
Combined Medical Devices: Which Classification for These
Borderline Products and Which Consequences for the
Manufacturers - About a Use Case in Skin Healing Area
Vaissière Anaïs
1,*
and Chevallier Thierry
2,3,4,†
1
Regentis-Pharma, 8B Rue Gabriel Voisin, Reims, France
2
Department of Biostatistics, Epidemiology, Public Health and Innovation in Methodology (BESPIM),
CHU Nîmes, Place du Pr. Robert Debré, 30029 Nîmes, France
3
UMR 1302, Institute Desbrest of Epidemiology and Public Health, INSERM, Univ. Montpellier, Montpellier, France
4
Tech4Health-FCRIN, France
Keywords: Medical Devices (MD), Combined Medical Devices, Combined Dressings, Cutaneous Healing, Ancillary
Substance, Peptide, Health Authorities, Classification, European Regulation 2017/746.
Abstract: Skin healing is a rapidly expanding field, especially with the growing needs of an aging population and the
increase in chronic pathologies (diabetes, venous ulcers, bedsores etc…). In order to offer ever more adapted
solutions, manufacturers are competing in ingenuity to propose innovative medical devices that meet the
expectations of patients, caregivers and the healthcare system. These developments raise many questions,
particularly with regard to the classification of devices in the various risk classes and the naming of these
wound healing devices. This article will focus on combined medical devices with the difficulties they pose
for manufacturers and health authorities in terms of development, financial investment, risk-taking and the
difficulty of classifying these so-called borderline products in the medical device universe.
1 COMBINED MEDICAL
DEVICES DEFINITION AND
EXAMPLES
A medical device (MD) is defined as “any instrument,
apparatus, equipment, material, product, except
products of human origin, or other article used alone
or in combination, […], the principal intended action
of which is not obtained by pharmacological or
immunological means or by metabolism, but the
function of which may be assisted by such means.”
(Collectif Dalloz: Jean-Paul Markus, 2010). The MD
are classified according to their destination and their
level of risk for the patient and the user according to
4 risk-categories (Class I: low-risk, IIa: moderate-
risk, IIb: elevated-risk and III: highest risk devices
(Stralin, 2020):
Combined MD are defined according to Rule 14
of Annex VIII of the European Regulation 2017/745
*
https://regentis-pharma.com/notre-equipe/
†
https://www.chu-nimes.fr/espace-recherche-clinique/eva
luation-des-dispositifs-medicaux-idil.html
as “All devices incorporating as an integral part a
substance which, when used separately, may be
considered a medicinal product within the meaning of
Article 1(10) of the said Directive, and whose action
is ancillary to that of the devices, are in Class III.”
According to the definition of the FDA (U.S.Food
and Drug Administration) in 2018, a combined MD is
defined as “diagnostic or therapeutic products that
combine drugs, devices, and/or biological products.”
(Morang J., 2019) (FDA, 2018).
Strictly speaking, a combined MD is a device
combining 2 elements, one of which is considered to
be a MD and the other substance is considered to be
a drug or to have a pharmacological or metabolic
action (Coronary stent with heparin coating (Biran R,
2016) or Bone substitute (hydroxyapatite) containing
an antibiotic (gentamicin) (Freischmidt H., 2020)).
The difficulty is then to prove that the main action is
brought by the device and not by the ancillary
substance. If the level of proof is not sufficient, there
Anaïs, V. and Thierry, C.
Combined Medical Devices: Which Classification for These Borderline Products and Which Consequences for the Manufacturers - About a Use Case in Skin Healing Area.
DOI: 10.5220/0010937300003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 281-288
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
281

is a risk that the entire device will be classified as a
medicine.
These combined MD, considered as high-risk
devices because of the active substance, will be
classified in class III.
2 MEDICAL DEVICES FOR
CUTANEOUS HEALING
The cutaneous healing is currently one of the biggest
challenges for healthcare professionals. Indeed, with
the aging population, chronic wounds are more and
more frequent and lead to considerable expenses in
terms of health care costs because they are hard and
long to heal (over six weeks) and often recur (Martin
P. &. N., 2015).
The challenge of manufacturers is then to propose
new and efficient MD to improve healing without
having a strong pharmacological effect. In these
cases, the risk is to be classified as a medicine or
alternatively as a combined MD (high-risk class III)
which is by definition “A device incorporating a
substance that when used separately can be
considered a medicine” (Européenne, 2017).
High-risk MD necessarily entail more constraints
for manufacturers in terms of development, financial
investment, and investigation time, which can have a
major impact on the company. The aim of
manufacturers is to prove the healing efficiency and
the safety of the device. In that purpose, each step of
MD development must be carefully planned upstream
of the development phase. A concrete case of
combine device will be used to illustrate the
development process and difficulties encountered by
industrials and health authorities for the evaluation
and classification of such borderline products.
3 DRESSINGS AS COMBINED
MEDICAL DEVICES
3.1 Definition of Dressings for Skin
Healing
A dressing is a device covering a wound and
providing a physical protection against external
attacks (mechanical or bacterial). Dressings also
maintain a moist environment in contact with the
wound, promoting optimal healing. In 1962, the
British researcher George Winters demonstrated the
beneficial effects of a moist environment for healing.
Since then, this criterion is therefore considered to be
a fundamental characteristic for a twice faster healing
(Turner, 1979) and led industrials to focus on the
design of modern dressings: occlusive and
moisturizer (Chaby G., 2007) (Vaneau M., 2007)
(Werdin F., 2009).
Dressings present a high-level of risk and are
subjected to great vigilance from the manufacturers
as well as the health authorities. These dressings have
different compositions and act on different stages of
the healing process (reduction of inflammation,
improvement of tissue synthesis, intense hydration,
absorption of bad odours, elimination of cellular
debris etc…).
In general, the main functions of dressings are:
Promote natural healing by maintaining a
moist environment and draining exudates.
Allow gas exchange.
Isolate the wound thermally and mechanically
from external aggression.
Provide a bacteriological barrier by preventing
infections from the outside.
The development of dressings is vast and varied
and requires, as for any MD, a well-determined
evaluation framework as allowed by the new
European regulation 2017/746 and the
standardization of the evaluation of MD.
3.2 Classification of Dressings for
Cutaneous Healing
The classification of MD, intended for skin healing,
is complex and involves following several rules based
on dressings characteristics to correctly classify them:
Their main action.
The duration of use. The longer the duration of
administration, the riskier the MD will be
considered. For example, the healing of acute
wounds will take less time than chronic
wounds, which do not heal in 6 weeks. As a
result, chronic wound healing will require
treatment for more than 30 days and in
accordance with the European regulation
2017/745. “Duration of use:
o “Temporally” normally means intended
for continuous use for less than sixty
minutes.
o “Short-term” normally means intended for
continuous use between sixty minutes and
thirty days.
o “Long-term” normally means intended for
continuous use for more than thirty days.”
ClinMed 2022 - Special Session on Dealing with the Change in European Regulations for Medical Devices
282
The pharmacological activity of the device:
According to Rule 8 of Annex VIII of the new
European Regulation 2017/745, “All invasive
surgical-type devices intended for long-term
use are classified as Class IIb unless:
o If they have a biological effect or are fully
or substantially absorbed, in which case
they are Class III […].
o If they are intended to administer drugs, in
which case they are Class III […].”
In addition, wound healing devices are applied on
open wounds and therefore represent a greater risk of
infection or that the carrier substances enter the
systemic circulation and induce side effects
Faced with the complexity of classification, each
device will be assessed on a case-by-case basis by
health authorities and manufacturers are responsible
for clearly defining the action of their MD and
providing a clear and precise claim. The new
European regulation 2017/746, implemented from
May 2021, brings more clarity on how to classify
MD.
3.3 Few Examples of Dressings and
Their Classification
Dressings can be classified in different risk classes
according to their characteristics. The table 1
illustrate some examples of dressings and their
repartition in the different risk-classes.
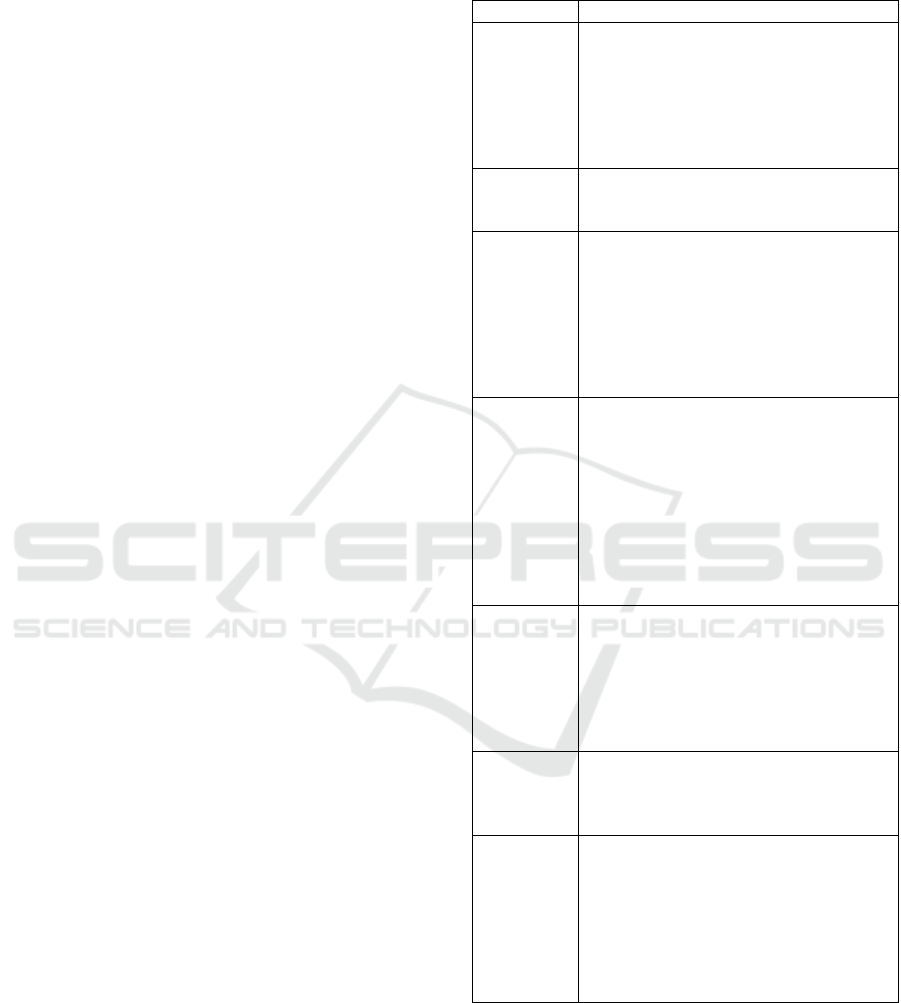
From this table, it is clear that the majority of
combined dressings are classified as Class III.
However, it is notable that combined dressings are not
automatically classified as Class III device and can be
classified in lower class risk like Prevena® or Askina
Carbosorb® dressings classified in IIa or the
Carbonet® or UrgoStart® dressings classified in IIb.
3.4 Reflections on the Classification of
Dressings
3.4.1 Silver Dressings
In general, silver dressings are considered as risky
MD and therefore classified as class III. Silver
molecules provide an antibacterial effect, considered
as a secondary function, and they are small molecules
which can be toxic if they reach the systemic
circulation. However, Prevena® dressing, although
claimed as a silver dressing and therefore at risk, is
still classified as a class IIa. Health authorities might
have considered that a silver dosage of 0.019% was
not sufficient to induce a toxic reaction.
Table 1: List of examples of marketed dressings.
TLC-NOSF: Technology Lipide-Colloid-Nano Oligo
Saccharide Factor.
Classification Dressin
g
, com
p
osition and intended use
Class I – Not
combined
Algoplaque® (e-pansement, e-
pansement Algoplaque, s.d.):
Hydrocolloid dressing composed of
((carboxymethylcellulose (CMC)) and
Urgo Hydrogel® (e-pansement, e-
pansement Urgo Hydrogel, s.d.):
Maintenance of a moist environment.
Class IIa –
Not
combine
d
Jelonet Plus® (e-pansement, e-
pansement Jelonet Plus, s.d.): Vaseline
dressing. Drainage of exudates.
Class IIa –
Combined
Prevena® (e-pansement, e-pansement
Prevena, s.d.): Hydrocellular dressing
with silver (0.019%). Reduction of
microbial colonization.
Askina Carbosorb® (e-pansement, e-
pansement Askina Carbosorb, s.d.):
Active carbon dressing. Adsorption of
b
acteria and odours.
Class IIb –
Not
combined
UrgoTul® (e-pansement, e-pansement
UrgoTul, s.d.) and Ialuset® (Vidal,
Vidal Ialuset, s.d.): Hydrocolloid
dressing (CMC). Maintenance of a moist
environment and management of
exudates.
Purilon gel® (e-pansement, e-
pansement Purilon, s.d.): Hydrogel
(sodium CMC). Effective and gentle
debridement.
Class IIb -
Combined
Carbonet® (Nephew, s.d.): Active
carbon dressing. Adsorption of bacteria
and odours.
UrgoStart® (Vidal, Vidal UrgoStart,
s.d.): Hydrocellular dressing composed
of a TLC-NOSF matrix. Inhibition of
metallo
p
roteinases
(
MMP
)
.
Class III –
Not
combined
Duoderm® (Vidal, Vidal Duoderm,
s.d.): Hydrocolloid dressing. Maintains a
moist environment and aids in autolytic
detersion.
Class III -
Combined
Urgotul®Ag (Vidal, Vidal UrgoTul Ag,
s.d.): Silver dressing. Maintains a moist
and antibacterial environment.
Promogran® (HAS, 2019): Active
dressing with anti-protease effect
composed of 55% collagen and 45%
regenerated oxidized cellulose. MMP
inhibitor.
3.4.2 Carbon Dressings
Carbon dressings are represented in all risk classes
except class III. However, carbon molecule is an
ancillary substance, not responsible for the main
action of the device (maintaining a moist
environment), but which has a supporting function in
Combined Medical Devices: Which Classification for These Borderline Products and Which Consequences for the Manufacturers - About a
Use Case in Skin Healing Area
283

wound healing (absorption of malodours). By this
definition, and also with regard to the fact that carbon,
as a small molecule, can penetrate the systemic
system, all carbon-based dressings should be
classified as class III MD.
3.4.3 Metalloproteinase Regulating
Dressings
Another special case is the MMP-regulating
dressings. These dressings contain molecules with
physiological activity since they are able to induce the
inhibition of MMP activity. However, as explained
previously, according to rule 8 of Annex VIII of the
new European regulation 2017/745, “All invasive
surgical-type devices intended for long term use are
class IIb, except: if they have a biological effect or
are fully or substantially absorbed, in which case they
are class III. […]”. This definition clearly states that
these MMP-regulator dressings should be classified
as class III. However, only the Promogran® dressing
is classified in class III. The UrgoStart® is classified
as a class IIb MD.
3.4.4 Non-combined Dressings Classified in
Class IIb or III
On the contrary of combined dressings being
classified in class IIa and IIb, it also exists some
dressings that might be considered as being at low
risk and non-combined, according to their
composition and their main action, and which still
found classified in higher risk-classes (IIb and III).
This is the case for example of the Ialuset dressing®,
whose main function is to maintain a moist
environment, and which is mainly composed of
hyaluronic acid for its strong hygroscopic power,
which is classified in class IIb. The explanation for
this high-risk classification certainly comes from the
hyaluronic acid which, depending on its size (the
smaller, the more it will be considered at risk because
of the risk of entering the systemic circulation), can
be considered as a MD or a drug.
Another example of a careful classification is the
UrgoTul® dressing which is composed of a
moisturizing matrix (CMC, Vaseline, Paraffin) and
apart from the fact that it is used over long periods
(more than 30 days), its composition does not
represent any particular danger for the patient.
Indeed, the Algoplaque® dressing, also composed of
CMC is classified as class I MD. Moreover, the
association paraffin/vaselin/glycerol is considered as
being one of the most moisturizing mixtures and is
often used in cosmetic moisturizing cream (Mylan®,
Biogaran®, Dextopia®…). The classification of
UrgoTul® as a high-risk class (IIb) is then difficult to
understand in view of these elements, especially
considering its counterparts, UrgoStart®, which is a
combined MD also classified in class IIb.
Another example is the Duoderm® dressing,
which is a hydrocolloid dressing composed of a
matrix of pectin, gelatin, sodium CMC and a
polyurethane foam. The main function is to maintain
a moist environment. Despite a description that seems
without particular risk, this dressing is classified as
class III. It is therefore difficult to explain why this
dressing is considered to be riskier than UrgoStart®,
for example, or of equivalent risk to all silver
dressings.
These are few examples illustrating the lack of
uniformity for MD classification before the
implementation of the new European regulation.
4 CONCRETE EXAMPLE OF AN
INDUSTRIAL DRESSING,
INTENDED FOR SKIN
HEALING, CLASSIFIED AS A
COMBINED MD
4.1 Medical Device under Study
The MD used as an example to illustrate this research
is intended for skin healing of chronic wounds. This
MD consists of the association of a moisturizing
dressing with a peptide solution. The peptide included
in the solution was developed, in partnership with the
CNRS, on the basis of the activity of matrikines,
molecules derived from natural degradation of
elastin. This innovative bifunctional peptide (BFP)
has the ability to activate the synthesis of the
extracellular matrix (ECM) on one hand and to
inhibit, by a competitive mechanism, the molecule
responsible for inflammation (MMP) on the other
hand (Attia-Vigneau J, 2014) (Figure 1).
The promising performances of the peptide led the
industrials, responsible of its development, to
consider a medical application. Indeed, considering
the effects of the peptide on cellular regeneration,
proved by in vitro studies (Attia-Vigneau J, 2014),
this peptide was integrated to a phosphate buffer
solution to be applied on chronic wounds, such as
Venous Leg Ulcers (VLU), in association with a
secondary dressing to promote healing mechanisms.
Apart from pathological cases, like diabetes or
chronic wounds (ulcers), the healing process is 6
weeks. In case of chronic wounds, this healing
ClinMed 2022 - Special Session on Dealing with the Change in European Regulations for Medical Devices
284
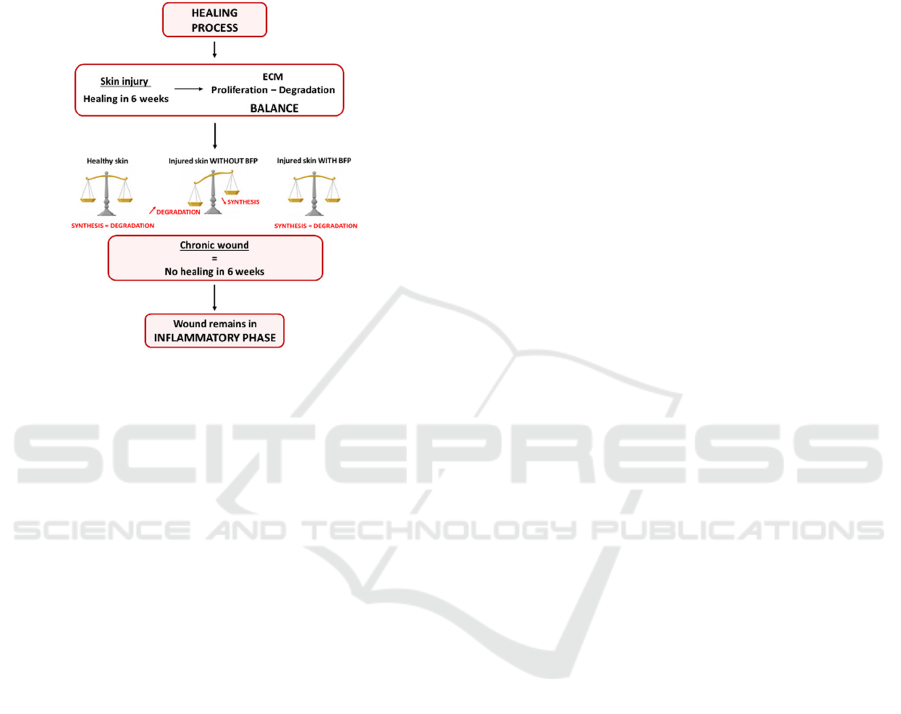
process is longer because of an unbalance between
the synthesis and the degradation of the ECM
(Extracellular Matrix). This state prevents the
reconstruction of the matrix and then an impairment
of healing. The application of the BFP peptide could
bring back the balance and leads to an efficient
healing of the wound (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Healing process of wounds and schematic
representation of BFP peptide effect.
Most of the marketed MD to treat these kinds of
wounds act either on matrix synthesis, by maintaining
a moist environment (UrgoTul®, Ialuset®…), or on
the inhibition of MMP (UrgoStart® or Promogran®).
The new device uses the bifunctional effect of the
peptide and propose an innovative device able to act
on both phenomenon, synthesis of the matrix and
inhibition of MMP. This MD (peptide solution +
Secondary dressing) was therefore developed to
perform a proof-of-concept trial and to verify the
healing efficiency of the device and its safety of use.
4.2 MD Claim: Adequacy with the
Business Need
The claim of the MD is of particular importance and
consists in highlighting the main action of the
secondary dressing (hydration) in wound healing and
the supporting action of the BFP peptide which
consists in:
Hydration of the microenvironment of the
wound, proved by in vitro RAMAN
spectroscopy and in vivo clinical trial on 10
women.
Decrease of inflammation by a competition
mechanism of the peptide which acts as a decoy
effect for MMP and thus diverts the enzymatic
activity of this protein towards itself, leaving
the possibility for the matrix to regenerate
properly without having physiological or
metabolic effect.
From the industrial point of view, the peptide can
be considered as an ancillary molecule, making the
proposed device a MD that has been claimed as such
by the health authorities.
4.3 Classification of the Developed MD
and State of the Art
The French health authorities considered that the
claimed device was in fact a medicine. Considering
the definition of a medicine by the Public Health
Code (Article L. 5111-1) as “Any substance […]
exerting a pharmacological, immunological or
metabolic action.”, an argument was developed to
respond to the health authorities by comparing the
proposed MD to those already on the market such as
UrgoStart® or Promogran®, which are protease
regulators and can therefore also be considered as
having a pharmacological or physiological effect.
Despite this comparison, the French authorities
remained on their position because they considered
the peptide solution alone as a medicine. They also
stated that the dressing is not an impregnated dressing
(MD dressing incorporating as an integral part a
substance with an accessory pharmacological action)
and the peptide release on the wound cannot be
evaluated. This lack of safety on peptide release as
well as the lack of hindsight of the health authorities
regarding this new molecule made it impossible to
classify it as a MD.
Another example of MD more comparable to the
“Peptide solution + Secondary dressing” is the
Cacipliq20®. This Cacipliq20® is a spray,
considered as a MD of class III, offering protection of
growth factors by decoy effect and whose mode of
action can be compared to that of the BFP peptide,
which also acts as a decoy for MMP (Barritault,
2020). Additional expertise was therefore requested
from another European health authority who stated on
this particular case that the Cacipliq20® is accepted
as a device but similar products may be considered
pharmaceutical. This statement demonstrates the
variability of classification that can be obtained from
one country to another.
The opinion of other European health authorities
is quite unanimous and in agreement with that of the
French health authorities. Only the Czech health
authorities (SUKL) considered the device presented
as a combined device of class III. As a risk device this
MD is subject to great vigilance in terms of
Combined Medical Devices: Which Classification for These Borderline Products and Which Consequences for the Manufacturers - About a
Use Case in Skin Healing Area
285
traceability and monitoring and consequently, a GMP
synthesis of the peptide has been required by the
health authorities in order to carry out a clinical
trial.DM. This GMP synthesis not originally planned
by the industrial and that will have heavy
consequences for the future of the project.
5 IMPACT OF A
CLASSIFICATION AS A
COMBINED MD OF CLASS III
A device classified in class IIb or III is considered as
high-risk class by health authorities and a GMP
synthesis would been required in any case. The debate
is not about the classification of the MD but about a
wrong evaluation of the project in its entirety and a
poor knowledge of the field. How this wrong
estimation impacts the project and its budget
according to the development stage of the MD?
5.1 MD Conception
The MD conception stage is an essential step
determining the whole project technically and
financially. A correct calibration is essential to avoid
budget expense and project delay. The longer is a
project and the more expensive it will be. The correct
definition of the MD is possible with a deeper
knowledge of the field of MD. Indeed, a MD
classified in class IIb or in class III as a combined MD
present risk and although the safety and innocuity
proof are high. Health authorities will not take any
chances to propose a product on which they do not
have hindsight and without strong, recorded and
tracked guarantees on the safety. Moreover, with the
sanitary scandals of the past few years, health
authorities are extra careful regarding new devices.
5.2 Clinical Phases
A poorly estimated project at the outset will have the
greatest impact during the clinical phases. The
acceptance of the clinical trial is submitted to the
approbation of health authorities that will request the
GMP synthesis. As the budget allocated for the trial
is not sufficient to cover this additional expense, the
project will inevitably fall behind schedule.
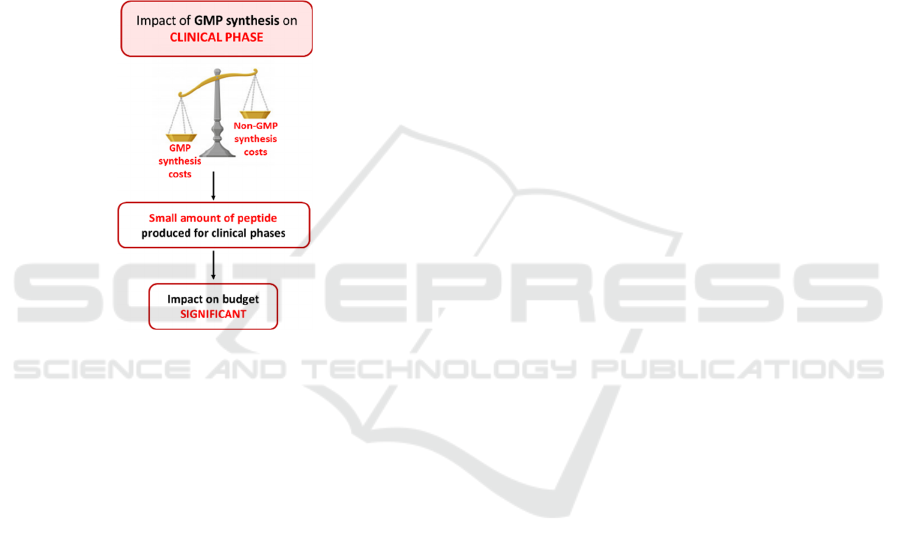
For clinical trial, the quantity of necessary peptide
(or molecule) is rather small, and the costs are
extremely high due to the tracking system to
implement, and the documentation requested for a
GMP synthesis (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Impact of unplanned GMP synthesis on clinical
phase of a project.
Produce a small amount of peptide, just
enough for the trial, pending verification that
the clinical trial is providing the expected
results.
Produce a larger amount of peptide in
anticipation of the continuation of the project
and the commercialisation of the MD after the
clinical trial.
The 2 options of production will have an
equivalent price and difference will not be significant.
A larger production of peptide during the clinical
phase can save valuable time for the
commercialization phase where important quantity of
peptide will be requested. It is then important to
correctly estimate the financial costs and benefits of a
larger molecule production upstream.
It is necessary to be well trained and advised by
experts of the field to avoid taking decision urgently
and make bad choices for the project.
5.3 Marketing and Post Marketing
An unplanned GMP synthesis at the marketing phase
can have a financial impact mainly according to the
decision taken at the previous steps. During the
marketing phase, there is 2 possibilities:
The peptide quantity produced at the previous
step was just sufficient to complete the trial. In
that case an additional budget and time increase
is to plan for the production of GMP synthesis.
The peptide quantity produced at the previous
step was increased in anticipation for the
marketing. In that case, the manufacturing of
the device can be launch immediately.
However, a reflexion is to be considered for the
future of the project and according to the marketing
ClinMed 2022 - Special Session on Dealing with the Change in European Regulations for Medical Devices
286
plan of the industrial. Indeed, either the industrial is
the exclusive manufacturer and seller of the MD, in
which case it will be necessary to provide a budget
for the GMP synthesis throughout the marketing and
life cycle of the MD. Or the industrial commercializes
its devices in the form of licensing by granting
licenses for the exploitation of its product. In this
case, the manufacturer does not have to budget the
GMP synthesis for the marketing part.
However, it is important to highlight that the
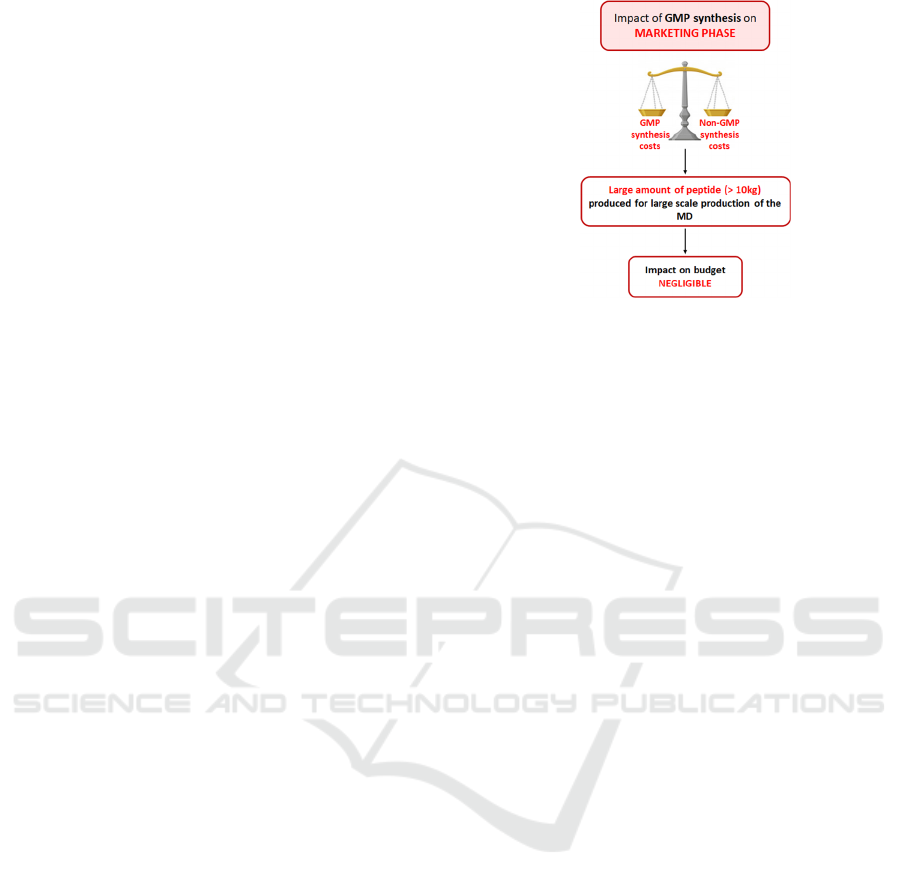
greater the quantity of GMP synthesis, the lower the
price per kilo will be. Therefore, for 10 kg of GMP
peptide produced, the price per kilo is equivalent to
that of a non-GMP synthesis (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Impact of unplanned GMP synthesis on marketing
phase of a project.
Therefore, the impact of a GMP synthesis not
foreseen by the industrial during the design of the
project will have no financial impact for the later
phases of the project, if the GMP synthesis is very
important (equivalent to about 10 kilo).
6 CONCLUSION
The classification of MD and in particular combined
devices is a very complicated process, hardly
harmonized before the implementation of the new
European regulation 2017/746. Some examples of
dressings classifications that do not comply with the
new European regulation can be cited as UrgoStart®
(a combined MD classified as class IIb) or Prevena®
dressing (a combined MD containing silver classified
as class IIa) or a product like Cacipliq20® that can be
considered as a medicine and yet is positioned as class
III MD under the old directive. In this logic, the
mechanism of action of the UrgoStart® dressing,
whose main function is the inhibition of proteases by
the NOSF molecule, could be considered as a
pharmacological activity (Européenne, 2017)and
then classified as a combined MD of class III. To
understand this classification, an expert opinion has
been requested from European health authorities who
stated that, in their opinion and according to the
regulation in force, the substance NOSF meets the
status of a medicine. According to the regulation,
combined MD are defined following the rule 14 of
Annex VIII of the European Regulation 2017/746 as
“All devices incorporating as an integral part a
substance which, when used separately, may be
considered as a medicinal product within the
meaning of Article 1(10) of the said Directive, and the
action of which is ancillary to that of the devices, fall
within Class III.” On this basis, the UrgoStart® MD
could therefore be considered as a combined MD.
The status of combined MD is not clear, and it was
noted through this article that:
Combined MD dressings are not clearly
defined as such on the contrary of combined
MD as stent or injector pens.
Combined MD dressings are widely
represented within the different risk classes,
and they are not systematically classified in
class III as they should be as high-risk MD.
As part of the evaluation of a MD, it is currently
essential to carry out one, or even several, clinical
trials to demonstrate efficiency and safety of the
device. In this case, the balance benefit-risk is very
important and cannot be unbalanced in one direction
or the other under penalty of considering the device
as a drug. Indeed, in the case of a combined MD, the
main objective is to prove the ancillary action of the
associated molecule compared to the main MD.
Although the manufacturer transmits all the safety
information and considers the benefit-risk to be well
balanced, the health authorities will tend to perceive
an unbalanced in the direction of risk.
Those combined MD are considered as
“borderline products”, they are indeed, at the frontier
between the MD and the medicine, it is then a
question of claim and most of all to prove the effect
of the ancillary substance, associated with the main
MD. Moreover, an associated and innovative
substance will always be considered at risk by health
authorities who will not take any risk and will
systematically classify it as a high-risk MD. It is also
clear that regardless of the classification of the device,
in class III as a combined MD or in class IIb, such as
UrgoStart®, a GMP synthesis will be requested for
the associated molecule in order to have a better
traceability.
Combined Medical Devices: Which Classification for These Borderline Products and Which Consequences for the Manufacturers - About a
Use Case in Skin Healing Area
287

The debate is therefore not about being classified
as a class IIb MD or as class III combined MD, but
really about avoiding being classified as a medicine.
The aim is then to provide as much proof of safety as
possible and to make a good claim that will avoid
being classified as a medicine by health authorities.
REFERENCES
Attia-Vigneau J, T. C. (2014). Regeneration of human
dermis by a multi-headed peptide. 134(58 - 67).
Barritault. (2020). Overview of 10 years of practice with
CACIPLIQ20® matrix therapy as a healing agent for
hard to heal wounds: Efficacy, cost-effectiveness and
future perspectives. 28.
Biran R, a. P. (2016). Heparin coatings for improving blood
compatibility of medical devices. Advanced Drug
Delivery Reviews, 112:12-23.
Chaby G., S. P.-A. (2007). Dressings for acute and chronic
wounds. 143(10:1297-1304).
Collectif Dalloz: Jean-Paul Markus, D. C. (2010, March
11). Code de la Santé Publique - Article L.5211-1.
Dalloz.
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Algoplaque. Récupéré sur
e-pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/algo
plaque
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Askina Carbosorb.
Récupéré sur e-pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/
dispositifs/askina-carbosorb
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Jelonet Plus. Récupéré
sur e-pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/
jelonet-plus
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Prevena. Récupéré sur e-
pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/prevena
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Purilon. Récupéré sur e-
pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/purilon-
gel
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement Urgo Hydrogel. Récupéré
sur e-pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/
urgo-hydrogel
e-pansement. (s.d.). e-pansement UrgoTul. Récupéré sur e-
pansement: https://e-pansement.fr/dispositifs/urgotul
Européenne, P. E. (2017). Règlement (UE) 2017/745 du
parlement et du conseil relatif aux dispositifs médicaux,
modifiant la directive 2001/83/CE, le règlement (CE)
n°178/2002 et le règlement (CE) n°1223/2009 et
abrogeant les directives du Conseil 90/385/CEE et
93/42/CEE. Actes législatifs.
FDA. (2018, March). Récupéré sur https://www.fda.gov/
CombinationProducts/AboutCombinationProducts/def
ault.htm.
Freischmidt H., A. J. (2020). Individualized techniques of
implant coating with an antibiotic-loaded,
hydroxyapatite/calcium sulphate bone graft substitute.
Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 16:689-
694.
HAS. (2019). Comission Nationale d'évaluation des
dispositifs médicaux et des technologies de santé Avis
de la CNEDiMTS sur le Promogran.
Martin P., &. N. (2015). Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound
healing. 173(370-378).
Morang J., &. P. (2019). Combination devices. Chapter
8(117-138).
Nephew, S. &. (s.d.). Smith & Nephew Carbonet. Récupéré
sur https://www.smith-nephew.com/fr-canada/
produits/traitement-avance-des-plaies/carbonet-/
Stralin, M. (2020). Classification of medical devices and
their routes to CE marking. Récupéré sur Support CE
check: https://support.ce-check.eu/hc/en-us/articles/
360008712879-Classification-Of-Medical-Devices-
And-Their-Routes-To-CE-Marking
Turner. (1979). Hospital usage of absorbent dressings.
222(421-426).
Vaneau M., C. G. (2007). Consensus panel
recommendations for chronic and acute wounds
dressings. 143(10:1291-1294).
Vidal. (s.d.). Vidal Duoderm. Récupéré sur
https://www.vidal.fr/parapharmacie/duoderm-e-pans-
hydrocolloide-31976.html
Vidal. (s.d.). Vidal Ialuset. Récupéré sur Vidal:
https://www.vidal.fr/parapharmacie/ialuset-creme-
acide-hyaluronique-69672.html
Vidal. (s.d.). Vidal UrgoStart. Récupéré sur
https://www.vidal.fr/parapharmacie/urgostart-pans-
micro-adherent-125005.html
Vidal. (s.d.). Vidal UrgoTul Ag. Récupéré sur
https://www.vidal.fr/parapharmacie/urgotul-ag-lite-
border-pans-fin-adhesif-antibacterien-109210.html
Werdin F., T. M. (2009). Evidence-based management
strategies for treatment of chronic wounds. 9(169-179).
ClinMed 2022 - Special Session on Dealing with the Change in European Regulations for Medical Devices
288
