
Clinical Efficacy and Pathogenetic Substantiation of Adjuvant
Extracorporeal Photochemotherapy in Pemphigus Vulgaris
A. V. Molochkov
1a
, Yu. V. Molochkova
2b
, A. V. Kildyushevsky
3c
, O. V. Karzanov
4d
and M. G. Kartashova
4e
1
Head of the Chair of Dermatovenereology and Dermatooncology of Doctors Improvement Faculty Moscow Regional
Research and Clinical Institute, Moscow, Russia
2
Head of Department of Dermatovenereology of Moscow Regional Research and Clinical Institute, Moscow, Russia
3
Leading Research Fellow, Surgical Hemocorrection and Detoxication Department of Moscow Regional Research and
Clinical Institute, Moscow, Russia
4
Senior Research Fellow, Department of Dermatovenereology of Moscow Regional Research and Clinical Institute,
Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Pemphigus Vulgaris, Extracorporeal Photochemotherapy, Extracorporeal Blood Irradiator "Kit-A".
Abstract: This article reportson our clinical experience of application of extracorporeal photochemotherapy conducted
with the ultraviolet extracorporeal blood irradiator or "KIT-A" (SJJ NPP "Cyclone-Test", Russia) as an
adjuvant method in treatment of pemphigus vulgaris. We assess pathogenetic substantiation and clinical
results of the proposed method as well as discussion on dynamics of immunological parameters in patients
receiving actual treatment. Also current article analyze the possibility of applyingextracorporeal
photochemotherapy method as an adjuvant treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with typicaldisease course.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3388-9224
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9021-6494
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7079-8383
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6176-1394
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0376-2644
1 INTRODUCTION
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is an autoimmune disorder
of skin and mucous membranes histologically
characterized by acantholysis resulting in the
formation of intraepidermal blisters (Stanley,1999).
Despite PV is one of the well studied tissue-specific
autoimmune diseases, autoantibodies against
keratinocyte antigens are presented not only by anti-
desmoglein antibodes. Number of studies have
demonstrated that T-cells are also actively involved
in the immunopathogenesis of this disease
(Veldman, et al,.,2003;Hertl & Riechers, 1999; Lin,
et al., 1997). An increased number of T cells, mainly
due to CD4, characterized by a Th2 - cytokine
profile (IL-4, IL-6) capable to modulate B-cells
pathogenic production of IgG4 are observed in PV
patients peripheral blood (Edelson, 2000).
Therefore, reports on the application of
extracorporeal photochemotherapy (ECP)- method
proposed by R. Edelson for patients with T-cell skin
lymphomas- in PV are of great interest (Edelson, et
al.,1987). Currently ECP is considered as first line
therapy for erythrodermic mycosis fungoides and
Sézary syndrome (Scarisbrick, et al., 2008). In
clinical practice of our Institution ECP was also
successfully used in patients with cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma and other autoimmune dermatoses
(Molochkov, et al.,2012; Molochkova, et al., 2019;
Molochkov, et al., 2016; Kil’dyushevskiy A.V., et
al., 2014).
The EСP method is based on the biological effect
of 8-methoxypsoralene (8-MOP) and ultraviolet A
(UVA) irradiation on mononuclear cells, collected
by apheresis and reinfused to the patient after UVA
exposure (Edelson, et al.,1987).
For a long time, until the clarification of the
dendritic cells role, mechanism of ECP’s therapeutic
Molochkov, A., Molochkova, Y., Kildyushevsky, A., Karzanov, O. and Kartashova, M.
Clinical Efficacy and Pathogenetic Substantiation of Adjuvant Extracorporeal Photochemotherapy in Pemphigus Vulgaris.
DOI: 10.5220/0010995500003123
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2022) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 217-222
ISBN: 978-989-758-552-4; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
217
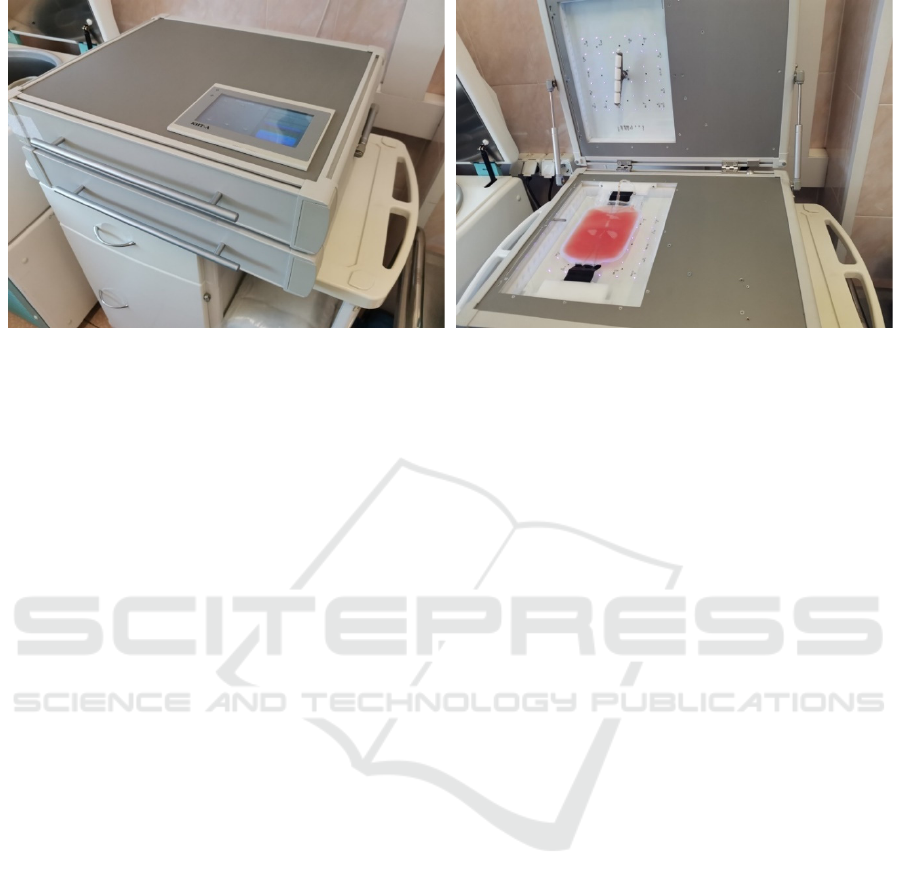

a
)
b)
Figure 1: Ultraviolet extracorporeal blood irradiator or "KIT-A" (SJJ NPP "Cyclone-Test", Russia).
effect has remained unclear. Thus S. Berger et al.
had demonstrated not only induction of the
programmed death of the tumour cell clone during
ECP, but also an activation of monocytes with their
subsequent transformation into the immature
dendritic cells, which determined the mechanisms of
immunological tolerance (Berger, et al., 2001).
Thereby the purpose of this research was to study
efficiency of ECP conducted with the ultraviolet
extracorporeal blood irradiator or "KIT-A" (SJJ NPP
"Cyclone-Test", Russia) in treatment of PV and to
explore the role of T-cell immunity in the
pathogenesis of PV in order to justify development
of new approaches in the PV treatment based on the
extracorporeal photochemotherapy (ECP).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Current study was performed on 28 PV patients (16
females, 12 males) hospitalized to the
dermatovenerology department of Moscow Regional
Scientific-Research Clinical Institute during acute
phase of the disease and receiving ECP in
combination with systemic corticosteroids. The
mean age of patients was 54 years (range: 34 - 72).
Diagnosis was made on the basis of a typical clinical
picture of the disease and in every case was verified
by cytological (acantholytic cells from the bottom of
erosion), histological (intraepidermal fissures and
blisters) and immunohistochemical (detection of
specific antibodies of the IgG class) examinations.
Duration of disease ranged from 1.5 months to 8
years (mean 1.2 years). 11 patients were suffering
from the disease for more than 2 years and their
condition had relapsing-remitting disease course; 17
patients were diagnosed PV for the first time.
Clinical results were compared with a group of 34
patients (20 females, 14 males), mean age 58 years
(range: 28-87), who received monotherapy with high
doses of systemic corticosteroids. 19 patients of
comparison group were diagnosed PV for the first
time (duration of disease ranged from 2 month to 1.5
years), and 15 patients of comparison group had
relapsing-remitting PV course with duration of
disease from 1.5 to 6 years.
3 ECP TECHNIQUE
In our practice we accomplished collection of the
peripheral blood mononuclear cells by apheresis,
using the cell separator Haemonetics MCS + (USA)
according to the PBSC (Peripheral Blood Stem Cell)
protocol, with the following irradiation of the cells
on the ultraviolet extracorporeal blood irradiator
registered in the Federal Service for Surveillance in
Healthcare of the Russian Federation
(Roszdravnadzor), registration number RZN
2021/15867 "KIT-A", produced by SJJ NPP
Cyclone-Test, Russia (Figure 1: a, b). The device is
equipped with 72 LED emitters that generate
electromagnetic energy with a wavelength of 365 +
10 nm. The emitters are located in two planes in
relation to the object - the upper and lower module
with 36 emitters, respectively. Also, device is
equipped with a tool for mixing of biological fluids
in a plastic container and a fan to maintain the set
temperature. The total power of ultraviolet radiation
is not more than 5 mW / cm2. The total exposure
dose for 10 minutes is 3.0 J / cm2. The exposure
time is 7 minutes, which corresponds to a radiation
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
218
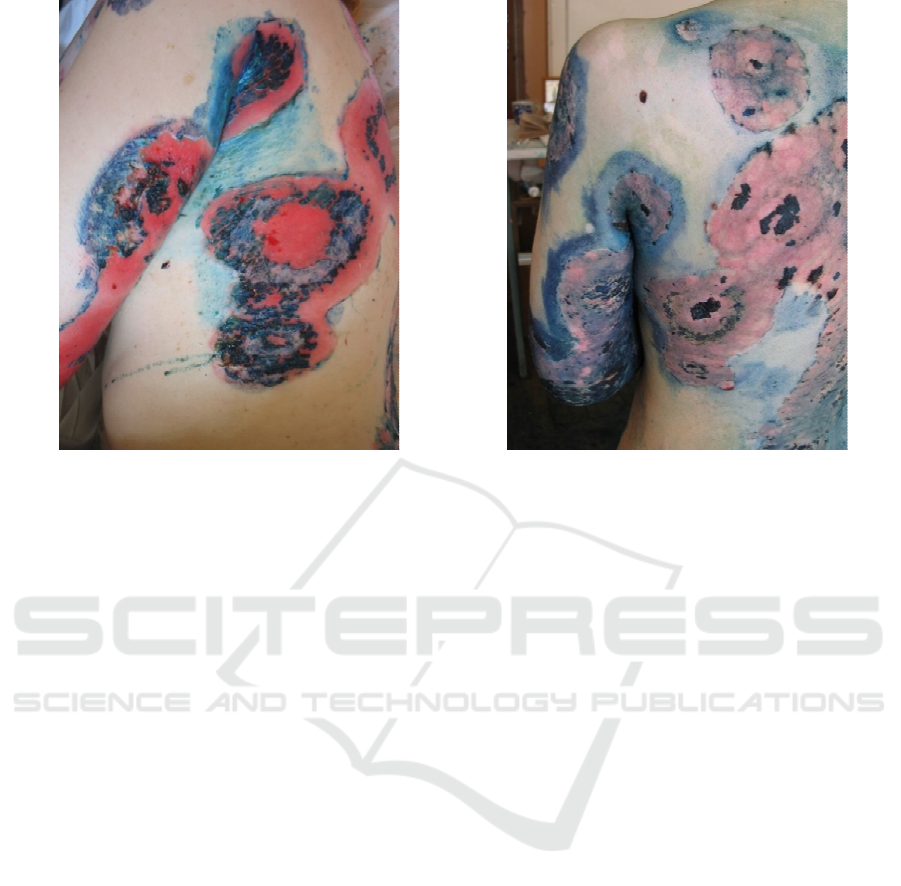
a
)
b
efore treatment
b)
14 da
y
s after treatment
Figure 2: Female patient with pemphigus vulgaris. Widespread cutaneous process with extensive erosive surfaces.
Treatment with prednisolone (100 mg / day, per os) for 10 days without clinical effect with daily appearance of new lesions.
After adding the adjuvant therapy with ECP technique, new lesions ceased to develop; during the next 2 weekswas noted
rapid epithelialization of erosions, which made it possible to start reducing the dose of systemic corticosteroids.
dose of 2.0 J / cm2. Two hours before the ECP
session patient took peroral photosensitizer (8-
methoxypsoralen at the dose of 0.6 mg/kg). After the
exposure to the UV irradiation, the cell suspension
was reinfused to the patient for 30 min. Course of
treatment included 4 sessions, procedure was carried
out every 2 days.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
ECP sessions were well tolerated by all patients, no
complications or side events were observed. On
average, in 3-4 days after initiation of ECP therapy
in every case we observed improvement of general
well-being, and improvement of the cutaneous
manifestations, particularly discontinuation or
significant reduction of wound exudation or absence
of a new lesions.
Epithelialization of epidermal defects,
accompanied by the decrease in IgG deposits in the
intercellular substance of the epidermis occurred in
7-14 days in all of the patients receiving treatment
with ECP (Figure 2: a, b). Thus, all patients in this
group had a complete clinical recovery.
In the comparison group, clinical recovery was
noted in 31 (91%) patients. In the majority of
patients (25 (74%)), complete epithelization of
epidermal defects occurred in 15 – 22 days, in 6
(18%) patients, clinical recovery was achieved, but
the effect was attained in a longer terms: from 1.5 to
2.5 months. In 3 (9%) patients, despite the ongoing
treatment with high doses of corticosteroid drugs,
clinical recovery was not achieved (1 patient had
new lesions, 2 patients had persistent oral erosions).
During investigation on the effectiveness of
provided treatment, it was noted that all
complications and side effects in both groups (23 of
the 28 patients in the control group (5 patients were
lost to follow-up, because after the therapy they have
left the country and 34 patients of comparison
group) were associated with systemic
corticosteroids. No complications associated with
the ECP procedure occured. In comparison, patients
of the control group in average had 3.1
complications per patients vs 4.5 complications per
patient in comparison group (Table 1). Also, in
control group we didn’t register such serious
complications as sepsis, stroke, myocardial
infarction, pneumonia, which occurred in
comparsion group and caused two deaths. Thus, high
clinical efficacy of therapy in control group was
combined with a significantly lower frequency of
adverse reactions and complications (follow-up
period 12-36 months).
Clinical Efficacy and Pathogenetic Substantiation of Adjuvant Extracorporeal Photochemotherapy in Pemphigus Vulgaris
219
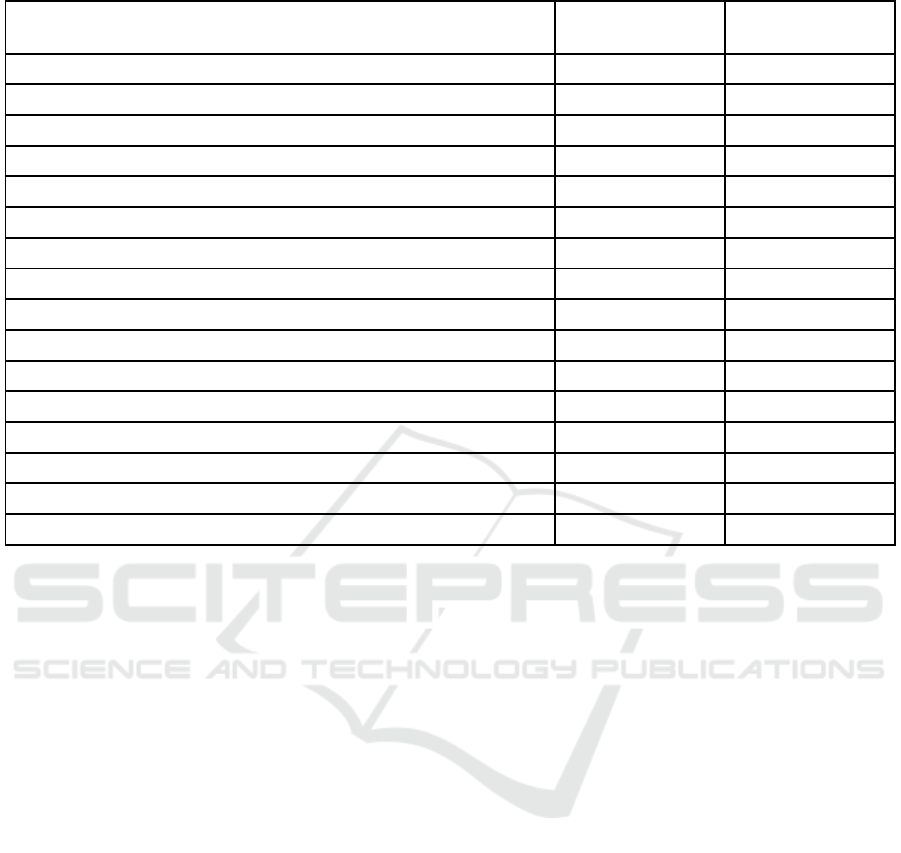
Table 1: Identified Complications and Side Effects of Sistemic Corticosteroid Therapy in Both Groups.
Complication Control group
(n=23)
Comparsion group
(n=34)
Cushing’s syndrome 23 34
Arterial hypertension 14 19
Stroke - 2
Myocardial infarction - 1
Pneumonia - 3
Sepsis - 1
Osteoporosis 5 15
Cataract 2 4
Erosive and ulcerative lesion of the gastrointestinal tract 9 18
Diabetes 2 8
Mucosal candidiasis 6 23
Pyoderma 9 21
Erysipelas 1 1
Thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities - 2
Total 71 152
Average (per one patient) 3.1 4.5
During the immunological study in patients with
PV, there was found a high level of correlation (r =
0.57, p <0.05) between the expression of the integrin
adhesion molecule MAC-1 (CD11b) and natural
killer (NK) cells (CD3-CD16 + CD56 +). Probably
it indicates the presence of this molecule on NK
cells, providing fixation of these cells on the
vascular endothelium with the subsequent
transendothelial migration into the lesion.
Patients with PV were characterized by the low
level of CD25 expression, - α-chain of the IL-2
receptor (1.89 ± 1.9%, at the normal rate of 4.2±
0.2%, p <0.05), as well as reduced content of Treg
cells with the phenotype: CD45RA + CD4 +
CD25
high
CD127
low
/
neg
(4.8 + 0.8%, with the normal
rate of 9.6 + 0.8% p <0.05). The interaction of the
CD25 molecule with its mediator IL-2 provides not
only proliferation and differentiation of the effector
cells, but primarily - activation and the proliferation
of Treg cells. Functionally active Treg cells are
characterized by the constitutive significant
expression of the α-chain of the receptor to IL-2
(CD25), through which suppressor function of these
cells is realized, providing the depletion of
autoreactive T-cells by triggering the apoptosis
processes in them, thus maintaining the tolerance to
their own antigens. Decrease of expression of CD25
molecule leads to insufficient control and
maintenance of the immunological tolerance to the
autoantigens in the periphery.
The detected immune disorders in patients with
PV were considered to be pathogenetic
substantiation for the immunomodulatory therapy of
this disease with the application of ECP.
As a result of the ECP course, clinical recovery
was achieved in all patients in 12 days on average,
resulting in reduction of the starting systemic
corticosteroid dosage during these period by 30%
and significant decrease of the side effects and
complications associated with high doses of
systemic corticosteroids (Table 1).
During immunological study after ECP, there
wasn’t found any correlation between CD11b and
CD3-CD16 + CD56 +, reflecting the absence of co-
expression of the adhesion molecule on NK cells.
Based on the obtained data, it could be concluded
that application of ECP leads tomodulation of co-
expression of the leukocyte integrin adhesion
molecule on the NK, which results in blockage of
transendothelial migration ofthese cells to the lesion.
After the course of ECP in PV patients, there was
also identified increased expression of the relative
quantity of Treg cells (from 4.8 + 0.8% to 13.3 +
2.3%, p <0.05), which indicated the restoring of the
Treg cells peripheral immunological tolerance
control over the autoreactive clone of the
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
220

lymphocytes, escaped the negative selection in the
thymus.
Thus, in short, it could be assumed that
immunomodulatory effect of ECP in PV is based on
the re-establishment of the receptor-ligand relations
between immunocompetent cells, intercellular
adhesion molecules and target cells - keratinocytes.
An important role in this process is devoted to the
restoration of the suppressor function of Treg cells
in relation to the autoreactive clone of cytotoxic
effector cells.
T-cell reactivity to self-antigens, as well as T-
and B-cell interactions in the formation and
progression of PVarenot yet fully understood,
therefore giving reasons for a detailed study of this
problem. At the same time, the solution of cell-cell
interactions is impossible without understanding of
the role and significance of intercellular adhesion
molecules and their ligands. The study of the
function of the adhesive-ligand system in PV seems
to be really important and crucial, since it concerns
both the intercellular interactions of
immunocompetent blood cells and the mechanisms
of their transendothelial migration to the target cells
(keratinocytes). Currently, the literature contains a
great deal of new fundamental data relating the
issues of the function and the classification of
human adhesion molecules,however, their
significance in the occurrence and progression of
autoimmune diseases, in particular in PV, hasn’t
been sufficiently studied yet.
Therefore, our research indicates that the
immunotherapeutic method - ECP conducted with
anextracorporeal blood irradiator "KIT-A" (SJJ NPP
"Cyclone-Test", Russia) is a highly effective and
promising method of treatment PV, which requires
deeper study for enhancing its clinical application.
5 CONCLUSION
High doses of systemic corticosteroids in
combination with adjuvant therapy with cytostatics,
traditionally used in PV, are quite effective in most
cases, however, they are associated with the
appropriate development of severe side effects such
as myelosuppression, anemia, visceral cancer,
hepatotoxic reactions, hemorrhagic cystitis, impaired
renal function (Ahmed & Hombal, 1984; Bystryn &
Steinman,1996; Fairley et al.,1972; McDonald,1985)
We consider that use of methods of adjuvant
therapy, targeted at the main links of the
immunopathogenesis of the disease to be the most
promising direction for improvement of the
PVtherapy. Only single observations of the mainly
drug-resistant PV treatment with the use of ECP
were published to date and summarized in 2020 with
review of ECP use in 11 cases of a resistant PV
(Knobler, et al.,2020).
Notably, this review outlines good clinical
efficacy of therapy, with a minimal side effects, and
the main factor supposed to limit the widespread use
of current technique is the high cost of the
procedure. "KIT-A" (SJJ NPP "Cyclone-Test",
Russia), which is used in the described above ECP
technique makes it possible to greatly reduce the
cost of the procedure and thereby ensure the
availability of ECP in wide clinical practice
(including the treatment of uncomplicated PV
variants). As for the clinical efficacy of proposed
method, we obtained results, comparable to review
of R.Knobler et al., but our study was conducted in
patients with a typical course of the disease with the
use of one ECP course, which consisted of 4
procedures (in comparison with 2-6 courses for
resistant PV in R.Knobler, et al review) (Knobler, et
al.,2020).
REFERENCES
Stanley JR. Pemphigus. in: Freedberg IM Eisen AZ Wolff
K Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine.
McGraw-Hill, New York, NY1999: 654-666
Veldman C., Stauber A., Wassmuth R., Uter W., Schuler
G., Hertl M.; Dichotomy of Autoreactive Th1 and Th2
Cell Responses to Desmoglein 3 in Patients with
Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) and Healthy Carriers of PV-
Associated HLA Class II Alleles. Journal of
immunology. 2003; 170. 635-42.
10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.635
Hertl M., Riechers R.; Analysis of the T cells that are
potentially involved in autoantibody production in
pemphigus vulgaris. J Dermatol. 1999; 26:748–752
Lin M., Swartz S., Lopez A., Ding X., Fernandez‐Vina
M., Stastny P. et al.; Development, and
characterization of desmoglein 3‐specific T cells from
patients with pemphigus vulgaris. J Clin Invest 1997;
99:31–40
Edelson R.; Pemphigus — Decoding the Cellular
Language of Cutaneous Autoimmunity. The new
England journal of medicine. 2000; 343: 60-61
Edelson R., Berger C., Gasparro F., Jegasothy B., Heald
P., Wintroub B., Vonderheid E., Knobler R., Wolff K.,
Plewig G., et al.; Treatment of cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma by extracorporeal photochemotherapy.
Preliminary results. N Engl J Med. 1987;316(6):297–
303. doi: 10.1056/ NEJM198702053160603
Scarisbrick J., Taylor P., Holtick U., Makar Y., Douglas
K., Berlin G., Juvonen E., Marshall S.; Photopheresis
Expert Group. U.K. consensus statement on the use of
Clinical Efficacy and Pathogenetic Substantiation of Adjuvant Extracorporeal Photochemotherapy in Pemphigus Vulgaris
221

extracorporeal photopheresis for treatment of
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and chronic graft-versus-
host disease. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158(4):659–78. doi:
10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08415.x
Molochkov V.A., Kil'diushevskiĭ A.V., Molochkov A.V.,
Karzanov O.V., Iakubovskaia E.S., Fedulkina V.A.;
Clinical and immunological aspects of extracorporeal
photochemotherapy for psoriasis and psoriatic
arthritis. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv, 2012; 84 (10), pp.
69-74.
Molochkova Y.V., Molochkov V.A., Pimenova Y.A.;
Lichen planus pigmentosus: report of effectiveness of
extracorporeal photochemotherapy in recalcitrant case.
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2019) 27, 75-78.
Molochkov V.A., Kil'dyushevskiy A.V., Karzanov O.V.;
Treatment of the tumor stage of mycosis fungoides
with extracorporeal photochemotherapy (a case
descript). Almanac of Clinical Medicine.
2016;44(1):103-106. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/
10.18786/2072-0505-2016-44-1-103-106
Kil’dyushevskiy A.V., Karzanov O.V., Aleksandrovа
N.M.; Extra-corporeal photochemotherapy in the
treatment of lymphomatoid papulosis and
folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: case reports.
Almanac of Clinical Medicine. 2014;(34):81-84. (In
Russ.) https://doi.org/10.18786/2072-0505-2014-34-
81-84
Berger C., Xu A., Hanlon D., Lee C., Schechner J., Glusac
E., Christensen I., Snyder E., Holloway V., Tigelaar
R., Edelson R.; Induction of human tumor-loaded
dendritic cells. Int J Cancer. 2001;91(4):438–47. doi:
10.1002/1097-0215(200002)9999:99993.0.CO;2-R.
Ahmed AR, Hombal SM. Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan).
A review on relevant pharmacology and clinical uses.
J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 Dec;11(6):1115-26. doi:
10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80193-0.
Bystryn JC, Steinman NM. The adjuvant therapy of
pemphigus. An update. Arch Dermatol. 1996
Feb;132(2):203-12.
Fairley KF, Barrie JU, Johnson W. Sterility and testicular
atrophy related to cyclophosphamide therapy. Lancet.
1972 Mar 11;1(7750):568-9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-
6736(72)90358-3.
McDonald CJ. Cytotoxic agents for use in dermatology. I.
J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 May;12(5 Pt 1):753-75.
doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70097-7.
European dermatology forum: Updated guidelines on the
use of extracorporeal photopheresis 2020 - Part 2 R.
Knobler, P. Arenberger, A. Arun, C. Assaf, M. Bagot,
G. Berlin, A. Bohbot, P. Calzavara-Pinton, F. Child,
A. Cho, L.E. French, A.R. Gennery, R. Gniadecki,
H.P.M. Gollnick, E. Guenova, P. Jaksch, C.
Jantschitsch, C. Klemke, J. Ludvigsson, E. Papadavid,
J. Scarisbrick, T. Schwarz, R. Stadler, P. Wolf, J. Zic,
C. Zouboulis, A. Zuckermann, H. Greinix J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 2021 Jan; 35 (1): 27-49. Published
online 2020 Sep 22. doi: 10.1111 / jdv.16889
BIODEVICES 2022 - 15th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
222
