
Predictive Modeling of Diabetes using EMR Data
Hasan Zafari
1a
, Jie Li
1b
, Farhana Zulkernine
1c
, Leanne Kosowan
2d
and Alexander Singer
2e
1
School of Computing, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada
2
Rady College of Medicine, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada
{leanne.Kosowan, alexander.singer}@umanitoba.ca
Keywords: Machine Learning, EMR Data, Diabetes, Ensemble Models, Classification Algorithms, Imbalanced Data.
Abstract: As the prevalence of diabetes continues to increase globally, an efficient diabetes prediction model based on
Electronic Medical Records (EMR) is critical to ensure the well-being of the patients and reduce the burden
on the healthcare system. Prediction of diabetes in patients at an early stage and analysis of the risk factors
can enable diabetes primary and secondary prevention. The objective of this study is to explore various
classification models for identifying diabetes using EMR data. We extracted patient information, disease,
health conditions, billing, and medication from EMR data. Six machine learning algorithms including three
ensemble and three non-ensemble classifiers were used namely XGBoost, Random Forest, AdaBoost,
Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes, and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN). We experimented with both imbalanced
data with the original class distribution and artificially balanced data for training the models. Our results
indicate that the Random Forest model overall outperformed other models. When applied to the imbalanced
data (112,837 instances), it results in the highest values in specificity (0.99) and F1-score (0.84), and when
training with balanced data (35,858 instances) it achieves better values in sensitivity (1.00) and AUC (0.96).
Analyzing feature importance, we identified a set of features that are more impactful in deciding the outcome
including a number of comorbid conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, osteoarthritis, CKD, and
depression as well as a number of medication codes such as A10, D08, C10, and C09.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic, metabolic disease characterized
by elevated levels of blood glucose (or blood sugar),
which leads to serious damage to the heart, blood
vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves over time (WHO,
2021). Diabetes is a progressive disease with a wide
range of presentations. Left unchecked, diabetes can
eventually lead to life-threatening complications and
diseases such as cardiovascular disease, kidney
disease, and neuropathy, and the development of
these complications is associated with a reduction in
lifespan by five to fifteen years (Deshpande et al.,
2008).
The global diabetes burden is expected to increase
from 463 million people in 2019 to 578 million
people by 2030 with developed countries seeing the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8602-3240
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4708-8180
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3326-0875
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8401-7878
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5436-8394
greatest increase in prevalence rates (Saeedi et al.,
2019). In Canada, diabetes prevalence is expected to
increase from 11.2 million in 2020 to 13.6 million or
32% of all Canadians by 2030. Moreover, the
increase in diabetes prevalence presents a significant
burden on the healthcare system. The direct cost to
the Canadian healthcare system is expected to
increase from 3.8 billion in 2020 to 4.9 billion by
2030 (Diabetes Canada, 2021).
Diabetes and its complications have brought
heavy burdens to not only medical resources but also
social economics. It is important to diagnose diabetes
at an early stage and to make sure high-risk people are
informed duly. This helps move the focus from
treatment to prevention of diabetes. Studies also show
that some lifestyles might increase the risk of
diabetes, including high sugar consumption of daily
Zafari, H., Li, J., Zulkernine, F., Kosowan, L. and Singer, A.
Predictive Modeling of Diabetes using EMR Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0010908900003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 211-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
211

diet, sedentary behavior, heavy drinking, and heavy
smoking (Sami et al., 2017). It is critical then to
develop improved monitoring methods to track the
overall health status of those living with diabetes to
reduce the burden on the healthcare system and to
ensure preventative actions before the development
of life-threatening complications.
Due to the complex and diverse pathophysiology
of diabetes, the American Diabetes Association
(ADA) recommends individualized treatment and
medication plans (Riddle et al., 2019). As such,
several studies have focused on personalizing
treatment by scoring or stratifying the relative health
of diabetic patients using clinical test values (Kaur
and Kumari, 2020). These stratification methods
allow for better resource allocation, help clinicians
better monitor the relative health of their patients and
improve overall diabetes outcomes (Lindström and
Tuomilehto, 2003).
Much of the research done in this field only
focuses on a small number of structured data and
limited features. Although these models mostly
achieved high accuracy, they provide limited
information that could not be implemented into real-
world primary care settings to prevent diabetes from
an early stage (Birjais et al., 2019, Muhammad et al.,
2020, Sisodia, and Sisodia, 2018).
The objective of this study is to take advantage of
a huge dataset extracted from the EMR data to build
supervised machine learning models to identify
diabetes cases.
Training data is one of the significant elements of
supervised machine learning as it may influence the
prediction positively or negatively based on how it is
prepared for the learning algorithm (De Silva et al.,
2020). The key contributions of our research are as
follows. To investigate the impact of artificially
balancing training datasets on the performance of
classification algorithms, we trained the classification
models with both balanced and imbalanced training
datasets and compared their performance. The dataset
was extracted from primary care providers
participating in the Manitoba Primary Care Research
Network (MaPCReN). We present an in-depth
literature review and demonstrate the architecture and
performance of six machine learning models to
predict patients who may have diabetes. The results
show that while all ensemble methods performed
well, overall the random forest model outperforms the
other models and achieves an F1-score of 0.83 on the
balanced dataset and an F1-score of 0.84 on the
imbalanced dataset.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. In
Chapter 2, we present the literature review. Chapter 3
presents the implementation details while Chapter 4
demonstrates the experimental results. A critical
discussion is presented in Chapter 5, and Chapter 6
concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Muhammad et al. (2020) used the data collected from
the Murtala Mohammed Specialist Hospital, which
contained 383 instances. The data used in this study
had nine attributes, including age, family history,
glucose, cholesterol (CHOL), blood pressure (BP),
HDL (high-density lipoprotein), triglyceride, BMI
(body mass index), and the diagnosis result. Logistic
regression, support vector machine, k-nearest
neighbor, random forest, naïve Bayes, and gradient
boosting algorithms were implemented with random
forest obtaining the overall best performance and an
accuracy of 88.76%. They also analyzed the data
features and reported that glucose, cholesterol, family
history, triglyceride, BMI, and age were correlated
with the outcome.
Sisodia and Sisodia (2018) explored the Pima
Indians Diabetes Dataset using classification
algorithms, namely decision tree, SVM, and naïve
Bayes. Among all these algorithms, naïve Bayes had
the highest accuracy of 76.30%. The dataset they used
contained 768 samples and 8 attributes.
Birjais et al. (2019) applied several techniques
including Gradient Boosting, Logistic Regression,
and Naive Bayes on Pima Indian diabetes data set to
diagnose diabetes. Their dataset included 768
instances and 8 attributes and the machine learning
models attained an accuracy of 86% for the Gradient
Boosting, 79% for Logistic Regression, and 77% for
Naive Bayes.
Nai-arun and Moungmai (2015) compared the
performance of four machine learning models on
predicting diabetes, namely decision tree, Artificial
Neural Networks (ANN), logistic regression, and
naïve Bayes to predict diabetes. The data was
collected from 26 Primary Care Units (PCU) in
Sawanpracharak Regional Hospital. According to
their experiments, random forest attained the best
performance with an accuracy of 85.56%.
Bi et al. (2012) assessed the risk factors that might
cause type 2 diabetes. They classified risk factors into
lifestyle risk factors, internal environment factors,
external environmental factors, and genetic risk
factors. For lifestyle risk factors, they point out that a
high sugar diet, sedentary behavior, smoking, and
alcohol consumption will increase diabetes risk. In
internal environmental factors, inflammatory factors,
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
212

adipocytokines, and hepatocyte factors were
analyzed. According to this study low-grade
inflammation, white blood cell (WBC), C-reactive
protein (CRP) positively affect diabetes risk factors.
De Silva et al. (2020) combined feature selection
and machine learning algorithms to identify
predictors of prediabetes. The data were collected
from a nationally representative sample of the US
population, containing 64,346 samples. They applied
four machine learning models, namely logistic
regression (linear), artificial neural network (ANN)
(non-linear), random forests (RF) (ensemble), and
gradient boosting (GB) (ensemble). Features included
in their study are age, income-property ratio, waist
circumference, BMI, and Hepatitis B.
Zou et al. (2018) applied decision trees, random
forest, and neural networks to a hospital dataset to
predict diabetes mellitus. The dataset they used was
the hospital physical examination data in Luzhou,
China that contained 14 attributes. They evaluated
their models with five-fold cross-validation where
prediction with random forest reached the highest
accuracy (0.81) when all the attributes were used.
Wei et al. (2018) performed a comprehensive
exploration of the most popular techniques including
deep neural network (DNN), SVM, logistic
regression, decision tree, and naïve Bayes to identify
diabetes based on the Pima Indian diabetes dataset.
They compared the accuracy of each classifier over
several data pre-processors. The best technique they
found was the DNN model that attained 77.86%
accuracy. They also analyzed the relevance between
each feature with the classification result. The three
most important features in this data set were: plasma
glucose concentration, pregnancy count, and age.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1 Data
This study uses Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
data from primary care providers participating in the
Manitoba Primary Care Research Network
(MaPCReN), which is a subset of The Canadian
Primary Care Sentinel Surveillance Network
(CPCSSN). Data is extracted on all patients in a
practice, including children. It contains electronic
records from primary care providers across the
country between 1995 and 2019. Out of the total
number of patients included in this study, 17,929 have
diabetes (15.88%). The information of patients was
de-identified prior to analyses to protect the identity
of the patients in the dataset.
We extracted data from the following tables:
patient demographics (patients' sex, age), disease case
(diagnosed chronic diseases), medication, health
condition, and billing codes.
The sex of the patient is demonstrated with binary
variables, as 1 representing male and 0 representing
female. The age was calculated based on the birthday
of that patient in 2019. The diagnosed chronic
diseases were limited to those with validated case
definitions: osteoarthritis, COPD, Parkinson's
disease, dyslipidemia, herpes zoster, pediatric
asthma, CKD, diabetes mellitus, osteoarthritis,
dementia, hypertension, depression, and epilepsy. It
is represented by binary variables for each disease.
The medications, billing codes, and health condition
diagnostic codes were included as categorical
features in our data set with 1,522, 7,102, and 7,695
different values, respectively. This large number of
unique values presented challenges in using one-hot
encoding. Therefore, prescribed medications were
identified using the ATC codes of the medications
(Chen et al., 2012).
We used the first three letters of the ATC code to
represent medication in our model. This reduced the
number of different medication codes from 1,522 to
88 values, which led to less complexity of the model
and grouped medication according to their
therapeutic or pharmaceutical subgroup. A similar
method was applied to the ICD9 diagnosis codes
found in the billing and health condition tables which
reduced the number of codes from over 7,000 in both
cases to 138 and 152, respectively.
We dropped patient id, Billing_250, and HC_250
columns as they either do not contribute to our
prediction or directly represent the outcome variable
that we are going to predict.
We combine each patient’s EMRs from multiple
visits into one row based on the strategy illustrated in
Table 1. After encoding the variables, the dataset
contained 112,837 rows of patient information and
included 392 different features (Table 1).
3.2 Predictive Modeling
In this study, we developed six machine learning
models namely XGBoost, AdaBoost, random forest,
K-Nearest Neighbors, Naïve Bayes, and Logistic
Regression to predict patients having diabetes using
our preprocessed dataset. These machine learning
models were chosen based on their proven reliability
and performance in classification tasks including in
the medical domain.
Predictive Modeling of Diabetes using EMR Data
213
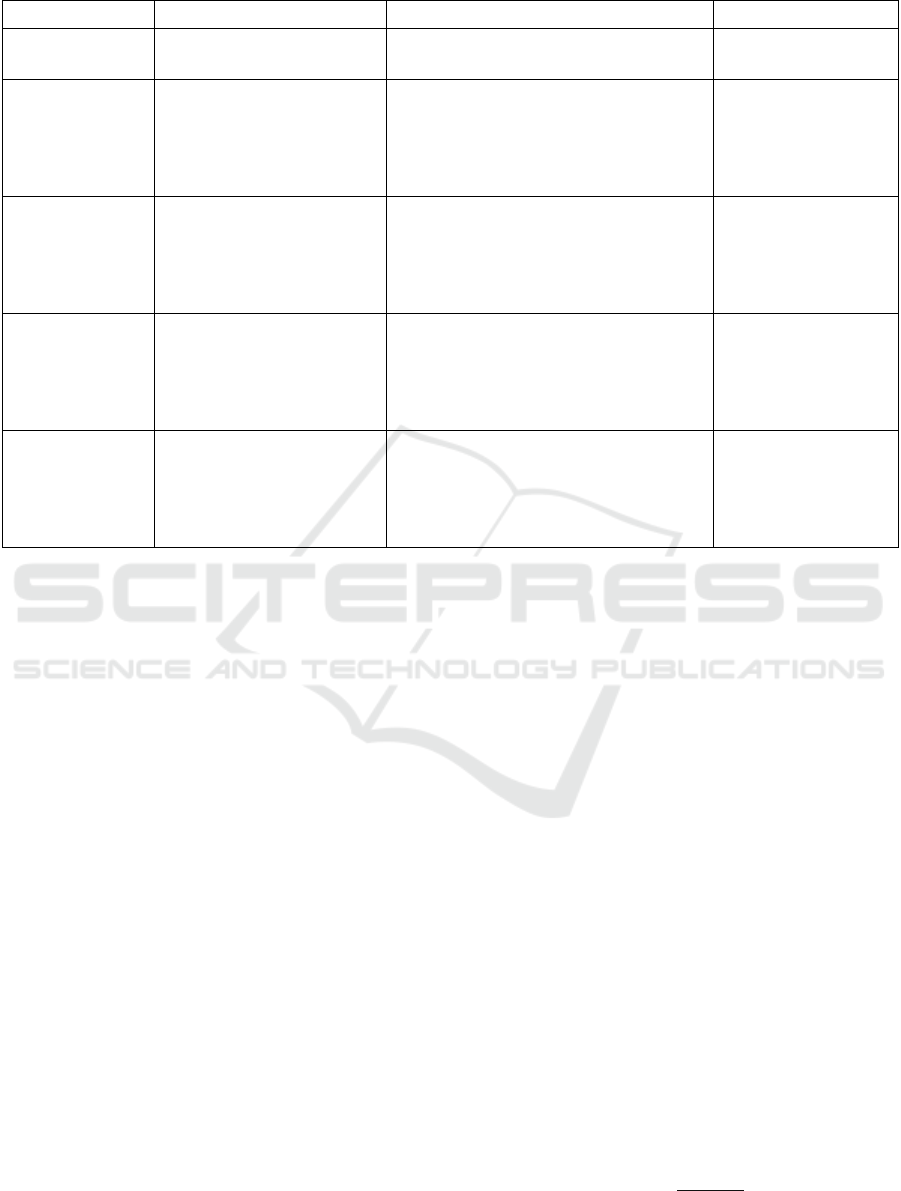
Table 1: Summary of features used in this study.
Feature Category Description Features after Encoding Variable Type
Patient Information
General information about the
patient
Sex, age
Sex binary,
age continuous
Disease
Diagnosis of 12 diseases with
a validated case definition
Osteoarthritis, COPD, Parkinson's Disease,
Dyslipidemia, Herpes Zoster, Pediatric
Asthma, CKD, Osteoarthritis, Dementia,
Hypertension, Depression, Epilepsy (12
features)
Binary variable, 1 if the
patient has the listed
diseases, otherwise 0
Medication
All medications prescribed to
a patient (study period). The
medications were generalized
to therapeutic/pharmaceutical
sub-group
Features obtained by counting the number
of medications each patient was on based
on the first 3 letters of its ATC code (88
features)
Discrete variables
representing the
frequency of taking
each medication type
by each patient
Health Condition
Diagnosis Code
All diagnostic codes recorded
in the patient’s EMR during
the study period. The codes
were generalized to their
three-level ICD-9 code
Features obtained by counting the number
of health conditions for each patient based
on the first 3 letters of the health condition
diagnosis code (138 features)
Discrete variables
representing the
frequency of each code
type in the EMR for
each patient
Billing Code
All billing codes given to a
patient during the study
period. The codes were
generalized to their ICD-9
code general category
Features obtained by counting the number
of billing codes for each patient based on
the first 3 letters of the billing diagnosis
code (152 features)
Discrete variables
representing the
frequency of each code
was entered into the
EMR for each patient
We performed a comparative study to investigate
the performance of these models in medical
diagnosis. In addition to comparing the models in
terms of prediction performance, we studied their
ability to deal with imbalanced data which is
commonplace in the medical domain.
For evaluating the influence of the balanced and
imbalanced training data on the disease identification
task, two different training datasets were created, a
balanced and an imbalanced training set. The
imbalanced dataset has the same distribution of
positive and negative instances as the original data.
The balanced dataset, however, contains an equal
number of positive and negative cases. To balance the
skewed distribution of the training partitions of the
dataset, we performed a random under-sampling on
the majority class. Random under-sampling tries to
balance the class distribution through the random
elimination of majority class examples. The major
drawback of random under-sampling is that this
method can discard examples that could be important
to the model in the training process.
We performed stratified 10-fold cross-validation
on the preprocessed dataset which divides each fold
into the training and testing dataset in a 9:1 ratio. We
implemented a stochastic hill-climbing algorithm for
tuning the hyperparameters for each classifier.
Stochastic hill-climbing chooses its next value at
random from the available search space (Stubbs et al.,
2019). This step aims to optimize the parameters for
each classifier. We then applied the models to the
holdout test dataset.
The classifiers were all implemented using Scikit-
learn libraries (Pedregosa et al., 2011). Python 3.6
was used for the data processing and programming
tasks.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
4.1 Validation
We evaluated our models with several metrics
including Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative
Predictive Value (NPV), specificity (SP), sensitivity
(SE), accuracy (ACC).
The equations used for calculation are shown
above, where TP is True Positive, FP is False
Positive, TN is True Negative, and FN is False
Negative. In addition to these threshold metrics, we
used the rank metrics of and the Area Under the curve
(AUC) of a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)
curve.
PPV precision
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃𝐹𝑃
(1)
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
214
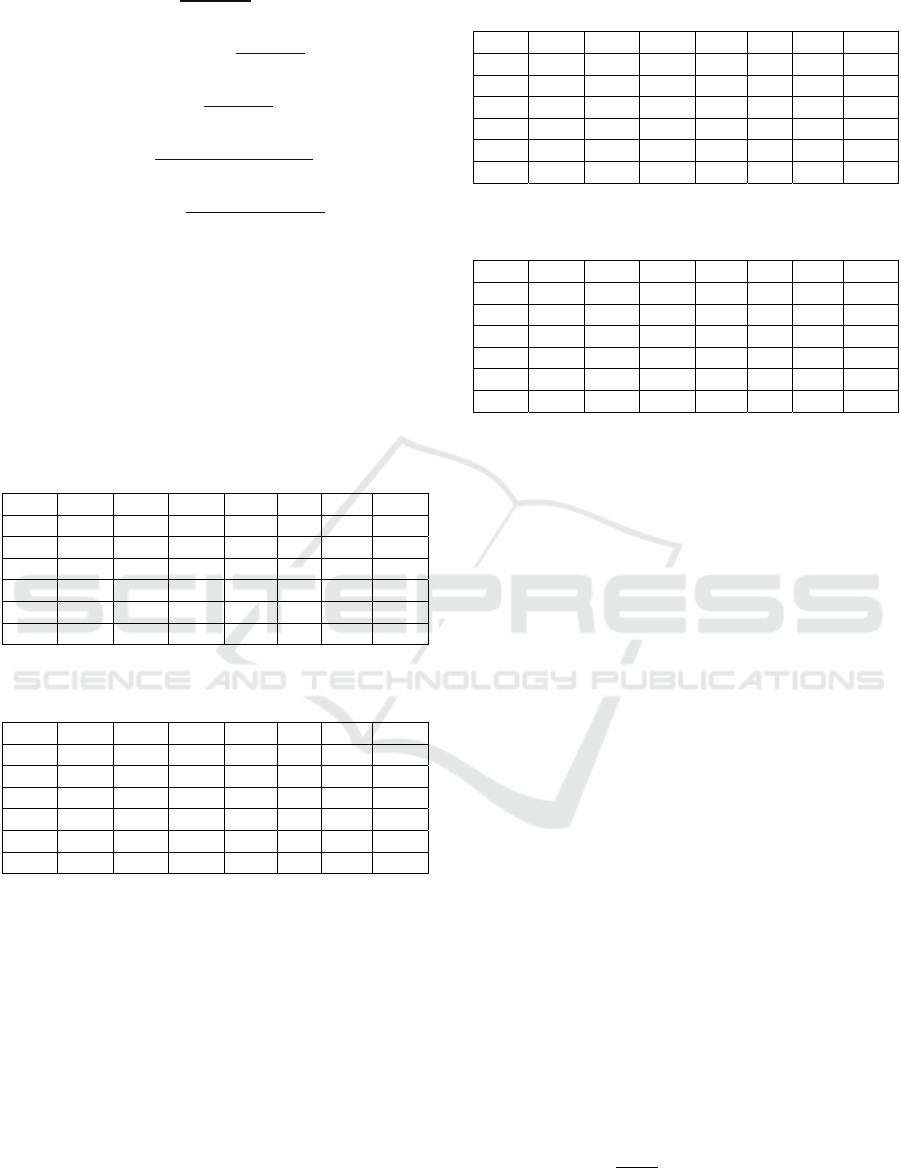
NPV
𝑇𝑁
𝑇𝑁𝐹𝑁
(2)
Sensitivity recall
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃𝐹𝑁
(3)
Specificity
𝑇𝑁
𝑇𝑁 𝐹𝑃
(4)
Accuracy
𝑇𝑃𝑇𝑁
𝑇𝑃𝐹𝑃𝐹𝑁𝑇𝑁
(5)
F1 score2
Precision Recall
Precision Recall
(6)
4.2 Results
Tables 2 and 3 report the results for the development
and the holdout parts of the balanced datasets,
respectively. The lowest and highest average values
are identified by italic and bold fonts respectively in
each column of the tables.
Table 2: Summary of model results for the development set
of the balanced dataset.
PPV NPV SN SP ACC F1 AUC
XGB
0.68 0.99 0.94 0.91 0.92 0.79 0.93
RF
0.71 1.00 1.00 0.92 0.94 0.83 0.96
AB
0.73 0.98 0.88 0.94 0.93 0.80 0.91
LR
0.72 0.98 0.90 0.93 0.93 0.80 0.91
KNN
0.51 0.96 0.83 0.85 0.85 0.63 0.84
NB
0.50 0.94 0.70 0.87 0.84 0.59 0.78
Table 3: Summary of model results for the test set of the
balanced dataset.
PPV NPV SN SP ACC F1 AUC
XGB 0.66 0.99 0.94 0.91 0.91 0.78 0.92
RF 0.71 1.00 1.00 0.92 0.93 0.83 0.96
AB 0.72 0.98 0.89 0.93 0.93 0.79 0.91
LR 0.71 0.98 0.89 0.93 0.92 0.79 0.91
KNN 0.51 0.96 0.82 0.85 0.84 0.63 0.84
NB 0.49 0.94 0.
7
0
0.86 0.84 0.58 0.78
As presented in the first three rows in Tables 2 and
3, the ensemble models outperform the other
individual models in almost all scores, with random
forest obtaining the best results and naïve Bayes
attaining mostly the lowest values.
Tables 4 and 5 report the results of the imbalanced
datasets for the development and the holdout parts
respectively.
Table 4: Summary of model results for the development set
of the imbalanced dataset.
PPV NPV SN SP ACC F1 AUC
XGB
0.95 0.95 0.73 0.99 0.95 0.83 0.86
RF
0.92 0.96 0.77 0.99 0.95 0.84 0.88
AB
0.88 0.95 0.76 0.98 0.95 0.82 0.87
LR
0.88 0.95 0.73 0.98 0.94 0.80 0.86
KNN
0.89 0.91 0.48 0.99 0.91 0.62 0.73
NB
0.48 0.94 0.71 0.85 0.83 0.57 0.78
Table 5: Summary of model results for the test set of the
imbalanced dataset.
PPV NPV SN SP ACC F1 AUC
XGB
0.96 0.95 0.72 0.99 0.95 0.83 0.86
RF
0.94 0.95 0.76 0.99 0.95 0.84 0.87
AB
0.88 0.95 0.75 0.98 0.94 0.81 0.86
LR
0.89 0.95 0.72 0.98 0.94 0.79 0.85
KNN
0.89 0.91 0.49 0.99 0.91 0.64 0.74
NB
0.49 0.94 0.71 0.86 0.83 0.58 0.78
Again for the imbalanced data, we witness a
similar pattern as what we saw for the balanced
dataset. The ensemble models generally performed
better than the other individual models. While the
random forest along with the XGB models obtained
the best results, naïve Bayes and KNN achieved the
lowest values. Comparing Tables 2 and 3 with Tables
4 and 5, we observe that each of the balanced and
imbalanced training datasets is advantageous for a
subset of metrics. While the balanced dataset
obtained better results in NPV, SN, and AUC, the
imbalanced training dataset resulted in improved
values in PPV, SP, and F1-score.
4.3 Feature Importance Analysis
To study the contribution of each predictor in the RF
model applied to both balanced and imbalanced
datasets, we performed a feature importance ranking.
Feature importance was assessed for the features
having importance greater than 0.005 in the RF
model. This is calculated based on Gini impurity
score or Mean Decrease Impurity (MDI). For
impurity reduction, classification trees commonly use
Gini coefficient index or information gain of
variables. The equation for calculating the importance
of variable 𝑥
𝑗
is shown in Eq. 7 (Hur et al., 2017). For
each variable or influencing feature in the model, the
sum of the impurity reductions in all the trees is
calculated as the importance of the feature.
𝐼𝑚𝑝𝑥
1
𝑛
1𝐺𝑖𝑛𝑖
𝑗
(7)
Predictive Modeling of Diabetes using EMR Data
215

Table 6: Features with a correlation 0.05 with the outcome.
Rank Variable Importance Category
1 A10 0.1994 Medication (Drugs used in diabetes)
2 Hypertension 0.1051 Disease
3 Dyslipidemia 0.0985 Disease
4 D08 0.0597 Medication (Antiseptics and disinfectants)
5 age 0.0373 Demographic
6 C10 0.0230 Medication (Lipid modifying agents)
7 Osteoarthritis 0.0220 Disease
8 A03 0.0212 Medication (Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders)
9 C09 0.0185 Medication (Agents acting on the renin–angiotensin system)
10 HC_401 0.0158 Health condition (Essential hypertension)
11 CKD 0.0135 Disease
12 Depression 0.0114 Disease
13 A11 0.0111 Medication (Vitamins)
14 B01 0.0092 Medication (Antithrombotic agents)
15 N02 0.0092 Medication (Medication (analgesics)
16 J01 0.0089 Medication (Antibacterials for systemic use
17 Blg_401 0.0089 Billing (Essential hypertension)
18 N06 0.0080 Medication (Psychoanaleptics)
19 A02 0.0079 Medication (Drugs for acid related disorders)
20 R03 0.0073 Medication (Drugs for obstructive airway diseases)
21 N05 0.0066 Medication (Psycholeptics)
22 M01 0.0065 Medication (Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products)
23 C03 0.0063 Medication (Diuretics)
24 R01 0.0059 Medication (Nasal preparations)
25 C08 0.0057 Medication (Calcium channel blockers)
26 HC_272 0.0057 Health condition (Hyperlipidemia, disorders of lipoid metabolism)
27 G03 0.0056 Medication (Sex hormones and modulators of the genital system)
28 G04 0.0051 Medication (Urologicals)
29 Sex 0.0050 Demographic
30 A12 0.0050 Medication (Mineral supplements)
Table 6 shows the features with the importance ≥
0.005 which comprise 30 features out of the whole
392 feature set.
5 DISCUSSION
In this study, we applied six machine learning models
including three ensemble and three non-ensemble
models to the structured fields of EMR data to
diagnose diabetes.
Based on our results, the ensemble models
outperformed the non-ensemble models by a high
margin. This suggests that the random forest model
along with the other ensemble models are reliable
machine learning algorithms in the clinical domain.
Many recent research studies in the domain of
predicting diabetes have reported the performance of
their model in terms of accuracy (Muhammad et al.,
2020, Sisodia and Sisodia, 2018, Birjais et al., 2019,
Nai-arun and Moungmai, 2015, Zou et al., 2018).
However, the different distribution of positive and
negative cases in the medical domain usually leads to
a skewed dataset. Not only this fact should be
considered in the model design and training, but in the
model validation and performance metrics, we have
to use proper settings to get a valid evaluation.
We experimented with both the original
imbalanced data and a preprocessed balanced dataset
obtained by subsampling the original dataset. Our
experiments revealed that the balanced dataset led to
higher type I error, i.e., the incorrect predictions are
mostly false positives while the imbalanced dataset
led to higher type II error, i.e., the incorrect
predictions are mostly false-negative. These are
reflected in the higher values in NPV and sensitivity
in the balanced dataset and higher values of PPV and
specificity in the imbalanced dataset. However, the
total number of errors was lower in the models trained
on the imbalanced dataset which resulted in an
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
216

improvement in F1-score in these models.
Considering that the F-measure is a popular metric for
imbalanced classification (Brownlee, 2020), overall
we can conclude that the imbalanced dataset is more
suitable for our problem. However, the decision on
whether to balance classes in the training dataset or
not depends on what we want to achieve from the
classification. In diagnosing disease, for example,
detecting positive cases is vital. Comparing the
results in Tables 2 and 3 with the results presented in
Tables 4 and 5 we realize that utilizing an imbalanced
dataset leads to higher values for PPV in almost all
classifiers used in this study. Sensitivity refers to the
true positive rate and summarizes how well the
positive class was predicted. Specificity is the
complement to sensitivity, or the true negative rate,
and summarises how well the negative class was
predicted. For imbalanced classification, the
sensitivity might be more interesting than the
specificity.
Regarding class separability, the result indicates
that the AUC values of the classifiers trained on the
imbalanced dataset are on average 5 percent lower.
This means that an imbalanced dataset leads to
classifiers with inferior separability power.
Our results highlighted that ensemble models in
general, and random forest in particular, are proven to
be very robust, consistent, and effective classifiers as
these can perform very well under both balanced and
imbalanced data situations. In the ensemble method,
the predictive potentials of various individual
classifiers are fused together. Thus ensemble methods
increase their performance by combining the
efficiency of individual classifiers and the chances of
misclassification are reduced significantly leading to
greater accuracy of the classification process.
The feature importance analysis identified a
number of comorbid conditions that happen with
diabetes including hypertension, dyslipidemia,
osteoarthritis, CKD, and depression. Hypertension
and depression are diabetes-related complications as
mentioned by Deshpande et al. (2008). According to
other studies, dyslipidemia and diabetes are closely
related. Diabetic dyslipidemia is characterized by
elevated fasting and postprandial triglycerides, low
HDL-cholesterol, elevated LDL-cholesterol. These
lipid changes represent the major link between
diabetes and the increased cardiovascular risk of
diabetic patients (Chahil and Ginsberg, 2006).
Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus often co-
exist in older adults (Piva et al., 2015). People who
have type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of
osteoarthritis, likely due to obesity which is also a risk
factor for type 2 diabetes. Dyslipidemia is one of the
major risk factors for cardiovascular disease in
diabetes mellitus (Mooradian, 2009).
The coincidence of hypertension and diabetes was
identified by other studies before (Sowers et al.,
2001), and was reported to be twice as more
compared to non-diabetic patients. However, in our
experimental dataset, the incidence of hypertension in
diabetic patients was found to be about four times
more as compared to patients without diabetes.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We conducted a study with MaPCReN patient EMR
data intending to develop machine learning models to
identify patients with diabetes and describe important
feature sets that assisted with the identification of
diabetes. Using a dataset containing 112,837 patient
records that include 17,929 diabetes-positive cases,
our study showed that machine learning models can
identify diabetes patients with good accuracy. We
implemented six machine learning models including
three ensemble and three non-ensemble methods to
investigate which methods are advantageous in the
clinical domain. According to our results, the
ensemble techniques obtained better results with the
F1-score values of 0.83, 0.84, and 0.82 for XGBoost,
RF, and AdaBoost, than the non-ensemble models
that acquired the F1-score values of 0.80, 0.62, and
0.57 for logistic regression, KNN, and naïve Bayes,
respectively, on the skewed holdout test dataset. This
suggests that associating the predictive performance
of multiple AI-based algorithms is superior in
comparison to all other individual counterparts. We
also experimented with both balanced and
imbalanced datasets to investigate the pros and cons
of subsampling. Our results suggest that both
balanced and imbalanced datasets have their
advantages and disadvantages, therefore, depending
on the desired metrics both types of datasets can be
applied to inform case detection models. Diagnostic
tools like this can assist primary care physicians by
providing likely predictions of patients’ health status
at each visit.
For future work, we will include the text chart
notes, which contain elaborate encounter notes
logged by the physicians during patients’ visits, in
developing or improving the models. It is also
important to provide good reasoning for the
prediction and highlight supporting information from
EMR. Therefore, explainable model development is
another future work direction.
Predictive Modeling of Diabetes using EMR Data
217

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to acknowledge William Peeler for his
assistance in data acquisition and preparation of the
data for research. Funding for this study was provided
by an Advanced Analytics Grant from IBM and
Canadian Institute for Military and Veteran Health
Research (CIMVHR).
REFERENCES
Bi, Y., Wang, T., Xu, M., Xu, Y., Li, M., Lu, J., ... & Ning,
G. (2012). Advanced research on risk factors of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews,
28, 32-39.
Birjais, R., Mourya, A. K., Chauhan, R., & Kaur, H. (2019).
Prediction and diagnosis of future diabetes risk: a
machine learning approach. SN Applied Sciences, 1(9),
1-8.
Brownlee, J. (2020). Imbalanced classification with
Python: better metrics, balance skewed classes, cost-
sensitive learning. Machine Learning Mastery.
Chen, L., Zeng, W. M., Cai, Y. D., Feng, K. Y., & Chou,
K. C. (2012). Predicting anatomical therapeutic
chemical (ATC) classification of drugs by integrating
chemical-chemical interactions and similarities. PloS
one, 7(4), e35254
Chahil, T. J., & Ginsberg, H. N. (2006). Diabetic
dyslipidemia. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics,
35(3), 491-510.
De Silva, K., Jönsson, D., & Demmer, R. T. (2020). A
combined strategy of feature selection and machine
learning to identify predictors of prediabetes. Journal of
the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(3),
396-406.
Deshpande, A. D., Harris-Hayes, M., & Schootman, M.
(2008). Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related
complications. Physical therapy, 88(11), 1254-1264.
Diabetes Canada. (2021). Canadian Diabetes Association:
https://www.diabetes.ca/DiabetesCanadaWebsite/medi
a/Advocacy-and-Policy/Backgrounder/
2020_Backgrounder_Canada_English_FINAL.pdf
Hur, J.H., Ihm, S.Y. and Park, Y.H., 2017. A variable
impacts measurement in random forest for mobile cloud
computing. Wireless communications and mobile
computing, 2017.
Kaur, H., & Kumari, V. (2020). Predictive modelling and
analytics for diabetes using a machine learning
approach. Applied computing and informatics.
Lindström, J., & Tuomilehto, J. (2003). The diabetes risk
score: a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk.
Diabetes care, 26(3), 725-731.
Moore, R., Lopes, J. (1999). Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SCITEPRESS.
Mooradian, A. D. (2009). Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 5(3), 150-
159.
Muhammad, L. J., Algehyne, E. A., & Usman, S. S. (2020).
Predictive supervised machine learning models for
diabetes mellitus. SN Computer Science, 1(5), 1-10.
Nai-arun, N., & Moungmai, R. (2015). Comparison of
classifiers for the risk of diabetes prediction. Procedia
Computer Science, 69, 132-142.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P.,
Weiss, R., Dubourg, V. and Vanderplas, J., 2011.
Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. the Journal of
machine Learning research, 12, pp.2825-2830.
Piva, S. R., Susko, A. M., Khoja, S. S., Josbeno, D. A.,
Fitzgerald, G. K., & Toledo, F. G. (2015). Links
between osteoarthritis and diabetes: implications for
management from a physical activity perspective.
Clinics in geriatric medicine, 31(1), 67-87.
Riddle, M. C., Bakris, G., Blonde, L., & Boulton, A. (2019).
American Diabetes Association standards of medical
care in diabetes–2019. Diabetes Care, 42(Suppl 1),
S34-60.
Saeedi, P., Petersohn, I., Salpea, P., Malanda, B.,
Karuranga, S., Unwin, N., ... & IDF Diabetes Atlas
Committee. (2019). Global and regional diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030
and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes
Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes research and
clinical practice, 157, 107843.
Sami, W., Ansari, T., Butt, N. S., & Ab Hamid, M. R.
(2017). Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A
review. International journal of health sciences, 11(2),
65.
Sisodia, D., & Sisodia, D. S. (2018). Prediction of diabetes
using classification algorithms. Procedia computer
science, 132, 1578-1585.
Stubbs, R., Wilson, K., & Rostami, S. (2019). Hyper-
parameter Optimisation by Restrained Stochastic Hill
Climbing. In UK Workshop on Computational
Intelligence (pp. 189-200). Springer, Cham.
Sowers, J. R., Epstein, M., & Frohlich, E. D. (2001).
Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an
update. Hypertension, 37(4), 1053-1059.
Wei, S., Zhao, X., & Miao, C. (2018). A comprehensive
exploration to the machine learning techniques for
diabetes identification. In 2018 IEEE 4th World Forum
on Internet of Things (WF-IoT) (pp. 291-295). IEEE.
WHO (2021). Diabetes. https://www.who.int/health-
topics/diabetes
Zou, Q., Qu, K., Luo, Y., Yin, D., Ju, Y., & Tang, H. (2018).
Predicting diabetes mellitus with machine learning
techniques. Frontiers in genetics, 9, 515.
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
218
