
Opportunities for System Dynamics towards the Support of
Technological Developments in Stroke Treatment Domain
Julia Kantorovich
a
and Jukka Ranta
b
VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Tekniikantie 21, Espoo, Finland
Keywords: System Dynamics, Stroke Diagnosis and Treatment, Technology Developer Support.
Abstract: Data driven solutions can facilitate and enhance stroke diagnostics and at the same time management of stroke
prevention and treatment in a cost-effective way. However, the potential and the utilization of data and AI
analytics in stroke solutions are largely neglected. At the same time, the process to enter to medical domain
for technology developer is not straightforward. There is a need for common vocabularies and design tools to
engage medical professionals in interaction with technologists during the research and development phase to
let them know what is needed. This paper valorises the opportunities for System Dynamics to support
technology developers in the developing of innovative solutions and applications for stroke diagnosis and
treatment. In addition, the value of System Dynamics to support the impact analysis (health outcome, decision
quality, care costs, etc.) and hereby to facilitate the business and market uptake of new innovative solutions
in this domain is demonstrated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Annually, approximately 15 million people
worldwide suffer a stroke with global projections that
the number of stroke survivors will rise to 77 million
by 2030 (Béjot et al., 2016; WSO, 2021). Following
transient ischaemic attack (TIA), at 5 years, the risk
of recurrent stroke is 18.3% and at 10 years following
stroke, the cumulative risk of recurrence is 39.2%,
with higher death and disability noted with recurrent
events. Furthermore, although 10.5% to 18.2% of
patients with TIA will have a stroke within 90 days,
more than 31-61% of the TIA patients are
misdiagnosed (Dawson et al., 2009; Sadighi et al.,
2019). Such high rates of cardiovascular morbidity
and associated disability indicate the need for
effective secondary prevention actions. Moreover,
rapid and accurate diagnosis and treatment of stroke
is important to improve health outcomes. A
significant delay in treatment that may happen due to
misinterpretation of stroke symptoms or inability of a
person to perform necessary follow-up actions, might
cause death, permanent disabilities, as well as more
expensive treatment and rehabilitation.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7598-6175
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1376-542X
There is a technology that has been developed to
address the needs of accurate and rapid diagnosis and
treatment of stroke. The examples of existing
technological solutions are stroke risk calculation
tools, computer-aided first stroke symptoms
recognition software, remote diagnosis- and
rehabilitation which is supported by telemedicine and
mobile solutions (e.g. Chen et al., 2018; Bat-Orgil,
2021). However, the potential of technological
solutions, data combinations and artificial
intelligence (AI) to support more advanced data-
driven decision support in the TIA and stroke
diagnostics are not fully leveraged (Ding et al., 2020;
Ali et al., 2020). Respective improvements have also
a massive business potential. They can facilitate
differential diagnostics, triaging, and management of
cerebrovascular conditions in a cost-effective way.
The Stroke-DATA research (StrokeData, 2020) is
setup to deal with these challenges and to propose a
number of data-driven technological solutions to
reduce the diagnostic time, to improve the outcome of
the diagnosis and secondary prevention as well as to
improve the satisfaction of patients and care-givers,
and effectiveness of overall stroke treatment
processes (see Figure 1).
Kantorovich, J. and Ranta, J.
Opportunities for System Dynamics towards the Support of Technological Developments in Stroke Treatment Domain.
DOI: 10.5220/0010983700003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 743-750
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
743
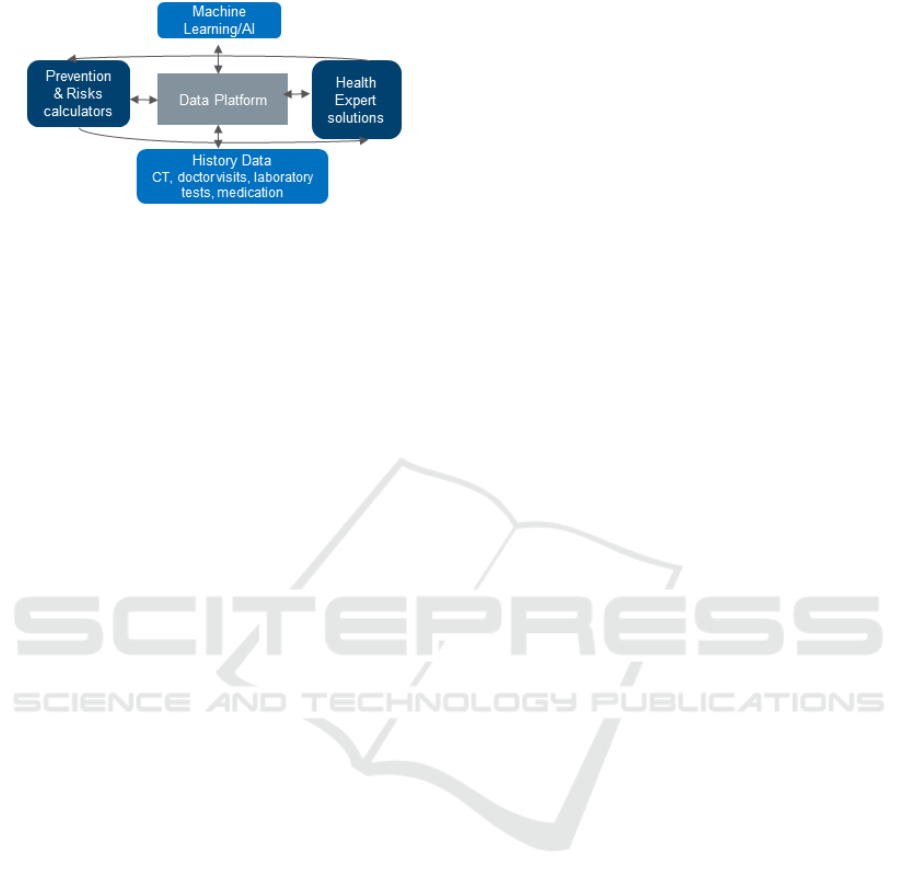
Figure 1: Envisioned Stoke-DATA solutions.
However the experience gained during the first six
months of the project had revealed that this task is far
from straightforward. It can be cumbersome for
technology developers to grasp the complex domain
of TIA- and stroke treatment, to master the needs and
to find a respective niche towards the technological
development and business success. Moreover, it is
also not an easy task to engage medical professionals
into discussion on needs, to demonstrate the ability of
technology, and to prove the impact value of the
proposed solution to various stakeholders involved in
the stroke care processes.
System Dynamics and Systems Thinking models
have potential to connect various stakeholders and to
provide technology developers with means to grasp
the complexity of stroke domain. System Dynamics
is based on Systems Thinking and Group Model
Building principles. Systems Thinking helps to learn
the definitive characteristics of the systems, how
systems fit in a larger context of day-to-today life,
how they behave and how to manage them (Sterman,
2000). Group Model Building has been found to be
a useful method for engaging different
stakeholders to both elicit their perspectives to
address difficult and complex problems and share
those perspectives and expertise (Richardson,
2007).
Consequently, the objective and the first
contribution of this research is to valorise the
opportunities for System Dynamics towards the
supporting of technology developers in the
developing of innovative solutions (applications) for
stroke diagnosis and treatment. The second
contribution of this research is to demonstrate a value
of System Dynamics to support the impact analysis
(health outcome, decision quality, care costs, etc.) and
hereby to facilitate the business and market uptake of
new innovative solutions in this domain.
This paper is organised as follows. Chapter 2
gives an introduction to the stroke domain and its
respective challenges and possibilities for the
technology development. The background related to
the System Dynamics modelling and its application to
stroke treatment are presented in chapter 3. The
identified opportunities and needs for System
Dynamics are also discussed there. The first
modelling efforts are presented to support the
respective discussion in Chapter 4. Chapter 5
concludes the paper, outlining also the aspects of next
steps of research.
2 STROKE AND TECHNOLOGY
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood
flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two
main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood
flow, and haemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause
parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs
and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to
move or feel on one side of the body, problems
understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision
to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon
after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less
than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient
ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke
(Donnan, 2008).
Early recognition of stroke is deemed important
as this can expedite diagnostic tests and treatments
and thus reduce the severity of damage. In fact, more
rapid and accurate diagnosis and early preventive
treatment, “the 90-day stroke risk” can be decreased
by 80% after the TIA episode. Accordingly all
attempt and means are needed to decrease the time
from symptom onset to acute stroke treatment.
Advanced age is the most important however
unmodifiable risk factor for stroke, as stroke rates
double for every 10 years of age after the age of 55.
The INTERSTROKE study performed in 22
countries identified 5 risk factors which together
accounted for 80% of the population-attributable-risk
for stroke, namely hypertension, current smoking,
abdominal obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical
activity (O'Donnell et al. 2010).
Furthermore, organization of stroke treatment and
care has advanced beyond stroke units and in-hospital
phase, and it includes multiple overlapping processes
including primary prevention, emergency medical
systems, acute care and rehabilitation, secondary
prevention to avert stroke recurrence and long-term
follow-up supported by public education, community
campaigns, and research.
Technology can potentially support and enhance
health outcomes in all treatment stages, we call them
stroke ‘care path’ stages. For example, in case of
incident of stroke, the sooner a diagnosis is made, the
earlier the treatment can begin and the better the
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
744

expected outcome is for the patients. An MRI scan is
very useful in detecting ischemic stroke, however it is
usually not available in pre-hospital phase
(emergency room, home) due to its cost. Clinical tests
like the Face Arm Speech Test (FAST) are helpful
tools used by neurologists and trained nurses, but
there may not be professional help immediately
available to conduct the tests.
The computer-aided stroke presence assessment
over facial motion weaknesses and speech inability
for patients with suspicion of stroke showing facial
paralysis and speech disorders in an acute setting
using for example camera and speech recognition
software on mobile phone is one example of
technology proposed by researchers (Khriyenko, et
al., 2018; Yu et. al, 2020). Other examples are the
computerized decision support tools, which are based
on risk scoring and may provide access to expert
advice, improve GPs' diagnostic accuracy (in primary
care setting), limit emergency department referrals of
high-risk patients and prompt GPs to initiate
secondary prevention in case of specialist
consultation is anticipated to be delayed.
Furthermore, numerous smartphone apps are
available that can assist with stroke rehabilitation and
recovery process.
Artificial neural networks are a powerful AI tool
for automatic diagnostics of diseases and has a
potential in decision-making support. Machine
learning and compute vision have been applied in
clinical informatics and have shown commercial
potential in symptom detection and classification
(Wang & Luo, 2016).
Finally, large databases of patient data are being
captured in hospitals which, if accessed, provide a
wealth of information about disease treatment and
prevention. Handling data sets and analysis of data
have become a major growth area of interest globally
(Marshall, 2016). Mobile medical technology is
expanding with multiple diagnostic and monitoring
platforms using mobile app systems which can
require new ways of approaching to data analytics.
Overall, it was predicted that technologies such as
telehealth, eHealth, big data and AI would have
significant 30-50% impact on the improved mortality
rates in acute care cases by 2025 (Polycom, 2015).
Last but not least, data platform economy has
emerged (Baltimore, et al., 2016). There are many
players such as Amazon, Google, Uber that are
making business and creating value with platforms.
Platform economy is based on data, components,
algorithms and applications that are creating an
infrastructure in which the platform-based markets
and ecosystems operate. However, this approach is
not yet fully utilized in the fragmented and highly
regulated healthcare market. In order to be successful
in the business perspective, the technology providers
should either build platform solutions that are
complementary between each other, or platform
solutions that are complementary between the
stakeholder players in their target market.
However, the process to enter to medical domain
of stroke treatment for technology developer is not
straightforward. There is a need for common
vocabularies and design tools to engage medical
professional in interaction with technologists during
the research and development phase and to let them
know what's needed.
System Dynamics is a perspective and a set of
conceptual tools that have been used decades to study
the structure and dynamics of complex systems such
urban and industrial systems (Forrester, 1961, 1969).
Later, System Dynamics has been also leveraged in
other fields including healthcare domain to support to
master the complex health processes, to plan actions
and to affect the respective domain policies.
However, its value to support technology developer
is not yet exploited widely. The related existing
research and the opportunities for System Dynamics
are further discussed in the following (Section 3).
3 SYSTEM DYNAMICS
System Dynamics is a Systems Thinking based
approach for examining how certain things in the real
world change over time. The system’s internal
structure, which is represented by system components
and the cause-and-effect connections among them,
determines the dynamic behaviour of the system and
how it responds to changes (Sterman 2000).
The causal loop diagrams and stock-and-flow
diagrams are used in system dynamics to capture the
interactions between components. Causal loop
diagrams consist of variables connected by arrows
denoting the causal influences among the variables
and the feedback loops, chains of causal links that
balance or reinforce on themselves, in the system.
Stock-and-flow diagrams highlight the
accumulation and flow of information, materials,
financial assets and people in and between the
components, respectively.
Overall, modelling is an iterative process of scope
selection, hypothesis generation, causal
diagramming, quantification, and reliability testing.
Qualitative models can be used to discuss and to
promote structural insights and the behaviours of the
system, thus, quantitative simulations allow users to
Opportunities for System Dynamics towards the Support of Technological Developments in Stroke Treatment Domain
745

see how different choices (selected parameters) lead
to different plausible futures. The models are
powerful tools for communicating across sectors and
for motivating stakeholders to work together to make
systemic changes in their systems. Furthermore,
System Dynamics models can be used to tackle ‘data-
poor’ problems. The information base for the
conceptualisation and formulation of System
Dynamics models can be based on experts’ opinion
and they can be also broader than the numerical
database applied in operations research and statistical
modelling. Group Model Building (GMB) is a tool to
acquire expert knowledge and to identify modelling
needs. Group Mode Building refers to a system
dynamics model building process in which the
stakeholders are actively involved in the process of
model construction that explore questions such as:
what is exactly the problem faced? How did the
problem situation originate? What are the underlying
causes? (Rouwette, et. al., 2020). On the other hand,
system dynamics can become very complex when
real world situations with lots of variables are
modelled. Some issues that may rise are related to the
data availability, domain understanding, and
modelling systems’ boundaries and uncertainties.
The System Dynamics modelling was actively
used in healthcare research to address a range of
issues (Davahli et al., 2020; Darabi et al., 2020), such
as organizing healthy community programs and
policy initiatives, improving processes and costs of
primary and acute healthcare as well as health
equality, developing new approaches for chronic
disease prevention and control, addressing the disease
epidemiology including work in heart disease,
diabetes, HIV/AIDS, cervical cancer and other
diseases. However, the existing effort is very much
dedicated to the medical side of the problem and
towards the enhancement of outcome and quality of
healthcare systems’ processes. The value of
systematic thinking and system dynamics to support
technology developers is not yet exploited. Therefore,
the aim of this study is to address this gap by
valorising the opportunities for System Dynamics to
support the development of new data driven solutions
in stroke treatment domain, more specifically:
How System Dynamics modelling can support
technology developers in the process of designing
new innovative solutions in the domain of stroke
diagnostics and treatment.
How System Dynamics modelling can engage
medical professionals in interaction with
technology developers to acquire the needs.
How System Dynamics approach can support
technology developers in successfully taking their
product to the market and the decision makers in
the process of planning for the procurement of a
new technology.
4 DEVELOPER SUPPORT
As discussed earlier, data driven approaches can
potentially facilitate and enhance differential
diagnostics, triaging and at the same time
management of stroke prevention and treatment in a
cost-effective way. However, the potential of the
mobile solutions and in particular utilization of data
combinations in the TIA and stroke risk evaluation
and diagnostics are largely neglected. At the same
time, possible efficient use of the available data, via
artificial intelligence, in the form of more advanced,
data-driven decision support systems is not yet under
development.
Accordingly, the focus of our first modelling
efforts has been put on improving our understanding
about the role of data in the stroke treatment domain.
We started with domain analysis (facilitated by
literature review and interviewing experts),
consequently the initial models have been created to
valorise the role of the data in various stages of stroke
treatment and care path. At the next step, the Group
Model Building (GMB) Workshop has been
organised to connect medical experts and
technologists and to collect medical experts’- and
technologists’ opinions on first models towards their
adjustment. The aim of GMB was to facilitate the
discussion and obtain more insights on the aspects
related to 1) what overarching data based stroke
treatment tools could be and 2) what is needed for a
data driven tools to become a successful product.
On the first point, more specifically:
What is the valid data to be used in TIA & stroke
diagnostics? What data need to be collected for TIA
& stroke service development? What data sources can
be used? What kind of solution and data combination
would work for TIA & stroke prevention? What is the
required quality of data to support the development of
algorithms to be used in effective stroke diagnostics?
How data is related to stroke ‘care and treatment
quality’ and ‘health outcome’?
On the second market uptake point, more
specifically:
What is needed for a data tool to become a
successful product and what stakeholders are needed
and what kind of ecosystems are to be created? What
will facilitate the adoption of developed solutions by
end users? How shall we orchestrate the connected
health ecosystem for the solution, so that it supports
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
746
the strategies and creates value for patients, hospitals
and technology providers?
The modelling effort and workshop discussions
have led us to the initial definition of two models
“Data flow” and “Market Uptake” models, which
are discussed in the following.
4.1 Stroke-DATA Models
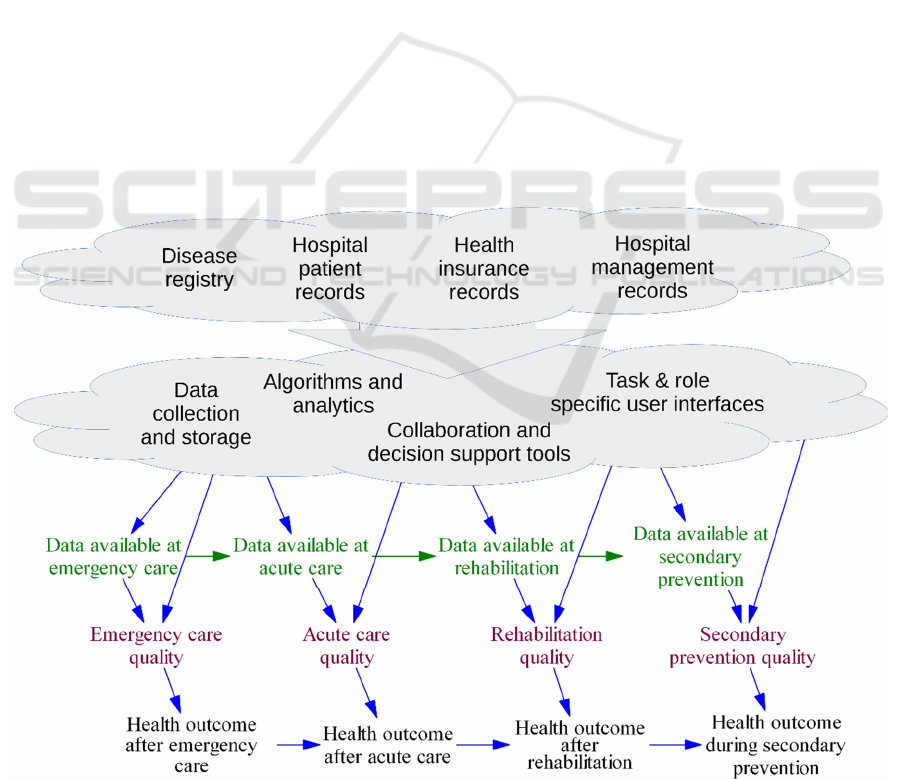
The model to facilitate planning of data driven
decision tools is presented in Figure 2. As a
conceptual framework it aims to structure discussions
on the relation between existing data, opportunities
for technological solutions, and the eventual value of
a tool. It gives an overview of three distinct layers,
listing from top to bottom: historical data available
for development, features and functionalities of the
tool, care pathway and impact of using the tool.
Different experts tend to have a strong focus on their
own topic. This model and respective discussions
helped them to see there interdependencies and
construct an overview while discussion potential
tools.
The top part summarizes the types of existing data
that can support the design of the tool, in particular
developing the analytics and the underlying
technological infrastructure. Considering a
hypothetical tool, the detailing of the data both places
constraints on the analytics that can be implemented
while design of the tool defines which of the existing
data should be acquired. Focus should not be limited
to constraints imposed by the data but also include
exploration of opportunities in discussion between
the experts, i.e. not only prune out ideas presented by
the technology experts. Actual access to the data and
also level of available detail are of concern as data
security and privacy protection limit how and for
what purposes these data may be used.
Below the data cloud are the specific use cases,
analytics, and functionalities that can provide added
value in the stroke care pathway. A key consideration
here is to bridge the gap between what the available
data can support and what generates added value
when implemented in the care pathway. This is
mainly the domain of expertise of the technology
developers.
The bottom part visualizes the influence of data
availability during care, impact on care quality, and
eventually on health outcomes. The causal effects run
down, from available data to care quality to health
outcome, and to the right, from one care stage to the
next. We are considering a tool based on using data
and analytics to support care both in each stage and to
integrate the care across stage. The purpose of the tool
Figure 2: Conceptual model of factors and their dependencies from available data and eventual impact on health outcomes.
Opportunities for System Dynamics towards the Support of Technological Developments in Stroke Treatment Domain
747
is to facilitate better data availability from patient
records, reflect these to research data via the analytics
and thus improve care quality and outcomes.
The availability of data is dependent on both
linking to various currently used records and also to
similar tools used in previous stages of care, i.e.
recording data and making it available in later stages
of care supports a better basis for decision making.
Such transfer of data involves crossing boundaries
between units and wards within a hospital and also
across organizational boundaries. Health outcomes
are dependent on both previous outcomes and quality
of care in the current stage of care. In particular,
failure to provide appropriate care in earlier stages
can lead to irreparable damage and disability.
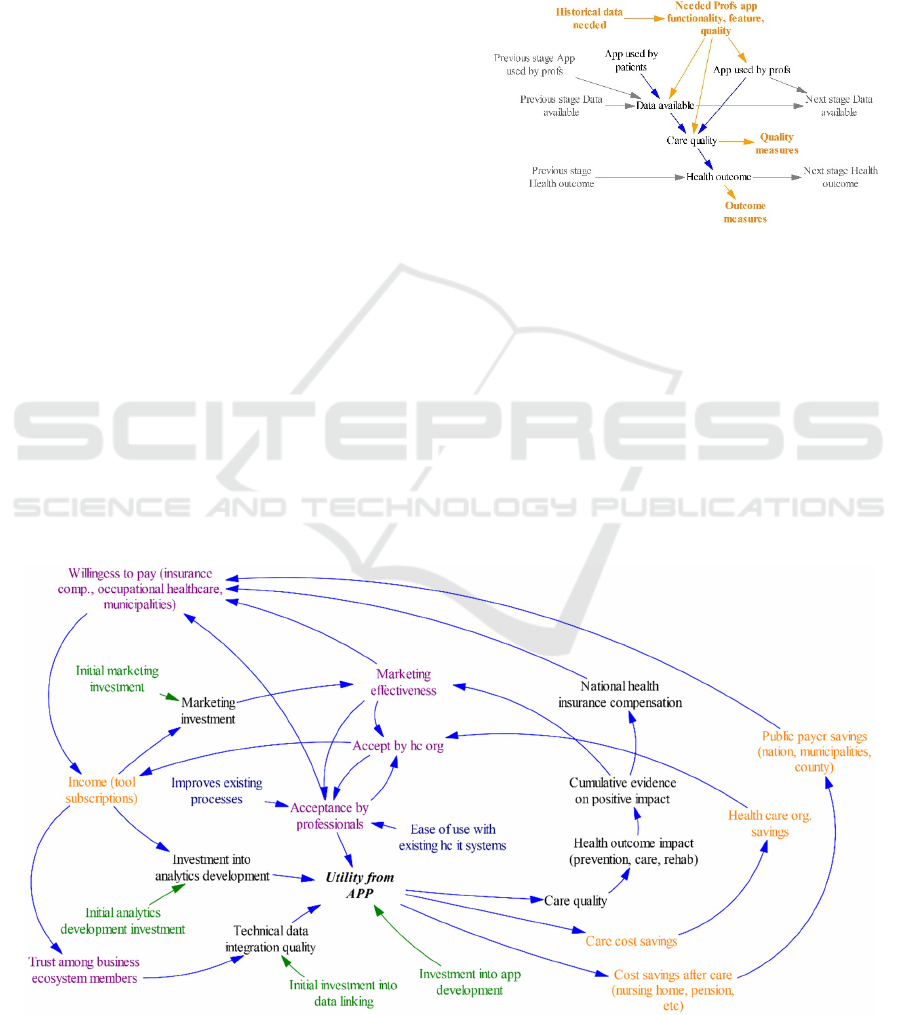
The different stages of care had their own focused
discussions in a workshop. More focused diagrams,
such as the one presented in Figure 3, were used. Only
one stage of care is included here, the data and app
feature are compacted, and the orange colour
indicates the desired focus of discussions. As an
example, we present here a summary of the results
from discussion on emergency care. Of the tools and
devices, it was noted that they should add as little as
possible to existing equipment in ambulances and
overall the simplicity of use and streamlining into
current protocol was considered crucial for success.
In particular, value was seen in the seamless
integration to existing systems both in ambulance and
hospital emergency department, and further, linking
the care stages by allowing early information to
doctors in hospital prior to patient’s arrival and
possibility of ambulance crew to consult specialists in
hospital.
Also, value was seen in analytics providing more
reliability in differentiating between stroke vs. TIA
vs. other condition and in case it is a stroke, clot vs.
bleeding - in particular when they would reduce the
needed measurements and imaging and the time to
make decisions.
Figure 3: Model for a single stage in the care-path used
during workshop discussions.
Other areas of potential utility were considered in
helping with triage with awareness of current hospital
resource constraints and linking to the patient’s
historical medical records (especially history of TIA
or stroke). Of outcome measures, mortality and
Cerebral Performance Categories Scale were
mentioned but the topic appeared to be difficult to
bring into discussion while discussing hypothetical
data tool properties. This possibly is a topic that only
surfaces once there is a more concrete plan of a tool
or the tool already exists, i.e. the value proposition on
Figure 4: Model of market update dynamics.
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
748

that level is something of an afterthought. The more
direct effects a data tool could have on care were more
easily covered in the discussions. Timeliness and
correctness of different decisions were brought up
along with possibility of reacting to weaker
indications before severe symptoms develop.
The market uptake model in Figure 4 is in the
format commonly used in Systems Thinking and
depicts a dynamic causal diagram with factors and
actors that can influence whether the tool is
eventually widely used and profitable for the
members of the business ecosystem. The causal
directional dependencies are represented using
arrows. Colouring of some of the variables indicates
grouping into monetary factors (orange), opinions
and perceptions (magenta), and initial investments
(green).
At the core is the Utility from APP, which
represents the various benefits (and drawbacks)
resulting from using the app (and its data backend
functionality) as a part of the care processes along the
care pathway. The benefits are dependent, first of all,
on the tool being used (Acceptance by professionals)
and then on integrating data (Technical data
integration quality; both historical research data and
case specific patient data) and developing analytics
that serve as basis for decision support functionality
(Investment into analytics development).
Using the app leads to savings in the active care
stage and later life and also to improved quality of
care and thereby health outcomes. Evidence of
improved quality of care and health outcomes
accumulates over time and can lead to positive
compensation decision by the national health
insurance and also more effective marketing to
various healthcare organizations. Though dropped
from the visualization, it was noted in the workshop
that such accumulation of evidence is enhanced by
co-operation also with researchers.
Implementing the app in the healthcare processes
is dependent on both organizations accepting it
(Accept by hc org) and individual professionals
accepting it (Acceptance by professionals), i.e. it is
made available by the organization and the employees
actually use it. As the doctors are respected experts in
their field and often also participate in management,
they have much say in the decisions of the
organizations. Therefore, there is the interplay,
arrows in both directions, of acceptance by healthcare
organization and the professionals. There was a
comment in the workshop that this interplay can vary
between organizations and also over time, which
should be taken into account when planning
marketing activities. Further, the degree to which
professional uses the app depends on how it fits into
existing routines, i.e. Ease of use with existing hc it
systems and Improves existing processes.
Income from licences and subscriptions allow
further investments into developing the tools, which
helps to better meet user needs and improving
outcomes. The income also allows further
investments into marketing, thus widening the user
base. Also, positive and profitable experiences of
cooperation between the business ecosystem leads to
greater Trust among business ecosystem members.
This allows arrangements to open more of the IPR to
the members, thus improving the interaction between
components of the app.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented the initial System Dynamics
models to support technology developers in entering
the complex domain of stroke diagnosis and
treatment. The modelling work has been supported by
the Group Model Building activities, where the
medical experts, technology developers and
researchers met to provide expertise and to share open
issues, challenges and opportunities for the
technology development in the stroke treatment
domain. During the workshop it was acknowledged
that the resulted models and the respective
discussions can service various stakeholders in
grasping the emerging important role of data and its
impact on stroke care quality and health outcomes as
well as what makes data tool to become a successful
product and what kind of ecosystems need to be
created to facilitate market uptake.
The level of details presentable in a system model
is coarse with regards to individual variables of the
model. They essentially are constrained to a few
words. On the other hand, a large number of
variables, i.e. detail on how many different things the
model tries to account for, results in a model unusable
in a workshop as the overall big picture is lost. In the
authors’ experience, presenting a preliminary model
based on e.g. interviews helps start the discussion as
it provides something to criticize and expand upon.
However, such initial models need to be sufficiently
simple to be understood after a short presentation.
As for the future work, a set of quantitative
simulations will be developed to support the
examination of care quality outcomes in various
stages of stroke treatment care path. Moreover, the
market uptake model will be quantitatively
instantiated to study the dependences between the
Opportunities for System Dynamics towards the Support of Technological Developments in Stroke Treatment Domain
749

initial technological investments and various impacts
such as care quality and cost savings.
The modelling and workshop with the ecosystem
members aimed to focus and strengthen the
ecosystem. It was brought up in the workshop that,
though the current activities of the ecosystem focus
on the stroke and a specific type of tools, longer time
horizon objectives can cover also other diseases and
tools. Thus the market uptake model could be
expanded or restructured to account for development
of new, as of yet unspecified, tools and applications.
For example, going from an uptake model to
ecosystem evolution model the specific “app” in the
model could be replaced by an evolving portfolio of
offerings from the ecosystem and the definitions of
other components of the model would need to be
redefined accordingly.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by Business Finland under
Stroke-DATA project
REFERENCES
Ali, F., Hamid, U., Zaidat, O., Bhatti, D., & Kalia, J. S.,
2020. Role of Artificial Intelligence in TeleStroke: An
Overview. Frontiers in neurology, 11, 559322. https://
doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.559322.
Baltimore, D. R. Charo, Kevles, J.D. Benjamin, R., 2016.
The Rise of the Platform Economy, Issues in science
and technology. Online, issues.org.
Bat-Orgil B.E & Jeffrey L., 2021. Automatic Acute Stroke
Symptom Detection and Emergency Medical Systems
Alerting by Mobile Health Technologies: A Review,
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 30 (7)
105826.
Béjot Y, Daubail B, Giroud M., 2016. Epidemiology of
stroke and transient ischemic attacks: Current
knowledge and perspectives. Rev Neurol (Paris).
172(1):59-68. PMID: 26718592.
Chen Y, Abel KT, Janecek JT, Chen Y, Zheng K, Cramer
SC., 2018. Home-based technologies for stroke
rehabilitation: A systematic review. Int J Med Inform.
123, 11-22.
Darabi, N., et al., 2020. System Dynamics Modeling in
Health and Medicine: A Systematic Literature Review.
Syst. Dyn. Rev.. doi: 10.1002/sdr.1646
Davahli, MR., et al., 2020. A System Dynamics Simulation
Applied to Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Int J
Environ Res Public Health, 17 (16), 5741.
Dawson J, et al., 2009. A recognition tool for transient
ischaemic attack. QJM, 102, 43-49.
Ding L, et al., 2020. Incorporating Artificial Intelligence
Into Stroke Care and Research, Stroke AHA, 15 (12),
351-354.
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM., 2008.
Stroke. The Lancet. 371 (9624), 1612–23.
Forrester, J.W., 1961. The book, Industrial Dynamics.
Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. Reprinted by Pegasus
Communications, Waltham, MA.
Forrester, J.W., 1969. The book, Urban Dynamics.
Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. Reprinted by Pegasus
Communications, Waltham, MA.
Khriyenko, O., Rönkkö, K., Tsybulko, V., Piik, K., Le, D.
P. M., & Riipinen, T., 2018. Stroke Cognitive Medical
Assistant (StrokeCMA). GSTF Journal on Computing,
6 (1). doi: 10.5176/2251-3043_6.1.112
Marshall DA, Burgos-Liz L, Pasupathy KS, Padula WV,
Ijzerman MJ, Wong PK, et al., 2016. Transforming
healthcare delivery: integrating dynamic simulation
modelling and big data in health economics and
outcomes research. Pharmacoeconomics. 34, 115–
1126. doi: 10.1007/s40273-015-0330-7
O'Donnell MJ et al., 2010. INTERSTROKE investigators.
Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral
haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries: a case-control
study. Lancet. 376 (9735):112-123.
Polycom, 2015. Healthcare in 2025 2025 Healthcare
Technology Innovation Survey, Online by Polycom.
Richardson, G.P., Vennix J., Andersen, D.F., Rouwette E.,
2007. Group model building: problem structuring,
policy simulation, and decision support. Journal of
Operational Research Society, 58, 691–694.
Rouwette E.A.J.A., Vennix J.A.M., 2020. The book, Group
Model Building. In: Dangerfield B. (eds) System
Dynamics. Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems
Science Series. Springer, New York, NY.
Sadighi, A., Stanciu, A., Banciu, M., Abedi, V., Andary, N.
E., Holland, N., & Zand, R., 2019. Rate and associated
factors of transient ischemic attack misdiagnosis.
eNeurologicalSci, 15, 100193.
Sterman J., 2000. The book, Business dynamics. Systems
thinking and modelling for a complex world. McGraw-
Hill.
StrokeData, 2021. The Stroke Data Research, https://
www.strokedataproject.com/.
Yu M. et al., 2020. Toward Rapid Stroke Diagnosis with
Multimodal Deep Learning. In: Martel A.L. et al. (eds)
Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted
Intervention – MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, vol 12263. Springer, Cham. https://
doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59716-0_59
Wang K, Luo J., 2016. Detecting Visually Observable
Disease Symptoms from Faces. EURASIP J Bioinform
Syst Biol. 1 (13), doi: 10.1186/s13637-016-0048-7.
PMID: 27688744; PMCID: PMC5007273.
WSO, 2021. World Stroke Organization facts. https://
www.world-stroke.org/world-stroke-day-campaign/
why-stroke-matters/learn-about-stroke
HEALTHINF 2022 - 15th International Conference on Health Informatics
750
