
Personalized Evaluation of Life-threatening Conditions in Chronic
Kidney Disease Patients: The Concept of Wearable Technology and Case
Analysis
Ana Santos Rodrigues
1 a
, Birut
˙
e Paliakait
˙
e
1 b
, Saulius Daukantas
1
, Andrius Solo
ˇ
senko
1 c
,
Andrius Petr
˙
enas
1,2 d
and Vaidotas Marozas
1,2 e
1
Biomedical Engineering Institute, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania
2
Department of Electronics Engineering, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania
Keywords:
Wearable Device, Smartwatch, Photoplethysmography, Arrhythmia Detection, Electrolyte Fluctuations,
Biosignal Sensors, Hemodialysis.
Abstract:
The progressive aging of society results in a one-third increase in mortality rates of chronic kidney disease
(CKD) patients over the past decade. In the end stage of CKD, 40% of deaths are sudden deaths due to
cardiac arrhythmias precipitated by electrolyte imbalance. Unfortunately, there is a lack of technology for
unobtrusive long-term monitoring of life-threatening conditions, leading to limited knowledge on arrhythmia
characteristics and their relationship with complications. This paper presents a wearable technology prototype
to monitor CKD patients between subsequent dialysis procedures. The proposed technology enables at-home
monitoring of electrolyte fluctuations and detection of cardiac arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia and
extreme bradycardia. A patient uses a wearable wrist-worn device to record continuous photoplethysmogram
and intermittent electrocardiogram signals together with a smart device, such as a tablet or a smartphone,
to enter meals and medications that may alter electrolyte levels. The application of the proposed wearable
technology is demonstrated in a case analysis. The developed wearable technology for monitoring CKD
patients in a home environment can be valuable for identifying patients susceptible to dangerous arrhythmias
due to electrolyte imbalance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects 13.4% of the
population and is especially common among older
individuals (>65 years), leading to a one-third in-
crease in mortality rates over the past decade (Wang
et al., 2016). In the end stage of CKD, 40% of all
deaths are sudden deaths due to cardiac arrhythmias,
namely, ventricular tachycardia and extreme brady-
cardia (Kalra et al., 2018; Saran et al., 2019). While
ventricular tachycardia that eventually progresses to
more advanced stages (ventricular flutter, ventricu-
lar fibrillation) often precedes sudden cardiac death,
recent research has shown that extreme bradycardia
leading to asystole is also a common cause in CKD
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5011-8192
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4831-6587
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1518-9366
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5700-7196
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6879-5845
patients (Wong et al., 2015b; Yamaguchi et al., 2020).
Thus, it is crucial to detect initial life-threatening ar-
rhythmia episodes as soon as possible to avoid a fa-
tal outcome. Unfortunately, the existing devices for
long-term continuous arrhythmia monitoring are ei-
ther invasive (implanted devices) or inconvenient for
the patient (Holter monitors, ECG patches). Further-
more, it is often unclear what factors contribute most
to arrhythmia initiation in a particular CKD patient.
The end-stage CKD is often treated with thrice-
weekly hemodialysis (HD), increasing the interval
between the procedures 1.5 times during the week-
end. About 50% of life-threatening arrhythmias oc-
cur on the last day of the long interval, linked to in-
creased volume of bodily fluids and electrolyte imbal-
ance (Wong et al., 2015a), with potassium being the
most suspected arrhythmogenic electrolyte (El-Sherif
and Turitto, 2011). Electrolyte imbalance is common
and often asymptomatic in CKD patients (Brunelli
et al., 2017), therefore gathering information on elec-
244
Rodrigues, A., Paliakait
˙
e, B., Daukantas, S., Sološenko, A., Petr
˙
enas, A. and Marozas, V.
Personalized Evaluation of Life-threatening Conditions in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: The Concept of Wearable Technology and Case Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010905700003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 244-250
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

trolyte fluctuations between HD procedures is of im-
portance for restoring the normal balance before the
onset of arrhythmias. Unfortunately, the only clini-
cally accepted method for evaluating electrolyte bal-
ance is an invasive blood test, which cannot be per-
formed at home.
Noninvasive assessment of electrolyte imbalance
spawns scientific research and technological innova-
tion. Electrolyte imbalance affects cardiac electrical
function and can be reflected in the electrocardiogram
(ECG). Based on this property, researchers at Mayo
Clinic (USA) are developing an ECG analysis-based
algorithm for the assessment of serum potassium lev-
els (Attia et al., 2016), whereas Medtronic (USA)
has patented the method for use in implantable de-
vices (Soykan et al., 2016).
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is the
primary treatment against sudden death due to ven-
tricular tachycardia, while a pacemaker is prescribed
for bradycardia management. However, the usage of
implantable devices for sudden death prevention is re-
stricted by various factors, mainly the significant cost
of the invasive device itself and implantation proce-
dures, unclear criteria for selection of CKD patients
for implantation, and their predisposition to infec-
tion (Boriani et al., 2014). Since implantable de-
vices are the only technology providing convenient
long-term monitoring of arrhythmias, such restriction
vastly limits the knowledge of arrhythmia character-
istics and their relationship with complications.
The growing interest in wearable biosensors in-
spires scientists to search for more convenient means
of arrhythmia monitoring. Detection of atrial fibril-
lation in a photoplethysmogram (PPG) has already
demonstrated promising results (Bonomi et al., 2018;
Solo
ˇ
senko et al., 2019; Perez et al., 2019; Pereira
et al., 2020). The potential of wrist-worn devices
capable of detecting atrial fibrillation will likely en-
courage the development of detectors for different ar-
rhythmia types. Nevertheless, thus far, only a few at-
tempts to detect life-threatening arrhythmias in PPG
have been published (Bonomi et al., 2017; Paliakait
˙
e
et al., 2021).
This paper presents the concept of wearable
technology for a personalized evaluation of life-
threatening conditions in CKD patients undergoing
HD. Electrolyte balance is usually altered prior to
HD and normalizes after the procedure. Accord-
ingly, we hypothesize that the corresponding differ-
ences in ECG morphology parameters are related to
the patient’s electrolyte balance before and after HD.
We also hypothesize that electrolyte fluctuations may
cause life-threatening arrhythmias in some patients.
The application of the proposed wearable technology
is illustrated with a case study involving a CKD pa-
tient with electrolyte fluctuations and ventricular ar-
rhythmias.
2 METHODS
2.1 The Components of Wearable
Technology
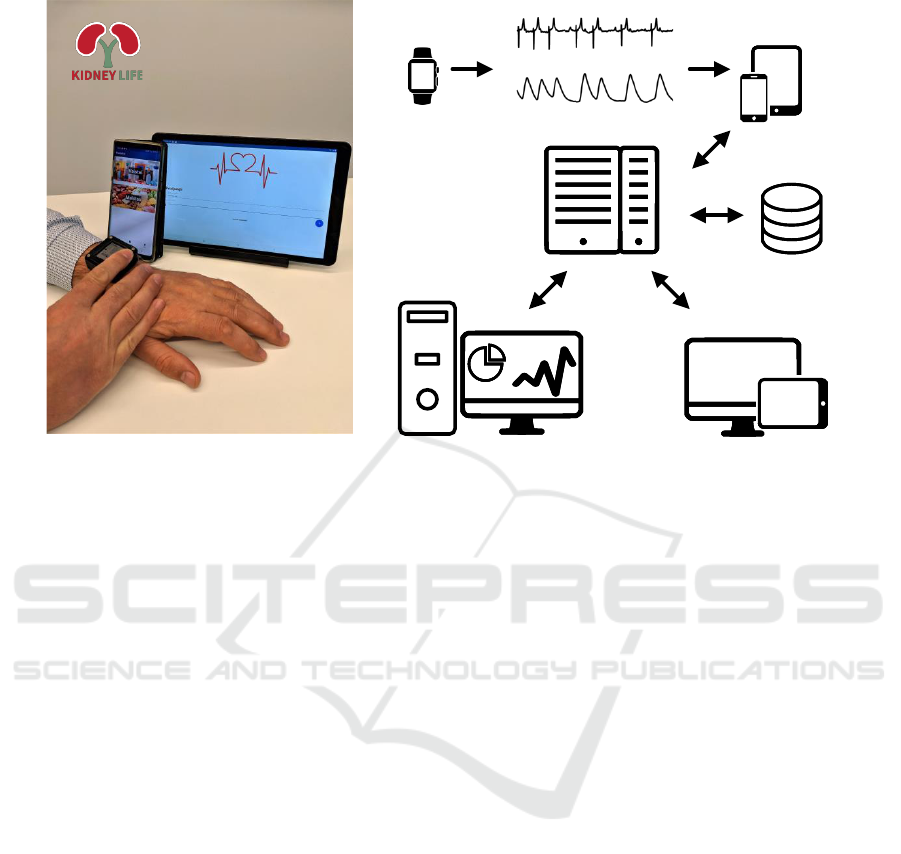
Figure 1 shows a prototype of a wearable technology
for CKD patient monitoring. A patient uses a wear-
able device for recording continuous PPG and inter-
mittent ECG signals. Also, the patient can enter meals
and medications, which may alter electrolyte levels,
using a smart device (tablet or smartphone) with a
dedicated software.
The technology ensures wearing comfort since
biosignal sensors are integrated into a wrist-worn de-
vice. By using the proposed technology, electrolyte
fluctuations are monitored relying on a single-lead
short-term (1-min) ECG. The use of wires is avoided
by integrating the ECG electrodes into the device –
one at the bottom, in contact with the skin, and the
other on the top. The ECG is recorded by touch-
ing the top electrode with a finger of the opposite
hand. Meanwhile, extreme bradycardia and ventric-
ular tachycardia are detected by analyzing a PPG sig-
nal, acquired using the same device. In case life-
threatening arrhythmia is detected, the patient is in-
formed by the device (e.g., by vibration) to touch the
integrated biopotential electrode. The recorded short-
term ECG can be sent to the physician for arrhythmia
type confirmation.
After the recording period, e.g., interdialytic in-
terval, the patient connects the wearable device to the
smart device where the app automatically opens the
most recent GDF (general data format) file and sends
it via HTTPS to a web API hosted on the server. The
web API is implemented in the Haskell programming
language using the Servant framework. The database
(PostgreSQL) stores data about meals and medica-
tions together with timestamps and performs synchro-
nization to the signal files. After each data file is
received, the MATLAB-based processing server, sit-
uated in a high-performance computing workstation
equipped with a GPU, processes the file and creates
a report that includes electrolyte estimates in rela-
tion to detected extreme bradycardia and tachycardia
episodes. Then the report is saved in the database and
emailed to the physician responsible for the patient.
Each of the components are described in more detail
below.
Personalized Evaluation of Life-threatening Conditions in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: The Concept of Wearable Technology and Case
Analysis
245
Patient-worn
device
Patient’s
smart device
Physician's
smart device or PC
Electrocardiogram
Photoplethysmogram
Server
Database
Signal and data
processing
PHOTO
(a) (b)
Figure 1: (a) A prototype of a wrist-worn device for arrhythmia detection and monitoring of electrolyte fluctuations to-
gether with a smartphone and a tablet for entering meals and medications. Note Lithuanian interface of an application
adapted for local patients. (b) A basic system architecture of a technology for CKD patient monitoring. Icons used from
www.onlinewebfonts.com/icon, licensed by CC BY 3.0.
2.2 Monitoring of Electrolyte
Fluctuations
Electrolyte fluctuations can be recognized in ECG
since anomalous electrolyte levels affect the cardiac
electrical conduction. For instance, potassium fluctu-
ations usually alter the T-wave morphology, whereas
calcium precipitates changes in the ST-segment du-
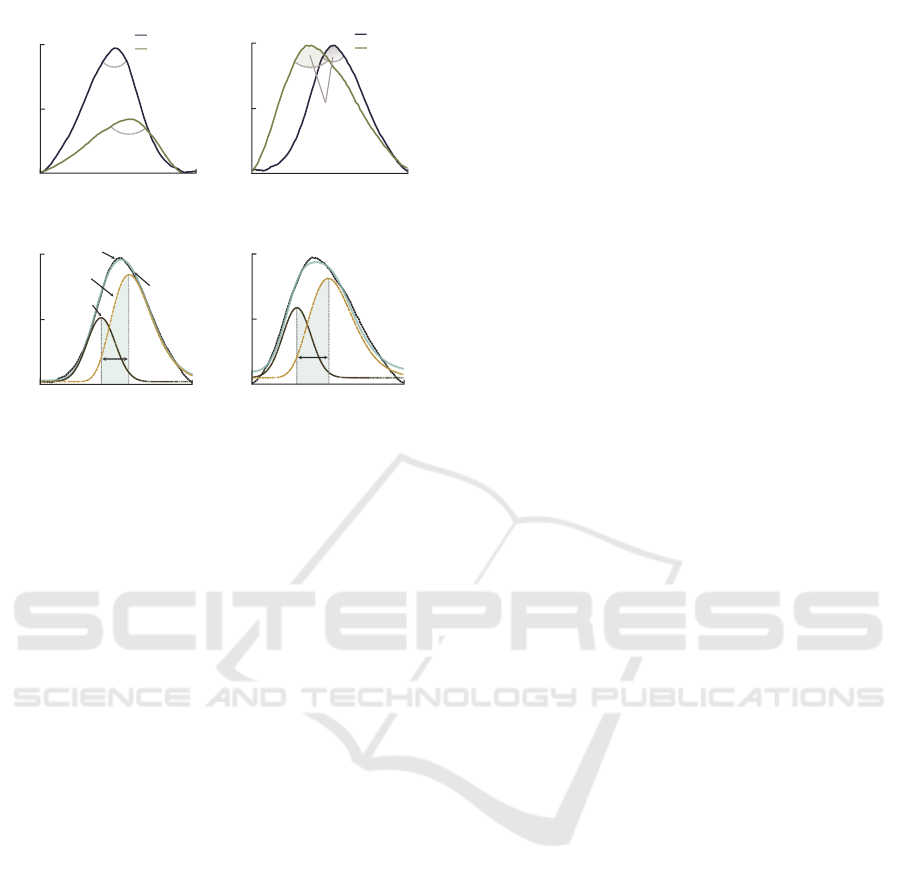
ration (Surawicz, 1967). To evaluate potassium-
induced T-wave morphology changes in HD patients,
we developed a model-based parameter, θ
δ
, that eval-
uates global changes in T-wave morphology (Ro-
drigues et al., 2020). The T-wave, composed of
two slopes—upward and downward—is parameter-
ized using a composite model comprising one Gaus-
sian and one lognormal functions to characterize each
individual slope. θ
δ
combines two parameters: (i) the
angle θ (in °) between the gradients of upward and
downward slopes (Figure 2a-b); and (ii) the tempo-
ral displacement δ (in s) between the modes of the
lognormal and Gaussian functions (Figure 2c-d). The
principle of θ
δ
is as follows. As potassium level rises
above the normal level, the T-wave tends to become
more peaked and decreases in duration. The angle θ
quantifies variations in T-wave peakedness, whereas δ
measures changes in T-wave elongation. θ
δ
amplifies
the response of θ and δ to potassium fluctuations and
is estimated as:
θ
δ
= − log
10
(θ · δ). (1)
The logarithm expands the dynamic range and en-
sures a positive correlation of θ
δ
with potassium fluc-
tuations. θ
δ
is estimated from an averaged heartbeat
representative of a defined short period. For this pa-
per, we used a sliding window of 90 s with a 20 s over-
lap to segment a single-lead ECG. The ECG signal
is preprocessed similarly to our previous study (Ro-
drigues et al., 2020).
2.3 Detection of Life-threatening
Arrhythmias
Extreme bradycardia is defined as at least 5 consecu-
tive beats at a heart rate lower than 40 bpm, and ven-
tricular tachycardia is defined as at least 5 consecutive
ventricular beats at a heart rate higher than 120 bpm.
Following these definitions, life-threatening arrhyth-
mias are detected in pulse rate series, obtained from
the peak-to-peak intervals where the occurrence times
of the PPG pulses are determined using a peak de-
tector similar to the one described in (Aboy et al.,
2005). To avoid false alarms, the threshold-based
life-threatening arrhythmia detector (Paliakait
˙
e et al.,
2021) is supplemented with a signal quality index pro-
posed in (Solo
ˇ
senko et al., 2019). A PPG pulse is con-
sidered to be of high quality if maximum correlation
coefficient between the pulse and a template pulse ex-
ceeds 0.8. Hence, an episode of a life-threatening
arrhythmia is detected only if at least 5 consecu-
BIOSIGNALS 2022 - 15th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
246
After HDBefore HD
0
1000
δ
1.0
0.5
0
Normalized amplitude
0
1000
Normalized time
(samples)
1.0
0.5
0
Normalized amplitude
δ
0
1000
Normalized time
(samples)
1.0
0.5
0
Normalized amplitude
Before HD
After HD
0
208
Time (ms)
Amplitude (mV)
0.28
0.14
0
(a)
(c)
(b)
θ
θ
θ
(d)
Normalized time
(samples)
Before HD
After HD
T-wave
Composite
Gaussian
Lognormal
Figure 2: Concept of θ
δ
calculation: (a) original T-waves
before and after HD; (b) variation of θ in amplitude normal-
ized T-waves before and after HD. Variation of δ: (c) before
and (d) after HD. Potassium decreased from 5.5 mmol/L to
3.2 mmol/L.
tive high-quality pulses satisfies one of the above-
described criteria for the pulse rate. In the case de-
scribed in this paper, a reference synchronously ac-
quired continuous ECG signal was used to confirm
the arrhythmia episodes detected in the PPG signal.
3 CASE ANALYSIS
3.1 Patient Description
Signals were recorded at the hospital of Lithuanian
University of Health Sciences Kaunas Clinics from
a 79-year-old male patient, with a body-mass in-
dex 30.1 kg/m
2
, hospitalized due to arteriovenous
fistula thrombosis. Chronic kidney inflammation
(pyelonephritis) is a suspected unconfirmed cause of
CKD in this patient. The study was conducted in ac-
cordance with the ethical principles of the Declara-
tion of Helsinki and approved by the Kaunas Region
Biomedical Research Ethics Committee (No. BE-2-
43). The patient gave written informed consent to
participate in the study.
3.2 Data Analysis
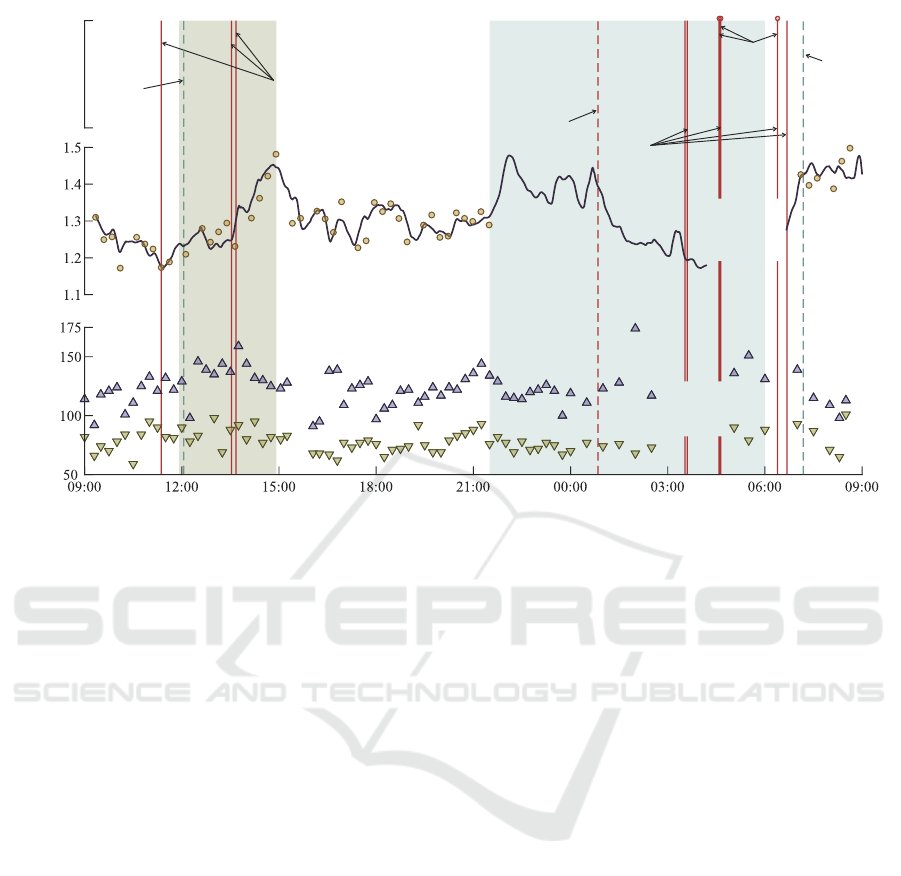
Figure 3 shows the variation of θ
δ
and blood pres-
sure throughout the monitoring period. Nine extreme
bradycardia episodes lasting for 6–10 heartbeats were
detected in the continuous PPG signal; however, three
could not be verified due to the loss of reference ECG
signal. The PPG-based algorithm also produced three
false-positive arrhythmia episodes, verified by simul-
taneously acquired ECG: one of extreme bradycardia
and two of ventricular tachycardia.
Throughout the monitoring period, systolic and
diastolic blood pressures were 121.8 ± 14.3 mmHg
and 77.6 ± 10.0 mmHg during the day, and 131.3 ±
18.5 mmHg and 79.5 ± 8.6 mmHg during the night.
Curiously, blood pressure was elevated during brady-
cardia episodes, and there was no clear indication of
nocturnal dipping.
Parameter θ
δ
increased during HD, suggesting an
unlikely increment of potassium level, which cannot
be confirmed since no blood samples were acquired.
Compared to other periods, the ECG signal quality
decreased during HD, which can disturb T-wave mor-
phology, leading to estimation errors of θ
δ
. We also
verified that the patient displayed unusual T-waves
throughout HD upon further inspection. As elec-
trolyte levels get corrected, T-waves tend to flatten.
Instead, the patient exhibited peaked and symmetrical
T-waves, typical of hyperkalemia and, perhaps, with
concomitant metabolic acidosis. Prolonged ST seg-
ments are also visible throughout the recording, hint-
ing at possible hypocalcemia.
θ
δ
varies coincidently with the expected potas-
sium circadian variation, decreasing from 09:00 to
11:00 and from 15:00 to 21:00 and rising from 00:00
to 09:00. Although θ
δ
decreased during the night, θ
δ
likely reacted to altered T-wave morphology due to
body position changes.
4 DISCUSSION
The proposed technology for in-home use is benefi-
cial for investigating electrolyte fluctuations as pos-
sible instigators of life-threatening arrhythmias. The
technology has both scientific and clinical signifi-
cance. The acquired knowledge of arrhythmia occur-
rence, progression, temporal distribution, and causal
relationship with electrolyte fluctuations could be
used to predict the course of the disease, personalize
medication, and assess the risk of sudden death for
individual patients.
Despite the recently spurred scientific interest in
non-invasive monitoring of electrolyte fluctuations,
most research focuses predominantly on the devel-
opment of potassium biomarkers (Rodrigues et al.,
2020; Palmieri et al., 2021; Attia et al., 2016; Corsi
et al., 2017), neglecting, thus far, calcium, bicarbon-
ate, and magnesium. While potassium is a well-
Personalized Evaluation of Life-threatening Conditions in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: The Concept of Wearable Technology and Case
Analysis
247
PPG
only
Bradycardia
Reference
ECG lost
Cu tube
kinked
Arrhythmia
Time
Hemodialysis Sleep
Blood Pressure
(mmHg)
θ (°s)
δ
Bradycardia
False
Tachycardia
False
Bradycardia
False
Tachycardia
Figure 3: Variation of θ
δ
and blood pressure throughout the monitoring period. Vertical lines indicate detected arrhythmia
episodes: solid red – true bradycardia, dashed red – false bradycardia, dashed blue – false tachycardia. A solid black curve is
a moving average of θ
δ
estimated from all 90 s segments in a single-lead continuous ECG, and dots are the estimated values
of θ
δ
every 15 min. Upward- and downward-pointing triangles indicate systolic and diastolic blood pressure values from an
ambulatory monitor, respectively.
known arrhythmogenic agent in CKD patients, the
entire panel of blood electrolyte levels is necessary
to understand what electrolyte combinations provoke
life-threatening arrhythmias. Even from a technolog-
ical point of view, any algorithm for assessing blood
potassium level needs to consider the remaining elec-
trolytes. Concomitant electrolyte imbalance (e.g., hy-
perkalemia and metabolic acidosis) can alter the T-
wave morphology differently than isolated potassium
abnormalities (Severi et al., 2002), thus influencing
the results of any developed biomarker (Rodrigues
et al., 2020).
Albeit unconfirmed with blood tests, the presented
case study illustrates the necessity of monitoring all
electrolytes instead of solely potassium. In our pre-
vious study, unexpected variations of θ
δ
were found
in patients with severe hypocalcemia and pH imbal-
ance (Rodrigues et al., 2020), which we suspect the
patient of this case study may have had due to a pro-
longed ST-segment and peaked T-waves. Hypocal-
cemia decreases cardiac contractility and is a likely
trigger of bradycardia (Loewe et al., 2019; Yam-
aguchi et al., 2020). The unanticipated variation of θ
δ
observed in this case study challenges us to question
our knowledge regarding the arrhythmogenic poten-
tial of different electrolyte fluctuations. It further sub-
stantiates the need to continue developing technolo-
gies for ambulatory assessment of electrolyte fluctua-
tions that take into account various electrolytes.
The rapid development of electronics opened the
possibility to acquire a short-term ECG by employ-
ing a wrist-worn device with two integrated biopoten-
tial electrodes. Thus far, such technological principle
is used only for personal purposes, such as obtaining
an instantaneous heart rate, without analyzing ECG
morphology which is unsurprising since comprehen-
sive ECG analysis requires good signal quality and
computational resources. In principle, the ECG sig-
nal quality can be assessed in real-time with an indi-
cation for the patient to make some contact adjust-
ments. However, real-time morphology analysis is
more challenging and still demands offline process-
ing, as preferred in the presented case study. Signal
quality issues are also particularly common in PPG
acquisition. While overlooked noise and artifacts may
produce false arrhythmia alarms, especially tachycar-
dia, eliminated poor-quality segments of PPG signal
may result in missed arrhythmia episodes (Paliakait
˙
e
et al., 2021). This issue should not be overlooked
when evaluating the relationship between electrolyte
fluctuations and life-threatening arrhythmias.
BIOSIGNALS 2022 - 15th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
248

5 FUTURE WORK
The proposed wearable technology could serve for
obtaining knowledge regarding causal relationships
of electrolyte fluctuations with arrhythmia develop-
ment and sudden cardiac death. Algorithms for iden-
tification of the causal direction, coupling delay, and
causal chain relations from time series could be ap-
plied (Huang et al., 2020).
Information on the occurrence of life-threatening
conditions is valuable for developing a system for per-
sonalized decision support, for instance, implemented
as a deep recurrent neural network based on long
short-term memory, such as described in (Kwon et al.,
2018). The neural network can consist of three time
series inputs involving information on signal quality,
electrolyte fluctuations, and temporal distribution of
arrhythmia episodes. Temporal distribution that car-
ries important information about arrhythmia progres-
sion can be characterized using a model-based ap-
proach (Henriksson et al., 2021). The output of the
personalized decision support system may be a sud-
den cardiac death risk score.
The proposed framework for personalized deci-
sion support can potentially be adapted for other
groups with an increased risk of electrolyte fluctua-
tions and life-threatening arrhythmias, e.g., those with
heart failure or receiving chemotherapy treatment.
6 CONCLUSION
An unobtrusive noninvasive technology for monitor-
ing electrolyte fluctuations and detecting ventricular
tachycardia and extreme bradycardia in a home en-
vironment can be of value for identifying patients
susceptible to dangerous arrhythmias precipitated by
electrolyte imbalance.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the European Regional
Development Fund with the Research Council of
Lithuania under the Project 01.2.2-LMT-K-718-01-
0030.
REFERENCES
Aboy, M., McNames, J., Tran Thong, Tsunami, D., El-
lenby, M. S., and Goldstein, B. (2005). An au-
tomatic beat detection algorithm for pressure sig-
nals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,
52(10):1662–1670.
Attia, Z. I., DeSimone, C. V., Dillon, J. J., Sapir, Y.,
Somers, V. K., Dugan, J. L., Bruce, C. J., Acker-
man, M. J., Asirvatham, S. J., Striemer, B. L., et al.
(2016). Novel bloodless potassium determination us-
ing a signal-processed single-lead ECG. Journal of
the American Heart Association, 5(1):e002746.
Bonomi, A. G., Eerik
¨
ainen, L. M., Schipper, F., Aarts,
R. M., De Morree, H. M., and Dekker, L. (2017).
Detecting episodes of brady- and tachycardia using
photo-plethysmography at the wrist in free-living con-
ditions. In 2017 Computing in Cardiology (CinC),
pages 1–4. IEEE.
Bonomi, A. G., Schipper, F., Eerik
¨
ainen, L. M., Margar-
ito, J., Van Dinther, R., Muesch, G., De Morree,
H. M., Aarts, R. M., Babaeizadeh, S., McManus,
D. D., et al. (2018). Atrial fibrillation detection using
a novel cardiac ambulatory monitor based on photo-
plethysmography at the wrist. Journal of the Ameri-
can Heart Association, 7(15):e009351.
Boriani, G., Glotzer, T. V., Santini, M., West, T. M.,
De Melis, M., Sepsi, M., Gasparini, M., Lewalter,
T., Camm, J. A., and Singer, D. E. (2014). Device-
detected atrial fibrillation and risk for stroke: an anal-
ysis of >10 000 patients from the SOS AF project
(Stroke preventiOn Strategies based on Atrial Fibrilla-
tion information from implanted devices). European
Heart Journal, 35(8):508–516.
Brunelli, S. M., Du Mond, C., Oestreicher, N., Rakov, V.,
and Spiegel, D. M. (2017). Serum potassium and
short-term clinical outcomes among hemodialysis pa-
tients: impact of the long interdialytic interval. Amer-
ican Journal of Kidney Diseases, 70(1):21–29.
Corsi, C., Cortesi, M., Callisesi, G., Bie, J. D., Napolitano,
C., Santoro, A., Mortara, D., and Severi, S. (2017).
Noninvasive quantification of blood potassium con-
centration from ECG in hemodialysis patients. Sci-
entific Reports, 7(1).
El-Sherif, N. and Turitto, G. (2011). Electrolyte disorders
and arrhythmogenesis. Cardiology Journal, 18(3):13.
Henriksson, M., Mart
´
ın-Yebra, A., Butkuvien
˙
e, M., Ras-
mussen, J. G., Marozas, V., Petr
˙
enas, A., Savelev, A.,
Platonov, P. G., and S
¨
ornmo, L. (2021). Modeling and
estimation of temporal episode patterns in paroxysmal
atrial fibrillation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical
Engineering, 68(1):319–329.
Huang, Y., Fu, Z., and Franzke, C. L. E. (2020). Detect-
ing causality from time series in a machine learning
framework. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of
Nonlinear Science, 30(6):063116.
Kalra, P. A., Green, D., and Poulikakos, D. (2018). Arrhyth-
mia in hemodialysis patients and its relation to sudden
death. Kidney International, 93(4):781–783.
Kwon, J.-m., Lee, Y., Lee, Y., Lee, S., and Park, J. (2018).
An algorithm based on deep learning for predicting in-
hospital cardiac arrest. Journal of the American Heart
Association, 7(13):e008678.
Loewe, A., Lutz, Y., Nairn, D., Fabbri, A., Nagy, N.,
Toth, N., Ye, X., Fuertinger, D. H., Genovesi, S.,
Personalized Evaluation of Life-threatening Conditions in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: The Concept of Wearable Technology and Case
Analysis
249

Kotanko, P., Raimann, J. G., and Severi, S. (2019).
Hypocalcemia-induced slowing of human sinus node
pacemaking. Biophysical Journal, 117(12):2244–
2254.
Paliakait
˙
e, B., Petr
˙
enas, A., Solo
ˇ
senko, A., and Marozas,
V. (2021). Modeling of artifacts in the wrist photo-
plethysmogram: Application to the detection of life-
threatening arrhythmias. Biomedical Signal Process-
ing and Control, 66:102421.
Palmieri, F., Gomis, P., Ferreira, D., Ruiz, J. E.,
Bergasa, B., Mart
´
ın-Yebra, A., Bukhari, H. A., Pueyo,
E., Mart
´
ınez, J. P., Ram
´
ırez, J., and Laguna, P.
(2021). Monitoring blood potassium concentration
in hemodialysis patients by quantifying T-wave mor-
phology dynamics. Scientific Reports, 11(1).
Pereira, T., Tran, N., Gadhoumi, K., Pelter, M. M., Do,
D. H., Lee, R. J., Colorado, R., Meisel, K., and Hu,
X. (2020). Photoplethysmography based atrial fib-
rillation detection: a review. NPJ Digital Medicine,
3(1):1–12.
Perez, M. V., Mahaffey, K. W., Hedlin, H., Rumsfeld,
J. S., Garcia, A., Ferris, T., Balasubramanian, V.,
Russo, A. M., Rajmane, A., Cheung, L., et al. (2019).
Large-scale assessment of a smartwatch to identify
atrial fibrillation. New England Journal of Medicine,
381(20):1909–1917.
Rodrigues, A. S., Petr
˙
enas, A., Paliakait
˙
e, B., Ku
ˇ
sleikait
˙
e-
Pere, N., Jaru
ˇ
sevi
ˇ
cius, G., Bumblyt
˙
e, I. A., Laguna,
P., and Marozas, V. (2020). Noninvasive monitoring
of potassium fluctuations during the long interdialytic
interval. IEEE Access, 8:188488–188502.
Saran, R., Robinson, B., Abbott, K. C., Agodoa, L. Y.,
Bragg-Gresham, J., Balkrishnan, R., Bhave, N., Di-
etrich, X., Ding, Z., Eggers, P. W., Gaipov, A., Gillen,
D., Gipson, D., Gu, H., Guro, P., and et. al. (2019).
US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report:
Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States.
American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 73(3):A7–A8.
Severi, S., Cavalcanti, S., Mancini, E., and Santoro, A.
(2002). Effect of electrolyte and pH changes on the
sinus node pacemaking in humans. Journal of Elec-
trocardiology, 35(2):115–124.
Solo
ˇ
senko, A., Petr
˙
enas, A., Paliakait
˙
e, B., S
¨
ornmo, L., and
Marozas, V. (2019). Detection of atrial fibrillation us-
ing a wrist-worn device. Physiological Measurement,
40(2):025003.
Soykan, O., Manda, V. R., Gerber, M. T., and Hobot, C. M.
(2016). Method and device to monitor patients with
kidney disease. US Patent 9,456,755.
Surawicz, B. (1967). Relationship between electrocar-
diogram and electrolytes. American Heart Journal,
73(6):814–834.
Wang, H., Naghavi, M., Allen, C., Barber, R. M., Bhutta,
Z. A., Carter, A., Casey, D. C., Charlson, F. J., Chen,
A. Z., Coates, M. M., et al. (2016). Global, re-
gional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mor-
tality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes
of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the
global burden of disease study 2015. The Lancet,
388(10053):1459–1544.
Wong, M. C., Kalman, J. M., Pedagogos, E., Toussaint, N.,
Vohra, J. K., Sparks, P. B., Sanders, P., Kistler, P. M.,
Halloran, K., Lee, G., et al. (2015a). Temporal dis-
tribution of arrhythmic events in chronic kidney dis-
ease: Highest incidence in the long interdialytic pe-
riod. Heart Rhythm, 12(10):2047–2055.
Wong, M. C., Kalman, J. M., Pedagogos, E., Toussaint, N.,
Vohra, J. K., Sparks, P. B., Sanders, P., Kistler, P. M.,
Halloran, K., Lee, G., Joseph, S. A., and Morton, J. B.
(2015b). Bradycardia and asystole is the predominant
mechanism of sudden cardiac death in patients with
chronic kidney disease. Journal of The American Col-
lege of Cardiology, 65(12):1263–1265.
Yamaguchi, S., Hamano, T., Doi, Y., Oka, T., Kajimoto, S.,
Kubota, K., Yasuda, S., Shimada, K., Matsumoto, A.,
Hashimoto, N., Sakaguchi, Y., Matsui, I., and Isaka,
Y. (2020). Hidden hypocalcemia as a risk factor for
cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality among
patients undergoing incident hemodialysis. Scientific
Reports, 10(1).
BIOSIGNALS 2022 - 15th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
250
