
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR
Jianshen Zhu
1
, Kazuya Haraguchi
1 a
, Hiroshi Nagamochi
1 b
and Tatsuya Akutsu
2 c
1
Department of Applied Mathematics and Physics, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan
2
Bioinformatics Center, Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji 611-0011, Japan
Keywords:
Machine Learning, Linear Regression, Integer Programming, Linear Program, Cheminformatics, Materials
Informatics, QSAR/QSPR, Molecular Design.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a new machine learning method, called adjustive linear regression, which can be
regarded as an ANN on an architecture with an input layer and an output layer of a single node, wherein an
error function is minimized by choosing not only weights of the arcs but also an activation function at each
node in the two layers simultaneously. Under some conditions, such a minimization can be formulated as a
linear program (LP) and a prediction function with adjustive linear regression is obtained as an optimal solution
to the LP. We apply the new machine learning method to a framework of inferring a chemical compound with
a desired property. From the results of our computational experiments, we observe that a prediction function
constructed by adjustive linear regression for some chemical properties drastically outperforms that by Lasso
linear regression.
1 INTRODUCTION
In this paper, we design a new learning method, called
“adjustive linear regression” in order to construct a
function that predicts a chemical property of a given
chemical compound and is further used for molecu-
lar design. We start with the background and related
work.
Background and Related Work. Computational
analysis of chemical compounds recently attracts at-
tentions not only in chemo-informatics but also in
bioinformatics and artificial intelligence because it
may lead to discovery of novel materials and drugs.
Indeed, various machine learning methods have been
applied to the prediction of chemical activities from
their structural data (Lo et al., 2018; Tetko and En-
gkvist, 2020). Recently, neural networks and deep-
learning technologies have been extensively applied
to this problem (Ghasemi et al., 2018).
Prediction of chemical activities from chemical
structure data has also been studied for many years
in the field of chemoinformatics, which is often re-
ferred to as quantitative structure activity relation-
ship (QSAR) (Muratov et al., 2020). In addition
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2479-3135
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8332-1517
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9763-797X
to QSAR, extensive studies have been done on in-
verse quantitative structure activity relationship (in-
verse QSAR), which seeks for chemical structures
having desired chemical activities under some con-
straints. In these studies, chemical compounds are
usually treated as undirected graphs (called chemical
graphs) and are further represented as feature vectors,
each of which is a vector of real and/or integer num-
bers where its elements are called descriptors. One
major approach in inverse QSAR is to infer feature
vectors from given chemical activities and constraints
and then reconstruct chemical structures from these
feature vectors (Miyao et al., 2016; Ikebata et al.,
2017; Rupakheti et al., 2015).
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) have also been
extensively applied to inverse QSAR. For exam-
ple, recurrent neural networks (Segler et al., 2017;
Yang et al., 2017), variational autoencoders (G
´
omez-
Bombarelli et al., 2018), grammar variational autoen-
coders (Kusner et al., 2017), generative adversarial
networks (De Cao and Kipf, 2018), and invertible
flow models (Madhawa et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2020)
have been applied, where graph convolutional net-
works (Kipf and Welling, 2016) have been often uti-
lized in such methods to directly handle chemical
graphs. However, these methods do not yet guaran-
tee optimal or exact solutions.
Recently, an exact approach has been proposed for
144
Zhu, J., Haraguchi, K., Nagamochi, H. and Akutsu, T.
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR.
DOI: 10.5220/0010853700003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 144-151
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
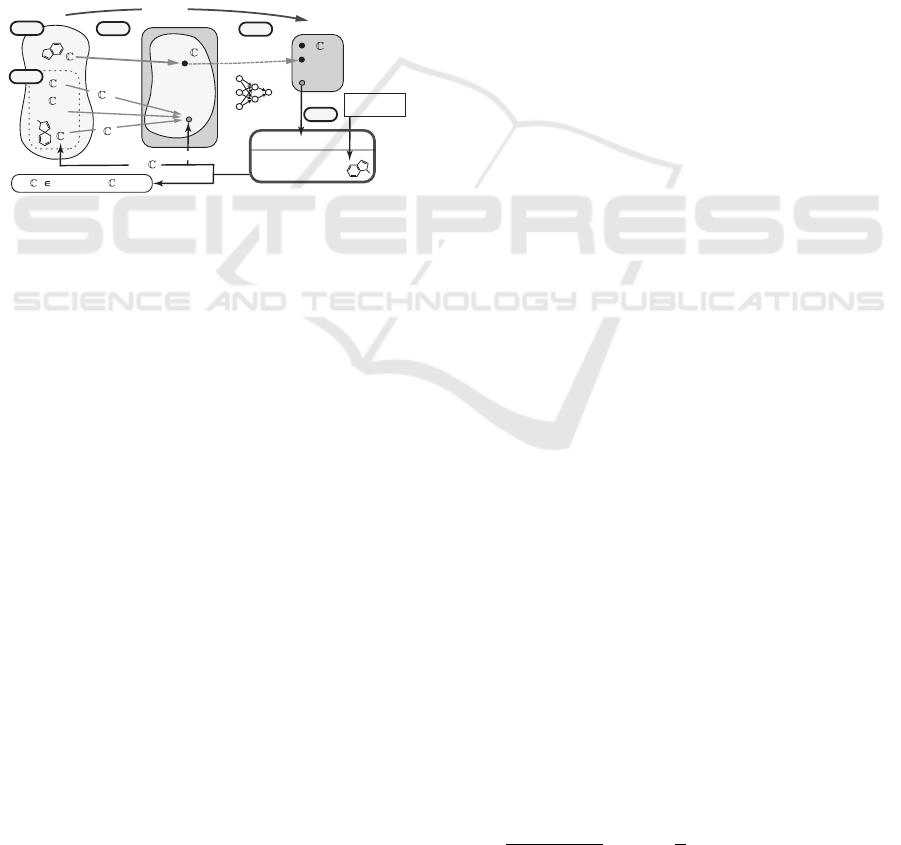
inference of feature vectors from trained ANNs (Shi
et al., 2021). This framework (Figure 1) consists of
two phases: ANNs are trained using existing meth-
ods in the first phase and in the second phase, fea-
ture vectors are inferred from desired output values
by solving mixed integer linear programming (MILP)
that models an inverse problem of the ANN, which is
the unique and novel point of this approach. Currently
this approach has been further extended so that (i) not
only feature vectors but also chemical graphs can be
inferred by solving MILP, (ii) other types of predic-
tion functions can be utilized, and (iii) any chemical
graphs can be treated. A sophisticated method (Zhu
et al., 2021a) has been studied in order to formulate a
sparse MILP instance even for a complicated require-
ments in a topological specification.
R
K
x*
MILP
y*,y*
input
output
R
1
*
M(g,x,y;C
1
,C
2
)
Stage 5
x*
detect
deliver
Stage 4
ANN
a: property
function
N
...
2
...
f( )
y* h(x*) y*
f( *)
G
: class of chemical
graphs
Stage 1
Stage 3
h: prediction
function
Stage 2
f : feature
function
x:=f( )
a( )
h(x)
i
s: topological
specification
͊
͊
͊
h
function
function
f
graph constraints
C
1
:
C
2
:
M(x,y;C
1
)
M(g,x;C
2
)
g :
͊
*
B
B
B
B
no * G s.t.
y* h(f( *)) y*
B
B
B B
B
B
Figure 1: An illustration of a framework for inferring a set
of chemical graphs C
∗
.
Contribution. In this paper, we develop a novel pre-
diction function and its machine learning method that
can be used in the above-mentioned framework. Let
us compare linear regression and ANNs. The former
uses a hyperplane to explain a given data set and the
latter can represent a more complex subspace than a
hyperplane. Importantly a best hyperplane that min-
imizes an error function can be found exactly in the
former whereas a local optimum solution to an error
function is constructed by an iterative procedure in
the latter and different local optimum solutions often
appear depending on how we have tuned many param-
eters in ANNs. Linear regression can be regarded as
an ANN on an architecture with an input layer and an
output layer of a single node with a linear activation
function. We consider an ANN on the same architec-
ture such that each node in the input and output layers
is equipped with a set of activation functions. Given
a data set, we consider a problem of minimizing an
error function on the data set by choosing a weight
of each arc, a bias of the output node and a best ac-
tivation function for each node simultaneously. With
some restriction on the set of activation functions and
the definition of an error function, we show that such
an minimization problem can be formulated as a lin-
ear program, which is much easier than an MILP to
solve exactly. We call this new method “adjustive lin-
ear regression” and implemented it in the two phase
framework. We compared adjustive linear regression
with Lasso linear regression in constructing predic-
tion functions for several chemical properties. From
the results of our computational experiments, we ob-
serve that a prediction function constructed by ad-
justive linear regression for some chemical proper-
ties drastically outperforms that by Lasso linear re-
gression. We refer to a full preprint version (Zhu
et al., 2021b) for some details on notions, modeling
of chemical compounds, the framework and feature
function used in this paper.
Organization. The paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 reviews the idea of prediction functions
based on linear regression and ANNs and designs “ad-
justive linear regression”, a new method for construct-
ing a prediction function by solving a linear program
to optimize a choice of weights/bias together with
activation functions in an ANN with no hidden lay-
ers. Section 3 reviews a method, called a two-layered
model for representing the feature of a chemical graph
in order to deal with an arbitrary graph in the frame-
work. Section 4 reports the results on some compu-
tational experiments conducted for the framework of
inferring chemical graphs by using our new method
of adjustive linear regression. Section 5 makes some
concluding remarks.
2 CONSTRUCTING PREDICTION
FUNCTIONS
Let R, R
+
, Z and Z
+
denote the sets of reals, non-
negative reals, integers and non-negative integers, re-
spectively. For two integers a and b, let [a,b] denote
the set of integers i with a ≤ i ≤ b. For a vector x ∈ R
p
,
the j-th entry of x is denoted by x( j), j ∈ [1, p].
2.1 Linear Prediction Functions
For an integer K ≥ 1, define a feature space R
K
. Let
X = {x
1
,x
2
,...,x
m
} be a set of feature vectors x
i
∈ R
K
and let a
i
∈ R be a real assigned to a feature vector
x
i
. Let A = {a
i
| i ∈ [1, m]}. A function η : R
K
→
R is called a prediction function. We wish to find a
prediction function η : R
K
→ R based on a subset of
{x
1
,x
2
,...,x
m
} so that η(x
i
) is closed to the value a
i
for many indices i ∈ [1, m].
For a prediction function η : R
K
→ R, define an
error function Err(η; X ) ,
∑
i∈[1,m]
(a
i
− η(x
i
))
2
, and
define the coefficient of determination R
2
(η,X ) to be
1 −
Err(η;X )
∑
i∈[1,m]
(a
i
−
e
a)
2
for
e
a =
1
m
∑
i∈[1,m]
a
i
.
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR
145
Many methods have been proposed in order to find
a prediction function η that minimizes the error func-
tion Err(η
w,b
;X ) possibly without using all elements
in X ; e.g., (Zou and Hastie, 2005).
For the feature space R
K
, a hyperplane is defined
to be a pair (w,b) of a vector w ∈ R
K
and a real b ∈ R.
A prediction function η is called linear if η is given
by η
w,b
(x) = w · x + b, x ∈ R
K
for a hyperplane (w,b).
The linear regression is to find a hyperplane (w,b) that
minimizes Err(η
w,b
;X ) =
∑
i∈[1,m]
(a
i
− (w · x
i
+ b))
2
.
In many cases, a feature vector f contains descrip-
tors that do not play an essential role in constructing
a good prediction function. When we solve the mini-
mization problem, the entries w( j) for some descrip-
tors j ∈ [1, K] in the resulting hyperplane (w, b) be-
come zero, which means that these descriptors were
not necessarily important for finding a prediction
function η
w,b
. It is proposed that solving the min-
imization with an additional penalty term to the er-
ror function often results in a more number of en-
tries w( j) = 0, reducing a set of descriptors neces-
sary for defining a prediction function η
w,b
. For an
error function with such a penalty term, a Ridge func-
tion
1
2m
Err(η
w,b
;X ) + λ[
∑
j∈[1,K]
w( j)
2
+ b
2
] (Hoerl
and Kennard, 1970a; Hoerl and Kennard, 1970b) and
a Lasso function
1
2m
Err(η
w,b
;X ) + λ[
∑
j∈[1,K]
|w( j)| +
|b|] (Tibshirani, 1996) are known, where λ ∈ R is
a given real number. As a hybridization of Ridge
linear regression and Lasso linear regression, a lin-
ear regression that minimizes an error function de-
fined to be
1
2m
Err(η
w,b
;X ) + λ
2
[
∑
j∈[1,K]
w( j)
2
+b
2
]+
λ
1
[
∑
j∈[1,K]
|w( j)| + |b|] is called elastic net linear re-
gression (Zou and Hastie, 2005), where λ
1
,λ
2
∈ R are
given real numbers.
2.2 ANNs for Linear Prediction
Functions
It is not difficult to see that a linear prediction func-
tion η with a hyperplane (w,b) can be represented by
an ANN N with an input layer L
in
= {u
1
,u
2
,...,u
K
}
of K input nodes and an output layer L
out
= {v} of
a single output node v such that the weight of an arc
(u
j
,v) from an input node u
j
to the output node v is
given by w( j), j ∈ [1, K]; the bias at node v is given
by b; and the activation function at node v is linear.
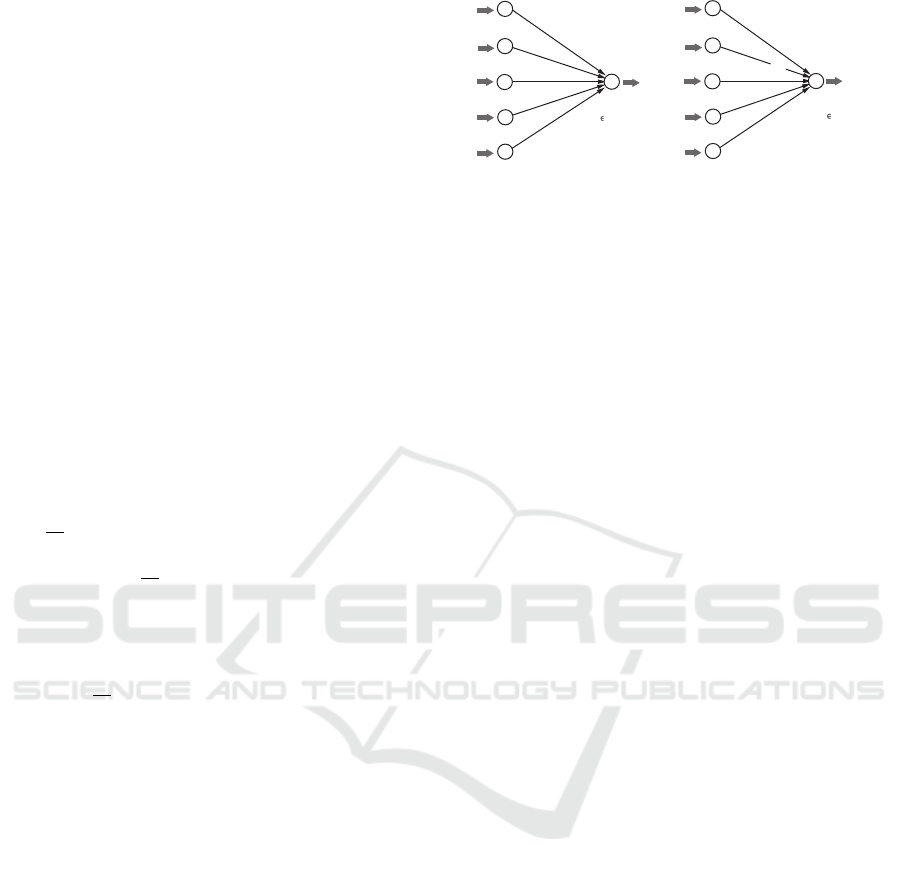
See Figure 2(a) for an illustration of an ANN N that
represents a linear prediction function η with a hy-
perplane (w, b). Given a vector x ∈ R
K
, the ANN N
outputs y :=
∑
j∈[1,K]
w( j)x( j) + b.
We consider an ANN N
φ
with the same architec-
ture with the ANN N and introduce activation func-
tions φ
j
at nodes u
j
, j ∈ [1, K] and an activation func-
tion φ
0
at node v. Given a vector x ∈ R
K
, the ANN N
φ
w(1)
(a)
(b)
u
1
u
j
v
u
2
u
K
w(j)
w(K)
b
x(1)
x(j)
x(K)
y:= S w(j)x(j)+b
y
j [1,K]
w(1)
u
1
u
j
v
u
2
u
K
w(j)
w(K)
b
x(1)
x(j)
x(K)
z(0):= S w(j)z(j)+b
j [1,K]
z(1):= f
1
(x(1))
z(K):= f
K
(x(K))
y:= f
0
(z(0))
z(j):= f
j
(x(j))
Figure 2: An illustration of the process in ANNs with no
hidden layers: (a) An ANN N that represents a linear pre-
diction function η with a hyperplane (w, b); (b) an ANN N
φ
with activation functions φ
j
, j ∈ [0,K] at all nodes.
outputs y := φ
0
(z(0)) for z(0) :=
∑
j∈[1,K]
w( j)z( j)+b
and z( j) := φ
j
(x( j)), j ∈ [1,K].
In a standard method of a prediction function η
N
φ
with the above ANN N
φ
, we specify each activation
function φ
j
and determine weights w and a bias b by
executing an iterative procedure that tries to minimize
an error function between the real values a
i
and the
predicted values η
N
φ
(x
i
).
2.3 Adjustive Linear Regression
In this paper, we design a new method of constructing
a prediction function with the above ANN N
φ
so that
(i) not only weights w and a bias b but also prediction
functions φ
j
are chosen so as to minimize an error
function and (ii) the minimization problem is formu-
lated as a linear programming problem.
We introduce a class Φ
j
of functions for a choice
of each activation function φ
j
, j ∈ [0,K]. When we
choose a function φ
j
∈ Φ
j
for each j ∈ [0, K] and a hy-
perplane (w, b), we define a prediction function η
Ψ,w,b
such that
η
Ψ,w,b
(x) , φ
0
(
∑
j∈[1,K]
w( j)(φ
j
(x( j))) − b)
for the set Ψ = {φ
j
| j ∈ [0,K]} of the functions.
In this paper, we use a function ξ(t) = ct + c
0
t
2
+
c
00
(1 − (t − 1)
2
),0 ≤ t ≤ 1 for a function φ
j
, j ∈ [1,K]
or the inverse φ
−1
0
of a function φ
0
, where c,c
0
and c
00
are nonnegative constant constants with c + c
0
+ c
00
=
1 which will be determined for each j ∈ [0,K] by our
method. Note that, for a domain 0 ≤ t ≤ 1, ξ(t) is a
monotone increasing function such that ξ(0) = 0 and
ξ(1) = 1 and admits an inverse function ξ
−1
(t).
We introduce a class Φ
j
of functions in the fol-
lowing way.
1. Normalize the set {x
i
( j) | x
i
∈ X }, j ∈ [1,K] and
the set {a
i
( j) | x
i
∈ X } so that the minimum and
maximum in the set become 0 and 1.
2. For each index j ∈ [0,K], define a class Φ
j
of
functions to be
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
146

Φ
j
, {c
0
( j)t + c
1
( j)t
2
+ c
2
( j)(1 − (t − 1)
2
),
0 ≤ t ≤ 1 | c
q
( j) ≥ 0, q ∈ [0,2],
∑
q∈[0,2]
c
q
( j) = 1}, j ∈ [1, K],
and define
e
Φ
0
, {c
0
(0)t + c
1
(0)t
2
+ c
2
(0)(1 − (t − 1)
2
),
0 ≤ t ≤ 1 | c
q
(0) ≥ 0,q ∈ [0,2],
∑
q∈[0,2]
c
q
(0) = 1},
Φ
0
, {ξ
−1
(t),0 ≤ t ≤ 1 | ξ(t) ∈
e
Φ
0
}.
To use linear programming, we measure an error
of a prediction function η over a data set X by the
sum of the absolute errors: SAE(η; X ) ,
∑
x
i
∈X
|a
i
−
η(x
i
)|.
Now our aim is to find a prediction function
η
Ψ,w,b
that minimizes the sum of the absolute er-
rors SAE(η
Ψ,w,b
;X ) over all functions φ
0
∈
e
Φ
0
,φ
j
∈
Φ
j
, j ∈ [1, K] and hyperplanes (w,b).
To formulate this minimization problem as a lin-
ear programming problem, we predetermine the sign
of w( j) for each descriptor j in a hyperplane (w, b)
that we will choose. Compute the correlation coef-
ficient σ(X
j
,A) between X
j
= {x
i
( j) | i ∈ [1,m]} and
A = {a
i
| i ∈ [1,m]} and partition the set of descrip-
tors into two sets I
+
:= { j ∈ [1,K] | σ(X
j
,A) ≥ 0} and
I
−
:= { j ∈ [1, K] | σ(X
j
,A) < 0}. We impose an ad-
ditional constraint that w( j) ≥ 0, j ∈ I
+
and w( j) ≤
0, j ∈ I
−
. Then the objective function is described
as follows, where we rewrite each term w( j), j ∈ I
+
(resp., −w( j), j ∈ I
−
) as w
0
( j):
∑
i∈[1,m]
c
0
(0)a
i
+ c
1
(0)a
2
i
+ c
2
(0)(1 − (a
i
−1)
2
)
−
∑
j∈I
+
[w
0
( j)
c
0
( j)x
i
( j) + c
1
( j)x
i
( j)
2
+c
2
( j)(1 − (x
i
( j)−1)
2
)
]
+
∑
j∈I
−
[w
0
( j)
c
0
( j)x
i
( j) + c
1
( j)x
i
( j)
2
+c
2
( j)(1 − (x
i
( j)−1)
2
)
] − b
.
We minimize this over all nonnegative reals c
q
( j),
q ∈ [0, 2], j ∈ [1,K], nonnegative reals w( j), j ∈ [1, K]
and a real b ∈ R such that
∑
q∈[0,2]
c
q
( j) = 1, j ∈ [1,K].
By introducing a penalty term for the weights
w( j), j ∈ [1,K], we consider the following problem
which we call adjustive linear regression ALR(X ,λ),
where w
0
( j)c
q
( j),q ∈ [0,2] is rewritten as w
q
( j).
min:
1
2m
∑
i∈[1,m]
|c
0
(0)a
i
+c
1
(0)a
2
i
+c
2
(0)(1−(a
i
−1)
2
)
−
∑
j∈I
+
[w
0
( j)x
i
( j)+w
1
( j)x
i
( j)
2
+w
2
( j)(1−(x
i
( j)−1)
2
)]
+
∑
j∈I
−
[w
0
( j)x
i
( j)+w
1
( j)x
i
( j)
2
+w
2
( j)(1−(x
i
( j)−1)
2
)]
− b| + λ
∑
j∈[1,K]
w
0
( j)+λ|b|
subject to c
0
(0) + c
1
(0) + c
2
(0) = 1.
We observe that adjustive linear regression is an
extension of the Lasso linear regression except that
the error function is the sum of absolute errors in the
former and the sum of square errors in the latter. It is
not difficult to see that the above minimization can be
formulated as a linear program with O(m + K) vari-
ables and constraints. In our experiment, we also pe-
nalize each weight w
q
( j),q ∈ [1,2] with the same con-
stant λ in a similar fashion to Lasso linear regression..
We solve the above minimization problem to con-
struct a prediction function η
Ψ,w,b
. Let c
∗
q
(0),q ∈
[0,2], w
∗
q
( j),q ∈ [0,2], j ∈ [1,K] and b
∗
denote the val-
ues of variables c
q
(0),q ∈ [0,2], w
q
( j),q ∈ [0,2], j ∈
[1,K] and b in an optimal solution, respectively. Let
K
0
denote the number of descriptors j ∈ [1, K] with
w
∗
0
( j) > 0 and I
K
0
denote the set of j ∈ [1,K] with
w
∗
0
( j) > 0. Then we set
w
∗
( j):=0, j ∈ [1,K] with w
∗
0
( j) = 0,
w
∗
( j):=w
∗
0
( j)/(w
∗
0
( j) + w
∗
1
( j) + w
∗
2
( j)), j ∈ I
+
∩I
K
0
,
w
∗
( j):=−w
∗
0
( j)/(w
∗
0
( j)+w
∗
1
( j)+w
∗
2
( j)), j ∈ I
−
∩I
K
0
,
c
∗
q
( j):=w
∗
q
( j)/w
∗
( j),q ∈ [0,2], j ∈ I
K
0
and
w
∗
:=(w
∗
0
(1),w
∗
0
(2),...,w
∗
0
(K)) ∈ R
K
.
For a set Ψ
∗
of selected functions φ
j
(t) = c
∗
0
( j)t +
c
∗
1
( j)t
2
+ c
∗
2
( j)(1 − (t − 1)
2
), j ∈ I
K
0
with and φ
0
(t)
with φ
−1
0
(t) = c
∗
0
(0)t + c
∗
1
(0)t
2
+ c
∗
2
(0)(1 − (t − 1)
2
)
and a hyperplane (w
∗
,b
∗
), we construct a prediction
function η
Ψ
∗
,w
∗
,b
∗
.
We propose the following scheme of executing
ALR for constructing a prediction function and eval-
uating the performance.
1. Given a data set X = {x
i
∈ R
K
| i ∈ [1, m]} of nor-
malized feature vectors and a set A = {a
i
∈ R | i ∈
[1,m]} of normalized observed values, we choose
a real λ > 0 possibly from a set of candidates for
λ > 0 so that the performance of a prediction func-
tion η
Ψ
∗
,w
∗
,b
∗
obtained from an optimal solution
(Ψ
∗
,w
∗
,b
∗
) to the ALR (X ,λ) attains a criterion,
where we may use cross-validation and the test
coefficient of determination to know the perfor-
mance.
2. With the real λ determined in 1, we evaluate
the performance of a prediction function obtained
with ALR based on cross-validation. We divide
the entire set X into five subsets X
(k)
,k ∈ [1, 5].
For each k ∈ [1, 5], we use the set X \ X
(k)
as
a training data to construct a prediction function
η
Ψ,w,b
with ALR (X \ X
(k)
,λ) and compute the
coefficient of determination R
2
(η
Ψ,w,b
;X
(k)
).
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR
147

3 TWO-LAYERED MODEL
Let C = (H,α,β) be a chemical graph (see (Zhu et al.,
2021b) for the detail) and ρ ≥ 1 be an integer, which
we call a branch-parameter.
A two-layered model of C is a partition of the
hydrogen-suppressed chemical graph hCi into an “in-
terior” and an “exterior” in the following way. We call
a vertex v ∈ V (hCi) of C an exterior-vertex if ht(v) <
ρ (see (Zhu et al., 2021b) for the detail of ht(v)). Let
V
ex
ρ
(C) denote the set of exterior-vertices. We call
an edge e ∈ E(hCi) of C exterior-edge if e is inci-
dent to an exterior-vertex. Let E
ex
ρ
(C) denote the set
of exterior-edges. Define V
int
ρ
(C) , V (hCi) \V
ex
ρ
(C)
and E
int
ρ
(C) , E(hCi) \ E
ex
ρ
(C). We call a vertex in
V
int
ρ
(C) (resp., an edge in E
int
ρ
(C)) an interior-vertex
(resp., interior-edge). The set E
ex
ρ
(C) of exterior-
edges forms a collection of connected graphs each of
which is regarded as a rooted tree T rooted at the ver-
tex v ∈ V (T ) with the maximum ht(v). Let T
ex
ρ
(hCi)
denote the set of these chemical rooted trees in hCi.
The interior C
int
ρ
of C is defined to be the subgraph
(V
int
ρ
(C),E
int
ρ
(C)) of hCi.
w
16
w
17
w
18
C
O
C
C
a
10
a
12
a
14
a
13
a
15
a
16
a
11
a
8
a
9
a
6
u
14
u
16
u
13
u
15
u
18
u
20
u
17
u
19 u
22
u
21
u
11
u
7
u
9
u
1
u
2
u
6
u
4
u
8
u
12
u
5
u
3
u
23
u
10
a
17
w
10
w
11
w
13
w
12
w
1
w
9
w
4
w
7
w
14
w
8
w
15
w
2
w
5
w
3
w
6
N
O
O
C
C
C
O
C
C
C
C
O
C
O
C
C
u
27
u
25
u
24
u
26
u
28
w
19
P
a
2
P
a
4
Q
u
5
Q
u
22
C
O
N
C
P
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
+
O
N
-
S(2)
S(6)
Q
u
18
P
a
3
P
a
1
P
a
5
-
N
Figure 3: An illustration of a hydrogen-suppressed chemi-
cal graph hCi obtained from a chemical graph C by remov-
ing all the hydrogens, where for ρ = 2, V
ex
ρ
(C) = {w
i
| i ∈
[1,19]} and V
int
ρ
(C) = {u
i
| i ∈ [1, 28]}.
Figure 3 illustrates an example of a hydrogen-
suppressed chemical graph hCi. For a branch-
parameter ρ = 2, the interior of the chemical graph
hCi in Figure 3 is obtained by removing the set of ver-
tices with degree 1 ρ = 2 times; i.e., first remove the
set V
1
= {w
1
,w
2
,...,w
14
} of vertices of degree 1 in
hCi and then remove the set V
2
= {w
15
,w
16
,...,w
19
}
of vertices of degree 1 in hCi−V
1
, where the removed
vertices become the exterior-vertices of hCi.
For each interior-vertex u ∈ V
int
ρ
(C), let T
u
∈
T
ex
ρ
(hCi) denote the chemical tree rooted at u (where
possibly T
u
consists of vertex u) and define the ρ-
fringe-tree C[u] to be the chemical rooted tree ob-
tained from T
u
by putting back the hydrogens origi-
nally attached with T
u
in C. Let T (C) denote the set
of ρ-fringe-trees C[u],u ∈ V
int
ρ
(C). Figure 4 illustrates
the set T (C) = {C[u
i
] | i ∈ [1,28]} of the 2-fringe-
trees of the example C with hCi in Figure 3.
O
C
C
C
O
C
C
H
C
CC
O
C
O
C
C
O
C
C N
N
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
N
H
C
H
C
H
C
H
C
C
H H
C
H H
C
H H
C
H H
C
H H
C
S(2)
P
C
C
O
N
C
O
-
[u
11
]
[u
6
]
[u
7
]
[u
12
]
[u
8
]
[u
10
]
[u
14
]
[u
15
]
[u
1
]
[u
2
]
[u
9
]
[u
13
]
[u
3
] [u
4
]
[u
5
]
[u
17
]
[u
16
]
[u
19
]
[u
22
]
[u
28
]
[u
21
]
[u
23
]
[u
24
]
[u
25
]
[u
20
]
[u
26
]
[u
27
]
C
[u
18
]
-
+
H
H
y
19
O
S(6)
y
4
y
11
y
11
y
11
y
11
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
6
y
11
y
1
y
1
y
1
y
1
y
8
y
2
y
15
y
27
y
23
y
24
y
26
y
30
y
25
Figure 4: The set T (C) of 2-fringe-trees C[u
i
],i ∈ [1, 28] of
the example C with hCiin Figure 3, where the hydrogens
attached to non-root vertices are omitted in the figure.
Topological Specification. A topological specifica-
tion is described as a set of the following rules pro-
posed (Shi et al., 2021):
(i) a seed graph G
C
as an abstract form of a target
chemical graph C;
(ii) a set F of chemical rooted trees as candidates for
a tree C[u] rooted at each interior-vertex u in C;
and
(iii) lower and upper bounds on the number of com-
ponents in a target chemical graph such as chemi-
cal elements, double/triple bonds and the interior-
vertices in C.
See (Zhu et al., 2021b) for a full description and
example of topological specification.
4 RESULTS
We implemented our method of Stages 1 to 5
(see (Zhu et al., 2021b) for the detail) for inferring
chemical graphs under a given topological specifica-
tion and conducted experiments to evaluate the com-
putational efficiency. We executed the experiments on
a PC with Processor: Core i7-9700 (3.0GHz; 4.7 GHz
at the maximum) and Memory: 16 GB RAM DDR4.
We used scikit-learn version 0.23.2 with Python 3.8.5
for executing linear regression with Lasso function or
constructing an ANN. To solve an LP or MILP in-
stance, we used CPLEX version 12.10.
Results on Phase 1. We implemented Stages 1, 2 and
3 in Phase 1 as follows.
We have conducted experiments of adjustive lin-
ear regression and for 37 chemical properties of
monomers (resp., ten chemical properties of poly-
mers) and we found that the test coefficient of de-
termination R
2
of ALR exceeds 0.6 for 28 proper-
ties of monomers: isotropic polarizability (ALPHA)
and boiling point (BP), critical pressure (CP); criti-
cal temperature (CT); heat capacity at 298.15K (CV);
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
148

dissociation constants (DC); electron density on the
most positive atom (EDPA); flash point (FP); en-
ergy difference between the highest and lowest un-
occupied molecular orbitals (GAP); heat of atomiza-
tion (HA); heat of combustion (HC); heat of for-
mation (HF); energy of highest occupied molecu-
lar orbital (HOMO); heat of vaporization (HV); iso-
baric heat capacities in liquid phase (IHCL); isobaric
heat capacities in solid phase (IHCS); Kov
´
ats reten-
tion index (KVI); octanol/water partition coefficient
(KOW); lipophilicity (LP); energy of lowest unoccu-
pied molecular orbital (LUMO); melting point (MP);
optical rotation (OPTR); refractive index (RF); solu-
bility (SL); surface tension (SFT); internal energy at
0K (U0); viscosity (VIS); and vapor density (VD) and
that the test coefficient of determination R
2
of ALR
exceeds 0.8 for eight properties of polymers: experi-
mental amorphous density (AMD); characteristic ra-
tio (CHAR); dielectric constant(DEC); heat capacity
liquid (HCL); heat capacity solid (HCS); mol volume
(MLV); refractive index (RFID); and glass transition
(TG), where we include the result of property permit-
tivity (PRM) for a comparison with Lasso linear re-
gression and ANN.
Stage 1. We set a graph class G to be the set of all
chemical graphs with any graph structure, and set a
branch-parameter ρ to be 2.
For each of the properties, we first select a set Λ
of chemical elements and then collect a data set D
π
on
chemical graphs over the set Λ of chemical elements.
Table 1 shows the size and range of data sets that
we prepared for each chemical property in Stage 1,
where we denote the following: |Λ|: the size |Λ| of Λ
used in the data set D
π
;
|D
π
|: the size of data set D
π
over Λ for the prop-
erty π; and K: the number of descriptors in a feature
vector f (C).
Stage 2. We used the feature function defined in our
chemical model without suppressing hydrogen. We
standardize the range of each descriptor and the range
of property values a(C),C ∈ D
π
.
Stage 3. For each chemical property π, we select a
penalty value λ
π
for a constant λ in ALR(X ,λ) by
conducting linear regression as a preliminary experi-
ment.
We conducted an experiment in Stage 3 to evalu-
ate the performance of the prediction function based
on cross-validation. For a property π, an execution of
a cross-validation consists of five trials of construct-
ing a prediction function as follows.
Tables 1 and 2 show the results on Stages 2 and 3
for the properties on monomers and polymers, respec-
tively, where we denote the following: time: the aver-
age time (sec.) to construct a prediction function with
Table 1: Results in Phase 1 for monomers.
π |Λ| |D
π
| K time ALR LLR ANN
ALPHA 10 977 297 3.00 0.953 0.961 0.888
BP 4 370 184 1.42 0.816 0.599 0.765
BP 7 444 230 2.02 0.832 0.663 0.720
CP 4 125 112 0.15 0.650 0.445 0.694
CP 6 131 119 0.12 0.690 0.555 0.727
CT 4 125 113 0.24 0.900 0.037 0.357
CT 6 132 121 0.28 0.895 0.048 0.356
CV 10 977 297 4.57 0.966 0.970 0.911
DC 7 161 130 0.35 0.602 0.574 0.622
EDPA 3 52 64 0.06 0.999 0.999 0.992
FP 4 36 183 1.31 0.719 0.589 0.746
FP 7 424 229 1.92 0.684 0.571 0.745
GAP 10 977 297 4.77 0.755 0.784 0.795
HA 4 115 115 0.29 0.998 0.997 0.926
HC 4 255 154 0.74 0.986 0.946 0.848
HC 7 282 177 0.84 0.986 0.951 0.903
HF 3 82 74 0.05 0.982 0.987 0.928
HOMO 10 977 297 4.95 0.689 0.841 0.689
HV 4 95 105 0.19 0.626 -13.7 -8.44
IHCL 4 770 256 3.24 0.987 0.986 0.974
IHCL 7 865 316 1.98 0.989 0.985 0.971
IHCS 7 581 192 1.72 0.971 0.985 0.971
IHCS 11 668 228 2.21 0.974 0.982 0.968
KVI 3 52 64 0.05 0.838 0.677 0.727
KOW 4 684 223 3.13 0.964 0.953 0.952
KOW 8 899 303 4.95 0.952 0.927 0.937
LP 4 615 186 1.81 0.844 0.856 0.867
LP 8 936 231 3.37 0.807 0.840 0.859
LUMO 10 977 297 2.75 0.833 0.841 0.860
MP 4 467 197 1.78 0.831 0.810 0.799
MP 8 577 255 2.99 0.807 0.810 0.820
OPTR 4 147 107 0.24 0.876 0.825 0.919
OPTR 6 157 123 0.27 0.870 0.825 0.878
RF 4 166 142 0.24 0.685 0.619 0.521
SL 4 673 217 1.21 0.784 0.808 0.848
SL 8 915 300 2.33 0.828 0.808 0.861
SFT 4 247 128 0.67 0.847 0.927 0.859
U0 10 977 297 2.40 0.995 0.999 0.890
VIS 4 282 126 0.37 0.911 0.893 0.929
VD 4 474 214 2.24 0.985 0.927 0.912
VD 7 551 256 2.28 0.980 0.942 0.889
ALR by solving an LP with O(|D
π
|+K) variables and
constraints over all 50 trials in ten cross-validations;
ALR: the median of test R
2
over all 50 trials in ten
cross-validations for prediction functions constructed
with ALR; LLR: the median of test R
2
over all 50
trials in ten cross-validations for prediction functions
constructed with Lasso linear regression; and ANN:
the median of test R
2
over all 50 trials in ten cross-
validations for prediction functions constructed with
ANNs (see (Zhu et al., 2021b) for the details of con-
structing a prediction function with ANNs).
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR
149

Table 2: Results in Phase 1 for polymers.
π |Λ| |D
π
| K time ALR LLR ANN
AMD 4 86 83 0.09 0.933 0.914 0.885
AMD 7 93 94 0.10 0.917 0.918 0.823
CHAR 3 24 56 0.02 0.904 0.650 0.616
CHAR 4 27 67 0.03 0.835 0.431 0.641
DEC 7 37 72 0.04 0.918 0.761 0.641
HCL 4 52 67 0.06 0.996 0.990 0.969
HCL 7 55 81 0.05 0.992 0.987 0.970
HCS 4 54 75 0.07 0.963 0.968 0.893
HCS 7 59 92 0.09 0.983 0.961 0.880
MLV 4 86 83 0.10 0.998 0.996 0.931
MLV 7 93 94 0.09 0.997 0.994 0.894
PRM 4 112 69 0.09 0.505 0.801 0.801
PRM 5 131 73 0.09 0.489 0.784 0.735
RFID 5 91 96 0.15 0.953 0.852 0.871
RFID 7 124 124 0.21 0.956 0.832 0.891
TG 4 204 101 0.23 0.923 0.902 0.883
TG 7 232 118 0.54 0.927 0.894 0.881
From Tables 1 and 2, we see that ALR performs
well for most of the properties in our experiments,
The performance by ALR is inferior to that by LLR
or ANN for some properities such as GAP, HOMO,
LUMO, OPTR, SL, SFT and PRM, whereas ALR out-
performs LLR and ANN for properties BP, CT, HV,
KVI, VD, CHAR, RFID and TG. It should be noted
that ALR drastically improves the result for properties
CT and HV.
Results on Phase 2. To execute Stages 4 and 5 in
Phase 2, we used a set of seven instances I
a
, I
i
b
,i ∈
[1,4], I
c
and I
d
based on the seed graphs prepared
in (Shi et al., 2021).
Stage 4. We executed Stage 4 for heat of vaporization
(HV).
Table 3 shows the computational results of the ex-
periment in Stage 4 for the two properties, where we
denote the following:
y
∗
, y
∗
: lower and upper bounds y
∗
,y
∗
∈ R on the
value a(C) of a chemical graph C to be inferred; I-
time: the time (sec.) to solve the MILP in Stage 4;
and n: the number n(C
†
) of non-hydrogen atoms in
the chemical graph C
†
inferred in Stage 4.
The result suggests that ALR is useful to infer rel-
atively large size chemical graphs from given chem-
ical properties. Note that hydrogen atoms can be re-
covered after getting hydrogen-suppressed chemical
graphs.
Stage 5. We executed Stage 5 to generate a more
number of target chemical graphs C
∗
, where we call
a chemical graph C
∗
a chemical isomer of a target
chemical graph C
†
of a topological specification σ if
Table 3: Results of Stages 4 and 5 for HV.
inst. y
∗
, y
∗
I-time n D-time C-LB #C
I
a
145, 150 24.9 37 0.0632 2 2
I
1
b
190, 195 146.6 35 0.121 30 30
I
2
b
290, 295 188.8 46 0.154 604 100
I
3
b
165, 170 1167.2 45 36.8 7.5×10
6
100
I
4
b
250, 255 313.7 50 0.166 2208 100
I
c
285, 290 102.5 50 0.016 1 1
I
d
245, 250 351.9 40 5.53 3.9×10
5
100
f (C
∗
) = f (C
†
) and C
∗
also satisfies the same topo-
logical specification σ. We computed chemical iso-
mers C
∗
of each target chemical graph C
†
inferred
in Stage 4. We execute the algorithm due to (Shi
et al., 2021) to generate chemical isomers of C
†
up
to 100 when the number of all chemical isomers ex-
ceeds 100.
The algorithm can compute a lower bound on the
total number of all chemical isomers C
†
without gen-
erating all of them.
Table 3 shows the computational results of the ex-
periment in Stage 5 for property HV, where we denote
the following: D-time: the running time (sec.) to ex-
ecute the dynamic programming algorithm in Stage 5
to compute a lower bound on the number of all chem-
ical isomers C
∗
of C
†
and generate all (or up to 100)
chemical isomers C
∗
; C-LB: a lower bound on the
number of all chemical isomers C
∗
of C
†
; and #C: the
number of all (or up to 100) chemical isomers C
∗
of
C
†
generated in Stage 5. The result suggests that ALR
is useful not only for inference of chemical graphs but
also for enumeration of chemical graphs.
5 CONCLUDING REMARKS
In this paper, we proposed a new machine learning
method, adjustive linear regression (ALR), which has
the following feature: (i) ALR is an extension of the
Lasso linear regression except for the definition of er-
ror functions; (ii) ALR is a special case of an ANN
except that a choice of activation functions is also op-
timized differently from the standard ANNs and the
definition of error functions; and (iii) ALR can be ex-
ecuted exactly by solving the equivalent linear pro-
gram with O(m + K) variables and constraints for a
set of m data with K descriptors. Even though ALR
is a special case of an ANN with non-linear activation
functions, we still can read the relationship between
cause and effect from a prediction function due to the
simple structure of ALR.
In this paper, we used a quadratic function for
a set Ψ of activation functions φ. We can use
many different functions such as sigmoid function
BIOINFORMATICS 2022 - 13th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
150

and ramp functions, where the non-linearity of a func-
tion does not affect to derive a linear program for
ALR. The proposed method/system is available at
GitHub https://github.com/ku-dml/mol-infer.
REFERENCES
De Cao, N. and Kipf, T. (2018). Molgan: An im-
plicit generative model for small molecular graphs.
arXiv:1805.11973.
Ghasemi, F., Mehridehnavi, A., P
´
erez-Garrido, A., and
P
´
erez-S
´
anchez, H. (2018). Neural network and deep-
learning algorithms used in qsar studies: merits and
drawbacks. Drug Discovery Today, 23:1784–1790.
G
´
omez-Bombarelli, R., Wei, J., Duvenaud, D., Hern
´
andez-
Lobato, J., S
´
anchez-Lengeling, B., Sheberla, D.,
Aguilera-Iparraguirre, J., Hirzel, T., Adams, R., and
Aspuru-Guzik, A. (2018). Automatic chemical de-
sign using a data-driven continuous representation of
molecules. ACS Cent. Sci., 4:268–276.
Hoerl, A. and Kennard, R. (1970a). Ridge regression: Ap-
plications to nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics,
12(1):69–82.
Hoerl, A. and Kennard, R. (1970b). Ridge regression: Bi-
ased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Techno-
metrics, 12(1):55–67.
Ikebata, H., Hongo, K., Isomura, T., Maezono, R., and
Yoshida, R. (2017). Bayesian molecular design with
a chemical language model. J. Comput. Aided Mol.
Des., 31:379–391.
Kipf, T. N. and Welling, M. (2016). Semi-supervised
classification with graph convolutional networks.
arXiv:1609.02907.
Kusner, M., Paige, B., and Hern
´
andez-Lobato, J. (2017).
Grammar variational autoencoder. In Proceedings of
the 34th International Conference on Machine Learn-
ing (ICML’17), volume 70, pages 1945–1954, Sydney,
NSW, Australia. JMLR.org.
Lo, Y.-C., Rensi, S., Torng, W., and Altman, R. (2018). Ma-
chine learning in chemoinformatics and drug discov-
ery. Drug Discovery Today, 23:1538–1546.
Madhawa, K., Ishiguro, K., Nakago, K., and Abe, M.
(2019). Graphnvp: an invertible flow model for gen-
erating molecular graphs. arXiv:1905.11600.
Miyao, T., Kaneko, H., and Funatsu, K. (2016). Inverse
QSPR/QSAR analysis for chemical structure genera-
tion (from y to x). J. Chem. Inf. Model., 56:286–299.
Muratov, E. N., Bajorath, J., Sheridan, R., Tetko, I., Fil-
imonov, D., Poroikov, V., Oprea, T., Baskin, I.,
Varnek, A., Roitberg, A., Isayev, O., Curtarolo, S.,
Fourches, D., Cohen, Y., Aspuru-Guzik, A., Winkler,
D., Agrafiotis, D., Cherkasov, A., and Tropsha, A.
(2020). QSAR without borders. Chemical Society Re-
views, 49(11):3525–3564.
Rupakheti, C., Virshup, A., Yang, W., and Beratan,
D. (2015). Strategy to discover diverse optimal
molecules in the small molecule universe. J. Chem.
Inf. Model., 55:529–537.
Segler, M., Kogej, T., Tyrchan, C., and Waller, M. (2017).
Generating focused molecule libraries for drug dis-
covery with recurrent neural networks. ACS Cent. Sci.,
4:120–131.
Shi, C., Xu, M., Zhu, Z., Zhang, W., Zhang, M., and Tang, J.
(2020). GraphAF: a flow-based autoregressive model
for molecular graph generation. arXiv:2001.09382.
Shi, Y., Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L.,
Nagamochi, H., and Akutsu, T. (2021). An inverse
qsar method based on a two-layered model and inte-
ger programming. International Journal of Molecular
Sciences, 22:2847.
Tetko, I. and Engkvist, O. (2020). From big data to artificial
intelligence: chemoinformatics meets new challenges.
J. Cheminformatics, 12:74.
Tibshirani, R. (1996). Regression shrinkage and selection
via the lasso. J. R. Statist. Soc. B, 58:267–288.
Yang, X., Zhang, J., Yoshizoe, K., Terayama, K., and
Tsuda, K. (2017). ChemTS: an efficient python library
for de novo molecular generation. STAM, 18:972–976.
Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., Nag-
amochi, H., and Akutsu, T. (2021a). An improved
integer programming formulation for inferring chemi-
cal compounds with prescribed topological structures.
In The 34th International Conference on Industrial,
Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intel-
ligent Systems (IEA/AIE 2021), pages 197–209, Kuala
Lumpur, Malaysia. Springer.
Zhu, J., Haraguchi, K., Nagamochi, H., and Akutsu, T.
(2021b). Adjustive linear regression and its appli-
cation to the inverse qsar. Department of Applied
Mathematics and Physics, Kyoto University, Tech-
nical Report, TR:2021-002 http://www.amp.i.kyoto-
u.ac.jp/tecrep.
Zou, H. and Hastie, T. (2005). Regularization and vari-
able selection via the elastic net. J. R. Statist. Soc.
B, 67(2):301–320.
Adjustive Linear Regression and Its Application to the Inverse QSAR
151
