
Implementation and Feasibility Analysis of a Javascript-based
Gambling Tool Device for Online Decision Making Task under Risk
in Psychological and Health Services Research
Sherine Franckenstein
1
, Sebastian Appelbaum
1,2
and Thomas Ostermann
1
1
Methods and Statistics in Psychology, Faculty of Health, Witten/Herdecke University, Germany
2
Trimberg Research Academy, University of Bamberg, Germany
Keywords: Decision Making, Online-surveys, Game of Dice Task, Javascript.
Abstract: Decision making is one of the most complex tasks in human behavior. In the past, researchers have tried to
understand how humans make decisions by designing neuropsychological tests to assess reward related
decision making by evaluating the preference for smaller but immediate rewards over larger but delayed
rewards or by evaluating the tolerance of risk in favor of a desired reward. The latter are also known as
gambling tasks. Today, information technology offers a variety of possibilities to investigate behaviour under
risk. After a short introduction on gambling tasks and in particular the game of dice task, this article describes
the development and implementation of a JavaScript-based gambling tool for online surveys based on a game
of dice task. In a pilot feasibility study with 170 medical students, participants were randomly assigned to a
“REAL condition”, based on the probabilities of the chosen bet and a “FAKE condition” where participants
lose all the time independently of the chosen bet. We were able to show that the software was well accepted
with only 14.7% of drop outs. Moreover, we also found a difference between the FAKE and the REAL group:
Participants in the FAKE condition in the mean steadily increased their stake while then control group quite
early tended to run a safer strategy. This is also obvious when the overall stake mean is compared: While in
the REAL condition the mean stake is 310.89 ± 222.98 €, the FAKE condition has an overall mean of 390.38
± 296.50 €. In conclusion, this article clearly indicates how a JavaScript based gambling tool can be used for
psychological online research.
1 INTRODUCTION
Decision-making is one of the most complex tasks in
human behavior (Brand, et al., 2005). In the past,
researchers have tried to understand how humans
make decisions, especially in risky situations. A few
researchers found neuropsychological correlates of
decision-making in risk situations and designed
neuropsychological tests to assess reward related
decision making by evaluating the preference for
smaller but immediate rewards over larger but
delayed rewards or by evaluating the tolerance of risk
in favor of a desired reward (Brand et al., 2006). The
latter are also known as gambling tasks.
Various types of those gambling tasks have been
used for experimental situations to investigate
decision-making under ambiguous conditions. The
most commonly known gambling tasks are the Iowa
Gambling Task (IGT) (Bechara et al., 1994). In this
task, the subjects can win or lose virtual money by
repealing cards from four different decks. Due to the
fact that the expected values are unknown,
participants have to learn by experience which decks
are advantageous. Bechara et al. (1994) developed the
IGT with two decks who are either overall
advantageous or overall disadvantageous. In previous
studies the research group has found that the
participants took cards towards the advantageous
decks.
Wagar & Dixon (2006) explained this fact that the
participants base their decision on conscious pleasant
feelings. Later in the IGT the participants got a
feedback (negative or positive) from the result by
picking cards the four different decks. In this game,
the participants were given a 2000 Euros as a bank
balance. They saw decks in front of them and had to
choose one of them. The players have 100 trials, but
this fact is unknown to the participants.
After picking cards from one of the four decks the
participants got a feedback, some cards generate a
profit and some cards generate a loss (Figure 1).
Franckenstein, S., Appelbaum, S. and Ostermann, T.
Implementation and Feasibility Analysis of a Javascript-based Gambling Tool Device for Online Decision Making Task under Risk in Psychological and Health Services Research.
DOI: 10.5220/0010826700003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 469-474
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
469
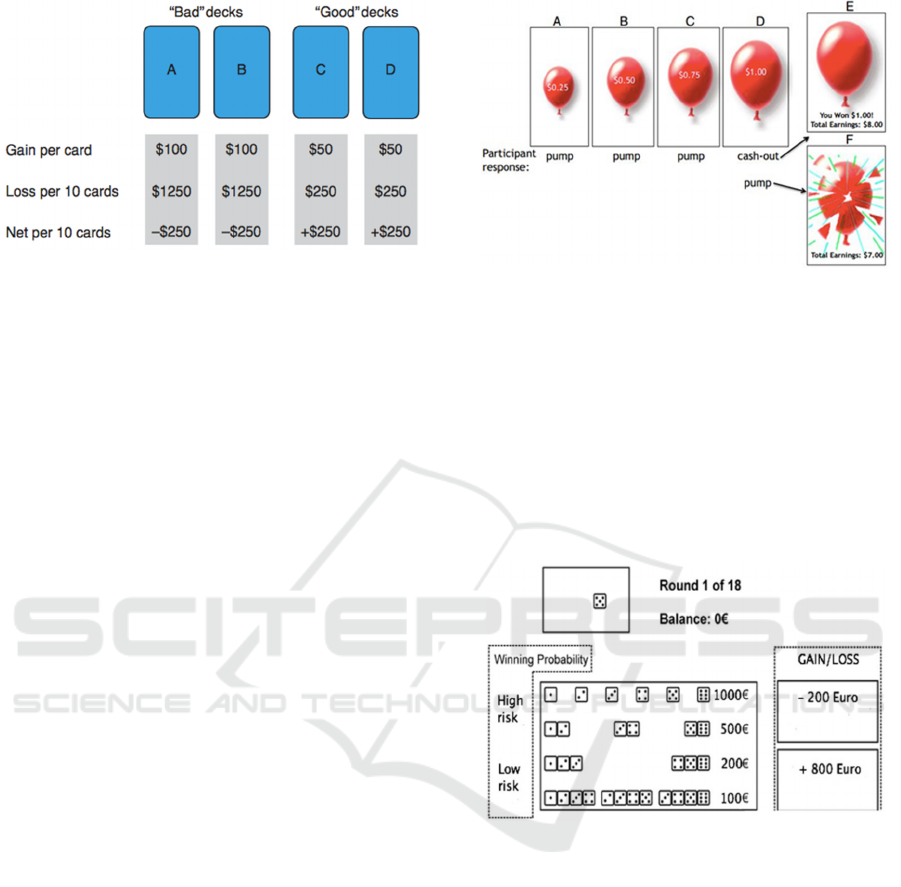
Figure 1: Screenshot of the Iowa Gamling Task from
Bechara, Damasio, Tranel & Damasio (2005).
The instruction of the game is that participants
play in such a way that they would win as much
money as possible, meaning the subjects had to learn
by previous trials, which is the best strategy for
winning. If participants decided to play cards mostly
from the disadvantageous decks, they lose 250 Euros
in every ten cards and if they play cards mostly from
the advantageous decks, they gain 250 Euros in every
ten cards (Bechara et al., 1994).
The Balloon Task
Another task to investigate research questions by
using computerized method is the Balloon Analogue
Risk Task (BART) (Lejuez et al., 2002) which
measures risk behavior of participants.
In the task, the subjects are presented different
kind of balloons. The participants` aim is to earn as
much money as possible by pumping air in the
balloon. Every click inflates air in the balloon, but
with each following click the balloon can explode
(Figure 2).
Thus, the participants entered a high risk by
inflating a lot of air by clicking the button. On the
other hand, they have the opportunity to gain more
money by taking the risk option. However, the
balloon breakpoints are unknown for the participants.
In this experimental design the subjects have 10
opportunities to win money by inflating air into
balloons.
The Game of Dice Task
In the original task which was developed by Brand et
al. (2006) the participants have to guess the outcome
of the game. The participants are introduced to the
gain maximum which can be achieved within 18
attempts with a virtual dice task.
Figure 2: Screenshot of Balloon Analogue Risk Task
(BART) from (Lejuez et al., 2002).
In the game, the participants can choose between
different options to play the game. There are the
options to choose one dice or a combination of two,
three or four dices. These different options are
associated with different bets. The bets are associated
with different expected values for gains and losses
(associated with 1:6, gains/losses 1000 Euros, 2:6,
500 Euros, 3:6, 200 Euros and 4:6, 100 Euros; Figure
3)).
Figure 3: Screenshot of Game of Dice task from Gorini et
al., (2014).
The game starts with a virtual capital of 1000
Euro. The participants lose, when there is
incongruency between the bet option and the real
outcome of the die. The different bet options die or a
combination of two, three or four dice are associated
with a risk or safe decision-making, because the best
choice is to play with four dice (expected values are
positive). In contrast, participants who choose the bet
options (one die), make a high-risk decision, because
they lose in 1:6 times.
In the original version the strategy of decision
making is reflected by the virtual starter capital.
Participants who make a safe decision-making gain a
higher starter capital at the end.
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
470
One important impact on decision-making
processes are the executive functions. In the Game of
Dice task the participants were explicitly informed
about the rules and the outcome was defined by
probabilities. Thus, the best choice to play this task is
to estimate the expected values. In the past,
researchers have focused on decision-making with
patients, who suffer from diseases like Korsakoff’s
syndrome (Brand et al., 2005) or Parkinson’s disease
(Brand et al., 2006).
Most gambling tasks originally were run without
a computer, however, today computerized versions of
gambling tasks are useful, as they allow for the task
to be used in more complex experimental and online
settings and can make the task more standardized
across studies (Dancy & Ritter, 2016).
Although there is a high demand for computerized
versions, only a few platform independent versions of
such tasks are freely available for download.
This article presents a JavaScript-based gambling
tool device for decision making tasks in
psychological research based on the Game of Dice
from Brand et. al. (2006).
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
We took the Game of Dice task from Brand et al.
(2006) as a template and developed a new version of
the Game of Dice task to investigate decision making
with negative Feedback.
For this reason, we developed a software in
JavaScript in which the participants either are
exposed with the mathematically expected feedback
based on the winning probabilities (control condition
“REAL”) or with negative feedback in all bets and
thus, lose all their virtual capital in the course of time
independently of the true probabilities (experimental
condition “FAKE”).
The software can be freely configured to deliver
random results as well as always losses for the player.
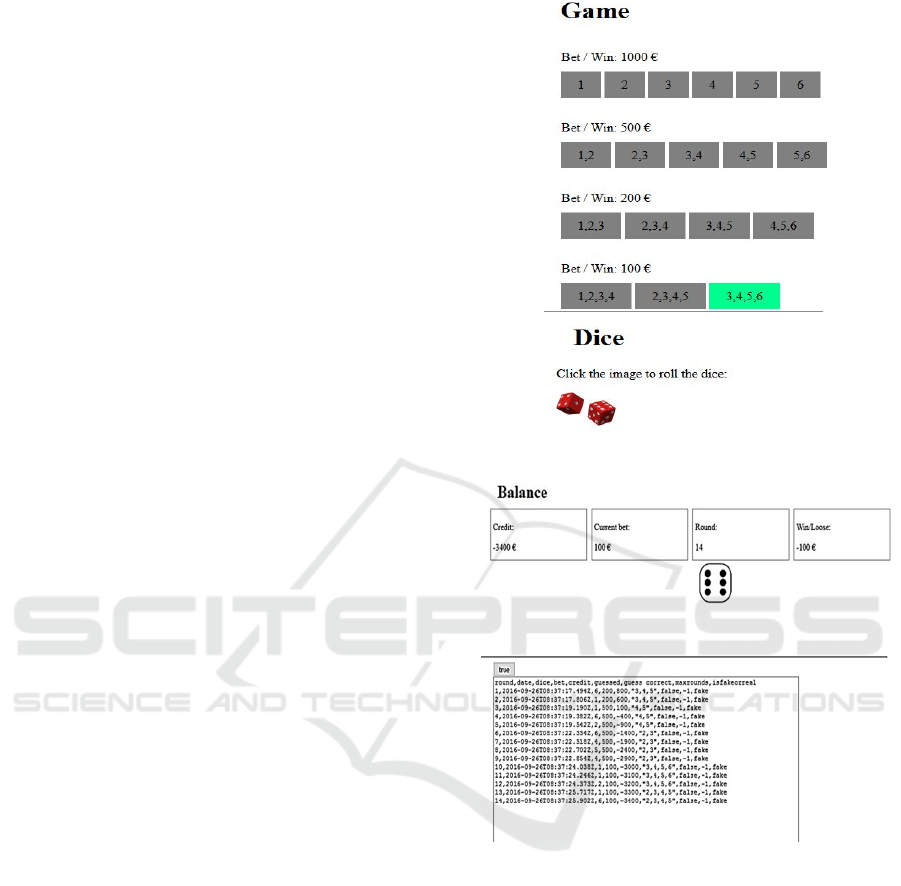
Figure 4 shows the different available bet options.
The players have to choose if they play the game with
one, two, three or four dices. In the heading,
participants have the opportunity to see the expected
values. Thus, all of them have the opportunity to
choose the best strategy.
Normally, the best mathematical strategy has to be
retained independently from processed feedback.
Therefore, we record all user responses. For further
processing, data is stored as a Comma Separated
Value (CSV-) file.
Figure 4: Screenshot of our proposed Dice Game.
Figure 5: Screenshot of bank balance and the hidden
capture choices.
Figure 5 shows the hidden capture choices.
Firstly, we document some standard information like
the day, time or reaction time of a player.
Additionally, we record which bet options were
chosen by each participant. Moreover, information
whether the bet was performed correctly and if the
subjects won the bet is documented. Furthermore, we
gather the experimental conditions (FAKE or REAL).
Figure 6 shows the decision diagram in the
experimental conditions.
As can be seen, the outcome in the FAKE
condition is independent from the participant’s
behavior, because the participants lose all the time
anyway.
Implementation and Feasibility Analysis of a Javascript-based Gambling Tool Device for Online Decision Making Task under Risk in
Psychological and Health Services Research
471
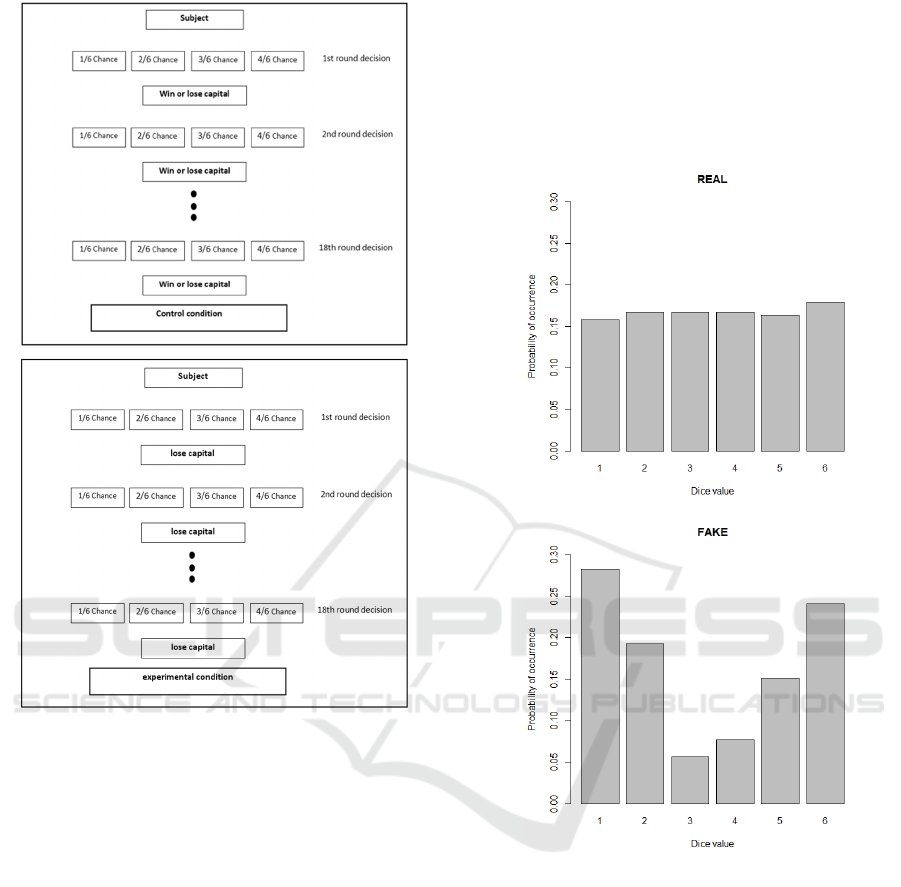
Figure 6: Flow chart of the control conditions “REAL” and
the experimental condition “FAKE”.
Based on JavaScript and HTML we developed a
program that it is platform independent. The
participant only needs a common Web-Browser to
play the game.
For our pilot study, we decided to integrate our
program into the survey tool “Unipark“ using the
common library jQuery which is already provided by
„Unipark“ (Questback GmbH, 2015). The source
code of our JavaScript gambling tool can be obtained
from the authors.
3 RESULTS
In a first pilot study, we tested the feasibility of our
approach in 170 students and staff members of the
School of Medicine of Witten/Herdecke University.
Two third of the participants were female (N=113,
66.5%) and 57 were male (33.5%) with a mean age of
24.18 ± 8.05 years.
Participants were equally allocated to either the
FAKE or the REAL condition. A total of 40 rounds
were preset. Participants were able to stop the
experiment after each round and 145 participants (70
in the FAKE group and 75 in the REAL group)
completed at least one round, which corresponds to a
dropout rate of 14.7%.
Figure 7: Distribution of the dice values in the FAKE and
the REAL condition.
Figure 7 shows the distribution of the dice values
in the FAKE and the REAL condition. As to be
expected, there is an almost uniform distribution in
the REAL condition whilst in the FAKE condition
shows a U-shaped distribution, which was also to be
expected based on the dice pattern distribution from
Figure 4. Thus, from the technical point of view, the
dice algorithm works.
Next, we wanted to know, whether the
participants behaved different in the two groups with
respect to the gambling strategy. We suspected that
participants in the FAKE group would increase their
bets as the game progressed due to the continued
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
472
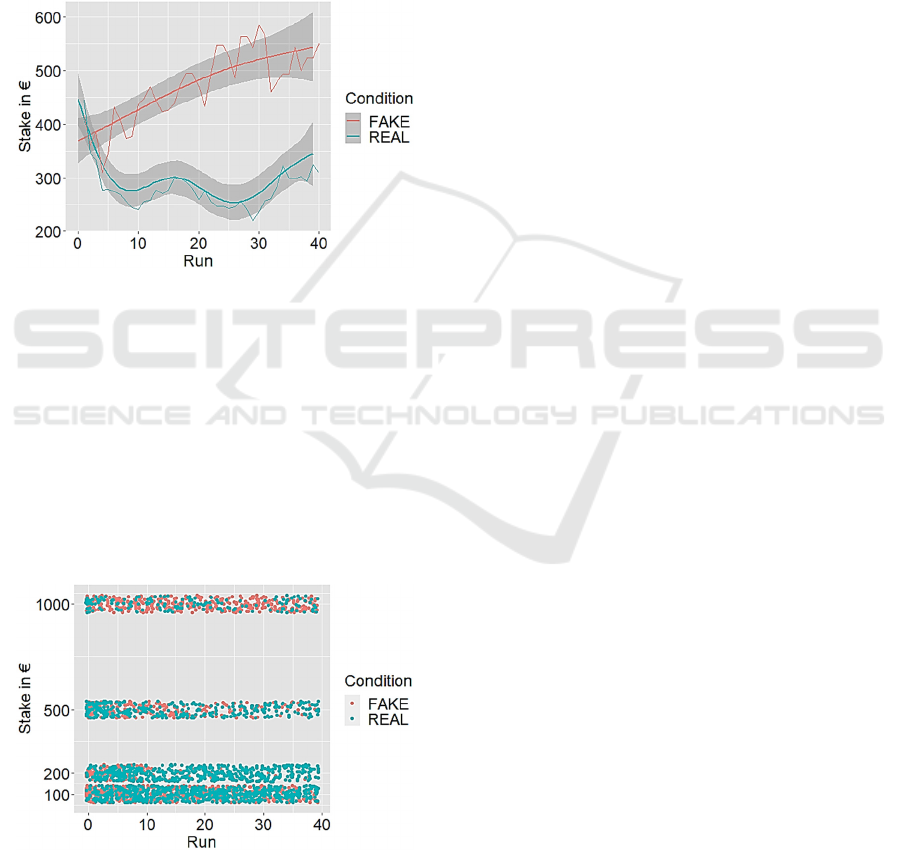
losing streak. Figure 8 shows the mean stake in € in
the course of the game subdivided by the two groups.
In accordance with our hypothesis, participants in
the FAKE condition in the mean steadily increased
their stake while then control group quite early tended
to run a safer strategy. This is also obvious when the
overall stake mean is compared: While in the REAL
condition the mean stake is 310.89 ± 222.98 €, the
FAKE condition has an overall mean of 390.38 ±
296.50 €. However, this overall mean difference did
not turn out to be significant (t-test; df= 127.85, p=
0.07193 95% CI: [-7.19; 166.17]).
Figure 8: Mean stake in € in the course of the game
subdivided by the FAKE and the REAL condition. The grey
area denotes the 95% confidence interval.
The difference in the gambling behavior is also
obvious in type of bet the
participants in each group
did choose. While for the 100€ and the 200€ bet (the
4-dice and 3-dice pattern bets) the number of blue
dots increase within the course of time, we similarly
observe an increase of the red dots in the risky bet of
1000€ (the 1-dice bet).
Fig 9 shows the distribution of the bets over the
four betting types as a scatterplot.
Figure 9: Distribution of the bets over the four betting types
as a scatterplot subdivided by FAKE (red dots) and REAL
(blue dots).
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study demonstrates the feasibility of a software
bundle for studies in decision-making analysis. We
were able to show that the software worked in line
with our hypotheses and was well accepted of the
participants of the study.
It clearly shows how an implementation of the
dice game in JavaScript can enrich online surveys in
psychological research i.e. in the framework like
“Unipark“ (Questback GmbH, 2015).
Online behavioral experiments have a number of
new technical and scientific challenge opportunities
(Gureckis et al., 2014). Testing participants online
with this kind of approach is more efficient and due
to its JavaScript based approach can be integrated in
other kinds of online surveys. Thus, accessibility and
availability for various populations are enhanced,
whereas Paper-Pencil studies are limited by
geographic reasons with respect to selecting
participants. Especially in challenging times such as
lockdowns this might serve as a good opportunity to
carry our behavioral experiments without a loss of
quality as demonstrated in (Nalbantoglu, 2021).
With respect to our survey a number of interesting
aspects to use our software are given: It might be
interesting to know whether an increased disposition
for risk taking behavior or tolerance of ambiguity
might correlate with a certain type of gambling
behavior.
Findings of a relationship between risk taking
behavior and gambling behavior was shown in the
study by Müller et al. (2021). They studied subjects
with problematic social network use. Problematic
social network use is a kind of gambling behavior and
Bouna-Pyrrou et al. (2018) showed that problematic
social network use has an addiction like potential.
Similar findings were found by Meshi et al.
(2019). They investigated whether subjects with
excessive SNS (social networking sites , like
Instagram) utilization correlated with difficulty
making decisions.
In other studies, the duration of use of social
media would be an interesting point, since the age of
our sample has a mean age of 24.18 ± 8.05 years. In
addition, FAKE`S analysis reveals a group of subjects
that chose a high-risk gambling behavior. This might
correspond to older findings of Huber (2004), who
showed that subjects under ambiguity use emotional
feedback from similar situations for the current
situation to make decisions.
An exciting question for further work would be,
whether the permanent use of social media, especially
Implementation and Feasibility Analysis of a Javascript-based Gambling Tool Device for Online Decision Making Task under Risk in
Psychological and Health Services Research
473

among young people, leads to a permanent change in
decision-making.
In conclusion, there are other relevant
psychological correlations to be investigated.
Nevertheless, physiological parameters should not be
neglected.
A further promising step is to combine this
software with the measurement of physiological
measures such as skin conductance response or heart
rate variability, which in current studies have shown
a response when manipulating the decks in the IGT
(Priolo et al., 2021)
Thus, the analysis of such traits and experimental
parameters in combination with this software bundle
will be the next challenge to be faced.
REFERENCES
Brand, M., Kalbe, E., Labudda, K., Fujiwara, E., Kessler,
J., & Markowitsch, H. J., 2005. Decision-making
impairments in patients with pathological gambling.
Psychiatry research 133(1), 91-99.
Brand, M., Labudda, K., & Markowitsch, H. J., 2006.
Neuropsychological correlates of decision-making in
ambiguous and risky situations. Neural Networks,
19(8), 1266-1276.
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Tranel, D., & Damasio, A. R.,
1997. Deciding advantageously before knowing the
advantageous strategy. Science, 275(5304), 1293-1295.
Bechara, A., Damasio, A. R., Damasio, H., & Anderson, S.
W., 1994. Insensitivity to future consequences
following damage to human prefrontal cortex.
Cognition, 50(1), 7-15.
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Tranel, D., & Damasio, A. R.,
2005. The Iowa Gambling Task and the somatic marker
hypothesis: some questions and answers. Trends in
cognitive sciences, 9(4), 159-162.
Bouna-Pyrrou, P., Aufleger, B., Braun, S., Gattnar, M.,
Kallmayer, S., Wagner, H., ... & Lenz, B. (2018).
Cross-sectional and longitudinal evaluation of the
social network use disorder and internet gaming
disorder criteria. Frontiers in psychiatry, 9, 692.
Dancy, C. L., & Ritter, F. E., 2016. IGT-Open: An open-
source, computerized version of the Iowa Gambling
Task. Behavior Research Methods, 1-7.
Gorini, A., Lucchiari, C., Russell-Edu, W., & Pravettoni,
G., 2014. Modulation of risky choices in recently
abstinent dependent cocaine users: a transcranial direct-
current stimulation study. Frontiers in human
neuroscience, 8, 661.
Gureckis, T. M., Martin, J., McDonnell, J., Rich, A. S.,
Markant, D., Coenen, A., Chan, P., 2015. psiTurk: An
open-source framework for conducting replicable
behavioral experiments online. Behavior research
methods 48(3):829-42.
Huber, O., 2004. Entscheiden unter Risiko: Aktive Risiko-
Entschärfung. Psychologische Rundschau, 55(3), 127-
134.
Lejuez, C. W., Read, J. P., Kahler, C. W., Richards, J. B.,
Ramsey, S. E., Stuart, G. L., Strong, D. R., & Brown,
R. A., 2002. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk
taking: the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART).
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 8, 75-84.
Meshi, D., Elizarova, A., Bender, A., & Verdejo-Garcia, A.
(2019). Excessive social media users demonstrate
impaired decision making in the Iowa Gambling
Task. Journal of behavioral addictions, 8(1), 169-173.
Müller, S. M., Wegmann, E., Arias, M. G., Brotóns, E. B.,
Giráldez, C. M., & Brand, M. (2021). Deficits in
executive functions but not in decision making under
risk in individuals with problematic social-network
use. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 106, 152228.
Nalbantoglu Yilmaz, F., 2021. Comparing Paper-Pencil and
Computer-Based Tests: A Meta-Analysis Study in the
Sample of Turkey. Eurasian Journal of Educational
Research, 93, 279-300.
Priolo, G., D’Alessandro, M., Bizzego, A., & Bonini, N.,
2021. Normatively Irrelevant Affective Cues Affect
Risk-Taking under Uncertainty: Insights from the Iowa
Gambling Task (IGT), Skin Conductance Response,
and Heart Rate Variability. Brain sciences, 11(3), 336.
Questback GmbH, 2015. EFS Survey, Version 10.5. Köln:
Questback GmbH.
Wagar, B. M., & Dixon, M., 2006. Affective guidance in
the Iowa gambling task. Cognitive, Affective, &
Behavioural Neuroscience, 6, 277–290.
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
474
