molecules CAMS”, “P53 signaling
pathway”, “olfactory transduction”, “progesterone
mediated oocyte maturation”, and “RNA
degradation”, “oocyte meiosis”, “neuroactive ligand
receptor interaction”, “calcium signaling” (Figure
4C). Whereas, the Kaiso associated downregulated,
differentially expressed genes were enriched in three
pathways, “ribosome”, “Al-Zheimers disease”,
“neurotrophin signaling” (Figure 4-D).
4 DISCUSSION
Racial/ethnic disparities related to HIV-1 infection
and increased incidence of HIV-1 infection in African
ancestry were described in 2016 in the CDC’s HIV
surveillance report (CDC 2017). HIV infections have
been reported more in African born black immigrants
rather than U.S. born blacks (Johnson et al., 2010;
Kent, 2005; Kerani et al., 2008; Ashton et al., 2012)
with higher prevalence in African born compared to
Kaiso expression to HIV-1 pathogenesis. Results of
US born blacks and US white (Ashton et al., 2012).
Further, it is known that disease progression to AIDS
is much faster in African Natives. However, the
mechanisms underlying in these disparities and faster
progression to AIDS in Africans has not been fully
delineated. Several reported studies including
published reports (Abisoye-Ogunniyan et al., 2018;
Ahmed et al., 2019; Jones et al., 2014; Jones et al.,
2012; Jones et al., 2015; Pierre et al., 2019) showed
higher expression of Kaiso in patients with different
cancers including prostate cancer. The level of Kaiso
expression and the pathways linked to higher level of
expression appear to be linked with a few
intermediary pathways, including the Wnt pathway
(Iioka et al., 2009). While some of these pathways
have also been linked to the pathogenesis of HIV
infections and the expression of several other
immune-related genes, to our knowledge no studies
have been reported showing the role of Kaiso in the
pathogenesis of HIV infections. More importantly,
level of Kaiso expression in HIV-infected African
versus all HIV infected patients in the U.S. has not
been reported.
A significant finding in this data analysis is the
higher level of Kaiso expression in HIV infected
African patients compared to patients in the United
States. This is the first study showing a significant
negative correlation between Kaiso expression and
CD4 count in HIV-1 infection (Figure 4). In addition,
the viral load and viral set point (VSP) were
significantly higher in African HIV-1 patients
compared to US patients (p = 0.0417). A few other
studies have referred to the importance of viral set
point as a key indicator for HIV progression to AIDS
and survival (Mellors et al., 1996; Quinn et al., 2000;
Mellors et al., 1997). Clearly, no studies have been
reported previously that correlated higher level of
Kaiso expression to HIV-1 pathogenesis. Results of
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection
93
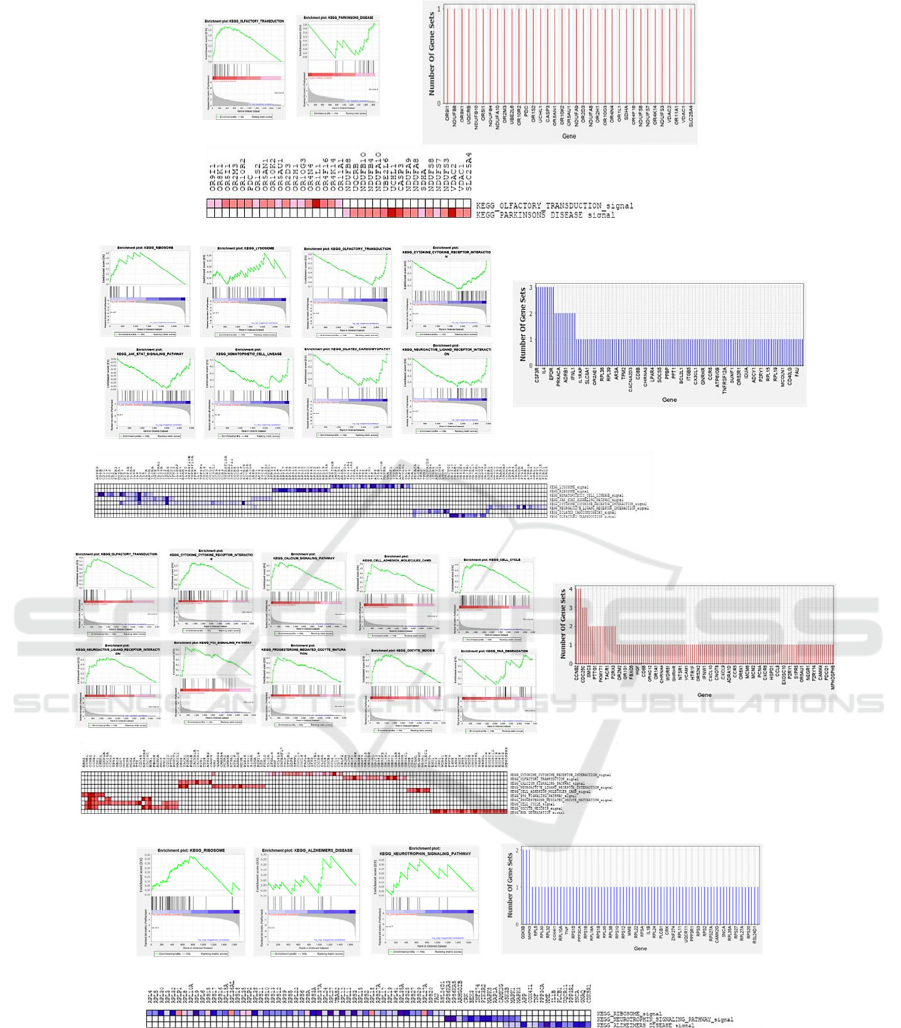
A. Upregulated genes in US patients
B.
Downregulated genes in US patients
C.
Upregulated genes in African Natives
D.
Downregulated genes in African Natives
Figure 4: Pathways correlated to high expression of Kaiso. Enrichment plot, heat map, and leading-edge analysis for the gene
sets of Kaiso associated differentially expressed genes identified in comparison between HIV infected US patients and African
Native patients. A. US Kaiso related upregulated pathways genes. B. Downregulated pathways genes. C. African Kaiso related
upregulated pathways genes. D. Downregulated pathways genes. Enrichment plot of the ranked list of significant genes (p ≤
0.05), and the heat map that shows the genes in the leading-edge subsets. In a heat map, expression values are represented by
colors, where the colors (red, pink, light blue, dark blue) represent the range of expression values (high, moderate, low, and
lowest) where red colored are upregulated genes and dark blue are downregulated genes. Bar graphs shows each gene and the
number of subsets in which it appears.
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
94

this data analysis study gives a preliminary indication
that higher rate of HIV progression to AIDS in
African patients compared to US patients may at least
partly be due to higher level of Kaiso expression.
The host factor β-catenin is the main component
of Wnt/β- catenin-signaling pathway. A study by
Iioka et al, 2009 found that, Kaiso functions as a
bimodal regulator of canonical Wnt signaling as
Kaiso enhanced Wnt/β-catenin signaling when it has
mild ectopic expression. While, moderate and higher
expression of Kaiso inhibited Wnt/βcatenin signaling
and Kaiso knockdown appears to suppress Wnt/β-
catenin activity. The same study showed that Kaiso
Binding to HDAC1 may inhibit the complex
formation between β- catenin and HDAC1 and this
may increase the negative effects of HDAC1 from the
β- catenin/TCF complex (Iioka et al., 2009).
Nonetheless, Wnt/β- catenin signaling has been
shown to interact with the life cycle of HIV-1during
infection and latency (Al-Harthi, 2012).
Different studies found that Wnt/β-catenin
pathway may be involved in HIV pathogenesis as
TCF4 has been shown to represses Tat-mediated
transactivation of HIV promoter (LTR) in astrocyte
cells (Wortman et al., 2002; Rossi et al., 2006;
Carroll-Anzinger et al., 2007). Wnt β-catenin
signaling interacts with the life cycle and replication
of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in different
target cells including, peripheral blood mononuclear
cells and astrocytes (Al-Harthi, 2012).
Our study revealed that upregulation of Kaiso is
associated with upregulation of olfactory function
genes in both US and African patients (Figure 4-A
and C), which act as a marker of HIV associated
neurological impairment (Serby et al., 1992). Studies
have shown that HIV infected patients with
neurocognitive impairment had diminished odor
sensitivity (Brody et al., 1990; Hornung et al., 1998;
Razani et al., 1996). In addition, high expression of
Kaiso was detected as methyl CpG binding protein in
nervous system cells (NS) (Martin Caballero et al.,
2009). In comparison, Kaiso improves the
locomotion mechanism and depressed behavior in a
review of Kaiso protein as a brain and behavior
regulator, Kaiso deficient mice has shown
antidepressant-like effect (Kulikova and Kulikov,
2018). Yet, Parkinson disease may develop early in
HIV infection following viral infection within the
basal ganglia or late in the disease course in
combination with AIDS dementia complex (ADC), or
as a result of underlying chronic neuroinflammation
leading to basal ganglia dysfunction, altered blood-
brain barrier (BBB) permeability, and
neurodegeneration (Berger et al., 2000).
Our study also revealed that Kaiso associated
pathways of African upregulated genes are p53, cell
cycle and CAMS (Figure 4-C). Cell cycle
dysregulated after HIV infection due to the virus
dominating cellular transcriptional machinery to
increase viral replication and proliferation (Devadas
et al., 2016). While, p53 is the main factor in host
restriction of HIV-1 replication and infection
(Mukerjee et al., 2010). However, the infection with
the virus enhances the expression of p53 in primary
CD4+ T cells (Imbeault et al., 2009a; Imbeault et al.,
2009b) in addition, p53 facilitates HIV-1 binding to
host cells by increasing expression of CD4 and
integration into host chromosome through
upregulation of integration cofactor p75 (Wang et al.,
2017a) and the activation of p53 target genes will lead
to cell apoptosis (Genini et al., 2001). Kaiso may
contribute to CD4 depletion in HIV-1 infection since
Kaiso regulate p53 and increase cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis (Koh et al., 2014) Yet, apoptosis could be
inhibited by blocking the interaction between Kaiso
and p53 by NF-kB (RelA/p65) expression which also
lead to depletion of nuclear Kaiso and sequestering
Kaiso in the cytoplasm (Koh et al., 2015). NF-kB
(RelA/p65) is important for HIV-1 transcription
initiation in primary infection and in reactivation of
HIV-1 latently infected cells (Wang et al., 2017b).
One of the upregulated pathways in African HIV-
1 infected patients correlated to high expression of
Kaiso is cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) that play a
basic role in regulating immune cell function such as
immune cell trafficking into tissues, cell proliferation
and immunological synapse formation during
homeostasis, inflammation and cancer (Harjunpää et
al., 2019). Circulating cell adhesion molecules such
as intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and
vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) are
significantly increase in HIV positive and AIDS
patients (Greenwood et al., 1998; Seigneur et al.,
1997). Also, HIV-1 gp120 significantly upregulate
ICAM-1 on brain endothelial cells in animal model
(Toneatto et al., 1999)) and increase ICAM-1 in glial
cells and leukocytes (Ren et al., 2002).
Cell adhesion cofactor p120-catenin, is the only
known binding partner for Kaiso (Daniel and
Reynolds, 1999). Interestingly, in another study by
Rodova et al, (2004) revealed that catenin delta which
is a brain-specific member of the p120 catenin
subfamily, create a complex with Kaiso and this
complex may regulates synapse-specific transcription
at the neuromuscular junction (Rodova et al., 2004).
Although multiple studies documented the role of
Kaiso in different cancer types, there are no studies
determining the Kaiso role in HIV-1 infection. In
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection
95

summary, this study with bioinformatics analysis of
the HIV infected patient data showed that Kaiso
expression is significantly higher in HIV-1 infected
males of younger ages of African ancestry compared
to other ethnic groups. Analysis of HIV-1 patient
datasets revealed that Kaiso might have a role in HIV
infection and replication in African Native patients
through different immune system genes and its
association with multiple intermediary pathways.
Moreover, a negative significant correlation between
Kaiso expression and CD4+ T cell count and this may
correlate the depletion of CD4+T cells in HIV-1
infection with Kaiso expression, additionally, our
analysis showed a positive correlation between Kaiso
expression and HIV viral load that was higher in
African ancestry compared to US patients. Taken
together, we suggest that Kaiso may act as a novel
therapeutic agent in HIV1 infection.
Further studies to analyze the role of Kaiso in
other HIV-1 infected groups needed, such as elite
controllers, and to investigate the role of Kaiso in
association with expression of different immune
system genes.
REFERENCES
Abisoye-Ogunniyan A, Lin H, Ghebremedhin A, Salam
AB, Karanam B, Theodore S, Jones-Trich J, Davis M,
Grizzle W, Wang H, Yates C., & information Abisoye-
Ogunniyan, Author. (2018). Transcriptional repressor
Kaiso promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition
and metastasis in prostate cancer through direct
regulation of miR-200c. Cancer Lett., 431, 1-10. doi:
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.044
Ashton, C., Bernhardt, S. A., Lowe, M., Mietchen, M., &
Johnston, J. (2012). Comparison of HIV/AIDS rates
between U.S.-born Blacks and African-born Blacks in
Utah, 2000 - 2009. Open AIDS J, 6, 156-162. doi:
10.2174/1874613601206010156
Albagli, O., Dhordain, P., Deweindt, C., Lecocq, G., &
Leprince, D. (1995). The BTB/POZ domain: a new
protein interaction motif common to DNA- and actin-
binding proteins. Cell Growth Differ, 6(9), 1193-1198.
Al-Harthi, L. (2012). Interplay between Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling and HIV: virologic and biologic
consequences in the CNS. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol,
7(4), 731-739. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9411-y
Ahmed Md Shakir U., Jenkins B, Adu-Addai B, Karanam
B, Davis MB, Grizzle WE, Wang H, Yates C. (2019).
Kaiso influences immune signaling of breast cancer
exosomes [abstract]. Proceedings of the American
Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting
2019; 2019 Mar 29-Apr 3; Atlanta, GA. Philadelphia
(PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2019, 79(13 Suppl), Abstract
nr 1525.
Bardwell, V. J., & Treisman, R. (1994). The POZ domain:
a conserved protein-protein interaction motif. Genes
Dev, 8(14), 1664-1677. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1664
Bassey-Archibong BI, Hercules SM, Rayner LGA, Skeete
DHA, Smith Connell SP, Brain I, Daramola A, Banjo
AAF, Byun JS, Gardner K, Dushoff J, Daniel JM.
(2017). Kaiso is highly expressed in TNBC tissues of
women of African ancestry compared to Caucasian
women. Cancer Causes Control. , 28(11), 1295-1304.
doi: doi: 10.1007/s10552-0170955
Berger, J. R., Nath, A., Greenberg, R. N., Andersen, A. H.,
Greene, R. A., Bognar, A., & Avison, M. J. (2000).
Cerebrovascular changes in the basal ganglia with HIV
dementia. Neurology, 54(4), 921-926. doi: 10.1212/
wnl.54.4.921
Brody, D., Adler, L. A., Kim, T., Angrist, B., Rotrosen, J.
(1990). Effects of buspirone in seven schizophrenic
subjects. J Clin Psychopharmacol, 10(1), 68-69. doi:
10.1097/00004714-199002000-00025
Carroll-Anzinger, D., Kumar, A., Adarichev, V.,
Kashanchi, F., Al-Harthi, L. (2007). Human
immunodeficiency virusrestricted replication in
astrocytes and the ability of gamma interferon to
modulate this restriction are regulated by a downstream
effector of the Wnt signaling pathway. J Virol, 81(11),
5864-5871. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02234-06
CDC. 2017 https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/statistics/overview/
ataglance html.
CMAJ Open, 2(4), E318-329. doi: 10.9778/
cmajo.20140017
Daniel, J. M., & Reynolds, A. B. (1999). The catenin
p120(ctn) interacts with Kaiso, a novel BTB/POZ
domain zinc finger transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol,
19(5), 3614-3623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.5.3614.
Devadas, K., Biswas, S., Haleyurgirisetty, M., Wood, O.,
Ragupathy, V., Lee, S., Hewlett, I. (2016). Analysis of
Host Gene Expression Profile in HIV-1 and HIV-2
Infected T-Cells. PLoS One, 11(1), e0147421. doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0147421
Greenwood, A. J., Hughes, J., Wallace, G., Seed, P.,
Stanford, M. R., Graham, E. M. (1998). Soluble
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) in
patients with HIV/AIDS does not appear to correlate
with cytomegalovirus retinitis. Int J STD AIDS, 9(11),
713-714.
Genini, D., Sheeter, D., Rought, S., Zaunders, J. J., Susin,
S. A., Kroemer, G., Richman, D. D., Carson, D. A.,
Corbeil, J., Leoni, L. M. (2001). HIV induces
lymphocyte apoptosis by a p53-initiated,
mitochondrial-mediated mechanism. FASEB J, 15(1),
5-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0336fje
Harjunpää Heidi, Llort Asens Marc, Guenther Carla,
Fagerholm Susanna C. (2019). Cell Adhesion
Molecules and Their Roles and Regulation in the
Immune and Tumor Microenvironment Frontiers in
Immunology, 10, 1078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01
078
Hall, H. I., Byers, R. H., Ling, Q., & Espinoza, L. (2007).
Racial/ethnic and age disparities in HIV prevalence and
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
96

disease progression among men who have sex with men
in the United States. Am J Public Health, 97(6), 1060-
1066. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2006.087551
Hornung, D. E., Kurtz, D. B., Bradshaw, C. B., Seipel, D.
M., Kent, P. F., Blair, D. C., Emko, P. (1998). The
olfactory loss that accompanies an HIV infection.
Physiol Behav, 64(4), 549-556. doi: 10.1016/s0031-
9384 (98)00112-7
Imbeault, M., Ouellet, M., Tremblay, M. J. (2009b).
Microarray study reveals that HIV-1 induces rapid
type-I interferondependent p53 mRNA up-regulation in
human primary CD4+ T cells. Retrovirology, 6, 5. doi:
10.1186/1742-4690-6-5
Imbeault, M., Lodge, R., Ouellet, M., Tremblay, M. J.
(2009a). Efficient magnetic bead-based separation of
HIV-1infected cells using an improved reporter virus
system reveals that p53 up-regulation occurs
exclusively in the virusexpressing cell population.
Virology, 393(1), 160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.
07.009
Jones, J., Wang, H., Karanam, B., Theodore, S., Dean-
Colomb, W., Welch, D.R., Yates, C. (2014). Nuclear
localization of Kaiso promotes the poorly differentiated
phenotype and EMT in infiltrating ductal carcinomas.
Clin Exp Metastasis, 31(5), 497-510. doi:
10.1007/s10585-014-9644-7
Jones, J., Wang, H., Zhou, J., Hardy, S., Turner, T., Austin,
D., Yates, C. (2012). Nuclear Kaiso indicates
aggressive prostate cancers and promotes migration and
invasiveness of prostate cancer cells. Am J Pathol,
181(5), 1836-1846. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.008
Jones J, Wang H, Theodore Sh, Karanam B, Welch DR,
Grizzle W, Yates C. (2015). Nuclear localization of
Kaiso is a prognostic biomarker in African American
Women and promoter of EMT in infiltrating ductal
breast carcinomas. Clinical and Experimental
Metastasis 32(3), 248. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.
15_suppl.e22061
Johnson, A. S., Hu, X., & Dean, H. D. (2010).
Epidemiologic differences between native-born and
foreign-born black people diagnosed with HIV
infection in 33 U.S. states, 2001-2007. Public Health
Rep, 125 Suppl 4, 61-69. doi: 10.1177/00333549
101250S410
Kent, J. B. (2005). Impact of foreign-born persons on HIV
diagnosis rates among Blacks in King County,
Washington. AIDS Educ Prev, 17(6 Suppl B), 60-67.
doi: 10.1521/aeap.2005.17.Supplement B.60
Kerani, R. P., Kent, J. B., Sides, T., Dennis, G., Ibrahim, A.
R., Cross, H., Golden, M. R. (2008). HIV among
African born persons in the United States: a hidden
epidemic? J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr, 49(1), 102-
106. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181831806
Klein, M. B., Young, J., Dunn, D., Ledergerber, B., Sabin,
C., Cozzi-Lepri, A., Canadian-European Clade,
Collaboration. (2014). The effects of HIV-1 subtype
and ethnicity on the rate of CD4 cell count decline in
patients naive to antiretroviral therapy: a Canadian-
European collaborative retrospective cohort study.
Kulikova, E. A., and Kulikov, A. V. (2018). Kaiso Protein
in the Regulation of Brain and Behavior. Curr Protein
Pept Sci, 19(7), 692-698. doi: 10.2174/1389203
718666171030104618
Koh, D. I., Han, D., Ryu, H., Choi, W. I., Jeon, B. N., Kim,
M. K., Hur, M. W. (2014). KAISO, a critical regulator
of p53-mediated transcription of CDKN1A and
apoptotic genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111(42),
15078-15083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318780111
Koh, D. I., An, H., Kim, M. Y., Jeon, B. N., Choi, S. H.,
Hur, S. S., Hur, M. W. (2015). Transcriptional activation
of APAF1 by KAISO (ZBTB33) and p53 is attenuated
by RelA/p65. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1849(9), 1170-
1178. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.008
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r/
http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp.
http://Rstudio.org.
Iioka, H., Doerner, S. K., Tamai, K. (2009). Kaiso is a
bimodal modulator for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
FEBS Lett, 583(4), 627-632. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.
2009.01.012
Martin Caballero, I., Hansen, J., Leaford, D., Pollard, S.,
Hendrich, B. D. (2009). The methyl-CpG binding
proteins Mecp2, Mbd2 and Kaiso are dispensable for
mouse embryogenesis, but play a redundant function in
neural differentiation. PLoS One, 4(1), e4315. doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0004315
Mellors, J. W., Rinaldo, C. R., Jr., Gupta, P., White, R. M.,
Todd, J. A., Kingsley, L. A. (1996). Prognosis in HIV-
1 infection predicted by the quantity of virus in plasma.
Science, 272(5265), 1167-1170. doi: 10.1126/science.
272.5265.1167
Mellors, J. W., Munoz, A., Giorgi, J. V., Margolick, J. B.,
Tassoni, C. J., Gupta, P., Kingsley, L. A., Todd, J. A.,
Saah, A. J., Detels, R., Phair, J. P., Rinaldo, C. R., Jr.
(1997). Plasma viral load and CD4+ lymphocytes as
prognostic markers of HIV-1 infection. Ann Intern
Med, 126(12), 946-954. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-
12-199706150-00003
Mukerjee, R., Claudio, P. P., Chang, J. R., Del Valle, L.,
Sawaya, B. E. (2010). Transcriptional regulation of
HIV-1 gene expression by p53. Cell Cycle, 9(22), 4569-
4578. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.22.13836
Pierre, C. C., Hercules, S. M., Yates, C., Daniel, J. M.
(2019). Dancing from bottoms up - Roles of the POZ-
ZF transcription factor Kaiso in Cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 1871(1), 64-74. doi:
10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.10.005
Quinn, T. C., Wawer, M. J., Sewankambo, N., Serwadda,
D., Li, C., Wabwire-Mangen, F., Meehan, M. O.,
Lutalo, T., Gray, R. H. (2000). Viral load and
heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency
virus type 1. Rakai Project Study Group. N Engl J Med,
342(13), 921-929. doi:10.1056/NEJM20000330342
1303
Razani, J., Murphy, C., Davidson, T. M., Grant, I.,
McCutchan, A. (1996). Odor sensitivity is impaired in
HIV-positive cognitively impaired patients. Physiol
Behav, 59(4-5), 877-881. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(95)
02163-9
Novel Role of Transcriptional Factor Kaiso in HIV Infection
97

Ren, Z., Yao, Q., Chen, C. (2002). HIV-1 envelope
glycoprotein 120 increases intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 expression by human endothelial cells. Lab
Invest, 82(3), 245-255.doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3780418.
Rodova, M., Kelly, K. F., VanSaun, M., Daniel, J. M., &
Werle, M. J. (2004). Regulation of the rapsyn promoter
by kaiso and delta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol, 24(16), 7188-
7196. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7188-7196.2004.
Rossi, A., Mukerjee, R., Ferrante, P., Khalili, K., Amini, S.,
Sawaya, B. E. (2006). Human immunodeficiency virus
type 1 Tat prevents dephosphorylation of Sp1 by TCF-
4 in astrocytes. J Gen Virol, 87(Pt 6), 1613-1623. doi:
10.1099/vir.0.81691-0
Serby M.J., Larson P.M., Kalkstein D. (1992) In: Serby
M.J., Chobor K.L. (eds) Science of Olfaction. Springer,
New York, NY. (1992). Olfaction and
Neuropsychiatry., 559-. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/
978-1-4612-2836-3_21.
Seigneur, M., Constans, J., Blann, A., Renard, M.,
Pellegrin, J. L., Amiral, J., Boisseau, M., Conri, C.
(1997). Soluble adhesion molecules and endothelial cell
damage in HIV infected patients. Thromb Haemost,
77(4), 646-649.
Toneatto, S., Finco, O., van der Putten, H., Abrignani, S.,
Annunziata, P. (1999). Evidence of blood-brain barrier
alteration and activation in HIV-1 gp120 transgenic
mice. AIDS, 13(17), 2343-2348. doi:
10.1097/00002030-19991203000005.
Wang H, Yates C., Liu, W., Black, S., Turner, O., Daniel,
J.M., Dean-Colomb, W., He, QP., Davis, M. (2016).
Kaiso, a transcriptional repressor, promotes cell
migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through
regulation of miR-31 expression. Oncotarget, 7(5),
5677-5689.
Wang X, Zhao J, Mbondji C, Hewlett I (2017a). p53
Expression Activation of HIV-1 Latency in U1 Cells.
Int J Virol AIDS 3, 036. doi: doi.org/10.23937/2469-
567X/1510036
Wang, P., Lu, P., Qu, X., Shen, Y., Zeng, H., Zhu, X., .Zhu,
H. (2017b). Reactivation of HIV-1 from Latency by an
Ingenol Derivative from Euphorbia Kansui. Sci Rep,
7(1), 9451. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07157-0
WHO, https://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en/. UNAIDS’AIDS
info’. (2019). accessed November 2019.
Wortman, B., Darbinian, N., Sawaya, B. E., Khalili, K., &
Amini, S. (2002). Evidence for regulation of long
terminal repeat transcription by Wnt transcription
factor TCF-4 in human astrocytic cells. J Virol, 76(21),
11159-11165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.21.11159-11165
.2002
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
98
