
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised
Learning of Optic Flow Patterns
Paul Fricker
1,2 a
, Tushar Chauhan
1 b
, Christophe Hurter
2 c
and Benoit R. Cottereau
1 d
1
Centre de Recherche Cerveau et Cognition, CNRS UMR5549, Toulouse, France
2
Ecole Nationale de l’Aviation Civile, Toulouse, France
Keywords:
Optic Flow, Spiking Neural Network, Unsupervised Learning, STDP.
Abstract:
We developed a Spiking Neural Network composed of two layers that processes event-based data captured
by a dynamic vision sensor during navigation conditions. The training of the network was performed using
a biologically plausible and unsupervised learning rule, Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity. With such an
approach, neurons in the network naturally become selective to different components of optic flow, and a
simple classifier is able to predict self-motion properties from the neural population output spiking activity.
Our network has a simple architecture and a restricted number of neurons. Therefore, it is easy to implement
on a neuromorphic chip and could be used for embedded applications necessitating low energy consumption.
1 INTRODUCTION
During locomotion, retinal optic flow patterns are
used by numerous animal species to monitor their
heading and moving speed. In primates, optic flow
is processed through a hierarchical network that first
extracts local motion components, combines them to
determine global motion properties, and subsequently
estimates navigation parameters. This process is very
efficient in terms of energy consumption as informa-
tion in the primate visual system is transmitted under
a binary form (spikes), and it is generally admitted
that the brain only requires about 20 watts to func-
tion (Mink et al., 1981). Reproducing these neural
mechanisms in artificial and embedded systems could
have significant implications in industrial (e.g., au-
tonomous vehicles) and clinical (e.g., navigation with
computer assistance in blind patients) domains. The
last years have seen the emergence of numerous stud-
ies where the optic flow was computed from a bio-
inspired perspective, thanks to the development of
event-based cameras. Similar to the human retina,
these cameras, also known as dynamic vision sensors
(DVS), emit spikes at locations where a change in log-
luminance (an increment or a decrement) is detected
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0560-7827
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0396-4820
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4318-6717
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2624-7680
in the visual inputs. Transmission is asynchronous
and has a very high temporal resolution (down to the
millisecond, (Posch et al., 2014)), which is potentially
very advantageous for real-time applications given the
subsequent treatment of the spikes is adequately per-
formed.
A natural way to process the spikes emitted by
event-based cameras is to use spiking neural networks
(SNNs). These networks favor low power computa-
tion as they can be directly implemented on neuro-
morphic chips such as Intel Loihi (Davies et al., 2018)
or IBM TrueNorth (Akopyan et al., 2015). Learning
with SNNs can be performed with or without super-
vision. In the first case, the discrete nature of spikes
makes it challenging to estimate the network param-
eters through back-propagation, even though recent
developments such as the surrogate gradient method
have led to promising results (Neftci et al., 2019;
Zenke et al., 2021). Learning in this case often ne-
cessitates a large amount of labeled data, and gener-
alization to other visual contexts is not always guar-
anteed. Unsupervised approaches can provide an in-
teresting alternative to supervised methods as they are
more flexible to modifications in the input and do not
need labeled datasets.
In this paper, we describe a simple, functional,
and efficient spiking neural network that learns to ex-
tract meaningful optic flow components during natu-
ral navigation conditions using a bio-inspired and un-
supervised rule, the spike-timing-dependent plastic-
702
Fricker, P., Chauhan, T., Hurter, C. and Cottereau, B.
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised Learning of Optic Flow Patterns.
DOI: 10.5220/0010836200003124
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2022) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
702-710
ISBN: 978-989-758-555-5; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ity or STDP. We demonstrate that after training, the
output units of the network become selective to optic
flow components, and notably, to translational, rota-
tional, and radial patterns. Moreover, we show that
the activation of these units can be used to predict
self-motion direction during navigation.
In the next sections, we begin with an overview
of the state-of-the-art in the field (section 1.1). This
is followed by a description of our methodology (sec-
tion 2) and then by a presentation of our results (sec-
tion 3).
1.1 Related Work
Over the last decade, an increasing number of studies
have used event-based data for computer vision, with
performances sometimes better than those obtained
from more classical frame-based cameras in appli-
cations like object recognition (Neil and Liu, 2016;
Stromatias et al., 2017), or visual odometry (Gal-
lego and Scaramuzza, 2017; Nguyen et al., 2019).
These studies were all based on deep convolutional
neural networks or SNNs, coupled with supervised
learning or classification approaches (see (Lakshmi
et al., 2019)). For example, (Zhu et al., 2019) used
an artificial neural network (ANN) to predict the op-
tic flow from event-based data collected from a cam-
era mounted on the top of a car moving within an ur-
ban environment (see also (Zhu et al., 2018)). In (Lee
et al., 2020), the authors used the same dataset but
processed it with a hybrid ANN/SNN neural network
which produced even better optic flow estimations.
Because they were not fully spiking, these approaches
are difficult to implement on neuromorphic chips di-
rectly. In addition, these supervised approaches also
require a large amount of labeled data which are not
always available.
Alternative approaches based on unsupervised
learning were also developed. In (Bichler et al.,
2012), the authors demonstrated that motion selectiv-
ity could be learned by SNNs equipped with a bio-
inspired STDP learning rule. Their network was able
to discriminate motion direction on synthetic event-
based data and also to count the vehicles in different
highway lanes from data collected with a dynamic vi-
sion sensor (DVS). In recent work, (Oudjail. and Mar-
tinet., 2019; Oudjail. and Martinet., 2020) showed
that only a small number of neurons are required to
learn simple motion patterns from the STDP rule.
However, in this case, the simulated inputs were re-
stricted to a 5 × 5 pixels window, as opposed to 16
× 16 pixels for the simulations and 128 × 128 for the
DVS data in (Bichler et al., 2012).
In (Paredes-Vall
´
es et al., 2020), a deep hierarchi-
cal network including transmission delays and numer-
ous layers was able to estimate the motion patterns of
moving objects after unsupervised learning through
STDP. This network was nonetheless complex and
comprised different data formatting approaches dis-
tributed across multiple layers and neurons. Even
more recently, (Debat et al., 2021) used the same type
of SNN to show that learning through STDP led to
neural populations whose spiking activity can be used
to predict trajectories.
Here, we build on these studies to develop a novel
SNN which, when equipped with STDP, learns to
extract optic flow properties, notably self-motion di-
rection during navigation, from event-based data col-
lected under natural locomotion conditions. Our SNN
is simpler than those proposed in previous works and
thus easier to set up and optimize. Given its straight-
forward nature and its small number of internal pa-
rameters, it can also be implemented easily on neuro-
morphic chips with low power consumption.
2 METHODS
Our processing pipeline consists of an SNN which
processes event-based data consistent with those re-
ceived by the primate retina during locomotion. In
this section, we first describe the different types of
event-based data used as inputs to our network (sec-
tion 2.1). We subsequently describe our neural net-
work’s properties (section 2.2) and the unsupervised
learning rule used for training (section 2.3). We fi-
nally detail the evaluations employed to characterize
the networks’ properties after learning (section 2.4).
2.1 Event-based Inputs
Two different datasets were used to train our network.
They are described in the following two sections.
2.1.1 Simple Simulations of Optic Flow
To characterize the ability of our network to learn
optic flow components, we designed simulations in
which four bright disks (one in each quadrant of the
visual field) were either translating (leftward, right-
ward, upward, and downward), rotating (clockwise
and counter-clockwise), or expanding/contracting in
front of a black background (see figure 1-A). The
disks had a diameter of 6 pixels, and the total size of
the visual field was 32 × 32 pixels (a quadrant was 16
× 16 pixels). Each simulation was generated from 16
temporal frames presented at different speeds: 120,
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised Learning of Optic Flow Patterns
703
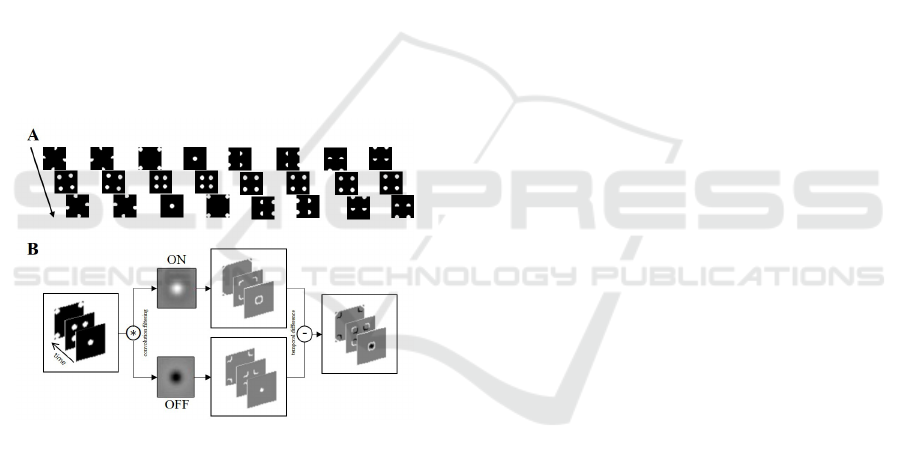
240, or 480 pixels per second, leading to video se-
quences of 133 ms, 67 ms, or 33 ms, respectively.
We used 800 simulations in total for the training of
our SNN (100 for each optic flow pattern, presented
in random order). These sequences were filtered by
spatial kernels consisting of a difference of Gaussian
(DoG) of 5 × 5 pixels. Spikes were generated each
time the difference between the outputs of these fil-
ters between two successive frames exceeded a given
threshold in absolute value (see figure 1B). For each
spike, the information transmitted to the SNN con-
tained its timing, location, and polarity (see section
2.1.3).
These simulations provided an excellent frame-
work to evaluate our approach because they permit-
ted full control of the optic flow patterns transmitted
to the SNN (see (Bichler et al., 2012) for another ex-
ample of synthetic event-based data with 2D motion).
They also permitted us to characterize the robustness
of the model to noise by manipulation of the signal-
to-noise ratio (SNR) in the input spikes. This SNR
manipulation was done by adding random spikes in
the input.
Figure 1: Generation and pre-processing of the optic flow
simulations A) From left to right: clockwise and counter-
clockwise rotations, contracting and expanding patterns,
rightward, leftward, upward and downward translations. B)
Spike generation from a spatio-temporal filtering of the dif-
ferent components through DoG filters (ON and OFF) and
temporal differences.
2.1.2 Event-based Data Collected during
Navigation in the Environment
We used a second dataset composed of visual input
spikes captured by an event-based camera mounted
on a pedestrian’s head as they walked within an urban
environment (Mueggler et al., 2017). The camera was
a DAVIS characterized by a spatial resolution of 240
× 180 pixels with a minimum latency of 3 µs and a
130 dB dynamic range (Brandli et al., 2014). To train
and evaluate our SNN, we restricted our analyses to
spikes generated from the central part (a square of 60
× 60 pixels) of the visual field. This restriction per-
mitted us to limit the number of incoming spikes pro-
cessed by our SNN and improve the processing speed.
An Internal Measurement Unit (IMU) was used
during the collection of the data. It provided the
ground-truth X, Y, and Z values for the acceleration
and angular velocity of the pedestrian trajectories at 1
kHz. The path followed during data acquisition con-
sisted of a large loop across an urban environment.
The pedestrian walked forward for 133 seconds, and
made lateral (left/right) turns. There were more right-
ward turns in the path, with only a few turns to the
left. As a consequence, the walking sequence mainly
featured forward and rightward motions.
2.1.3 Data Format
Whether from simulated data or event-based cameras,
spikes were coded using an Address-Event Represen-
tation (AER), which contained their spatial coordi-
nates, timestamps, and polarities. They were subse-
quently grouped into batches of the same duration and
transmitted to the SNN through a scheduler, treating
all incoming events. After each batch processing, the
SNN entered a resting period. During it, the mem-
brane potentials of all the neurons were reset to their
baseline level.
2.2 Spiking Neural Network
2.2.1 Architecture
Our SNN was composed of two layers with lateral in-
hibition. This reduced, 2-layer structure, allowed us
to keep the number of parameters low, which could
facilitate its implementation on a neuromorphic chip.
The first layer was retinotopically organized: each
of its neurons received afferent spikes from only one
quadrant of the visual field. We used 64 neurons in
total in this layer (16 for each quadrant). They re-
ceived AER data via the scheduler (see section 2.1.3).
Neurons in the second layer (64 in total) were fully
connected to the outputs of the first layer. Figure 2
provides an overview of our architecture.
2.2.2 Spiking Neuron Model
Our neuron model is based on Leaky-Integrate-and-
Fire (LIF) units (Gerstner and Kistler, 2002). A LIF
neuron has a membrane potential V
m
, a resting poten-
tial V
rest
, a membrane resistance R
m
, a time constant
τ
m
, and an input current I. The membrane potential of
a LIF neuron increases every time it receives an input
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
704
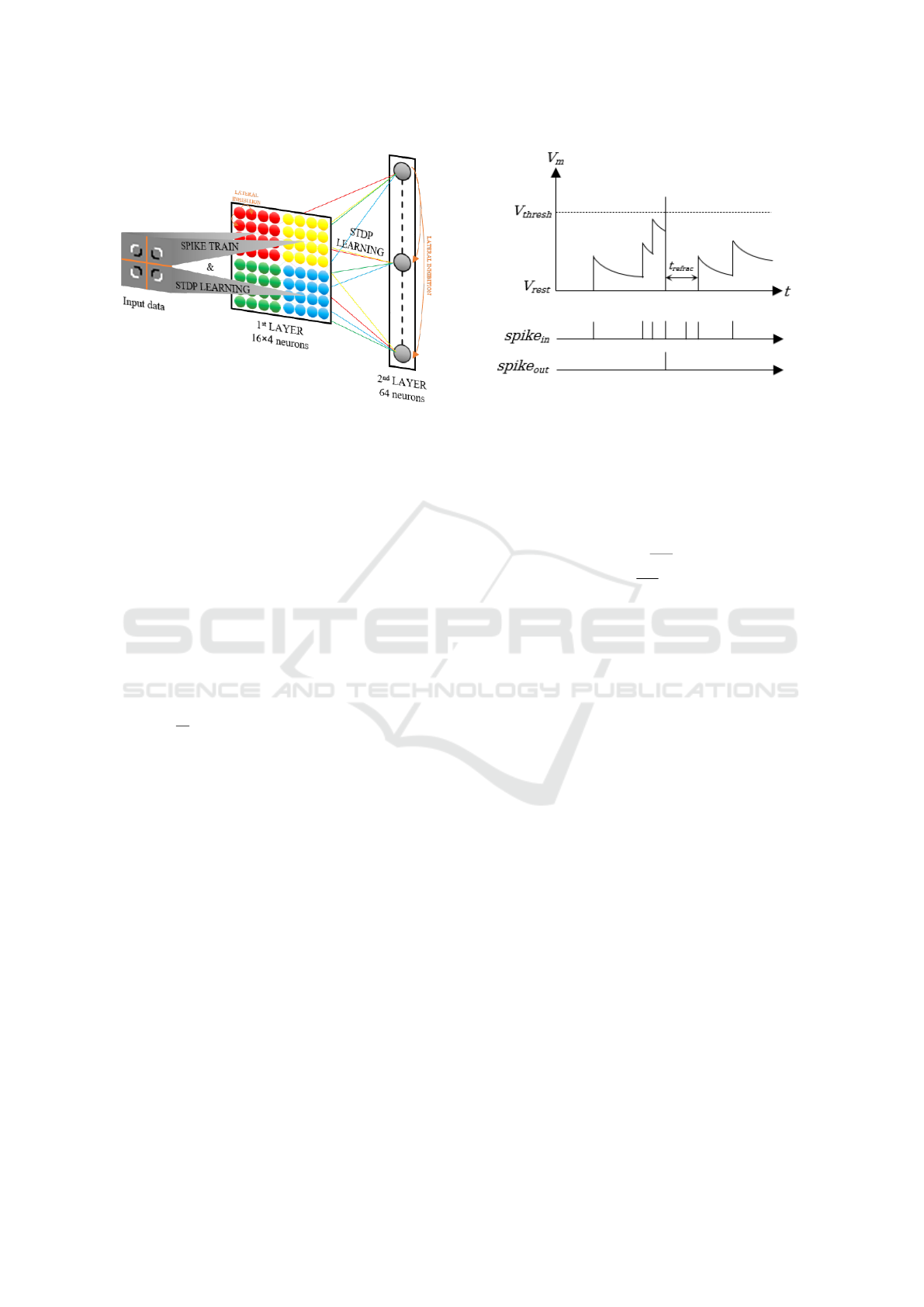
Figure 2: General architecture of our SNN. Neurons in the
first layer are retinotopically organized and only received
afferent spikes from one quadrant of the visual field (see the
different colours). Neurons in the second layers are fully
connected to the outputs of the first layer. Unsupervised
learning is first performed in the first layer. After conver-
gence of the synaptic weights, spikes are transmitted to the
second layer and the STDP rule is applied.
spike. In the absence of inputs, the membrane poten-
tial exponentially decays over time. When the mem-
brane potential reaches the threshold potential V
thresh
,
the neuron emits a spike, and its potential remains at a
resting state during a refractory period. This behavior
is illustrated in figure 3 and can be characterized by
the following equation:
τ
m
d
dt
V
m
(t) = −(V
m
(t) −V
rest
) + R
m
I(t) (1)
During the refractory period following a spike
emission, the membrane potentials of the other neu-
rons in the network were not updated.
2.3 Unsupervised Learning with
Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity
Learning in our SNN is unsupervised and regulated by
the STDP rule. Originally described by (Bi and Poo,
1998; Markram et al., 1997), the STDP is believed
to reflect a general learning principle in the nervous
system of living organisms (Dan and Poo, 2004). It
relies on the spike time difference between pre and
post-synaptic neurons. When a pre-synaptic neuron
emits a spike just before a post-synaptic neuron, its
synaptic weight is reinforced through long-term po-
tentiation (LTP). On the other hand, when the post-
synaptic neuron fires first, the synaptic weight is de-
creased through long-term depression (LTD). In our
study, we used an additive version of the STDP rule,
Figure 3: LIF neuron. The membrane potential V
m
varies as
a function of the incoming spikes spike
in
. When the thresh-
old V
thresh
is reached, the neuron emits a spike spike
out
an-
dreturns to its resting state. It remains in this resting state
for a refractory period t
re f rac
.
which can be described by the equation 2 below and
is graphically represented in figure 4.
∆w =
(
−A
LTD
+ w · e
∆t
τ
LTD
, ∆t ≤ 0
A
LTP
+ w · e
−∆t
τ
LTP
, otherwise.
(2)
Here, ∆w is the synaptic weight change, A the am-
plitude of this change, w the current weight, τ the
time constant, and ∆t the time difference between the
input and output spikes. To prevent neurons in our
SNN from learning the same patterns, we added a
lateral inhibition mechanism in each of our two lay-
ers (see (Chauhan et al., 2018)). Whenever a neuron
emits a spike, it prevents all the other neurons from
the same layer from firing until the next input batch is
processed.
2.4 Evaluation
To characterize the ability of our network to process
optic flow, we used different evaluation metrics. We
first characterized the selectivity of the SNN after
learning. Because optic flow patterns are widespread
in our inputs, we expected neurons in the second layer
to progressively become responsive to the different
patterns. This expectation was measured by charac-
terizing their receptive fields and responses after train-
ing.
To complete these observations, we also computed
confusion matrices using the approach proposed by
(Diehl and Cook, 2015). After learning, we character-
ized the responses of each neuron in the second layer
to the different optic flow patterns by presenting it the
training set used for learning, with the learning rate
set to zero. For a given neuron, the preferred optic
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised Learning of Optic Flow Patterns
705
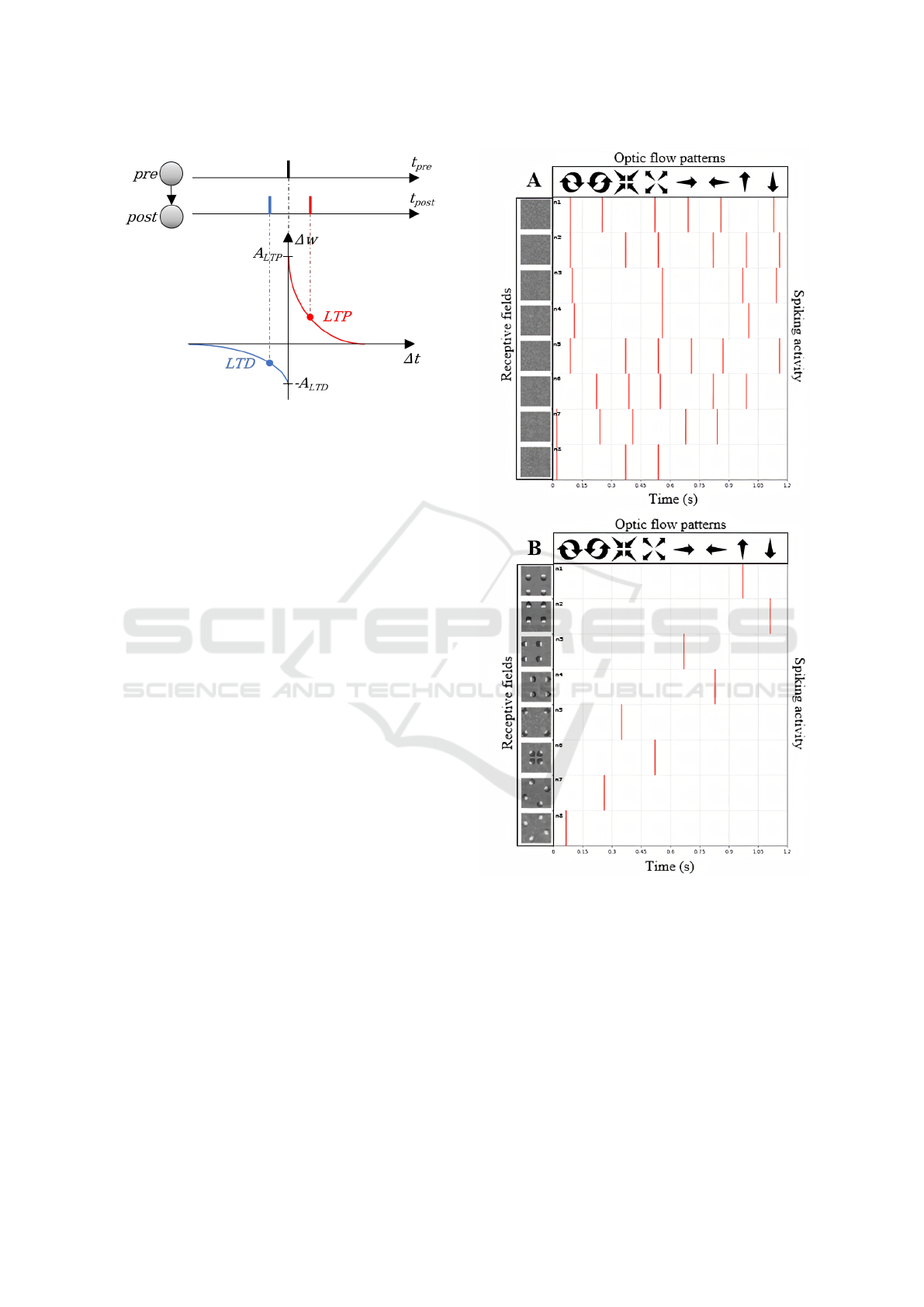
Figure 4: Illustration of the STDP learning rule. When
a pre-synaptic neuron spikes just before the post-synaptic
neuron, their associated synaptic weight is increased by
∆w via long-term potentiation (LTP). The increase is more
important for short spike time differences ∆t = t
post
− t
pre
(see the red curve). At the opposite, the synaptic weight
is decreased via long-term depression (LTD) when the pre-
synaptic neurons emits a spike after the post-synaptic neu-
ron (see the blue curve).
flow component corresponds to the one which leads
to the maximum number of output spikes across all
the trials. Once this labeling was done, predicting the
label of any new trial was determined by selecting the
most frequent label in the population response. The
confusion matrix specifies the distribution of the la-
bels associated with our simulation’s different optic
flow components. In an ideal SNN, the confusion ma-
trix is the identity matrix.
3 RESULTS
We present here the results obtained by training our
SNN with the two event-based datasets (see sections
2.1.1 and 2.1.2).
3.1 Learning from Optic Flow
Simulations
After learning on the synthetic event-based optic flow
dataset, 50 percent of the neurons in the second layer
of our SNN developed a selectivity to optic flow. Fig-
ure 5 illustrates the responses of eight of these neu-
rons before (5-A) and after (5-B) unsupervised train-
ing through STDP. While the receptive fields (on the
left) are initially random, we can observe that they
became highly structured and responsive to different
optic flow patterns after learning. For example, the
neuron illustrated in the first row is selective to up-
Figure 5: Illustration of the spiking activity of our SNN
before (A) and after (B) unsupervised training using syn-
thetic event-based data with different optic flow patterns.
We show the receptive fields of the neurons on the leftward
columns. White and dark regions respectively correspond
to luminance onsets and offsets. Responses to different op-
tic flow patterns (the different conditions are provided on
the upward row) are shown on the rightward columns.
ward translation. The rightward columns present the
spiking activity of these neurons in responses to dif-
ferent optic flow patterns (optic flow conditions are
shown on the top). Before learning, each neuron re-
sponds to different optic flow conditions. In contrast,
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
706
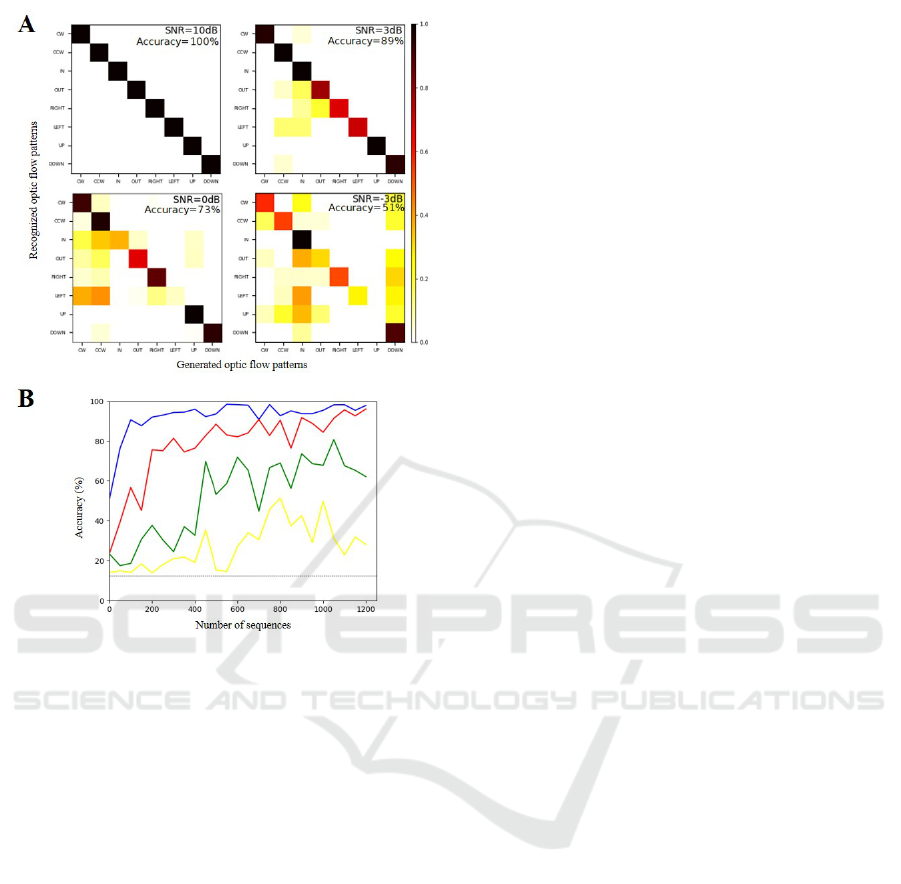
Figure 6: Performances of our SNN on the synthetic event-
based dataset. A) Confusion matrices obtained when label-
ing eight different optic flow patterns for four different noise
levels (SNR = 10, 3, 0 and -3 dB). Global performances are
provided on the upper right corners. B) Accuracy level (in
percentages) as a function of the number of presented se-
quences (from 1 to 1200) for different SNR values (10 dB
in blue, 3 dB in red, 0 dB in green, and -3 dB in yellow).
The dashed line gives the chance level (12.5 percent in this
case).
after training, when presented 80 sequences (10 for
each optic flow condition in random order), responses
are sparse, and each neuron only spikes to one optic
flow pattern.
Next, we examined the properties of our SNN at
the population level using confusion matrices. Figure
6 provides matrices estimated under multiple noisy
conditions (A) and a varying number of sequences
presented to the network (B). In the absence of noise,
the nature of the optic flow pattern can be fully re-
covered from the spiking activity of the network.
When noise is added, performances decrease but re-
main largely above chance (12.5 percent) even for
high noise levels. For example, there are still 73 per-
cent correct predictions for an SNR of 0 dB. Impor-
tantly, to control that learning in our SNN was not
based on the initial positions of the discs, we ran ad-
ditional simulations where these positions were ran-
domly picked along the trajectories. Classification
performances of the network after convergence re-
mained unchanged. Notably, the optic flow compo-
nent was always fully recovered in the absence of
noise. This demonstrates that the network learns the
displacement of the discs.
With this simulated dataset, the second layer neu-
rons, which did not converge, kept random recep-
tive fields after learning, even when we increased the
number of presented motions in the training set. This
is likely to be driven by the fact that our simulations
only included eight conditions, and in this case, only
a limited number of neurons is needed to extract mo-
tion direction from the inputs. In addition, lateral in-
hibition in our network (see section 2.3) prevented
other neurons from learning the same patterns. As
we will see below, all the second layer neurons con-
verged when the training was performed using real
(and therefore more complex) data.
3.2 Learning from Navigation DVS
Data
We now examine the performances of our SNN on
real event-based data collected during locomotion.
Using the ground-truth angular velocities provided
by the IMU (see section 2.1.2), we segmented this
dataset into three distinct categories: leftward, on-
ward, and rightward self-motions. After training, all
neurons in the second layer of the SNN developed
specific responses to optic flow. In figure 7, we show
the spiking activity from eight of these neurons before
(7-A) and after (7-B) unsupervised training through
STDP. The labels of the optic flow patterns are shown
on the top. As with the synthetic event-based data,
we can observe that neural activity is initially random
(receptive fields are noisy, and neurons respond to all
optic flow conditions). After training, it is much more
specific as neurons show structured receptive fields
and fire only for one optic flow category. For exam-
ple, the neuron presented on the first raw became se-
lective to leftward motion. All the other neurons are
only responsive to one condition.
Next, we tested whether the spiking activity of the
SNN can predict these labels. This process is the same
as described in section 2.4. In this case, the chance
level is at 33.33 percent. In figure 7-C, we show the
performances of our SNN on this navigation dataset.
Training led to an overall accuracy of 87.5 percent of
correct classification between the three optic flow pat-
terns. This score is well above chance, even though
some of the leftward (and less frequently forward) se-
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised Learning of Optic Flow Patterns
707
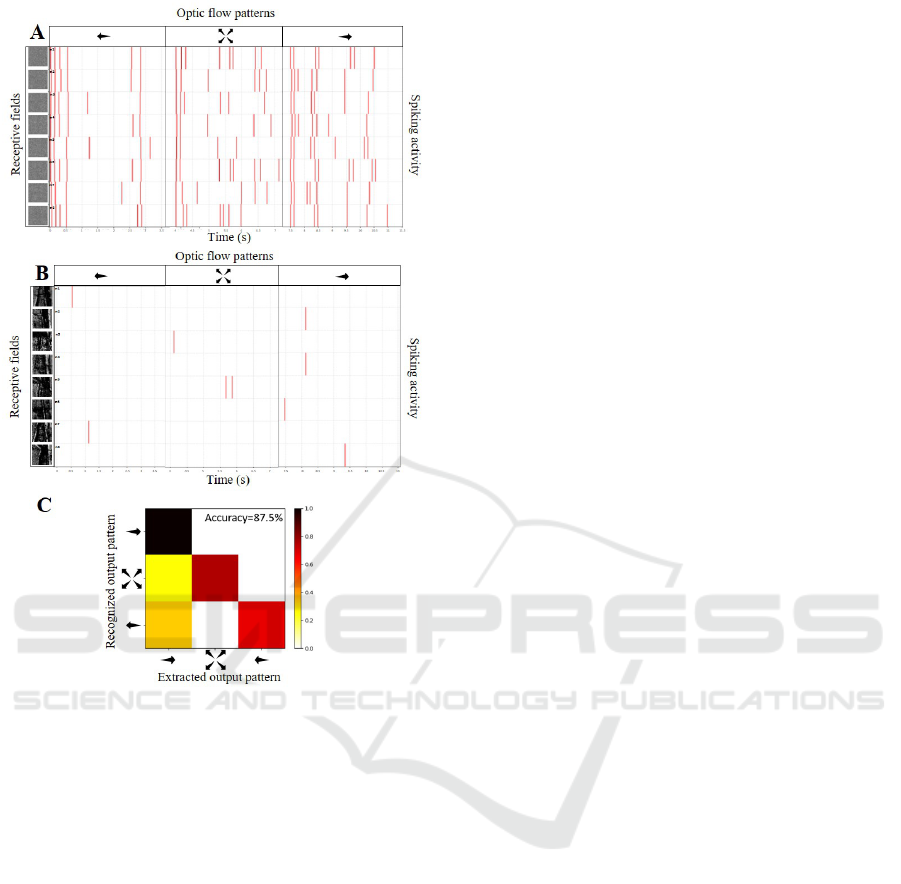
Figure 7: Performances of our SNN on event-based data
collected during navigation in the environment. Receptive
fields (leftward columns) and spiking activity (rightward
columns) are shown before (A) and after (B) training for
eight representative neurons in the second layer of our SNN.
C) Confusion matrix after training. Our SNN was able to la-
bel 87.5 percent of the sequences correctly.
quences were misclassified as rightward motions. As
mentioned in section 2.1.2, the navigation data mostly
contained rightward and forward motions, which may
explain the classifications biases observed here. Fu-
ture works should examine in more detail whether the
same SNN trained with more balanced motion inputs
would reach better classification performances.
4 DISCUSSION
In this paper, we present a simple SNN (see figure
2) capable of extracting optic flow components from
event-based data. Learning in our network is fully
unsupervised and depends on a bio-inspired learning
rule, spike-timing-dependent plasticity (see figure 4).
After convergence, neurons in the network become
selective to different optic flow components, and their
spiking activity at the population level can be used
to determine self-motion direction during navigation.
These properties are observed with both simulated
data (see figure 6) as well as real data collected with
a DVS camera during locomotion (see figure 7).
Our SNN comprises 128 neurons in its two lay-
ers while (Paredes-Vall
´
es et al., 2020), (Bichler et al.,
2012) and (Diehl and Cook, 2015) respectively used
177, 266 and 6400 neurons in their networks (NB: A
much smaller number of neurons was used by (Oud-
jail. and Martinet., 2019; Oudjail. and Martinet.,
2020), but in their case, inputs were restricted to trans-
lations in four directions in a small grid of 5 x 5 pix-
els). After learning, our SNN requires 10 spikes on
average to correctly classify an optic flow pattern. As
a single spike is estimated to consume between 700
and 900 pJ on a neuromorphic chip (Indiveri et al.,
2006; Aamir et al., 2018; Asghar et al., 2021), our
network would therefore need between 7 and 9 nJ to
characterize self-motion. Because of its simple archi-
tecture (only two layers and 128 neurons) and low en-
ergy consumption when implemented on a chip, our
SNN is a good candidate for embedded applications
where an accurate estimation of optic flow is neces-
sary, for example, in autonomous vehicles or for nav-
igation with computer assistance in blind patients.
The event-based navigation dataset that we used
here was limited, and the walking path of the pedes-
trian mostly contained forward and rightward dis-
placements. In the near future, the properties of our
SNN will be characterized using a more balanced and
fuller dataset. Also, the predictions obtained from the
output spiking activity of our network were restricted
to the pattern of optic flow (i.e., to the direction of
self-motion). Future improvements could include an
estimation of the exact displacement and velocities of
the camera within the 3D environment (see for exam-
ple (Debat et al., 2021) for an estimation of the 2D
trajectories from the outputs of an SNN trained with
STDP). This could be realized by adding other layers
to the SNN or including a second event-based camera
to support stereoscopic vision.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Paul Fricker was funded by a PhD fellowship from
the Occitanie region awarded to Benoit R. Cottereau
and Christophe Hurter. This research was also sup-
ported by a grant from the ‘Agence Nationale de
la Recherche’ (ANR-16-CE37-0002-01, ANR JCJC
3D3M) awarded to Benoit R. Cottereau.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
708

REFERENCES
Aamir, S. A., Stradmann, Y., M
¨
uller, P., Pehle, C., Hartel,
A., Gr
¨
ubl, A., Schemmel, J., and Meier, K. (2018).
An accelerated lif neuronal network array for a large-
scale mixed-signal neuromorphic architecture. IEEE
Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Pa-
pers, 65(12):4299–4312.
Akopyan, F., Sawada, J., Cassidy, A., Alvarez-Icaza, R.,
Arthur, J., Merolla, P., Imam, N., Nakamura, Y., Datta,
P., Nam, G.-J., Taba, B., Beakes, M., Brezzo, B.,
Kuang, J. B., Manohar, R., Risk, W. P., Jackson,
B., and Modha, D. S. (2015). TrueNorth: Design
and Tool Flow of a 65 mW 1 Million Neuron Pro-
grammable Neurosynaptic Chip. IEEE Transactions
on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and
Systems, 34(10):1537–1557. Conference Name: IEEE
Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated
Circuits and Systems.
Asghar, M. S., Arslan, S., and Kim, H. (2021). A low-power
spiking neural network chip based on a compact lif
neuron and binary exponential charge injector synapse
circuits. Sensors, 21(13):4462.
Bi, G.-q. and Poo, M.-m. (1998). Synaptic Modifications
in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons: Dependence on
Spike Timing, Synaptic Strength, and Postsynaptic
Cell Type. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(24):10464–
10472. Publisher: Society for Neuroscience Section:
ARTICLE.
Bichler, O., Querlioz, D., Thorpe, S. J., Bourgoin, J.-P.,
and Gamrat, C. (2012). Extraction of temporally
correlated features from dynamic vision sensors with
spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Neural Networks,
32:339–348.
Brandli, C., Berner, R., Yang, M., Liu, S.-C., and Delbruck,
T. (2014). A 240 × 180 130 db 3 µs latency global
shutter spatiotemporal vision sensor. IEEE Journal of
Solid-State Circuits, 49(10):2333–2341.
Chauhan, T., Masquelier, T., Montlibert, A., and Cottereau,
B. R. (2018). Emergence of Binocular Disparity Se-
lectivity through Hebbian Learning. Journal of Neu-
roscience, 38(44):9563–9578. Publisher: Society for
Neuroscience Section: Research Articles.
Dan, Y. and Poo, M.-m. (2004). Spike Timing-Dependent
Plasticity of Neural Circuits. Neuron, 44(1):23–30.
Davies, M., Srinivasa, N., Lin, T.-H., Chinya, G., Cao, Y.,
Choday, S. H., Dimou, G., Joshi, P., Imam, N., Jain,
S., Liao, Y., Lin, C.-K., Lines, A., Liu, R., Math-
aikutty, D., McCoy, S., Paul, A., Tse, J., Venkatara-
manan, G., Weng, Y.-H., Wild, A., Yang, Y., and
Wang, H. (2018). Loihi: A Neuromorphic Many-
core Processor with On-Chip Learning. IEEE Micro,
38(1):82–99. Conference Name: IEEE Micro.
Debat, G., Chauhan, T., Cottereau, B. R., Masquelier, T.,
Paindavoine, M., and Baures, R. (2021). Event-based
trajectory prediction using spiking neural networks.
Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 15:47.
Diehl, P. U. and Cook, M. (2015). Unsupervised learning of
digit recognition using spike-timing-dependent plas-
ticity. Front. Comput. Neurosci.
Gallego, G. and Scaramuzza, D. (2017). Accurate angu-
lar velocity estimation with an event camera. IEEE
Robotics and Automation Letters, 2(2):632–639.
Gerstner, W. and Kistler, W. M. (2002). Spiking Neu-
ron Models: Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Indiveri, G., Chicca, E., and Douglas, R. (2006). A
vlsi array of low-power spiking neurons and bistable
synapses with spike-timing dependent plasticity.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 17(1):211–
221.
Lakshmi, A., Chakraborty, A., and Thakur, C. S. (2019).
Neuromorphic vision: From sensors to event-based
algorithms. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Dis-
covery, 9(4):e1310.
Lee, C., Kosta, A. K., Zhu, A. Z., Chaney, K., Daniilidis, K.,
and Roy, K. (2020). Spike-flownet: event-based opti-
cal flow estimation with energy-efficient hybrid neural
networks. In European Conference on Computer Vi-
sion, pages 366–382. Springer.
Markram, H., L
¨
ubke, J., Frotscher, M., and Sakmann, B.
(1997). Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coinci-
dence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science (New
York, N.Y.), 275(5297):213–215.
Mink, J. W., Blumenschine, R. J., and Adams, D. B. (1981).
Ratio of central nervous system to body metabolism
in vertebrates: its constancy and functional basis. The
American Journal of Physiology, 241(3):R203–212.
Mueggler, E., Rebecq, H., Gallego, G., Delbruck, T., and
Scaramuzza, D. (2017). The event-camera dataset and
simulator: Event-based data for pose estimation, vi-
sual odometry, and SLAM. The International Jour-
nal of Robotics Research, 36(2):142–149. Publisher:
SAGE Publications Ltd STM.
Neftci, E. O., Mostafa, H., and Zenke, F. (2019). Surro-
gate Gradient Learning in Spiking Neural Networks:
Bringing the Power of Gradient-Based Optimization
to Spiking Neural Networks. IEEE Signal Process-
ing Magazine, 36(6):51–63. Conference Name: IEEE
Signal Processing Magazine.
Neil, D. and Liu, S.-C. (2016). Effective sensor fusion with
event-based sensors and deep network architectures.
In 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits
and Systems (ISCAS), pages 2282–2285. ISSN: 2379-
447X.
Nguyen, A., Do, T.-T., Caldwell, D. G., and Tsagarakis,
N. G. (2019). Real-time 6dof pose relocalization for
event cameras with stacked spatial lstm networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Work-
shops.
Oudjail., V. and Martinet., J. (2019). Bio-inspired event-
based motion analysis with spiking neural networks.
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Con-
ference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer
Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume 4: VIS-
APP,, pages 389–394. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Oudjail., V. and Martinet., J. (2020). Meta-parameters ex-
ploration for unsupervised event-based motion anal-
ysis. In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint
Event-based Extraction of Navigation Features from Unsupervised Learning of Optic Flow Patterns
709

Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Com-
puter Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume 4:
VISAPP,, pages 853–860. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Paredes-Vall
´
es, F., Scheper, K. Y. W., and de Croon, G. C.
H. E. (2020). Unsupervised Learning of a Hierarchi-
cal Spiking Neural Network for Optical Flow Estima-
tion: From Events to Global Motion Perception. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intel-
ligence, 42(8):2051–2064. Conference Name: IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelli-
gence.
Posch, C., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Linares-Barranco, B.,
and Delbruck, T. (2014). Retinomorphic Event-Based
Vision Sensors: Bioinspired Cameras With Spiking
Output. Proceedings of the IEEE, 102(10):1470–
1484. Conference Name: Proceedings of the IEEE.
Stromatias, E., Soto, M., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., and
Linares-Barranco, B. (2017). An event-driven classi-
fier for spiking neural networks fed with synthetic or
dynamic vision sensor data. Frontiers in neuroscience,
11:350.
Zenke, F., Boht
´
e, S. M., Clopath, C., Coms¸a, I. M., G
¨
oltz,
J., Maass, W., Masquelier, T., Naud, R., Neftci, E. O.,
Petrovici, M. A., Scherr, F., and Goodman, D. F. M.
(2021). Visualizing a joint future of neuroscience and
neuromorphic engineering. Neuron, 109(4):571–575.
Zhu, A. Z., Yuan, L., Chaney, K., and Daniilidis, K.
(2018). Ev-flownet: Self-supervised optical flow es-
timation for event-based cameras. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1802.06898.
Zhu, A. Z., Yuan, L., Chaney, K., and Daniilidis, K.
(2019). Unsupervised event-based learning of opti-
cal flow, depth, and egomotion. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, pages 989–997.
VISAPP 2022 - 17th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
710
