
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images
George Killick
a
, Gerardo Aragon-Camarasa
b
and J. Paul Siebert
c
School of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, U.K.
Keywords:
Foveated, Convolution, Retina, Implict, Neural, Representations.
Abstract:
Foveated vision captures a visual scene at space-variant resolution. This makes the application of parame-
terized convolutions to foveated images difficult as they do not have a dense-grid representation in cartesian
space. Log-polar space is frequently used to create a dense grid representation of foveated images, however
this image representation may not be appropriate for all applications. In this paper we rephrase the convo-
lution operation as the Monte-Carlo estimation of the filter response of the foveated image and a continuous
filter kernel, an idea that has seen frequent use for deep learning on point clouds. We subsume our convolu-
tion operation into a simple CNN architecture that processes foveated images in cartesian space. We evaluate
our system in the context of image classification and show that our approach significantly outperforms an
equivalent CNN processing a foveated image in log-polar space.
1 INTRODUCTION
We are concerned with the application of parame-
terized convolution filters to non-uniformly sampled
images, particularly those produced by foveated sen-
sors. Foveated sensors reduce image size by decreas-
ing sampling resolution as a function of eccentricity
from some location within the visual scene (the fixa-
tion location). In some computer vision applications,
it may be desirable to extract high-frequency informa-
tion and operate on a wide field of view. This may be
computationally intractable if the required resolution
and field of view is excessively high, as many com-
puter vision algorithms have a computational com-
plexity that scales with image size. Foveated sensors
aim to emulate operating on the full resolution image
by fixating on important high-frequency information
while still sampling a large field of view. The out-
put of a foveated sensor is significantly smaller than
the full resolution image and is consequently compu-
tationally feasible to operate on with deep neural net-
works.
Due to the non-uniform sampling of a visual scene
through a foveated sensor, applying convolutional
neural networks to foveated images is difficult as con-
volution layers expect input data to have a uniform
grid representation. To solve this, a log-polar trans-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6881-5535
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3756-5569
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9405-4872
form is usually applied to the image to create a com-
pressed representation that is in a grid format (Oz-
imek et al., 2019), (Schwartz, 1980). While this for-
mat is compatible with convolution layers, it fun-
damentally changes the representation of the data.
Log-polar image representations do not have transla-
tion equivariance like cartesian images, instead hav-
ing scale and rotation equivariance (about the fixa-
tion location) (Weiman and Chaikin, 1979). While
not an inherently poor representation of visual data,
log-polar representations may not be desirable for all
applications. To this end, we aim to remove the need
to apply a log-polar transform to foveated images in
order to use them with CNNs.
In this paper, we propose a convolution operation
that can directly operate on foveated images in carte-
sian space without requiring a log-polar representa-
tion. Our operation is inspired by convolution opera-
tors designed for point clouds (Wu et al., 2019)(Her-
mosilla et al., 2018)(Wang et al., 2018), which frame
the convolution operation as the Monte-Carlo estima-
tion of the continuous convolution integral. Monte-
Carlo convolution operations require the convolution
kernel to be represented continuously in the spa-
tial domain. Typically, this is achieved through a
coordinate-based MLP, which maps spatial locations
to a filter weight. The current convention is to use the
ReLU activation function within the MLP. However,
adjacent work in implicit neural representations sug-
gests that the Sine activation function is more suitable
444
Killick, G., Aragon-Camarasa, G. and Siebert, J.
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0010832400003124
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2022) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
444-451
ISBN: 978-989-758-555-5; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

for this task. To this end, we propose a novel formu-
lation of the Monte Carlo Convolution operation that
uses a Sine activated MLP to represent spatially con-
tinuous convolution kernels.
We use our proposed convolution operation to
build a simple CNN architecture and evaluate its per-
formance on the CUB-200-2011 Dataset (Wah et al.,
2011), a popular fine-grained image classification
dataset comprised of images of 200 species of birds.
We simulate a foveated sensor in software using the
method proposed in (Balasuriya, 2006). We compare
our convolution operation against a standard CNN
processing foveated images represented in a log-polar
space and show that classification performance is im-
proved when applying convolutions in the cartesian
coordinate frame. Additionally, we compare differ-
ent MLP designs for representing spatially continu-
ous convolution filters. We show that classification
performance is significantly improved when using an
MLP with the Sine activation function compared to
the more traditional ReLU MLP. We do not intend to
show that foveated vision itself is beneficial to this
particular classification task. Rather, we intend to
show that if one wishes to use foveated vision in a
computer vision pipeline, our proposed convolution
operation can operate on this data in the cartesian co-
ordinate frame effectively. Finally, we show that in
the case of a single hidden layer MLP with Sine acti-
vations, it suffices to freeze first layer weights at ini-
tialization and only learn the bias terms with no sig-
nificant performance decrease.
To summarise, our contributions in this work are
three-fold:
• We demonstrate that Monte-Carlo convolutions,
frequently used for point clouds, can be applied
effectively to foveated images in the cartesian co-
ordinate frame.
• We empirically show that the expressiveness of
the continuous filter kernel derived from a coordi-
nated based MLP is significantly improved when
using the Sine activation instead of ReLUs.
• We propose a parameter efficient coordinate based
MLP that can achieve comparable performance to
its inefficient counterpart and provide intuition on
why it works through a comparison to Fourier se-
ries synthesis.
While the results from this work are promising, it
is in its infancy, with many issues still present. We
address these in the limitations section. Nonetheless,
we believe the work presented in this paper will be
helpful as a strong baseline for future work on pro-
cessing foveated images with deep neural networks in
the cartesian coordinate frame.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Deep Learning on Foveated Images
Foveated vision has been incorporated into deep
learning vision systems in a variety of forms. (Karpa-
thy et al., 2014) adopt a simple approach to foveated
vision using two images, a high-resolution crop and
a low-resolution full field of view. Each image is
processed by its own CNN before being concate-
nated and fed to further fully connected layers. (Li
et al., 2017) approach differs slightly through sharing
weights between the Convolution Neural Networks
(CNNs) that process the high-resolution crop and the
low-resolution full field of view. This approach does
not require a log-polar representation and is easily in-
tegrated into CNN architectures. (Balasuriya, 2006)
comments on the potential pitfalls of this approach,
particularly in the extraction of features that span dif-
ferent fields of view. To our knowledge, no one has
reported on whether this discontinuity has significant
effects on a deep learning system in practice. While a
comparison could be made between this approach and
log-polar foveated images, it is not a like for like com-
parison as the log-polar space fundamentally changes
the way filters are applied to visual scene. In this
paper, we provide a framework for investigating this
claim in the future.
(Nakada et al., 2018) use a random distribution of
points in log-polar space to sample a simulated visual
scene. These points are passed to an MLP to pro-
cess the visual scene. While this approach is simple
in design and does not require a log-polar represen-
tation, it is likely impractical for real images which
have much richer visual information than simulated
visual scenes. (Balasuriya and Siebert, 2003) apply
difference-of-gaussian and Gabor filters to a Software
Retina (Balasuriya, 2006). Support regions are con-
structed using distance on the Delaunay triangulated
graph of the sampling locations. Spatial offsets of
points in the support relative to the centre of the sup-
port are used to compute filter weights with the an-
alytic expressions for difference-of-gaussian and Ga-
bor filters. This method is similar to the Monte-Carlo
convolutions used in point clouds (Section 2.2)
Log-polar representations are the prevalent ap-
proach to integrating foveated images into CNNs.
(Esteves et al., 2017) extend spatial transformer net-
works (Jaderberg et al., 2015) to use the log-polar
transform allowing them to fixate the high-resolution
region on objects of interest. (Amorim et al., 2018)
evaluate the rotation invariance of log-polar image
representations in conjunction with CNNs. (Kim
et al., 2020) similarly evaluate scale and rotation in-
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images
445
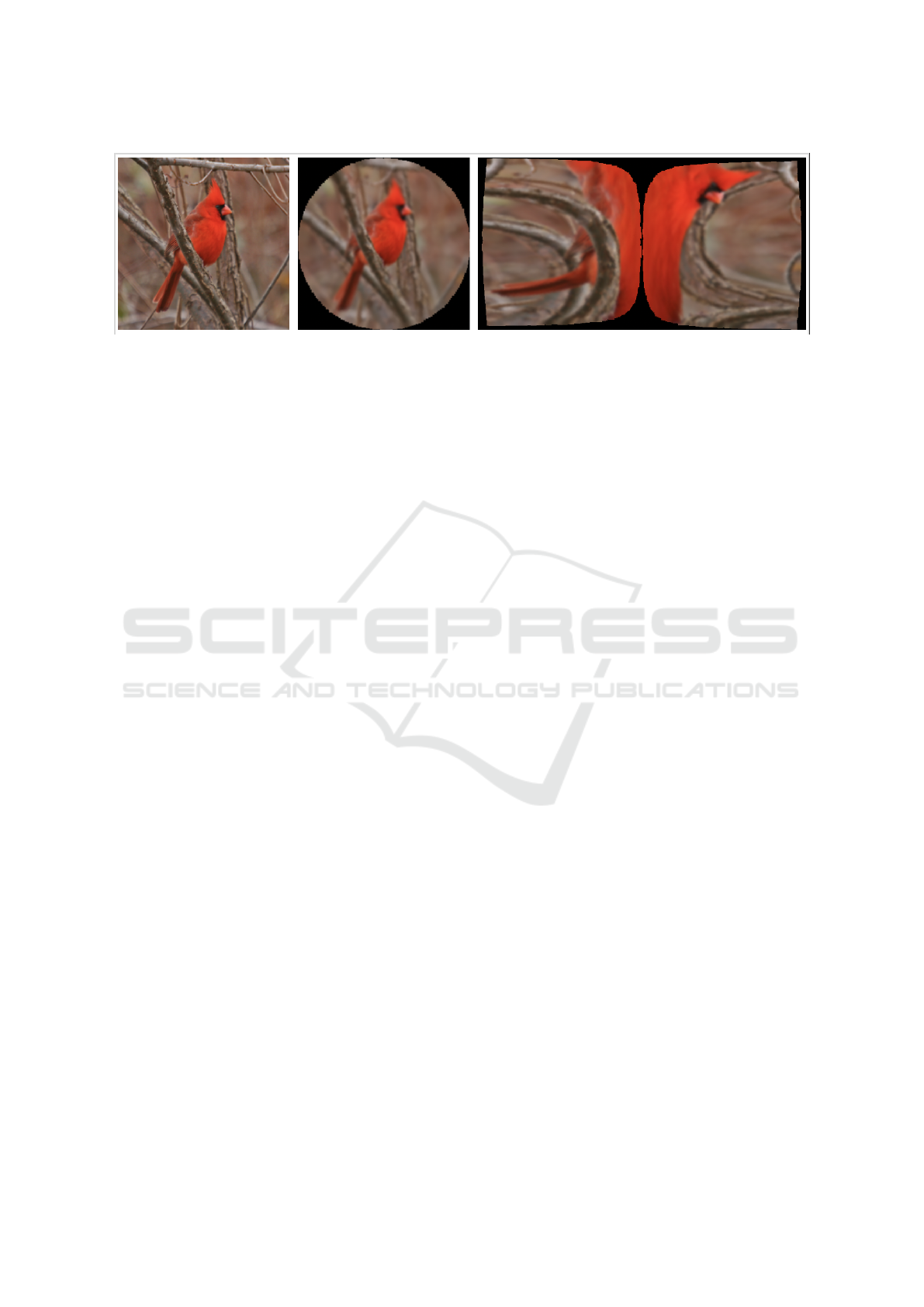
Figure 1: Left to Right: An image from the CUB-200-2011 Dataset of a cardinal bird, represented as a standard uniform
image grid. The image sampled by a 8192 receptive field Software Retina (Balasuriya, 2006), resampled to a uniform grid.
The Software Retina sampled image represented in cortical space ((Schwartz, 1980)), a biologically plausible variant of the
log-polar transform.
variance of log-polar and polar images with wrap
around padding. In both cases, network performance
suffered under the log-polar and polar image repre-
sentations, only benefiting in the specific case of train-
ing on non-rotated images and testing on rotated im-
ages. Interestingly, networks that had been trained
on rotated images and tested on rotated images out-
perform log-polar images as well. (Ozimek et al.,
2019) evaluate a more biologically plausible variant
of the log-polar transform, dubbed the cortical trans-
form (Schwartz, 1980), applied to Balasuriya’s Soft-
ware Retina (Balasuriya, 2006). Ozimek et al. again
reported decreased performance for cortical images
when processed by a CNN for image classification.
Ozimek et al. also evaluated the foveated sensor
resampled to a uniform grid in cartesian space and
showed an increase in performance more comparable
to the full resolution image. This suggests that much
of the performance decrease is from the log-polar
space and not reduced information through foveated
sampling.
2.2 Deep Learning on Point Clouds
2D images can be considered a specific case of 2D
point clouds where diagnostic information is only car-
ried in the RGB values attached to each point and not
in the spatial relationships between points. While in
the conventional uniform sampling setting of 2D im-
ages, the application of convolutions is possible using
the standard discrete convolution. However, this is not
the case when the image is sampled non-uniformly.
For this reason, methods developed for performing
deep learning on point clouds are of particular rele-
vance to performing deep learning on foveated im-
ages. In this subsection, we give a general overview
of deep learning architectures designed for processing
point clouds.
PointNet (Qi et al., 2017a) stands as one of the
first successful attempts in applying deep learning ar-
chitectures directly on point clouds. Shared MLPs are
applied in a point-wise fashion to each point in the
set, projecting them into a higher dimensional space.
These features are aggregated spatially with a global
max-pooling operation before being passed to further
layers for classification. Due to the global spatial ag-
gregation, PointNet cannot capture local features in
the input signal, only global features. PointNet++ (Qi
et al., 2017b) addresses this by applying a PointNet
to local neighbourhoods on the point cloud to capture
local information hierarchically.
(Wang et al., 2018) use Monte-Carlo integration to
estimate the convolution integral where points from
the point cloud serve as random samples of the un-
derlying continuous signal. Support regions are con-
structed on a point cloud using nearest neighbours.
The spatial offset of each point in the support region,
relative to the centre of the support region, is passed to
a coordinate-based MLP to produce the filter weights
for the corresponding spatial location. A weighted
sum between point features and filter weights is then
computed to estimate the convolution response at that
location. (Hermosilla et al., 2018) adopt a similar
approach, but inversely weight samples with their
probability density function (PDF) given the support
region, obtained through kernel density estimation
(KDE). This method is a more accurate approxima-
tion of Monte-Carlo integration and allows the esti-
mation of the convolution response to be more robust
to non-uniform sampling. (Wu et al., 2019) similarly
employ inverse weighting through a point’s PDF but
first pass the PDF to a parameterised MLP to allow
the network to decide how to use PDFs to inversely
weight samples. In our use case, robustness to non-
uniform sampling is not as pertinent as in point clouds
as a local support region on our foveated sensor is ap-
proximately uniform.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
446

(Wang et al., 2018) (Hermosilla et al., 2018) (Wu
et al., 2019) use ReLU MLPs to map spatial offsets
to filter values. (Xu et al., 2021) instead map spa-
tial offsets to a vector applied with the Softmax ac-
tivation function using an MLP. This vector is used
to softly combine a set of weights stored in a weight
bank into a single weight matrix for that specific spa-
tial location. (Thomas et al., 2019) adopt a similar
approach but use a predetermined interpolation func-
tion to combine the weights of a weight bank into a
position-specific weight matrix.
While the methods presented by (Xu et al., 2021),
(Thomas et al., 2019) outperform coordinate based
MLP approaches, we believe the performance dis-
crepancy can be partially explained by adjacent work
in implicit neural representations. That is, (Tan-
cik et al., 2020) show that coordinate based MLPs
with ReLU activations have a spectral bias to low-
frequency functions. In Monte-Carlo convolutions,
the coordinate-based MLP is an implicit neural rep-
resentation of a filter bank. (Mildenhall et al., 2020)
overcome this bias by first applying a positional en-
coding to the coordinates, significantly improving the
networks ability to model high-frequency functions.
SIRENs (Sitzmann et al., 2020) similarly show the
benefits of periodic activations when modelling con-
tinuous signals by using an MLP with Sine activa-
tions.
3 METHOD
3.1 Foveated Sensor
To produce foveated images from uniform images,
we simulate a foveated sensor in software using the
method proposed by (Balasuriya, 2006). A self-
similar neural network (Clippingdale and Wilson,
1996) is used to produce a foveated sampling pat-
tern that serves as the centres for overlapping Gaus-
sian receptive fields. These receptive fields are used
to sample a uniform image and output a list of RGB
values along with their corresponding receptive fields
2D spatial location in cartesian space. We use this ap-
proach to foveated sensing as the Gaussian receptive
fields remove aliasing in the output image; however,
our method for performing convolutions is aimed to
be largely agnostic to the foveated sampling strategy.
Our foveated sensor has 8192 receptive fields with a
fovea radius of 0.1 to sample a 256x256 image.
To compare our method with previous methods,
we use the cortical transform proposed by (Schwartz,
1980) to produce a compact, dense representation of
Balasuriya’s Software Retina.
3.2 Non-uniform Convolution
Our approach to convolution is the same in concept to
that of (Hermosilla et al., 2018), (Wu et al., 2019),
(Wang et al., 2018). We frame convolution as the
Monte-Carlo estimation of convolution integral and
represent convolution kernels continuously through
a parameterized MLP. Our novel contribution comes
from how we design the MLP (section 3.4), not the
overall operation. The integral definition of the 2D
continuous convolution operation is given by equa-
tion. 1, and the Monte-Carlo estimation of the convo-
lution operation is given by equation. 2
f ∗ g(x, y) =
∞
Z
n=−∞
∞
Z
m=−∞
f (n, m)·g(x − n, y − m)∂n∂m
(1)
f ∗ G(x, y) ≈
∑
δ(x,y)∈S
f
δ(x, y)
r
· G(x + δx, y + δy)
(2)
Where f is the continuous convolution kernel rep-
resented by a coordinate-based MLP, G is the discrete
function of the foveated image, S is the set of spatial
offsets of points in a given support region relative to
the support centre, and r is the radius of the support
region.
(Hermosilla et al., 2018) and (Wu et al., 2019) in-
versely weight each sample by its probability density
function. While this is important in point clouds due
to the potential for the sampling to be highly non-
uniform, this is less important in our use case as we
can guarantee an approximately uniform sampling for
any small local neighbourhood of the foveated sen-
sor. Consequently, we avoid this inverse weighting as
it adds unnecessary computation to the process. For
foveated sensors, such as that used by (Nakada et al.,
2018), which have a less uniform sampling scheme,
the inclusion of inverse weighting by PDF may prove
beneficial.
3.3 Support Regions
The support region of the standard discrete 2D convo-
lutional operation is defined by the height and width
of the kernel used for convolution. To define a support
region on a non-uniformly sampled image, we use a
nearest-neighbours search to find the k nearest neigh-
bours to the centre of our receptive field where k is
a hyperparameter analogous to filter size in standard
convolutions. Unlike point clouds, the spatial loca-
tions of points are consistent across all input images
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images
447

Figure 2: The pixel locations of the foveated image (blue)
and the support region centres established over the foveated
image (orange). Both are generated by a Self-Similar Neu-
ral Network ((Clippingdale and Wilson, 1996). The ratio
between the number of pixels and the number of support re-
gions determines the downsampling factor the convolution
operation provides.
meaning we can compute nearest neighbours once at
initialization of the network, removing the need for a
nearest neighbours search in the forward pass of the
network. To maintain foveated sampling in the in-
termediate feature maps, support centre locations use
the sampling locations of the input feature map or
the sampling locations of a lower resolution Software
Retina to perform downsampling (Figure 2).
For every support region, a shared MLP is applied
to the spatial offsets of the support points relative to
the support centre, normalized by the maximum spa-
tial offset (equivalent to the radius of the support re-
gion). Utilizing the normalized spatial offsets pro-
duces translation-invariant filter weights and scale the
filter appropriately for the sampling resolution. Eval-
uating the MLP for all sampling locations in the sup-
port produces a k × I × O weight tensor representing
the filter, where k is filter size, I is the depth of the in-
put feature map, and O is the number of filters in the
convolutional layer. The filter response is computed
as the weighted sum of the filter and the feature values
of the support region. In accordance with the integral
definition of the convolution operation, this method is
equivalent to the Monte-Carlo estimation of the con-
volution integral.
3.4 Continuous Filter Representations
We use a coordinate-based MLP to map the spatial
offsets of pixels relative to the receptive field centre
to filter coefficients. (Hermosilla et al., 2018), (Wu
et al., 2019), (Wang et al., 2018) use the ReLU ac-
tivation function for their MLPs, however (Sitzmann
et al., 2020), (Tancik et al., 2020) show that coordi-
nate based MLPs struggle to effectively learn high-
frequency functions when using the ReLU activation
function. This may impede the CNNs ability to learn
expressive filters for higher frequency signals. (Tan-
cik et al., 2020), (Mildenhall et al., 2020) demonstrate
that the mapping of coordinates first through multi-
ple sinusoids of different frequencies allows the MLP
to learn higher frequency functions. (Tancik et al.,
2020), (Sitzmann et al., 2020) scale the input data by
some scaling factor to increase the range of frequen-
cies the MLP can easily learn.
Our MLP design uses one hidden layer of size 64
with the Sine activation function and outputs I x O
where I is the depth of the input featuremap and O is
the depth of the output featuremap. Like (Sitzmann
et al., 2020) (Tancik et al., 2020), we apply a scaling
factor to the first layer weights. This scaling factor is
a hyperparameter with 6 giving the best network per-
formance (Figure 4). We draw our first layer weights
from a uniform distribution of -1 to 1.
In the case of a Sine activated MLP with one hid-
den layer, the functionality of this network is similar
to the synthesis of a function through a Fourier series.
In this case, input layer weights, bias terms, and out-
put weights correspond to the frequency, phase and
amplitude of the Fourier basis functions. We find it
suffices to freeze first layer weights at initialization
and only learn the bias terms. Provided that the first
layer weights cover a sufficient frequency range uni-
formly, this should provide the network with a se-
ries of sine basis functions suitable for approximating
continuous functions without the need to learn their
frequencies. Freezing the bias terms proved detrimen-
tal to network performance, suggesting that learning
appropriate phase offsets is crucial to the modelling
of continuous functions for the size of the MLP we
use.
3.5 CNN Architecture
The overall CNN architecture for all experiments uses
5 convolutional blocks where a block has the form
of Conv-BatchNorm-ReLU. Each convolution layer
uses a receptive field size of 9 nearest neighbours. At
each block we double the number of filters, giving
an overall signature of (32, 64, 128, 256, 512). The
final feature maps are global average pooled in the
spatial dimension before being flattened and passed
to a fully connected layer that outputs class predic-
tions under the softmax activation. Each convolution
block reduces the spatial dimensionality by a factor
of 4. For experiments that use standard convolutions,
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
448
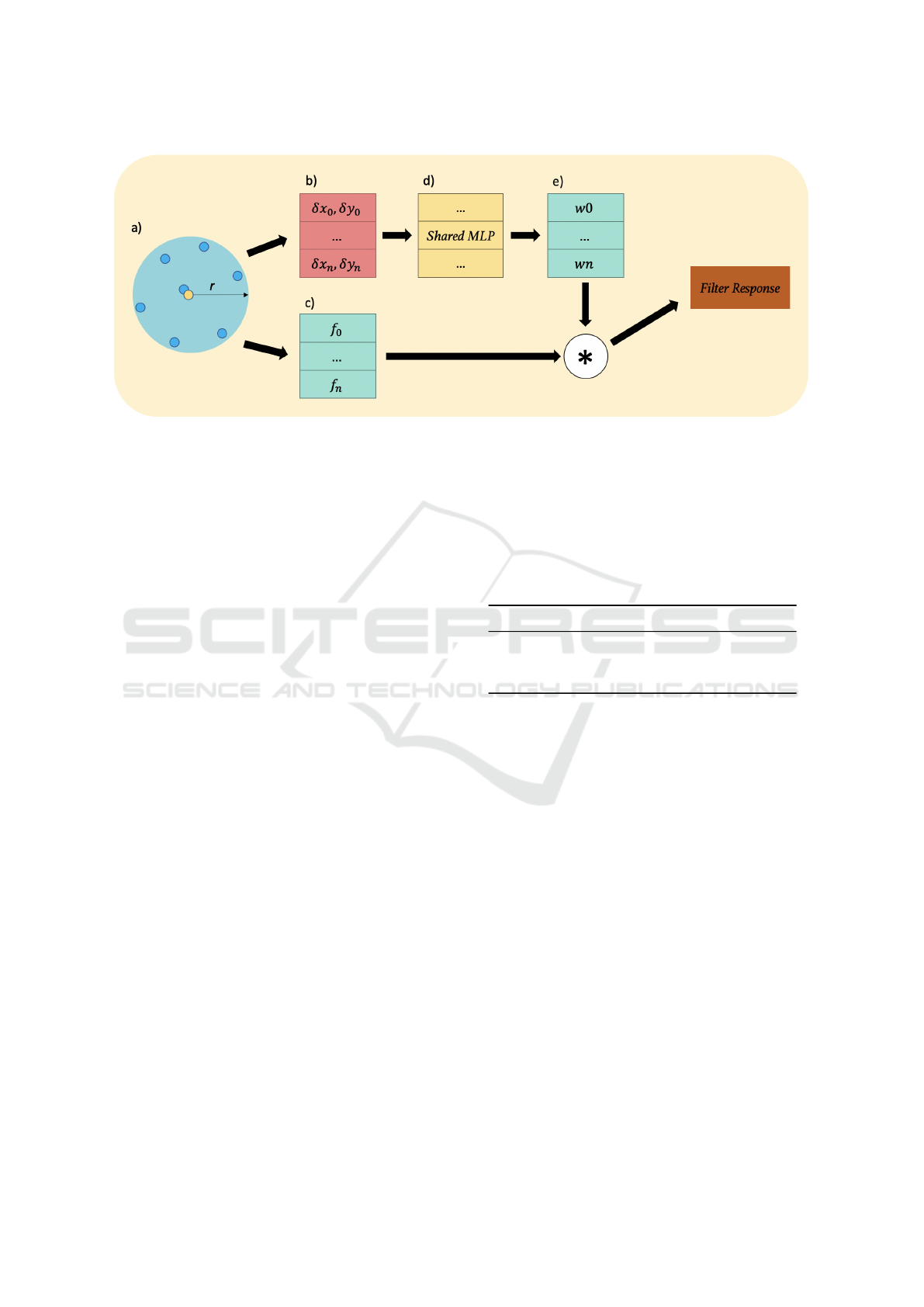
Figure 3: A demonstration of the Monte-Carlo convolution process. a) The local support region established on the foveated
image using 7 nearest neighbours from the support centre (yellow point). b) the spatial offsets of all points in the support
region from the support region centre, normalized by radius r. c) the features associated with each point in the support. d)
normalized spatial offsets are passed to a shared MLP to produce the filter weights. e) these weights are used to perform a
weighted sum of the point features and in turn produce the filter responses for that support region.
we use a kernel size of 3x3 and a stride of 2 to make a
fair comparison between the discrete convolution and
Monte-Carlo Convolution.
3.6 Training and Dataset
We evaluate our method on the CUB-200-2011
Dataset (Wah et al., 2011), a fine-grained classifi-
cation dataset comprised of 11,788 images of 200
species of birds. The dataset has a train-test split pro-
vided by the dataset creators (an approximately 50-50
split). We further split the test set into a test and vali-
dation set with a 4:1 ratio respectively. We choose the
CUB-200-2011 dataset as it is challenging due to its
fine-grained nature and will require expressive convo-
lution filters to disambiguate the classes.
All images are normalized to the range of 0-1 and
resized to 256x256. At training time we apply ran-
dom rotations of ±20 degrees, randomly flip horizon-
tally, and randomly crop 80% of the image and re-
size to 256x256. This data augmentation scheme pro-
duces translation, rotation and scale transformations
of input data. Depending on the image representation
used, the subsequent CNN will have a degree of in-
variance to these transformations. We assume that the
augmentation scheme is equally useful for all image
representations as they are either invariant to trans-
lation or rotation but never both. We train for 100
epochs using the Adam optimizer (Kingma and Ba,
2014). We take the best performing model across all
epochs as the final model and report its performance
on the held-out test set as the final performance.
Table 1: Classification performance on the CUB-200-2011
Dataset using Monte-Carlo Convolutions. Bracketed num-
bers refer to the width of each layer of the network. SIREN
refers to the networks proposed by (Sitzmann et al., 2020),
while ReLU refers to a standard MLP with ReLU activation.
MLP Design Classification Accuracy (%)
ReLU (32-32) 19.4
SIREN (64-64-64) 29.5
Ours (64) 28.7
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Effect of MLP Design
We evaluate different MLP designs for use within our
proposed convolution operation and report how they
impact classification accuracy for a CNN trained on
the CUB-200-2011 Dataset (Table 4). The role of the
MLP within the Monte-Carlo convolution operation is
to act as an implicit neural representation of convolu-
tion filters. The ReLU MLP, as used in (Wang et al.,
2018), (Wu et al., 2019), (Hermosilla et al., 2018),
performs significantly worse than SIRENs (Sitzmann
et al., 2020) which can be considered state-of-the-
art for implicit neural representations. Our proposed
MLP design, which can be seen as a special case of a
SIREN, uses only one hidden layer and has first layer
weights frozen at initialization (not including biases).
We show that despite operating under far fewer learn-
able parameters, there is a negligible performance de-
crease over the best performing SIREN. These results
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images
449

suggest that it suffices to represent convolution ker-
nels continuously through a linear combination of dif-
ferent sinusoids and that a many hidden layer SIREN
is not strictly necessary to achieve good performance.
4.2 Scaling Factor Hyperparameter
An important hyperparameter in the MLP is the scal-
ing factor applied to the input coordinates (equivalent
to the omega hyperparameter in SIRENs (Sitzmann
et al., 2020)). Figure 4 shows how classification ac-
curacy changes under different scaling factors. The
CNN’s classification accuracy is highly dependent on
this hyperparameter with 6 providing the best perfor-
mance. The scaling factor is closely tied to the fre-
quency range the MLP can represent. The sampling
rate of the continuous convolution filter increases with
kernel size. Therefore, it is likely that the scaling pa-
rameter should be tuned in accordance to the convo-
lutional layer’s kernel size. We do not explore this
further in this paper, however he importance of this
hyperparameter makes this an important avenue to ex-
plore in future work.
Figure 4: The effect of changing the input scaling factor of
the MLP in our proposed convolution operation on classifi-
cation accuracy on the CUB-200-2011 Dataset.
4.3 Image Representations
We compare classification accuracy when operating
on the foveated image in cartesian space against a
foveated image represented in log-polar space (Ta-
ble 4.3). We provide additional context for perfor-
mance by also reporting classification accuracy on
the uniform image before foveated sampling. For the
foveated image in cartesian space we use our pro-
posed Monte-Carlo Convolution operation. For all
other experiments standard 2D discrete convolutions
are applied. We show that classification accuracy
on the cartesian foveated image when using Monte-
Carlo convolutions is significantly higher than stan-
dard convolutions applied to the log-polar foveated
Table 2: Classification performance on the CUB-200-2011
Dataset. Unless specified to use MC-Conv, all results are
obtained with a CNN using standard convolutions. Results
are averaged over 5 training runs.
Image type
Classification
Accuracy (%)
Uniform (256x256) 33.1
Foveated - Cortical Transform 22.0
Foveated w/ MC-Conv (Ours) 28.7
image. Both foveated images carry the same amount
of information but differ in their representation, sug-
gesting that the performance discrepancy is simply
due to the log-polar space being a poor image rep-
resentation for this task. Operating on the cartesian
foveated image also produced results comparable to
that of standard convolutions operating on the uni-
form image suggesting that our proposed convolution
operation can achieve similar representational power
to standard convolutions.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose a method for performing
convolutions on non-uniform foveated images in the
cartesian coordinate frame. Our approach uses the
Monte-Carlo estimation of the convolution operation
between the foveated image and a continuous filter
kernel represented by a coordinate MLP. Unlike pre-
vious approaches, which use an MLP with ReLU ac-
tivations, we adopt Sine activation functions which
have been shown to significantly improve our model’s
ability to learn filters that can extract diagnostic fea-
tures from a foveated image. Our approach sig-
nificantly outperforms standard convolutions applied
to foveated images represented in a log-polar space
and approaches performance comparable to applying
standard convolutions to the full resolution uniform
image.
6 LIMITATIONS
The computational overhead of the computer vision
system operating on the foveated image should be less
than operating on the full resolution image. A stan-
dard convolution layer requires a k x I x O weight
tensor to represent its convolution filters, where k is
the size of the filter, I is the number of input channels,
and O is the number of filters. Our convolution oper-
ation requires k x I x O x N, where N is the number of
support regions established on the featuremap. This
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
450

factor N increase significantly increases the memory
overhead of our operation beyond the memory sav-
ings achieved through a reduced image size through
foveated sensing. In future work, we would like to
address this limitation through factorization methods
to achieve memory savings that make operating on
foveated images in cartesian space viable from a com-
putational overhead point of view.
REFERENCES
Amorim, M., Bortoloti, F., Ciarelli, P. M., de Oliveira,
E., and de Souza, A. F. (2018). Analysing rotation-
invariance of a log-polar transformation in convolu-
tional neural networks. In 2018 International Joint
Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pages 1–6.
IEEE.
Balasuriya, L. and Siebert, J. (2003). A low level vision hi-
erarchy based on an irregularly sampled retina. In Pro-
ceedings of the International Conference on Compu-
tational Intelligence, Robotics and Autonomous Sys-
tems, Singapore.
Balasuriya, S. (2006). A computational model of space-
variant vision based on a self-organised artificial
retina tessellation. PhD thesis, University of Glasgow.
Clippingdale, S. and Wilson, R. (1996). Self-similar neural
networks based on a kohonen learning rule. Neural
Networks, 9(5):747–763.
Esteves, C., Allen-Blanchette, C., Zhou, X., and Daniilidis,
K. (2017). Polar transformer networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1709.01889.
Hermosilla, P., Ritschel, T., V
´
azquez, P.-P., Vinacua,
`
A.,
and Ropinski, T. (2018). Monte carlo convolution
for learning on non-uniformly sampled point clouds.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 37(6):1–12.
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A., et al. (2015).
Spatial transformer networks. Advances in neural in-
formation processing systems, 28:2017–2025.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Suk-
thankar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Large-scale video
classification with convolutional neural networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, pages 1725–1732.
Kim, J., Jung, W., Kim, H., and Lee, J. (2020). Cy-
cnn: a rotation invariant cnn using polar mapping
and cylindrical convolution layers. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2007.10588.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Li, X., Jie, Z., Wang, W., Liu, C., Yang, J., Shen, X., Lin,
Z., Chen, Q., Yan, S., and Feng, J. (2017). Foveanet:
Perspective-aware urban scene parsing. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE International Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 784–792.
Mildenhall, B., Srinivasan, P. P., Tancik, M., Barron, J. T.,
Ramamoorthi, R., and Ng, R. (2020). Nerf: Repre-
senting scenes as neural radiance fields for view syn-
thesis. In European conference on computer vision,
pages 405–421. Springer.
Nakada, M., Chen, H., and Terzopoulos, D. (2018). Deep
learning of biomimetic visual perception for virtual
humans. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Symposium
on Applied Perception, pages 1–8.
Ozimek, P., Hristozova, N., Balog, L., and Siebert, J. P.
(2019). A space-variant visual pathway model for data
efficient deep learning. Frontiers in cellular neuro-
science, 13:36.
Qi, C. R., Su, H., Mo, K., and Guibas, L. J. (2017a). Point-
net: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification
and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition,
pages 652–660.
Qi, C. R., Yi, L., Su, H., and Guibas, L. J. (2017b). Point-
net++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets
in a metric space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02413.
Schwartz, E. L. (1980). Computational anatomy and func-
tional architecture of striate cortex: a spatial map-
ping approach to perceptual coding. Vision research,
20(8):645–669.
Sitzmann, V., Martel, J., Bergman, A., Lindell, D., and Wet-
zstein, G. (2020). Implicit neural representations with
periodic activation functions. Advances in Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, 33.
Tancik, M., Srinivasan, P. P., Mildenhall, B., Fridovich-
Keil, S., Raghavan, N., Singhal, U., Ramamoor-
thi, R., Barron, J. T., and Ng, R. (2020). Fourier
features let networks learn high frequency func-
tions in low dimensional domains. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2006.10739.
Thomas, H., Qi, C. R., Deschaud, J.-E., Marcotegui, B.,
Goulette, F., and Guibas, L. J. (2019). Kpconv: Flex-
ible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Confer-
ence on Computer Vision, pages 6411–6420.
Wah, C., Branson, S., Welinder, P., Perona, P., and Be-
longie, S. (2011). The caltech-ucsd birds-200-2011
dataset.
Wang, S., Suo, S., Ma, W.-C., Pokrovsky, A., and Urtasun,
R. (2018). Deep parametric continuous convolutional
neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 2589–2597.
Weiman, C. F. and Chaikin, G. (1979). Logarithmic spi-
ral grids for image processing and display. Computer
Graphics and Image Processing, 11(3):197–226.
Wu, W., Qi, Z., and Fuxin, L. (2019). Pointconv: Deep
convolutional networks on 3d point clouds. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 9621–9630.
Xu, M., Ding, R., Zhao, H., and Qi, X. (2021). Paconv:
Position adaptive convolution with dynamic kernel
assembling on point clouds. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, pages 3173–3182.
Monte-Carlo Convolutions on Foveated Images
451
